Influence of Renal Function and Age on the Pharmacokinetics of Levofloxacin in Patients with Bone and Joint Infections
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patients and Collected Data
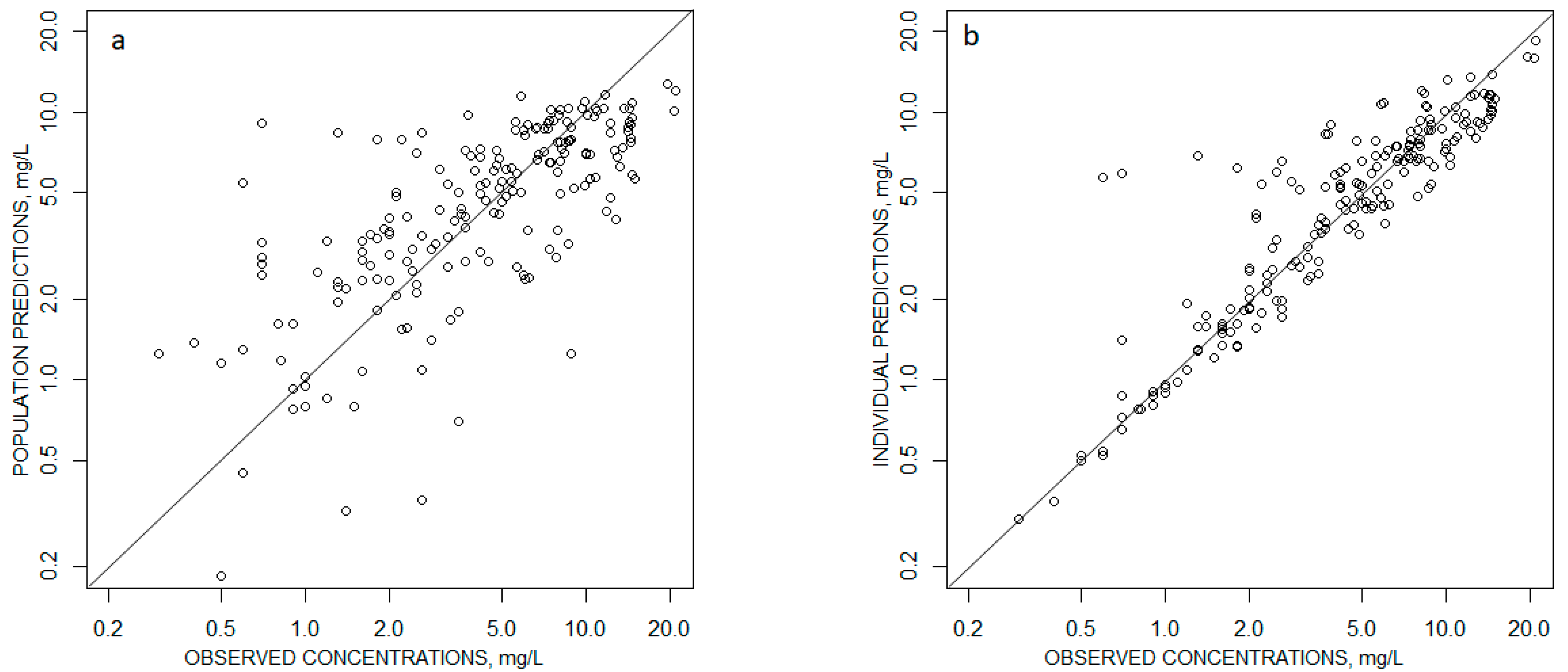
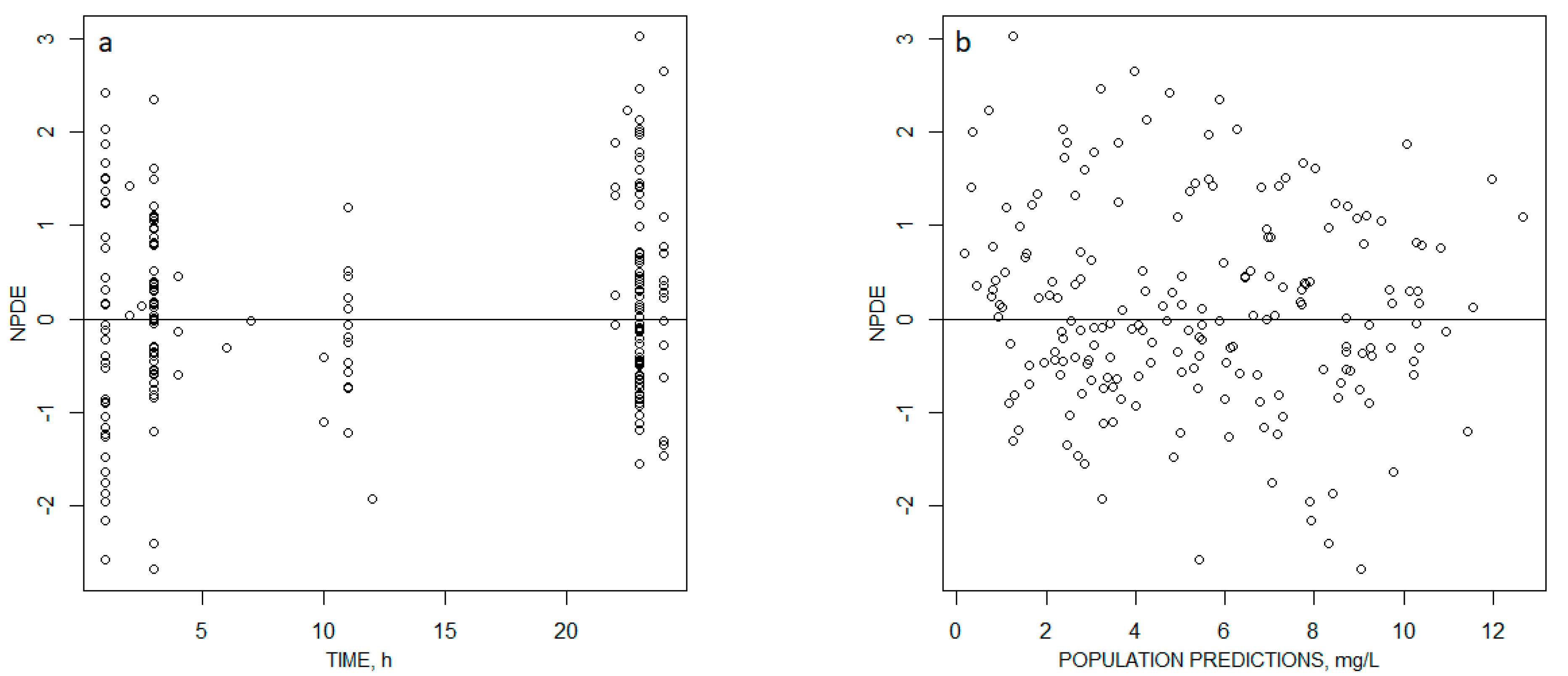
2.2. Pharmacokinetic Modeling
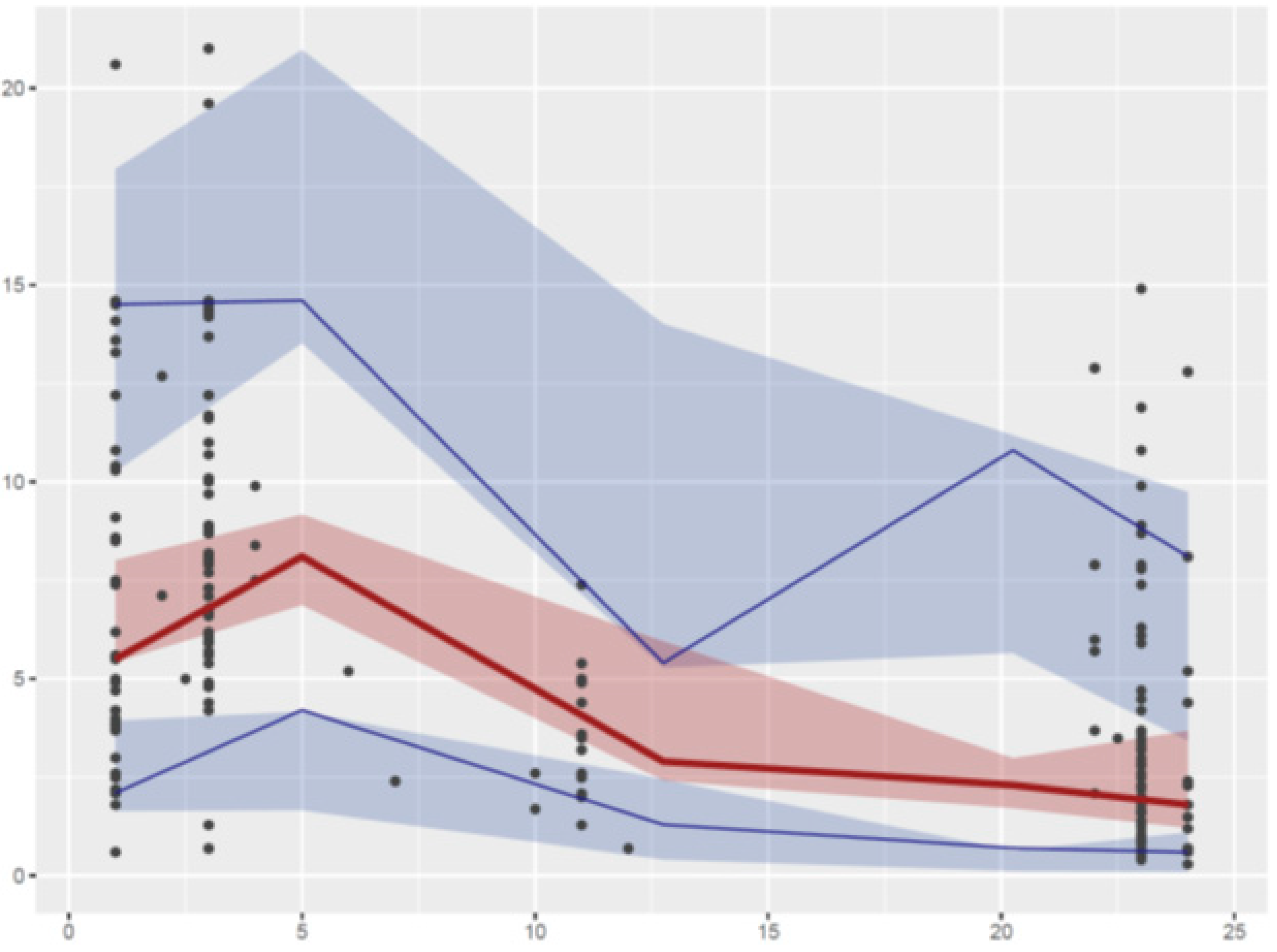
2.3. Dose Evaluation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients and Collected Data
4.2. Levofloxacin Assay
4.3. Population PK Modeling
4.4. Dose Evaluation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Norrby, S.R. Levofloxacin. Expert. Opin. Pharmacother. 1999, 1, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, O.; Kojima, C.; Hakusui, H.; Nakashima, M. Enantioselective disposition of ofloxacin in humans. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1991, 35, 2106–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- North, D.S.; Fish, D.N.; Redington, J.J. Levofloxacin, a Second-Generation Fluoroquinolone. Pharmacotherap 1998, 18, 915–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminimanizani, A.; Beringer, P.; Jelliffe, R. Comparative pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the newer fluoroquinolone antibacterials. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2001, 40, 169–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimmelé, T.; Boselli, E.; Breilh, D.; Djabarouti, S.; Bel, J.C.; Guyot, R.; Saux, M.C.; Allaouchiche, B. Diffusion of levofloxacin into bone and synovial tissues. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2004, 53, 533–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Asseray, N.; Bourigault, C.; Boutoille, D.; Happi, L.; Touchais, S.; Corvec, S.; Bemer, P.; Navas, D. Levofloxacin at the usual dosage to treat bone and joint infections: A cohort analysis. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2016, 47, 478–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senneville, E.; Poissy, J.; Legout, L.; Dehecq, C.; Loïez, C.; Valette, M.; Beltrand, E.; Caillaux, M.; Mouton, Y.; Migaud, H.; et al. Safety of prolonged high-dose levofloxacin therapy for bone infections. J. Chemother. 2007, 19, 688–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, W.A. Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic parameters: Rationale for antibacterial dosing of mice and men. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1998, 26, 1–10; quiz 11–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schentag, J.J.; Meagher, A.K.; Forrest, A. Fluoroquinolone AUIC break points and the link to bacterial killing rates. Part 2: Human trials. Ann. Pharmacother. 