Antimicrobial Activity of Silver-Treated Bacteria against other Multi-Drug Resistant Pathogens in Their Environment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Bacteria
2.3. Determination of the Minimum Inhibitory Concentration of AgNO3
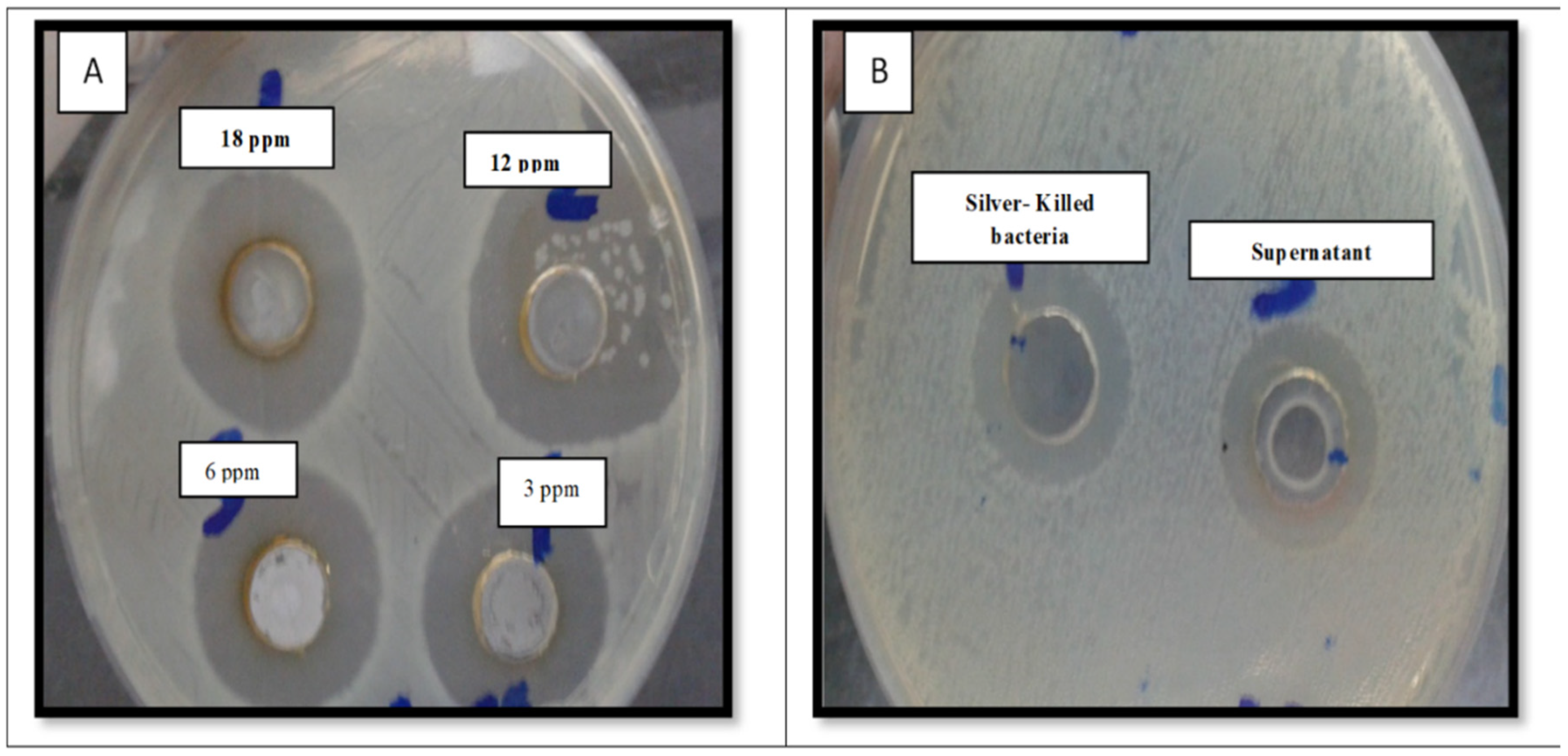
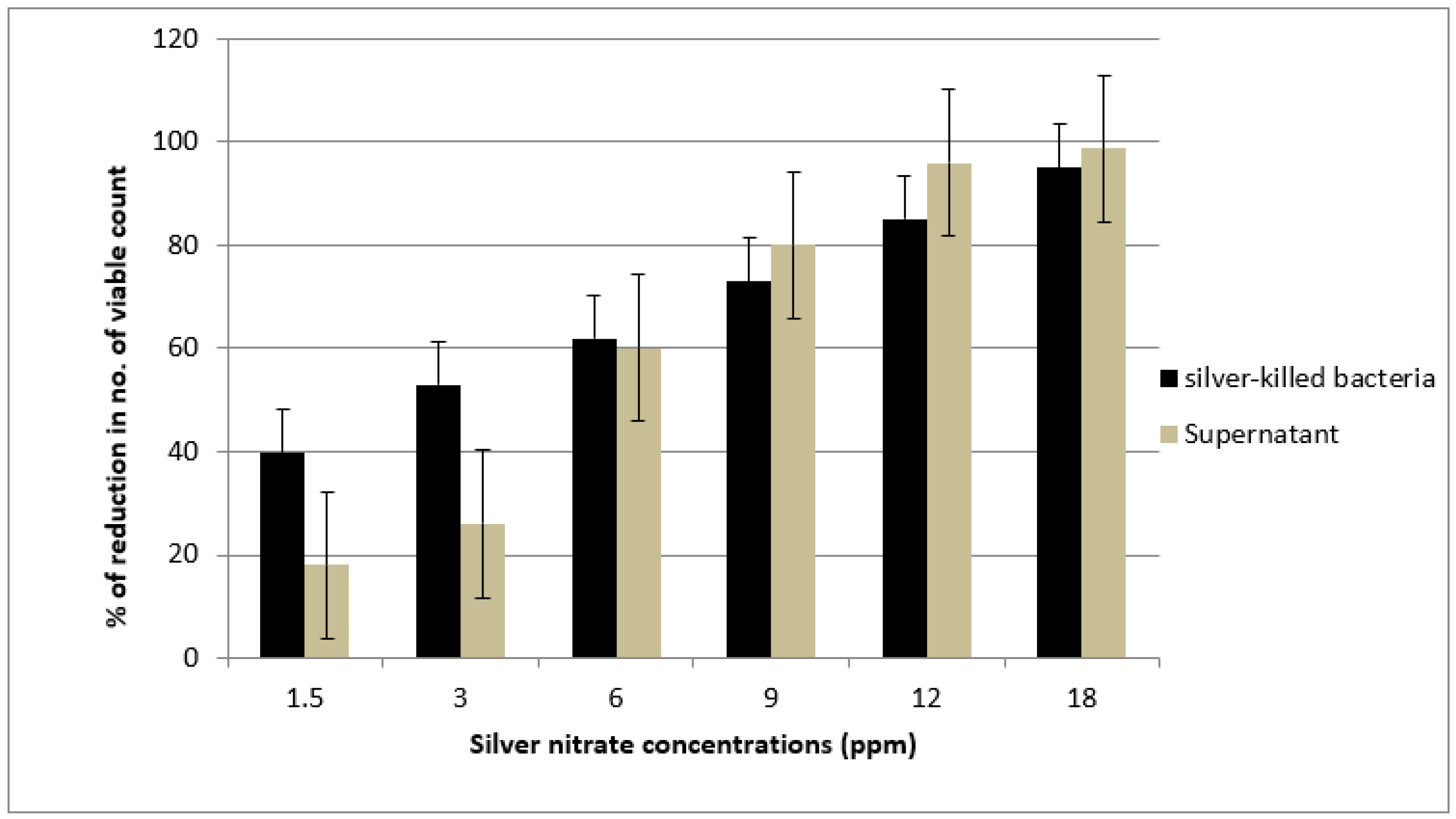
2.4. Evaluating the Antibacterial Effect of Silver-Killed Bacteria
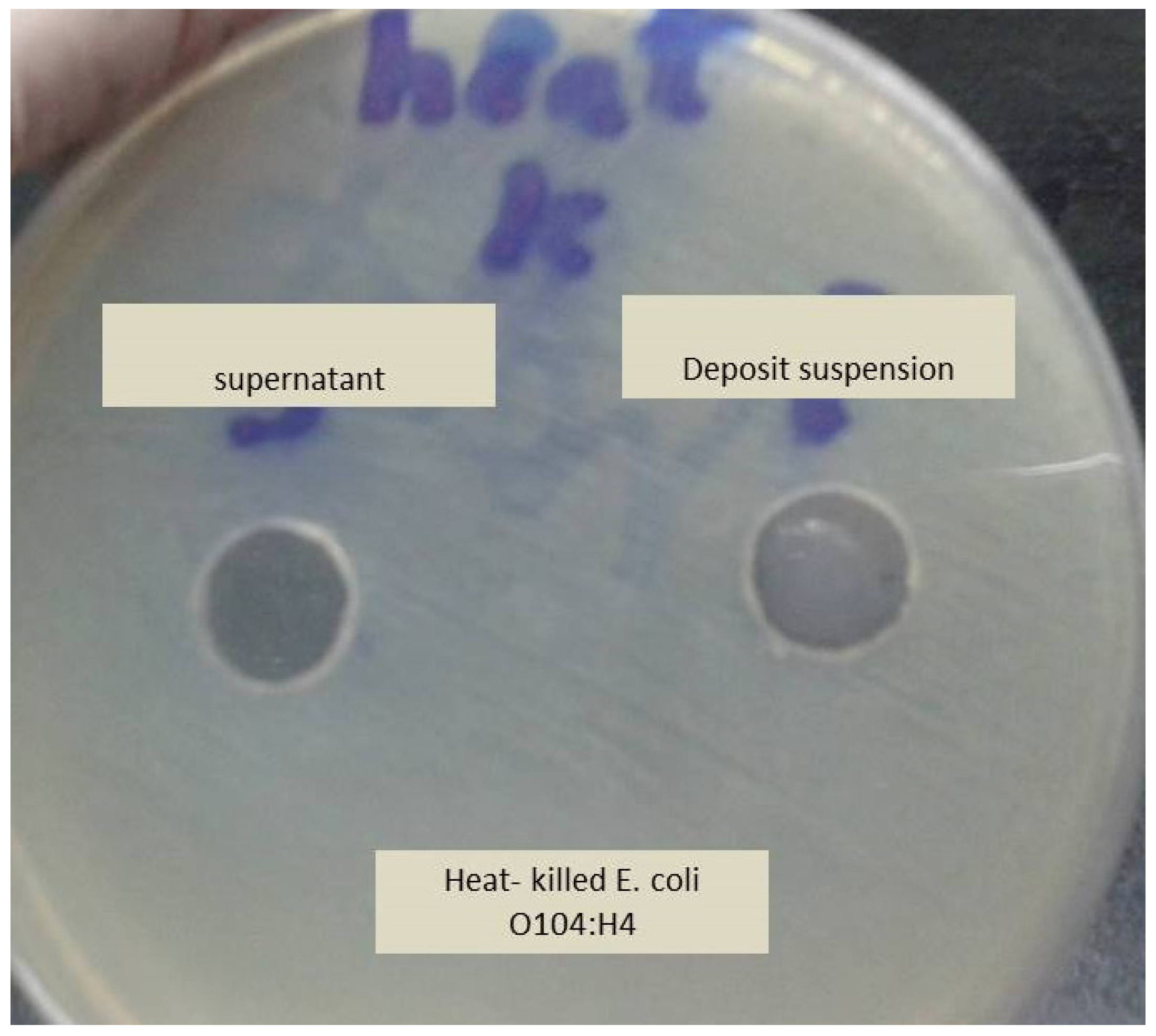
2.5. Heat-Treated Bacteria Control Test
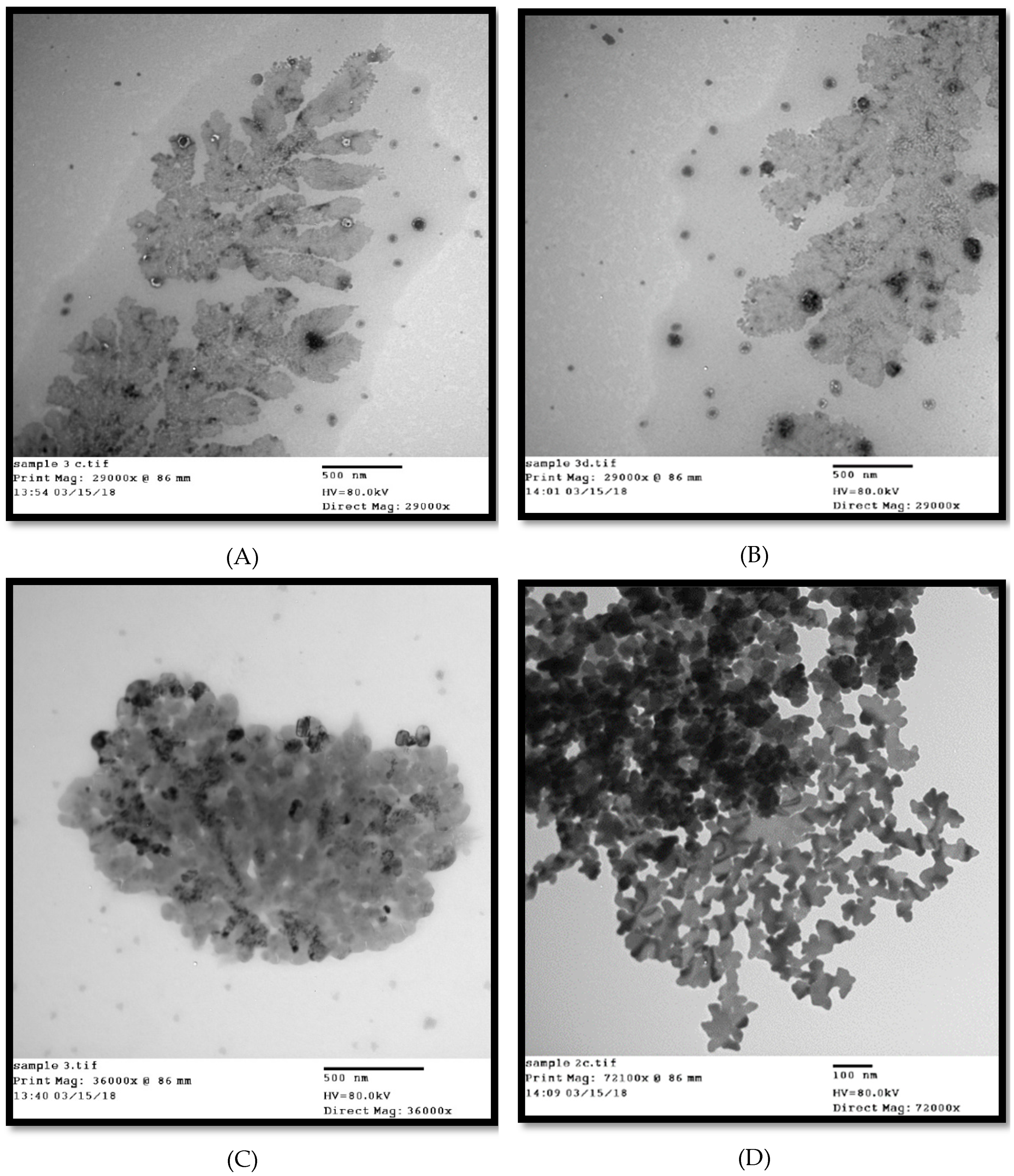
2.6. Transmission Electron Micrograph
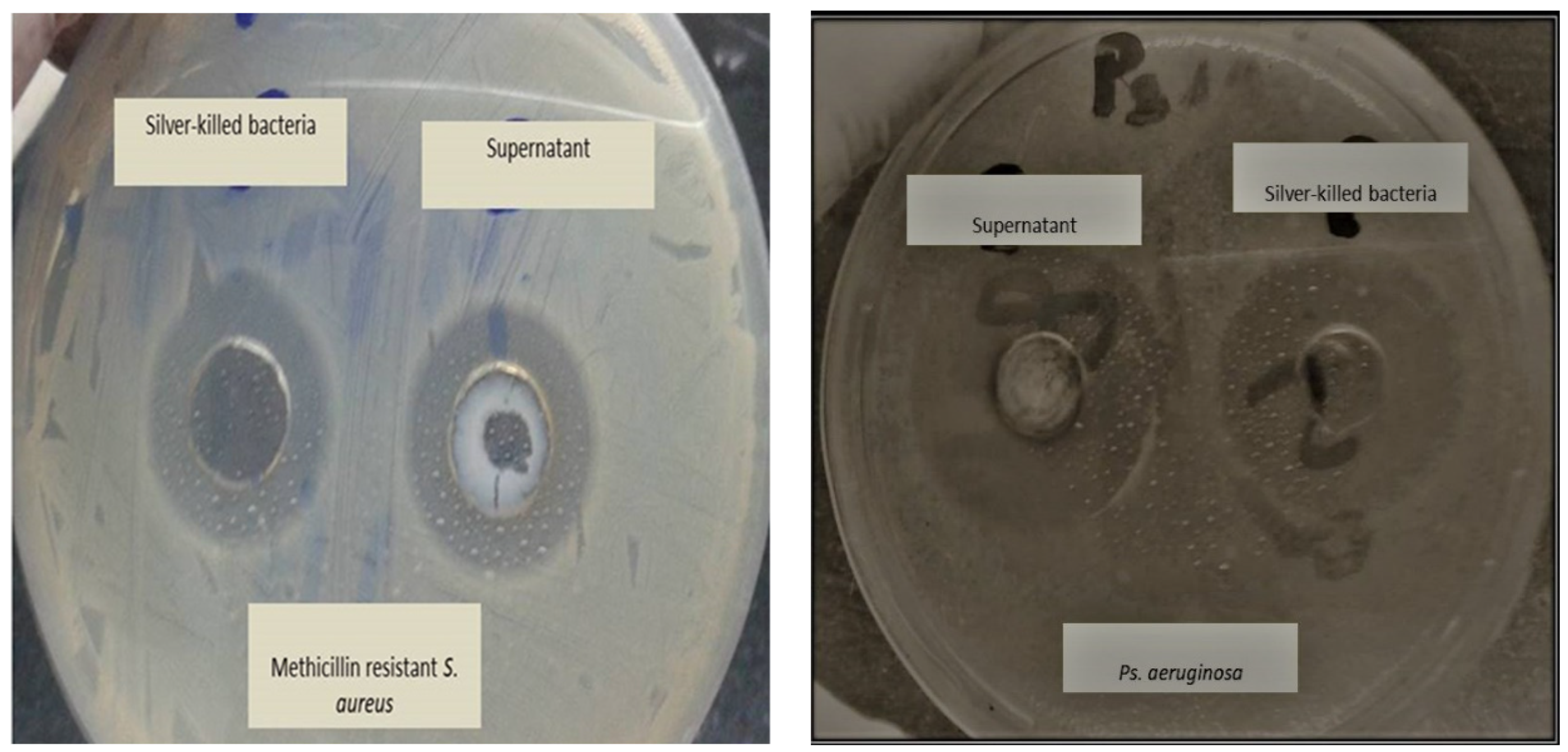
2.7. Testing Antibacterial Effect of Silver-Killed E.coli O104:H4 Against other Bacterial Species
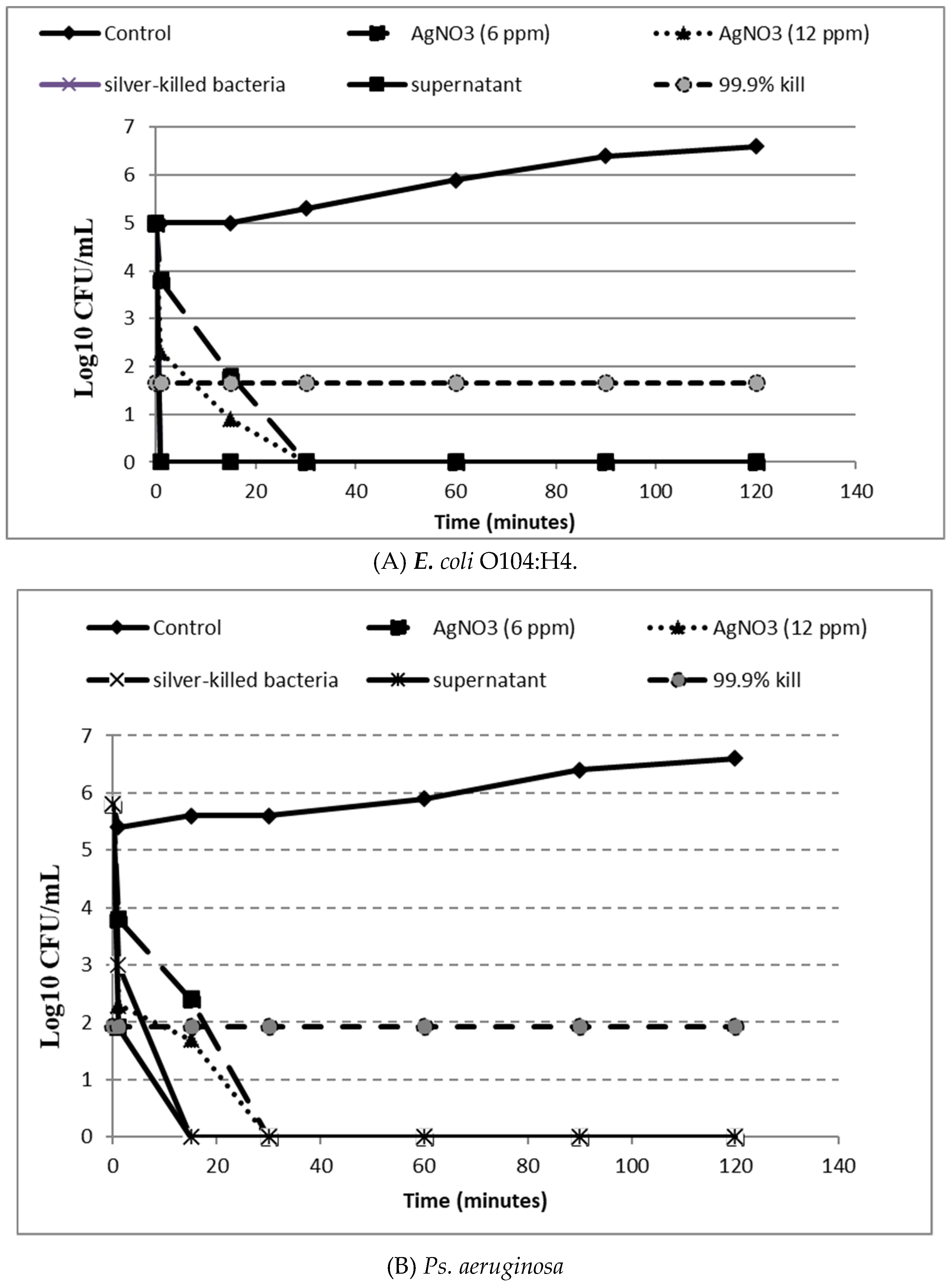
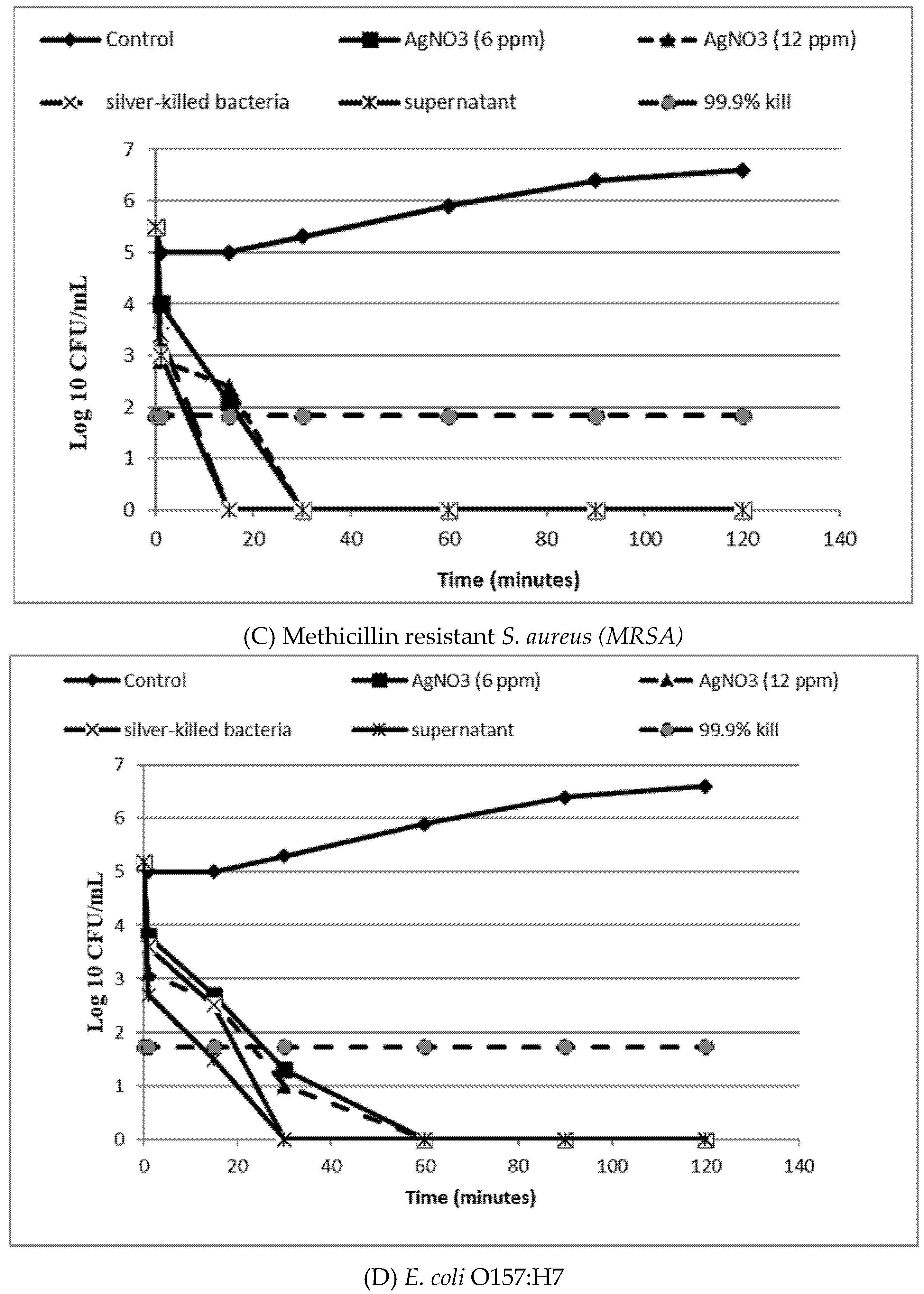
2.8. In-Vitro Time Kill Assay
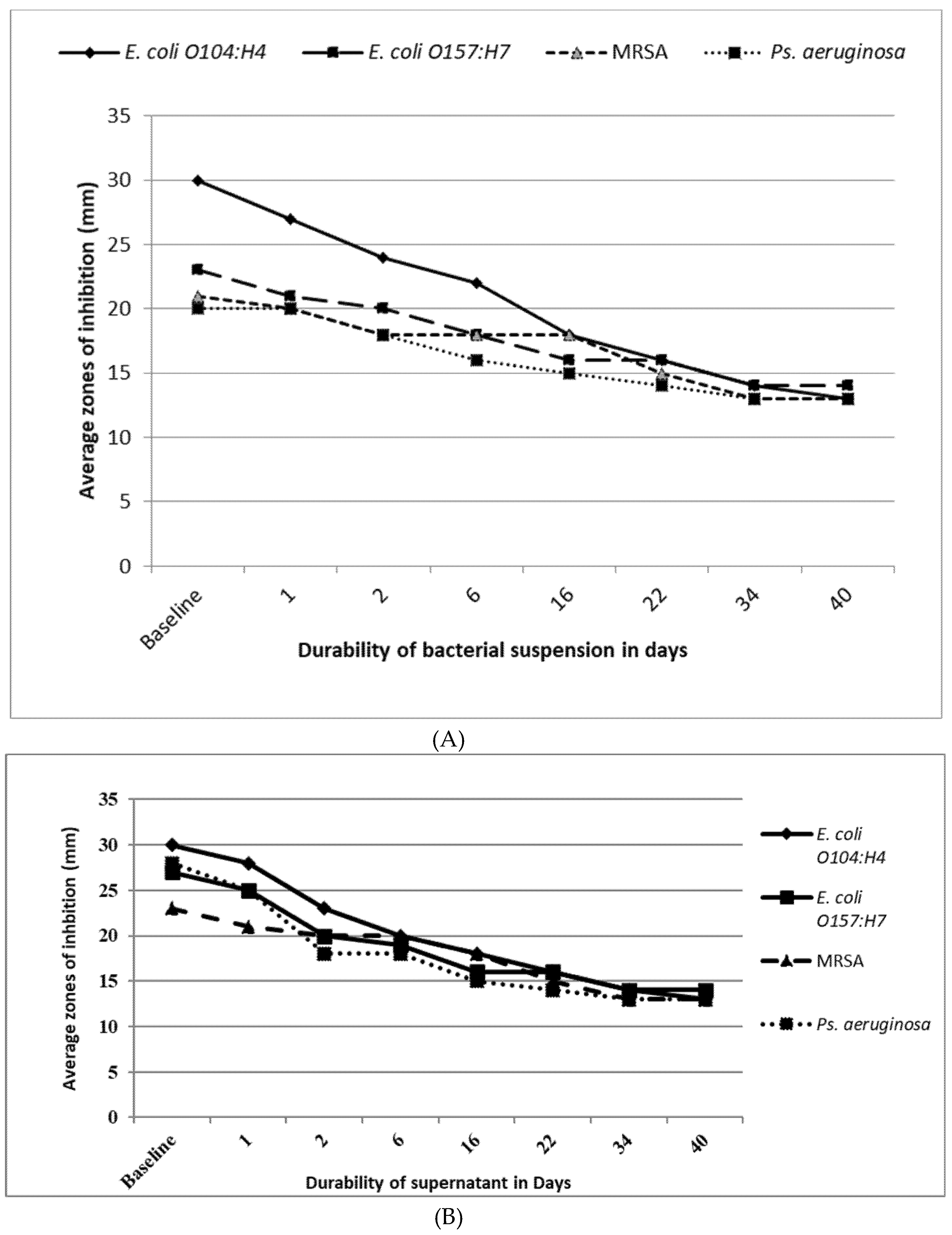
2.9. Antimicrobial Efficacy and Durability of Silver Killed Bacteria And Supernatant Against the Tested Strains
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Golkar, Z.; Bagasra, O.; Pace, D.G. Bacteriophage Therapy: A Potential Solution for the Antibiotic Resistance Crisis. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2014, 8, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morones, J.R.; Elechiguerra, J.L.; Camacho, A.; Holt, K.; Kouri, J.B.; Ramírez, J.T.; Yacaman, M.J. The Bactericidal Effect of Silver Nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventola, C.L. The Antibiotic Resistance Crisis: Part 1: Causes and Threats. Pharm. Ther. 2015, 40, 277. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, A.; Nelson, T.B.; Kierski, P.R.; Schurr, M.J.; Murphy, C.J.; Czuprynski, C.J.; McAnulty, J.F.; Abbott, N.L. Polymeric Multilayers That Localize the Release of Chlorhexidine from Biologic Wound Dressings. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 6783–6792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Nie, X.; Zou, M.; Shi, Y.; Cheng, G. Recent Advances in Materials for Extended-Release Antibiotic Delivery System. J. Antibiot. 2011, 64, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Knaz, R.; Pedahzur, R.; Avnir, D. Bioactive Doped Metals: High Synergism in the Bactericidal Activity of Chlorhexidine@ Silver Towards Wound Pathogenic Bacteria. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 8009–8015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritu, G.; Macri, L.K.; Kaplan, H.M.; Kohn, J. Nanoparticles and Nanofibers for Topical Drug Delivery. J. Control. Release 2016, 240, 77–92. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Sonshine, D.A.; Shervani, S.; Hurt, R.H. Controlled Release of Biologically Active Silver from Nanosilver Surfaces. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 6903–6913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.H.; Yeo, S.Y.; Yi, S.C. The Effect of Filler Particle Size on the Antibacterial Properties of Compounded Polymer/Silver Fibers. J. Mater. Sci. 2005, 40, 5407–5411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffi, M.; Hussain, F.; Bhatti, T.M.; Akhter, J.I.; Hameed, A.; Hasan, M.M. Antibacterial Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles against E. Coli Atcc-15224. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2008, 24, 192–196. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, P.L.; Ussher, A.L.; Burrell, R.E. Impact of Heat on Nanocrystalline Silver Dressings: Part I: Chemical and Biological Properties. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 7221–7229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jawal, S.; Dodoo, C.C.; Walker, M.; Parsons, D.; Stapleton, P.; Beezer, A.E.; Gaisford, S. An in Vitro Test of the Efficacy of Silver-Containing Wound Dressings against Staphylococcus Aureus and Pseudomonas Aeruginosa in Simulated Wound Fluid. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 462, 123–128. [Google Scholar]
- Panáček, A.; Kvitek, L.; Prucek, R.; Kolar, M.; Vecerova, R.; Pizurova, N.; Zboril, V.K.S.A.T.N.R. Silver Colloid Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Their Antibacterial Activity. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 16248–16253. [Google Scholar]
- Volker, A.; Bechert, T.; Steinrücke, P.; Wagener, M.; Seidel, P.; Dingeldein, E.; Domann, E.; Schnettler, R. An in Vitro Assessment of the Antibacterial Properties and Cytotoxicity of Nanoparticulate Silver Bone Cement. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 4383–4391. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, J.W. History of the Medical Use of Silver. Surg. Infect. 2009, 10, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lansdown Alan, B.G. Silver in Health Care: Antimicrobial Effects and Safety in Use. In Biofunctional Textiles and the Skin; Karger Publishers: Basel, Switzerland, 2006; pp. 17–34. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, W.K.; Koo, H.C.; Kim, K.W.; Shin, S.; Kim, S.H.; Park, Y.H. Antibacterial Activity and Mechanism of Action of the Silver Ion in Staphylococcus Aureus and Escherichia Coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 2171–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, C.; Perez-Ballestero, R.; Luo, Z.; Bashir, S.; Liu, J. Comparison of Bactericidal Activities of Silver Nanoparticles with Common Chemical Disinfectants. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2011, 84, 88–96. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Mahendra, S.; Lyon, D.Y.; Brunet, L.; Liga, M.V.; Li, D.; Alvarez, P.J. Antimicrobial Nanomaterials for Water Disinfection and Microbial Control: Potential Applications and Implications. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4591–4602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, N.; Li, X.; Mehrabi, S.; Mintz, E.; Economy, J. Silver-Modified Iron Oxide Nanoparticle Impregnated Fiberglass for Disinfection of Bacteria and Viruses in Water. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 1191–1193. [Google Scholar]
- Tim, S. A Silver Lining? The Use of Antimicrobial Bandages. Arab. Med. Hyg. 2012, 6, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Morgane, B.; Gauthier, Y.; Lacroix, C.; Verrier, B.; Monge, C. Nanoparticle-Based Dressing: The Future of Wound Treatment? Trends Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 770–784. [Google Scholar]
- Rajeshkumar, S.; Malarkodi, C. In Vitro Antibacterial Activity and Mechanism of Silver Nanoparticles against Foodborne Pathogens. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2014, 2014, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, F.A.; Maia, K.R.; Mallman, E.J.; Cunha, M.D.; Maciel, A.A.; Souza, I.P.; Menezes, E.A.; Fechine, P.B. Silver Nanoparticles-Disk Diffusion Test against Escherichia Coli Isolates. Rev. do Inst. de Med. Trop. de São Paulo 2016, 58, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakshlak, R.B.; Pedahzur, R.; Avnir, D. Antibacterial Activity of Silver-Killed Bacteria: The Zombies Effect. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marycz, K.; Marędziak, M.; Lewandowski, D.; Zachanowicz, E.; Zięcina, A.; Wiglusz, R.J.; Pązik, R. The Effect of Co0. 2mn0. 