Policies to Reduce Antibiotic Consumption: The Impact in the Basque Country
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
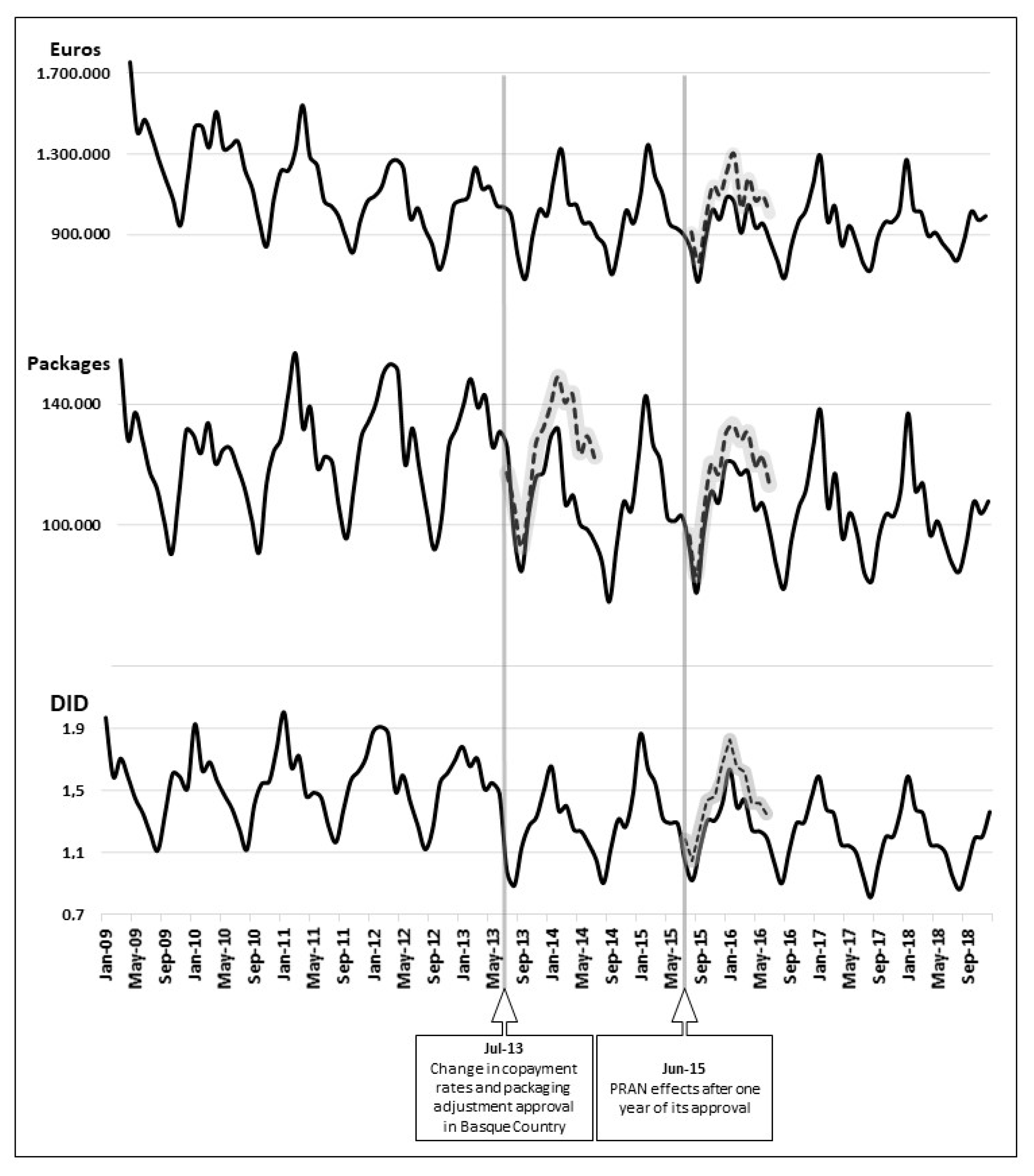
3. Results
3.1. Copayment and Adjustment of Packaging
3.2. PRAN Approval
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Series | Costs (euros) | Packages | DID | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | Real Value | Prediction | Confidence Interval (80%) | Real Value | Prediction | Confidence Interval (80%) | Real Value | Prediction | Confidence Interval (80%) |
| Jun. 2013 | 994,437 * | 918,145 * | 843,114–993,176 | 125,760 * | 117,301 * | 109,310–125,474 | 1.286 * | 1.197 * | 1.111–1.283 |
| Jul. 2013 | 778,627 * | 894,975 * | 790,709–999,241 | 95,966 * | 106,961 * | 98,926–114,997 | 0.975 * | 1.112 * | 1.025–1.197 |
| Aug. 2013 | 677,717 | 716,160 | 598,665–833,655 | 84,092 * | 92,684 * | 84,118–101,350 | 0.882 | 0.940 | 0.849–1.030 |
| Sep. 2013 | 890,812 | 818,366 | 700,871–935,862 | 100,232 * | 106,253 * | 100,587–114,920 | 1.131 | 1.088 | 0.996–1.179 |
| Oct. 2013 | 1,022,801 | 1,039,945 | 922,450–1,157,440 | 115,925 * | 126,973 * | 118,307–135,640 | 1.269 | 1.295 | 1.204–1.387 |
| Nov. 2013 | 992,537 | 1,064,936 | 947,441–1,182,431 | 117,578 * | 131,980 * | 123,313–140,646 | 1.329 | 1.337 | 1.246–1.429 |
| Dec. 2013 | 1,185,331 | 1,080,010 | 962,515–1,197,506 | 129,174 * | 139,341 * | 130,675–148,007 | 1.500 | 1.412 | 1.320–1.503 |
| Jan. 2014 | 1,320,501 | 1,231,031 | 1,113,536–1,348,526 | 131,722 * | 149,125 * | 140,461–157,789 | 1.652 | 1.562 | 1.471–1.653 |
| Feb. 2014 | 1,051,123 | 1,112,522 | 995,027–1,230,018 | 106,900 * | 140,592 * | 131,928–149,255 | 1.366 | 1.456 | 1.365–1.548 |
| Mar. 2014 | 1,047,866 | 1,126,069 | 1,008,573–1,243,564 | 110,981 * | 143,465 * | 134,802–152,129 | 1.399 | 1.484 | 1.392–1.575 |
| Apr. 2014 | 956,060 | 1,047,480 | 929,984–1,164,975 | 105,361 * | 123,841 * | 115,177–132,505 | 1.246 | 1.283 | 1.192–1.374 |
| May 2014 | 954,021 | 1,033,550 | 916,055–1,151,046 | 108,572 * | 129,514 * | 120,851–138,178 | 1.233 | 1.318 | 1.227–1.410 |
| Jun. 2014 | 884,376 | 1,000,323 | 882,827–1,117,818 | 99,485 * | 122,447 * | 113,783–131,110 | 1.152 | 1.240 | 1.148–1.331 |
| Total (*) | 1,773,064 | 1,813,120 | 1,431,748 | 1,630,477 | 2.261 | 2.309 | |||
| Difference (*) | −40,056 | −198,729 | −0.048 | ||||||
| Variation (*) | −2.20% | −12.19% | −2.07% | ||||||
| Stockpiling effect (var. Jun. 2013) | 8.31% | 7.21% | 7.44% | ||||||
| Active Substance | Cefditoren | Moxifloxacin | Doxycycline | Cloxacillin | ||||
| Group | “watch” | “watch” | “access” | “access” | ||||
| Chosen by | High cost (€43/recipe) | High cost (€24/recipe) | Low cost (€5/recipe) | Low cost (€4/recipe) | ||||
| Included in RDL | No | No | Yes | Yes | ||||
| Serie | Costs (euros) | Packages | Costs (euros) | Packages | Costs (euros) | Packages | Costs (euros) | Packages |
| ARIMA model | (0,0,1) (1,1,0) | (0,0,1) (1,1,0) | (0,0,1) (1,1,0) | (1,0,2) (1,1,0) | (2,0,0) (0,1,1) | (0,1,1) (0,1,1) | (2,0,0) (1,1,0) | (1,0,2) (1,1,0) |
| AR1 | - | - | - | 0.48345 * | 0.29353 * | - | 0.29846 * | 0.773629 *** |
| AR2 | - | - | - | - | 0.37230 * | - | −0.34330 ** | - |
