Drivers of Antibiotic Resistance Transmission in Low- and Middle-Income Countries from a “One Health” Perspective—A Review
Abstract
1. Background
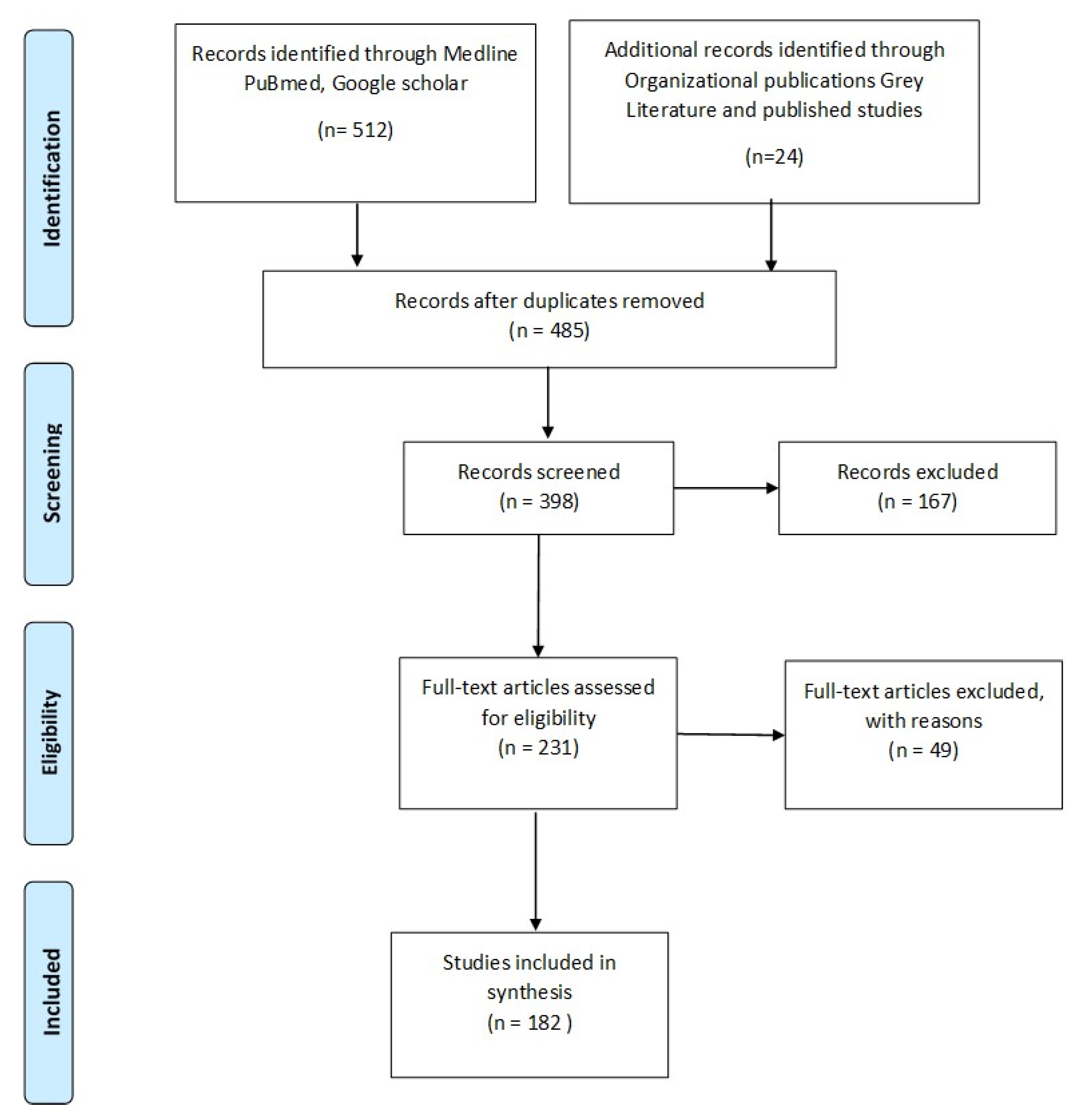
2. Method of Literature Search
- Ovid MEDLINE(R) Epub Ahead of Print, In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations, Ovid MEDLINE(R) Daily and Ovid MEDLINE(R) 1946 to Present
- PubMed http://pubmed.gov
- Google Scholar
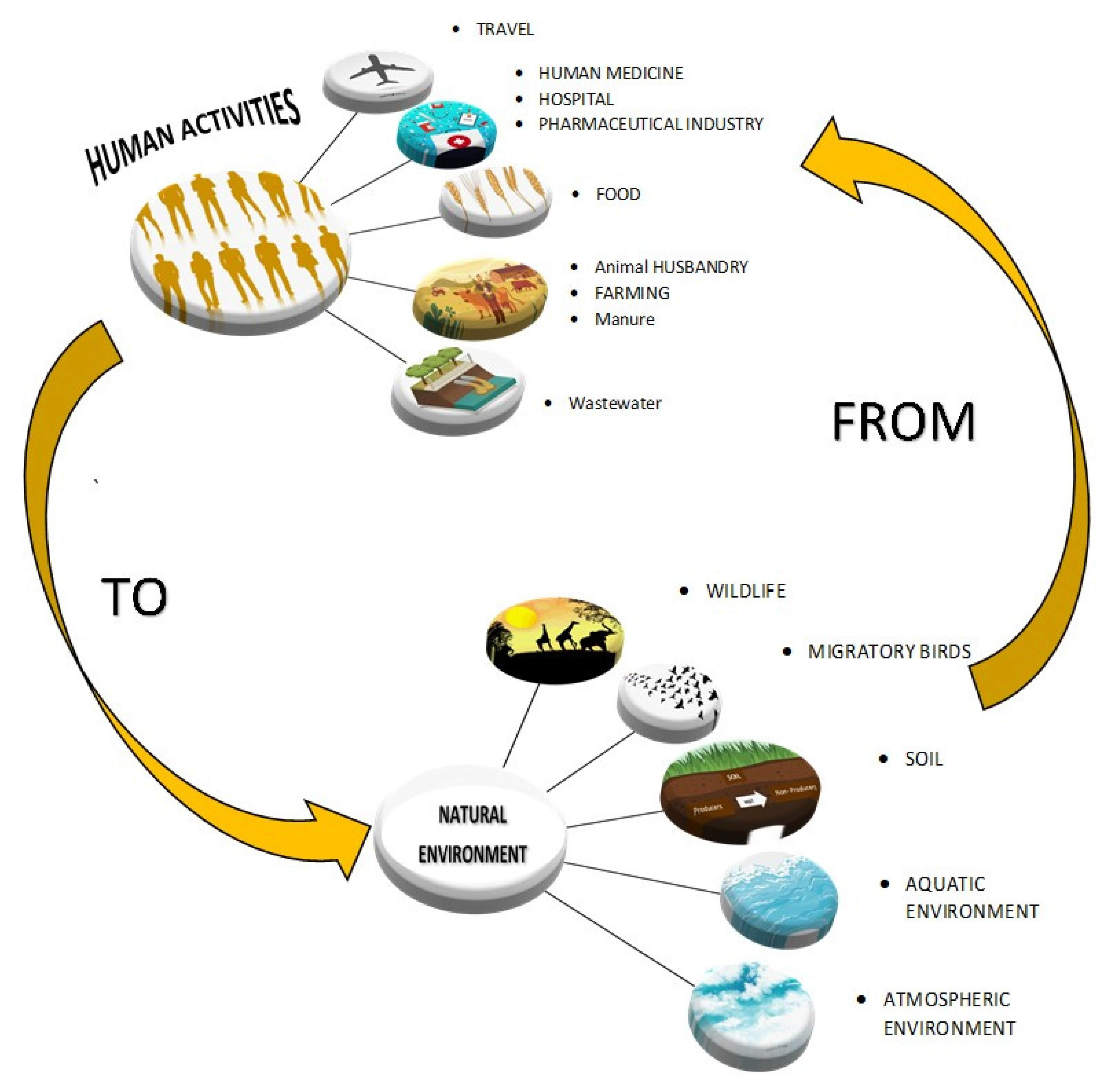
3. The Environmental Resistome
4. Drivers of Antibiotic Resistance Transmission
4.1. Socio-Economic Factors and Related Socio-Ecological Behaviors
4.2. Antibiotic Uses in Human Medicine
4.3. Counterfeit Antibiotics
4.4. Non-Prescription Antibiotics
4.5. Antibiotic Uses in Animal Health and the Agricultural Sector
4.6. Other Drivers of Resistance
5. The Economics of One Health
6. Surveillance of Antibiotic Consumption in Humans and Animals
7. Surveillance of AMR in Humans and Animals
8. Adaptation of Preventive Measures Strategies
8.1. Antibiotic Stewardship Programs
8.2. Vaccines
8.3. Rapid Diagnostic Tests
8.4. Pharmaceutical Waste
9. Highlights
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABR | Antibiotic resistance |
| ARG | Antibiotic resistant genes |
| AGPs | Antimicrobial growth promoters |
| MCR-1 | mobilized colistin resistance-1 |
| NDM-1 | New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase 1 |
| UK | United Kingdom |
| WHO | World health organization |
| US | United States of America |
| CDC | Center of Disease Control and Prevention |
| NAMCS | National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey |
| NHAMCS | National Hospital Ambulatory Medical Care Survey |
| LMICs | Low- and Middle-income countries |
| HICs | High income countries |
| FAO | Food and Agriculture Organization |
| OIE | World Organization for Animal Health |
| UN | united Nations |
| ESAC- Net | European surveillance of antimicrobial consumption Network (ESAC-Net) |
| GAP | Global Action Plan |
| GLASS | Global Antimicrobial Surveillance System |
| GHSA | Global Health Security Agenda |
| UHC | Universal Health Coverage |
| IPC | Infection prevention and control |
| DMS | Diagnostic Market Stimulus |
| APIs | Active Pharmaceutical ingredients |
| R&D | Research and development |
References
- White, A.; Hughes, J.M. Critical Importance of a One Health Approach to Antimicrobial Resistance. EcoHealth 2019, 16, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank Group. Operational Framework for Strengthening Human, Animal, and Environmental Public Health Systems at Their Interface; International Bank for Reconstruction and Development/The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, J.; Lockhart, C.; Pongolini, S.; Karesh, W.B.; Baylis, M.; Goldberg, T.; Slingenbergh, J.; Gale, P.; Venturini, T.; Catchpole, M.; et al. Drivers for emerging issues in animal and plant health. EFSA J. 2016, 14, e00512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwen, S.A.; Collignon, P.J. Antimicrobial resistance: A One Health perspective. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6, 521–547. [Google Scholar]
- Holmes, A.H.; Moore, L.S.; Sundsfjord, A.; Steinbakk, M.; Regmi, S.; Karkey, A.; Guerin, P.J.; Piddock, L.J. Understanding the mechanisms and drivers of antimicrobial resistance. Lancet 2016, 387, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinsstag, J. Convergence of ecohealth and one health. Ecohealth 2012, 9, 371–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collignon, P.J.; McEwen, S.A. One health—Its importance in helping to better control antimicrobial resistance. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2019, 4, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huijbers, P.M.; Blaak, H.; de Jong, M.C.; Graat, E.A.; Vandenbroucke-Grauls, C.M.; de Roda Husman, A.M. Role of the environment in the transmission of antimicrobial resistance to humans: A review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 11993–12004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, B.J.; Hungate, B.A.; Price, L.B. Food-animal production and the spread of antibiotic resistance: The role of ecology. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2017, 15, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. The European Union summary report on antimicrobial resistance in zoonotic and indicator bacteria from humans, animals and food in 2016. EFSA J. 2018, 16, e05182. [Google Scholar]