8fe2o4 Ferrite Nanoparticles on the C2 Canine Mastocytoma Cell Line and Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Stem Cells (Ascs) Cultured under a Static Magnetic Field: Possible Implications in the Treatment of Dog Mastocytoma. Cell. Mol. Bioeng. 2017, 10, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudano Roccaro, A.; Blanco, A.R.; Giuliano, F.; Rusciano, D.; Enea, V. Epigallocatechin-Gallate Enhances the Activity of Tetracycline in Staphylococci by Inhibiting Its Efflux from Bacterial Cells. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 1968–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiban, G.; Hanna, H.; Dvorak, T.; Raad, I. A Rapid Method of Impregnating Endotracheal Tubes and Urinary Catheters with Gendine: A Novel Antiseptic Agent. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2005, 55, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandian, K.; Ram, S.; Deepak, V.; Kalishwaralal, K.; Viswanathan, P.; Gurunathan, S. Mechanism of Bactericidal Activity of Silver Nitrate – a Concentration Dependent Bi-Functional Molecule. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2010, 41, 805–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, O.; Hu, Z. Size Dependent and Reactive Oxygen Species Related Nanosilver Toxicity to Nitrifying Bacteria. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 4583–4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, C.; Hussain, S.M.; Schrand, A.M.; KBraydich-Stolle, L.; Hess, K.L.; Jones, R.L.; Schlager, J.J. Unique Cellular Interaction of Silver Nanoparticles: Size-Dependent Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 13608–13619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondi, I.; Salopek-Sondi, B. Silver Nanoparticles as Antimicrobial Agent: A Case Study on E. Coli as A model for Gram-Negative Bacteria. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 275, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosetti, M.; Massè, A.; Tobin, E.; Cannas, M. Silver Coated Materials for External Fixation Devices: In Vitro Biocompatibility and Genotoxicity. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.Y.; Perrett, S.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, Z.; Nie, G. Chirality of Glutathione Surface Coating Affects the Cytotoxicity of Quantum Dots. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 5860–5864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chernousova, S.; Epple, M. Silver as Antibacterial Agent: Ion, Nanoparticle, and Metal. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 1636–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yao, Y.; Sullivan, N.; Chen, Y. Modeling the Primary Size Effects of Citrate-Coated Silver Nanoparticles on Their Ion Release Kinetics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 4422–4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zook, J.M.; Long, S.E.; Cleveland, D.; Geronimo, C.L.; MacCuspie, R.I. Measuring Silver Nanoparticle Dissolution in Complex Biological and Environmental Matrices Using Uv–Visible Absorbance. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 401, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, Z.M.; Zhang, Q.B.; Puppala, H.L.; Colvin, V.L.; Alvarez, P.J. Negligible Particle-Specific Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 4271–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooti, M.; Sedeh, A.N.; Motamedi, H.; Rezatofighi, S.E. Magnetic Graphene Oxide Inlaid with Silver Nanoparticles as Antibacterial and Drug Delivery Composite. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 3607–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Ouay, B.; Stellacci, F. Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles: A Surface Science Insight. Nano Today 2015, 10, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, C.; Pradhan, A.; Pakstis, L.; Pochan, D.J.; Shah, S.I. Synthesis and Antibacterial Properties of Silver Nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2005, 5, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Dash, S.K.; Mandal, D.; Ghosh, T.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Tripathy, S.; Das, S.; Dey, S.K.; Das, D.; Roy, S. Green Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles Destroy Multidrug Resistant Bacteria Via Reactive Oxygen Species Mediated Membrane Damage. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, 862–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, M.; Hara, K.; Kudo, J. Bactericidal Actions of a Silver Ion Solution on Escherichia Coli, Studied by Energy-Filtering Transmission Electron Microscopy and Proteomic Analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 7589–7593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Tak, Y.K.; Song, J.M. Does the Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Depend on the Shape of the Nanoparticle? A Study of the Gram-Negative Bacterium Escherichia Coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1712–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, R.J.; Wen, J.; Gao, Y.; Li, T.Y.; Yan, H.; Wang, H.F.; Niu, B.L.; Jiang, K.Y. Effect of the Adhesion of Ag Coatings on the Effectiveness and Durability of Antibacterial Properties. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 4759–4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brett, D.W. A Discussion of Silver as an Antimicrobial Agent: Alleviating the Confusion. Ostomy/wound Manag. 