Reactive High-Power Impulse Magnetron Sputtering of Chromium-Carbon Films
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
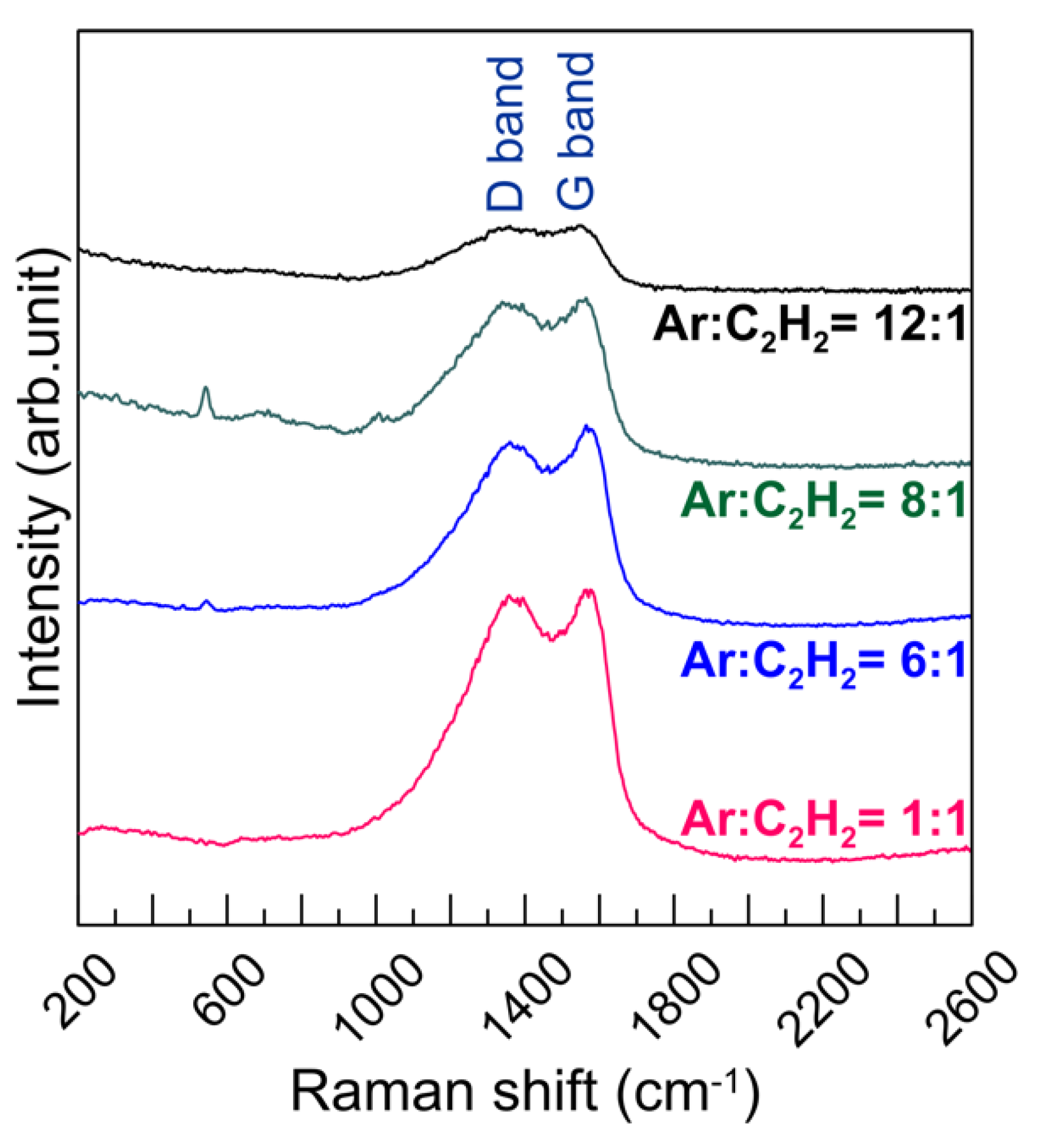
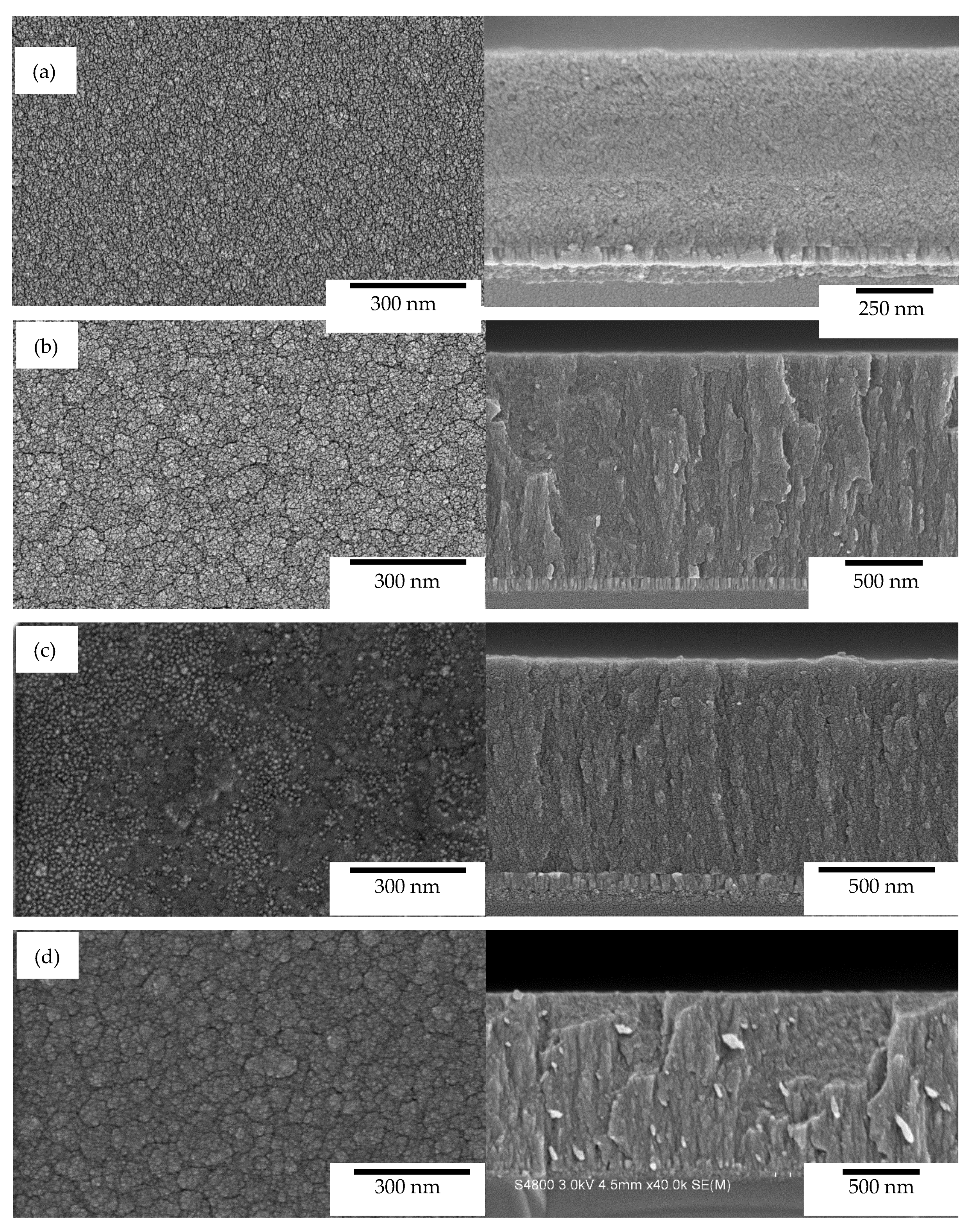
3.1. The Influences of Different Ar/C2H2 Flow Ratios
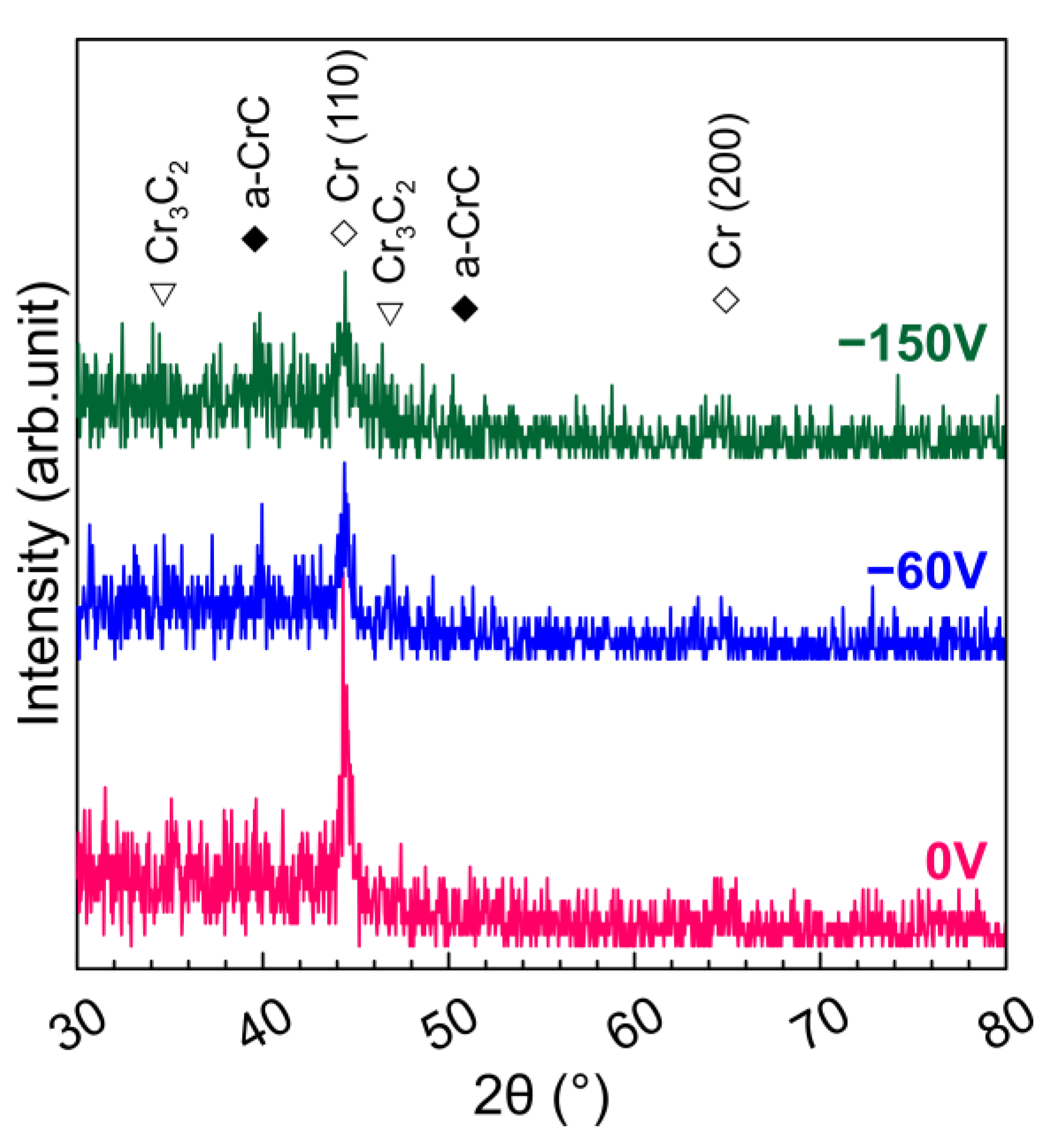
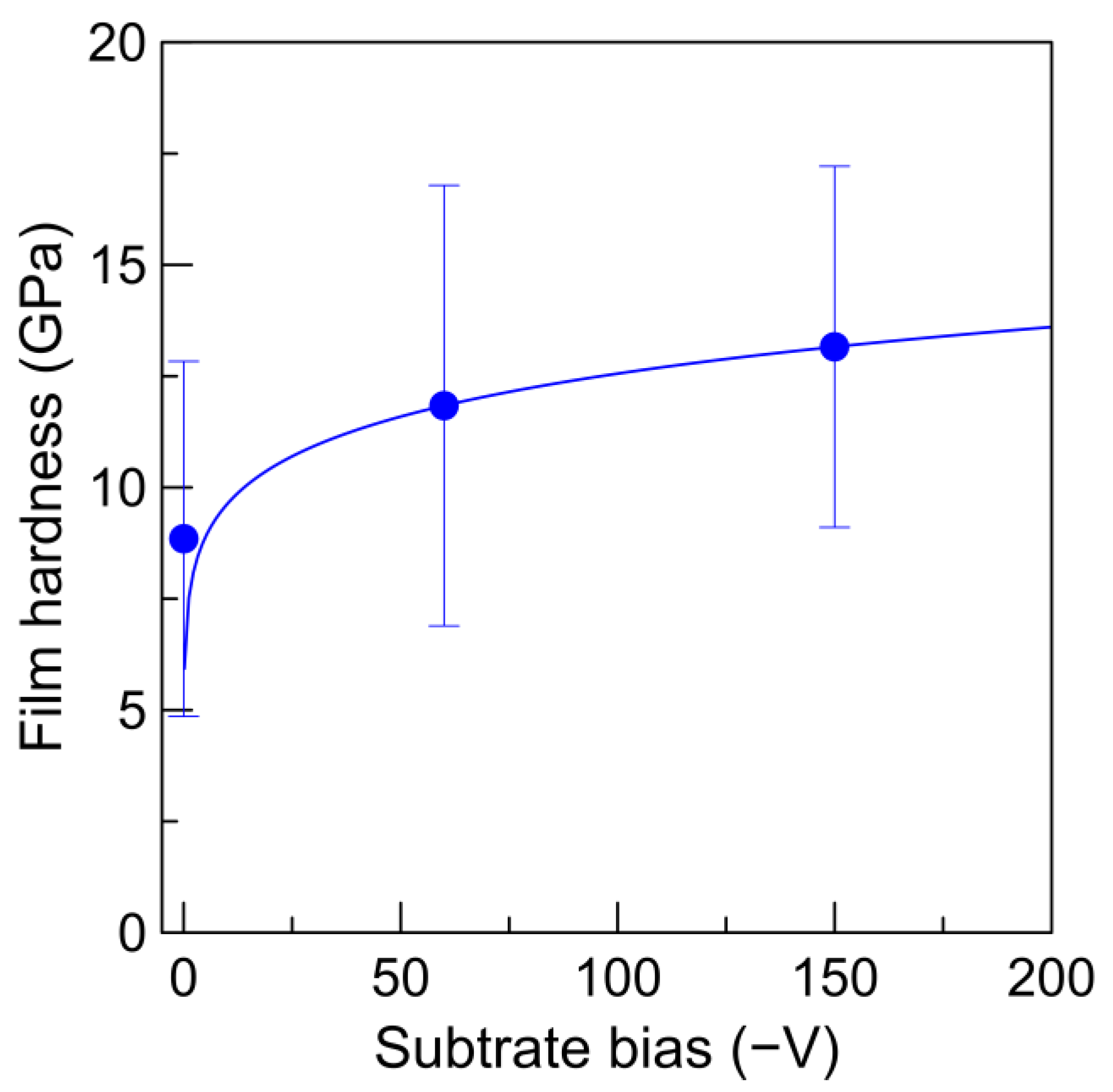
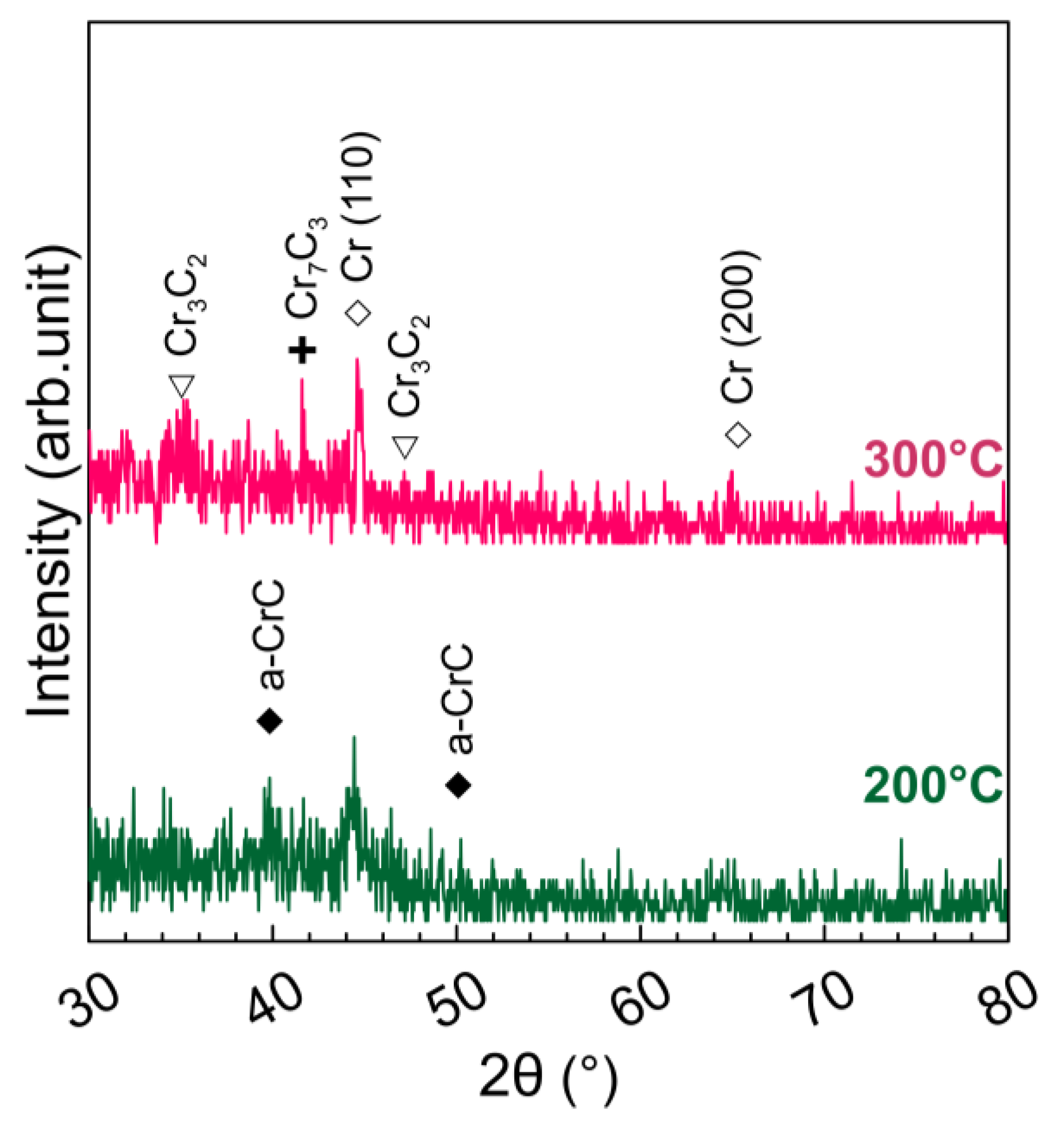
3.2. Influences of the Synchronized Substrate Bias and Deposition Temperature
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Komiya, S.; Ono, S.; Umezu, N.; Narusawa, T. Characterization of thick chromium-carbon and chromium-nitrogen films deposited by hollow cathode discharge. Thin Solid Films 1977, 45, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, L.E. Transition Metal Carbides and Nitrides; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1971; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Aubert, A.; Gillet, R.; Gaucher, A.; Terrat, J.P. Hard chrome coatings deposited by physical vapour deposition. Thin Solid Films 1983, 108, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierson, H.O. Handbook of Refractory Carbides and Nitrides, 1st ed.; Noyes Publications: New Jersey, NJ, USA, 1996; pp. 100–116. [Google Scholar]
- Merl, D.K.; Panjan, P.; Čekada, M.; Maček, M. The corrosion behavior of Cr–(C,N) PVD hard coatings deposited on various substrates. Electrochim. Acta 2004, 49, 1527–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Lee, J.W.; Chang, K.L.; Hsieh, W.J.; Wang, C.Y.; Chang, Y.A.; Shih, H.C. The