| MA1 | 0.41060 ** | 0.42849 ** | 0.83520 *** | 0.31378 * | - | −0.632895 *** | - | 0.369473* |
| MA2 | - | - | - | −0.40898 * | - | - | - | 0.150730 * |
| SAR1 | −0.53195 *** | −0.55235 *** | −0.65118 *** | −0.49804 ** | - | - | −0.54423 ** | −0.503722 * |
| SMA1 | - | - | - | - | −0.56709 * | −0.400906 * | - | - |
| Q test (p-value, delay 18) | 7.4520 (0.5962) | 7.7591 (0.5586) | 7.3600 (0.5997) | 7.4616 (0.3824) | 10.337 (0.2422) | 7.8494 (0.5494) | 10.721 (0.218) | 8.6277 (0.2805) |
| AIC | −10.764 | −10.130 | −11.577 | −10.929 | −9.03q | −10.878 | −8.825 | −9.405 |
| Residual sum of squares | 0.0604 | 0.0595 | 0.0624 | 0.0605 | 0.0824 | 0.0557 | 0.0793 | 0.0655 |
| Standard error of the regression | 0.0472 | 0.0443 | 0.0511 | 0.0502 | 0.0712 | 0.0466 | 0.069 | 0.0583 |
| Effect on the series (calculations of savings in Table A3) | not significant | not significant | not significant | Stockpiling effect of 7.63% Packaging reduction of 19.68% including Jun. 2013 to Jun. 2014 (last month with significant effect) | not significant | Stockpiling effect of 7.23% Packaging reduction of 23.62% including Jun. 2013 to Jun. 2014 (last month with significant effect) | ||
| Active Substance | Amoxicillin | Amoxicillin and Inhibitors | Azithromycin | Levofloxacin | ||||
| Group | “access” | “access” | “watch” | “watch” | ||||
| Chosen by | High prescription (23% of recipes) | High prescription (21% of recipes) | High prescription (12% of recipes) | High prescription (5% of recipes) | ||||
| Included in RDL | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||||
| Serie | Costs (euros) | Packages | Costs (euros) | Packages | Costs (euros) | Packages | Costs (euros) | Packages |
| ARIMA model | (1,1,0) (1,1,0) | (1,0,0) (1,1,0) | (1,0,0) (1,1,0) | (0,0,1) (1,1,0) | (0,1,2) (0,1,1) | (0,1,2) (1,1,0) | (0,1,2) (1,1,0) | (0,0,1) (0,1,1) |
| AR1 | 0.75416 ** | 0.807218 *** | 0.822603 *** | - | - | - | - | - |
| AR2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| MA1 | - | - | - | 0.524390 *** | −0.12776 * | −0.11887 * | 0.44500 *** | 0.61486 *** |
| MA2 | - | - | - | - | −0.48812 ** | −0.50298 * | 0.04571 *** | - |
| SAR1 | −0.57297 ** | −0.365231 ** | −0.358346 ** | −0.55124 ** | - | −0.55869 *** | −0.31785 *** | - |
| SMA1 | - | - | - | - | −0.33576 * | - | - | −0.42197 ** |
| Q test (p-value, delay 18) | 7.6307 (0.5997) | 13.476 (0.1422) | 12.467 (0.1882) | 12.416 (0.1909) | 13.514 (0.0953) | 14.477 (0.0942) | 9.2410 (0.1845) | 2.0625 (0.9904) |
| AIC | −10.895 | −11.526 | −11.094 | −11.118 | −9.646 | −9.054 | −8.016 | −17.643 |
| Residual sum of squares | 0.0613 | 0.0650 | 0.0649 | 0.0646 | 0.0708 | 0.0696 | 0.0856 | 0.0545 |
| Standard error of the regression | 0.0495 | 0.0866 | 0.0848 | 0.0855 | 0.0917 | 0.0864 | 0.072 | 0.0387 |
| Effect on the series (calculations in Table A2) | not significant | Stockpiling effect of 9.16% Packaging reduction of 26.79% including Jun. 2013 to Jun. 2014 (last month with significant effect) | not significant | Stockpiling effect of 8.40% Packaging reduction of 26.05% including Jun. 2013 to Jun. 2014 (last month with significant effect) | not significant | not significant | ||
| Series Active Substance | Packages Doxycycline | Packages Cloxacillin | ||||