- Nagy, B.; Szmolka, A.; Možina, S.S.; Kovač, J.; Strauss, A.; Schlager, S.; Beutlich, J.; Appel, B.; Lušicky, M.; Aprikian, P.; et al. Virulence and antimicrobial resistance determinants of verotoxigenic Escherichia coli (VTEC) and of multidrug-resistant E. coli from foods of animal origin illegally imported to the EU by flight passengers. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 209, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presi, P.; Stärk, K.D.; Stephan, R.; Breidenbach, E.; Frey, J.; Regula, G. Risk scoring for setting priorities in a monitoring of antimicrobial resistance in meat and meat products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 130, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, A.R.; Pinho, D.B.; de Oliveira, S.A.; Pereira, O.L. New occurrences of Botryosphaeriaceae causing black root rot of cassava in Brazil. Trop. Plant Pathol. 2014, 39, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czekalski, N.; Berthold, T.; Caucci, S.; Egli, A.; Bürgmann, H. Increased levels of multiresistant bacteria and resistance genes after wastewater treatment and their dissemination into Lake Geneva, Switzerland. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A.; Modarai, M.; Naylor, N.R.; Boyd, S.E.; Atun, R.; Barlow, J.; Holmes, A.H.; Johnson, A.; Robotham, J.V. Quantifying drivers of antibiotic resistance in humans: A systematic review. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, e368–e378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.; Walsh, T.R.; Yi, L.X.; Zhang, R.; Spencer, J.; Doi, Y.; Tian, G.; Dong, B.; Huang, X.; et al. Emergence of plasmid-mediated colistin resistance mechanism MCR-1 in animals and human beings in China: A microbiological and molecular biological study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; van Dorp, L.; Shaw, L.P.; Bradley, P.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Jin, L.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Rieux, A.; et al. The global distribution and spread of the mobilized colistin resistance gene mcr-1. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.U.; Maryam, L.; Zarrilli, R. Structure, genetics and worldwide spread of New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase (NDM): A threat to public health. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Islam, M.; Hasan, R.; Hossain, M.I.; Nabi, A.; Rahman, M.; Goessens, W.H.; Endtz, H.P.; Boehm, A.B.; Faruque, S.M. Environmental spread of New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase-1-producing multidrug-resistant bacteria in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e00793-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, C.M.; Christgen, B.; Roberts, J.A.; Su, J.Q.; Arnold, K.E.; Gray, N.D.; Zhu, Y.G.; Graham, D.W. Understanding drivers of antibiotic resistance genes in High Arctic soil ecosystems. Environ. Int. 2019, 125, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Boeckel, T.P.; Gandra, S.; Ashok, A.; Caudron, Q.; Grenfell, B.T.; Levin, S.A.; Laxminarayan, R. Global antibiotic consumption 2000 to 2010: An analysis of national pharmaceutical sales data. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versporten, A.; Bolokhovets, G.; Ghazaryan, L.; Abilova, V.; Pyshnik, G.; Spasojevic, T.; Korinteli, I.; Raka, L.; Kambaralieva, B.; Cizmovic, L.; et al. Antibiotic use in eastern Europe: A cross-national database study in coordination with the WHO Regional Office for Europe. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, T.P.; Bu, D.P.; Carrique-Mas, J.; Fèvre, E.M.; Gilbert, M.; Grace, D.; Hay, S.I.; Jiwakanon, J.; Kakkar, M.; Kariuki, S.; et al. Antibiotic resistance is the quintessential One Health issue. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 110, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harbarth, S.; Balkhy, H.H.; Goossens, H.; Jarlier, V.; Kluytmans, J.; Laxminarayan, R.; Saam, M.; Van Belkum, A.; Pittet, D. Antimicrobial resistance: One world, one fight! Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2015, 4, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surette, M.D.; Wright, G.D. Lessons from the environmental antibiotic resistome. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 71, 309–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, J.L. Ecology and Evolution of Chromosomal Gene Transfer between Environmental Microorganisms and Pathogens. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6, 139–160. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, S.B. The challenge of antibiotic resistance. Sci. Am. 1998, 278, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Kristiansson, E.; Larsson, D.J. Environmental factors influencing the development and spread of antibiotic resistance. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 42, fux053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajardo, A.; Martínez-Martín, N.; Mercadillo, M.; Galán, J.C.; Ghysels, B.; Matthijs, S.; Cornelis, P.; Wiehlmann, L.; Tümmler, B.; Baquero, F.; et al. The neglected intrinsic resistome of bacterial pathogens. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, G.; Wright, G.D. Intrinsic antibiotic resistance: Mechanisms, origins, challenges and solutions. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 303, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, G.D. The antibiotic resistome: The nexus of chemical and genetic diversity. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hoek, A.H.; Mevius, D.; Guerra, B.; Mullany, P.; Roberts, A.P.; Aarts, H.J. Acquired antibiotic resistance genes: An overview. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas, G.; Sommer, M.O. Context matters—The complex interplay between resistome genotypes and resistance phenotypes. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2012, 15, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essack, S.Y.; Connolly, C.; Sturm, A.W. Antibiotic use and resistance in public-sector hospitals in KwaZulu-Natal. S. Afr. Med. J. 2005, 95, 865–870. [Google Scholar]
