Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) Simulation for Dosage Optimization of Colistin Against Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae and Carbapenem-Resistant Escherichia coli
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microbiology
2.2. Pharmacokinetic Model
2.3. Pharmacodynamic Model
2.4. Monte Carlo Simulation
3. Results
3.1. Microbiology
3.2. Pharmacokinetic-Pharmacodynamic Simulations
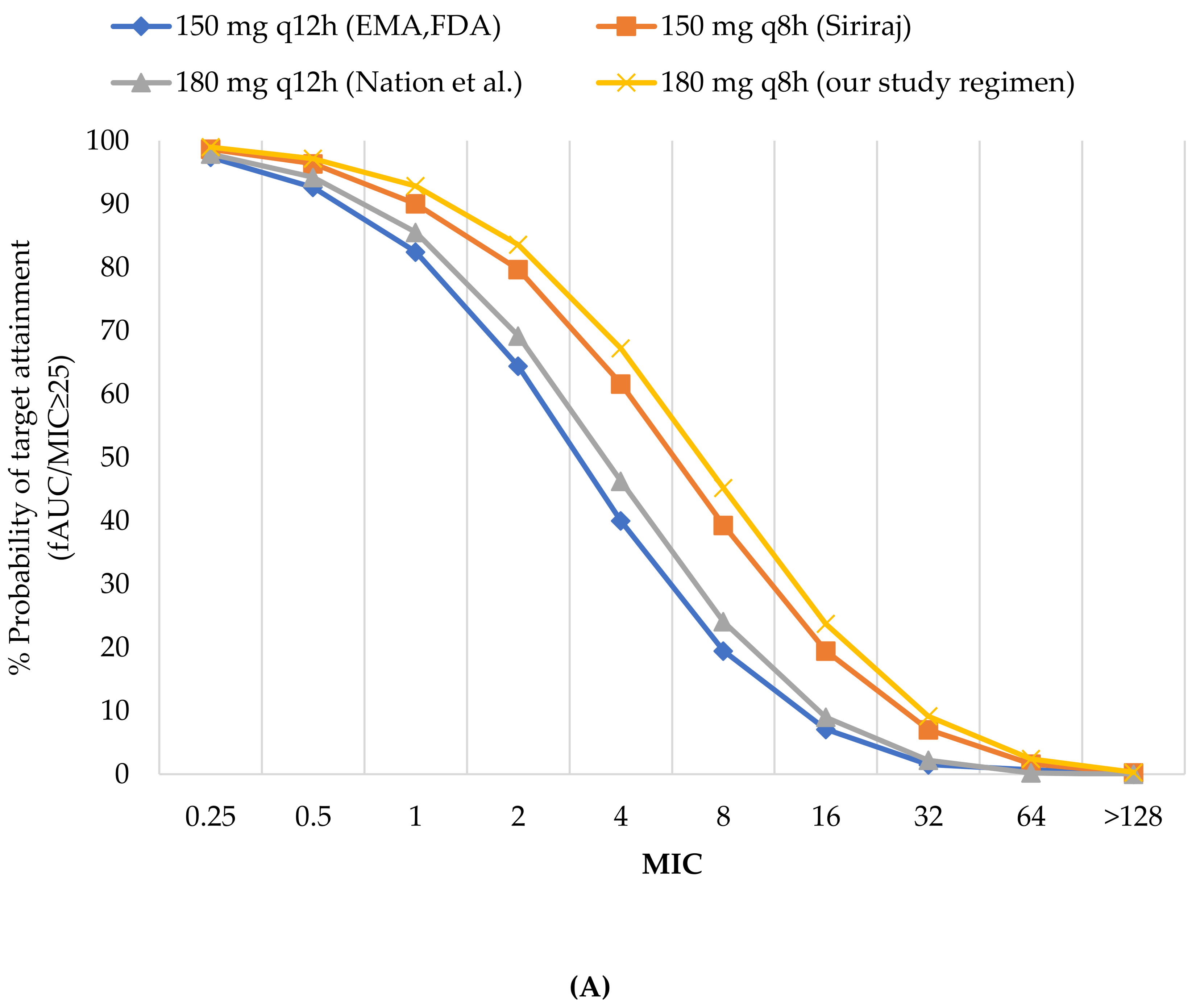
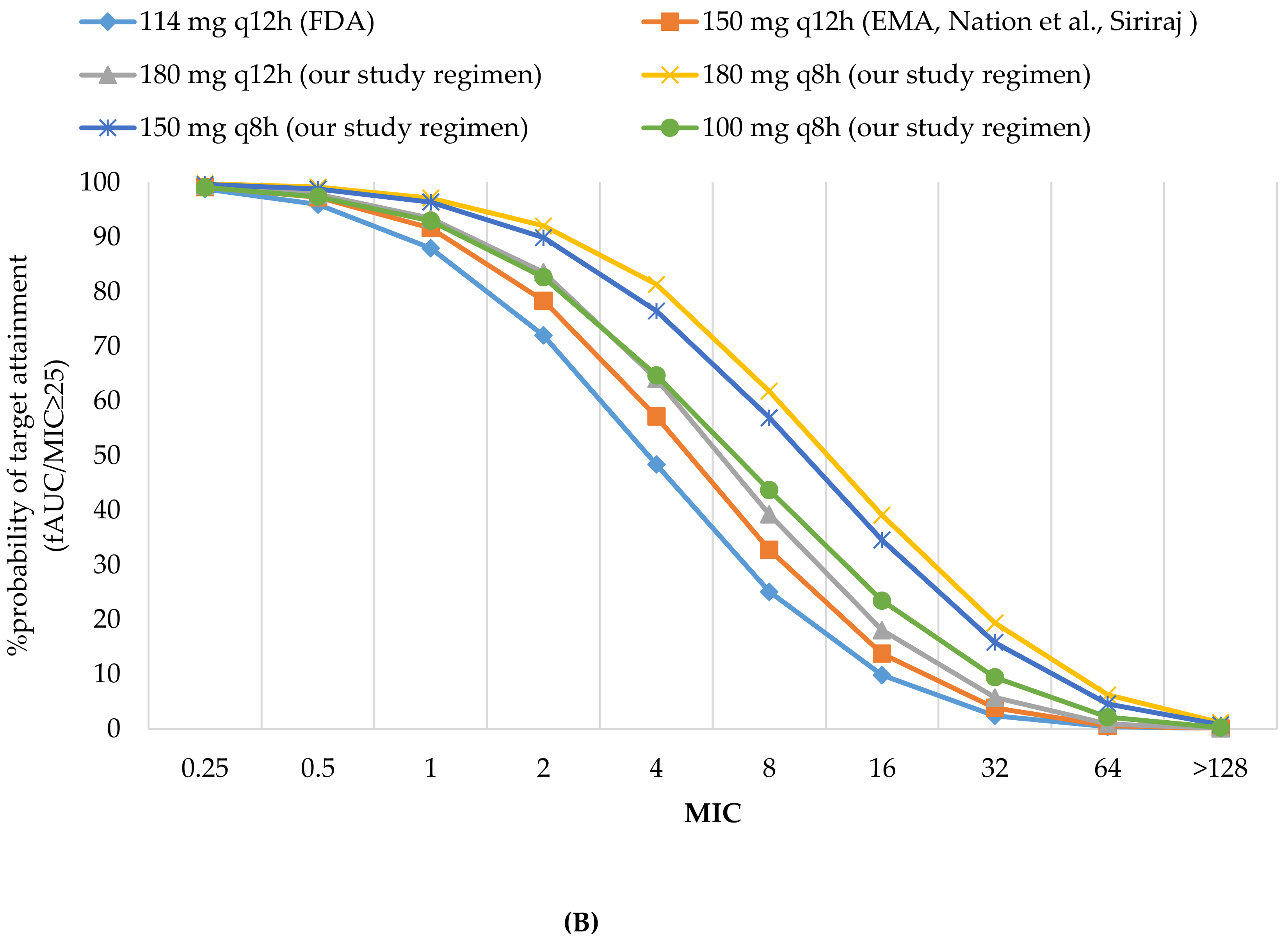
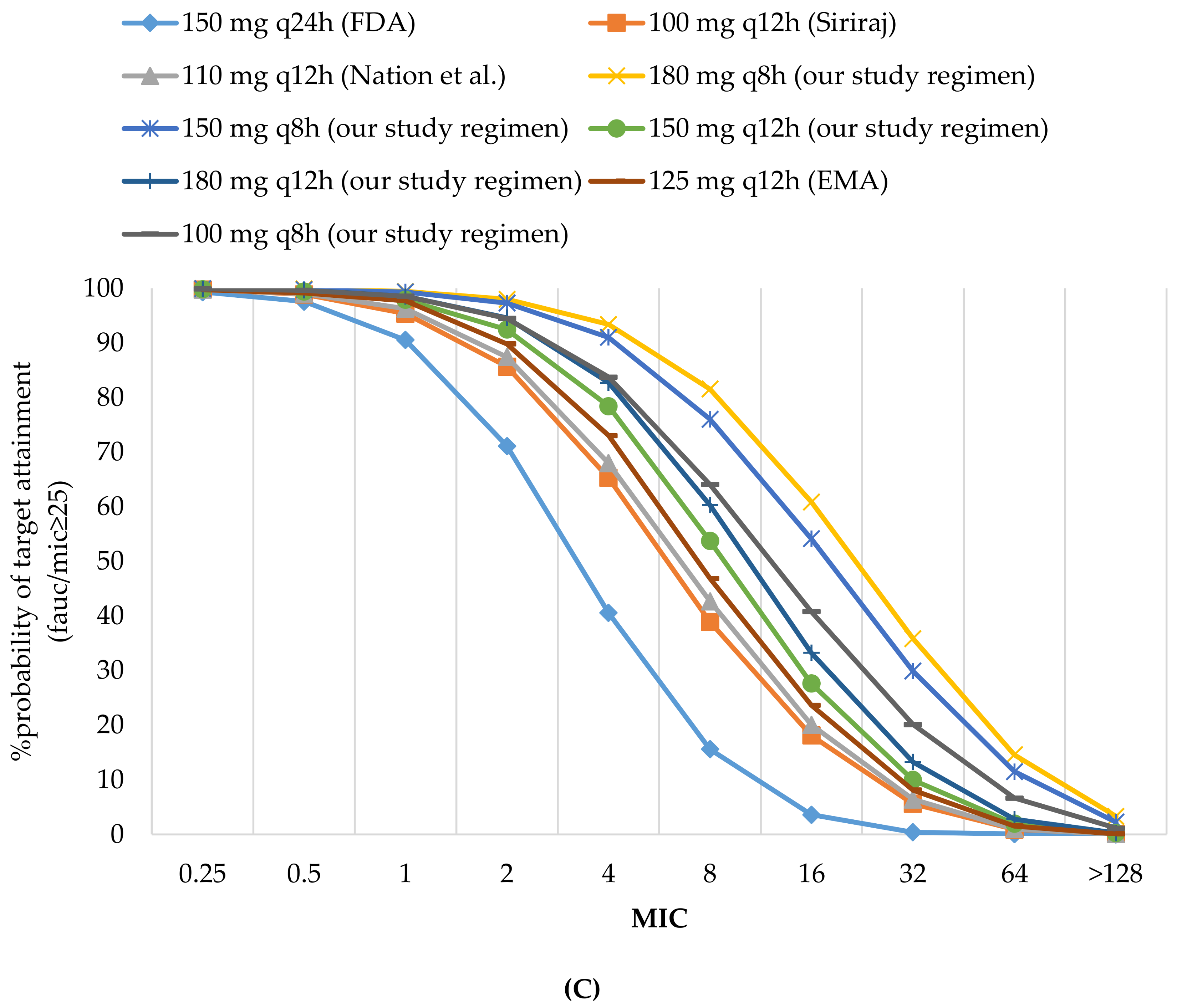
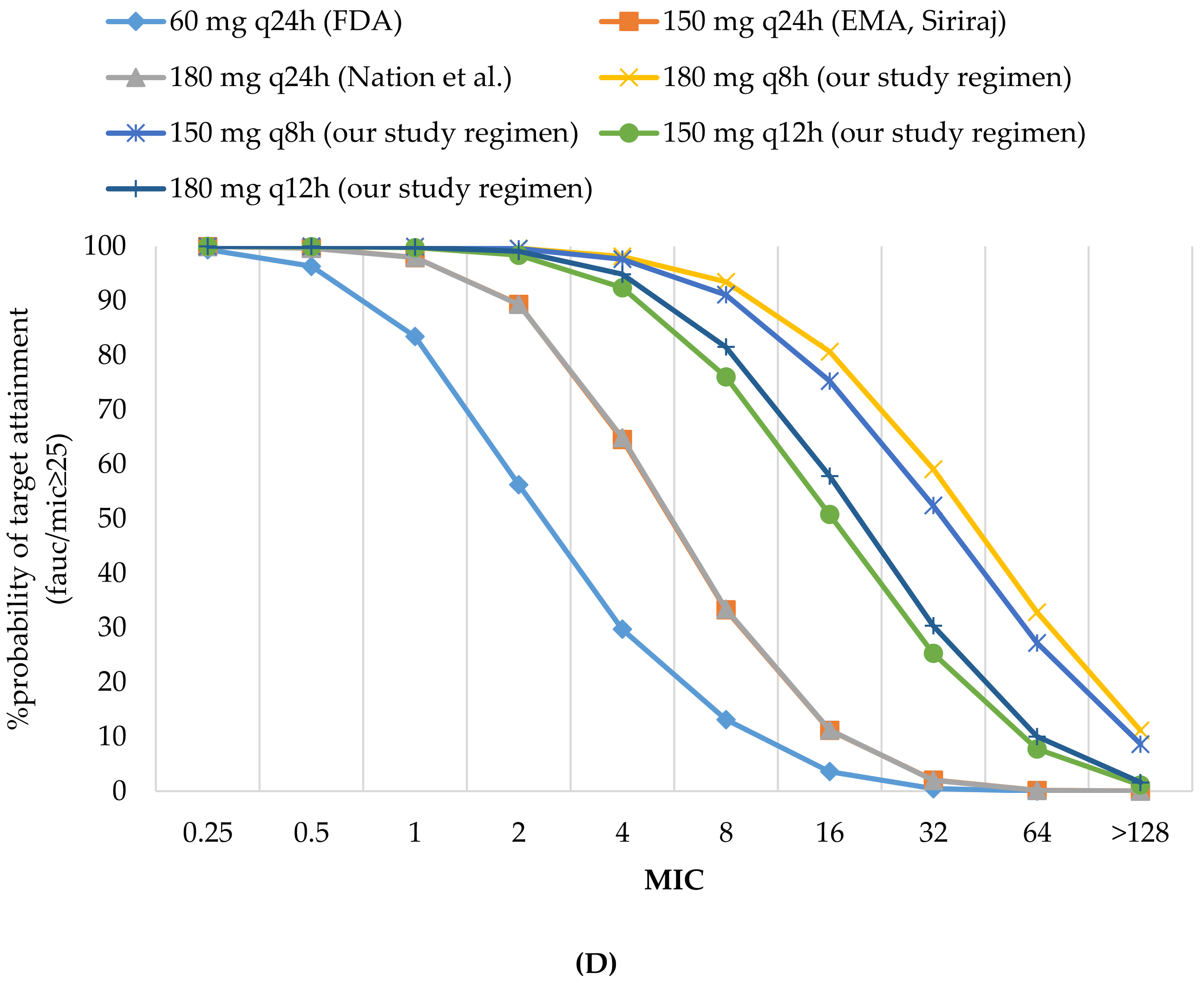
3.2.1. Probability of Target Attainment
3.2.2. Cumulative Fraction of Response
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zarkotou, O.; Pournaras, S.; Tselioti, P.; Dragoumanos, V.; Pitiriga, V.; Ranellou, K.; Prekates, A.; Themeli-Digalaki, K.; Tsakris, A. Predictors of mortality in patients with bloodstream infections caused by KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae and impact of appropriate antimicrobial treatment. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011, 17, 1798–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz-Price, L.S.; Poirel, L.; Bonomo, A.R.; Schwaber, M.J.; Daikos, G.L.; Cormican, M.; Cornaglia, G.; Garau, J.; Gniadkowski, M.; Hayden, M.K.; et al. Clinical epidemiology of the global expansion of Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemases. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordmann, P.; Naas, T.; Poirel, L. Global Spread of Carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1791–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Center, Thailand. Antibiograms. Available online: http://narst.dmsc.moph.go.th/antibiograms.html. (accessed on 20 July 2017).