effect of the substrate bias voltage on the mechanical and corrosion properties of chromium carbide thin films by filtered cathodic vacuum arc deposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 200, 2679–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edigaryan, A.A.; Safonov, V.A.; Lubnin, E.N.; Vykhodtseva, L.N.; Chusova, G.E.; Polukarov, Y.M. Properties and preparation of amorphous chromium carbide electroplates. Electrochim. Acta 2002, 47, 2775–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, D.D.L. Carbon Composites: Composites with Carbon Fibers, Nanofibers and Nanotubes, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 387–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteve, J.; Romero, J.; Go´mez, M.; Lousa, A. Cathodic chromium carbide coatings for molding die applications. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2004, 188–189, 506–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.; Högström, J.; Urbonaite, S.; Furlan, A.; Nyholm, L.; Jansson, U. Deposition and characterization of magnetron sputtered amorphous Cr–C films. Vacuum 2012, 86, 1408–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maréchal, N.; Quesnel, E.; Pauleau, Y. Deposition process and characterization of chromium-carbon coatings produced by direct sputtering of a magnetron chromium carbide target. J. Mater. Res. 1994, 9, 1820–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygren, K.; Samuelsson, M.; Flink, A.; Ljungcrantz, H.; Rudolphi, Å.K.; Jansson, U. Growth and characterization of chromium carbide films deposited by high rate reactive magnetron sputtering for electrical contact applications. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 260, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Wu, G.; Wang, A. Structure and elastic recovery of Cr-C:H films deposited by a reactive magnetron sputtering technique. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 257, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziebert, C.; Ye, J.; Stüber, M.; Ulrich, S.; Edinger, M.; Barzen, I. Ion bombardment-induced nanocrystallization of magnetron-sputtered chromium carbide thin films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 205, 4844–4849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassner, G.; Mayrhofer, P.H.; Mitterer, C.; Kiefer, J. Structure-property relations in Cr-C/a-C:H coatings deposited by reactive magnetron sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 200, 1147–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poletika, I.M.; Ivanov, S.F.; Gnyusov, S.F.; Perovskaya, M.V. Electron-beam deposition of chromium carbide–based coatings with an ultradispersed structure or a nanostructure. Russ. Metall. 2016, 1275–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, D.E.; Singh, J.; Narasimhan, K. Synthesis of titanium carbide/chromium carbide multilayers by the co-evaporation of multiple ingots by electron beam physical vapor deposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2002, 160, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-L.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Wang, C.-J.; Lee, J.-W. Comparison of chromium carbide thin films grown by different power supply systems. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 353, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, T.; Yukimura, K.; Takaki, K. Fabrication of diamond-like carbon films using short-pulse HiPIMS. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 286, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, W.; Dias, N.F.L.; Stangier, D. Tribo-mechanical properties of CrC/a-C thin films sequentially deposited by HiPIMS and mfMS. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 335, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richert, M.; Mazurkiewicz, A.; Smolik, J. Chromium carbide coatings obtained by the hybrid PVD methods. J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng. 2010, 43, 145–152. [Google Scholar]
- Yate, L.; Martínez-de-Olcoz, L.; Esteve, J.; Lousa, A. Effect of the bias voltage on the structure of nc-CrCx/a-C:H coatings with high carbon content. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2012, 206, 2877–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Jiang, J.C.; Meletis, E.I. Cr-diamond like carbon nanocomposite films: Synthesis, characterization and properties. Thin Solid Films 2005, 489, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassner, G.; Patscheider, J.; Mayrhofer, P.H.; Mitterer, C. Thermal stability of nanocomposite CrC/a-C:H thin films. Thin