Powder and High-Solid Coatings as Anticorrosive Solutions for Marine and Offshore Applications? A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Protection and Failure Mechanisms
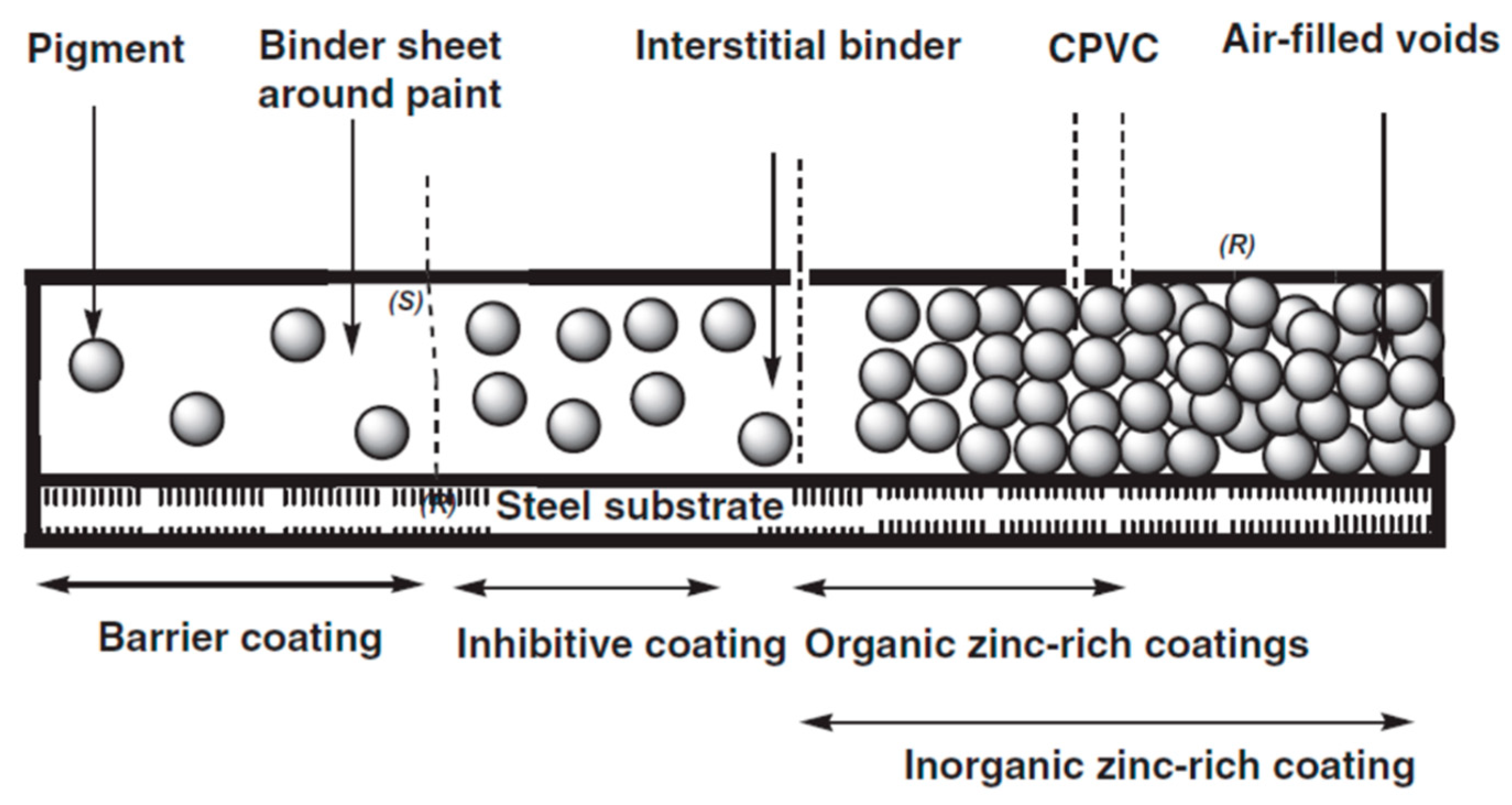
2.1. What Is an Anticorrosive Coating?
- Creating an effective barrier against the corrosion reactants (water, oxygen and ions);
- Creating a path of extremely high electrical resistance, thus inhibiting anode-cathode reactions;
- Passivating the metal surface with soluble pigments;
- Providing an alternative anode for the dissolution process.
2.2. Protection Mechanisms
2.2.1. Barrier Protection
2.2.2. Sacrificial Protection
2.2.3. Inhibitive/Passive Protection
2.2.4. Adhesion: A Protective Mechanism or a Pre-Requisite for Corrosion Protection?
2.3. Other Important Aspects Related to Anticorrosive Performance
2.3.1. Surface Preparation
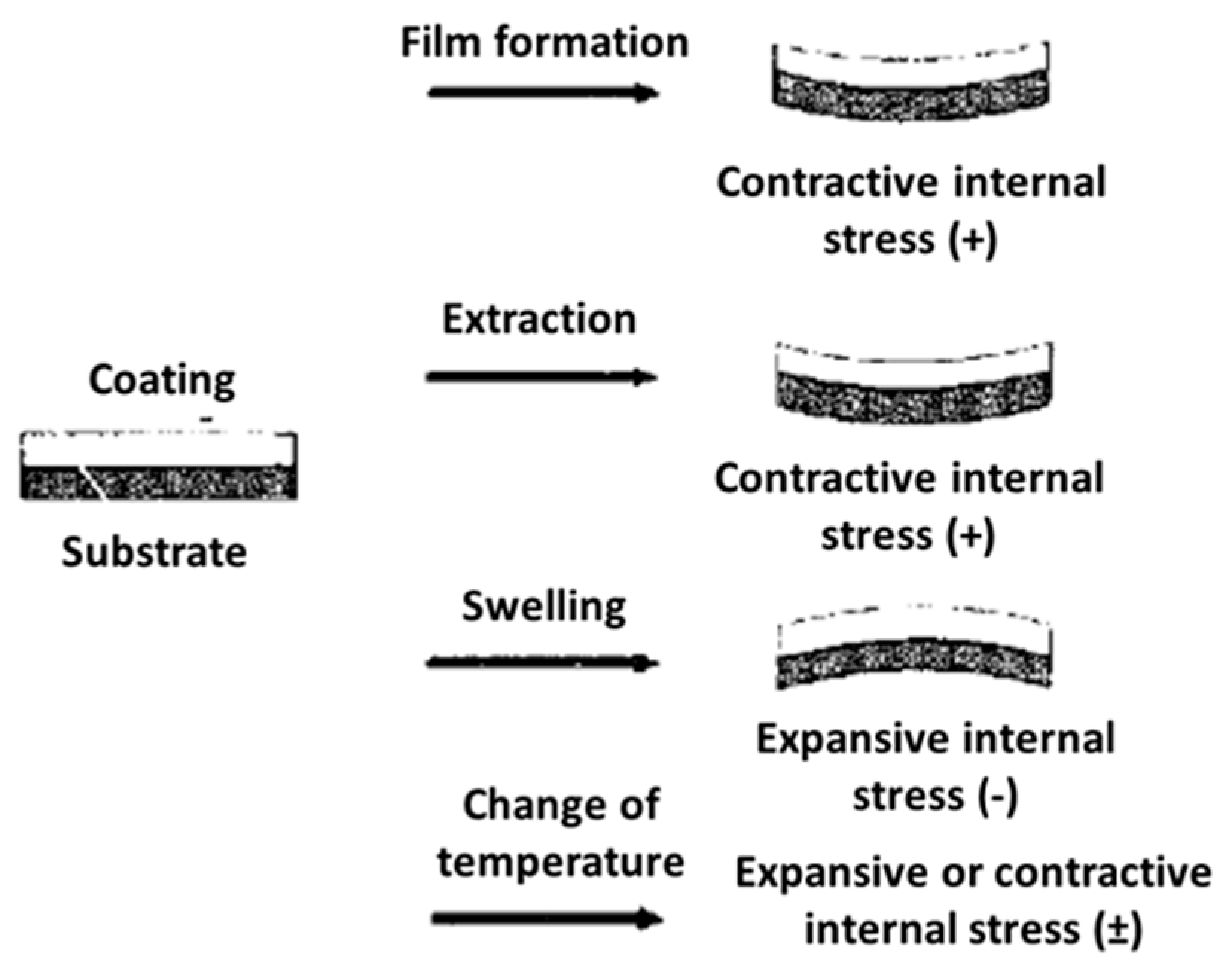
2.3.2. Internal Stresses
- The film formation: solvent evaporation, volume change associated with the curing reaction, etc.;
- Thermal stress induced by differences in the coefficient of thermal expansion of the coating and the substrate at ambient temperature;
- Stress associated with the degradation of the coating polymer;
- Stress induced by the exposition of the system to humidity and temperature.
