From Erythromycin to Azithromycin and New Potential Ribosome-Binding Antimicrobials
Abstract
:1. Introduction
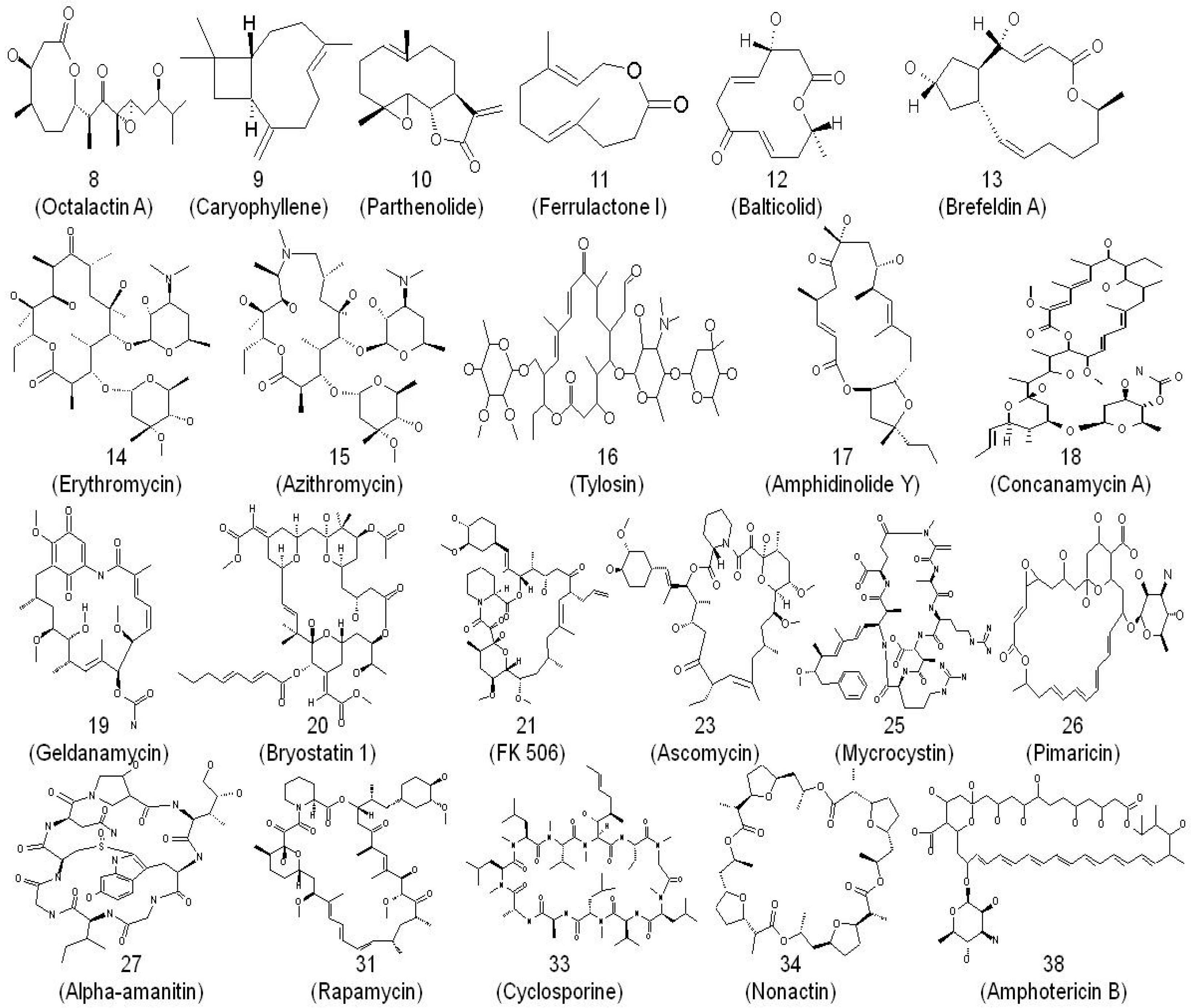
2. Macrolides and Their Mode of Action as Anti-Infectives
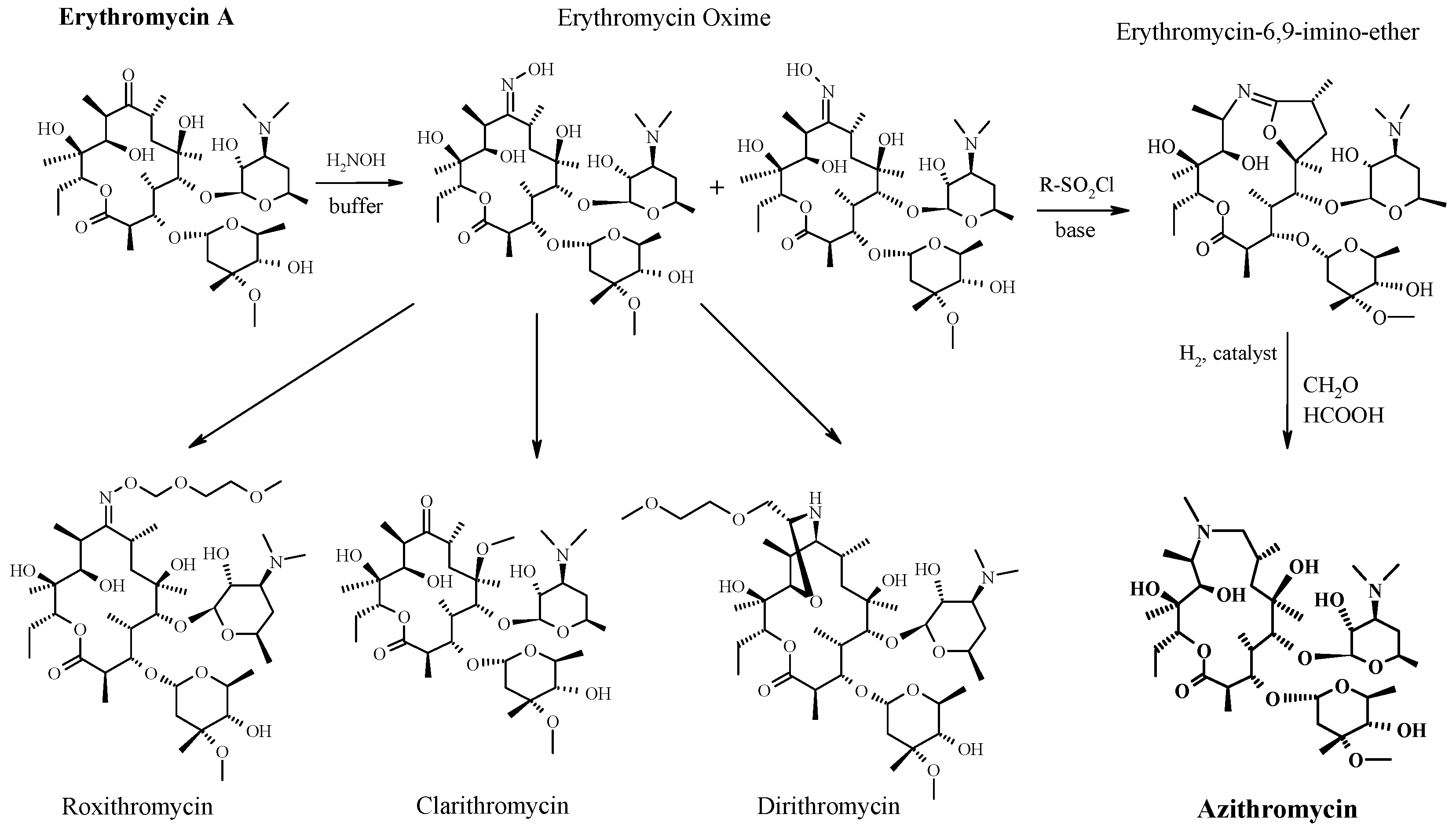
3. From Erythromycin to Azithromycin
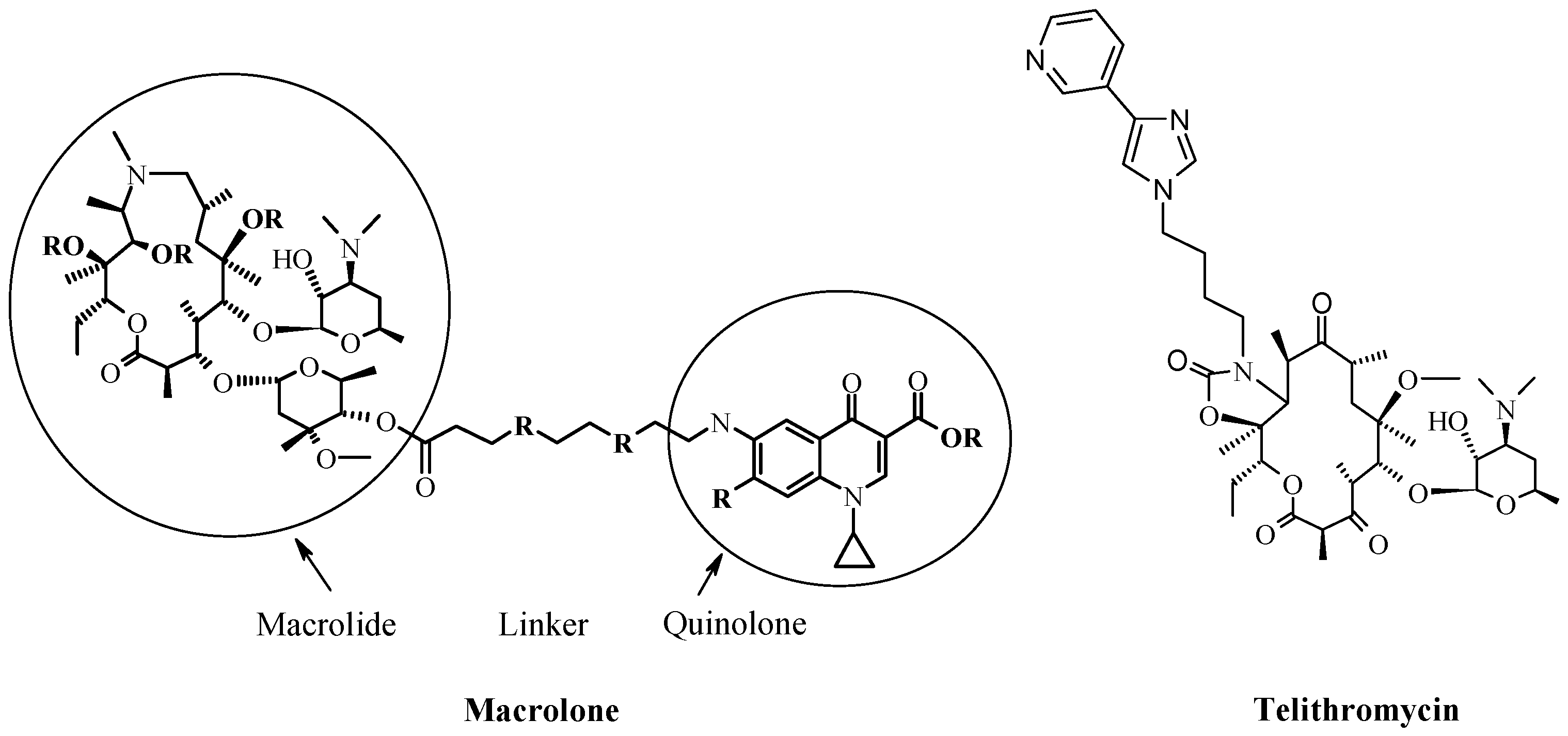
4. New Macrocyclic Ribosome Inhibitors as Possible Way to Avoid Resistance Problem
5. Concluding Remarks
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| rRNA | ribosomal Ribonucleic acid |
| tRNA | transfer Ribonucleic acid |
| MIC | Minimal inhibitory concentration |
| i.v | Intravenous injection, a route of administration of a drug |
| p.o | Per oral, a route of administration of a drug |
| LD50 | The median lethal dose |
| EryS | Erythromycin susceptible |
| EryR | Erythromycin resistant |
| MLSb | Macrolide-Lincosamide-Streptogramin b |
References
- Labro, M.T. Anti-inflammatory activity of macrolides: A new therapeutic potential? J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1998, 41, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labro, M.T. Macrolide antibiotics: Current and future uses. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2004, 5, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čulić, O.; Eraković, V.; Parnham, M.J. Anti-inflammatory effects of macrolide antibiotics. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 429, 209–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amsden, G.W. Anti-inflammatory effects of macrolides—An underappreciated benefit in the treatment of community-acquired respiratory tract infections and chronic inflammatory pulmonary conditions? J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2005, 55, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sassa, K.; Mizushima, Y.; Fujishita, T.; Oosaki, R.; Kobayashi, M. Therapeutic effect of clarithromycin on a transplanted tumor in rats. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1999, 43, 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Bukvić Krajačić, M.; Perić, M.; Smith, K.S.; Ivezić Schönfeld, Z.; Žiher, D.; Fajdetić, A.; Kujundžić, N.; Schönfeld, W.; Landek, G.; Padovan, J.; et al. Synthesis, structure-activity relationship, and antimalarial activity of ureas and thioureas of 15-membered azalides. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 3595–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perić, M.; Fajdetić, A.; Rupčić, R.; Alihodžić, S.; Žiher, D.; Bukvić Krajačić, M.; Smith, K.S.; Ivezić-Schönfeld, Z.; Padovan, J.; Landek, G.; et al. Antimalarial activity of 9a-N substituted 15-membered azalides with improved in vitro and in vivo activity over azithromycin. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 1389–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolter, J.; Seeney, S.; Bell, S.; Bowler, S.; Masel, P.; McCormack, J. Effect of long term treatment with azithromycin on disease parameters in cystic fibrosis: a randomised trial. Thorax 2002, 57, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marjanović, N.; Bosnar, M.; Michielin, F.; Willé, D.R.; Anić-Milić, T.; Čulić, O.; Popović-Grle, S.; Bogdan, M.; Parnham, M.J.; Eraković Haber, V. Macrolide antibiotics broadly and distinctively inhibit cytokine and chemokine production by COPD sputum cells in vitro. Pharmacol. Res. 2011, 63, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piacentini, G.L.; Peroni, D.G.; Bodini, A.; Pigozzi, R.; Costella, S.; Loiacono, A.; Boner, A.L. Azithromycin reduces bronchial hyperresponsiveness and neutrophilic airway inflammation in asthmatic children: A preliminary report. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2007, 28, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernando-Sastre, V. Macrolide antibiotics in the treatment of asthma. An update. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2010, 38, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kino, T.; Hatanaka, H.; Hashimoto, M.; Nishiyama, M.; Goto, T.; Okuhara, M.; Kohsaka, M.; Aoki, H.; Imanaka, H. FK-506, a novel immunosuppressant isolated from a Streptomyces I. Fermentation, isolation, and physico-chemical and biological characteristics. J. Antibiot. 1987, 40, 1249–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vézina, C.; Kudelski, A.; Sehgal, S.N. Rapamycin (AY-22,989), a new antifungal antibiotic. J. Antibiot. 1975, 28, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandeputte, P.; Ferrari, S.; Coste, A.T. Antifungal resistance and new strategies to control fungal infections. Int. J. Microbiol. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omura, S.; Shiomi, K. Discovery, chemistry, and chemical biology of microbial products. Pure Appl. Chem. 2007, 79, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacar, O.; Sriamornsak, P.; Dass, C.R. Doxorubicin: An update on anticancer molecular action, toxicity and novel drug delivery systems. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2013, 65, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecht, S.M. Bleomycin: New perspectives on the mechanism of action. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omura, S. Macrolide Antibiotics. Chemistry, Biology and Practice; Academic Press Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman, H.E. Spiramycin. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1961, 66, 609–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, S.K.; Lassman, H.B. Roxithromycin: A pharmacokinetic review of a macrolide. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1987, 20, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, P.B.; Hardy, D.J. Comparative in vitro potencies of nine new macrolides. Drugs Exp. Clin. Res. 1988, 14, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, Y.; Morimoto, S.; Adachi, T.; Kashimura, M.; Asaka, T. Selective methylation at the C-6 hydroxyl group of erythromycin A oxime derivatives and preparation of clarithromycin. J. Antibiot. 