| Date | Real Value | Prediction | Confidence Interval (80%) | Real Value | Prediction | Confidence Interval (80%) |
| Jun. 2013 | 1410 | 1310 | 1217–1403 | 2475 | 2308 | 2160–2456 |
| Jul. 2013 | 1009 | 1302 | 1210–1,395 | 2371 | 2437 | 2398–2476 |
| Aug. 2013 | 802 | 1053 | 954–1151 | 2168 | 2441 | 2376–2506 |
| Sep. 2013 | 1211 | 1319 | 1215–1423 | 1985 | 2469 | 2383–2555 |
| Oct. 2013 | 1308 | 1628 | 1518–1737 | 1790 | 2431 | 2329–2533 |
| Nov. 2013 | 1342 | 1659 | 1545–1774 | 1641 | 2349 | 2233–2464 |
| Dec. 2013 | 1234 | 1543 | 1424–1662 | 1536 | 2281 | 2154–2407 |
| Jan. 2014 | 1425 | 1745 | 1621–1869 | 1544 | 2218 | 2081–2354 |
| Feb. 2014 | 1458 | 1794 | 1666–1923 | 1567 | 2230 | 2085–2375 |
| Mar. 2014 | 1490 | 1902 | 1769–2035 | 1565 | 2242 | 2089–2395 |
| Apr. 2014 | 1347 | 1792 | 1655–1930 | 1557 | 2317 | 2157–2477 |
| May 2014 | 1271 | 1694 | 1553–1835 | 1545 | 2356 | 2189–2522 |
| Jun. 2014 | 965 | 1517 | 1372–1662 | 1521 | 2379 | 2207–2551 |
| Total | 16,272 | 20,258 | 23,265 | 30,458 | ||
| Difference | −3986 | −7193 | ||||
| Variation | −19.68% | −23.62% | ||||
| Stockpiling effect (var. Jun. 2013) | 7.63% | 7.23% | ||||
| Series Active Substance | Packages Amoxicillin | Packages Amoxicillin and Beta-Lactamase Inhibitors | ||||
| Date | Real Value | Prediction | Confidence Interval (80%) | Real Value | Prediction | Confidence Interval (80%) |
| Jun. 2013 | 34,671 | 31,763 | 28,860–34,662 | 25,897 | 23,889 | 22,018–25,760 |
| Jul. 2013 | 22,177 | 25,553 | 22,672–28,433 | 21,009 | 24,240 | 22,400–26,079 |
| Aug. 2013 | 17,158 | 21,420 | 17,719–25,122 | 19,012 | 23,343 | 21,266–25,421 |
| Sep. 2013 | 24,811 | 30,277 | 26,127–34,427 | 21,377 | 25,021 | 22,944–27,098 |
| Oct. 2013 | 31,244 | 35,922 | 31,504–40,340 | 21,151 | 28,156 | 26,079–30,233 |
| Nov. 2013 | 36,462 | 41,326 | 36,742–45,910 | 18,909 | 27,648 | 25,571–29,725 |
| Dec. 2013 | 31,615 | 43,703 | 39,014–48,393 | 23,170 | 29,024 | 26,947–31,101 |
| Jan. 2014 | 29,702 | 42,492 | 37,735–47,248 | 23,802 | 32,634 | 30,557–34,711 |
| Feb. 2014 | 24,601 | 43,483 | 38,684–48,283 | 18,246 | 31,123 | 29,046–33,200 |
| Mar. 2014 | 25,047 | 43,360 | 38,532–48,188 | 18,852 | 31,016 | 28,939–33,093 |
| Apr. 2014 | 21,518 | 33,168 | 28,322–38,014 | 17,605 | 26,614 | 24,536–28,691 |
| May 2014 | 20,855 | 37,643 | 32,785–42,501 | 17,288 | 27,619 | 25,541–29,696 |
| Jun. 2014 | 20,149 | 34,337 | 29,471–39,202 | 16,864 | 25,570 | 23,493–27,647 |
| Total | 340,010 | 464,447 | 263,182 | 355,897 | ||
| Difference | −124,437 | −92,715 | ||||
| Variation | −26.79% | −26.05% | ||||
| Stockpiling effect (var. Jun. 2013) | 9.16% | 8.40% | ||||
| Series | Costs (euros) | Packages | DID | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | Real Value | Prediction | Confidence Interval (80%) | Real Value | Prediction | Confidence Interval (80%) | Real Value | Prediction | Confidence Interval (80%) |
| Jul. 2015 | 821,322 | 866,160 | 828,657–903,663 | 92,620 | 96,947 | 92,666–101,228 | 1.137 | 1.185 | 1.160–1.211 |
| Aug. 2015 | 662,357 | 722,741 | 672,212–773,270 | 77,694 | 83,878 | 77,715–90,041 | 1.019 | 1.049 | 1.024–1.075 |
| Sep. 2015 | 864,798 | 926,602 | 874,631–978,573 | 98,640 | 105,538 | 98,962–112,115 | 1.227 | 1.262 | 1.237–1.288 |