2.4. Mechanisms of Degradation
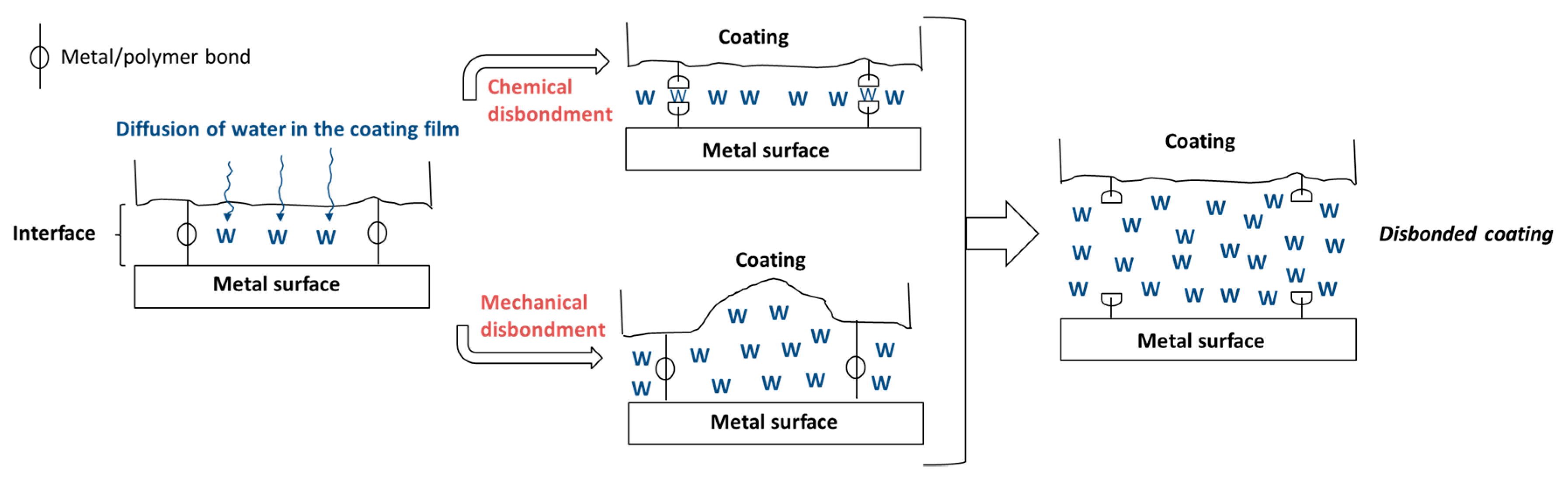
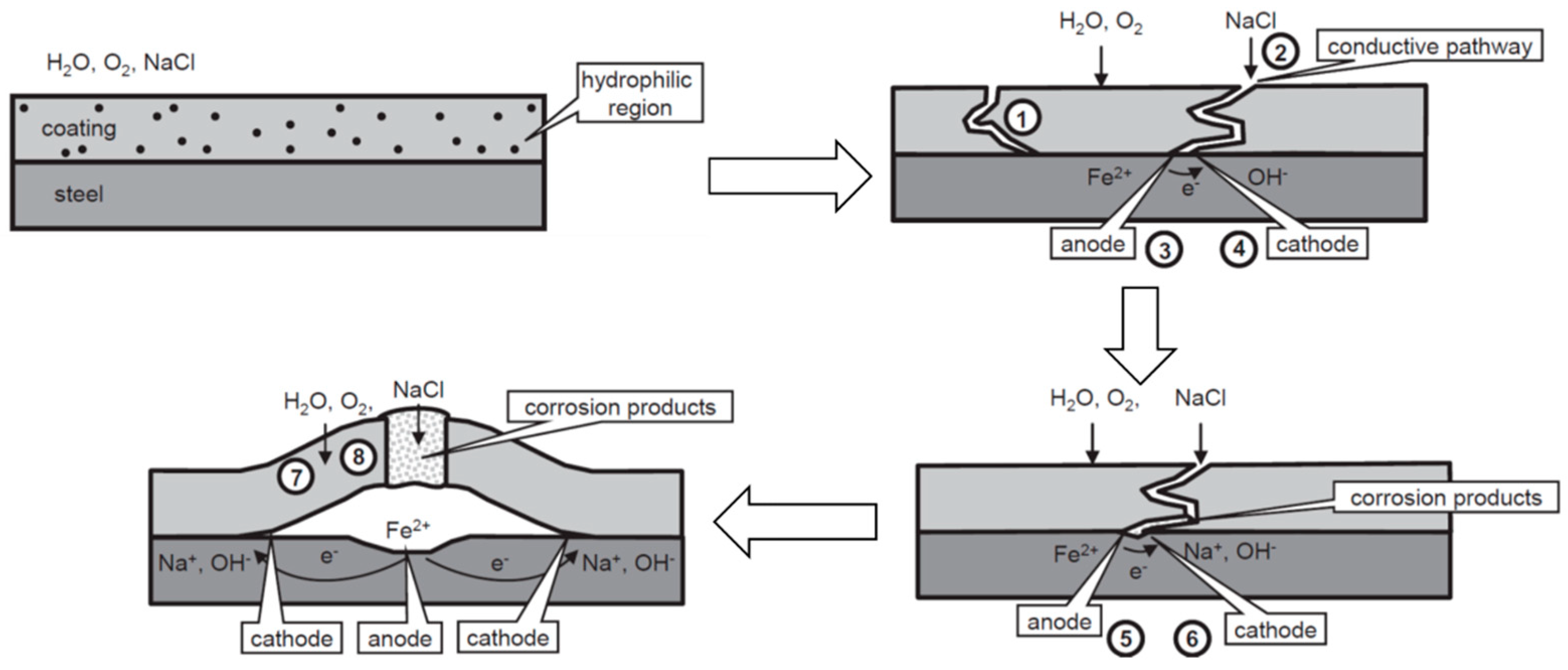
2.4.1. Loss of Protection Due to Corrosion Initiated at Defects
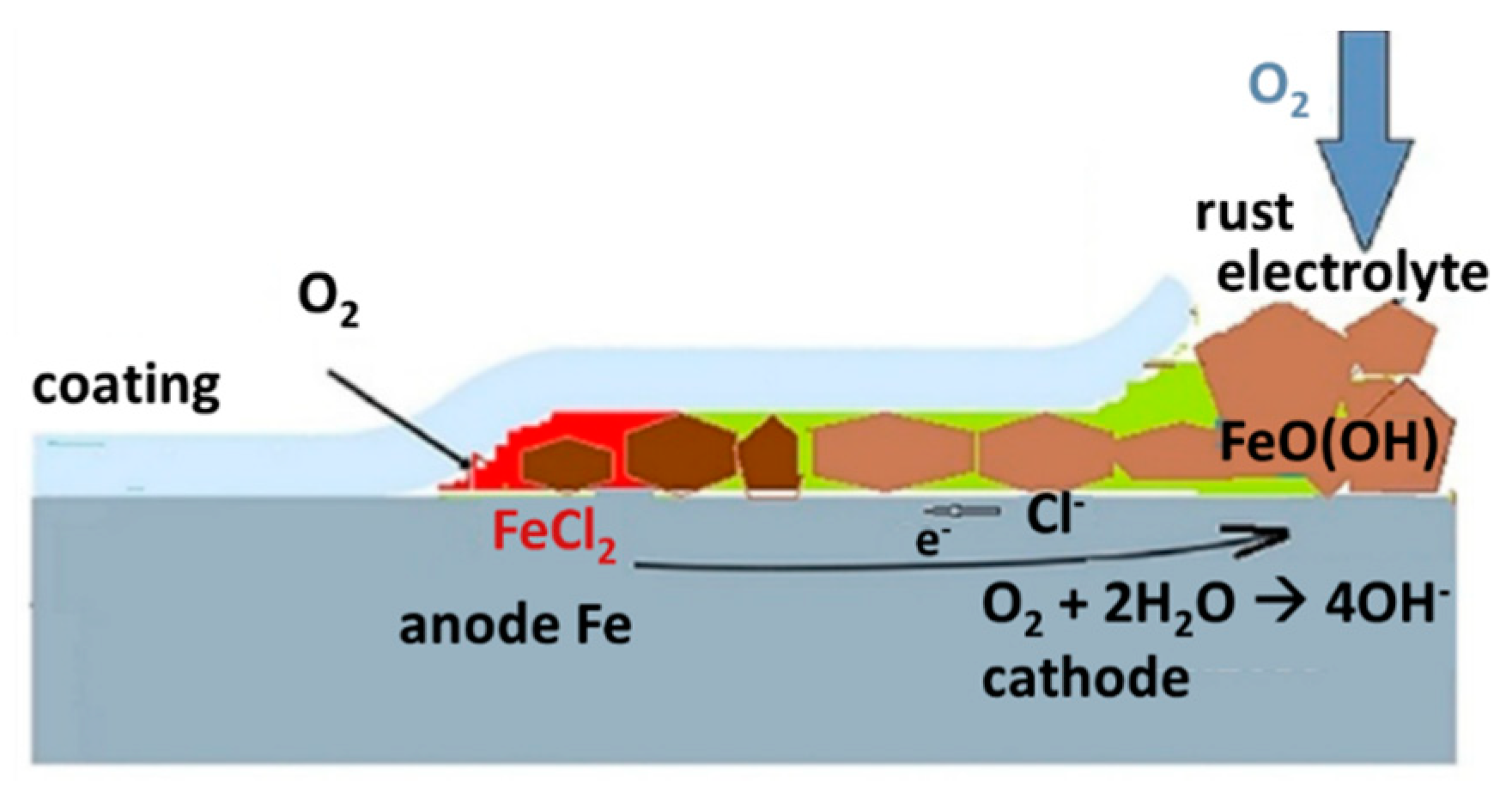
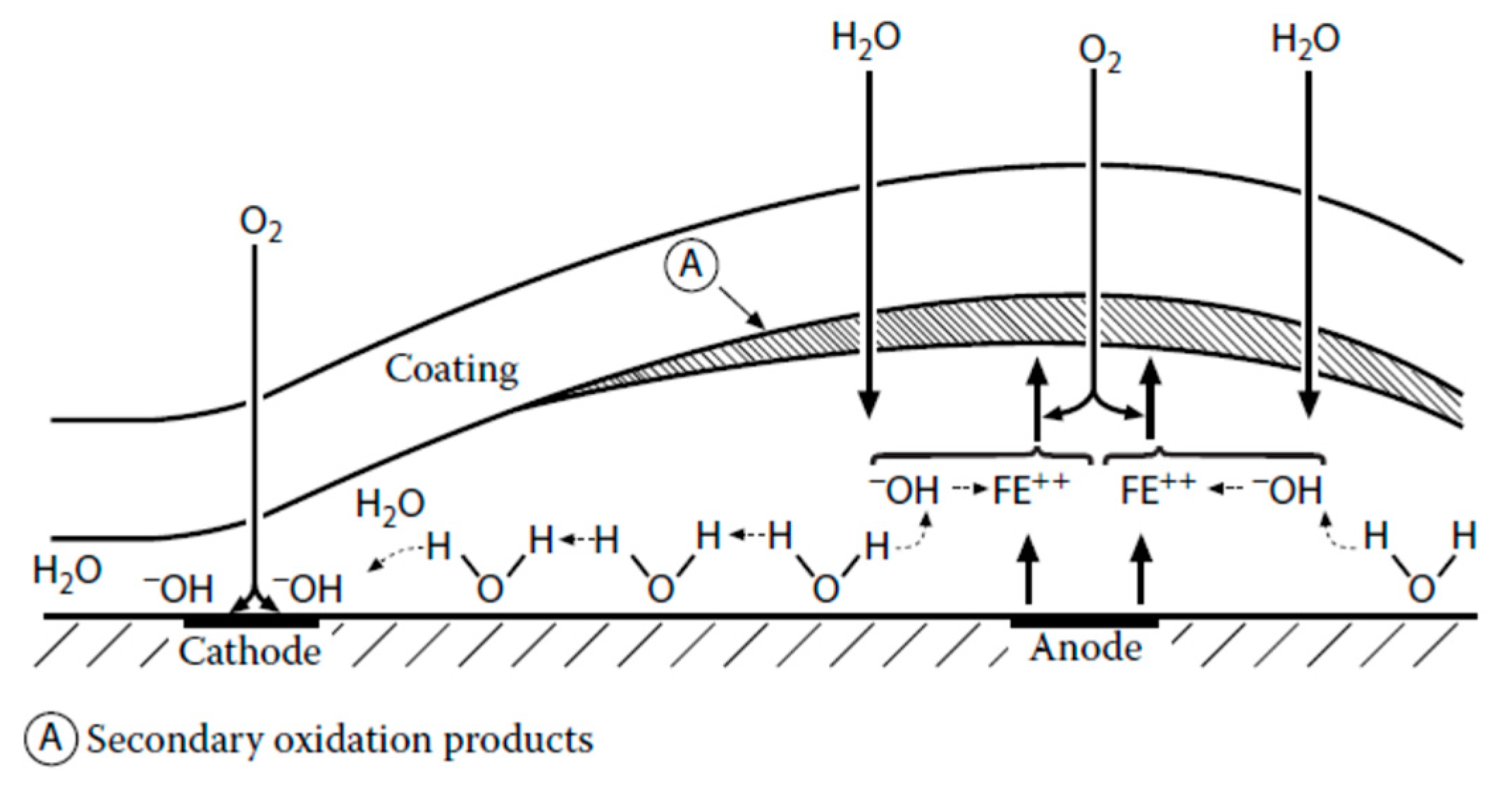
Cathodic Delamination
Anodic Undermining
Filiform Corrosion
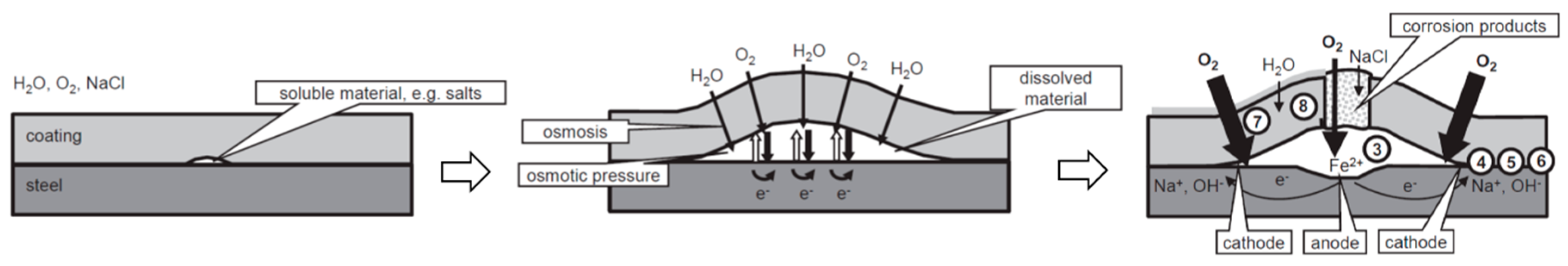
2.4.2. Blistering
2.4.3. Loss of Protection Due to the Weathering of the Paint
3. What Are High-Solid and Powder Coatings?
3.1. Why Formulate Low VOCs Coatings
3.2. High Solid Coating
3.2.1. Generalities
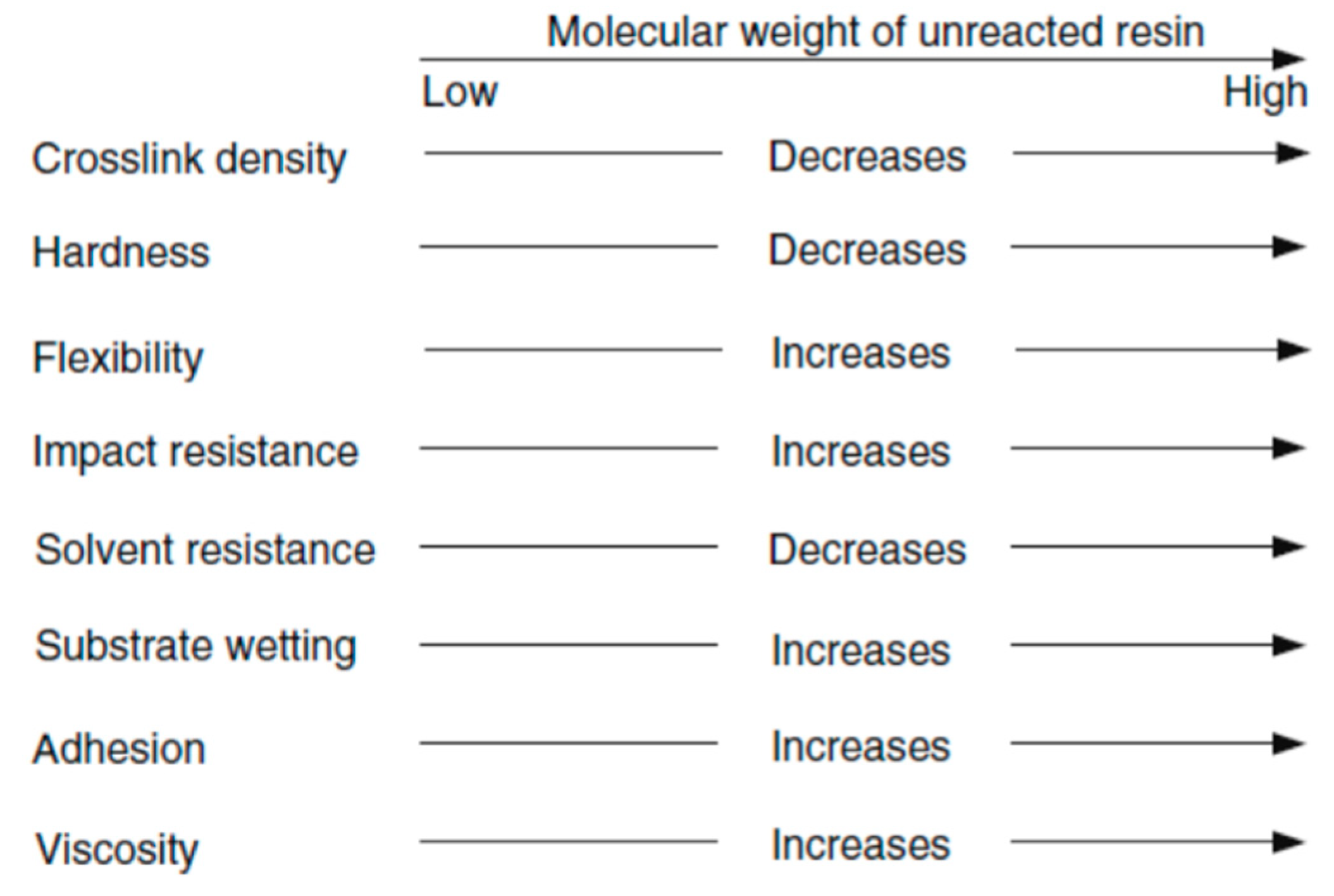
3.2.2. Parameters Influencing Film Formation
