Resistance Mechanisms of Fluoroquinolone in Escherichia coli Isolated from Taihe Black-Boned Silky Fowl Exhibiting Abnormally Slow Fluoroquinolone Metabolism in Jiangxi, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. E. coli FQ-Resistant Phenotypes
2.2. Prevalence and Genetic Environment of PMQR Determinants Among E. coli Strains
2.3. Analysis of Mutations in the QRDRs
2.4. FQ Residues in TBSF Samples
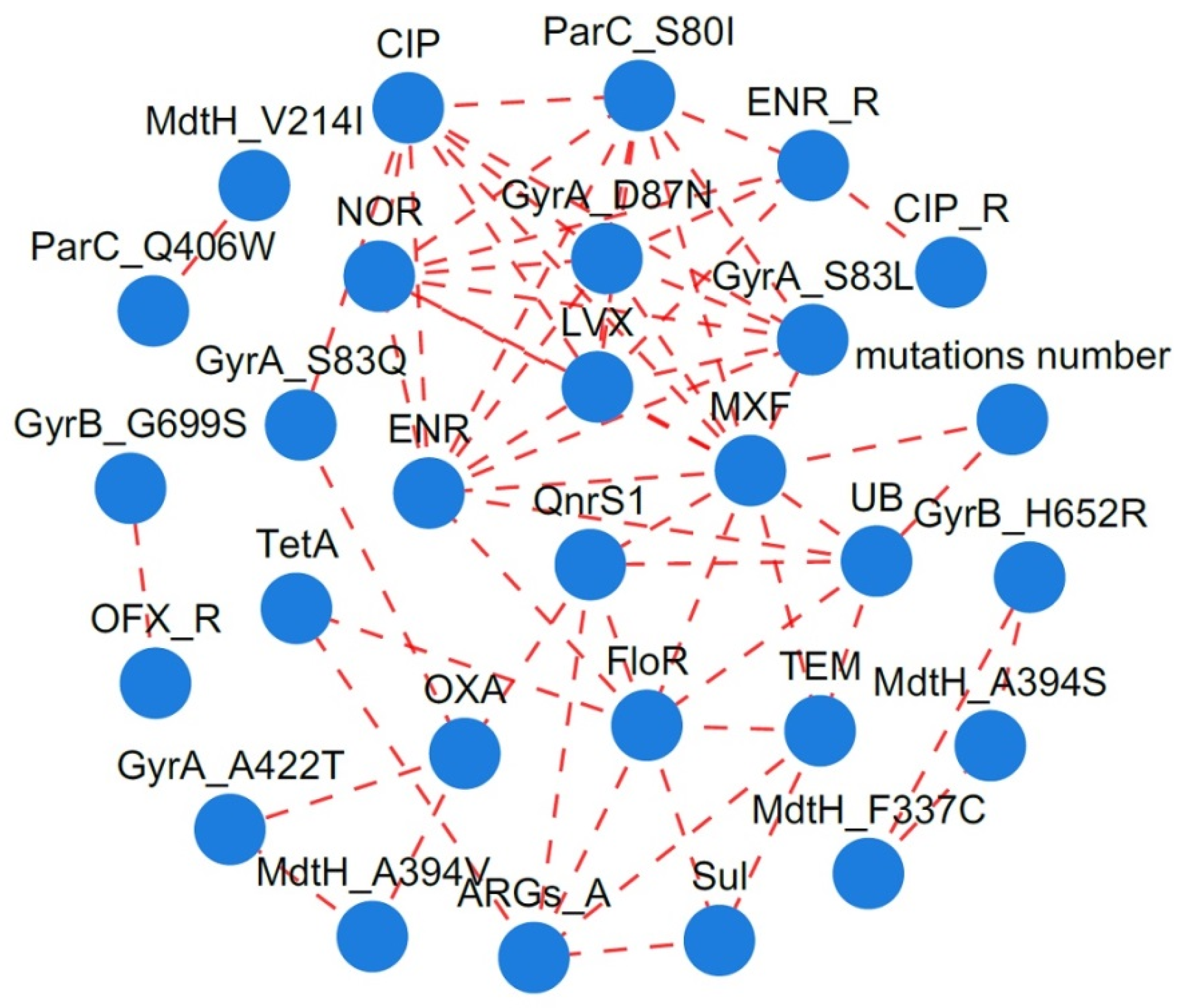
2.5. Correlation Between FQ Residues, Resistance Phenotypes, and ARGs
3. Discussion
3.1. The Prevalence of FQ-Resistant E. coli Strains Across Different Environments
3.2. Epidemiological Characteristics of PMQR Genes
3.3. Mutations in QRDR Determinants of E. coli Strains
3.4. Factors Influencing FQ Resistance in E. coli Strains
4. Materials and Methods
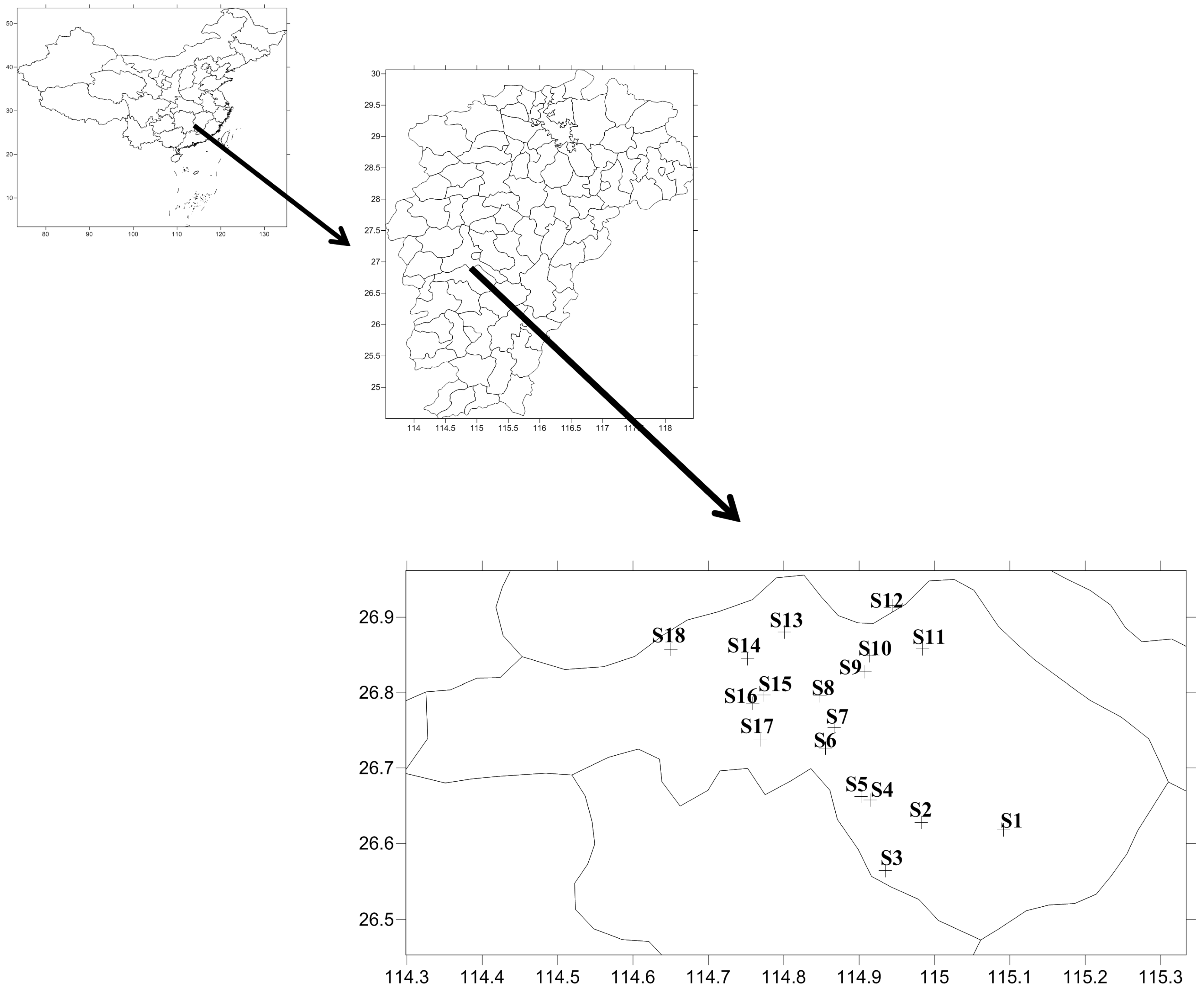
4.1. Sampling, Bacterial Isolation, and FQs Detection
4.2. FQs Susceptibility Testing
4.3. Whole-Genome Sequencing and Identification of ARGs
4.4. Correlation Between FQ Residues, Resistance Phenotypes and ARGs
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aggarwal, R.; Mahajan, P.; Pandiya, S.; Bajaj, A.; Verma, S.K.; Yadav, P.; Kharat, A.S.; Khan, A.U.; Dua, M.; Johri, A.K. Antibiotic resistance: A global crisis, problems and solutions. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 50, 896–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, K.W.; Lee, Y.J. Molecular characterization of fluoroquinolone-resistant Escherichia coli from broiler breeder farms. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.; Kesselheim, A.S.; Hollis, A. Persistence of resistance: A panel data analysis of the effect of antibiotic usage on the prevalence of resistance. J. Antibiot. 2023, 76, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Boeckel, T.P.; Pires, J.; Silvester, R.; Zhao, C.; Song, J.; Criscuolo, N.G.; Gilbert, M.; Bonhoeffer, S.; Laxminarayan, R. Global trends in antimicrobial resistance in animals in low- and middle-income countries. Science 2019, 365, eaaw1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Z.E.; Wang, J.; Yu, K. Spatiotemporal distribution and potential risks of antibiotics in coastal water of Beibu Gulf, South China Sea: Livestock and poultry emissions play essential effect. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 466, 133550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, N.G.; Diez-Santos, I.; Abbott, L.R.; Maxwell, A. Quinolones: Mechanism, lethality and their contributions to antibiotic resistance. Molecules 2020, 25, 5662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, S.; Tajbakhsh, S.; Naeimi, B.; Yousefi, F. Investigation of gyrA and parC mutations and the prevalence of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance genes in Klebsiella pneumoniae clinical isolates. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharbi, M.; Abbas, M.A.S.; Hamrouni, S.; Maaroufi, A. First report of aac(6′)-Ib and aac(6′)-Ib-cr variant genes associated with mutations in gyrA encoded fluoroquinolone resistance in avian Campylobacter coli strains collected in Tunisia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, D.; Awad, A.; Younis, G. Prevalence and characterization of quinolone-resistant Escherichia coli isolated from retail raw beef and poultry meat in Egypt. J. Adv. Vet. Anim. Res. 2023, 10, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaleva, M.D.; Ilieva, Y.; Zaharieva, M.M.; Dimitrova, L.; Kim, T.C.; Tsvetkova, I.; Georgiev, Y.; Orozova, P.; Nedev, K.; Najdenski, H. Antimicrobial resistance and biofilm formation of Escherichia coli isolated from pig farms and surroundings in Bulgaria. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccarelli, D.; Hesp, A.; Van Der Goot, J.; Joosten, P.; Sarrazin, S.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Dewulf, J.; Mevius, D.J.; on behalf of the EFFORT consortium. Antimicrobial resistance prevalence in commensal Escherichia coli from broilers, fattening turkeys, fattening pigs and veal calves in European countries and association with antimicrobial usage at country level. J. Med. Microbiol. 2020, 69, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croxen, M.A.; Law, R.J.; Scholz, R.; Keeney, K.M.; Wlodarska, M.; Filay, B.B. Recent advances in understanding enteric pathogenic Escherichia coli. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 822–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, A.; Patro, A.R.K.; Khajuria, A.; Dhal, S.; Praharaj, A.K. Ciprofloxacin-resistant Gram-negative isolates from a tertiary care hospital in Eastern India with novel gyrA and parC gene mutations. Med. J. Armed Forces India 2022, 78, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Toro, M.; Garcilláon-Barcia, M.P.; De La Cruz, F. Plasmid diversity and adaptation analyzed by massive sequencing of Escherichia coli plasmids. Microbiol. Spectr. 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Yang, Y.; Li, F.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Fazilani, S.A.; Guo, W.; Xu, G.; Zhang, X. The prevalence and mechanism of fluoroquinolone resistance in Escherichia coli isolated from swine farms in China. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zych, S.; Adaszyńska-Skwirzyńska, M.; Szewczuk, M.A.; Szczerbińska, D. Interaction between enrofloxacin and three essential oils (Cinnamon Bark, Clove Bud and Lavender Flower)-A study on multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli strains isolated from 1-day-old broiler chickens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, P.; Barton, G.; Kietzmann, M.; Meißner, J. Treatment of pigs with enrofloxacin via different oral dosage forms—Environmental contaminations and resistance development of Escherichia coli. J. Vet. Sci. 2022, 23, e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Sun, J.; Liao, X.P.; Shao, Y.; Li, L.; Fang, L.X.; Liu, Y.H. Impact of enrofloxacin and florfenicol therapy on the spread of OqxAB gene and intestinal microbiota in chickens. Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 192, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swinkels, A.F.; Fischer, E.A.J.; Korving, L.; Kusters, N.E.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Zomer, A.L. Selection for amoxicillin-, doxycycline-, and enrofloxacin-resistant Escherichia coli at concentrations lower than the ECOFF in broiler-derived cecal fermentations. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0097024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.; Zhang, J.; Hu, J.; Li, X.; Li, B. Fluoroquinolone residues in the environment rapidly induce heritable fluoroquinolone resistance in Escherichia coli. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 4784–4795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Wu, H.; Wang, J.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, L.; Xiang, J.; Liao, Q.; Luo, L.; Qian, M.; Zhang, D. Pharmacokinetics, withdrawal time, and dietary risk assessment of enrofloxacin and its metabolite ciprofloxacin, and sulfachloropyridazine–trimethoprim in Taihe black-boned silky fowls. J. Food Sci. 2023, 88, 1743–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kherroubi, L.; Bacon, J.; Rahman, K.M. Navigating fluoroquinolone resistance in Gram-negative bacteria: A comprehensive evaluation. JAC Antimicrob. Resist. 2024, 6, dlae127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.; Chen, K.; Li, R.; Liu, L.; Guo, J.; Yao, W.; Chen, S. Selection of target mutation in rat gastrointestinal tract E. coli by minute dosage of enrofloxacin. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Oh, J.; Park, S.; Sum, S.; Song, W.; Chae, J.; Park, H. Antimicrobial resistance and novel mutations detected in the gyrA and parC genes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from companion dogs. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, K.; Zhao, Y.; Cui, L.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, F.; Wang, X.; Peng, Z.; Feng, J.; Hu, T.; Dai, M. Longitudinal surveillance and risk assessment of resistance in Escherichia coli to enrofloxacin from a large-scale chicken farm in Hebei, China. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Cui, Z.; Qu, Z.; Cui, J.; Du, X.; Huang, X.; Zhao, J. Molecular classification and drug resistance analysis of Escherichia coli isolated from poultry in China. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jerzsele, Á.; Szabó, Á.; Barnácz, F.; Csirmaz, B.; Kovács, L.; Kerek, Á. Antimicrobial susceptibility profiles of Escherichia coli isolates from clinical cases of chickens in Hungary between 2022 and 2023. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.; Nath, C.; Das, P.; Ghosh, K.; Logno, T.A.; Debnath, P.; Dash, S.; Devnath, H.S.; Das, S.; Islam, M.Z. High prevalence of ciprofloxacin resistance in Escherichia coli isolated from chickens, humans and the environment: An emerging one health issue. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0294043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, R.L.; Hoogstra, S.; Mahoney, D.; Lubberts, M.; Reid-Smith, R.; Signorelli, T.; Robertson, J.; Eagle, S.H.; Jurga, E.; Nash, J.; et al. Genomic characterization of pathotype diversity and drug resistance among generic Escherichia coli isolated from broiler chickens in Canada. Can. J. Microbiol. 2025, 71, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerek, Á.; Szabó, Á.; Jerzsele, Á. Antimicrobial susceptibility profiles of commensal Escherichia coli isolates from chickens in Hungarian poultry farms between 2022 and 2023. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mustapha, A.I.; Alada, S.A.; Raufu, I.A.; Lawal, A.N.; Eskola, K.; Brouwer, M.S.; Adetunji, V.; Heikinheimo, A. Co-occurrence of antibiotic and disinfectant resistance genes in extensively drug-resistant Escherichia coli isolated from broilers in Ilorin, North Central Nigeria. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2022, 31, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodagari, H.R.; Wang, P.; Robertson, I.; Abraham, S.; Sahibzada, S.; Habib, I. Antimicrobial resistance and genomic characterisation of Escherichia coli isolated from caged and non-caged retail table eggs in Western Australia. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 340, 109054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, F.; Zhu, D.; Wang, F.; Wang, M. Current Status and Trends of Antibacterial Resistance in China. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 67 (Suppl. 2), S128–S134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, K.; Shenoy, M.S.; Baliga, S.; Unnikrishnan, B.; Baliga, B.S.; Shetty, V.K. Research Note: Characterization of antibiotic resistant phenotypes and linked genes of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae from healthy broiler chickens, Karnataka, India. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aworh, M.K.; Kwaga, J.K.P.; Hendriksen, R.S.; Okolocha, E.C.; Harrell, E.; Thakur, S. Quinolone-resistant Escherichia coli at the interface between humans, poultry and their shared environment- a potential public health risk. One Health Outlook 2023, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, K.; Lee, Y. Prevalence and characterization of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance determinants qnr and aac(6′)-Ib-cr in ciprofloxacin-resistant Escherichia coli isolates from commercial layer in Korea. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 30, 1180–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeili, M.; Salehzeinali, H.; Mirzaei, S.; Pishnian, Z.; Ahmadi, A. Molecular characterization of quinolone resistance and antimicrobial resistance profiles of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli isolated from human and broiler chickens. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2022, 32, 1382–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.T.; Liao, X.P.; Yang, S.S.; Wang, X.M.; Li, L.L.; Sun, J.; Yang, Y.R.; Fang, L.X.; Li, L.; Zhao, D.H.; et al. Detection of mutations in the gyrA and parC genes in Escherichia coli isolates carrying plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance genes from diseased food-producing animals. J. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 61 Pt 11, 1591–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.L.; Wu, S.L.; Fu, J.L.; Jiang, H.X.; Ding, H.Z. Research Note: Epidemiological cutoff values and acquired resistance mechanisms of three veterinary antibiotics against Escherichia coli from chicken respiratory tract infections. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 1093–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Martínez, J.M.; Lopez-Cerero, L.; García-Duque, A.; Rodriguez-Baño, J.; Pascual, A. Interplay between IncF plasmids and topoisomerase mutations conferring quinolone resistance in the Escherichia coli ST131 clone: Stability and resistance evolution. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021; epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinué, L.; Hooper, D.C.; Jacoby, G.A. Chromosomal mutations that accompany qnr in clinical isolates of Escherichia coli. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2018, 51, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Regan, E.; Quinn, T.; Frye, J.G.; Pages, J.M.; Porwollik, S.; Fedorka-Cray, P.J.; McClelland, M.; Fanning, S. Fitness costs and stability of a high-level ciprofloxacin resistance phenotype in Salmonella enterica serotype enteritidis: Reduced infectivity associated with decreased expression of Salmonella pathogenicity island 1 genes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huseby, D.L.; Pietsch, F.; Brandis, G.; Garoff, L.; Tegehall, A.; Hughes, D. Mutation supply and relative fitness shape the genotypes of ciprofloxacin-resistant Escherichia coli. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 1029–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofer, U. Overcoming the cost of plasmid carriage. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, K.M.; Wassermann, T.; Jensen, P.Ø.; Hengzuang, W.; Molin, S.; Høiby, N.; Ciofu, O. Sublethal ciprofloxacin treatment leads to rapid development of high-level ciprofloxacin resistance during long-term experimental evolution of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 4215–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gullberg, E.; Cao, S.; Berg, O.G.; Ilbäck, C.; Sandegren, L.; Hughes, D.; Andersson, D.I. Selection of resistant bacteria at very low antibiotic concentrations. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imkamp, F.; Bodendoerfer, E.; Mancini, S. QUIRMIA-A phenotype-based algorithm for the inference of quinolone resistance mechanisms in Escherichia coli. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, M.Y.; Kim, Y.B.; Ha, J.S.; Seo, K.W.; Noh, E.B.; Son, S.H.; Lee, Y.J. Molecular characteristics of fluoroquinolone-resistant avian pathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 3628–3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanni, M.; Meucci, V.; Tognetti, R.; Cagnardi, P.; Montesissa, C.; Piccirillo, A.; Rossi, A.M.; Di Bello, D.; Intorre, L. Fluoroquinolone resistance and molecular characterization of gyrA and parC quinolone resistance-determining regions in Escherichia coli isolated from poultry. Poult. Sci. 2014, 93, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forcella, C.; Alessiani, A.; Perilli, M.; Zilli, K.; Di Giannatale, E.; Amicosante, G. Characterization of quinolone resistance in Escherichia coli strains of animal origin from Italy. J. Chemother. 2010, 22, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, D.I.; Hughes, D. Antibiotic resistance and its cost: Is it possible to reverse resistance? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcusson, L.L.; Frimodt-Møller, N.; Hughes, D. Interplay in the selection of fluoroquinolone resistance and bacterial fitness. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shariati, A.; Arshadi, M.; Khosrojerdi, M.A.; Abedinzadeh, M.; Ganjalishahi, M.; Maleki, A.; Heidary, M.; Khoshnood, S. The resistance mechanisms of bacteria against ciprofloxacin and new approaches for enhancing the efficacy of this antibiotic. Front. Public. Health 2022, 10, 1025633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callens, B.; Cargnel, M.; Sarrazin, S.; Dewulf, J.; Hoet, B.; Vermeersch, K.; Wattiau, P.; Welby, S. Associations between a decreased veterinary antimicrobial use and resistance in commensal Escherichia coli from Belgian livestock species (2011–2015). Prev. Vet. Med. 2018, 157, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, L.; Agunos, A.; Gow, S.P.; Carson, C.A.; Van Boeckel, T.P. Reduction in antimicrobial use and resistance to Salmonella, Campylobacter, and Escherichia coli in broiler chickens, Canada, 2013–2019. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 2434–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin-Guyomard, A.; Jouy, E.; Urban, D.; Chauvin, C.; Granier, S.A.; Mourand, G.; Chevance, A.; Adam, C.; Moulin, G.; Kempf, I. Decrease in fluoroquinolone use in French poultry and pig production and changes in resistance among E. coli and Campylobacter. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 243, 108637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misumi, W.; Magome, A.; Okuhama, E.; Uchimura, E.; Tamamura-Andoh, Y.; Watanabe, Y.; Kusumoto, M. CTX-M-55-type ESBL-producing fluoroquinolone-resistant Escherichia coli sequence type 23 repeatedly caused avian colibacillosis in Kagoshima Prefecture, Japan. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2023, 35, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Koster, S.; Ringenier, M.; Xavier, B.B.; Lammens, C.; De Coninck, D.; De Bruyne, K.; Mensaert, K.; Kluytmans-Van den Bergh, M.; Kluytmans, J.; Dewulf, J.; et al. Genetic characterization of ESBL-producing and ciprofloxacin-resistant Escherichia coli from Belgian broilers and pigs. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1150470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Much, P.; Sun, H.; Lassnig, H.; Koeberl-Jelovcan, S.; Schliessnig, H.; Stueger, H.P. Differences in antimicrobial resistance of commensal Escherichia coli isolated from caecal contents of organically and conventionally raised broilers in Austria, 2010-2014 and 2016. Prev. Vet. Med. 2019, 171, 104755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mughini-Gras, L.; Di Martino, G.; Moscati, L.; Buniolo, F.; Cibin, V.; Bonfanti, L. Natural immunity in conventionally and organically reared turkeys and its relation with antimicrobial resistance. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.; Cardo, M.; Cara d’Anjo, M.; Leite, A. Assessing antimicrobial resistance occurrence in the Portuguese food system: Poultry, pigs and derived food, 2014–2018. Zoonoses Public Health 2022, 69, 312–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truswell, A.; Lee, Z.Z.; Stegger, M.; Blinco, J.; Abraham, R.; Jordan, D.; Milotic, M.; Hewson, K.; Pang, S.; Abraham, S. Augmented surveillance of antimicrobial resistance with high-throughput robotics detects transnational flow of fluoroquinolone-resistant Escherichia coli strain into poultry. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2023, 78, 2878–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, T. Distribution of fluoroquinolone-resistant Escherichia coli in parent flocks treated with fluoroquinolones on chick stage and their broiler offspring. J. Poult. Sci. 2024, 61, 2024013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, N.M.; Wales, A.D.; Ridley, A.M.; Davies, R.H. Farm level risk factors for fluoroquinolone resistance in E. coli and thermophilic Campylobacter spp. on poultry farms. Avian Pathol. 