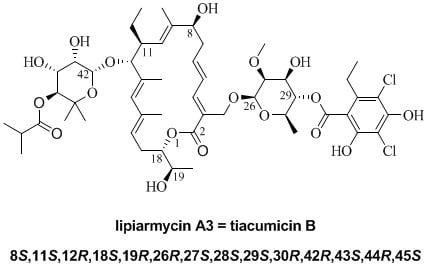
Final Demonstration of the Co-Identity of Lipiarmycin A3 and Tiacumicin B (Fidaxomicin) through Single Crystal X-ray Analysis
Abstract
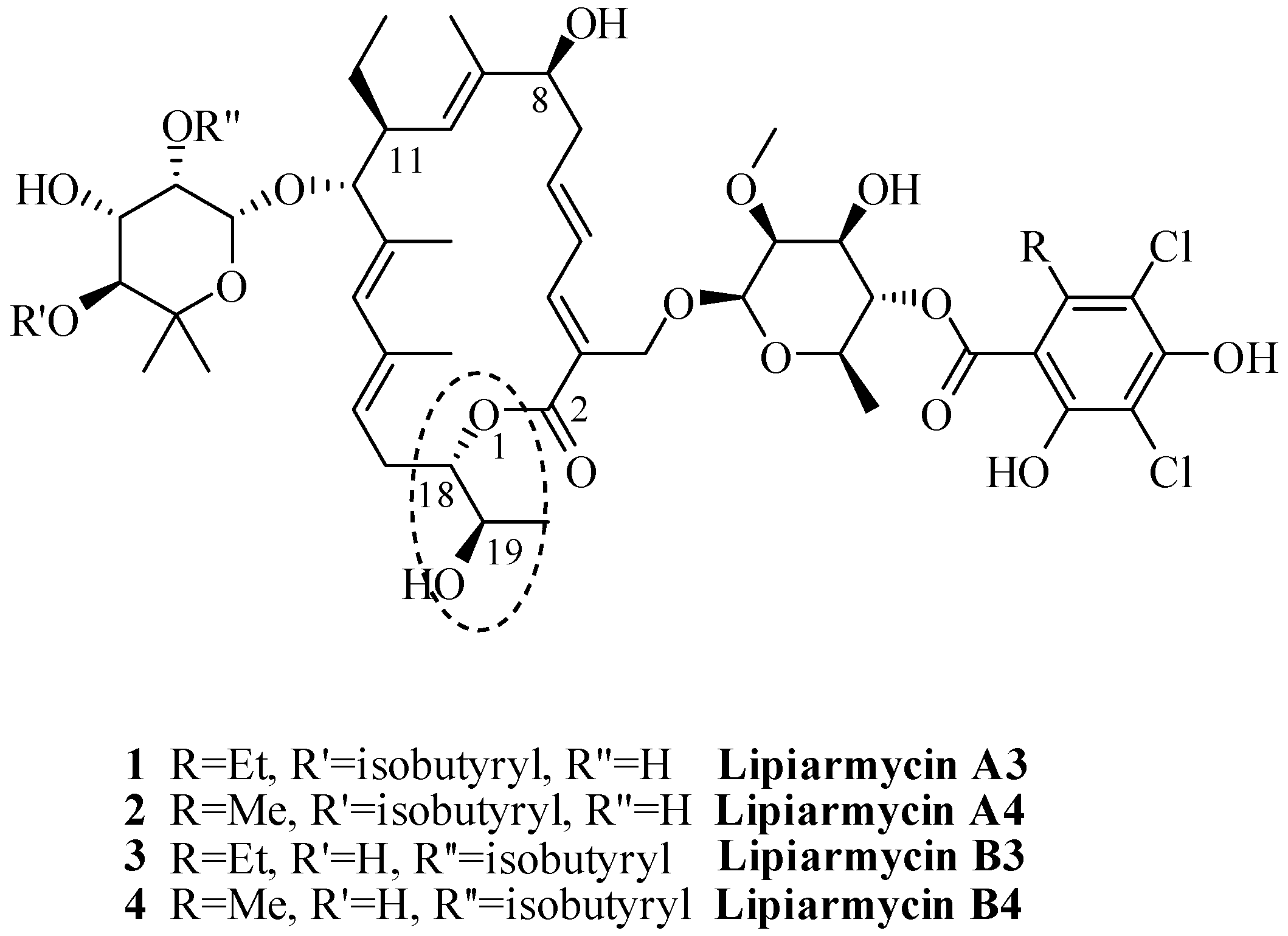
:1. Introduction
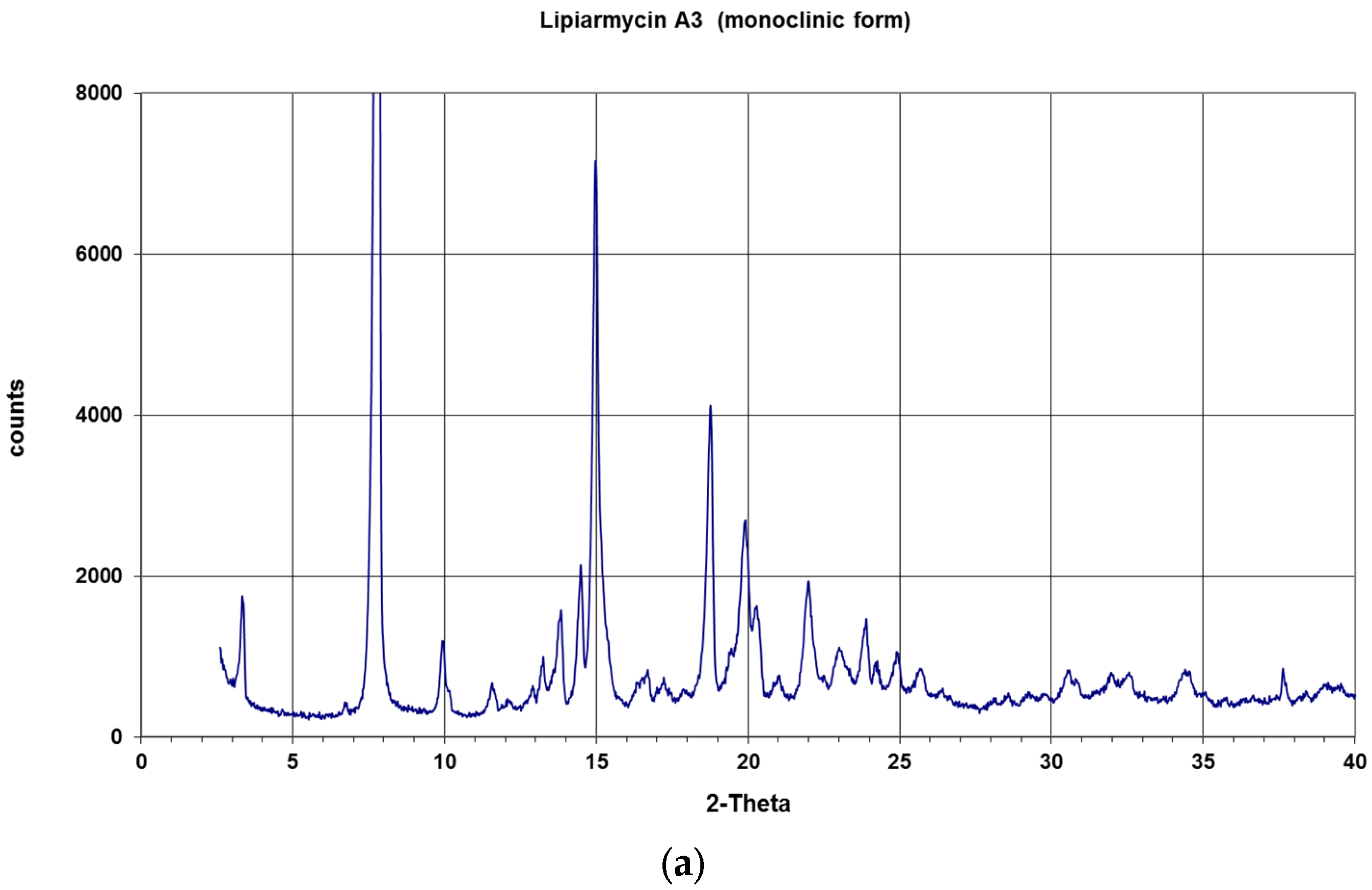
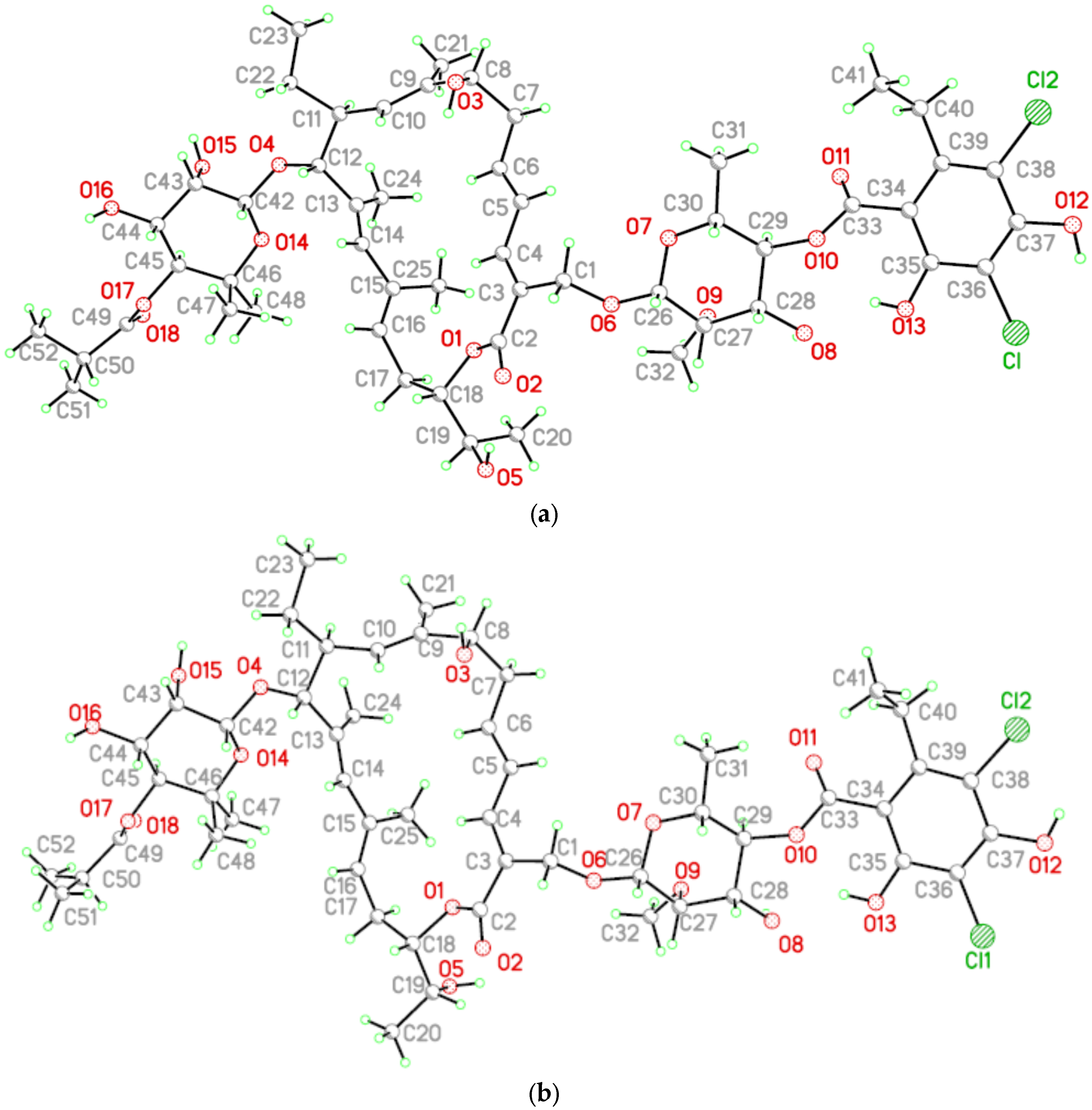
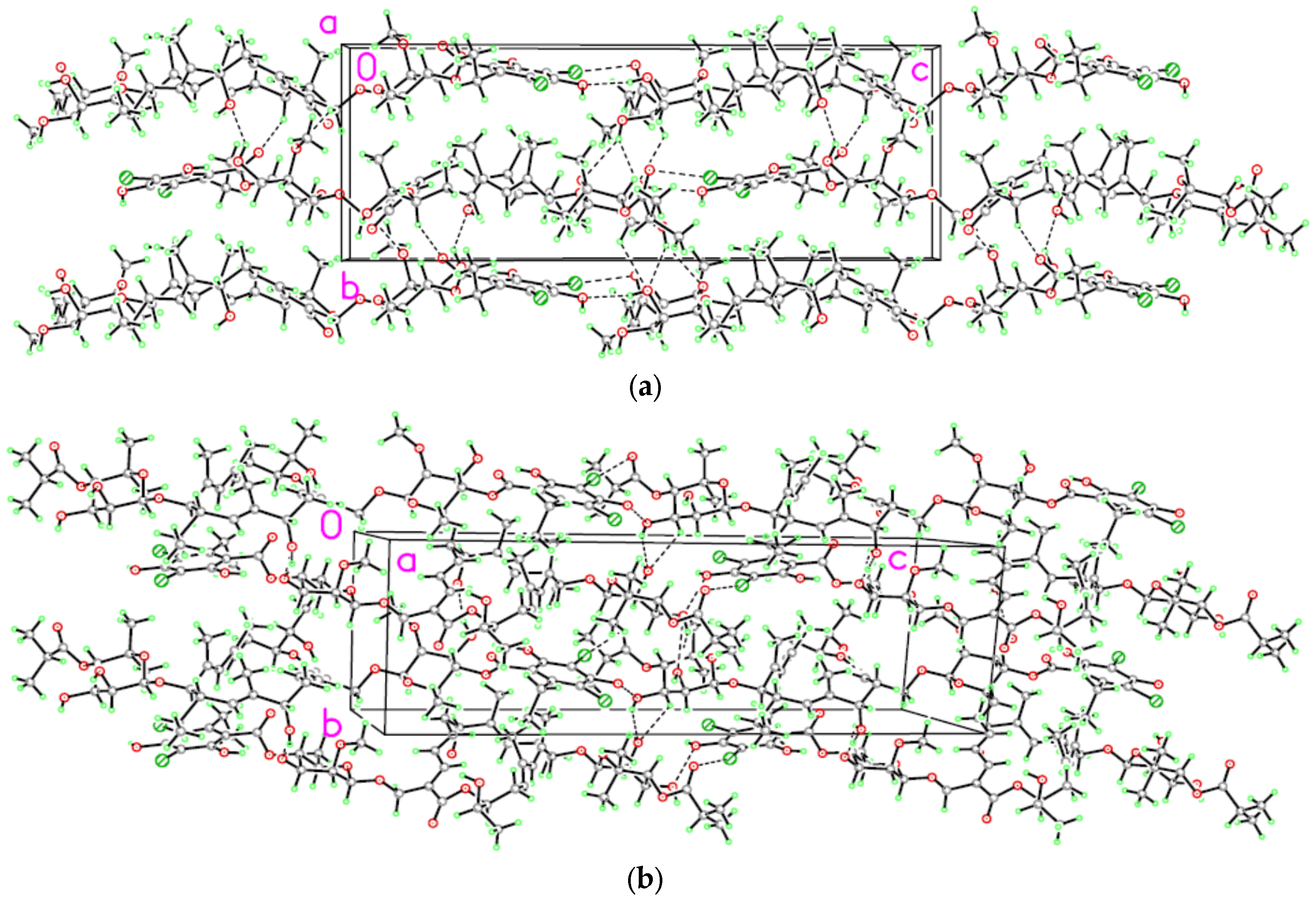
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Single Crystal Structure Determination
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parenti, F.; Pagani, H.; Beretta, G. Lipiarmycin, a new antibiotic from Actinoplanes I. Description of the producer strain and fermentation studies. J. Antibiot. 