- Agyepong, N.; Govinden, U.; Owusu-Ofori, A.; Essack, S.Y. Multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacterial infections in a teaching hospital in Ghana. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2018, 7, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsamy, Y.; Mlisana, K.P.; Allam, M.; Amoako, D.G.; Abia, A.L.; Ismail, A.; Singh, R.; Kisten, T.; Han, K.S.; Muckart, D.J.; et al. Genomic Analysis of Carbapenemase-Producing Extensively Drug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates Reveals the Horizontal Spread of p18-43_01 Plasmid Encoding blaNDM-1 in South Africa. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousham, E.K.; Unicomb, L.; Islam, M.A. Human, animal and environmental contributors to antibiotic resistance in low-resource settings: Integrating behavioural, epidemiological and One Health approaches. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 285, 20180332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadimpalli, M.; Delarocque-Astagneau, E.; Love, D.C.; Price, L.B.; Huynh, B.T.; Collard, J.M.; Lay, K.S.; Borand, L.; Ndir, A.; Walsh, T.R.; et al. Combating global antibiotic resistance: Emerging one health concerns in lower-and middle-income countries. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 66, 963–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Boeckel, T.P.; Pires, J.; Silvester, R.; Zhao, C.; Song, J.; Criscuolo, N.G.; Gilbert, M.; Bonhoeffer, S.; Laxminarayan, R. Global trends in antimicrobial resistance in animals in low-and middle-income countries. Science 2019, 365, eaaw1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herindrainy, P.; Randrianirina, F.; Ratovoson, R.; Hariniana, E.R.; Buisson, Y.; Genel, N.; Decre, D.; Arlet, G.; Talarmin, A.; Richard, V. Rectal carriage of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing gram-negative bacilli in community settings in Madagascar. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundborg, C.S.; Diwan, V.; Pathak, A.; Purohit, M.R.; Shah, H.; Sharma, M.; Mahadik, V.K.; Tamhankar, A.J. Protocol: A ‘One health’two year follow-up, mixed methods study on antibiotic resistance, focusing children under 5 and their environment in rural India. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 1321. [Google Scholar]
- Roess, A.A.; Winch, P.J.; Akhter, A.; Afroz, D.; Ali, N.A.; Shah, R.; Begum, N.; Seraji, H.R.; El Arifeen, S.; Darmstadt, G.L.; et al. Household animal and human medicine use and animal husbandry practices in rural Bangladesh: Risk factors for emerging zoonotic disease and antibiotic resistance. Zoonoses Public Health 2015, 62, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanta, I.S.; Hasnat, M.A.; Zeidner, N.; Gurley, E.S.; Azziz-Baumgartner, E.; Sharker, M.A.; Hossain, K.; Khan, S.U.; Haider, N.; Bhuyan, A.A.; et al. Raising backyard poultry in rural Bangladesh: Financial and nutritional benefits, but persistent risky practices. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 1454–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karthik, L.; Kumar, G.; Keswani, T.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Chandar, S.S.; Rao, K.B. Protease inhibitors from marine actinobacteria as a potential source for antimalarial compound. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Xie, M.; Qu, Z.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; He, T.; Wang, H.; Zuo, Z.; Wu, C. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella isolated from an integrated broiler chicken supply chain in Qingdao, China. Food Control 2016, 62, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finley, R.L.; Collignon, P.; Larsson, D.J.; McEwen, S.A.; Li, X.Z.; Gaze, W.H.; Reid-Smith, R.; Timinouni, M.; Graham, D.W.; Topp, E. The scourge of antibiotic resistance: The important role of the environment. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 57, 704–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laxminarayan, R.; Chaudhury, R.R. Antibiotic resistance in India: Drivers and opportunities for action. PLoS Med. 2016, 13, e1001974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Estimates of the Global Burden of Foodborne Diseases: Foodborne Disease Burden Epidemiology Reference Group 2007–2015; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Carruth, L.; Roess, A.A.; Terefe, Y.; Hosh, F.M.; Salman, M.D. Antimicrobial resistance and food safety in Africa. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 575–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkor, E.S.; Newman, M.J.; Tay, S.C.; Dayie, N.T.; Bannerman, E.; Olu-Taiwo, M. Investigation into the risk of exposure to antibiotic residues contaminating meat and egg in Ghana. Food Control 2011, 22, 869–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, J.; Umoh, V.J.; Audu-Okoh, E.; Umoh, J.U.; Kwaga, J.K.P. Veterinary drug use in poultry farms and determination of antimicrobial drug residues in commercial eggs and slaughtered chicken in Kaduna State, Nigeria. Food Control 2004, 15, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abiola, F.A.; Diop, M.M.; Teko-Agbo, A.; Delepine, B.; Biaou, F.C.; Roudaut, B.; Gaudin, V.; Sanders, P. Résidus d’antibactériens dans le foie et le gésier de poulets de chair dans les régions de Dakar et de Thiès (Sénégal). Rev. Méd. vét. 2005, 156, 264–268. [Google Scholar]