2003, 37, 1478–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schentag, J.J.; Gilliland, K.K.; Paladino, J.A. What have we learned from pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic theories? Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 32 (Suppl. S1), S39–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.A.; Abdul-Aziz, M.H.; Lipman, J.; Mouton, J.W.; Vinks, A.A.; Felton, T.W.; Hope, W.W.; Farkas, A.; Neely, M.N.; Schentag, J.J.; et al. Individualised antibiotic dosing for patients who are critically ill: Challenges and potential solutions. Lancet. Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, S.L.; Drusano, G.L.; Berman, A.L.; Fowler, C.L.; Chow, A.T.; Dornseif, B.; Reichl, V.; Natarajan, J.; Corrado, M. Pharmacodynamics of Levofloxacin: A New Paradigm for Early Clinical Trials. JAMA 1998, 279, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, M.R. Optimisation of antimicrobial therapy using pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic parameters. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2001, 7, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cojutti, P.G.; Ramos-Martin, V.; Schiavon, I.; Rossi, P.; Baraldo, M.; Hope, W.; Pea, F. Population Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Levofloxacin in Acutely Hospitalized Older Patients with Various Degrees of Renal Function. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e02134-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanigawara, Y.; Nomura, H.; Kagimoto, N.; Okumura, K.; Hori, R. Premarketing population pharmacokinetic study of levofloxacin in normal subjects and patients with infectious diseases. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1995, 18, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Preston, S.L.; Drusano, G.L.; Berman, A.L.; Fowler, C.L.; Chow, A.T.; Dornseif, B.; Reichl, V.; Natarajan, J.; Wong, F.A.; Corrado, M. Levofloxacin population pharmacokinetics and creation of a demographic model for prediction of individual drug clearance in patients with serious community-acquired infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1998, 42, 1098–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peloquin, C.A.; Hadad, D.J.; Molino, L.P.D.; Palaci, M.; Boom, W.H.; Dietze, R.; Johnson, J.L. Population Pharmacokinetics of Levofloxacin, Gatifloxacin, and Moxifloxacin in Adults with Pulmonary Tuberculosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, J.-F.; Liu, Y.-B.; Xiao, Z.-K.; Huang, J.-A.; Si, B.; Sun, S.-H.; Xia, Q.-M.; Wu, X.