| Oct. 2015 | 1,019,837 | 1,085,420 | 1,030,836–1,140,004 | 111,074 | 120,644 | 112,646–128,642 | 1.405 | 1.438 | 1.413–1.464 |
| Nov. 2015 | 972,651 | 1,042,835 | 984,719–1,098,951 | 107,508 | 117,163 | 108,265–126,061 | 1.405 | 1.458 | 1.433–1.484 |
| Dec. 2015 | 1,083,567 | 1,156,014 | 1,096,441–1,215,587 | 120,723 | 130,513 | 121,019–140,006 | 1.513 | 1.565 | 1.538–1.592 |
| Jan. 2016 | 1,060,474 | 1,234,741 | 1,172,778–1,296,704 | 120,736 | 133,723 | 123,332–144,115 | 1.736 | 1.824 | 1.797–1.851 |
| Feb. 2016 | 905,632 | 981,301 | 917,010–1,045,592 | 116,703 | 127,823 | 116,757–138,890 | 1.490 | 1.64 | 1.613–1.667 |
| Mar. 2016 | 1,044,753 | 1,123,100 | 1,056,539–1,189,661 | 117,945 | 130,498 | 118,828–142,169 | 1.540 | 1.618 | 1.591–1.645 |
| Apr. 2016 | 931,082 | 1,017,023 | 948,246–1,085,800 | 105,186 | 120,087 | 107,735–132,439 | 1.345 | 1.415 | 1.388–1.442 |
| May 2016 | 951,560 | 1,040,102 | 969,158–1,111,046 | 107,255 | 119,942 | 107,009–132,876 | 1.335 | 1.421 | 1.391–1.451 |
| Jun. 2016 | 864,528 | 954,471 | 881,408–1,027,534 | 97,951 | 111,215 | 97,719–124,711 | 1.292 | 1.345 | 1.315–1.375 |
| Total | 11,182,561 | 12,149,510 | 1.274.035 | 1.397.972 | 16.441 | 17.220 | |||
| Difference | −966,949 | −123,937 | −0.779 | ||||||
| Variation | −7.96% | −8.87% | −4.51% | ||||||
| Active Substance | Amoxicillin | Amoxicillin and Inhibitors | Azithromycin | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | “access” | “access” | “watch” | |||
| Chosen by | High prescription (23% of recipes) | High prescription (21% of recipes) | High prescription (12% of recipes) | |||
| Series | Costs (euros) | DID | Costs (euros) | DID | Costs (euros) | DID |
| ARIMA model | (2,0,0) (2,1,0) | (2,1,2) (0,1,1) | (0,1,2) (0,1,1) | (1,0,0) (2,1,1) | (0,1,2) (0,1,1) | (0,1,2) (0,1,1) |
| AR1 | 0.438 *** | −0.441 *** | - | 0.560 *** | - | - |
| AR2 | 0.098 * | −0.292 * | - | - | - | - |
| MA1 | - | −0.151 * | 0.270 *** | - | −0.052597 * | −0.040777 * |
| MA2 | - | −0.841 * | 0.580 *** | - | −0.547567 *** | −0.638842 *** |
| SAR1 | −0.547 *** | - | - | −0.194 ** | - | - |
| SAR2 | −0.405 *** | - | - | −0.374 *** | - | - |
| SMA1 | - | 0.845 *** | 0.811 *** | 0.376 * | −0.521205 *** | −0.577372 *** |
| V1 | −0.047 * | −0.041 * | −0.045 * | −0.040 * | - | - |
| Q test (p-value, delay 18) | 15.412 (0.3951) | 9.606 (0.7260) | 17.420 (0.3214) | 15.011 (0.377) | 16.517 (0.223) | 17.906 (0.1611) |
| AIC | −7.222 | −6.511 | −7.182 | −7.147 | −18.42 | −12.45 |
| Residual sum of squares | 0.078 | 0.088 | 0.091 | 0.087 | 0.0615 | 0.0655 |
| Standard error of the regression | 0.017 | 0.026 | 0.016 | 0.018 | 0.0807 | 0.0822 |
| Effect on the series (calculations of savings in Table A6) | −9.26% | −0.277 DID (−6.69%) | −10.65% | −0.193 DID (−4.19%) | −14.29% | −0.174 DID (−12.30%) |
| Series Active Substance | Euros Amoxicillin | DID Amoxicillin | ||||
| Date | Real Value | Prediction | Confidence Interval (80%) | Real Value | Prediction | Confidence Interval (80%) |
| Jul. 2015 | 236,664 | 257,412 | 240,284–274,540 | 0.261 | 0.271 | 0.264–0.278 |
| Aug. 2015 | 165,798 | 186,423 | 169,294–203,552 | 0.200 | 0.247 | 0.240–0.255 |
