Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacterial Pathogens and Detection of Carbapenemases in Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates from Hospital Wastewater
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Bacterial Isolation
2.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.3. Phenotyping Screening and Carbapenemases Detection
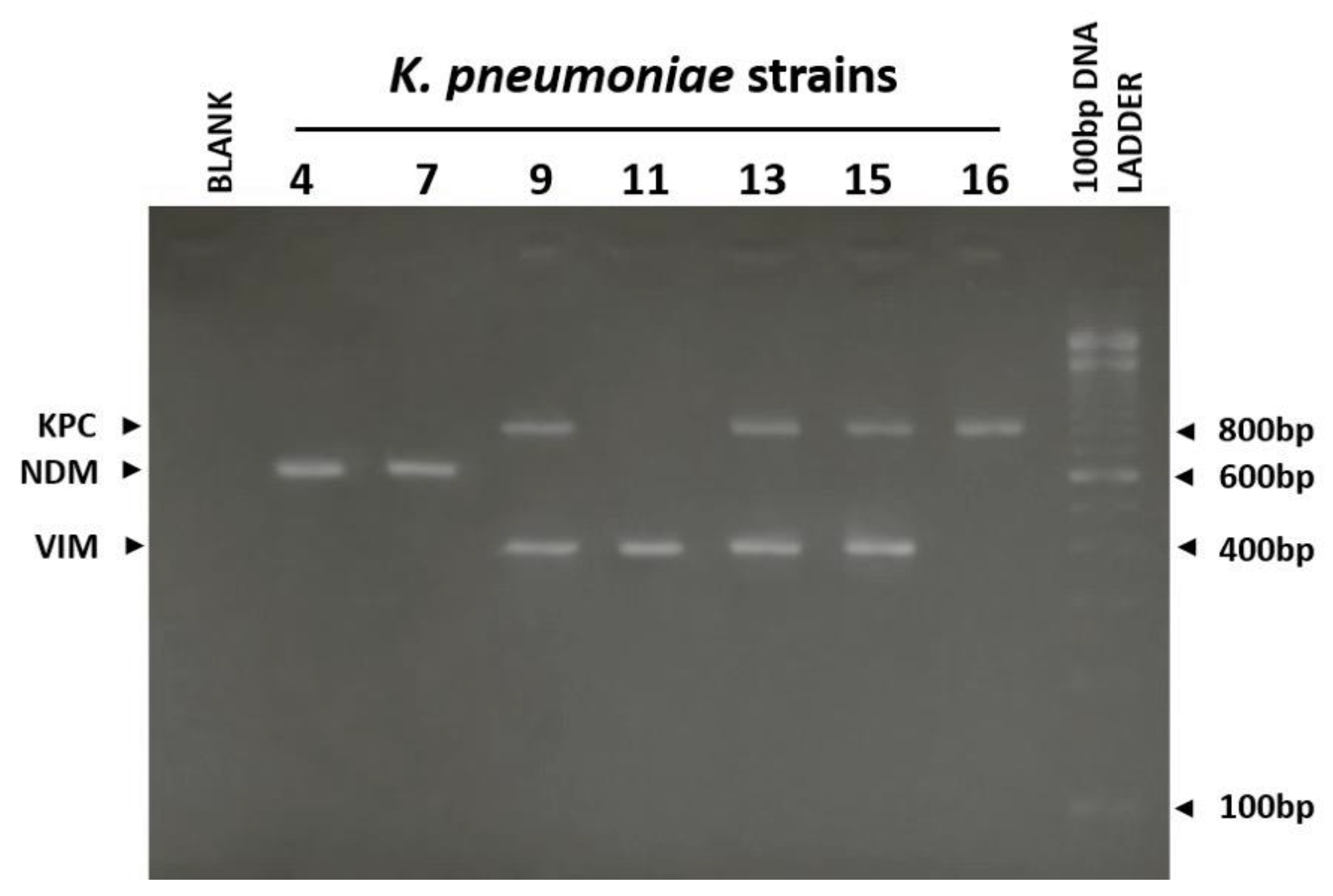
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aminov, R.I. A brief history of the antibiotic era: Lessons learned and challenges for the future. Front. Microbiol. 2010, 134, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabri, N.A.; Schmitt, H.; Van der Zaan, B.; Gerritsen, H.W.; Zuidema, T.; Rijnaarts, H.H.M.; Langenhoff, A.A.M. Prevalence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in a wastewater effluent-receiving river in the Netherlands. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, (in press). [CrossRef]
- Bhagirath, A.; Yangi, L.; Patidar, R.; Yerex, K.; Ma, X.; Kumar, A.; Duan, K. Two Component Regulatory Systems and Antibiotic Resistance in Gram-Negative Pathogens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvez, S.; Khan, A. Hospital sewage water: A reservoir for variants of New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase (NDM)- and extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Enterobacteriaceae. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2018, 51, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaruzzaman, N.F.; Tan, L.P.; Hamdan, R.H.; Choong, S.S.; Wong, W.K.; Gibson, A.J.; Chivu, A.; Pina, M.F. Antimicrobial Polymers: The Potential Replacement of Existing Antibiotics? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvin, S.; Boyle, F.; Hickey, P.; Vellinga, A.; Morris, D.; Cormican, M. Enumeration and characterization of antimicrobial-resistant Escherichia coli bacteria in effluent from municipal, hospital, and secondary treatment facility sources. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 4772–4779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picão, R.C.; Cardoso, J.P.; Campana, E.H.; Nicoletti, A.G.; Petrolini, F.V.B.; Assis, D.M.; Juliano, L.; Gales, A.C. The route of antimicrobial resistance from the hospital effluent to the environment: Focus on the occurrence of KPC-producing Aeromonas spp. and Enterobacteriaceae in sewage. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 76, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Economou, V.; Sakkas, H.; Delis, G.; Gousia, P. Antibiotic resistance in Enterococcus spp. Friend or Foe? In Foodborne Pathogens and Antibiotic Resistance, 1st ed.; Singh, Om V., Ed.; Weinheim, Wiley–VCH Verlag GmbH & Co.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 365–395. [Google Scholar]