1993, 46, 647–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlünzen, F.; Zarivach, R.; Harms, J.; Bashan, A.; Tocilj, A.; Albrecht, R.; Yonath, A.; Franceschi, F. Structural basis for the interaction of antibiotics with the peptidyl transferase centre in eubacteria. Nature 2001, 413, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petropoulos, A.D.; Kouvela, E.C.; Starosta, A.L.; Wilson, D.N.; Dinos, G.P. Time-resolved binding of azithromycin to Excherichia coli ribosomes. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 385, 1179–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrov, A.S.; Bernier, C.R.; Hershkovits, E.; Xue, Y.; Waterbury, C.C.; Hsiao, C.; Stepanov, V.G.; Gaucher, E.A.; Grover, M.A.; Harvey, S.C.; et al. Secondary structure and domain architecture of the 23S and 5S rRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 7522–7535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlünzen, F.; Harms, J.M.; Franceschi, F.; Hansen, A.S.; Bartels, H.; Zarivach, R.; Yonath, A. Structural basis for the antibiotic activity of ketolides and azalides. Structure 2003, 11, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajdetić, A.; Cipcić Paljetak, H.; Lazarevski, G.; Hutinec, A.; Alihodzić, S.; Derek, M.; Stimac, V.; Andreotti, D.; Sunjić, V.; Berge, J.M.; et al. 4″-O-(omega-Quinolylamino-alkylamino)propionyl derivatives of selected macrolides with the activity against the key erythromycin resistant respiratory pathogens. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 6559–6568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fajdetić, A.; Vinter, A.; Paljetak, H.Č.; Padovan, J.; Jakopović, I.P.; Kapić, S.; Alihodžić, S.; Filić, D.; Modrić, M.; Košutić-Hulita, N.; et al. Synthesis, activity and pharmacokinetics of novel antibacterial 15-membered ring macrolones. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 3388–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapić, S.; Cipčić Paljetak, H.; Palej Jakopović, I.; Fajdetić, A.; Ilijaš, M.; Stimac, V.; Brajša, K.; Holmes, D.J.; Berge, J.; Alihodžić, S. Synthesis of macrolones with central piperazine ring in the linker and its influence on antibacterial activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 7281–7298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amsden, G.W. Advanced-generation macrolides: Tissue-directed antibiotics. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2001, 18, S11–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelić, D.; Mutak, S.; Lazarevski, G. The azithromycin success story. In Medicinal Chemistry in Drug Discovery. Design, Synthesis and Screening; Research Signpost: Kerala, India, 2013; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Gaynor, M.; Mankin, A.S. Macrolide antibiotics: Binding site, mechanism of action, resistance. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2003, 3, 949–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulkley, D.; Innis, C.A.; Blaha, G.; Steitz, T.A. Revisiting the structures of several antibiotics bound to the bacterial ribosome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 17158–17163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornish, P.V.; Ermolenko, D.N.; Noller, H.F.; Ha, T. Spontaneous intersubunit rotation in single ribosomes. Mol. Cell 2008, 30, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ban, N.; Nissen, P.; Hansen, J.; Moore, P.B.; Steitz, T.A. The complete atomic structure of the large ribosomal subunit at 2.4 A resolution. Science 2000, 289, 905–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harms, J.; Schluenzen, F.; Zarivach, R.; Bashan, A.; Gat, S.; Agmon, I.; Bartels, H.; Franceschi, F.; Yonath, A. High resolution structure of the large ribosomal subunit from a mesophilic eubacterium. Cell 2001, 107, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonath, A. Antibiotics targeting ribosomes: Resistance, selectivity, synergism, and cellular regulation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2005, 74, 649–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Zhang, C.; Qin, P.; Cornish, V.P.; Xu, D. RNA-protein distance patterns in ribosomes reveal the mechanism of translational attenuation. Sci. China Life Sci. 2014, 57, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Rodnina, M.V.; Wintermayer, W. Peptide bond formation on the ribosome structure and mechanism. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2003, 13, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, T. Drugs targeting the ribosome. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2005, 15, 335–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leclercq, R. Macrolides, lincosamides, and streptogramins. In Antibiogram; Courvalin, P., Leclercq, R., Rice, L., Eds.; ESKA: Portland, OR, USA, 2010; pp. 305–326. [Google Scholar]
- Djokić, S.; Kobrehel, G.; Lopotar, N.; Kamenar, B.; Nagl, A.; Mrvos, D. Erythromycin series. Part 13. Synthesis and structure elucidation of 10-dihydro-10-deoxo-11-methyl-11-azaerythromycin A. J. Chem. Res. 1988, 1988, 152–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirst, H.A. Macrolide Antibiotics; Schoenfeld, W., Kirst, H.A., Eds.; Birkhauser Verlag: Basel, Switzerland, 2002; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Neu, H.C.; Young, L.S.; Zinner, S.H.; Acar, J.F. New Macrolides, Azalides and Streptogramins in Clinical Practice; Dekker, M., Ed.; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Schoenfeld, W.; Mutak, S. Macrolide Antibiotics; Schoenfeld, W., Kirst, H.A., Eds.; Birkhauser Verlag: Basel, Switzerland, 2002; p. 96. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.V.; Goldsmith, M.; Rizzi, A. A novel product from Beckmann rearrangement of erythromycin A 9(E)-oxime. Tetrahedron Lett. 1994, 55, 3025–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattori, R.; Pelacini, F.; Romagnano, S.; Fronza, G.; Rallo, R. Unusual isoxazoline formation by intramolecular cyclization of (9E)-erythromycin A oxime. J. Antibiot. 1996, 49, 938–940. [Google Scholar]
