Risk Factors for Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacterales Infection or Colonization in a Korean Intensive Care Unit: A Case–Control Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
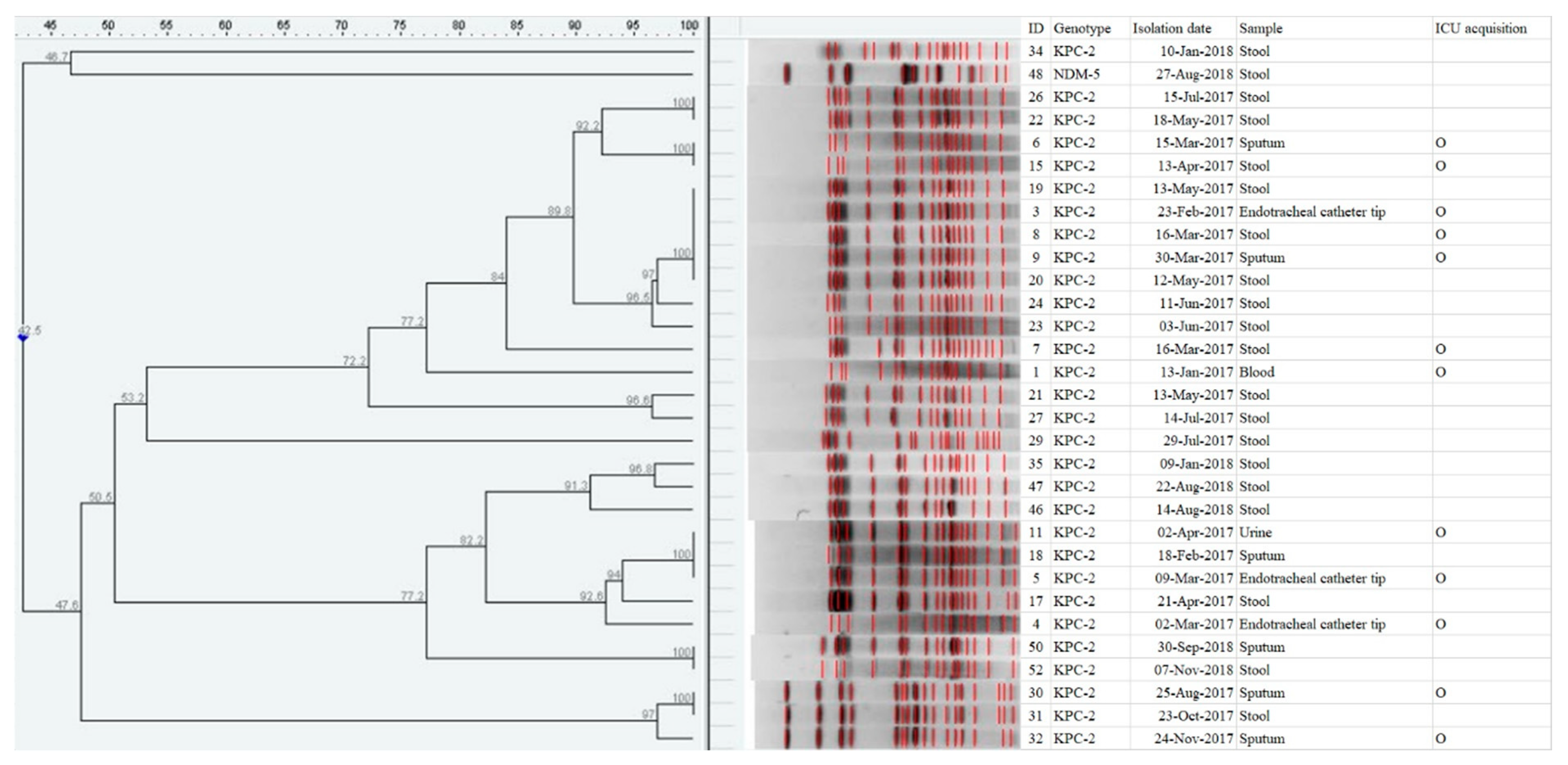
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Global Priority List of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria to Guide Research, Discovery, and Development of New Antibiotics. 2017. Available online: https://www.who.int/medicines/publications/global-priority-list-antibiotic-resistant-bacteria/en/ (accessed on 27 February 2017).