| Sep. 2015 | 235,282 | 255,462 | 238,332–272,592 | 0.290 | 0.300 | 0.293–0.307 |
| Oct. 2015 | 304,086 | 326,475 | 308,695–344,255 | 0.330 | 0.341 | 0.334–0.348 |
| Nov. 2015 | 300,430 | 319,920 | 302,140–337,700 | 0.326 | 0.343 | 0.336–0.350 |
| Dec. 2015 | 298,582 | 318,720 | 301,588–335,852 | 0.384 | 0.393 | 0.386–0.400 |
| Jan. 2016 | 318,228 | 338,012 | 320,878–355,146 | 0.378 | 0.487 | 0.480–0.494 |
| Feb. 2016 | 260,585 | 342,410 | 324,672–360,148 | 0.390 | 0.399 | 0.392–0.406 |
| Mar. 2016 | 288,645 | 311,984 | 294,246–329,722 | 0.377 | 0.399 | 0.392–0.406 |
| Apr. 2016 | 251,430 | 281,903 | 264,165–299,641 | 0.319 | 0.328 | 0.321–0.335 |
| May 2016 | 266,836 | 291,412 | 273,674–309,150 | 0.321 | 0.334 | 0.324–0.344 |
| Jun. 2016 | 244,219 | 264,347 | 246,609–282,085 | 0.283 | 0.294 | 0.284–0.304 |
| Total | 3,170,785 | 3.494.480 | 3.859 | 4.136 | ||
| Difference | −323,695 | −0.277 | ||||
| Variation | −9.26% | −6.69% | ||||
| Series Active Substance | Euros Amoxicillin and Inhibitors | DID Amoxicillin and Inhibitors | ||||
| Date | Real Value | Prediction | Confidence Interval (80%) | Real Value | Prediction | Confidence Interval (80%) |
| Jul. 2015 | 135,686 | 143,620 | 137,669–149,571 | 0.336 | 0.349 | 0.341–0.357 |
| Aug. 2015 | 120,658 | 134,021 | 122,677–145,366 | 0.302 | 0.316 | 0.308–0.324 |
| Sep. 2015 | 146,708 | 160,125 | 148,329–171,921 | 0.339 | 0.360 | 0.352–0.368 |
| Oct. 2015 | 159,832 | 174,841 | 161,689–187,993 | 0.384 | 0.396 | 0.389–0.403 |
| Nov. 2015 | 152,695 | 170,423 | 156,503–184,343 | 0.381 | 0.394 | 0.387–0.401 |
| Dec. 2015 | 172,782 | 191,200 | 176,314–206,086 | 0.428 | 0.448 | 0.441–0.455 |
| Jan. 2016 | 169,610 | 187,921 | 172,230–203,612 | 0.455 | 0.468 | 0.458–0.478 |
| Feb. 2016 | 165,837 | 184,701 | 168,181–201,221 | 0.403 | 0.420 | 0.410–0.430 |
| Mar. 2016 | 156,092 | 177,730 | 160,440–195,020 | 0.401 | 0.420 | 0.410–0.430 |
| Apr. 2016 | 135,329 | 158,001 | 139,953–176,049 | 0.338 | 0.354 | 0.344–0.364 |
| May 2016 | 139,558 | 161,741 | 142,967–180,515 | 0.331 | 0.351 | 0.341–0.361 |
| Jun. 2016 | 131,058 | 154,379 | 134,898–173,860 | 0.329 | 0.347 | 0.337–0.357 |
| Total | 1,785,846 | 1.998.703 | 4.427 | 4,621 | ||
| Difference | −212,858 | −0.193 | ||||
| Variation | −10.65% | −4.19% | ||||
| Series Active Substance | Euros Azithromycin | DID Azithromycin | ||||
| Date | Real Value | Prediction | Confidence Interval (80%) | Real Value | Prediction | Confidence Interval (80%) |
| Jul. 2015 | 76,836 | 86,747 | 77,667–95,826 | 0.081 | 0.089 | 0.082–0.097 |
| Aug. 2015 | 63,910 | 76,970 | 64,463–89,477 | 0.066 | 0.078 | 0.067.20 0.090 |
| Sep. 2015 | 81,021 | 95,662 | 82,639–108,685 | 0.087 | 0.101 | 0.089–0.112 |
| Oct. 2015 | 95,210 | 110,230 | 96,711–123,750 | 0.101 | 0.115 | 0.103–0.127 |
| Nov. 2015 | 95,016 | 109,752 | 95,754–123,751 | 0.090 | 0.104 | 0.092–0.117 |
| Dec. 2015 | 119,522 | 135,372 | 120,911–149,834 | 0.123 | 0.139 | 0.126–0.152 |
| Jan. 2016 | 128,086 | 154,055 | 139,144–168,965 | 0.144 | 0.159 | 0.145–0.172 |
| Feb. 2016 | 118,522 | 135,161 | 119,815–150,507 | 0.123 | 0.139 | 0.126–0.153 |
| Mar. 2016 | 112,412 | 130,740 | 114,971–146,510 | 0.119 | 0.135 | 0.121–0.150 |