- Kang’ethe, E.K.; Aboge, G.O.; Arimi, S.M.; Kanja, L.W.; Omore, A.O.; McDermott, J.J. Investigation of risk of consuming marketed milk with antimicrobial residues in Kenya. Food Control 2005, 16, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurwijila, L.R.; Omore, A.; Staal, S.; Mdoe, N.S.Y. Investigation of the risk of exposure to antimicrobial residues present in marketed milk in Tanzania. J. Food Prot. 2006, 69, 2487–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission (EC). Report on the results of residue monitoring in food of animal origin in the Member States; EC: Brussels, Belgium, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Om, C.; McLaws, M.L. Antibiotics: Practice and opinions of Cambodian commercial farmers, animal feed retailers and veterinarians. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2016, 5, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Antibiotic resistance threats in the United States; CDC: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2013.
- Laxminarayan, R.; Duse, A.; Wattal, C.; Zaidi, A.K.; Wertheim, H.F.; Sumpradit, N.; Vlieghe, E.; Hara, G.L.; Gould, I.M.; Goossens, H.; et al. Antibiotic resistance—The need for global solutions. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 1057–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Public Health Agency of Canada. Canadian Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance System Report—2015: Protecting Canadians from Illness; PHAC: Ottawa, ON, Canada, March 2015.
- Weist, K.; Högberg, L.D. ECDC publishes 2015 surveillance data on antimicrobial resistance and antimicrobial consumption in Europe. Eurosurveillance 2016, 21, 30401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. The Evolving Threat of Antimicrobial Resistance: Options for Action; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Costelloe, C.; Metcalfe, C.; Lovering, A.; Mant, D.; Hay, A.D. Effect of antibiotic prescribing in primary care on antimicrobial resistance in individual patients: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2010, 340, c2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra-Kumar, S.; Lammens, C.; Coenen, S.; Van Herck, K.; Goossens, H. Effect of azithromycin and clarithromycin therapy on pharyngeal carriage of macrolide-resistant streptococci in healthy volunteers: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Lancet 2007, 369, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, H.; Ferech, M.; Vander Stichele, R.; Elseviers, M.; ESAC Project Group. Outpatient antibiotic use in Europe and association with resistance: A cross-national database study. Lancet 2005, 365, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridkin, S.K.; Edwards, J.R.; Courval, J.M.; Hill, H.; Tenover, F.C.; Lawton, R.; Gaynes, R.P.; McGowan, J.E., Jr. The effect of vancomycin and third-generation cephalosporins on prevalence of vancomycin-resistant enterococci in 126 US adult intensive care units. Ann. Intern. Med. 2001, 135, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. Drug-Resistant Infections: A Threat to Our Economic Future; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Fleming-Dutra, K.E.; Hersh, A.L.; Shapiro, D.J.; Bartoces, M.; Enns, E.A.; File, T.M.; Finkelstein, J.A.; Gerber, J.S.; Hyun, D.Y.; Linder, J.A.; et al. Prevalence of inappropriate antibiotic prescriptions among US ambulatory care visits, 2010–2011. JAMA 2016, 315, 1864–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owens, R.C., Jr. Antimicrobial stewardship: Concepts and strategies in the 21st century. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2008, 61, 110–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, N. Antimicrobial stewardship. Am. J. Infect. Control 2006, 34, S55–S63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lautenbach, E.; Fishman, N.O.; Bilker, W.B.; Castiglioni, A.; Metlay, J.P.; Edelstein, P.H.; Strom, B.L. Risk factors for fluoroquinolone resistance in nosocomial Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae infections. Arch. Intern. Med. 2002, 162, 2469–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conly, J.M.; Johnston, B.L. Antibiotic Resistance in Canada at the Dawn of the New Millennium--A Model for the Developed World? Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med Microbiol. 2000, 11, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Surveillance of Antimicrobial Consumption in Europe 2012; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control: Stockholm, Sweden, 2014; Available online: http://ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications/Publications/antimicrobialconsumption-europe-esac-net-2012.pdf (accessed on 22 May 2015).