- Sidler, J.; Battegay, M.; Tschudin-Sutter, S.; Widmer, A.; Weisser, M. Enterococci, Clostridium difficile, and ESBL-producing bacteria: Epidemiology, clinical impact and prevention in ICU patients. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2014, 144, w14009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcone, M.; Russo, A.; Venditti, M. Optimizing antibiotic therapy of bacteremia and endocarditis due to staphylococci and enterococci: New insights and evidence from the literature. J. Infect. Chemother. 2015, 21, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Surveillance of antimicrobial resistance in Europe. Annual report of the European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Network (EARS-Net) 2017. Stockholm: ECDC. 2018. Available online: https://ecdc.europa.eu/sites/portal/files/documents/EARS-Net-report-2017-update-jan-2019.pdf (accessed on 5 June 2019).
- Howard, A.; O’Donoghue, M.; Feeney, A.; Sleator, R.D. Acinetobacter baumannii: An emerging opportunistic pathogen. Virulence 2012, 3, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, S.; De Simone, G. Update on the main MDR pathogens: Prevalence and treatment options. Infez. Med. 2017, 25, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Daoud, Z.; Farah, J.; Sokhn, E.S.; El Kfoury, K.; Dahdouh, E.; Masri, K.; Afif, C.; Abdel-Massih, R.M.; Matar, G.M. Multidrug-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae in Lebanese Hospital Wastewater: Implication in the One Health Concept. Microb. Drug Resist. 2018, 24, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, K.E.; Wertheim, H.; Zadoks, R.N.; Baker, S.; Whitehouse, C.A.; Dance, D.; Jenney, A.; Connor, T.R.; Hsu, L.Y.; Severin, J.; et al. Genomic analysis of diversity, population structure, virulence, and antimicrobial resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae, an urgent threat to public health. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E3574-81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.H.; Song, X.Y.; Ma, X.B.; Zhang, S.Y.; Zhang, J.Q. Molecular characterization of multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2015, 46, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Runcharoen, C.; Moradigaravand, D.; Blane, B.; Paksanont, S.; Thammachote, J.; Anun, S.; Parkhill, J.; Chantratita, N.; Peacock, S. Whole genome sequencing reveals high-resolution epidemiological links between clinical and environmental Klebsiella pneumoniae. Genome Med. 2017, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (2015) Annual epidemiological report 2014. Antimicrobial resistance and healthcare-associated infections. Available online: https://ecdc.europa.eu/sites/portal/files/media/en/publications/Publications/antimicrobial-resistance-annual-epidemiological-report.pdf (accessed on 12 January 2019).
