Focus on the Outer Membrane Factor OprM, the Forgotten Player from Efflux Pumps Assemblies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Structural Aspects
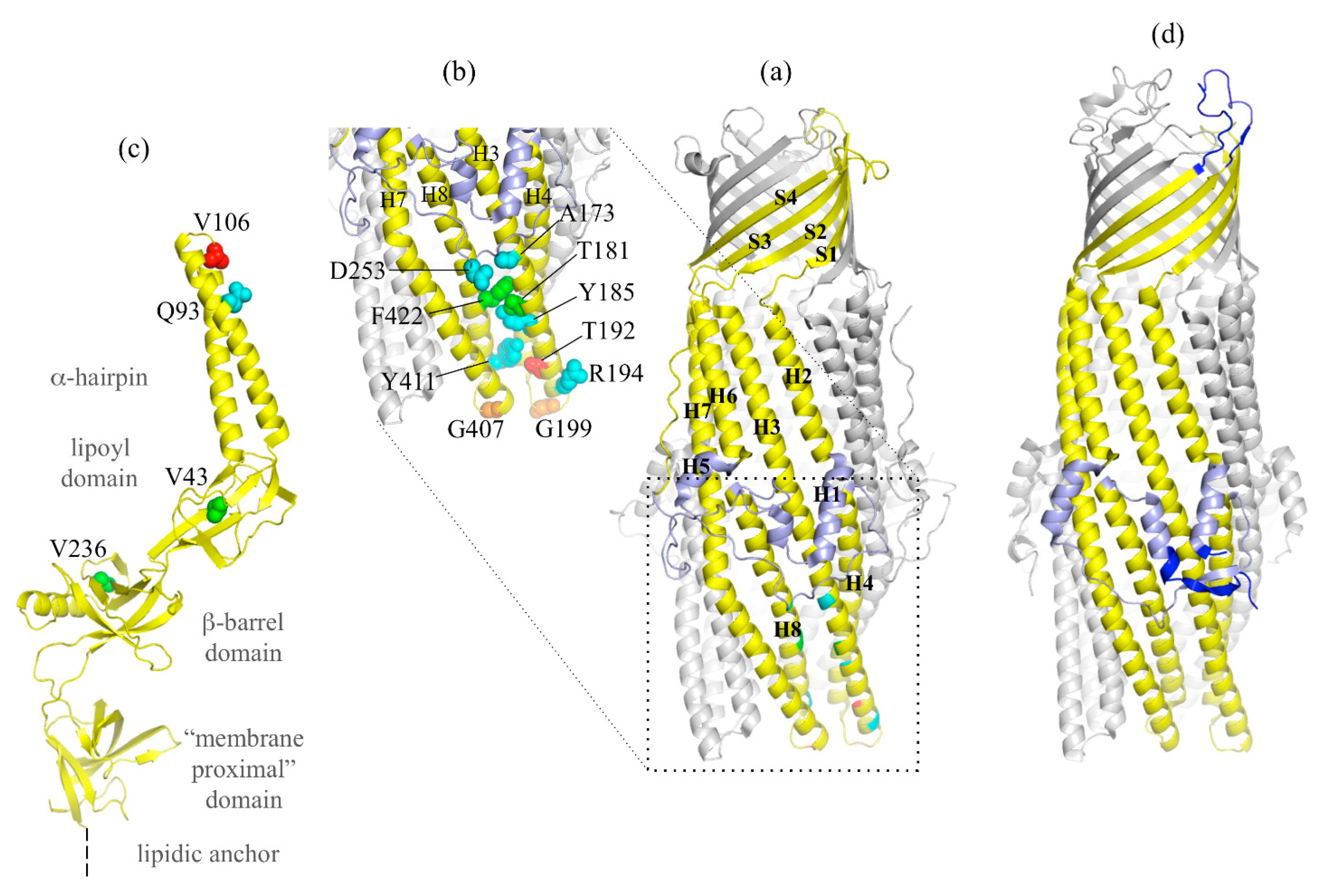
2.1. Description of the OprM Solved Structures
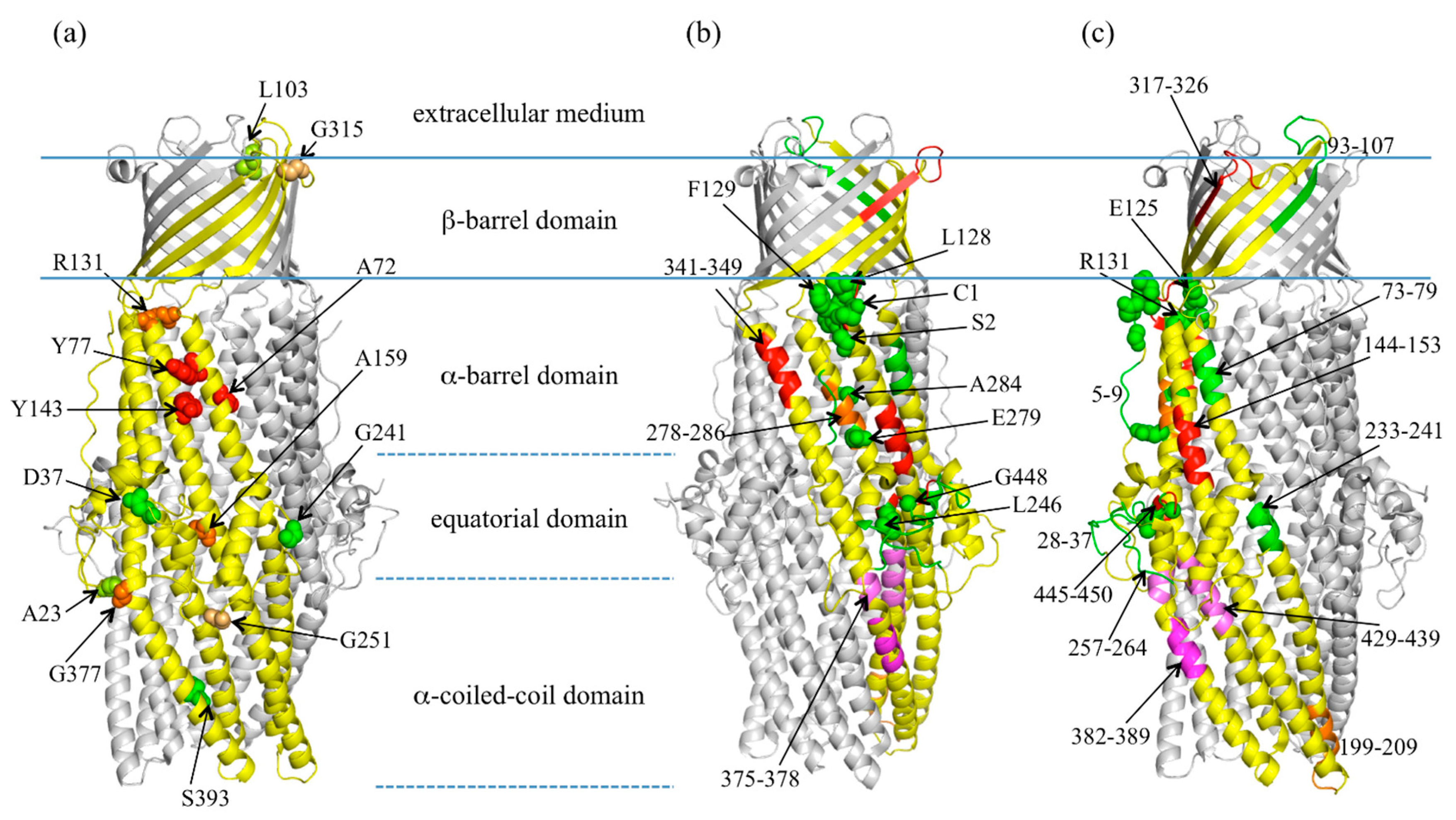
2.2. Highlight on Hotspot Residues
3. Role of OprM in the Assembly with the Other Protein Partners
3.1. Structural Aspects
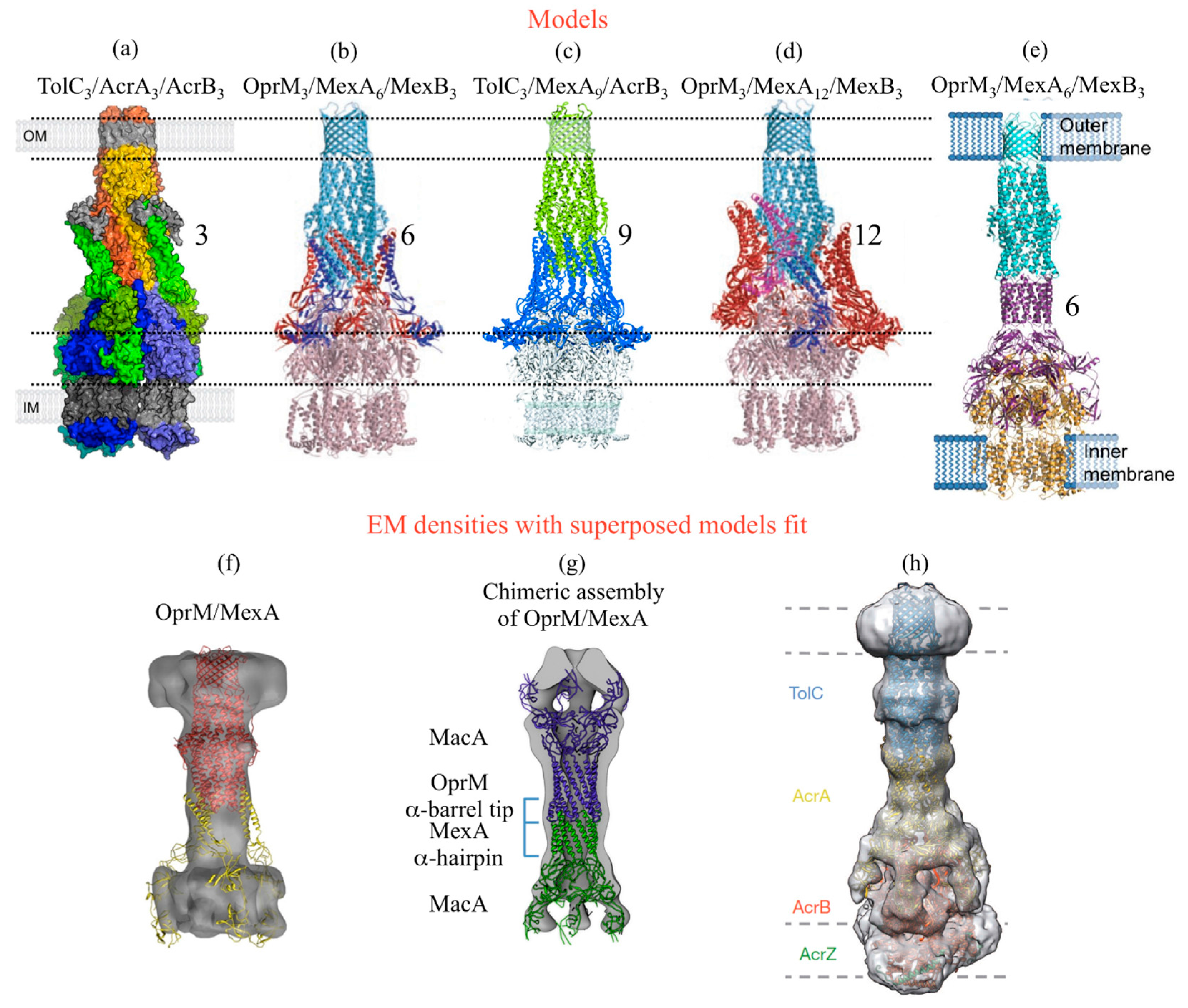
3.2. Mutational Analysis
| Antibiotic Resistance Experiments Performed in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strains | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OMF | OprM | OprM | OprM | OprM | OprM | OprM | OprM | OprN | OprM | OprN | OprM | OprMN * | OprNM * | OprMN * | OprNM * | |||||||||||
| MFP | MexA | MexX | MexX | MexA | MexJ | MexC | MexE | MexA | MexA hairpin/MexE | MexA hairpin/MexE | MexE hairpin/MexA | MexA | MexA | MexE | MexE | |||||||||||
| RND | MexB | MexY | MexB | MexY | MexK | MexD | MexF | MexB | MexF | MexF | MexB | MexB | MexB | MexF | MexF | |||||||||||
| Functionality | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | |||||||||||
| References | [66,72,77,80,87] | [8,73] | [66] | [66] | [75] | [76] | [77,79] | [77] | [79] | [79] | [79] | [80] | [80] | [80] | [80] | |||||||||||
| Antibiotic Resistance Experiments Performed in E. coli Strains | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OMF | OprM | OprM | OprM | OprM | OprM | OprM | TolC | TolC | TolC | TolC | TolC | TolC | ||||||||||||||
| MFP | MexA | MexX | AcrA | MexA | MexA hairpin/AcrA | VceA | AcrA | MexA hairpin/AcrA | MexA | VceA | MexC | MexX | ||||||||||||||
| RND | MexB | MexY | AcrB | AcrB60/MexB | AcrB | VceB | MexB | AcrB | MexB | VceB | MexD | MexY | ||||||||||||||
| Cross-linked evidenced assembly formation | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||||||||||||||
| Functionality | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||||||||||||||
| reference | [89] | [74] | [81,82] | [81] | [82] | [84] | [83] | [82] | [83,85] | [85] | [85] | [85] | ||||||||||||||
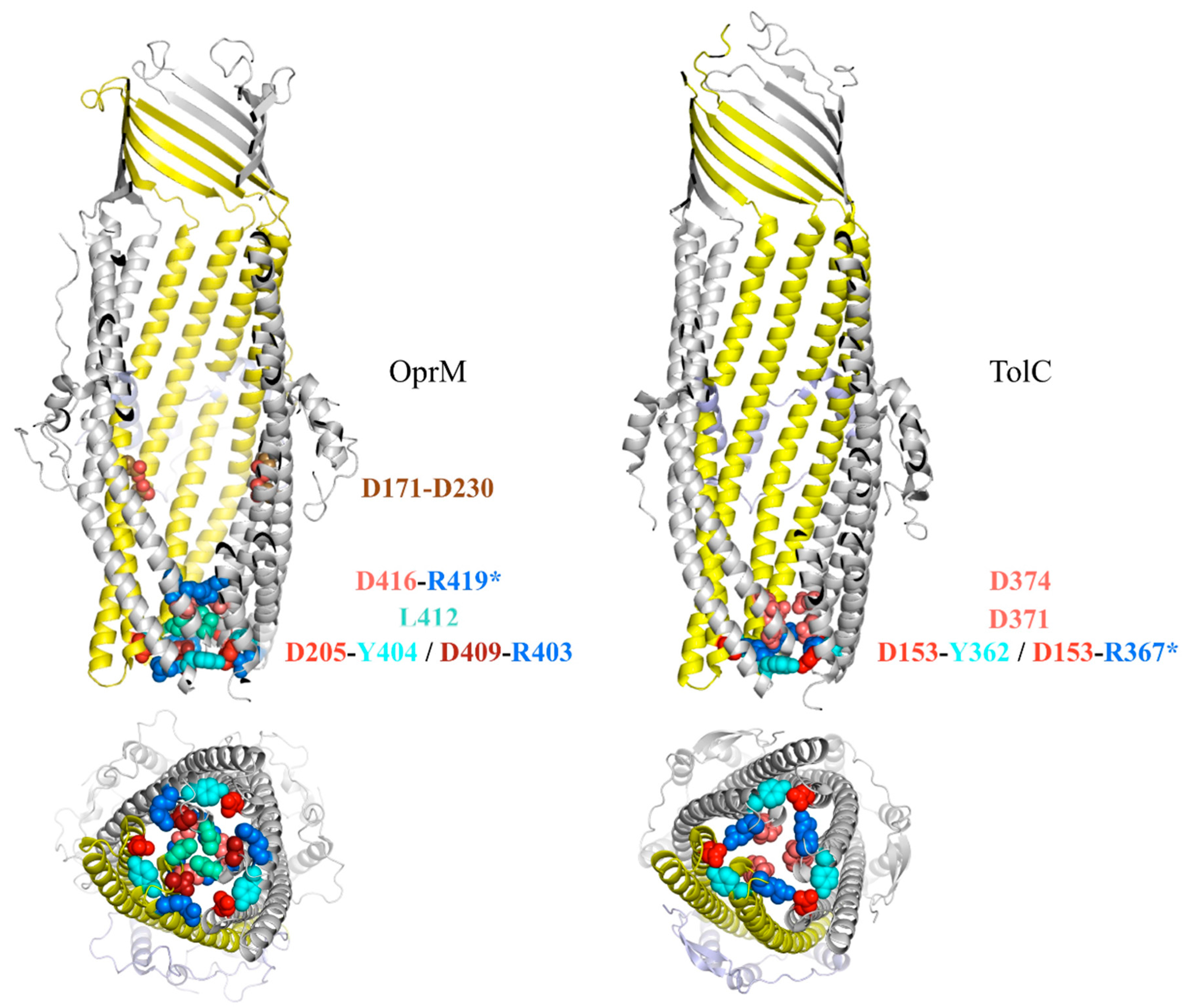
4. The Outflow Mechanism through OprM Channel
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hede, K. Antibiotic resistance: An infectious arms race. Nature 2014, 509, S2–S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boucher, H.W.; Talbot, G.H.; Bradley, J.S.; Edwards, J.E.; Gilbert, D.; Rice, L.B.; Scheld, M.; Spellberg, B.; Bartlett, J. Bad bugs, no drugs: No eskape! An update from the infectious diseases society of america. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frieden, T. Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States, 2013; CS239559-B; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2013; p. 114.
- Zgurskaya, H.I.; Nikaido, H. Multidrug resistance mechanisms: Drug efflux across two membranes. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 37, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattoir, V. Efflux-mediated antibiotics resistance in bacteria. Pathol.-biol. 2004, 52, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Z.; Nikaido, H. Efflux-mediated drug resistance in bacteria: An update. Drugs 2009, 69, 1555–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikaido, H.; Pages, J.M. Broad-specificity efflux pumps and their role in multidrug resistance of gram-negative bacteria. FEMS Microbio. Rev. 2012, 36, 340–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westbrock-Wadman, S.; Sherman, D.R.; Hickey, M.J.; Coulter, S.N.; Zhu, Y.Q.; Warrener, P.; Nguyen, L.Y.; Shawar, R.M.; Folger, K.R.; Stover, C.K. Characterization of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa efflux pump contributing to aminoglycoside impermeability. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1999, 43, 2975–2983. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Murakami, S.; Nakashima, R.; Yamashita, E.; Yamaguchi, A. Crystal structure of bacterial multidrug efflux transporter AcrB. Nature 2002, 419, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zgurskaya, H.I.; Weeks, J.W.; Ntreh, A.T.; Nickels, L.M.; Wolloscheck, D. Mechanism of coupling drug transport reactions located in two different membranes. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, C.F.; Linton, K.J. The ATP switch model for ABC transporters. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2004, 11, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saier, M.H., Jr.; Beatty, J.T.; Goffeau, A.; Harley, K.T.; Heijne, W.H.; Huang, S.C.; Jack, D.L.; Jahn, P.S.; Lew, K.; Liu, J.; et al. The major facilitator superfamily. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1999, 1, 257–279. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tseng, T.T.; Gratwick, K.S.; Kollman, J.; Park, D.; Nies, D.H.; Goffeau, A.; Saier, M.H., Jr. The RND permease superfamily: An ancient, ubiquitous and diverse family that includes human disease and development proteins. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1999, 1, 107–125. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lomovskaya, O.; Lee, A.; Hoshino, K.; Ishida, H.; Mistry, A.; Warren, M.S.; Boyer, E.; Chamberland, S.; Lee, V.J. Use of a genetic approach to evaluate the consequences of inhibition of efflux pumps in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1999, 43, 1340–1346. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maseda, H.; Saito, K.; Nakajima, A.; Nakae, T. Variation of the MexT gene, a regulator of the MexEF-OprN efflux pump expression in wild-type strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2000, 192, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, A.; Sugimoto, Y.; Yoneyama, H.; Nakae, T. High-level fluoroquinolone resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa due to interplay of the MexAB-OprM efflux pump and the DNA gyrase mutation. Microbiol. Immunol. 2002, 46, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aendekerk, S.; Ghysels, B.; Cornelis, P.; Baysse, C. Characterization of a new efflux pump, MexGHI-OpmD, from Pseudomonas aeruginosa that confers resistance to vanadium. Microbiology 2002, 148, 2371–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Mima, T.; Komori, Y.; Morita, Y.; Kuroda, T.; Mizushima, T.; Tsuchiya, T. A new member of the tripartite multidrug efflux pumps, MexVW-OprM, in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 52, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schweizer, H.P. Efflux as a mechanism of resistance to antimicrobials in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and related bacteria: Unanswered questions. Genet. Mol. Res. 2003, 2, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chuanchuen, R.; Murata, T.; Gotoh, N.; Schweizer, H.P. Substrate-dependent utilization of OprM or OpmH by the Pseudomonas aeruginosa MexJK efflux pump. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 2133–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mima, T.; Joshi, S.; Gomez-Escalada, M.; Schweizer, H.P. Identification and characterization of TriABC-OpmH, a triclosan efflux pump of Pseudomonas aeruginosa requiring two membrane fusion proteins. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 7600–7609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunham, S.A.; McPherson, C.J.; Miller, A.A. The relative contribution of efflux and target gene mutations to fluoroquinolone resistance in recent clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2010, 29, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hocquet, D.; Muller, A.; Blanc, K.; Plesiat, P.; Talon, D.; Monnet, D.L.; Bertrand, X. Relationship between antibiotic use and incidence of MexXY-OprM overproducers among clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 1173–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikolosko, J.; Bobyk, K.; Zgurskaya, H.I.; Ghosh, P. Conformational flexibility in the multidrug efflux system protein AcrA. Structure 2006, 14, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, E.W.; McDermott, G.; Zgurskaya, H.I.; Nikaido, H.; Koshland, D.E., Jr. Structural basis of multiple drug-binding capacity of the AcrB multidrug efflux pump. Science 2003, 300, 976–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, S.; Nakashima, R.; Yamashita, E.; Matsumoto, T.; Yamaguchi, A. Crystal structures of a multidrug transporter reveal a functionally rotating mechanism. Nature 2006, 443, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeger, M.A.; Schiefner, A.; Eicher, T.; Verrey, F.; Diederichs, K.; Pos, K.M. Structural asymmetry of AcrB trimer suggests a peristaltic pump mechanism. Science 2006, 313, 1295–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koronakis, V.; Sharff, A.; Koronakis, E.; Luisi, B.; Hughes, C. Crystal structure of the bacterial membrane protein TolC central to multidrug efflux and protein export. Nature 2000, 405, 914–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bavro, V.N.; Pietras, Z.; Furnham, N.; Perez-Cano, L.; Fernandez-Recio, J.; Pei, X.Y.; Misra, R.; Luisi, B. Assembly and channel opening in a bacterial drug efflux machine. Mol. Cell. 2008, 30, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akama, H.; Matsuura, T.; Kashiwagi, S.; Yoneyama, H.; Narita, S.; Tsukihara, T.; Nakagawa, A.; Nakae, T. Crystal structure of the membrane fusion protein, MexA, of the multidrug transporter in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 25939–25942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, M.K.; Bokma, E.; Koronakis, E.; Hughes, C.; Koronakis, V. Structure of the periplasmic component of a bacterial drug efflux pump. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 9994–9999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sennhauser, G.; Bukowska, M.A.; Briand, C.; Grutter, M.G. Crystal structure of the multidrug exporter MexB from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 389, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakashima, R.; Sakurai, K.; Yamasaki, S.; Hayashi, K.; Nagata, C.; Hoshino, K.; Onodera, Y.; Nishino, K.; Yamaguchi, A. Structural basis for the inhibition of bacterial multidrug exporters. Nature 2013, 500, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akama, H.; Kanemaki, M.; Yoshimura, M.; Tsukihara, T.; Kashiwagi, T.; Yoneyama, H.; Narita, S.; Nakagawa, A.; Nakae, T. Crystal structure of the drug discharge outer membrane protein, OprM, of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Dual modes of membrane anchoring and occluded cavity end. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 52816–52819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, G.; Benabdelhak, H.; Lascombe, M.B.; Benas, P.; Rety, S.; Picard, M.; Ducruix, A.; Etchebest, C.; Broutin, I. Structural and dynamical insights into the opening mechanism of P. aeruginosa OprM channel. Structure 2010, 18, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.C.; Yang, F.; Long, F.; Reyon, D.; Routh, M.D.; Kuo, D.W.; Mokhtari, A.K.; Van Ornam, J.D.; Rabe, K.L.; Hoy, J.A.; et al. Crystal structure of the membrane fusion protein CusB from Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 393, 342–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, F.; Su, C.C.; Zimmermann, M.T.; Boyken, S.E.; Rajashankar, K.R.; Jernigan, R.L.; Yu, E.W. Crystal structures of the CusA efflux pump suggest methionine-mediated metal transport. Nature 2010, 467, 484–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulathila, R.; Indic, M.; van den Berg, B. Crystal structure of Escherichia coli CusC, the outer membrane component of a heavy metal efflux pump. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e15610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, H.T.; Chou, T.H.; Su, C.C.; Bolla, J.R.; Kumar, N.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Long, F.; Delmar, J.A.; Do, S.V.; Rajashankar, K.R.; et al. Crystal structure of the open state of the Neisseria gonorrhoeae MtrE outer membrane channel. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.C.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Kumar, N.; Long, F.; Bolla, J.R.; Lei, H.T.; Delmar, J.A.; Do, S.V.; Chou, T.H.; Rajashankar, K.R.; et al. Crystal structure of the Campylobacter jejuni CmeC outer membrane channel. Protein Sci. 2014, 23, 954–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federici, L.; Du, D.; Walas, F.; Matsumura, H.; Fernandez-Recio, J.; McKeegan, K.S.; Borges-Walmsley, M.I.; Luisi, B.F.; Walmsley, A.R. The crystal structure of the outer membrane protein VceC from the bacterial pathogen Vibrio cholerae at 1.8 a resolution. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 15307–15314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Angelis, F.; Lee, J.K.; O'Connell, J.D., 3rd; Miercke, L.J.; Verschueren, K.H.; Srinivasan, V.; Bauvois, C.; Govaerts, C.; Robbins, R.A.; Ruysschaert, J.M.; et al. Metal-induced conformational changes in ZneB suggest an active role of membrane fusion proteins in efflux resistance systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 11038–11043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolla, J.R.; Su, C.C.; Do, S.V.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Kumar, N.; Long, F.; Chou, T.H.; Delmar, J.A.; Lei, H.T.; Rajashankar, K.R.; et al. Crystal structure of the Neisseria gonorrhoeae MtrD inner membrane multidrug efflux pump. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pak, J.E.; Ekende, E.N.; Kifle, E.G.; O'Connell, J.D., 3rd; De Angelis, F.; Tessema, M.B.; Derfoufi, K.M.; Robles-Colmenares, Y.; Robbins, R.A.; Goormaghtigh, E.; et al. Structures of intermediate transport states of ZneA, a Zn(ii)/proton antiporter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 18484–18489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Symmons, M.F.; Marshall, R.L.; Bavro, V.N. Architecture and roles of periplasmic adaptor proteins in tripartite efflux assemblies. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, A.; Sugimoto, Y.; Yoneyama, H.; Nakae, T. Localization of the outer membrane subunit OprM of resistance-nodulation-cell division family multicomponent efflux pump in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 30064–30068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monlezun, L.; Phan, G.; Benabdelhak, H.; Lascombe, M.B.; Enguene, V.Y.; Picard, M.; Broutin, I. New OprM structure highlighting the nature of the N-terminal anchor. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanaka, H.; Izawa, H.; Okamoto, K. Carboxy-terminal region involved in activity of Escherichia coli TolC. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 6961–6964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bokma, E.; Koronakis, E.; Lobedanz, S.; Hughes, C.; Koronakis, V. Directed evolution of a bacterial efflux pump: Adaptation of the E. coli TolC exit duct to the Pseudomonas MexAB translocase. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 5339–5343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, K.K.; Hancock, R.E. Insertion mutagenesis and membrane topology model of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane protein OprM. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 2402–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Li, X.Z.; Poole, K. Mutational analysis of the OprM outer membrane component of the MexA-MexB-OprM multidrug efflux system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, K.K.; Brinkman, F.S.; Benz, R.S.; Hancock, R.E. Evaluation of a structural model of Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane protein OprM, an efflux component involved in intrinsic antibiotic resistance. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaccaro, L.; Koronakis, V.; Sansom, M.S. Flexibility in a drug transport accessory protein: Molecular dynamics simulations of MexA. Biophys. J. 2006, 91, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Recio, J.; Walas, F.; Federici, L.; Venkatesh Pratap, J.; Bavro, V.N.; Miguel, R.N.; Mizuguchi, K.; Luisi, B. A model of a transmembrane drug-efflux pump from gram-negative bacteria. FEBS Lett. 2004, 578, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Symmons, M.F.; Bokma, E.; Koronakis, E.; Hughes, C.; Koronakis, V. The assembled structure of a complete tripartite bacterial multidrug efflux pump. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 7173–7178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.C.; Long, F.; Zimmermann, M.T.; Rajashankar, K.R.; Jernigan, R.L.; Yu, E.W. Crystal structure of the CusBA heavy-metal efflux complex of Escherichia coli. Nature 2011, 470, 558–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, D.; Wang, Z.; James, N.R.; Voss, J.E.; Klimont, E.; Ohene-Agyei, T.; Venter, H.; Chiu, W.; Luisi, B.F. Structure of the AcrAB-TolC multidrug efflux pump. Nature 2014, 509, 512–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrandez, Y.; Monlezun, L.; Phan, G.; Benabdelhak, H.; Benas, P.; Ulryck, N.; Falson, P.; Ducruix, A.; Picard, M.; Broutin, I. Stoichiometry of the MexA-OprM binding, as investigated by blue native gel electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2012, 33, 1282–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reffay, M.; Gambin, Y.; Benabdelhak, H.; Phan, G.; Taulier, N.; Ducruix, A.; Hodges, R.S.; Urbach, W. Tracking membrane protein association in model membranes. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoneyama, H.; Maseda, H.; Kamiguchi, H.; Nakae, T. Function of the membrane fusion protein, MexA, of the MexA, B-OprM efflux pump in Pseudomonas aeruginosa without an anchoring membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 4628–4634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weeks, J.W.; Nickels, L.M.; Ntreh, A.T.; Zgurskaya, H.I. Non-equivalent roles of two periplasmic subunits in the function and assembly of triclosan pump TriABC from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol. Microbiol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verchere, A.; Dezi, M.; Adrien, V.; Broutin, I.; Picard, M. In vitro transport activity of the fully assembled MexAB-OprM efflux pump from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ntsogo Enguene, V.Y.; Verchere, A.; Phan, G.; Broutin, I.; Picard, M. Catch me if you can: A biotinylated proteoliposome affinity assay for the investigation of assembly of the MexA-MexB-OprM efflux pump from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, J.L.; Gnanakaran, S. A data-driven approach to modeling the tripartite structure of multidrug resistance efflux pumps. Proteins 2015, 83, 