Viscosity
Sensitivity to Inadequate Substrate Cleaning—Surface Tension Issue
Shorter Pot Life
Flocculation of Pigment
Cure Window
Sagging
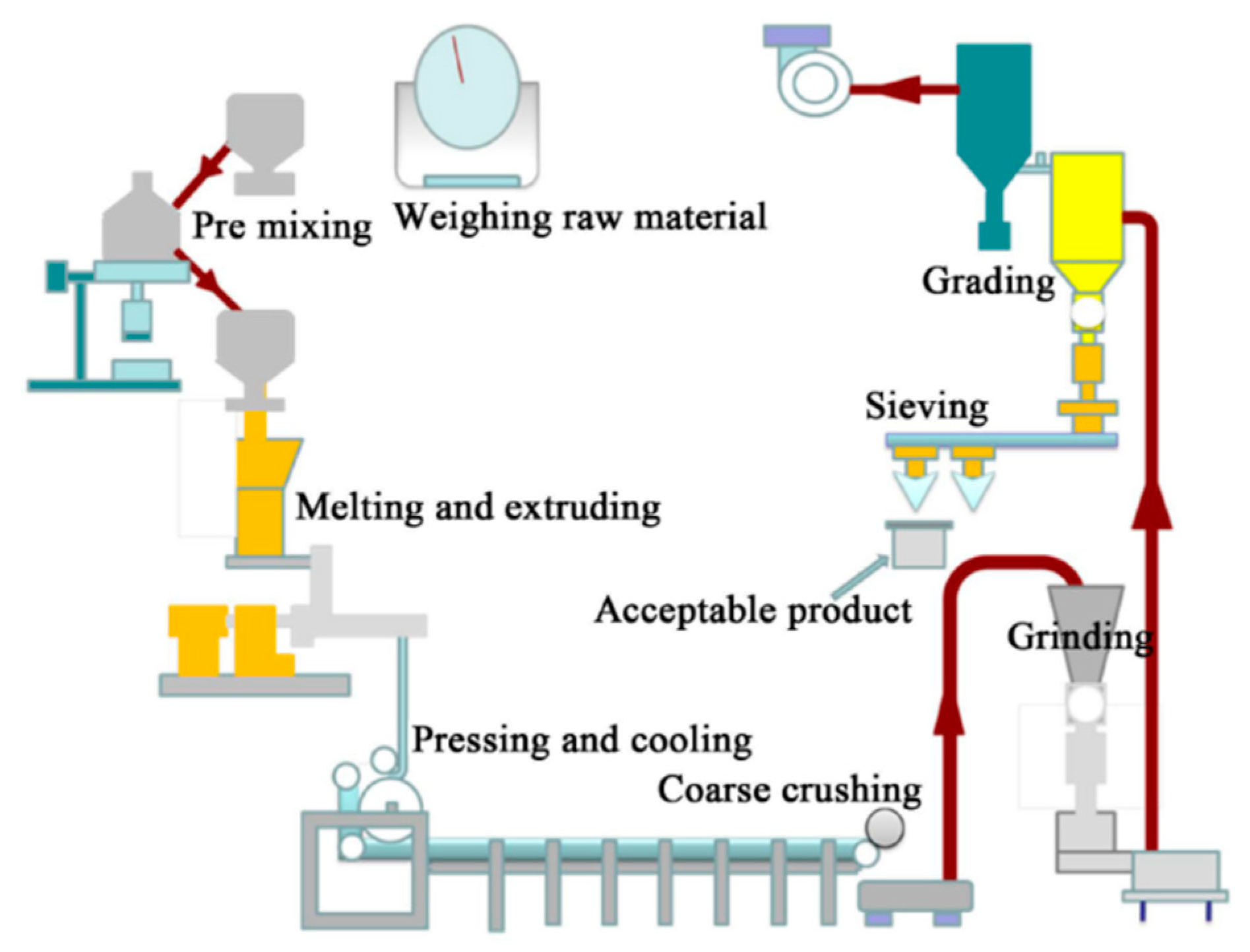
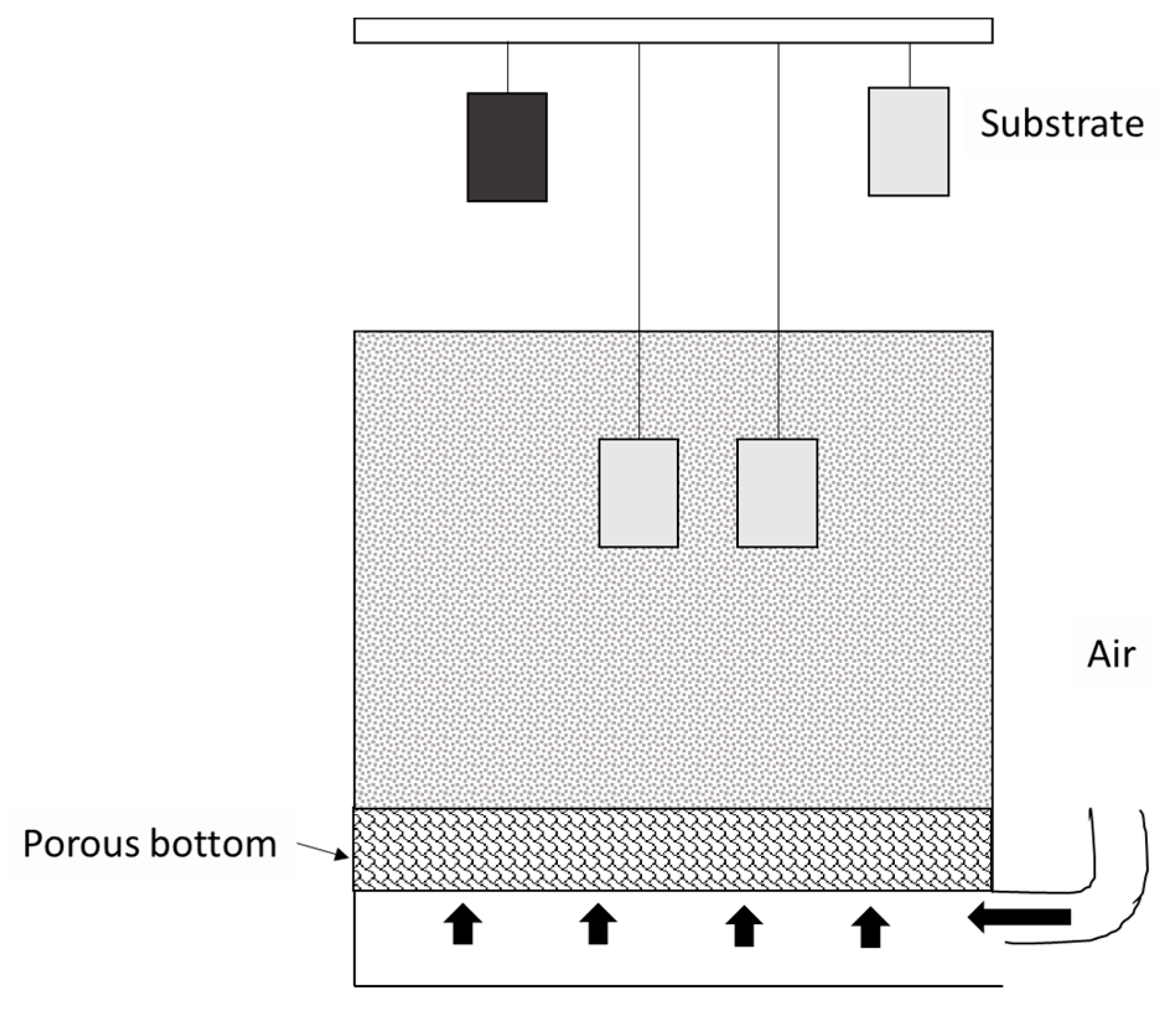
3.3. Powder Coating
3.3.1. Generalities
- -
- In the case of electrostatic spraying, since the powder is drawn to the substrate by electrostatic charge, a very high ratio of the powder ends up on the substrate. This ratio is higher than the one observed for conventional coating. Furthermore, the little fraction which does not hit the substrate can be recycled in the application booth and sprayed again.