- Djokić, S.; Tamburasev, Z. 9-Amino-3-O-cladinosyl-6,11,12-trihydroxy 2,4,6,8,10,12-hexamethylpentadecane-13-olide. Tetrahedron Lett. 1967, 17, 1645–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobrehel, G.; Radobolja, G.; Tamburasev, Z.; Djokic, S. 11-Aza-10-Deozo-10-Dihydroerythromycin A and Derivatives Thereof as Well as a Process for their Preparation. U.S. Patent 4,328,334, 4 May 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Kobrehel, G.; Djokic, S. 11-Methyl-11-Aza-4-O-Cladinosyl-6-O-Desosamynyl-15-Ethyl-7,13,14-Trihydroxy-3,5,7,9,12,14-Hexamethyloxacyclopentadecane-2-One and Derivatives Thereof. U.S. Patent 4,517,359, 14 May 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Djokić, S.; Kobrehel, G.; Lazarevski, G.; Lopotar, N.; Tamburašev, Z.; Kamenar, B.; Nagl, A.; Vicković, I. Ring expansion of erythromycin A oxime by the Beckmann rearrangement. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. I 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Đokić, S. From erythromycin to azithromycin—From macrolides to azalides. PLIVA Saopć. 1988, 31, 1–2. (In Croatian) [Google Scholar]
- Mutak, S. Azalides from azithromycin to new azalide derivatives. J. Antibiot. 2007, 60, 85–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Retsema, J.; Girard, A.; Schelkly, W.; Manousos, M.; Anderson, M.; Bright, G.; Borovoy, R.; Brenan, L.; Mason, R. Spectrum and mode of action of azithromycin (CP-62,993), a new 15-membered-ring macrolide with improved potency against gram-negative organisms. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1987, 31, 1939–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeruva, L.; Melnyk, S.; Spencer, N.; Bowlin, A.; Rank, R.G. Differential susceptibilities to azithromycin treatment of chlamydial infection in the gastrointestinal tract and cervix. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 6290–6294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bright, G.M.; Nagel, A.A.; Bordner, J.; Desai, K.A.; Dibrino, J.N.; Nowakowska, J.; Vincent, L.; Watrous, R.M.; Sciavolino, F.C.; English, A.R.; et al. Synthesis, in vitro and in vivo activity of novel 9-deoxo-9a-aza-9a-homoerythromycin A derivatives; a new class of macrolide antibiotics, the azalides. J. Antibiot. 1988, 41, 1029–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girard, A.E.; Girard, D.; English, A.R.; Gotz, T.D.; Cimochowski, C.R.; Faiella, J.A.; Haskell, S.L.; Retsema, J.A. Pharmacokinetic and in vivo studies with azithromycin (CP-62,993), a new macrolide with an extended half-life and excellent tissue distribution. Antimicrob. Agent Chemother. 