- Findlay, J.; Hopkins, K.L.; Alvarez-Buylla, A.; Meunier, D.; Mustafa, N.; Hill, R.; Pike, R.; McCrae, L.X.; Hawkey, P.M.; Woodford, N. Characterization of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in the West Midlands region of England: 2007-14. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing, 27th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pournaras, S.; Zarkotou, O.; Poulou, A.; Kristo, I.; Vrioni, G.; Themeli-Digalaki, K.; Tsakris, A. A combined disk test for direct differentiation of carbamenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in surveillance rectal swabs. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 2986–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakris, A.; Poulou, A.; Pournaras, S.; Voulgari, E.; Vrioni, G.; Themeli-Digalaki, K.; Petropoulou, D.; Sofianou, D. A simple phenotypic method for the differentiation of metallo-beta-lactamases and classA KPC carbapenemases in Enterobacteriaceae clinical isolates. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 1664–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cointe, A.; Bonacorsi, S.; Truong, J.; Hobson, C.; Doit, C.; Monjault, A.; Bidet, P.; Birgy, A. Detection of carbapenemases-producing Enterobacteriaceae in positive blood culture using Immunochromatographic RESIST-4 O.K.N.V assay. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greissl, C.; Saleh, A.; Hamprecht, A. Rapid detection of OXA-48-like, KPC, NDM, and VIM carbapenemases in Enterobacterales by a new multiplex immunochromatographic test. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Kolenda, C.; Benoit, R.; Carricajo, A.; Bonnet, R.; Dauwalder, O.; Laurent, F. Evaluation of the New Multiplex Immunochromatographic O.K.N.V. K-SeT Assay for Rapid Detection of OXA-48-like, KPC, NDM, and VIM Carbapenemases. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza, L.L.; Pfennigwerth, N.; Greissl, C.; Göttig, S.; Saleh, A.; Stelzer, Y.; Gatermann, S.G.; Hamprecht, A. Comparison of five methods for detection of carbapenemases in Enterobacterales with proposal of a new algorithm. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rösner, S.; Kamalanabhaiah, S.; Küsters, U.; Kolbert, M.; Pfennigwerth, N.; Mack, D. Evaluation of a novel immunochromatographic lateral flow assay for rapid detection of OXA-48, NDM, KPC and VIM carbapenemases in multidrug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. J. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 379–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glupczynski, Y.; Evrard, S.; Huang, T.D.; Bogaerts, P. Evaluation of the RESIST-4 K-SeT assay, a multiplex immunochromatographic assay for the rapid detection of OXA-48-like, KPC, VIM and NDM carbapenemases. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirel, L.; Walsh, T.; Cuvillier, V.; Nordmann, P. Multiplex PCR for detection of acquired carbapenemase genes. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 70, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Depardieu, F.; Perichon, B.; Courvalin, P. Detection of the van Alphabet and identification of enterococci and staphylococci at the species level by multiplex PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 5857–5860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galler, H.; Feierl, G.; Petternel, C.; Reinthaler, F.; Haas, D.; Habib, J.; Kittinger, C.; Luxner, J.; Zarfel, G. Multiresistant bacteria isolated from activated sludge in Austria. Inter. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quach-Cu, J.; Herrera-Lynch, B.; MarciniaK, C.; Adams, S.; Simmerman, A.; Reinke, R. The effect of primary, secondary, and tertiary wastewater treatment processes on antibiotic resistance gene (ARG) concentrations in solid and dissolved wastewater fractions. Water 2018, 10, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manaia, C.M. Assessing the risk of antibiotic resistance transmission from the environment to humans: Non-direct proportionality between abundance and risk. Trends Microbioliol. 2017, 25, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, P.H.; Touchon, M.; Cury, J.; Rocha, E.P.C. The chromosomal organization of horizontal gene transfer in bacteria. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, J.L. Ecology and evolution of chromosomal gene transfer between environmental microorganisms and pathogens. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Economou, V.; Gousia, P. Agriculture and food animals as a source of antimicrobial-resistant bacteria. Infect. Drug Resist. 