- -
- The high temperature of application (160 to 210 °C) makes it faster to cure and allows the formation of a very dense and highly protective film.
- -
- They are ready to use since no dilution or thinning is needed.
- -
- They are easy to apply because they do not run, drip or sag, unlike conventional liquid coating
- -
- They can cover irregular shapes.
3.3.2. Application Methods
Electrostatic Spraying
Fluidized Bed
Other Minor Methods
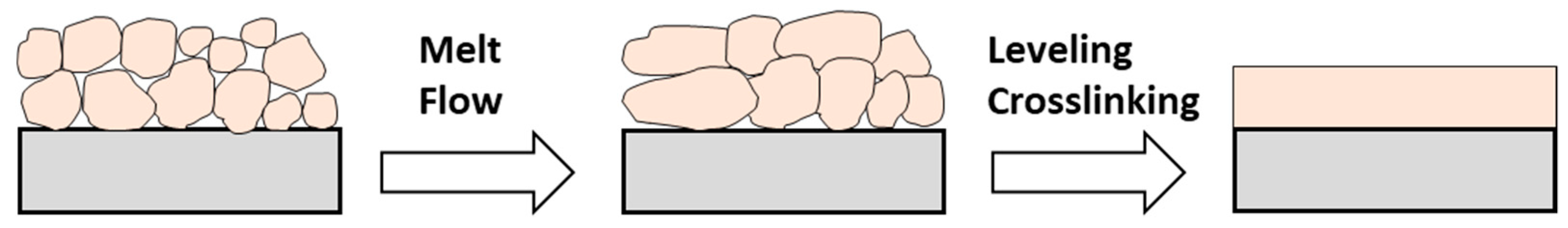
3.3.3. Formulation and Film Formation of Powder Coatings
Formulation of Powder Coatings
Film Formation
Parameters Influencing Film Formation
4. Main Binder Types When Anticorrosive Properties Are Considered
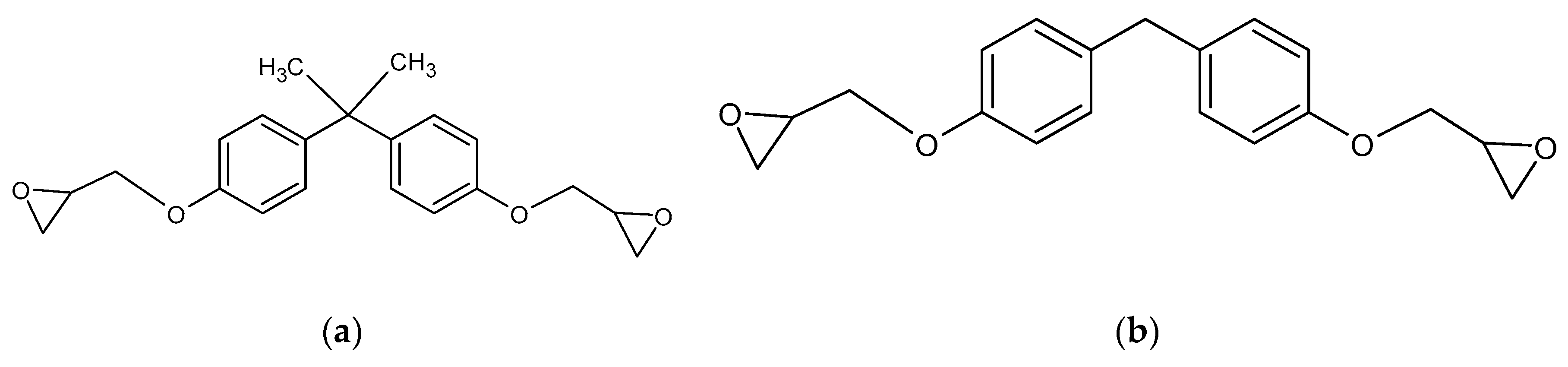
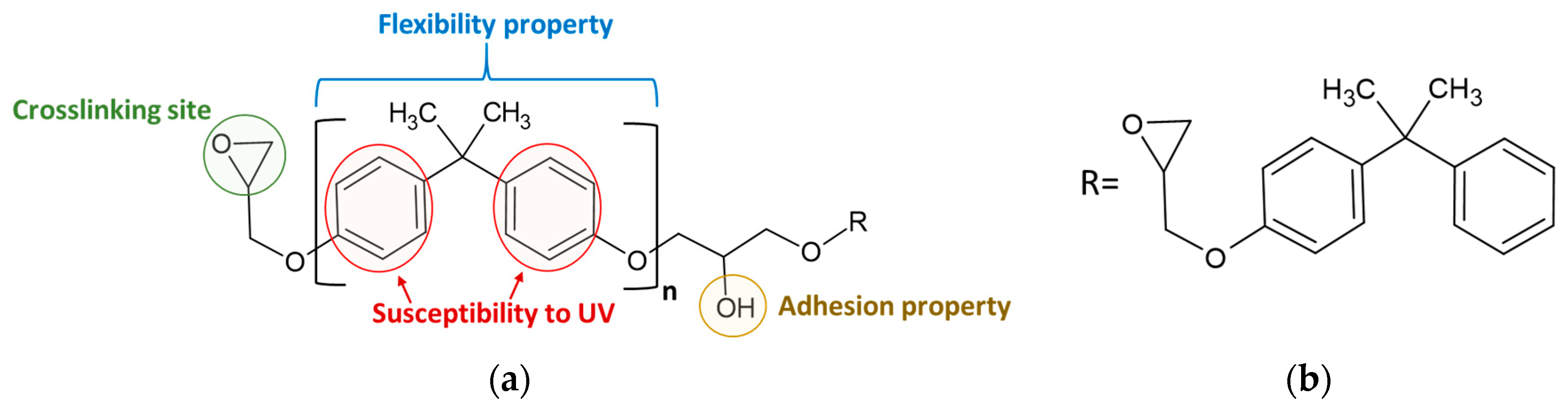
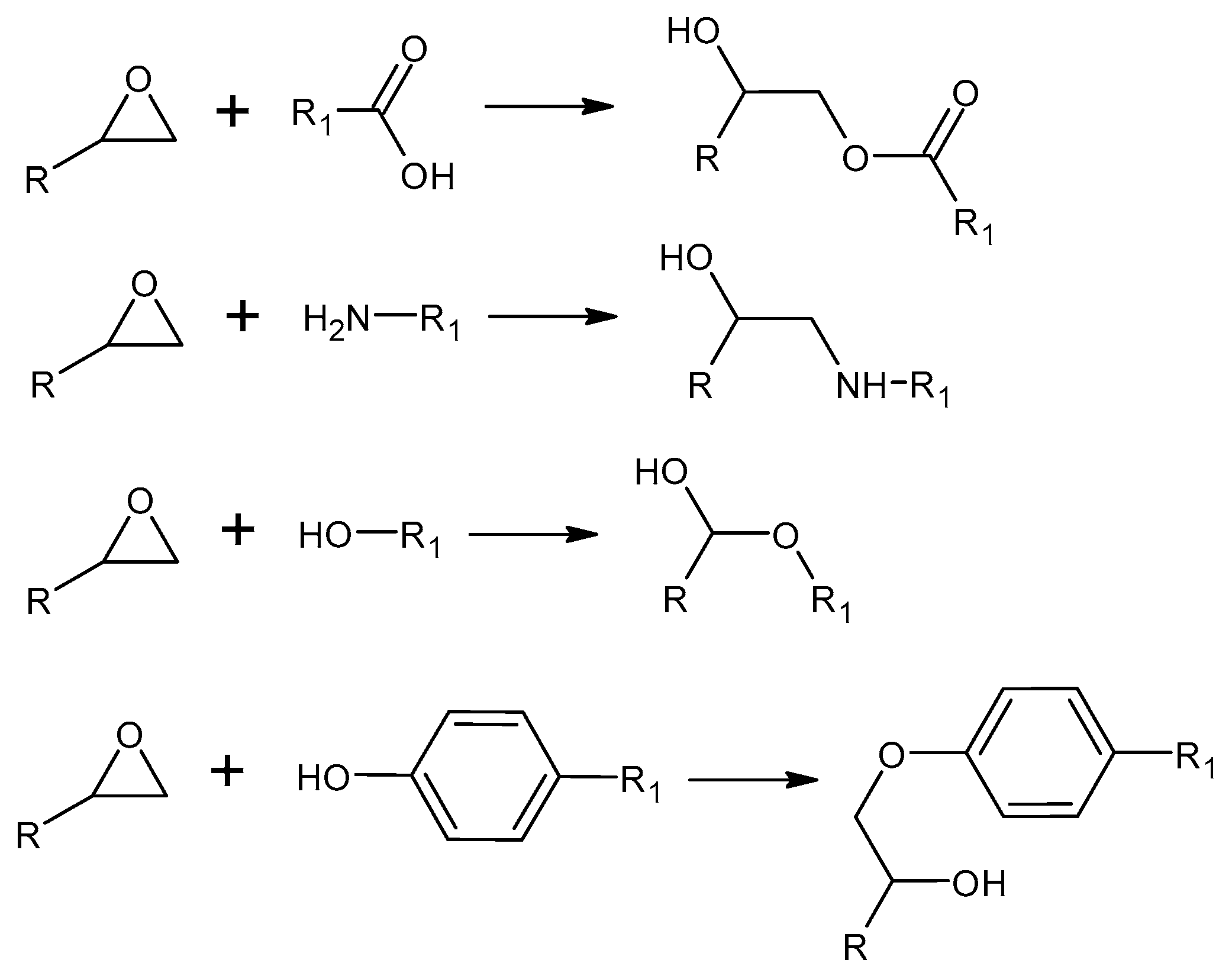
4.1. Epoxy Technology
4.1.1. Generalities
4.1.2. High Solid Epoxy Coatings
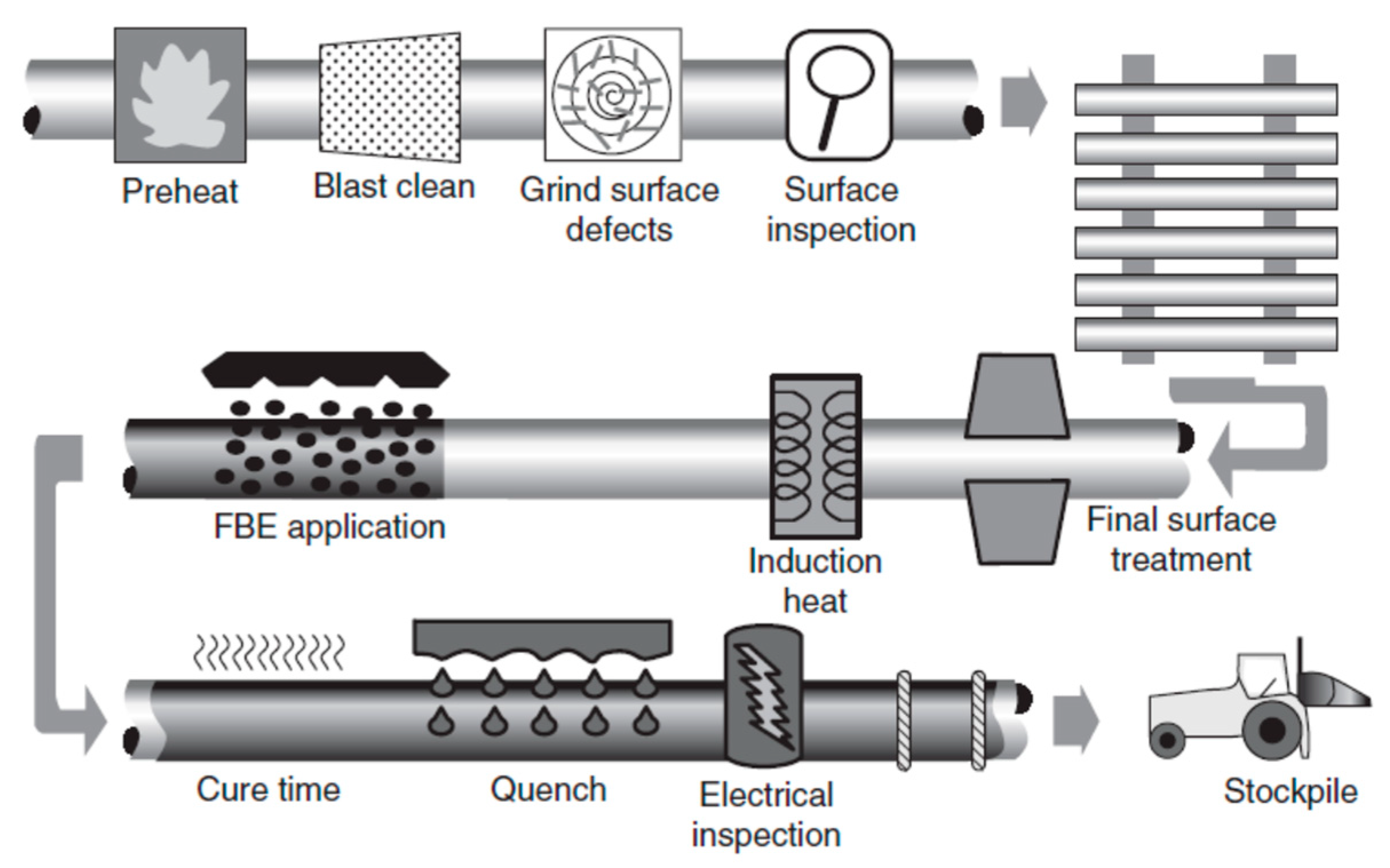
4.1.3. Epoxy Powder Coatings
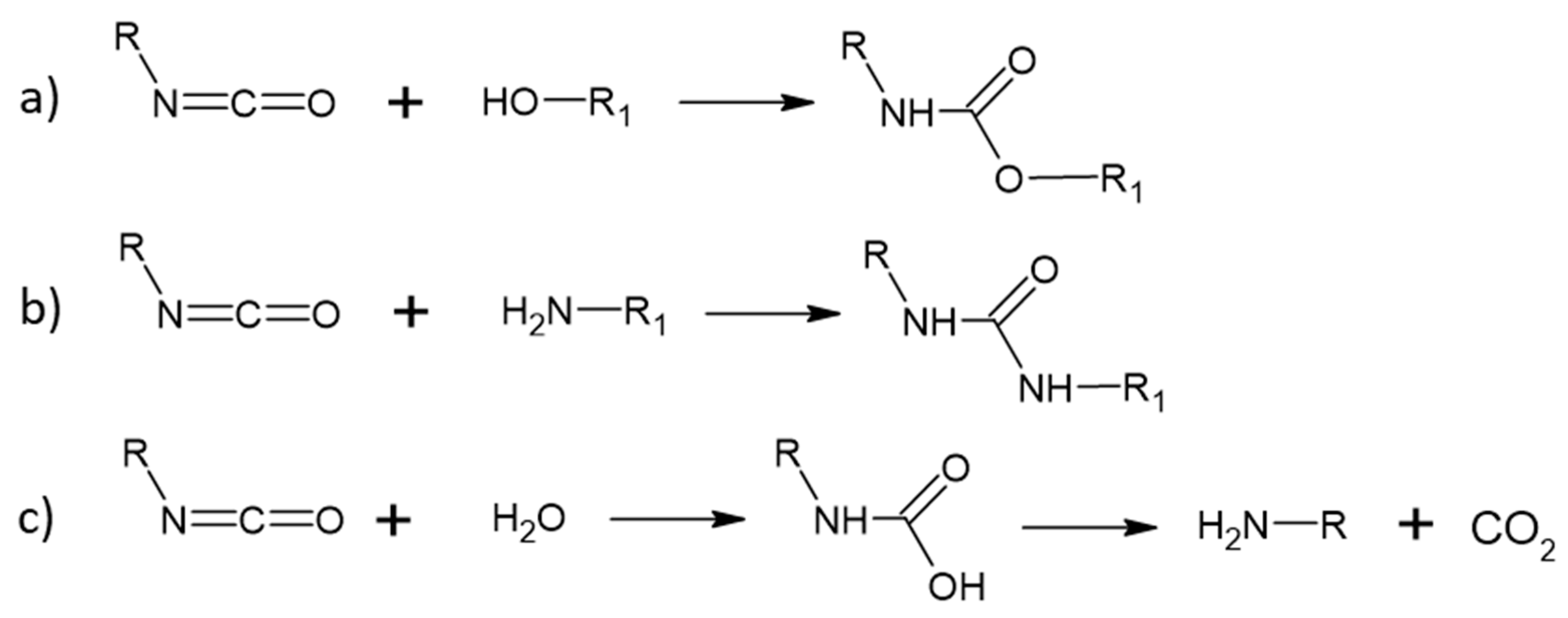
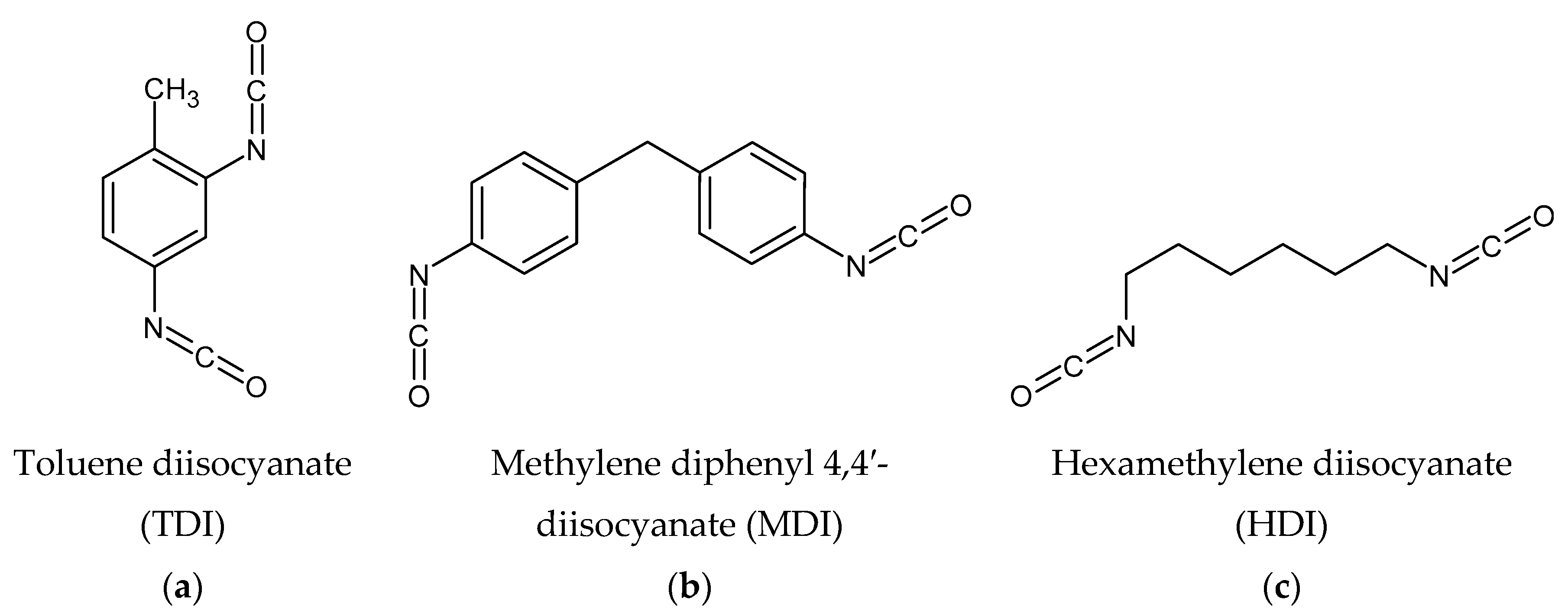
4.2. Polyurethane Technology
4.2.1. Generalities
4.2.2. High Solid Polyurethane Coatings
4.3. Powder Polyester Technology
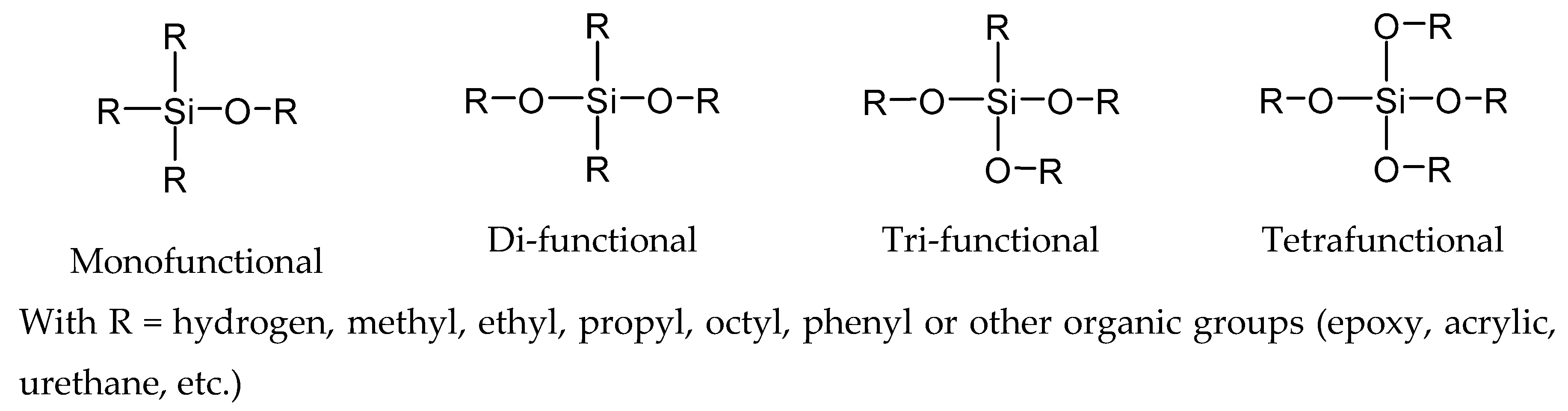
4.4. High Solid Polysiloxane
4.5. Other Technologies
4.5.1. Inorganic Zinc Silicate Coating
4.5.2. Other Types of Powder Coatings
Thermosetting Powder Coatings
Thermoplastic Coatings
5. High-Solid and Powder Coatings for Marine and Offshore Application
5.1. How to Define Marine and Offshore Applications?—Stresses Encountered
5.1.1. Atmospheric Exposure
5.1.2. Immersion
5.1.3. Intermediate Zones
5.2. Coating Behavior
5.2.1. High-Solid Coatings
5.2.2. Powder Coatings
Typical Powder Coatings Use in Offshore Application
Performance of Powder Coatings
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sørensen, P.A.; Kiil, S.; Dam-Johansen, K.; Weinell, C.E. Anticorrosive coatings: A review. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2009, 6, 135–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bierwagen, G.P. Reflections on corrosion control by organic coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 1996, 28, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Bhattacharya, A. Demand for Low-VOC Coatings Continues to Rise. 2020. Available online: https://www.pcimag.com/articles/107370-demand-for-low-voc-coatings-continues-to-rise (accessed on 23 September 2020).