- Falagas, M.E.; Tansarli, G.S.; Karageorgopoulos, D.E.; Vardakas, K.Z. Deaths attributable to carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae infections. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaye, K.S.; Pogue, J.M. Infections caused by resistant gram-negative bacteria: Epidemiology and management. Pharmacotherapy 2015, 35, 949–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonomo, R.A.; Burd, E.M.; Conly, J.; Limbago, B.M.; Poirel, L.; Segre, J.A.; Westblade, L.F. Carbapenemase-producing organisms: A global scourge. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 66, 1290–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Duin, D.; Doi, Y. The global epidemiology of carbapenemase-producing enterobacteriaceae. Virulence 2017, 8, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otter, J.A.; Burgess, P.; Davies, F.; Mookerjee, S.; Singleton, J.; Gilchrist, M.; Parsons, D.; Brannigan, E.T.; Robotham, J.; Holmes, A.H. Counting the cost of an outbreak of carbapenemase-producing enterobacteriaceae: An economic evaluation from a hospital perspective. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 23, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.K.; Yong, D.; Kim, K.; Hong, S.S.; Hong, S.G.; Khosbayar, T.; Song, W.; Roh, K.H.; Jeong, S.H.; Lee, K. First outbreak of kpc-2-producing klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type 258 in a hospital in south korea. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 3877–3879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jeong, S.H.; Lee, K.M.; Lee, J.; Bae, I.K.; Kim, J.-S.; Kim, H.-S.; Song, W. Clonal and horizontal spread of the blaoxa-232 gene among enterobacteriaceae in a korean hospital. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 82, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-N.; Yong, D.; An, D.; Chung, H.-S.; Woo, J.H.; Lee, K.; Chong, Y. Nosocomial clustering of ndm-1-producing klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type 340 strains in four patients at a south korean tertiary care hospital. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 1433–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, E.; Lee, S.; Lee, H. Status of carbapenemase-producing enterobacteriaceae incidences in korea, 2015-2016. Public Health Wkly. Rep. 2017, 10, 1243–1247. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Yoon, E.J.; Kim, D.; Jeong, S.H.; Won, E.J.; Shin, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Shin, J.H.; Shin, K.S.; Kim, Y.A. Antimicrobial resistance of major clinical pathogens in south korea, may 2016 to april 2017: First one-year report from kor-glass. Euro Surveill 2018, 23, 1800047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-David, D.; Masarwa, S.; Navon-Venezia, S.; Mishali, H.; Fridental, I.; Rubinovitch, B.; Smollan, G.; Carmeli, Y.; Schwaber, M.J.; Israel, P. Carbapenem-resistant klebsiella pneumoniae in post-acute-care facilities in israel. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2011, 32, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swaminathan, M.; Sharma, S.; Blash, S.P.; Patel, G.; Banach, D.B.; Phillips, M.; LaBombardi, V.; Anderson, K.F.; Kitchel, B.; Srinivasan, A. Prevalence and risk factors for acquisition of carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae in the setting of endemicity. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2013, 34, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.C.; Xu, X.H.; Liu, M.B.; Wu, J.; Lin, J.; Li, B. Fecal carriage of carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae in a chinese university hospital. Am. J. Infect. Control 2014, 42, e61–e64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, N.; Asada, R.; Kawahara, R.; Hagiya, H.; Akeda, Y.; Shanmugakani, R.K.; Yoshida, H.; Yukawa, S.; Yamamoto, K.; Takayama, Y.; et al. Prevalence of, and risk factors for, carriage of carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae among hospitalized patients in japan. J. Hosp. Infect. 2017, 97, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, B.; Prasad, A.; Kaur, H.; Hallur, V.; Gautam, N.; Taneja, N. Fecal carriage of carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae and risk factor analysis in hospitalised patients: A single centre study from india. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2017, 35, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jeong, S.H.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, J.-S.; Shin, D.H.; Kim, H.S.; Park, M.-J.; Shin, S.; Hong, J.S.; Lee, S.S.; Song, W. Prevalence and molecular characteristics of carbapenemase-producing enterobacteriaceae from five hospitals in korea. Ann. Lab. Med. 2016, 36, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Loon, K.; Voor In ‘t Holt, A.F.; Vos, M.C. A systematic review and meta-analyses of the clinical epidemiology of carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e01730-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madueno, A.; Gonzalez Garcia, J.; Ramos, M.J.; Pedroso, Y.; Diaz, Z.; Oteo, J.; Lecuona, M. Risk factors associated with carbapenemase-producing klebsiella pneumoniae fecal carriage: A case-control study in a spanish tertiary care hospital. Am. J. Infect. Control 2017, 45, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas-Chanoine, M.H.; Vigan, M.; Laouenan, C.; Robert, J.; E-carb Study Group. Risk factors for carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae infections: A french case-control-control study. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 38, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiotos, K.; Tamma, P.D.; Flett, K.B.; Naumann, M.; Karandikar, M.V.; Bilker, W.B.; Zaoutis, T.; Han, J.H. Multicenter study of the risk factors for colonization or infection with carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae in children. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e01440-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasink, L.B.; Edelstein, P.H.; Lautenbach, E.; Synnestvedt, M.; Fishman, N.O. Risk factors and clinical impact of klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase-producing k. Pneumoniae. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2009, 30, 1180–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.Y.; Song, J.E.; Kim, M.H.; Choi, H.; Kim, J.K.; Ann, H.W.; Kim, J.H.; Jeon, Y.; Jeong, S.J.; Kim, S.B. Risk factors for the acquisition of carbapenem-resistant escherichia coli at a tertiary care center in south korea: A matched case-control study. Am. J. Infect. Control 2014, 42, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thom, K.A.; Hsiao, W.W.; Harris, A.D.; Stine, O.C.; Rasko, D.A.; Johnson, J.K. Patients with acinetobacter baumannii bloodstream infections are colonized in the gastrointestinal tract with identical strains. Am. J. Infect. Control 2010, 38, 751–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horan, T.C.; Andrus, M.; Dudeck, M.A. Cdc/nhsn surveillance definition of health care-associated infection and criteria for specific types of infections in the acute care setting. Am. J. Infect. Control 2008, 36, 309–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 26th ed.; Clsi m100s. CLSI, Ed.: Wayne, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nordmann, P.; Naas, T.; Poirel, L. Global spread of carbapenemase-producing enterobacteriaceae. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.S.; Bae, I.K.; Kim, J.; Jeong, S.H.; Hwang, S.-s.; Seo, Y.-H.; Cho, Y.K.; Lee, K.; Kim, J.M. Risk factors and molecular epidemiology of community-onset extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing escherichia coli bacteremia. Yonsei Med. J. 2014, 55, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Infection (N = 13) | Colonization (N = 32) | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 78 (71–85) | 73 (61–83) | 0.15 |
| Male | 8 (62) | 25 (78) | 0.285 |
| Previous admission to long-term care facility | 8 (62) | 9 (28) | 0.048 |
| Associated disease | |||
| End-stage renal disease | 4 (31) | 4 (13) | 0.202 |
| Gastrointestinal disease | 2 (15) | 6 (19) | 1 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 3 (23) | 5 (16) | 0.672 |
| Localized infection | 2 (15) | 4 (13) | 1 |
| Pneumonia/chronic pulmonary disease | 10 (77) | 21 (66) | 0.724 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 3 (23) | 5 (16) | 0.672 |
| Cardiovascular disease | 2 (15) | 3 (9) | 0.617 |
| Malignancy | 3 (23) | 1 (3) | 0.066 |
| Sepsis | 3 (23) | 7 (22) | 1 |
| Charlson comorbidity index | 6 (6–8) | 5 (4–6) | 0.019 |
| Previous usage of antibiotics within 90 days | |||
| Penicillin | 9 (69) | 18 (56) | 0.514 |