- Kazmierczak, K.M.; Rabine, S.; Hackel, M.; McLaughlin, R.E.; Biedenbach, D.J.; Bouchillon, S.K.; Sahm, D.F.; Bradford, P.A. Multiyear, Multinational Survey of the Incidence and Global Distribution of Metallo-β-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 1067–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, L.Y.; Apisarnthanarak, A.; Khan, E.; Suwantarat, A.; Ghafur, A.; Tambyah, P.A. Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii and Enterobacteriaceae in South and Southeast Asia. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 3, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Nation, R.L.; Turnidge, J.D.; Milne, R.W.; Coulthard, K.; Rayner, C.R.; Paterson, D.L. Colistin: The re-emerging antibiotic for multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2006, 6, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, L.M.; Neang, L.Y.; Anderson, D.; Yang, J.C.; Macander, L.; Jarkowski III, A.; Forrest, A.; Bulitta, J.B.; Tsuji, B.T. Resurgence of Colistin: A Review of Resistance, Toxicity, Pharmacodynamics and Dosing. Pharmacotherapy 2010, 30, 1279–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garonzik, S.M.; Li, J.; Thamlikitkul, V.; Paterson, D.L.; Shoham, S.; Jacob, J.; Silveira, F.P.; Forrest, A.; Nation, R.L. Population Pharmacokinetics of Colistin Methanesulfonate and Formed Colistin in Critically Ill Patients from a Multicenter Study Provide Dosing Suggestions for Various Categories of Patients. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 3284–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Twenty-Seven Informational Supplement. CLSI Document M100-Swayne; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST). Available online: http: www.eucast.org/clinical_breakpoints/ (accessed on 20 July 2017).
- Nation, R.L.; Garonzik, S.M.; Thamlikitkul, V.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Forrest, A.; Paterson, D.L. Dosing Guidance for Intravenous Colistin in Critically Ill Patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsala, M.; Vourli, S.; Georgiou, P.C.; Pournaras, S.; Tsakris, A.; Daikos, G.L.; Mouton, J.W.; Meletiadis, J. Exploring colistin pharmacodynamics against Klebsiella pneumoniae: A need to revise current susceptibility breakpoints. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, S.E.; Wang, J.; Nguyen, V.T.T.; Turnidge, J.D.; Li, J.; Nation, R.L. New pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic studies of systemically administered colistin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii in mouse thigh and lung infection models: Smaller response in lung infection. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015, 70, 3291–3297. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, M.; Grégoire, N.; Mégarbane, B.; Gobin, P.; Balayn, D.; Marchand, S.; Mimoz, O.; Couet, W. Population Pharmacokinetics of Colistin Methanesulfonate and Colistin in Critically Ill Patients with Acute Renal Failure Requiring Intermittent Hemodialysis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 1788–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nation, R.L.; Garonzik, S.M.; Li, J.; Thamlikitkul, V.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Paterson, D.L.; Turnidge, J.D.; Forrest, A.; Silveira, F.P. Updated US and European Dose Recommendations for Intravenous Colistin: How Do They Perform? Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 62, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency Completes Review of Polymyxin-based Medicines: Recommendations Issued for Safe Use in Patients with Serious Infections Resistant to Standard Antibiotics. Available online: https: //www.ema.europa.eu/documents/press-release/european-medicines-agency-completes-review-polymyxin-based-medicines_en.pdf (accessed on 2 December 2017).
- FDA Approved Drug Products. Label and Approval History for Coly-Mycin M, NDA 050108. Available online: https: //www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/daf/index.cfm?event=overview.process&ApplNo=050108 (accessed on 2 December 2017).