- Krockow, E.M.; Colman, A.M.; Chattoe-Brown, E.; Jenkins, D.R.; Perera, N.; Mehtar, S.; Tarrant, C. Balancing the risks to individual and society: A systematic review and synthesis of qualitative research on antibiotic prescribing behaviour in hospitals. J. Hosp. Infect. 2019, 101, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.P.; Hoffmann, T.C.; McCullough, A.R.; van Driel, M.L.; Del Mar, C.B. Antibiotic resistance: What are the opportunities for primary care in alleviating the crisis? Front. Public Health 2015, 3, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, A.R.; Ferreira, M.; Roque, F.; Falcão, A.; Ramalheira, E.; Figueiras, A.; Herdeiro, M.T. Physicians’ attitudes and knowledge concerning antibiotic prescription and resistance: Questionnaire development and reliability. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Muras, M.; Krajewski, J.; Nocun, M.; Godycki-Cwirko, M. A survey of patient behaviours and beliefs regarding antibiotic self-medication for respiratory tract infections in Poland. Arch. Med. Sci. AMS 2013, 9, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, J.; Davies, S.; Rex, J.; White, L.J.; Murray, R. Review on Antimicrobial Resistance, Tackling Drug-Resistant Infections Globally: Final Report and Recommendations; Wellcome Trust and UK Government: London, UK, 2016.
- Arnold, S.R.; Straus, S.E. Interventions to improve antibiotic prescribing practices in ambulatory care. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2005, 2005, CD00359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livermore, D.M.; Hope, R.; Reynolds, R.; Blackburn, R.; Johnson, A.P.; Woodford, N. Declining cephalosporin and fluoroquinolone non-susceptibility among bloodstream Enterobacteriaceae from the UK: Links to prescribing change? J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 2667–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnidge, J.; Christiansen, K. Antibiotic use and resistance--proving the obvious. Lancet (Lond. Engl.) 2005, 365, 548–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delepierre, A.; Gayot, A.; Carpentier, A. Update on counterfeit antibiotics worldwide; public health risks. Med. Mal. Infect. 2012, 42, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelesidis, T.; Falagas, M.E. Substandard/counterfeit antimicrobial drugs. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 443–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cockburn, R.; Newton, P.N.; Agyarko, E.K.; Akunyili, D.; White, N.J. The global threat of counterfeit drugs: Why industry and governments must communicate the dangers. PLoS Med. 2005, 2, e100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attaran, A.; Barry, D.; Basheer, S.; Bate, R.; Benton, D.; Chauvin, J.; Garrett, L.; Kickbusch, I.; Kohler, J.C.; Midha, K.; et al. How to achieve international action on falsified and substandard medicines. BMJ 2012, 345, e7381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO, C.D. Guidelines for the Development of Measures to Combat Counterfeit Drugs; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan, B.A.; Chan, F.; Fenoff, R.; Wilson, J.M. Assessing the developing knowledge-base of product counterfeiting: A content analysis of four decades of research. Trends Organ. Crime 2017, 20, 338–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, P.; Proux, S.; Green, M.; Smithuis, F.; Rozendaal, J.; Prakongpan, S.; Chotivanich, K.; Mayxay, M.; Looareesuwan, S.; Farrar, J.; et al. Fake artesunate in Southeast Asia. Lancet 2001, 357, 1948–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syhakhang, L.; Lundborg, C.S.; Lindgren, B.; Tomson, G. The quality of drugs in private pharmacies in Lao PDR: A repeat study in 1997 and 1999. Pharm. World Sci. 2004, 26, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okeke, I.N.; Lamikanra, A.; Edelman, R. Socioeconomic and behavioral factors leading to acquired bacterial resistance to antibiotics in developing countries. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1999, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byarugaba, D.K. Antimicrobial resistance in developing countries and responsible risk factors. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2004, 24, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainous, A.G.; Everett, C.J.; Post, R.E.; Diaz, V.A.; Hueston, W.J. Availability of antibiotics for purchase without a prescription on the internet. Ann. Fam. Med. 2009, 7, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guinovart, M.C.; Figueras, A.; Llor, C. Selling antimicrobials without prescription• far beyond an administrative problem. Enferm. Infecc. Y Microbiol. Clin. (Engl. Ed.) 2018, 36, 290–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roque, F.; Soares, S.; Breitenfeld, L.; Figueiras, A.; Herdeiro, M.T. Influence of community pharmacists’ attitudes on antibiotic dispensing behavior: A cross-sectional study in Portugal. Clin. Ther. 2015, 37, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auta, A.; Hadi, M.A.; Oga, E.; Adewuyi, E.O.; Abdu-Aguye, S.N.; Adeloye, D.; Strickland-Hodge, B.; Morgan, D.J. Global access to antibiotics without prescription in community pharmacies: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Infect. 2019, 78, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, U.; Duerink, D.O.; Lestari, E.S.; Nagelkerke, N.J.; Werter, S.; Keuter, M.; Suwandojo, E.; Rahardjo, E.; van den Broek, P.; Gyssens, I.C. Survey of antibiotic use of individuals visiting public healthcare facilities in Indonesia. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 12, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Väänänen, M.H.; Pietilä, K.; Airaksinen, M. Self-medication with antibiotics—Does it really happen in Europe? Health Policy 2006, 77, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsi, G.; Jelastopulu, E.; Basiaris, H.; Skoutelis, A.; Gogos, C. Patterns of antibiotic use among adults and parents in the community: A questionnaire-based survey in a Greek urban population. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2005, 25, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, M.A.; Scicluna, E.A. Over-the-counter acquisition of antibiotics in the Maltese general population. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2002, 20, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco-Garrido, P.; Jiménez-García, R.; Barrera, V.H.; Gil de Miguel, A. Predictive factors of self-medicated drug use among the Spanish adult population. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2008, 17, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigoryan, L.; Haaijer-Ruskamp, F.M.; Burgerhof, J.G.; Mechtler, R.; Deschepper, R.; Tambic-Andrasevic, A.; Andrajati, R.; Monnet, D.L.; Cunney, R.; Di Matteo, A.; et al. Self-medication with antimicrobial drugs in Europe. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cars, O.; Nordberg, P. Antibiotic resistance–The faceless threat. Int. J. Risk Saf. Med. 2005, 17, 103–110. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, J.; Ferech, M.; Lazaro, E.; de Abajo, F.; Oteo, J.; Stephens, P.; Goossens, H. Surveillance of outpatient antibiotic consumption in Spain according to sales data and reimbursement data. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 60, 698–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Morgan, D.J.; Okeke, I.N.; Laxminarayan, R.; Perencevich, E.N.; Weisenberg, S. Non-prescription antimicrobial use worldwide: A systematic review. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2011, 11, 692–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Pharmaceutical Federation (FIP). Fighting Antimicrobial Resistance: The Contribution of Pharmacists; International Pharmaceutical Feder- Ation: The Hague, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Erku, D.A.; Mekuria, A.B.; Surur, A.S.; Gebresillassie, B.M. Extent of dispensing prescription-only medications without a prescription in community drug retail outlets in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: A simulated-patient study. Drug Healthc. Patient Saf. 2016, 8, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Critically Important Antimicrobials for Human Medicine: Ranking of Antimicrobial Agents for Risk Management of Antimicrobial Resistance Due to Non-human Use; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Goel, P.; Ross-Degnan, D.; Berman, P.; Soumerai, S. Retail pharmacies in developing countries: A behavior and intervention framework. Soc. Sci. Med. 1996, 42, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwena, Z.; Sharma, A.; Wamae, N.; Muga, C.; Bukusi, E. Provider characteristics among staff providing care to sexually transmitted infection self-medicating patients in retail pharmacies in Kibera slum, Nairobi, Kenya. Sex. Transm. Dis. 2008, 35, 480–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santa-Ana-Tellez, Y.; Mantel-Teeuwisse, A.K.; Dreser, A.; Leufkens, H.G.; Wirtz, V.J. Impact of over-the-counter restrictions on antibiotic consumption in Brazil and Mexico. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavestrello, L.; Cabello, A.; Casanova, D. Impact of regulatory measures in the trends of community consumption of antibiotics in Chile. Rev. Med. Chile 2002, 130, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Soumerai, S.B.; Adams, A.S.; Finkelstein, J.A.; Jang, S.; Ross-Degnan, D. Antibiotic use following a Korean national policy to prohibit medication dispensing by physicians. Health Policy Plan. 2005, 20, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, D.I.; Hughes, D. Antibiotic resistance and its cost: Is it possible to reverse resistance? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, S.W.; Gautier, P. Use of antimicrobial agents in livestock. Rev. Sci. T63echnique-OIE 2012, 31, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mather, A.E.; Matthews, L.; Mellor, D.J.; Reeve, R.; Denwood, M.J.; Boerlin, P.; Reid-Smith, R.J.; Brown, D.J.; Coia, J.E.; Browning, L.M.; et al. An ecological approach to assessing the epidemiology of antimicrobial resistance in animal and human populations. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2011, 279, 1630–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steven, S.; Jim, F.; Rob, M.; Jane, P.; René, R.; Marco, V.; Melissa, M.; Megan, B.; Colleen, M.; Gabriela, G. Antimicrobial Stewardship in Food Animals in Canada: Progress on Recommendations and Stakeholder Activities; National Farmed Animal Health and Welfare Council (NRAHWC): Bluevale, ON, Canada, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC); European Food Safety Authority (EFSA); European Medicines Agency (EMA). ECDC/EFSA/EMA second joint report on the integrated analysis of the consumption of antimicrobial agents and occurrence of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria from humans and food-producing animals: Joint Interagency Antimicrobial Consumption and Resistance Analysis (JIACRA) Report. EFSA J. 2017, 15, e04872. [Google Scholar]
- Lazarus, B.; Paterson, D.L.; Mollinger, J.L.; Rogers, B.A. Do human extraintestinal Escherichia coli infections resistant to expanded-spectrum cephalosporins originate from food-producing animals? A systematic review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 60, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, B.A.; Mateus, A.L.; Marshall, L.; Pfeiffer, D.U.; Lubroth, J.; Ormel, H.J.; Otto, P.; Patriarchi, A. Drivers, Dynamics and Epidemiology of Antimicrobial Resistance in Animal Production; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Molechan, C.; Amoako, D.G.; Abia, A.L.; Somboro, A.M.; Bester, L.A.; Essack, S.Y. Molecular epidemiology of antibiotic-resistant Enterococcus spp. from the farm-to-fork continuum in intensive poultry production in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 692, 868–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoako, D.G.; Somboro, A.M.; Abia, A.L.; Molechan, C.; Perrett, K.; Bester, L.A.; Essack, S.Y. Antibiotic Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus from Poultry and Poultry Products in uMgungundlovu District, South Africa, Using the “Farm to Fork” Approach. Microb. Drug Resist. 2020, 26, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Founou, L.L.; Founou, R.C.; Essack, S.Y.; Djoko, C.F. Mannitol-fermenting methicillin-resistant staphylococci (MRS) in pig abattoirs in Cameroon and South Africa: A serious food safety threat. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 285, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faife, S.L.; Zimba, T.; Sekyere, J.O.; Govinden, U.; Chenia, H.Y.; Simonsen, G.S.; Sundsfjord, A.; Essack, S.Y. β-lactam and fluoroquinolone resistance in Enterobacteriaceae from imported and locally-produced chicken in Mozambique. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2020, 14, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skov, R.L.; Monnet, D.L. Plasmid-mediated colistin resistance (mcr-1 gene): Three months later, the story unfolds. Eurosurveillance 2016, 21, 30155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kariuki, S.; Onsare, R.; Mwituria, J.; Ng’etich, R.; Nafula, C.; Karimi, K.; Karimi, P.; Njeruh, F.; Irungu, P.; Mitema, E. Improving Food Safety in Meat Value Chains in Kenya. Food Protection Trends; FAO/WHO Project Report: Córdoba, Argentina, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kimera, Z.I.; Mshana, S.E.; Rweyemamu, M.M.; Mboera, L.E.; Matee, M.I. Antimicrobial use and resistance in food-producing animals and the environment: An African perspective. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2020, 9, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, B.M.; Levy, S.B. Food animals and antimicrobials: Impacts on human health. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 24, 718–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padungtod, P.; Kaneene, J.B.; Hanson, R.; Morita, Y.; Boonmar, S. Antimicrobial resistance in Campylobacter isolated from food animals and humans in northern Thailand. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 47, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aarestrup, F.M. The origin, evolution, and local and global dissemination of antimicrobial resistance. In Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacteria of Animal Origin; American Society of Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; pp. 339–360. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Statistics Fisheries and Aquaculture Statistics Statistiques Des Pêches; FAO: Santiago, Chile, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Report of a Joint FAO/OIE/WHO Expert Consultation on Antimicrobial Use in Aquaculture and Antimicrobial Resistance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, S.Q.; Colquhoun, D.J.; Nikuli, H.L.; Sørum, H. Prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes in the bacterial flora of integrated fish farming environments of Pakistan and Tanzania. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 8672–8679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, C.D.; Tello, A.; Keen, P.L. Mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance in finfish aquaculture environments. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabello, F.C.; Godfrey, H.P.; Tomova, A.; Ivanova, L.; Dölz, H.; Millanao, A.; Buschmann, A.H. Antimicrobial use in aquaculture re-examined: Its relevance to antimicrobial resistance and to animal and human health. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 1917–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, T.J.; Evenhuis, J.; White, D.G.; McDermott, P.F.; Harbottle, H.; Miller, R.A.; Griffin, M.; Wise, D. IncA/C plasmid-mediated florfenicol resistance in the catfish pathogen Edwardsiella ictaluri. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 845–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Diana, A.; Julian, D.; Sumanth, G.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Joakim, L.; Jean, M.; Andrew, S.; Jason, S.; Herman, S.; Andrew, S.; et al. Initiatives for Addressing Antimicrobial Resistance in the Environment: Current Situation and Challenges; Wellcome Trust: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- You, Y.; Silbergeld, E.K. Learning from agriculture: Understanding low-dose antimicrobials as drivers of resistome expansion. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 284. [Google Scholar]
- Aminov, R.I.; Mackie, R.I. Evolution and ecology of antibiotic resistance genes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2007, 271, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SCENIHR. Scientific Comitee on Emerging and Newly Identified Health Risks, Health Effects of Exposure to EMF; SCENIHR: Brussels, Belgium, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, S.B.; Marshall, B. Antibacterial resistance worldwide: Causes, challenges and responses. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, S122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davin-Regli, A.; Pagès, J.M. Cross-resistance between biocides and antimicrobials: An emerging question. Rev. Sci. Tech. OIE 2012, 31, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barancheshme, F.; Munir, M. Strategies to combat antibiotic resistance in the wastewater treatment plants. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruden, A.; Larsson, D.J.; Amézquita, A.; Collignon, P.; Brandt, K.K.; Graham, D.W.; Lazorchak, J.M.; Suzuki, S.; Silley, P.; Snape, J.R.; et al. Management options for reducing the release of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes to the environment. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 878–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, D.J. Pollution from drug manufacturing: Review and perspectives. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Mozaz, S.; Chamorro, S.; Marti, E.; Huerta, B.; Gros, M.; Sànchez-Melsió, A.; Borrego, C.M.; Barceló, D.; Balcázar, J.L. Occurrence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in hospital and urban wastewaters and their impact on the receiving river. Water Res. 2015, 69, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aidara-Kane, A.; Angulo, F.J.; Conly, J.M.; Minato, Y.; Silbergeld, E.K.; McEwen, S.A.; Collignon, P.J. World Health Organization (WHO) guidelines on use of medically important antimicrobials in food-producing animals. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2018, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Ten Threats to Global Health in 2019; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; Retrieved January. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. The Tripartite’s Commitment Providing Multi-sectoral Collaborative Leadership in Addressing Health Challenges; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. At UN Global Leaders Commit to Act on Antimicrobial Resistance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mendelson, M.; Matsoso, M.P. The World Health Organization global action plan for antimicrobial resistance. SAMJ South Afr. Med. J. 2015, 105, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. People, Pathogens and Our Planet: The Economics of One Health; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. WHO Report on Surveillance of Antibiotic Consumption: 2016–2018 Early Implementation; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Global Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. WHO Global Strategy for Containment of Antimicrobial Resistance (No. WHO/CDS/CSR/DRS/2001.2); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Courtenay, M.; Castro-Sanchez, E.; Fitzpatrick, M.; Gallagher, R.; Lim, R.; Morris, G. Tackling antimicrobial resistance 2019–2024–The UK’s five-year national action plan. J. Hosp. Infect. 2019, 101, 426–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). The FAO action plan on antimicrobial resistance 2016–2020; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- World Organization for Animal Health. The OIE Strategy on Antimicrobial Resistance and the Prudent Use of Antimicrobials; World Organization for Animal Health: Paris, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Iskandar, K.; Sartelli, M.; Tabbal, M.; Ansaloni, L.; Baiocchi, G.L.; Catena, F.; Coccolini, F.; Haque, M.; Labricciosa, F.M.; Moghabghab, A.; et al. Highlighting the gaps in quantifying the economic burden of surgical site infections associated with antimicrobial-resistant bacteria. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2019, 14, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, O.A.; Hasan, R.; Schlundt, J.; Harbarth, S.; Caleo, G.; Dar, F.K.; Littmann, J.; Rweyemamu, M.; Buckley, E.J.; Shahid, M.; et al. Exploring the evidence base for national and regional policy interventions to combat resistance. Lancet 2016, 387, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opintan, J.A.; Newman, M.J.; Arhin, R.E.; Donkor, E.S.; Gyansa-Lutterodt, M.; Mills-Pappoe, W. Laboratory-based nationwide surveillance of antimicrobial resistance in Ghana. Infect. Drug Resist. 2015, 8, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colson, A.; Cohen, M.A.; Regmi, S.; Nandi, A.; Laxminarayan, R.; Macauley, M.K. Structured Expert Judgment for Informing the Return on Investment in Surveillance: The Case of Environmental Public Health Tracking. In Vanderbilt Owen Graduate School of Management Research Paper; SSRN: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; p. 2704189. [Google Scholar]
- Coulter, S.; Merollini, K.; Roberts, J.A.; Graves, N.; Halton, K. The need for cost-effectiveness analyses of antimicrobial stewardship programmes: A structured review. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2015, 46, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathwani, D.; Varghese, D.; Stephens, J.; Ansari, W.; Martin, S.; Charbonneau, C. Value of hospital antimicrobial stewardship programs [ASPs]: A systematic review. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2019, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Core Elements of Hospital Antibiotic Stewardship Programs; US Department of Health and Human Services, CDC: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2014.