46–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trepout, S.; Mornet, S.; Benabdelhak, H.; Ducruix, A.; Brisson, A.R.; Lambert, O. Membrane protein selectively oriented on solid support and reconstituted into a lipid membrane. Langmuir 2007, 23, 2647–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhonov, V.V.; Mokhonova, E.I.; Akama, H.; Nakae, T. Role of the membrane fusion protein in the assembly of resistance-nodulation-cell division multidrug efflux pump in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 322, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trepout, S.; Taveau, J.C.; Benabdelhak, H.; Granier, T.; Ducruix, A.; Frangakis, A.S.; Lambert, O. Structure of reconstituted bacterial membrane efflux pump by cryo-electron tomography. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1798, 1953–1960. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20599691 (accessed on 6 November 2015). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, N.; Nishino, K.; Yamaguchi, A. Novel macrolide-specific ABC-type efflux transporter in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 5639–5644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Sim, S.H.; Song, S.; Piao, S.; Kim, H.M.; Jin, X.L.; Lee, K.; Ha, N.C. The tip region of the MacA alpha-hairpin is important for the binding to TolC to the Escherichia coli MacAB-TolC pump. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 394, 962–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Lee, M.; Moeller, A.; Song, S.; Yoon, B.Y.; Kim, H.M.; Jun, S.Y.; Lee, K.; Ha, N.C. Funnel-like hexameric assembly of the periplasmic adapter protein in the tripartite multidrug efflux pump in gram-negative bacteria. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 17910–17920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Moeller, A.; Jun, S.Y.; Le, M.; Yoon, B.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, K.; Ha, N.C. Assembly and channel opening of outer membrane protein in tripartite drug efflux pumps of gram-negative bacteria. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 11740–11750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoneyama, H.; Ocaktan, A.; Gotoh, N.; Nishino, T.; Nakae, T. Subunit swapping in the Mex-extrusion pumps in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 244, 898–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aires, J.R.; Kohler, T.; Nikaido, H.; Plesiat, P. Involvement of an active efflux system in the natural resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to aminoglycosides. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1999, 43, 2624–2628. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mine, T.; Morita, Y.; Kataoka, A.; Mizushima, T.; Tsuchiya, T. Expression in Escherichia coli of a new multidrug efflux pump, MexXY, from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1999, 43, 415–417. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chuanchuen, R.; Narasaki, C.T.; Schweizer, H.P. The MexJK efflux pump of Pseudomonas aeruginosa requires OprM for antibiotic efflux but not for efflux of triclosan. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 5036–5044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotoh, N.; Tsujimoto, H.; Nomura, A.; Okamoto, K.; Tsuda, M.; Nishino, T. Functional replacement of OprJ by OprM in the MexCD-OprJ multidrug efflux system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1998, 165, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maseda, H.; Yoneyama, H.; Nakae, T. Assignment of the substrate-selective subunits of the MexEF-OprN multidrug efflux pump of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohler, T.; Michea-Hamzehpour, M.; Henze, U.; Gotoh, N.; Curty, L.K.; Pechere, J.C. Characterization of MexE-MexF-OprN, a positively regulated multidrug efflux system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol. Microbiol. 