- Knudsen, O.Ø.; Forsgren, A. Weathering and Aging of paint. In Corrosion Control Through Organic Coatings, 2nd ed.; Philip, A., Schweitzer, P.E., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; Chapter 11; pp. 149–180. [Google Scholar]
- Lyon, S.B.; Bingham, R.; Mills, D.J. Advances in corrosion protection by organic coatings: What we know and what we would like to know. Prog. Org. Coat. 2017, 102, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, D.J.; Jamali, S. The best tests for anti-corrosive paints. And why: A personal viewpoint. Prog. Org. Coat. 2017, 102, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, A.S. Key issues in applying organic paint coatings. In High Performance Organic Coatings, 1st ed.; Khanna, A.S., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2008; Chapter 1; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- de Wit, J.H.M. Inorganic and Organic Coatings. In Corrosion Mechanisms in Theory and Practice, 1st ed.; Marcus, P., Oudar, J., Eds.; Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 581–628. [Google Scholar]
- Leidheiser, H. Corrosion of painted metals—A Review. Corrosion 1982, 38, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayne, J.E.O. How paints prevent corrosion. Anti-Corros. Methods Mater. 1954, 1, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, N.L. The barrier properties of paint coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 1991, 19, 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittelberger, W.W.; Elm, A.C. Diffusion of chloride through various paint systems. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1952, 44, 326–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacon, R.C.; Smith, J.J.; Rugg, F.M. Electrolytic resistance in evaluating protective merit of coatings on metals. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1948, 40, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinsella, E.M.; Mayne, J.E.O. Ionic conduction in polymers films I. Influence of electrolyte resistance. Br. Polym. J. 1969, 1, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayne, J.E.O.; Scantelbury, J.D. Ionic conduction in polymer films II. Inhomogeneous structure of varnish films. Br. Polym. J. 1970, 2, 240–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croll, S.G. Electrolyte transport in polymer barrier coatings: Perspectives from other disciplines. Prog. Org. Coat. 2018, 124, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykes, J.M.; Whyte, E.P.; Pu, X.; Shaher Sahir, Z. Does “coating resistance” control corrosion? Prog. Org. Coat. 2017, 102, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, O.Ø.; Forsgren, A. Corrosion-Protective Pigments. In Corrosion Control Through Organic Coatings, 2nd ed.; Philip, A., Schweitzer, P.E., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; Chapter 4; pp. 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Bieganska, B.; Zubielewicz, M.; Smieszek, E. Influence of barrier pigments on the performance of protective coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 1988, 16, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leidheiser, H.; Wang, W.; Ingetoft, L. The mechanism for the cathodic delamination of organic coatings from a metal surface. Prog. Org. Coat. 1983, 11, 19–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hare, C.H.; Wright, S. Anti-corrosive primers based on zinc flake. J. Coat. Technol. 1982, 54, 65–77. [Google Scholar]
- Feliu, S.; Barajas, R.; Bastisdas, J.M.; Morcillo, M. Mechanism of cathodic protection of zinc-rich paints by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. 1. Galvanic Stage. J. Coat. Technol. 1989, 61, 63–69. [Google Scholar]
- Feliu, S.; Barajas, R.; Bastisdas, J.M.; Morcillo, M. Mechanism of cathodic protection of zinc-rich paints by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. 2. Barrier Stage. J. Coat. Technol. 1989, 61, 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Kalendova, A. Effects of particle sizes and shapes of zinc metal on the properties of anticorrosive coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2003, 46, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rammelt, U.; Reinhard, R. Characterization of active pigments in damage of organic coatings on steel by means of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Prog. Org. Coat. 1994, 24, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romagnoli, R.; Vetere, V.F. Non-pollutant corrosion inhibitive pigments: Zinc phosphate, a review. Corros. Rev. 1995, 13, 45–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chromy, L.; Kaminska, E. Non-toxic anticorrosive pigments. Prog. Org. Coat. 1990, 18, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deyà, M.; Vetere, V.F.; Romagnoli, R.; del Amo, B. Zinc tripolyphosphate: An anticorrosive pigment for paints. Surf. Coat. Int. Part B 2003, 86, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pryor, M.J.; Cohen, M. The inhibition of the corrosion of iron by some anodic inhibitors. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1953, 100, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leidheiser, H. Mechanism of corrosion inhibition with special attention to inhibitors in organic coatings. J. Coat. Technol. 1981, 53, 29–39. [Google Scholar]
- Clay, M.F.; Cox, J.H. Chromate and phosphate pigments in anti-corrosive primers. J. Oil Colour Chem. 1973, 56, 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez, M.; Genesca, J.; Uruchurtu, J.; Galliano, F.; Landolt, D. Effect of inhibitive pigment zinc-aluminium-phosphate (ZAP) on the corrosion mechanisms of steel in waterborne coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2006, 56, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubielewicz, M.; Gnot, W. Mechanisms of non-toxic anticorrosive pigments in organic waterborne coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2004, 49, 358–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Ayana, Y.M.; El-Sawy, S.M.; Salah, S.H. Zinc-ferrite pigment for corrosion protection. Anti-Corros. Methods Mater. 1997, 44, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beland, M. New non-toxic pigment performance profile equivalent to zinc chromate. Am. Paint Coat. J. 1991, 76, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Funke, W. Problems and progress in organic coatings science and technology. Prog. Org. Coat. 1997, 31, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funke, W. How organic coatings systems protect against corrosion. Polym. Mater. Control Corros. Control. 1986, 200–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBain, J.W.; Hopkins, D.G. On adhesives and adhesive action. J. Phys. Chem. 1925, 29, 188–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpe, L.H.; Schonhorn, H. Surface energetics, adhesion and adhesive joints. Adv. Chem. Ser. 1964, 8, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voyutski, S.S. Autohesion and adhesion of high polymers. In Polymer Reviews; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1963; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Buchan, S.; Rae, W.D. Chemical nature of the rubber to glass bond. Trans. Inst. Rubber Ind. 1946, 20, 205–216. [Google Scholar]
- Bikerman, J.J. Causes of poor adhesion: Weak boundary layers. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1967, 59, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldan, A. Adhesion phenomena in bonded joints. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2012, 38, 95–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourche, G. An overview of the basic aspects of polymer adhesion. Part I: Fundamentals. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1995, 35, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, J.; Scantlebury, J.D.; Lyon, S.B. The effect of surface/primer treatments on the performance of alkyd coated steel. Corros. Sci. 2001, 43, 829–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leidheiser, H.; Funke, W. Water disbondment and wet adhesion of organic coatings on metals: A review and interpretation. J. Oil Color Chem. Assoc. 1987, 70, 121–132. [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield, D.; Scantelbury, J.D. The protective action of organic coatings on steel: A review. J. Corros. Sci. Eng. 2000, 3, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Funke, W. Blistering of paint films and filiform corrosion. Prog. Org. Coat. 1981, 9, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pommersheim, J.M.; Nguyen, T. Prediction of blistering in coating systems. ACS Symp. Ser. 1998, 689, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Fuente, D.; Rohwerder, M. Fundamental investigation on the stability of the steel/coating interfaces contaminated by submicroscopy salt particles. Prog. Org. Coat. 2008, 61, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morcillo, M. Soluble salts: Their effect on premature degradation of anticorrosive paints. Prog. Org. Coat. 1999, 36, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, A.S. Surface preparation for organic paint coatings. In High Performance Organic Coatings, 1st ed.; Khanna, A.S., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2008; Chapter 2; pp. 27–41. [Google Scholar]
- ISO Standard. ISO 8501 Preparation of Steel Substrates before Application of Paints and Related Products—Visual Assessment of Surface Cleanliness; ISO Standard: Brussels, Belgium, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Le Calvé, P.; Pautasso, J.-P.; Le Bozec, N. Characterizing Surfaces after UHP Waterjetting in New Ship Construction. 2011. Available online: https://www.paintsquare.com/store/assets/JPCL_uhp_ebook1.pdf#page=38 (accessed on 23 September 2020).
- Le Calvé, P.; Pautasso, J.-P.; Le Bozec, N. Characterizing Surfaces after UHP Waterjetting on Shop-Primed Steel in New Ship Construction, Part 3. 2012. Available online: https://search.proquest.com/openview/e9c43a2ce5adcfc5d99d620eb9dde947/1?pq-origsite=gscholar&cbl=36623 (accessed on 23 September 2020).