-J.; Cao, G.-Y.; et al. Population pharmacokinetics of oral levofloxacin 500 mg once-daily dosage in community-acquired lower respiratory tract infections: Results of a prospective multicenter study in China. J. Infect. Chemother. 2009, 15, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiem, S.; Ryu, S.-M.; Lee, Y.-M.; Schentag, J.J.; Kim, Y.-W.; Kim, H.-K.; Jang, H.-J.; Joo, Y.-D.; Jin, K.; Shin, J.-G.; et al. Population pharmacokinetics of levofloxacin in Korean patients. J. Chemother. 2016, 28, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, L.-Q.; Wang, N.; Zhao, X.; Yang, W.; Ji, S.; Sun, L. Population pharmacokinetics of intravenous levofloxacin 500 mg/day dosage in infected patients. Pharmazie 2014, 69, 553–557. [Google Scholar]
- Bulitta, J.B.; Kinzig, M.; Naber, C.K.; Wagenlehner, F.M.E.; Sauber, C.; Landersdorfer, C.B.; Sörgel, F.; Naber, K.G. Population Pharmacokinetics and Penetration into Prostatic, Seminal, and Vaginal Fluid for Ciprofloxacin, Levofloxacin, and Their Combination. CHE 2011, 57, 402–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drusano, G.L.; Preston, S.L.; Van Guilder, M.; North, D.; Gombert, M.; Oefelein, M.; Boccumini, L.; Weisinger, B.; Corrado, M.; Kahn, J. A population pharmacokinetic analysis of the penetration of the prostate by levofloxacin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 2046–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Drusano, G.L.; Preston, S.L.; Gotfried, M.H.; Danziger, L.H.; Rodvold, K.A. Levofloxacin penetration into epithelial lining fluid as determined by population pharmacokinetic modeling and monte carlo simulation. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 586–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gergs, U.; Ihlefeld, D.; Clauss, T.; Weiss, M.; Pönicke, K.; Hofmann, G.O.; Neumann, J. Population Pharmacokinetics of Levofloxacin in Plasma and Bone of Patients Undergoing Hip or Knee Surgery. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug. Dev. 2018, 7, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kervezee, L.; Stevens, J.; Birkhoff, W.; Kamerling, I.M.C.; de Boer, T.; Dröge, M.; Meijer, J.H.; Burggraaf, J. Identifying 24 h variation in the pharmacokinetics of levofloxacin: A population pharmacokinetic approach. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 81, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, J.A.; Cotta, M.O.; Cojutti, P.; Lugano, M.; Rocca, G.D.; Pea, F. Does Critical Illness Change Levofloxacin Pharmacokinetics? Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 1459–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froissart, M.; Rossert, J.; Jacquot, C.; Paillard, M.; Houillier, P. Predictive performance of the modification of diet in renal disease and Cockcroft-Gault equations for estimating renal function. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, K.; Fujimoto, Y.; Morimoto, Y.; Kanbayashi, Y.; Matsumoto, Y.; Taniwaki, M. Population pharmacokinetics of levofloxacin as prophylaxis for febrile neutropenia. Intern. Med. 2008, 47, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- van den Elsen, S.H.J.; Sturkenboom, M.G.G.; van’t Boveneind-Vrubleuskaya, N.; Skrahina, A.; van der Werf, T.S.; Heysell, S.K.; Mpagama, S.; Migliori, G.B.; Peloquin, C.A.; Touw, D.J.; et al. Population Pharmacokinetic Model and Limited Sampling Strategies for Personalized Dosing of Levofloxacin in Tuberculosis Patients. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e01092-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Zhang, J.; Wu, X.; Yu, J.; Chen, Y.; Ye, X.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, B.; Shi, Y. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of levofloxacin injection in healthy Chinese volunteers and dosing regimen optimization. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2013, 38, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blot, S.I.; Pea, F.; Lipman, J. The effect of pathophysiology on pharmacokinetics in the critically ill patient--concepts appraised by the example of antimicrobial agents. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 77, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemi, M.; Backman, J.T.; Fromm, M.F.; Neuvonen, P.J.; Kivistö, K.T. Pharmacokinetic interactions with rifampicin: Clinical relevance. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2003, 42, 819–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bidell, M.R.; Lodise, T.P. Fluoroquinolone-Associated Tendinopathy: Does Levofloxacin Pose the Greatest Risk? Pharmacotherapy 2016, 36, 679–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landersdorfer, C.B.; Bulitta, J.B.; Kinzig, M.; Holzgrabe, U.; Sörgel, F. Penetration of antibacterials into bone: Pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic and bioanalytical considerations. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2009, 48, 89–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Baum, H.; Böttcher, S.; Abel, R.; Gerner, H.J.; Sonntag, H.G. Tissue and serum concentrations of levofloxacin in orthopaedic patients. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2001, 18, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Coresh, J.; Greene, T.; Stevens, L.A.; Zhang, Y.L.; Hendriksen, S.; Kusek, J.W.; Van Lente, F.; Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration. Using standardized serum creatinine values in the modification of diet in renal disease study equation for estimating glomerular filtration rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2006, 145, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cockcroft, D.W.; Gault, M.H. Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron 1976, 16, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergstrand, M.; Hooker, A.C.; Wallin, J.E.; Karlsson, M.O. Prediction-corrected visual predictive checks for diagnosing nonlinear mixed-effects models. AAPS J. 2011, 13, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parke, J.; Holford, N.H.; Charles, B.G. A procedure for generating bootstrap samples for the validation of nonlinear mixed-effects population models. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 1999, 59, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brendel, K.; Comets, E.; Laffont, C.; Laveille, C.; Mentré, F. Metrics for external model evaluation with an application to the population pharmacokinetics of gliclazide. Pharm. Res. 2006, 23, 2036–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Clinical Characteristics | |
|---|---|
| Age (mean ± SD) | 57.5 ± 20.1 |
| BW, kg (mean ± SD) | 72.1 ± 15.9 |
| Diagnosis | |
| Spine surgical site infection, n (%) | 33 (57%) |
| Limb surgical site infection, n (%) | 19 (33%) |
| Osteoarthritis, n (%) | 5 (9%) |
| Spondylodiscitis, n (%) | 1 (1%) |
| Surgical Materials | |
| Yes, n (%) | 44 (76%) |
| No, n (%) | 14 (24%) |
| Microbiologic Characteristics | |
| Monomicrobial infection, n (%) | 39 (66%) |
| Polymicrobial infection, n (%) | 20 (34%) |
| Methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus, n (%) | 31 (53%) |
| Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, n (%) | 4 (7%) |
| Escherichia coli, n (%) | 7 (12%) |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa, n (%) | 4 (7%) |
| Cutibacterium acnes, n (%) | 2 (3%) |
| Biologic Characteristics | |
| GFR, mL/min/1.73m² (mean ± SD) CLcr (mL/min) | 104.8 ± 46.4 120.2 ± 74.35 |
| CRP, mg/L (mean ± SD) | 38.5 ± 41.3 |
| Bilirubin, µmol/L (mean ± SD) | 9.6 ± 7.5 |
| Proteinemia, g/L (mean ± SD) | 64.7 ± 8.6 |
| SGOT, IU/L (mean ± SD) | 25.1 ± 24.3 |
| SGPT, IU/L (mean ± SD) | 24.4 ± 23.4 |
| Alkaline phosphatase, IU/L (mean ± SD) | 135.2 ± 81.8 |
| LEVO, mg/l (mean ± SD) | 5.52 ± 4.41 |