1975, 28, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coronelli, C.; White, R.J.; Lancini, G.C.; Parenti, F. Lipiarmycin, a new antibiotic from Actinoplanes II. Isolation, chemical, biological and biochemical characterization. J. Antibiot. 1975, 28, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Somma, S.; Pirali, G.; White, R.; Parenti, F. Lipiarmycin, a new antibiotic from Actinoplanes III. Mechanism of action. J. Antibiot. 1975, 28, 543–549. [Google Scholar]
- Martinelli, E.; Faniuolo, L.; Tuan, G.; Gallo, G.G.; Cavalleri, B. Structural studies on lipiarmycin I. Characterization by 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy and isolation of methyl 2-O-methyl-4-O-homodichloroorsellinate-β-rhamnoside. J. Antibiot. 1983, 36, 1312–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnone, A.; Nasini, G.; Cavalleri, B. Structure elucidation of the macrocyclic antibiotic lipiarmycin. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1987, 1353–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalleri, B.; Arnone, A.; Dimodugno, E.; Nasini, G.; Goldstein, B.P. Structure and biological-activity of lipiarmycin-B. J. Antibiot. 1988, 41, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omura, S.; Imamura, N.; Oiwa, R.; Kuga, H.; Iwata, R.; Masuma, R.; Iwai, Y. Clostomicins, new antibiotics produced by Micromonospora echinospora subsp. armeniaca subsp. Nov. I. Production, isolation, and physical-chemical and biological properties. J. Antibiot. 1986, 39, 1407–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theriault, R.J.; Karwowski, J.P.; Jackson, M.; Girolami, R.L.; Sunga, G.N.; Vojtko, C.M.; Coen, L.J. Tiacumicins, a novel complex of 18-membered macrolide antibiotics. 