- Eiamphungporn, W.; Yainoy, S.; Jumderm, C.; Tan-Arsuwongkul, R.; Tiengrim, S.; Thamlikitkul, V. Prevalence of the colistin resistance gene mcr-1 in colistin-resistant Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from humans in Thailand. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2018, 15, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, P.A.; Kazmierczak, K.M.; Biedenbach, D.J.; Wise, M.G.; Hackel, M.; Sahm, D.F. Correlation of β-Lactamase Production and Colistin Resistance among Enterobacteriaceae Isolates from a Global Surveillance Program. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 1385–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maalej, S.; Meziou, M.; Rhimi, F.; Hammami, A. Comparison of disc diffusion, Etest and agar dilution for susceptibility testing of colistin against Enterobacteriaceae. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 53, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nation, R.L.; Li, J.; Cars, O.; Couet, W.; Dudley, M.N.; Kaye, K.S.; Mouton, J.W.; Paterson, D.L.; Tam, V.H.; Theuretzbacher, U.; et al. Framework for optimisation of the clinical use of colistin and polymyxin B: The Prato polymyxin consensus. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nation, R.L.; Velkov, T.; Li, J. Colistin and polymyxin B: Peas in a pod, or chalk and cheese? Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 59, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.G.; Shah, S.R. Treatment and Outcome of Carbapenem-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacilli Blood-Stream Infections in a Tertiary Care Hospital. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2015, 63, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- De Maio Carrilho, C.M.D.; de Oliveira, L.M.; Gaudereto, J.; Perozin, J.S.; Urbano, M.R.; Camargo, C.H.; Grion, C.M.C.; Levin, A.S.S.; Costa, S.F. A prospective study of treatment of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae infections and risk factors associated with outcome. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, I.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Wi, Y.M.; Kwan, B.S.; Jung, K.H.; Hong, W.P.; Kim, J.M. Predictors of mortality in patients with extensively drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii pneumonia receiving colistin therapy. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2016, 48, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorlì, L.; Luque, S.; Grau, S.; Berenguer, N.; Segura, C.; Montero, M.M.; Álvarez-Lerma, F.; Knobel, H.; Benito, N.; Horcajada, J.P. Trough colistin plasma level is an independent risk factor for nephrotoxicity: A prospective observational cohort study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horcajada, J.P.; Sorlí, L.; Luque, S.; Benito, N.; Segura, C.; Campillo, N.; Montero, M.; Esteve, E.; Mirelis, B.; Pomar, V.; et al. Validation of a colistin plasma concentration breakpoint as a predictor of nephrotoxicity in patients treated with colistin methanesulfonate. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2016, 48, 725–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falagas, M.E.; Fragoulis, K.N.; Kasiakou, S.K.; Sermaidis, G.J.; Michalopoulos, A. Nephrotoxicity of intravenous colistin: A prospective evaluation. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2005, 26, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Category | Parameter | Units | Estimate | %SE | %IIV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMS | V1 | L | 12.9 | - | 40.4 |
| V2 | L | 16.1 | - | 70.9 | |
| CLD1 | L | 9.57 | 10.5 | 80.1 | |
| CLR | L/h/CrCL | 0.0340 | 6.85 | 75.2 | |
| CLNRCMS | L/h | 2.52 | 3.71 | 39.8 | |
| Colistin | V3 | L | 57.2 | 5.13 | 43.5 |
| CLTC | L/h | 3.59 | - | 37.9 | |
| CLRC | L/h/CrCL | 0.00834 | 27.7 | - | |
| CLNRC | L/h | 3.11 | 4.38 | - |
| Creatinine Clearance | Daily Dose (CBA) | |
|---|---|---|
| ≥80 mL/min | 150 mg every 8 h | Siriraj Hospital regimen |
| 180 mg every 12 h | Nation, et al. regimen | |
| 150 mg every 12 h | EMA-approved regimen FDA-approved regimen | |