| Parameter | Original Dataset | Bootstrap | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Estimate | RSE (%) | Mean Estimate | RSE (%) | |
| Ka (h−1) | 0.895 | 34 | 0.948 | 38 |
| CL/F (L/h) | 6.10 | 6 | 6.00 | 6.8 |
| V/F (L) | 90.6 | 8 | 88.4 | 9.9 |
| ΘGFR,CL | 0.48 | 41 | 0.54 | 31 |
| ΘAGE,CL | −0.52 | 28 | −0.47 | 42 |
| ωCL/F | 0.157 | 19 | 0.155 | 22 |
| ωV/F | 0.061 | 43 | 0.043 | 65 |
| CovCL,V | 0.043 | NE | 0.047 | 72 |
| σ | 0.118 | 13 | 0.113 | 13 |
| AGE (year) | GFR (mL/min/1.73 m²) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 50 | 70 | |
| 147 ± 59 | 196 ± 82 | 233 ± 97 | 40 |
| 115 ± 45 | 148 ± 60 | 176 ± 73 | 70 |
| 98 ± 40 | 128 ± 52 | 154 ± 65 | 100 |
| 84 ± 33 | 109 ± 43 | 132 ± 52 | 130 |
| 79 ± 35 | 100 ± 42 | 122 ± 51 | 160 |
| AGE (year) | GFR (mL/min/1.73 m²) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 50 | 70 | |
| 80 | 93 | 97 | 40 |
| 56 | 81 | 91 | 70 |
| 40 | 65 | 84 | 100 |
| 26 | 52 | 69 | 130 |
| 20 | 40 | 62 | 160 |
| AGE (year) | GFR (mL/min/1.73 m²) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 50 | 70 | |
| 99 | 100 | 100 | 40 |
| 99 | 99 | 100 | 70 |
| 94 | 98 | 99 | 100 |
| 87 | 97 | 99 | 130 |
| 81 | 95 | 98 | 160 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eloy, G.; Lebeaux, D.; Launay, M.; Fernandez-Gerlinger, M.-P.; Billaud, E.; Douez, E.; Mainardi, J.-L.; Bouyer, B.; Jullien, V. Influence of Renal Function and Age on the Pharmacokinetics of Levofloxacin in Patients with Bone and Joint Infections. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9070401
Eloy G, Lebeaux D, Launay M, Fernandez-Gerlinger M-P, Billaud E, Douez E, Mainardi J-L, Bouyer B, Jullien V. Influence of Renal Function and Age on the Pharmacokinetics of Levofloxacin in Patients with Bone and Joint Infections. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(7):401. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9070401
Chicago/Turabian StyleEloy, Gauthier, David Lebeaux, Manon Launay, Marie-Paule Fernandez-Gerlinger, Eliane Billaud, Emmanuel Douez, Jean-Luc Mainardi, Benjamin Bouyer, and Vincent Jullien. 2020. "Influence of Renal Function and Age on the Pharmacokinetics of Levofloxacin in Patients with Bone and Joint Infections" Antibiotics 9, no. 7: 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9070401
APA StyleEloy, G., Lebeaux, D., Launay, M., Fernandez-Gerlinger, M.-P., Billaud, E., Douez, E., Mainardi, J.-L., Bouyer, B., & Jullien, V. (2020). Influence of Renal Function and Age on the Pharmacokinetics of Levofloxacin in Patients with Bone and Joint Infections. Antibiotics, 9(7), 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9070401