1987, 31, 1948–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foulds, G.; Shepard, R.M.; Johnson, R.B. The pharmacokinetics of azithromycin in human serum and tissues. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1990, 25, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, D.H.; Friedel, H.A.; McTavish, D. Azithromycin. A review of its antimicrobial activity, pharmacokinetic properties and clinical efficacy. Drugs 1992, 44, 750–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schönwald, S.; Skerk, V.; Petricevic, I.; Car, V.; Majerus-Misic, L.; Gunjaca, M. Comparison of three-day and five-day courses of azithromycin in the treatment of atypical pneumonia. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1991, 10, 877–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazarevski, G.; Vinković, M.; Kobrehel, G.; Đokic, S.; Metelko, B.; Vikić-Topić, D. Conformational analysis of azithromycin by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and molecular modelling. Tetrahedron 1993, 49, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiese, E.F.; Steffen, S.H. Comparison of the acid stability of azithromycin and erythromycin A. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1990, 25, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, J.L.; Ippolito, J.A.; Ban, N.; Nissen, P.; Moore, P.B.; Steitz, T.A. The structures of four macrolide antibiotics bound to the large ribosomal subunit. Mol. Cell 2002, 10, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, M.; Gregory, S.T.; Dahlberg, A.E. Multiple defects in translation associated with altered ribosomal protein L4. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 5750–5756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bailey, M.; Chettiath, T.; Mankin, A.S. Induction of erm(C) expression by noninducing antibiotics. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 866–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maravić, G. Macrolide resistance based on the Erm-mediated rRNA methylation. Curr. Drug Targets Infect. Disord. 2004, 4, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leclercq, R.; Courvalin, P. Resistance to macrolides and related antibiotics in Streptococcus pneumonia. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 2727–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Kong, F.; Gilbert, G.L. Three new macrolide efflux (mef) gene variants in Streptococcus agalactiae. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 2754–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Burnie, J.P.; Matthews, R.C.; Carter, T.; Beaulieu, E.; Donohoe, M.; Chapman, C.; Williamson, P.; Hodgetts, S.J. Identification of an immunodominant ABC transporter in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 3200–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheinfeld, N. Telithromycin: A brief review of a new ketolide antibiotic. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2004, 3, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Agouridas, C.; Denis, A.; Auger, J.M.; Benedetti, Y.; Bonnefoy, A.; Bretin, F.; Chantot, J.F.; Dussarat, A.; Fromentin, C.; D’Ambrières, S.G.; et al. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of ketolides (6-O-methyl-3-oxoerythromycin derivatives): A new class of antibacterials highly potent against macrolide-resistant and -susceptible respiratory pathogens. J. Med. Chem. 1998, 41, 4080–4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evrard-Tedeschi, N.; Gharbi-Benarous, J.; Gaillet, C.; Verdier, L.; Bertho, G.; Lange, C.; Parent, A.; Girault, J.-P. Conformations in solution and bound to bacterial ribosomes of ketolides, HMR 3647 (telithromycin) and RU 72366: A new class of highly potent antibacterials. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2000, 8, 1579–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukvić Krajačić, M.; Novak, P.; Cindrić, M.; Brajša, K.; Dumić, M.; Kujundžić, N. Azithromycin-sulfonamide conjugates as inhibitors of resistant Streptococcus pyogenes strains. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 42, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cipcic Paljetak, H.; Banjanac, M.; Ergovic, G; Peric, M.; Padovan, J.; Dominis-Kramaric, M.; Kelneric, Z.; Verbanac, D.; Holmes, D.J.; Erakovic Haber, V. Macrolones—Novel class of macrolide antibiotics active against key resistant respiratory pathogens. In Proceedings of the 53rd ICAAC Meeting, Denver, CO, USA, 10–13 September 2013.
- Munić Kos, V.; Koštrun, S.; Fajdetić, A.; Bosnar, M.; Kelnerić, Ž.; Stepanić, V.; Eraković Haber, V. Structure-property relationship for cellular accumulation of macrolones in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs). Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 49, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jelić, D.; Antolović, R. From Erythromycin to Azithromycin and New Potential Ribosome-Binding Antimicrobials. Antibiotics 2016, 5, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics5030029
Jelić D, Antolović R. From Erythromycin to Azithromycin and New Potential Ribosome-Binding Antimicrobials. Antibiotics. 2016; 5(3):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics5030029
Chicago/Turabian StyleJelić, Dubravko, and Roberto Antolović. 2016. "From Erythromycin to Azithromycin and New Potential Ribosome-Binding Antimicrobials" Antibiotics 5, no. 3: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics5030029
APA StyleJelić, D., & Antolović, R. (2016). From Erythromycin to Azithromycin and New Potential Ribosome-Binding Antimicrobials. Antibiotics, 5(3), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics5030029