| 51 to 79 mL/min | 150 mg every 12 h | EMA-approved regimen Siriraj Hospital regimen Nation, et al. regimen |
| 114 mg every 12 h | FDA-approved regimen | |
| 30 to 50 mL/min | 125 mg every 12 h | EMA-approved regimen |
| 110 mg every 12 h | Nation, et al. regimen | |
| 150 mg every 24 h | FDA-approved regimen | |
| 100 mg every 12 h | Siriraj Hospital regimen | |
| 11 to 29 mL/min | 180 mg every 24 h | Nation, et al. regimen |
| 150 mg every 24 h | EMA-approved regimen Siriraj Hospital regimen | |
| 60 mg every 24 h | FDA-approved regimen | |
| ≤10 mL/min | 150 mg every 24 h | Nation, et al. regimen |
| 120 mg every 24 h | EMA-approved regimen | |
| 60 mg every 24 h | FDA-approved regimen | |
| Creatinine Clearance | Daily Dose (CBA) |
|---|---|
| ≥80 mL/min | 180 mg every 8 h |
| 51 to 79 mL/min | 180 mg every 8 h |
| 150 mg every 8 h | |
| 180 mg every 12 h | |
| 100 mg every 8 h | |
| 30 to 50 mL/min | 180 mg every 8 h |
| 150 mg every 8 h | |
| 180 mg every 12 h | |
| 150 mg every 12 h | |
| 100 mg every 8 h | |
| 11 to 29 mL/min | 180 mg every 8 h |
| 180 mg every 12 h | |
| 150 mg every 12 h | |
| 150 mg every 8 h | |
| ≤10 mL/min | 180 mg every 8 h |
| 150 mg every 8 h | |
| 100 mg every 8 h | |
| 180 mg every 12 h | |
| 150 mg every 12 h | |
| 100 mg every 12 h | |
| 180 mg every 24 h |
| MIC (mcg/mL) | 0.25 | 0.5 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 32 | 64 | >128 | MIC50 (mcg/mL) | MIC90 (mcg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All isolates (n = 116) | 3 | 55 | 19 | 14 | 4 | 5 | 10 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 16 |
| % | 2.58 | 47.41 | 16.38 | 12.07 | 3.45 | 4.31 | 8.6 | 3.45 | 0.86 | 0.86 | ||
| Colistin-Susceptible Isolates (MIC ≤ 2 mcg/mL) | ||||||||||||
| K. pneumoniae (n = 74) | 3 | 40 | 18 | 13 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.5 | 2 |
| E.coli (n = 17) | - | 15 | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Colistin-Resistant Isolates (MIC > 2 mcg/mL) | ||||||||||||
| K. pneumoniae (n = 22) | - | - | - | - | 3 | 4 | 10 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 16 | 32 |
| E. coli (n = 3) | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | 8 | 32 |
| Creatinine Clearance (mL/min) | MIC 0.5 mcg/mL Daily Dose (CBA) | MIC 2 mcg/mL Daily Dose (CBA) | MIC 8 mcg/mL Daily Dose (CBA) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ≥80 | 150 mg every 12 h (EMA, FDA) | Not recommended | Not recommended |
| 51–79 | 114 mg every 12 h (FDA) | 180 mg every 8 h (our study) | Not recommended |
| 30–50 | 150 mg every 24 h (FDA) | 150 mg every 12 h (our study) | Not recommended |
| 11–29 | 60 mg every 24 h (FDA) | 150 mg every 12 h (our study) | 150 mg every 8 h (our study) |
| ≤10 | 60 mg every 24 h (FDA) | 120 mg every 24 h (EMA) | 180 mg every 12 h (our study) |
| Creatinine Clearance (mL/min) | MIC 16 mcg/mL Daily Dose (CBA) | MIC 32 mcg/mL Daily Dose (CBA) |
|---|---|---|
| ≥80 | Not recommended | Not recommended |
| 51–79 | Not recommended | Not recommended |
| 30–50 | Not recommended | Not recommended |
| 11–29 | Not recommended | Not recommended |
| ≤10 | 180 mg every 8 h (our study) | Not recommended |
| All Isolates | Colistin-Susceptible Isolates | Colistin-Resistant Isolates | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| %CFR | Colistin-Susceptible K. pneumoniae Subgroup | Colistin-Susceptible E. coli Subgroup | %CFR for all Sus-Ceptible Isolates | Colistin-Resistant K. pneumoniae Subgroup | Colistin-Resistant E. coli Subgroup | %CFR for all Resistant Isolates | |||||||||||
| %PTA | %PTA | %CFR | %PTA | %CFR | %PTA | %CFR | %PTA | %CFR | |||||||||
| MIC (mcg/mL) | MIC50 | MIC90 | MIC50 | MIC90 | MIC50 | MIC90 | MIC50 | MIC90 | MIC50 | MIC90 | |||||||
| 1 | 16 | 0.5 | 2 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 16 | 32 | 8 | 32 | ||||||||
| CrCl ≥80 mL/min | |||||||||||||||||
| 150 mg q12 h (EMA, FDA) | 82.47 | 7.08 | 70.68 | 92.66 | 64.41 | 85.41 | 92.66 | 92.66 | 90.40 | 86.34 | 7.08 | 1.51 | 12.45 | 19.48 | 1.51 | 20.33 | 13.40 |