Solid Films 2007, 515, 5411–5417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundin, D.; Minea, T.; Gudmundsson, J.T. High Power Impulse Magnetron Sputtering: Fundamentals, Technologies, Challenges and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; ISBN 9780128124543. [Google Scholar]
- Anders, A. Tutorial: Reactive high power impulse magnetron sputtering (R-HiPIMS). J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 121, 171101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, A.; Andersson, J.; Ehiasarian, A. High power impulse magnetron sputtering: Current-voltage-time characteristics indicate the onset of sustained self-sputtering. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 102, 113303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouznetsov, V.; Macak, K.; Schneider, J.; Helmersson, U.; Petrov, I. Hybrid HIPIMS and DC magnetron sputtering deposition of TiN coatings: Deposition rate, structure and tribological properties. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1999, 12, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machunze, R.; Ehiasarian, A.; Tichelaar, F.; Janssen, G.; Ehiasarian, A. Stress and texture in HIPIMS TiN thin films. Thin Solid Films 2009, 518, 1561–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.C.; Lin, Y.T.; Chan, A.; Chang, J.T. High temperature wear behavior of titanium nitride coating deposited using high power impulse magnetron sputtering. Coatings 2019, 9, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.C.; Lin, C.H.; Lin, Y.T.; Chang, J.T. Effects