1997, 23, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eda, S.; Maseda, H.; Yoshihara, E.; Nakae, T. Assignment of the outer-membrane-subunit-selective domain of the membrane fusion protein in the tripartite xenobiotic efflux pump of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 254, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshihara, E.; Eda, S.; Kaitou, S. Functional interaction sites of OprM with MexAB in the Pseudomonas aeruginosa multidrug efflux pump. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 299, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tikhonova, E.B.; Wang, Q.; Zgurskaya, H.I. Chimeric analysis of the multicomponent multidrug efflux transporters from gram-negative bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 6499–6507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stegmeier, J.F.; Polleichtner, G.; Brandes, N.; Hotz, C.; Andersen, C. Importance of the adaptor (membrane fusion) protein hairpin domain for the functionality of multidrug efflux pumps. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 10303–10312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, A.; Awah, C.U.; Jing, S.; van Veen, H.W.; Venter, H. Promiscuous partnering and independent activity of MexB, the multidrug transporter protein from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem. J. 2010, 430, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Bhagavathi, R.; Tran, P.; Muzzarelli, K.; Wang, D.; Fralick, J. Evidence that the C-terminal region is involved in the stability and functionality of OprM in E. coli. Microbiol. Res. 2014, 169, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vediyappan, G.; Borisova, T.; Fralick, J.A. Isolation and characterization of VceC gain-of-function mutants that can function with the AcrAB multiple-drug-resistant efflux pump of Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 3757–3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Nehme, D.; Poole, K. Assembly of the MexAB-OprM multidrug pump of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Component interactions defined by the study of pump mutant suppressors. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 6118–6127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nehme, D.; Li, X.Z.; Elliot, R.; Poole, K. Assembly of the MexAB-OprM multidrug efflux system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Identification and characterization of mutations in MexA compromising MexA multimerization and interaction with MexB. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 2973–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middlemiss, J.K.; Poole, K. Differential impact of MexB mutations on substrate selectivity of the MexAB-OprM multidrug efflux pump of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 1258–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srikumar, R.; Kon, T.; Gotoh, N.; Poole, K. Expression of Pseudomonas aeruginosa multidrug efflux pumps MexA-MexB-OprM and MexC-MexD-OprJ in a multidrug-sensitive Escherichia colistrain. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1998, 42, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Andersen, C.; Koronakis, E.; Bokma, E.; Eswaran, J.; Humphreys, D.; Hughes, C.; Koronakis, V. Transition to the open state of the TolC periplasmic tunnel entrance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11103–11108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eswaran, J.; Hughes, C.; Koronakis, V. Locking TolC entrance helices to prevent protein translocation by the bacterial type I export apparatus. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 327, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, M.K.; Eswaran, J.; Edwards, P.; Schertler, G.F.; Hughes, C.; Koronakis, V. Structure of the ligand-blocked periplasmic entrance of the bacterial multidrug efflux protein TolC. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 342, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, X.Y.; Hinchliffe, P.; Symmons, M.F.; Koronakis, E.; Benz, R.; Hughes, C.; Koronakis, V. Structures of sequential open states in a symmetrical opening transition of the TolC exit duct. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2112–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Monlezun, L.; Picard, M.; Benas, P.; Francais, O.; Broutin, I.; Le Pioufle, B. Activity monitoring of functional OprM using a biomimetic microfluidic device. Analyst 2012, 137, 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruggerone, P.; Vargiu, A.V.; Collu, F.; Fischer, N.; Kandt, C. Molecular dynamics computer simulations of multidrug RND efflux pumps. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2013, 5, e201302008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, N.; Kandt, C. Porter domain opening and closing motions in the multi-drug efflux transporter AcrB. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1828, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaccaro, L.; Scott, K.A.; Sansom, M.S. Gating at both ends and breathing in the middle: Conformational dynamics of TolC. Biophys. J. 2008, 95, 5681–5691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, R.; Kleinekathofer, U. Transitions between closed and open conformations of TolC: The effects of ions in simulations. Biophys. J. 2009, 96, 3116–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raunest, M.; Kandt, C. Locked on one side only: Ground state dynamics of the outer membrane efflux duct TolC. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 1719–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Weng, J.; Wang, W. Multiple conformational states and gate opening of outer membrane protein TolC revealed by molecular dynamics simulations. Proteins 2014, 82, 2169–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, D.C.; Raunest, M.; Harder, T.; Kandt, C. Unilateral access regulation: Ground state dynamics of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane efflux duct OprM. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Meng, J.; Jia, M.; Ma, X.; He, G.; Yu, J.; Wang, R.; Bai, H.; Hou, Z.; Luo, X. OprM as a new target for reversion of multidrug resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by antisense phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotides. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Phan, G.; Picard, M.; Broutin, I. Focus on the Outer Membrane Factor OprM, the Forgotten Player from Efflux Pumps Assemblies. Antibiotics 2015, 4, 544-566. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics4040544
Phan G, Picard M, Broutin I. Focus on the Outer Membrane Factor OprM, the Forgotten Player from Efflux Pumps Assemblies. Antibiotics. 2015; 4(4):544-566. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics4040544
Chicago/Turabian StylePhan, Gilles, Martin Picard, and Isabelle Broutin. 2015. "Focus on the Outer Membrane Factor OprM, the Forgotten Player from Efflux Pumps Assemblies" Antibiotics 4, no. 4: 544-566. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics4040544
APA StylePhan, G., Picard, M., & Broutin, I. (2015). Focus on the Outer Membrane Factor OprM, the Forgotten Player from Efflux Pumps Assemblies. Antibiotics, 4(4), 544-566. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics4040544