2016, 45, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 32nd ed.; CLSI Supplement M100; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Malvern, PA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, R.; Liu, B.; Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Huang, W.; Yuan, J.; He, G.; Chen, Y.; Pan, Q.; Liu, Y.; et al. SOAPdenovo2: An empirically improved memory-efficient short-read de novo assembler. Gigascience 2012, 1, 2047-217X-1-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delcher, A.L.; Harmon, D.; Kasif, S.; White, O.; Salzberg, S.L. Improved microbial gene identification with GLIMMER. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 4636–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Resistance Phenotype | NOR | ENR | CIP | LVX | MXF | UB | Number of Strains | Strain Names |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | R | R | R | R | R | R | 2 | DJF_19/JF_G_32 |
| 2 | S | I | R | S | R | R | 1 | JF_G_33 |
| 3 | S | I | S | S | I | R | 2 | TR_30/DJF_18 |
| 4 | S | S | S | S | I | R | 1 | DSL_15 |
| 5 | S | I | S | S | I | I | 1 | JF_29 |
| 6 | S | S | S | S | I | I | 6 | TR_16/TR_20/JF_27/DJF_13/DJF_20/TR_01 |
| 7 | S | S | S | S | S | I | 5 | DJF_12/JF_32/TR_19/JF_01/DJF_14 |
| 8 | S | S | S | S | I | S | 1 | JF_33 |
| 9 | S | S | S | S | S | S | 15 | others |
| Stain No. | PMQR Determinants | Location Scaffold | Gene No. | Plasmid Type | Acc No. | Acc Plasmid Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JF_G_33 | qnrS1 | 44 | 4388 | IncHI2 | NZ_KY421937.1 | pFS13Z2S |
| TR_16 | qnrS1 | 54 | 4820 | IncHI2 | NZ_KY421937.1 | pFS13Z2S |
| JF_27 | qnrS1 | 90 | 4535 | IncHI2 | NZ_KY421937.1 | pFS13Z2S |
| DJF_12 | qnrS1 | 99 | 4603 | IncX1 | NZ_CP037995.1 | psg_ww281 |
| JF_29 | qnrS1 | 34 | 3995 | IncX1 | NZ_CP022964.1 | pQJDsal1 |
| TR_30 | qnrS1 | 29 | 4575 | IncFIB(K) | NZ_LR213454.1 | 3 |
| TR_20 | qnrS1 | 68 | 4415 | IncFIC(FII) | CP043737.1 | pN17EC0616-1 |
| DSL_15 | qnrS1 | 90 | 4316 | - | - | - |
| DJF_13 | qnrS1 | 67 | 4576 | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Ye, M.; Dong, Y.; Yuan, L.; Xiang, J.; Yu, X.; Liao, Q.; Ai, Q.; Qiu, S.; Zhang, D. Resistance Mechanisms of Fluoroquinolone in Escherichia coli Isolated from Taihe Black-Boned Silky Fowl Exhibiting Abnormally Slow Fluoroquinolone Metabolism in Jiangxi, China. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 955. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090955
Zhang L, Ye M, Dong Y, Yuan L, Xiang J, Yu X, Liao Q, Ai Q, Qiu S, Zhang D. Resistance Mechanisms of Fluoroquinolone in Escherichia coli Isolated from Taihe Black-Boned Silky Fowl Exhibiting Abnormally Slow Fluoroquinolone Metabolism in Jiangxi, China. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(9):955. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090955
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Li, Mengjun Ye, Yifan Dong, Lijuan Yuan, Jianjun Xiang, Xiren Yu, Qiegen Liao, Qiushuang Ai, Suyan Qiu, and Dawen Zhang. 2025. "Resistance Mechanisms of Fluoroquinolone in Escherichia coli Isolated from Taihe Black-Boned Silky Fowl Exhibiting Abnormally Slow Fluoroquinolone Metabolism in Jiangxi, China" Antibiotics 14, no. 9: 955. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090955
APA StyleZhang, L., Ye, M., Dong, Y., Yuan, L., Xiang, J., Yu, X., Liao, Q., Ai, Q., Qiu, S., & Zhang, D. (2025). Resistance Mechanisms of Fluoroquinolone in Escherichia coli Isolated from Taihe Black-Boned Silky Fowl Exhibiting Abnormally Slow Fluoroquinolone Metabolism in Jiangxi, China. Antibiotics, 14(9), 955. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090955