| 180 mg q12 h (Nation et al.) | 85.55 | 8.99 | 73.14 | 97.91 | 69.2 | 87.87 | 97.91 | 97.91 | 92.25 | 88.69 | 8.99 | 2.2 | 15.08 | 24.09 | 2.2 | 24.18 | 16.18 |
| 150 mg q8 h (Siriraj) | 90.07 | 19.48 | 78.56 | 98.68 | 79.7 | 92.02 | 98.68 | 98.68 | 95.06 | 92.58 | 19.48 | 7.02 | 25.45 | 39.3 | 7.02 | 35.99 | 26.71 |
| CrCl 51 to 79 mL/min | |||||||||||||||||
| 114 mg q12 h (FDA) | 87.96 | 9.8 | 74.90 | 95.95 | 71.98 | 89.91 | 95.95 | 95.95 | 94.07 | 90.69 | 9.8 | 2.36 | 15.94 | 25.05 | 2.36 | 25.26 | 17.06 |
| 150 mg q12 h (Siriraj, EMA, Nation et al) | 91.66 | 13.73 | 77.96 | 97.26 | 78.32 | 92.65 | 97.26 | 97.26 | 95.82 | 93.24 | 13.73 | 3.8 | 20.53 | 32.72 | 3.8 | 31.22 | 21.81 |
| CrCl 30 to 50 mL/min | |||||||||||||||||
| 150 mg q24 h (FDA) | 90.53 | 3.58 | 74.65 | 97.55 | 71.1 | 91..27 | 97.55 | 97.55 | 95.58 | 92.07 | 3.58 | 0.39 | 10.05 | 15.59 | 0.39 | 18.84 | 11.10 |
| 100 mg q12 h (Siriraj) | 95.34 | 18.09 | 81.26 | 98.89 | 85.65 | 95.74 | 98.89 | 98.89 | 97.90 | 96.14 | 18.09 | 5.58 | 25 | 38.9 | 5.58 | 36.58 | 26.39 |
| 110 mg q12 h (Nation et al.) | 96.29 | 20.03 | 82.17 | 99.03 | 87.43 | 96.35 | 99.03 | 99.03 | 98.19 | 96.70 | 20.03 | 6.41 | 27.05 | 42.66 | 6.41 | 39.01 | 28.48 |
| 125 mg q12 h (EMA) | 97.71 | 23.65 | 83.51 | 99.15 | 89.8 | 97.18 | 99.15 | 99.15 | 98.52 | 97.43 | 23.65 | 8.09 | 30.41 | 46.87 | 8.09 | 42.66 | 31.87 |
| CrCl 11 to 29 mL/min | |||||||||||||||||
| 60 mg q24 h (FDA) | 83.41 | 3.57 | 70.63 | 96.33 | 56.2 | 86.26 | 96.33 | 96.33 | 97.91 | 87.56 | 3.57 | 0.42 | 8.11 | 13.11 | 0.42 | 14.41 | 8.87 |
| 150 mg q24 h (EMA, Siriraj) | 97.92 | 11.16 | 81.45 | 99.67 | 89.35 | 97.44 | 99.67 | 99.67 | 99.61 | 97.73 | 11.16 | 2.02 | 20.20 | 33.24 | 2.02 | 33.27 | 21.77 |
| 180 mg q24 h (Nation et al.) | 97.93 | 11.23 | 81.45 | 99.63 | 89.32 | 97.41 | 99.63 | 99.63 | 99.93 | 97.70 | 11.23 | 1.94 | 20.29 | 33.41 | 1.94 | 33.4 | 21.87 |
| CrCl≤10 mL/min | |||||||||||||||||
| 60 mg q24 h (FDA) | 94.94 | 11.81 | 78.82 | 99.5 | 77.09 | 94.47 | 99.5 | 99.5 | 99.99 | 95.11 | 11.81 | 2.61 | 17.88 | 28.19 | 2.61 | 27.44 | 19.03 |
| 120 mg q24 h (EMA) | 99.34 | 21.74 | 84.70 | 99.94 | 94.92 | 98.91 | 99.94 | 99.94 | 99.99 | 99.04 | 21.74 | 5.98 | 29.99 | 48.29 | 5.98 | 43.72 | 31.63 |
| 150 mg q24 h (Nation et al.) | 99.76 | 28.36 | 86.51 | 99.98 | 97.4 | 99.47 | 99.98 | 99.98 | 100 | 99.54 | 28.36 | 8.69 | 36.24 | 57.76 | 8.69 | 50.55 | 37.96 |
| All Isolates | Colistin-Susceptible Isolates | Colistin-Resistant Isolates | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| %CFR | Colistin-Susceptible K. pneumoniae Subgroup | Colistin-Susceptible E. coli Subgroup | %CFR for all Sus-Ceptible Isolates | Colistin-Resistant K. pneumoniae Subgroup | Colistin-Resistant E. coli Subgroup | %CFR for all Resistant Isolates | |||||||||||
| %PTA | %PTA | %CFR | %PTA | %CFR | %PTA | %CFR | %PTA | %CFR | |||||||||
| MIC (mcg/mL) | MIC50 | MIC90 | MIC50 | MIC90 | MIC50 | MIC90 | MIC50 | MIC90 | MIC50 | MIC90 | |||||||
| 1 | 16 | 0.5 | 2 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 16 | 32 | 8 | 32 | ||||||||
| CrCl ≥80 mL/min | |||||||||||||||||
| 180 mg q8h | 92.88 | 23.74 | 80.80 | 97.19 | 83.61 | 93.83 | 97.19 | 97.19 | 96.14 | 92.58 | 23.74 | 9.17 | 29.55 | 45.2 | 9.17 | 40.54 | 30.87 |
| CrCl 51 to 79 mL/min | |||||||||||||||||
| 100 mg q8 h | 92.96 | 23.43 | 80.60 | 97.36 | 82.62 | 93.77 | 97.36 | 97.36 | 96.23 | 94.23 | 23.43 | 9.4 | 28.79 | 43.67 | 9.4 | 39.25 | 30.05 |
| 180 mg q12 h | 93.43 | 18.04 | 80.15 | 97.82 | 83.54 | 94.31 | 97.82 | 97.82 | 96.72 | 94.76 | 18.04 | 5.7 | 24.88 | 39.23 | 5.7 | 36.31 | 26.25 |
| 150 mg q8 h | 96.39 | 34.52 | 85.01 | 98.79 | 89.88 | 96.68 | 98.79 | 98.79 | 98.12 | 96.94 | 34.52 | 15.78 | 38.86 | 56.93 | 15.78 | 49.72 | 40.16 |
| 180 mg q8 h | 97.13 | 39.07 | 86.51 | 99.15 | 92.05 | 97.44 | 99.15 | 99.15 | 98.61 | 97.65 | 39.07 | 19.36 | 43.05 | 61.77 | 19.36 | 54.16 | 44.38 |
| CrCl 30 to 50 mL/min | |||||||||||||||||
| 100 mg q8 h | 98.54 | 40.8 | 87.65 | 99.64 | 94.49 | 98.48 | 99.64 | 99.64 | 99.27 | 98.63 | 40.8 | 20.09 | 44.71 | 64.06 | 20.09 | 55.97 | 46.06 |