| Apr. 2016 | 96,023 | 112,525 | 96,344–128,707 | 0.102 | 0.117 | 0.103–0.132 |
| May 2016 | 94,177 | 112,275 | 95,691–128,859 | 0.101 | 0.117 | 0.102–0.132 |
| Jun. 2016 | 94,204 | 111,289 | 94,313–128,265 | 0.098 | 0.114 | 0.099–0.129 |
| Total | 1,174,938 | 1,370,780 | 1.24055 | 1.414558 | ||
| Difference | −195,841 | −0.17401 | ||||
| Variation | −14.29% | −12.30% | ||||
References
- Infosalud. 26.000 Muertes este año por Resistencia a Antibióticos: 22 Veces más que en Accidente de Tráfico. Available online: https://www.infosalus.com/salud-investigacion/noticia-26000-muertes-ano-resistencia-antibioticos-22-veces-mas-accidente-trafico-20190523134012.html (accessed on 23 December 2019).
- Día Europeo para el Uso Prudente de los Antibióticos. Declaración de Vytenis Andriukaitis, Comisario de Salud y Seguridad Alimentaria, y Carlos Moedas, Comisario de Investigación, Ciencia e Innovación. 2017. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/commission/presscorner/detail/es/STATEMENT_17_4607 (accessed on 16 January 2020).
- Royal Decree-Law no. 16/2012, Containing Urgent Measures to Guarantee the Sustainability of the National Health System and thE quality and Safety of Its Services. Boletín Oficial del Estado, 24 April 2012, no. 98, pp. 30–31. Available online: https://www.boe.es/diario_boe/txt.php?id=BOE-A-2012-5403 (accessed on 7 January 2020).
- Gobierno de España. Ley 14/1986, de 25 de abril, General de Sanidad. Available online: https://www.boe.es/buscar/act.php?id=BOE-A-1986-10499 (accessed on 19 May 2020).
- Decreto 114/2012, de 26 de Junio, Sobre Régimen de las Prestaciones Sanitarias del Sistema Nacional de Salud en el Ámbito de la Comunidad Autónoma de Euskadi. Available online: https://www.euskadi.eus/y22-bopv/es/bopv2/datos/2012/06/1202973a.epub (accessed on 7 January 2020).
- Edicto Dimanante del Conflicto Positivo de Competencia Número 4540-2012.12 de diciembre de 2012. Available online: https://www.euskadi.eus/y22-bopv/es/bopv2/datos/2013/02/1300620a.shtml (accessed on 8 January 2020).
- Instituto Nacional de Estadística (INE). Padrón. Población por Municipios. Available online: https://www.ine.es/dyngs/INEbase/es/categoria.htm?c=Estadistica_P&cid=1254734710990 (accessed on 27 May 2020).
- Memoria Osakidetza. 2019. Available online: https://www.osakidetza.euskadi.eus/contenidos/informacion/osk_pro_publicaciones_memorias/es_def/adjuntos/Memoria_Osakidetza_2019.pdf (accessed on 27 May 2020).
- Antoñanzas, F.; Rodríguez, R.; Juárez-Castelló, C.; Lorente, M.R. Impacto del Real Decreto-ley 16/2012 sobre el copago farmacéutico en elnúmero de recetas y en el gasto farmacéutico. Rev. Esp. Salud Pública 2014, 882, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Agencia Española de Medicamentos y Productos Sanitarios (AEMPS). Misión y Visión de la AEMPS. Available online: https://www.aemps.gob.es/la-aemps/quienes-somos/ (accessed on 8 January 2020).
- Resolución de la Agencia Española de Medicamentos y Productos Sanitarios sobre la Adecuación de los Formatos de los Medicamentos de los Grupos Terapéuticos J01 y J02. Available online: https://www.aemps.gob.es/legislacion/espana/medicamentosUsoHumano/docs/regMedicamentos/resolucion-formato-antibioticos.pdf (accessed on 8 January 2020).