of cathode voltage pulse width in high power impulse magnetron sputtering on the deposited chromium thin films. Coatings 2020, 10, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greczynski, G.; Lu, J.; Jensen, J. Metal versus rare-gas ion irradiation during Ti1-xAlxN film growth by hybrid high power pulsed magnetron/dc magnetron co-sputtering using synchronized pulsed substrate bias. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 2012, 30, 061504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, K.E.; Hampshire, J.; Southall, W.; Teer, D.G. Industrial application of pulsed dc bias power supplies in closed field unbalanced magnetron sputter ion plating. Surf. Eng. 2004, 20, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellad, A.; Labdi, S.; Malibert, C.; Renou, G. Nanomechanical and nanowear properties of Cr3C2 thin films deposited by rf sputtering. Wear 2008, 264, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisbiers, G.; Herth, E.; Buchaillot, L.; Pardoen, T. Fracture toughness, hardness, and Young’s modulus of tantalum nanocrystalline films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 143115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallant, D.R.; Parmeter, J.E.; Siegal, M.P.; Simpson, R.L. The thermal stability of diamond-like carbon. Diam. Relat. Mater. 1995, 4, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Deposition Parameters | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere | Pressure (Pa) | 0.8 |
| Ar/C2H2 flow ratio | 1:1, 6:1, 8:1, 12:1 | |
| Target HiPIMS power | Average power (kW) | 3 |
| Peak voltage (V) | −518~−612 | |
| Peak current (A) | 254~199 | |
| Pulse frequency (Hz) | 332 | |
| Pulse width (μs) | 60 (duty cycle 2%) | |
| Cr ion bombardment | Synchronized bias voltage pulse | −1000 V (pulse width 96 μs) |
| Bombardment time | 40 s | |
| Cr–C film deposition | Synchronized bias voltage pulse | Ground 0 V, −60 V, −150 V (pulse width 96 μs) |
| Deposition time | 10 min, 190 min | |
| Deposition temperature (°C) | 200, 300 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuo, C.-C.; Lin, C.-H.; Chang, J.-T.; Lin, Y.-T. Reactive High-Power Impulse Magnetron Sputtering of Chromium-Carbon Films. Coatings 2020, 10, 1269. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10121269
Kuo C-C, Lin C-H, Chang J-T, Lin Y-T. Reactive High-Power Impulse Magnetron Sputtering of Chromium-Carbon Films. Coatings. 2020; 10(12):1269. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10121269
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuo, Chin-Chiuan, Chun-Hui Lin, Jing-Tang Chang, and Yu-Tse Lin. 2020. "Reactive High-Power Impulse Magnetron Sputtering of Chromium-Carbon Films" Coatings 10, no. 12: 1269. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10121269
APA StyleKuo, C.-C., Lin, C.-H., Chang, J.-T., & Lin, Y.-T. (2020). Reactive High-Power Impulse Magnetron Sputtering of Chromium-Carbon Films. Coatings, 10(12), 1269. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10121269