1. Taxonomy, fermentation and antibacterial activity. J. Antibiot. 1987, 40, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, R.N.; Hardy, D.J.; Shipkowitz, N.L.; Hanson, C.W.; Ramer, N.C.; Fernandes, P.B.; Clement, J.J. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of tiacumicins B and C against Clostridium difficile. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1991, 35, 1108–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lancaster, J.W.; Matthews, S.J. Fidaxomicin: The newest addition to the armamentarium against Clostridium difficile infections. Clin. Ther. 2012, 34, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornely, O.A.; Nathwani, D.; Ivanescu, C.; Odufowora-Sita, O.; Retsa, P.; Odeyemi, I.A.O. Clinical efficacy of fidaxomicin compared with vancomycin and metronidazole in Clostridium difficile infections: A meta-analysis and indirect treatment comparison. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 2892–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shue, Y.-K.; Hwang, C.-K.; Chiu, Y.-H.; Romero, A.; Babakhani, F.; Sears, P.; Okumu, F. 18-Membered Macrocycles and Analogs Thereof. WO 2006/085838, 17 August 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ihle, T.N.C.; Guzei, I.A.; Rheingold, A.L. CCDC 100349: Experimental Crystal Structure Determination. CCDC Accession Number 114782. Available online: https://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/structures-beta/Search?Ccdcid=114782 (accessed on 5 December 2016).