- Resolución por la que se Modifica la Resolución de la Agencia Española de Medicamentos y Productos Sanitarios de Fecha 31 de Julio de 2012, Sobre la Adecuación de los Formatos de los Medicamentos de los Grupos Terapéuticos J01 y J02. Corrección de Errores. Available online: https://www.aemps.gob.es/legislacion/espana/medicamentosUsoHumano/docs/regMedicamentos/resolucion-formato-antibioticos-2.pdf (accessed on 7 January 2020).
- Plan Nacional Frente a la Resistencia a los Antibióticos (PRAN) ¿Quiénes Somos? Available online: http://www.resistenciaantibioticos.es/es/quienes-somos (accessed on 12 January 2020).
- Sviestina, I.; Mozgis, D. Observational Study of Antibiotic Usage at the Children’s Clinical University Hospital in Riga, Latvia. Medicina 2018, 54, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Dyar, O.J.; Rosales-Klintz, S.; Zhang, J.; Tomson, G.; Hao, M.; Stalsby, C. Trends and patterns of antibiotic consumption in Shanghai municipality, China: A 6 year surveillance with sales records, 2009–2014. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 1723–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooqui, H.H.; Selvaraj, S.; Mehta, A.; Heymann, D. Community level antibiotic utilization in India and its comparison vis-à-vis European countries: Evidence from pharmaceutical sales data. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olesen, S.W.; Barnett, M.L.; MacFadden, D.R.; Lipsitch, M.; Grad, Y.H. Trends in outpatient antibiotic use and prescribing practice among US older adults, 2011–2015: Observational study. BMJ 2018, 362, k3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Li, Q.; Sun, Q. Antibiotic consumption in Shandong Province, China: An analysis of provincial pharmaceutical centralized bidding procurement data at public healthcare institutions, 2012–2016. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lallana-Alvarez, M.J.; Feja-Solana, C.; Armesto-Gómez, J.; Bjerrum, L.; Rabanaque-Hernández, M.J. Outpatient antibiotic prescription in Aragón and the differences by gender and age. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2012, 30, 589–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisneros, J.M.; Neth, O.; Gil-Navarro, M.V.; Lepe, J.A.; Jiménez-Parrilla, F.; Cordero, E.; Rodríguez-Hernández, M.J.; Amaya-Villar, R.; Cano, J.; Gutiérrez-Pizarraya, A.; et al. Global impact of an educational antimicrobial stewardship programme on prescribing practice in a tertiary hospital centre. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demoré, B.; Humbert, P.; Boschetti, E.; Bevilacqua, S.; Clerc-Urmès, I.; May, T.; Pulcini, C.; Thilly, N. Evaluation of effects of an operational multidisciplinary team on antibiotic use in the medium to long term at a French university hospital. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2017, 39, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Zhang, Z.; Hicks, J.P.; Walley, J.D.; King, R.; Newell, J.N.; Yin, J.; Zeng, J.; Guo, Y.; Lin, M.; et al. Long-term outcomes of an educational intervention to reduce antibiotic prescribing for childhood upper respiratory tract infections in rural China: Follow-up of a cluster-randomised controlled trial. PLoS Med. 2019, 16, e1002733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agencia Española del Medicamento y Producto Sanitario (AEMPS). 2019. Available online: https://www.aemps.gob.es/publicaciones/publica/plan-estrategico-antibioticos/v2/docs/plan-estrategico-antimicrobianos-AEMPS.pdf (accessed on 19 May 2020).
- WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology. ATC/DDD Methodology. Available online: https://www.whocc.no/atc_ddd_methodology/purpose_of_the_atc_ddd_system/ (accessed on 9 January 2020).
- Araujo, A.R.; Albernaz, D.C.; Marques, A.F.; Biscaia, C.; Murni, I.K.; Dramowski, A.; Sharland, M.; Huebner, J.; Zingg, W. Role of antimicrobial stewardship programmes in children: A systematic review. J. Hosp. Infect. 2018, 99, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Departamento de Salud del Gobierno Vasco. El impacto Económico del Copago en la Factura Farmacéutica de los Meses de Julio y Agosto ha Supuesto un Total de 4.160.476,52 Euros. 2013. Available online: https://www.euskadi.eus/web01-s2osa/es/contenidos/noticia/2013_09_21_el_impacto_economic/es_15943/15943.html (accessed on 17 January 2020).
- World Health Organization Releases the 2019 AWaRe Classification Antibiotics. Available online: https://www.who.int/medicines/news/2019/WHO_releases2019AWaRe_classification_antibiotics/en/ (accessed on 7 January 2020).