- Knudsen, O.Ø.; Forsgren, A. Blast cleaning and other heavy surface pretreatments. In Corrosion Control Through Organic Coatings, 2nd ed.; Philip, A., Schweitzer, P.E., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; Chapter 7; pp. 89–108. [Google Scholar]
- Momber, A.W.; Greverath, W.D. Surface preparation standards for steel substrates—A critical review. J. Prot. Coat. Linings 2004, 21, 48–52. [Google Scholar]
- Momber, A.W.; Koller, S.; Dittmers, H.J. Effects of surface preparation methods on adhesion of organic coatings to steel substrates. J. Prot. Coat. Linings 2004, 21, 44–50. [Google Scholar]
- Hare, C. Internal stress-related coating system failures. J. Prot. Coat. Linings 1996, 13, 99–113. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, K. The internal stress of coating films. Prog. Org. Coat. 1980, 8, 143–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clyne, T.W. Residual stresses in surface coatings and their effects on interfacial debonding. Key Eng. Mater. 1996, 5, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piens, M.; de Deurwaerder, H. Effect of coating stress on adherence and on corrosion protection. Prog. Org. Coat. 2001, 43, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negele, O.; Funke, W. Internal stress and wet adhesion of organic coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 1996, 28, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarov, A.; Thierry, D. Application of Scanning Kelvin Probe in the study of protective paints. Front. Mater. 2019, 6, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharman, C.F. Filiform underfilm corrosion of lacquered steel surfaces. Nature 1944, 153, 621–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castle, J.E.; Watts, J.F. Cathodic disbondment of well characterized steel/coating interfaces. In Corrosion Control by Organic Coatings; Leidhieser, H., Jr., Ed.; NACE International: Houston, TX, USA, 1981; p. 78. [Google Scholar]
- Hammond, J.S.; Holubka, J.W.; de Vries, J.E.; Dickie, R.A. The application of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy to a study of interfacial composition in corrosion-induced paint de-adhesion. Corros. Sci. 1981, 21, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, P.A.; Dam-Johansen, K.; Weinell, C.E.; Kiil, S. Cathodic delamination of seawater-immersed anticorrosive coatings: Mapping of parameters affecting the rate. Prog. Org. Coat. 2010, 68, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, P.A.; Dam-Johansen, K.; Weinell, C.E.; Kiil, S. Cathodic delamination: Quantification of ionic transport rates along coating-steel interfaces. Prog. Org. Coat. 2010, 68, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarov, A.; Thierry, D. Mechanism of the corrosion exfiolation of a polymer coating from a carbon steel. Prot. Met. Phys. Chem. Surf. 2009, 45, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarov, A.; Thierry, D.; Le Calvé, P.; Pautasso, J.-P. Scanning Kelvin Probe investigation of corrosion under thick marine paint systems applied on carbon steel. Corrosion 2012, 68, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steel, G.D. Filiform corrosion on architectural aluminium—A review. Anti-Corros. Methods Mater. 1994, 41, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slabaugh, W.H.; Hutchins, L.L.; Dejager, W.; Hoover, S.E. Filiform corrosion of aluminium. J. Paint Technol. 1972, 44, 76–80. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, H.; Nisancioglu, K. Filiform corrosion of aluminium sheet. I. Corrosion behaviour of painted steel. Corros. Sci. 1998, 40, 1179–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Wit, J.H.W.; Mol, J.M.C. Organic coatings for marine and shipping applications. In High Performance Organic Coatings, 1st ed.; Khanna, A.S., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2008; Chapter 16; pp. 337–388. [Google Scholar]
- Ngyuen, T.N.; Hubbard, J.B.; McFadden, G.B. A mathematical model for the cathodic blistering of organic coatings on steel immersed in electrolytes. J. Coat. Technol. 1991, 63, 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Funke, W. Toward a unified view of the mechanism responsible for paint defects by metallic corrosion. Ind. Eng. Chem. Prod. Res. Dev. 1985, 24, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hare, C.H. Mechanisms of photolytically induced degradation. J. Prot. Coat. Linings 2000, 17, 73–86. [Google Scholar]
- Galant, C.; Fayolle, B.; Kuntz, M.; Verdu, J. Thermal and radio-oxidation of epoxy coating. Prog. Org. Coat. 2010, 69, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, S.S.; Khanna, A.S. Waterborne coatings for corrosion protection. In High Performance Organic Coatings, 1st ed.; Khanna, A.S., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2008; Chapter 13; pp. 247–286. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, L.W. Design consideration for high solids coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 1982, 10, 55–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, K.D. Paint and coatings: A mature industry in transition. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1997, 22, 203–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S. Rheology of high solid coatings I. Analysis of Sagging and Slumping. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1978, 22, 2769–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, F.N.; Nichols, M.E.; Pappas, S.P. Solventborne and high solids coatings. In Organic Coatings: Science and Technology, 4th ed.; Wiley, J., Ed.; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; Chapter 25; pp. 357–365. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, D.R.; Budde, G.F. Cross-linking chemistry and network structure in high solids acrylic-melamine coatings. Ind. Eng. Chem. Process. Des. Dev. 1981, 20, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M. Recent advances in high solids coatings. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 1980, 15, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, O.Ø.; Forsgren, A. Powder Coatings. In Corrosion Control through Organic Coatings, 2nd ed.; Philip, A., Schweitzer, P.E., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; Chapter 6; pp. 71–87. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Z.; Wen, S.; Wang, J.; Yin, C.; Yu, D.; Luo, J. The review of powder coatings. J. Mater. Sci. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroschwitz, J.J.; Mark, H.F. Coatings methods, Powder technology. In Encyclopedia of Polymer Science and Technology, 4th ed.; Mark, H.F., Ed.; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; Volume 5, pp. 570–603. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, F.N.; Nichols, M.E.; Pappas, S.P. Powder coatings. In Organic Coatings: Science and Technology, 4th ed.; Wiley, J., Ed.; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; Chapter 28; pp. 385–402. [Google Scholar]
- Spyrou, E. Powder Coatings Chemistry and Technology, 3rd ed.; Vincentz Network GmbH: Hanover, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, A.G. The science and technology of electrostatic powder spraying, transport and coating. J. Electrost. 1998, 45, 85–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boncza-Tomaszewski, Z.; Penczek, P. Tribo charging powder coatings. Macromol. Symp. 2002, 187, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karidkar, S.; Mali, R. Optimization of powder spray process parameters using Taguchi methodology. Adv. Intell. Syst. Res. 2017, 137, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlmann, P.; Grundke, K. Influence of additives on interfacial phenomena during film formation of powder coatings. J. Coat. Technol. 2001, 73, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barletta, M.; Lusvarghi, L.; Pighetti Mantini, F.; Rubino, G. Epoxy-based thermosetting powder coatings: Surface appearance, scratch adhesion and wear resistance. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 201, 7449–7504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafi, R.; Mirabedini, S.M.; Naderi, R.; Attar, M.M. Effect of curing characterization on the corrosion performance of polyester and polyester/epoxy powder coatings. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 3280–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerje, S.; Mazumder, M.K. Adhesion of charged powders to metal surface in the powder coating process. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1996, 32, 1243–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO Standard. ISO 12944-5: Paints and Varnishes—Corrosion Protection of Steel Structures by Protective Paints—Part 5: Protective Paint Systems; ISO Standard: Brussels, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Knudsen, O.Ø.; Forsgren, A. Generic types of anticorrosion coatings. In Corrosion Control through Organic Coatings, 2nd ed.; Philip, A., Schweitzer, P.E., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; Chapter 3; pp. 11–30. [Google Scholar]
- Kanitkar, S. High performance epoxies and solvent-less epoxies for corrosion protection. In High Performance Organic Coatings, 1st ed.; Khanna, A.S., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2008; Chapter 8; pp. 145–164. [Google Scholar]
- Banfield, T.A. The protective aspects of marine paints. Prog. Org. Coat. 1979, 7, 253–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaner, W.L.; Aguirre-Vargas, F.; Ge, S.; Xu, N.; Krishnan Karunakaran, K.; Weishuhn, J. Tunning Toughness and Flexibility in Liquid Applied High Solids Epoxy Coatings; Corpus ID: 102500379; The Dow Chemical Company: Midland, TX, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Saunders, T.F.; Lévy, M.F.; Serino, F.F. Mechanisms of the tertiary amine-catalyzed dicyandiamide cure of epoxy resins. J. Polym. Sci. Part A 1967, 5, 1609–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahir, S.A. The mechanism of cure epoxide resins by cyanamide and dicyandiamide. Adv. Org. Coat. Sci. Technol. 1982, 4, 82–102. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, M.D.; Schneider, N.S. Mechanism of the dicyandiamide/epoxide reaction. Macromolecules 1991, 24, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaukler, J.C. Oligomer formation in epoxy-dicyandiamide systems. J. Adhes. 2012, 88, 720–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickerson, J.G. FBE evolves to meet industry need for pipeline protection. Pipeline Gas Ind. 2001, 84, 64–74. [Google Scholar]
- Kehr, A.; Enos, D.G. FBE, a foundation for pipeline corrosion coatings. In Proceedings of the NACE International’s CORROSION Conference, Orlando, FL, USA, 26–31 March 2000; p. 00757. [Google Scholar]
- Kehr, A.; Dabiri, M.; Hislop, R. Dual-Layer Fusion Bonded Epoxy (FBE) Coatings Protect Pipelines. In Proceedings of the INDOPIPE, Jakarta, Indonesia, 30 May–1 June 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay, D.K.; Raju, K.V.S.N. Structural engineering of polyurethane coatings for high performance applications. Prog. Polym. Mater. Sci. 2007, 32, 352–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somarathna, H.M.C.C.; Raman, S.N.; Mohotti, D.; Mutalib, A.A.; Badri, K.H. The use of polyurethane for structural and infrastructural engineering applications: A state-of-the-art review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 190, 995–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; He, Z.; Hihara, L.H.; Mehr, H.S.; Soucek, M.D. Outdoor exposure and accelerated weathering of polyurethane/polysiloxane hybrid coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 130, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keene, L.T.; Halada, G.P.; Clayton, C.R. Failure of navy coatings systems 1: Chemical depth profiling of artificially and naturally weathered high-solids aliphatic poly(ester-urethane) military coating systems. Prog. Org. Coat. 2005, 52, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM Standard D16-00. Technology for Paint, Related Coatings, Materials and Applications; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Potter, T.A.; Schmelzer, H.G.; Baker, R.D. High-solids coatings based on polyurethane chemistry. Prog. Org. Coat. 1984, 12, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.W. 100% solids polyurethane and polyurea coatings technology. Coat. World 2003, 49–58. [Google Scholar]
- Renz, H.; Bruchmann, B. Pathways targeting solvent-free PUR coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2001, 43, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannari, V.M.; Massingill, J.L. Two-component high-solid polyurethane coatings systems based on soy polyols. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2006, 3, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misev, T.A.; van der Linde, R. Powder coatings technology: New developments at the turn of the century. Prog. Org. Coat. 1998, 34, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaesler, K.H. Polysiloxane coatings for corrosion protection. In High performance Organic Coatings, 1st ed.; Khanna, A.S., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2008; Chapter 12; pp. 225–246. [Google Scholar]