- Erb, W.; Zhu, J. From natural product to marketed drug: The tiacumicin odyssey. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2013, 30, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurabachew, M.; Lu, S.H.J.; Krastel, P.; Schmitt, E.K.; Suresh, B.L.; Goh, A.; Knox, J.E.; Ma, N.L.; Jiricek, J.; Beer, D.; et al. Lipiarmycin targets RNA polymerase and has good activity against multidrug-resistant strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008, 62, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedeschi, A.; Fonte, P.; Fronza, G.; Fuganti, C.; Serra, S. The co-identity of lipiarmycin A3 and tiacumicin B. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2014, 9, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Erb, W.; Grassot, J.-M.; Linder, D.; Neuville, L.; Zhu, J. Enantioselective synthesis of putative lipiarmycin aglycon related to fidaxomicin/tiacumicin B. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2015, 54, 1929–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyatake-Ondozabal, H.; Kaufmann, E.; Gademann, K. Total synthesis of the protected aglycon of fidaxomicin (tiacumicin B, lipiarmycin A3). Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2015, 54, 1933–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaus, F.; Altmann, K.-H. Total synthesis of the tiacumicin B (lipiarmycin A3/fidaxomicin) aglycone. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2015, 54, 1937–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufmann, E.; Hattori, H.; Miyatake-Ondozabal, H.; Gademann, K. Total synthesis of the glycosylated macrolide antibiotic fidaxomicin. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 3514–3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flack, H.D. On enantiomorph-polarity estimation. Acta Crystallogr. 1983, 39, 876–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altomare, A.; Burla, M.C.; Camalli, M.; Cascarano, G.L.; Giacovazzo, C.; Guagliardi, A.; Moliterni, A.G.G.; Polidori, P.; Spagna, R. SIR97: A new tool for crystal structure determination and refinement. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1999, 32, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Program for the Refinement of Crystal Structures; University of Göttingen: Göttingen, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]