- Aldeyab, M.A.; Monnet, D.L.; López-Lozano, J.M.; Hughes, C.M.; Scott, M.G.; Kearney, M.P.; Magee, F.A.; McElnay, J.C. Modelling the impact of antibiotic use and infection control practices on the incidence of hospital-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: A time-series analysis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008, 62, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernaz, N.; Huttner, B.; Muscionico, D.; Salomon, J.L.; Bonnabry, P.; López-Lozano, J.M.; Beyaert, A.; Schrenzel, J.; Harbarth, S. Modelling the impact of antibiotic use on antibiotic resistant Escherichia coli using population-based data from a large hospital and its surrounding community. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 66, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pankratz, A. Forecasting with Univariate Box-Jenkins Models: Concepts and Cases; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-0-470-31727-3. [Google Scholar]
- Puig-Junoy, J.; Rodríguez-Feijoo, S.; López-Valcárcel, B.; Gómez-Navarro, V. Impacto de la reforma del copago farmacéutico sobre la utilización de medicamentos antidiabéticos, antitrombóticos y para la obstrucción crónica del flujo aéreo. Rev. Esp. Salud Pública 2016, 90, e1–e15. [Google Scholar]
- Masiero, G.; Filippini, M.; Ferech, M.; Goossens, H. Socioeconomic determinants of outpatient antibiotic use in Europe. Int. J. Public Health 2010, 55, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, L.; Masiero, G. Disentangling Spillover Effects of Antibiotic Consumption: A Spatial Panel Approach; Università Degli Studi di Bergamo Scholarly Publishing Initiatives: Lugano, Switzerland, 2011; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, J.A.; Abdul-Aziz, M.H.; Lipman, J.; Mouton, J.W.; Vinks, A.A.; Felton, T.W.; Hope, W.W.; Farkas, A.; Neely, M.N.; Schentag, J.J.; et al. Individualised antibiotic dosing for patients who are critically ill: Challenges and potential solutions. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruyndonckx, R.; Coenen, S.; Hens, N.; Vandael, E.; Catry, B.; Goossens, H. Antibiotic use and resistance in Belgium: The impact of two decades of multi-faceted campaigning. Acta Clinica Bélgica 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, P.; Antoñanzas, F. Effects of economic and health policies on the consumption of antibiotics in a Spanish region. Expert Rev. Pharm. Out. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PRAN. Surveillance and Consumption Maps. 2020. Available online: http://resistenciaantibioticos.es/en/node/459 (accessed on 18 May 2020).
| Serie | Total Costs (euros) | Total Packages | Total DID |
|---|---|---|---|
| ARIMA model | (0,0,1) (0,1,1)12 | (0,0,1) (0,1,1)12 | (0,0,1) (0,1,1)12 |
| MA1 | 0.519478 * | 0.403930 * | 0.352600 * |
| SMA1 | 0.080095 * | −0.419430 ** | −0.446311 ** |
| Q test (p-value, delay 18) | 10.9600 (0.2785) | 8.9238 (0.4443) | 8.3222 (0.5020) |
| AIC | −10.681 | −11.744 | −11.545 |
| Residual sum of squares | 0.0564 | 0.0796 | 0.0758 |
| Standard error of the regression | 0.0395 | 0.0447 | 0.0435 |
| Effect on the series (calculations in Table A1) | Stockpiling effect of 8.31% Savings of 2.20% in expenses, including Jun-13 to Jul-13 (last month with significant effect) | Stockpiling effect of 7.21% Savings of 12.19% in packages, including Jun-13 to Jun-14 (last month with significant effect) | Stockpiling effect of 7.44% Savings of 2.07% in DID, including Jun-13 to Jul-13 (last month with significant effect) |
| Serie | Total Costs (euros) | Total Packages | Total DID |
|---|---|---|---|
| ARIMA model | (0,1,2) (0,1,1)12 | (2,0,0) (2,1,0)12 | (1,1,2) (0,1,1)12 |
| AR1 | - | 0.340 *** | −0.423 *** |
| AR2 | - | 0.061 * | - |
| MA1 | 0.490 *** | - | −0.188 * |
| MA2 | 0.381 *** | - | −0.812 * |
| SAR1 | - | −0.446 ** | - |
| SAR2 | - | −0.463 *** | - |
| SMA1 | 0.754 *** | - | 0.772 * |
| V1 | −0.019 * | - | −0.015 * |
| V2 | - | −0.093 ** | - |
| Q test (p-value, delay 18) | 18.206 (0.252) | 18.934 (0.167) | 14.701 (0.399) |
| AIC | −7.138 | −7.309 | −7.374 |
| Residual sum of squares | 0.073 | 0.076 | 0.076 |
| Standard error of the regression | 0.020 | 0.017 | 0.015 |
| Effect on the series (calculations in Table A2) | Savings of 7.96% from Jul. 2015 to Jun. 2016 | Savings of 8.87% from Jul. 2015 to Jun. 2016 | Savings of 0.779 DID (−4.51% from Jul. 2015 to Jun. 2016) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rojas, P.; Antoñanzas, F. Policies to Reduce Antibiotic Consumption: The Impact in the Basque Country. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9070423
Rojas P, Antoñanzas F. Policies to Reduce Antibiotic Consumption: The Impact in the Basque Country. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(7):423. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9070423
Chicago/Turabian StyleRojas, Paula, and Fernando Antoñanzas. 2020. "Policies to Reduce Antibiotic Consumption: The Impact in the Basque Country" Antibiotics 9, no. 7: 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9070423
APA StyleRojas, P., & Antoñanzas, F. (2020). Policies to Reduce Antibiotic Consumption: The Impact in the Basque Country. Antibiotics, 9(7), 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9070423