| 150 mg q12 h | 97.9 | 27.61 | 84.91 | 99.41 | 92.44 | 97.84 | 99.41 | 99.41 | 98.91 | 98.04 | 27.61 | 9..97 | 34.47 | 53.71 | 9.97 | 47.36 | 36.01 |
| 180 mg q12 h | 98.52 | 33.25 | 86.48 | 99.67 | 94.6 | 98.51 | 99.67 | 99.67 | 99.30 | 98.66 | 33.25 | 13.25 | 39.30 | 60.3 | 13.25 | 52.09 | 40.84 |
| 150 mg q8 h | 99.33 | 54.13 | 90.59 | 99.76 | 97.29 | 99.23 | 99.76 | 99.76 | 99.59 | 99.30 | 54.13 | 29.89 | 55.53 | 76.01 | 29.89 | 65.64 | 56.75 |
| 180 mg q8 h | 99.41 | 60.87 | 91.96 | 99.9 | 97.97 | 99.44 | 99.9 | 99.9 | 99.76 | 99.50 | 60.87 | 35.86 | 60.93 | 81.54 | 35.86 | 70.26 | 62.05 |
| CrCl 11 to 29 mL/min | |||||||||||||||||
| 150 mg q12 h | 99.76 | 50.76 | 90.39 | 99.91 | 98.35 | 99.60 | 99.91 | 99.91 | 99.81 | 99.64 | 50.76 | 25.25 | 53.34 | 76.03 | 25.25 | 64.55 | 54.68 |
| 180 mg q12 h | 99.83 | 57.93 | 91.71 | 99.97 | 99.06 | 99.78 | 99.97 | 99.97 | 99.91 | 99.80 | 57.93 | 30.34 | 58.70 | 81.51 | 30.34 | 68.9 | 59.93 |
| 150 mg q8 h | 99.91 | 75.28 | 94.91 | 99.96 | 99.57 | 99.88 | 99.96 | 99.96 | 99.93 | 99.89 | 75.28 | 52.4 | 72.87 | 91.10 | 52.4 | 80.38 | 73.77 |
| 180 mg q8 h | 99.93 | 80.65 | 95.87 | 100 | 99.63 | 99.92 | 100 | 100 | 99.97 | 99.93 | 80.65 | 59.11 | 77.09 | 93.47 | 59.11 | 83.57 | 77.87 |
| CrCl≤10 mL/min | |||||||||||||||||
| 180 mg q24 h | 99.89 | 33.88 | 87.73 | 100 | 98.53 | 99.72 | 100 | 100 | 99.91 | 99.75 | 33.88 | 10.94 | 40.91 | 64.74 | 10.94 | 54.99 | 42.60 |
| 100 mg q12 h | 99.93 | 59.11 | 92.02 | 99.98 | 99.18 | 99.83 | 99.98 | 99.98 | 99.93 | 99.85 | 59.11 | 34.22 | 59.95 | 81.32 | 34.22 | 70.5 | 61.16 |
| 100 mg q8 h | 99.99 | 81.59 | 96.14 | 100 | 99.79 | 99.96 | 100 | 100 | 99.99 | 99.96 | 81.59 | 61.67 | 78.21 | 93.13 | 61.67 | 84.47 | 78.96 |
| 150 mg q12 h | 99.98 | 71.94 | 94.13 | 100 | 99.84 | 99.98 | 100 | 100 | 99.99 | 99.97 | 71.94 | 46.32 | 69.86 | 89.74 | 46.32 | 78.00 | 70.84 |
| 180 mg q12 h | 99.98 | 77.7 | 95.30 | 100 | 99.90 | 99.97 | 100 | 100 | 99.99 | 99.98 | 77.7 | 52.76 | 74.31 | 92.85 | 52.76 | 81.47 | 75.17 |
| 150 mg q8 h | 99.99 | 89.51 | 97.76 | 100 | 99.97 | 99.99 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 99.99 | 89.51 | 74.47 | 85.46 | 97.26 | 74.47 | 90.46 | 86.06 |
| 180 mg q8 h | 99.99 | 92.31 | 98.30 | 100 | 99.94 | 99.99 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 99.99 | 92.31 | 78.66 | 87.97 | 98.18 | 78.66 | 92.19 | 88.48 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jitaree, K.; Sathirakul, K.; Houngsaitong, J.; Asuphon, O.; Saelim, W.; Thamlikitkul, V.; Montakantikul, P. Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) Simulation for Dosage Optimization of Colistin Against Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae and Carbapenem-Resistant Escherichia coli. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8030125
Jitaree K, Sathirakul K, Houngsaitong J, Asuphon O, Saelim W, Thamlikitkul V, Montakantikul P. Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) Simulation for Dosage Optimization of Colistin Against Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae and Carbapenem-Resistant Escherichia coli. Antibiotics. 2019; 8(3):125. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8030125
Chicago/Turabian StyleJitaree, Kamonchanok, Korbtham Sathirakul, Jantana Houngsaitong, Orarik Asuphon, Weerayuth Saelim, Visanu Thamlikitkul, and Preecha Montakantikul. 2019. "Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) Simulation for Dosage Optimization of Colistin Against Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae and Carbapenem-Resistant Escherichia coli" Antibiotics 8, no. 3: 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8030125
APA StyleJitaree, K., Sathirakul, K., Houngsaitong, J., Asuphon, O., Saelim, W., Thamlikitkul, V., & Montakantikul, P. (2019). Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) Simulation for Dosage Optimization of Colistin Against Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae and Carbapenem-Resistant Escherichia coli. Antibiotics, 8(3), 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8030125