| Fluoroquinolone | 8 (62) | 17 (53) | 0.745 |
| Carbapenem | 7 (54) | 12 (38) | 0.341 |
| 1st generation cephalosporin | 0 | 1 (3) | |
| 2nd generation cephalosporin | 0 | 2 (6) | |
| Expanded-spectrum cephalosporin | 4 (31) | 9 (28) | 1 |
| Glycopeptide | 7 (54) | 14 (44) | 0.743 |
| Macrolide | 0 | 2 (6) | 1 |
| Previous history of intervention within 90 days | |||
| Urinary catheterization | 13 (100) | 30 (94) | 1 |
| Central catheterization | 12 (92) | 28 (88) | 1 |
| Intubation/tracheostomy | 9 (69) | 19 (59) | 0.737 |
| Nasogastric tube | 12 (92) | 29 (91) | 0.546 |
| Major surgery | 2 (15) | 3 (9) | 0.617 |
| Head | Controls (N = 90) | Cases (N = 45) | OR (95% CI) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 76 (59–82) | 76 (63–84) | 0.330 | |
| Male | 48 (53) | 33 (73) | 2.4 (1.1–5.2) | 0.027 |
| Previous admission to long-term care facility | 17 (19) | 17 (38) | 2.6 (1.2–5.8) | 0.021 |
| Associated disease | ||||
| End-stage renal disease | 14 (16) | 8 (18) | 1.2 (0.5–3.0) | 0.806 |
| Gastrointestinal disease | 14 (16) | 8 (18) | 1.2 (0.5–3.0) | 0.806 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 21 (23) | 8 (18) | 0.7 (0.3–1.8) | 0.512 |
| Localized infection | 6 (7) | 6 (13) | 2.2 (0.7–7.1) | 0.214 |
| Pneumonia/chronic pulmonary disease | 29 (32) | 31 (69) | 4.7 (2.2–10.0) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 17 (19) | 8 (18) | 0.9 (0.4–2.4) | 1 |
| Cardiovascular disease | 14 (16) | 5 (11) | 0.7 (0.2–2.0) | 0.604 |
| Malignancy | 10 (11) | 4 (9) | 0.8 (0.2–2.6) | 0.774 |
| Sepsis | 15 (17) | 10 (22) | 1.4 (0.6–3.5) | 0.484 |
| Charlson comorbidity index | 5 [4,5,6,7] | 6 [5,6,7] | 0.526 | |
| Previous usage of antibiotics within 90 days | ||||
| Penicillin | 47 (52) | 27 (60) | 1.4 (0.7–2.8) | 0.464 |
| Fluoroquinolone | 19 (21) | 25 (56) | 4.7 (2.2–10.1) | <0.001 |
| Carbapenem | 30 (33) | 19 (42) | 1.5 (0.7–3.1) | 0.346 |
| 1st generation cephalosporin | 6 (7) | 1 (2) | 0.3 (0.04–2.7) | 0.424 |
| 2nd generation cephalosporin | 3 (3) | 2 (4) | 1.3 (0.2–8.4) | 1 |
| Expanded-spectrum cephalosporin | 41 (46) | 13 (29) | 0.5 (0.2–1.0) | 0.066 |
| Glycopeptide | 34 (38) | 21 (47) | 1.4 (0.7–3.0) | 0.356 |
| Macrolide | 7 (8) | 2 (4) | 0.6 (0.1–2.8) | 0.717 |
| Previous history of intervention within 90 days | ||||
| Urinary catheterization | 73 (81) | 43 (96) | 5.0 (1.1–22.7) | 0.033 |
| Central catheterization | 50 (56) | 40 (89) | 6.4 (2.3–17.7) | <0.001 |
| Intubation/tracheostomy | 32 (36) | 28 (62) | 3.0 (1.4–6.3) | 0.006 |
| Nasogastric tube | 46 (51) | 42 (93) | 13.4 (3.9–46.4) | <0.001 |
| Major surgery | 4 (4) | 5 (11) | 2.7 (0.7–10.5) | 0.160 |
| Head | OR (95% CI) | P-value |
|---|---|---|
| Pneumonia/chronic pulmonary disease | 2.5 (1.02–6.3) | 0.045 |
| Previous use of fluoroquinolone | 2.7 (1.07–6.8) | 0.035 |
| Previous use of nasogastric tube | 10.7 (3.0–38.7) | < 0.001 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.A.; Lee, S.J.; Park, Y.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Yeon, J.H.; Seo, Y.H.; Lee, K. Risk Factors for Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacterales Infection or Colonization in a Korean Intensive Care Unit: A Case–Control Study. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9100680
Kim YA, Lee SJ, Park YS, Lee YJ, Yeon JH, Seo YH, Lee K. Risk Factors for Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacterales Infection or Colonization in a Korean Intensive Care Unit: A Case–Control Study. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(10):680. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9100680
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Young Ah, Se Ju Lee, Yoon Soo Park, Yeo Jin Lee, Jeong Hwa Yeon, Young Hee Seo, and Kyungwon Lee. 2020. "Risk Factors for Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacterales Infection or Colonization in a Korean Intensive Care Unit: A Case–Control Study" Antibiotics 9, no. 10: 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9100680
APA StyleKim, Y. A., Lee, S. J., Park, Y. S., Lee, Y. J., Yeon, J. H., Seo, Y. H., & Lee, K. (2020). Risk Factors for Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacterales Infection or Colonization in a Korean Intensive Care Unit: A Case–Control Study. Antibiotics, 9(10), 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9100680