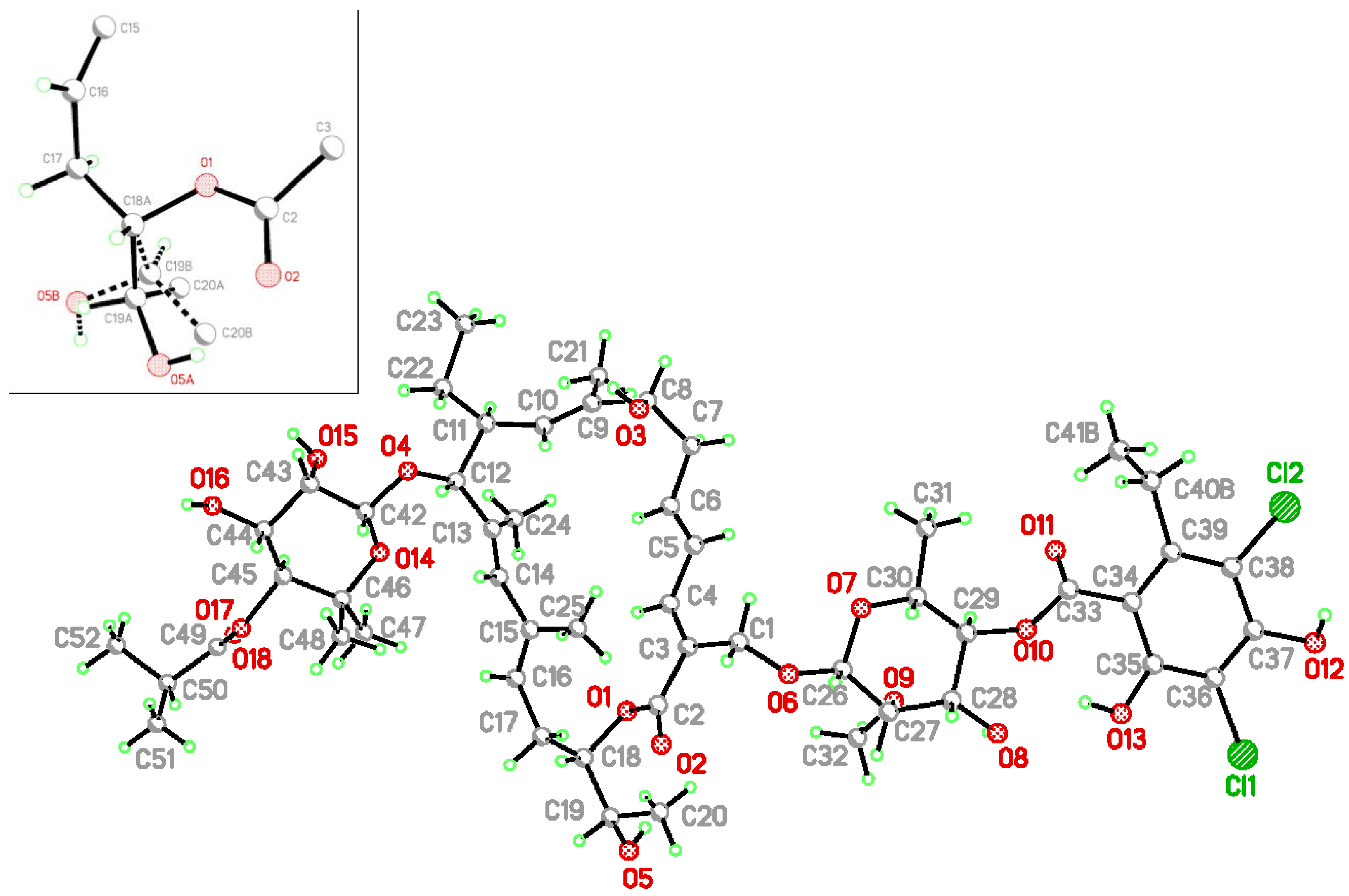
| C−Cl···O | C−Cl | Cl···O | C−Cl···O | |
| (I) | ||||
| C36−Cl1···O18 i | 1.724(3) | 3.233(4) | 170.0(1) | |
| (II) | ||||
| C36A−Cl1A···O18A ii | 1.743(4) | 3.158(4)(4) | 161.8(2) | |
| C36B−Cl1B···O18B i | 1.723(5) | 3.033(9) | 162.4(3) | |
| D−H...A | d(D−H) | d(H···A) | d(D···A) | D−H···A |
| (I) | ||||
| O8−H8O···O9 | 0.84 | 2.28 | 2.719(2) | 112.9 |
| O13-H13O···O10 | 0.84 | 2.10 | 2.736(2) | 132.5 |
| O13-H13O···O8 | 0.84 | 2.18 | 2.907(2) | 144.5 |
| O15-H15O···O12 iii | 0.84 | 2.20 | 2.883(2) | 138.7 |
| O16-H16O···O15 iv | 0.84 | 2.24 | 2.954(3) | 143.6 |
| O16-H16O···O14 iv | 0.84 | 2.49 | 3.211(3) | 144.7 |
| (II) | ||||
| O3A-H3OA...O8B v | 0.84 | 2.187 | 2.754(3) | 124.8 |
| O8A-H8OA...O3B ii | 0.84 | 2.166 | 2.831(3) | 136.0 |
| O12A-H12O...O16A ii | 0.84 | 2.037 | 2.752(4) | 142.6 |
| O13A-H13O...O8A | 0.84 | 2.040 | 2.773(4) | 145.4 |
| O16A-H16O...O15B vi | 0.84 | 2.170 | 2.940(3) | 154.0 |
| O3B-H3OB...O5B vii | 0.84 | 2.187 | 2.754(3) | 124.8 |
| O8B-H8OB...O3A viii | 0.84 | 1.950 | 2.769(4) | 164.6 |
| O13B-H13O...O8B | 0.84 | 2.087 | 2.809(4) | 143.7 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Serra, S.; Malpezzi, L.; Bedeschi, A.; Fuganti, C.; Fonte, P. Final Demonstration of the Co-Identity of Lipiarmycin A3 and Tiacumicin B (Fidaxomicin) through Single Crystal X-ray Analysis. Antibiotics 2017, 6, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics6010007
Serra S, Malpezzi L, Bedeschi A, Fuganti C, Fonte P. Final Demonstration of the Co-Identity of Lipiarmycin A3 and Tiacumicin B (Fidaxomicin) through Single Crystal X-ray Analysis. Antibiotics. 2017; 6(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics6010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleSerra, Stefano, Luciana Malpezzi, Angelo Bedeschi, Claudio Fuganti, and Piera Fonte. 2017. "Final Demonstration of the Co-Identity of Lipiarmycin A3 and Tiacumicin B (Fidaxomicin) through Single Crystal X-ray Analysis" Antibiotics 6, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics6010007
APA StyleSerra, S., Malpezzi, L., Bedeschi, A., Fuganti, C., & Fonte, P. (2017). Final Demonstration of the Co-Identity of Lipiarmycin A3 and Tiacumicin B (Fidaxomicin) through Single Crystal X-ray Analysis. Antibiotics, 6(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics6010007