- Chrusciel, J.J.; Lesniak, E. Modification of epoxy resins with functional silanes, polysiloxanes, silsesquioxanes, silica and silicates. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2015, 41, 67–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byczynski, L.; Dutkiewicz, M.; Maciejewski, H. Synthesis and properties of high-solids hybrid materials obtained from epoxy functional urethanes and siloxanes. Prog. Org. Coat. 2015, 84, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gommans, J.H.P. Polysiloxane Coatings—A mature technology. In Proceedings of the Corrosion & Prevention Conference, Auckland, New Zealand, 1 January 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Parashar, G.; Srivastava, D.; Kumar, P. Ethyl silicate binders for high performance coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2001, 42, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO Standard. ISO 12944-2: Paints and Varnishes—Corrosion Protection of Steel Structures by Protective Paints—Part 2: Environment Classification; ISO Standard: Brussels, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Thierry, D.; Persson, D.; Le Bozec, N. Atmospheric corrosion of zinc and zinc alloyed coated steel. In Encyclopedia of Interfacial Chemistry: Surface Science and Electrochemistry, 1st ed.; Wandelt, K., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 55–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivier, M.-G.; Romano, A.P.; Vandermeiers, C.; Mathieu, X.; Boelman, M. Influence of the stress generated during an ageing cycle on the barrier properties of catophoretic coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2008, 63, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drodten, P. Marine atmosphere, splash, tidal and immersion zones. In Corrosion Handbook Online, 1st ed.; Kreysa, G., Schutze, M., Eds.; Dechema: Frankfurt, Germany, 2008; pp. 263–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeide, E.; Diamantino, T.C.; de Sousa, O. Marine paints: The particular case of antifouling paints. Prog. Org. Coat. 2007, 59, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, L.D.; Stokes, K.R.; Walsh, F.C.; Wood, R.J.K. Modern approaches to marine antifouling coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 201, 3642–3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detty, M.; Ciriminna, R.; Bright, F.V.; Pagliaro, M. Environmentally benign sol-gel antifouling and foul-releasing coatings. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 678–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buskens, P.; Wouters, M.; Rentrop, C.; Vroon, Z. A brief review of environmentally benign antifouling and foul-release coatings for marine applications. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2013, 10, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Lyon, S.B. Investigation using localized SVET into protection at defects in epoxy coated mild steel under intermittent cathodic protection simulating inter-tidal and splash zones. Prog. Org. Coat. 2017, 102, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, T.; Wang, H.; Hou, B. A new solvent-free super high build epoxy coating evaluated by marine corrosion simulation apparatus. Mater. Corros. 2012, 63, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubielewicz, M.; Krolikowska, A. The influence of ageing of epoxy coatings on adhesion of polyurethane topcoats and protective properties of coating systems. Prog. Org. Coat. 2009, 66, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bozec, N.; Thierry, D.; Le Calvé, P.; Favennec, C.; Pautasso, J.-P.; Hubert, C. Performance of marine and offshore paints systems: Correlation of accelerated corrosion tests and field exposure on operating ships. Mater. Corros. 2013, 66, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bozec, N.; Thierry, D.; Pélissier, K. A new accelerated corrosion test for marine paint systems used for ship’s topsides and superstructures. Mater. Corros. 2018, 69, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, F.; Sharif, F.; Sarabi, A.A.; Kasiriha, S.M.; Rahmanian, M.; Akbarinezhad, E. Experimental evaluation of high solid polyurethane coating in the presence of salt at high temperature. Mater. Corros. 2010, 61, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, I.; Chico, B.; de la Fuente, D.; Simancas, J.; Vega, J.M.; Morcillo, M. Corrosion resistance of new epoxy-siloxane hybrid coatings. A laboratory study. Prog. Org. Coat. 2010, 69, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO Standard. ISO 12944-6: Paints and Varnishes—Corrosion Protection of Steel Structures by Protective Paints—Part 6: Laboratory Performance Test Methods; ISO Standard: Brussels, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Yang, J.; Ma, C. Analysis on causes of polysiloxanes surface coating peeling on a special ship. Key Eng. Mater. 2019, 815, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, O.O. Review of coating failure incidents on the Norwegian continental shelf since the introduction of NORSOK-501. In Proceedings of the NACE International’s CORROSION Conference, Orlando, FL, USA, 17–21 March 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Husain, A.; Al Madaj, M. Optimization of AC impedance test cell for accelerated evaluation of marine industrial coating in Kuwait. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 51, 1980–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shreepathi, S. Physicochemical parameters influencing the testing of cathodic delamination resistance of high build pigmented epoxy coating. Prog. Org. Coat. 2016, 90, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.; Brites, C.; Costa, M.R.; Santos, M.T. Performance of paint systems with polyurethane topcoats, proposed for atmospheres with very high corrosvity category. Prog. Org. Coat. 2005, 54, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Amaya, J.M.; Osuna, R.M.; Bethencourt, M.; Botana, F.J. Monitoring the degradation of a high solids epoxy coating by means of EIS and ENS. Prog. Org. Coat. 2007, 60, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.W.; Liu, D.; Moreno, M.; Garneau, R. 100% solids rigid polyurethane coatings technology for corrosion protection of ballast tanks. In Proceedings of the NACE International’s CORROSION Conference, New Orleans, LA, USA, 28 March–1 April 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Fathabadi, H.E. Investigation of fusion bonded epoxy (FBE) as a protective coating for pipes. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Color and Coating Congress, Teheran, Iran, 16 November 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Khanna, A.S. Application for high-performance organic coatings. In High Performance Organic Coatings, 1st ed.; Khanna, A.S., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2008; Chapter 14; pp. 287–307. [Google Scholar]
- Norsworthy, R. Selection and use of coatings for underground or submersion service. In Uhlig’s Corrosion Handbook, 3rd ed.; Winston Revie, R., Ed.; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; Chapter 68; pp. 985–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttunen-Saarivirta, E.; Vagarov, G.V.; Yudin, V.E.; Vuorinen, J. Characterization and corrosion protection properties of epoxy powder coatings containing nanoclays. Prog. Org. Coat. 2013, 76, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boerschel, V. New developments of mid-Tg FBE powder coatings to meet the requirements of pipe coaters and pipeline owners. In Proceedings of the NACE International’s CORROSION Conference, San Antonio, TX, USA, 14–18 March 2010. Paper 10012. [Google Scholar]
- Mobin, M.; Malik, A.U.; Andijani, I.N.; Al-Muaili, F.; Al-Hajri, M.; Ozair, G.; Mohammad, N.M.K. Performance evaluation of some fusion-bonded epoxy coatings under water transmission line conditions. Prog. Org. Coat. 2008, 62, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetiner, M.; Abes, J.; Slingh, P.; Gilroy-Scott, A. UV degradation of fusion bonded epoxy coating in stockpiled pipes. In Proceedings of the International Pipeline Conference, Calgary, AB, Canada, 1–5 October 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ramezanzadesh, B.; Rostami, M. The effect of cerium-based conversion treatment on the cathodic delamination and corrosion protection performance of carbon steel fusion bonded epoxy coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 392, 1004–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papavinasam, S. Mitigation-External Corrosion. In Corrosion Control in the Oil and Gas Industry, 1st ed.; Gulf Professional Publishing: London, UK, 2014; Chapter 9; pp. 529–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliba, P.A.; Mansur, A.A.; Santos, D.B.; Mansur, H.S. Fusion bonded epoxy composite coatings on chemically functionalized API steel surfaces for potential deep-water petroleum exploration. Appl. Adhes. Sci. 2015, 3, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, R.E.; Trautman, B.L.; Payer, J.H. Influencing factors in cathodic disbondment of fusion bonded epoxy coatings. In Proceedings of the NACE International’s CORROSION Conference, Orlando, FL, USA, 26–31 March 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ramezanzadesh, M.; Bahlakeh, G.; Ramezanzadesh, B.; Rostani, M. Mild steel surface eco-friendly treatment by neodymium-based nanofilm for fusion bonded epoxy coating anti-corrosion/adhesion properties enhancement in simulated seawater. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 72, 474–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabadi, M.; Terryn, H.; Mol, J.M.C. The influence of a Zr-based conversion treatment on interfacial bonding strength and stability of epoxy coated carbon steel. Prog. Org. Coat. 2017, 105, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchoquesi Diodjo, M.R.; Belec, L.; Aragon, E.; Joliff, Y.; Lanarde, L.; Perrin, F.-X. Silane coupling agent for attracting FBE to steel. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 6751–6761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radhakrishnan, S.; Sonaware, N.; Siju, C.R. Epoxy powder coatings containing polyaniline for enhanced corrosion protection. Prog. Org. Coat. 2009, 64, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhi, G.; Bhandani, H.; Dhawan, S.K. Designing of corrosion resistant epoxy coatings embedded with polypyrrole/SiO2 composite. Prog. Org. Coat. 2014, 77, 1484–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.H.; Zhang, L.X.; Ke, W. Evaluation of corrosion protection of carbon black filled FBE coatings on mild steel during exposure to a quiescent 3% NaCl. Corros. Sci. 2007, 49, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jingcheng, L.; Xiuli, J.; Shengwen, Z.; Ren, L.; Xiaya, L. Preparation and characterization of carboxyl terminated poly(butadiene-co-acrylonitrile) epoxy resin prepolymers for FBE powder coatings. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 2012, 27, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyvani, B.; Sharif, A.; Khorassani, M. Determination of Arrhenius equation constants for curing reaction kinetics of fusion bonded epoxy. Org. Chem. J. 2010, 1, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, B.T.A.; Sue, H.-J.; Jiang, H.; Browing, B.; Wong, D.; Pham, H.; Guo, S.; Kehr, A.; Mallozzi, M.; Snider, W.; et al. Integrity of 3LPE pipeline coatings: Residual stresses and adhesion degradation. In Proceedings of the 7th International Pipeline Conference, Calgary, AB, Canada, 29 September–3 October 2008; p. 64048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadoon, A.N.K.; Thompson, I. Fusion bonded epoxy mainline and field joint coatings performance from the X100 field trial—A case study. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2012, 92, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joliff, Y.; Belec, L.; Aragon, E. Influence of the thickness of pipeline coating on internal stresses during the manufacture process by finite element analysis. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2013, 68, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payer, J.H.; Moore, D.P.; Lee Magnon, J. Performance testing of fusion bonded epoxy coatings. In Proceedings of the NACE International’s CORROSION Conference, Orlando, FL, USA, 26–31 March 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Al Borno, A.; Chen, X.; Dhoke, S.K. Effect of high temperature sodium hydroxide immersion on FBE coating. Int. J. Corros. 2015, 903478, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legghe, E.; Aragon, E.; Belec, L.; Margaillan, A.; Melot, D. Correlation between water diffusion and adhesion loss study of an epoxy primer steel. Prog. Org. Coat. 2009, 66, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvant-Moret, V.; Kittel, J.; Melot, D.; Roche, M. Three layers polyolefin coatings: How the FBE primer properties govern the long-term adhesion. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Pipeline Protection, Edinburgh, UK, 17–19 October 2007. [Google Scholar]




| Nomenclature | % Solid Content | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-solid coatings | 60–80% |
|
|
| Powder coatings | 100% |
|
|
| Waterborne coatings | Same as solvent-borne coatings |
|
|
| Chemical Factors | Physical Factors | Biological Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Soluble salts | Temperature | Fouling |
| Solute gases (O2, CO2) | Movement | Animals (consumption or production of gases) |
| pH levels | Pressure | Plants (consumption or production of gases) |
| - | Solids | - |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pélissier, K.; Thierry, D. Powder and High-Solid Coatings as Anticorrosive Solutions for Marine and Offshore Applications? A Review. Coatings 2020, 10, 916. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10100916
Pélissier K, Thierry D. Powder and High-Solid Coatings as Anticorrosive Solutions for Marine and Offshore Applications? A Review. Coatings. 2020; 10(10):916. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10100916
Chicago/Turabian StylePélissier, Krystel, and Dominique Thierry. 2020. "Powder and High-Solid Coatings as Anticorrosive Solutions for Marine and Offshore Applications? A Review" Coatings 10, no. 10: 916. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10100916
APA StylePélissier, K., & Thierry, D. (2020). Powder and High-Solid Coatings as Anticorrosive Solutions for Marine and Offshore Applications? A Review. Coatings, 10(10), 916. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10100916