2006, 52, 34–41. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Luo, G.; Wang, Y.; Xu, R.; Wang, Y.; He, W.; Tan, J.; Xing, M.; Wu, J. Nano-Silver-Decorated Microfibrous Eggshell Membrane: Processing, Cytotoxicity Assessment and Optimization, Antibacterial Activity and Wound Healing. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shobhit, G.; Kumar, N.; Tiwari, V.K. Silver Sulfadiazine Versus Sustained-Release Silver Dressings in the Treatment of Burns: A Surprising Result. Indian J. Burns 2017, 25, 38. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohamed, D.S.; Abd El-Baky, R.M.; Sandle, T.; Mandour, S.A.; Ahmed, E.F. Antimicrobial Activity of Silver-Treated Bacteria against other Multi-Drug Resistant Pathogens in Their Environment. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9040181
Mohamed DS, Abd El-Baky RM, Sandle T, Mandour SA, Ahmed EF. Antimicrobial Activity of Silver-Treated Bacteria against other Multi-Drug Resistant Pathogens in Their Environment. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(4):181. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9040181
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohamed, Doaa Safwat, Rehab Mahmoud Abd El-Baky, Tim Sandle, Sahar A. Mandour, and Eman Farouk Ahmed. 2020. "Antimicrobial Activity of Silver-Treated Bacteria against other Multi-Drug Resistant Pathogens in Their Environment" Antibiotics 9, no. 4: 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9040181
APA StyleMohamed, D. S., Abd El-Baky, R. M., Sandle, T., Mandour, S. A., & Ahmed, E. F. (2020). Antimicrobial Activity of Silver-Treated Bacteria against other Multi-Drug Resistant Pathogens in Their Environment. Antibiotics, 9(4), 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9040181