- Ramsamy, Y.; Hardcastle, T.C.; Muckart, D.J. Surviving sepsis in the intensive care unit: The challenge of antimicrobial resistance and the trauma patient. World J. Surg. 2017, 41, 1165–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brink, A.J.; Messina, A.P.; Feldman, C.; Richards, G.A.; Becker, P.J.; Goff, D.A.; Bauer, K.A.; Nathwani, D.; Van den Bergh, D.; Alliance, N.A. Antimicrobial stewardship across 47 South African hospitals: An implementation study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brink, A.J.; Messina, A.P.; Feldman, C.; Richards, G.A.; van den Bergh, D. Netcare Antimicrobial Stewardship Study Alliance. From guidelines to practice: A pharmacist-driven prospective audit and feedback improvement model for peri-operative antibiotic prophylaxis in 34 South African hospitals. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ramsamy, Y.; Muckart, D.J.; Bruce, J.L.; Hardcastle, T.C.; Han, K.S.; Mlisana, K.P. Empirical antimicrobial therapy for probable v. directed therapy for possible ventilator-associated pneumonia in critically injured patients. S. Afr. Med. J. 2016, 106, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsamy, Y.; Muckart, D.J.; Han, K.S. Microbiological surveillance and antimicrobial stewardship minimise the need for ultrabroad-spectrum combination therapy for treatment of nosocomial infections in a trauma intensive care unit: An audit of an evidence-based empiric antimicrobial policy. S. Afr. Med. J. 2013, 103, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleaveland, S.; Sharp, J.; Abela-Ridder, B.; Allan, K.J.; Buza, J.; Crump, J.A.; Davis, A.; Del Rio Vilas, V.J.; De Glanville, W.A.; Kazwala, R.R.; et al. One Health contributions towards more effective and equitable approaches to health in low-and middle-income countries. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 372, 20160168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Shefer, A.; Wenger, J.; Messonnier, M.; Wang, L.Y.; Lopez, A.; Moore, M.; Murphy, T.V.; Cortese, M.; Rodewald, L. Economic evaluation of the routine childhood immunization program in the United States, 2009. Pediatrics 2014, 133, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frontieres, M.S. The Right Shot: Bringing Down Barriers to Affordable and Adapted Vaccines; Medecins Sans Frontieres: Paris, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sahoo, A. Vaccines 2011: Market Analysis, Key Players and Critical Trends in a Fast-Changing Industry; Kalorama Information: Rockville, MD, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hampton, L.M.; Farley, M.M.; Schaffner, W.; Thomas, A.; Reingold, A.; Harrison, L.H.; Lynfield, R.; Bennett, N.M.; Petit, S.; Gershman, K.; et al. Prevention of antibiotic-nonsusceptible Streptoco. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 203, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laxminarayan, R.; Matsoso, P.; Pant, S.; Brower, C.; Røttingen, J.A.; Klugman, K.; Davies, S. Access to effective antimicrobials: A worldwide challenge. Lancet 2016, 387, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommerset, I.; Krossøy, B.; Biering, E.; Frost, P. Vaccines for fish in aquaculture. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2005, 4, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAdams, D.; Waldetoft, K.W.; Tedijanto, C.; Lipsitch, M.; Brown, S.P. Resistance diagnostics as a public health tool to combat antibiotic resistance: A model-based evaluation. PLoS Biol. 2019, 17, e3000250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramasawmy, D.; Pillay, M.; Hardcastle, T.C. Correlation of procalcitonin to positive blood culture results in a sample of South African trauma ICU patients between 2016 and 2017. Eur. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2020, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmah, A.K.; Meyer, M.T.; Boxall, A.B. A global perspective on the use, sales, exposure pathways, occurrence, fate and effects of veterinary antibiotics (VAs) in the environment. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 725–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Counterfeit antibiotics |
| Availability of antibiotics over-the-counter |
| Limited public awareness and knowledge about antibiotics and antibiotic resistance |
| Strong belief that adding antibiotics to animals feed and drinks is part of raising healthy animal |
| Lack of food safety measures and controls |
| Lack or inadequate food safety regulations |
| Unmonitored food supply chain |
| Added antibiotics directly to dairy products in order to extend their shelf life |
| Inappropriate amount of antibiotics used to grow livestock, poultry and aquatic animals |
| Need to intensify food-animal and aquaculture production to meet the populations accelerated growth demands |
| Increase demand on meat due to urbanization, high-protein diet |
| Overcrowding |
| Household sharing habitat with poultry and livestock |
| Shared surface waters by humans and animals |
| Poverty and related economic and political drivers |
| Poor sanitation and hygiene |
| Poor farming hygiene |
| Veterinary vaccines are unavailable to farmers (either due to poverty and/or ignorance) |
| Eating behaviors and preferences (i.e. raw or undercooked meat) |
| Absence of farm biosecurity and frameworks for training farmers |
| High levels of environmental contamination with antibiotic residues, heavy metals and biocides |
| Behaviors relating to the slaughter and processing of food-animals (e.g. modalities of animal waste disposal, uses as animals feed) |
| Irrigation with untreated wastewater due to water shortage and poverty |
| Untreated animal waste is used for a variety of purposes including their use as fertilizers |
| Poultry waste is commonly used for feeding of fish and shellfish in aquaculture |
| Untreated wastewater originating from pharmaceutical industries, hospitals markets, manure and sewage runoffs |
| Animal waste is often discarded on open land and then after consumed by domestic and wildlife animals |
| Liquid waste from markets, including blood, feces and wastewater is disposed into municipal drains through direct wash out |
| Surveillance systems of antibiotic consumption and epidemiology of ABR are emerging trends |
| The epidemiology of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in animals are poorly documented |
| Lack or scarce evidence-base data on the magnitude and economic burden of AMR in humans |
| The need for strong laboratory capacity |
| Lack the financial capacity for establishing an adequate surveillance program |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iskandar, K.; Molinier, L.; Hallit, S.; Sartelli, M.; Catena, F.; Coccolini, F.; Craig Hardcastle, T.; Roques, C.; Salameh, P. Drivers of Antibiotic Resistance Transmission in Low- and Middle-Income Countries from a “One Health” Perspective—A Review. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9070372
Iskandar K, Molinier L, Hallit S, Sartelli M, Catena F, Coccolini F, Craig Hardcastle T, Roques C, Salameh P. Drivers of Antibiotic Resistance Transmission in Low- and Middle-Income Countries from a “One Health” Perspective—A Review. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(7):372. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9070372
Chicago/Turabian StyleIskandar, Katia, Laurent Molinier, Souheil Hallit, Massimo Sartelli, Fausto Catena, Federico Coccolini, Timothy Craig Hardcastle, Christine Roques, and Pascale Salameh. 2020. "Drivers of Antibiotic Resistance Transmission in Low- and Middle-Income Countries from a “One Health” Perspective—A Review" Antibiotics 9, no. 7: 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9070372
APA StyleIskandar, K., Molinier, L., Hallit, S., Sartelli, M., Catena, F., Coccolini, F., Craig Hardcastle, T., Roques, C., & Salameh, P. (2020). Drivers of Antibiotic Resistance Transmission in Low- and Middle-Income Countries from a “One Health” Perspective—A Review. Antibiotics, 9(7), 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9070372