2015, 8, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gousia, P.; Economou, V.; Bozidis, P.; Papadopoulou, C. Vancomycin-Resistance Phenotypes, Vancomycin-Resistance Genes and Resistance to antibiotics of Enterococci isolated from Food of animal origin. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2015, 12, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, S.M.; Ghosh, A.K.; Pati, B.R. Dissemination of antibiotic resistance in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and vancomycin-resistant S aureus strains isolated from hospital effluents. Am. J. Infect. Control 2015, 43, e87–e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naquin, A.; Shrestha, A.; Sherpa, M.; Nathaniel, R.; Boopathy, R. Presence of antibiotic resistance genes in a sewage treatment plant in Thibodaux, Louisiana, USA. Bioresour. Techol. 2015, 188, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez, P.; Lozano, C.; Benito, D.; Estepa, V.; Tenorio, C.; Zarazaga, M.; Torres, C. Characterization of staphylococci in urban wastewater treatment plants in Spain, with detection of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus ST398*. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 212, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boopathy, R. Presence of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in sewage treatment plant. Bioresour. Techol. 2017, 240, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, S.; Nayak, B.; Sun, S.; Badgley, B.; Rohr, J.; Harwood, V. Vancomycin-resistant enterococci and bacterial community structure following a sewage spill into an aquatic environment. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 5653–5660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, A.R.; Ferro, G.; Vredenburg, J.; Yanike, M.; Vieira, L.; Rizzo, L.; Lameiras, C.; Manaia, M. Vancomycin resistant enterococci: From the hospital effluent to the urban wastewater treatment plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 450–451, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korzeniewska, E.; Korzeniewska, A.; Harnisz, M. Antibiotic resistant Escherichia coli in hospital and municipal sewage and their emission to their environment. Exotoxicol. Environ. Safety 2013, 91, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalaiselvi, K.; Mangayarkarasi, V.; Balakrishnan, D.; Chitraleka, V. Survival of antibacterial resistance microbes in hospital-generated recycled wastewater. J. Water Health 2016, 14, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamba, M.; Graham, D.; Ahammad, S.Z. Hospital wastewater releases of carbapenem-resistance pathogens and genes in urban India. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 13906–13912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabbani, M.A.G.; Howlader, Z.H.; Kabir, Y. Detection of multidrug resistant (MDR) bacteria in untreated wastewater disposals of hospitals in Dhaka City, Bangladesh. J. Global Antimicrob. Resist. 2017, 10, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haller, L.; Chen, H.; Ng, C.; Le, T.H.; Koh, T.H.; Barkham, T.; Sobsey, M.; Gin, K.Y. Occurrence and characteristics of extended-spectrum β-lactamase- and carbapenemase- producing bacteria from hospital effluents in Singapore. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, P.; Yang, Q. Occurrence and diversity of antibiotic resistance in untreated hospital wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giakkoupi, P.; Pappa, O.; Polemis, M.; Vatopoulos, A.C.; Miriagou, V.; Zioga, A.; Papagiannitsis, C.C.; Tzouvelekis, L.S. Emerging Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates coproducing KPC-2 and VIM-1 carbapenemases. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 4048–4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falagas, M.E.; Kasiakou, S.K. Colistin: The revival of polymyxins for the management of multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 40, 1333–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satlin, M.J. The Search for a Practical Method for Colistin Susceptibility Testing: Have We Found It by Going Back to the Future? J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 57, e01608-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, L.J.; Salim, M.; Cober, E.; Richter, S.S.; Perez, F.; Salata, R.A.; Kalayjian, R.C.; Watkins, R.R.; Marshall, S.; Rudin, S.D.; et al. Antibacterial Resistance Leadership Group. Colistin resistance in carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: Laboratory detection and impact on mortality. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Satlin, M.J.; Chen, L.; Patel, G.; Gomez-Simmonds, A.; Weston, G.; Kim, A.C.; Seo, S.K.; Rosenthal, M.E.; Sperber, S.J.; Jenkins, S.G.; et al. Multicenter clinical and molecular epidemiological analysis of bacteremia due to carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) in the CRE epicenter of the United States. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e02349-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Shen, H.; Zhu, C.; Yu, Y. Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Infections among ICU Admission Patients in Central China: Prevalence and Prediction Model. Biomed. Res. Int 2019, 9767313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, N.K.; Alkhawaja, S.; Azam, N.F.; Alaradi, K.; Al Biltagi, M. Epidemiology of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae in a Tertiary Care Center in the Kingdom of Bahrain. J. Lab. Physicians 2019, 11, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aygun, F.; Aygun, F.D.; Varol, F.; Durak, C.; Çokuğraş, H.; Camcıoğlu, Y.; Cam, H. Infections with Carbapenem-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria are a Serious Problem Among Critically Ill Children: A Single-Centre Retrospective Study. Pathogens 2019, 8, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathers, A.; Carroll, J.; Sifri, C.; Hazen, K. Modified Hodge Test versus Indirect Carbapenemase Test: Prospective Evaluation of a Phenotypic Assay for Detection of Klebsiella pneumoniae Carbapenemase (KPC) in Enterobacteriaceae. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 1291–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
| Bacteria/Antibiotics * | S.aureus (n = 6) | Enterococcus spp (n = 7) | E. coli (n = 24) | K. pneumoniae (n = 24) | P. aeruginosa (n = 9) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEN | 100% | 57.1% | |||
| AMP | 85.7% | 100% | |||
| AMC | 79.2% | 75% | |||
| PTZ | 55.5% | ||||
| TCC | 77.7% | ||||
| VAN | 16.7% | 57.1% | |||
| TEC | 16.7% | 57.1% | |||
| ERY | 100% | 71.4% | |||
| CC | 100% | ||||
| AMK | 25% | 62.5% | 88.8% | ||
| GEN | 66.6% | 29.2% | 45.8% | 88.8% | |
| TOB | 100% | 100% | |||
| FOX | 100% | 66.6% | 83.3% | ||
| CRO | 100% | 100% | |||
| CAZ | 70.8% | 95.8% | 33.3% | ||
| FEP | 54.2% | 83.3% | 66.6% | ||
| CIP | 100% | 71.4% | 79.2% | 87.5% | 88.8% |
| IPM | 79.2% | 88.8% | |||
| MEM | 79.2% | 100% | |||
| ATM | 45.8% | 58.3% | 55.5% | ||
| QDA | 33.3% | 100% | |||
| LZD | 85.7% | ||||
| SXT | 66.6% | 95.8% | |||
| CT | 22.2% | ||||
| TET | 71.4% | 45.8% | 58.3% | ||
| TGC | 5.3% |
| K. pneumoniae | MHT | CDT (β-lactamase detected) | IT | PCR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KP1 | + | KPC/MBL | VIM | VIM |
| KP2 | + | KPC | KPC | KPC |
| KP3 | + | KPC | KPC | KPC |
| KP4 | − | MBL | NDM | NDM |
| KP5 | + | KPC/MBL | KPC+NDM | KPC+NDM |
| KP6 | − | KPC/MBL | KPC+NDM | KPC+NDM |
| KP7 | − | MBL | NDM | NDM |
| KP8 | + | KPC/MBL | KPC+VIM | KPC+VIM |
| KP9 | + | KPC/MBL | KPC+VIM | KPC+VIM |
| KP10 | + | KPC | KPC | KPC |
| KP11 | + | KPC/MBL | VIM | VIM |
| KP12 | + | MBL | VIM | VIM |
| KP13 | + | KPC/MBL | VIM | KPC+VIM |
| KP14 | + | KPC/MBL | KPC+VIM | KPC+VIM |
| KP15 | + | KPC/MBL | KPC | KPC+VIM |
| KP16 | + | KPC | KPC | KPC |
| KP17 | + | KPC/MBL | VIM | VIM |
| KP18 | + | KPC | KPC | KPC |
| KP19 | − | KPC/MBL | KPC+VIM | KPC+VIM |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sakkas, H.; Bozidis, P.; Ilia, A.; Mpekoulis, G.; Papadopoulou, C. Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacterial Pathogens and Detection of Carbapenemases in Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates from Hospital Wastewater. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8030085
Sakkas H, Bozidis P, Ilia A, Mpekoulis G, Papadopoulou C. Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacterial Pathogens and Detection of Carbapenemases in Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates from Hospital Wastewater. Antibiotics. 2019; 8(3):85. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8030085
Chicago/Turabian StyleSakkas, Hercules, Petros Bozidis, Afrodite Ilia, George Mpekoulis, and Chrissanthy Papadopoulou. 2019. "Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacterial Pathogens and Detection of Carbapenemases in Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates from Hospital Wastewater" Antibiotics 8, no. 3: 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8030085
APA StyleSakkas, H., Bozidis, P., Ilia, A., Mpekoulis, G., & Papadopoulou, C. (2019). Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacterial Pathogens and Detection of Carbapenemases in Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates from Hospital Wastewater. Antibiotics, 8(3), 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8030085







