Co-Culturing Bacillus Strains for Enhanced Antimicrobial Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
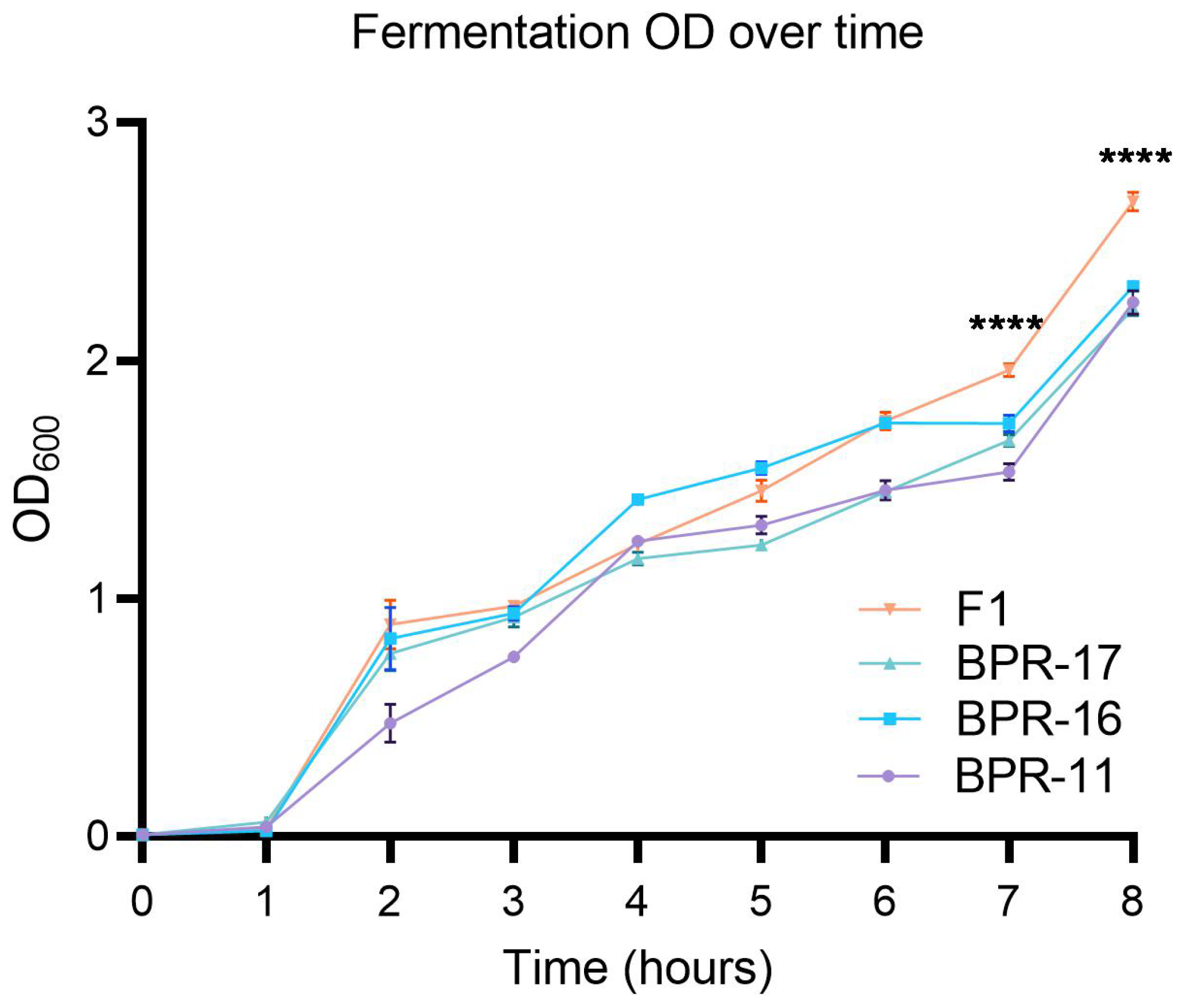
2.1. Fermentation of Mixed Bacillus Strains
2.2. Antimicrobial Activity
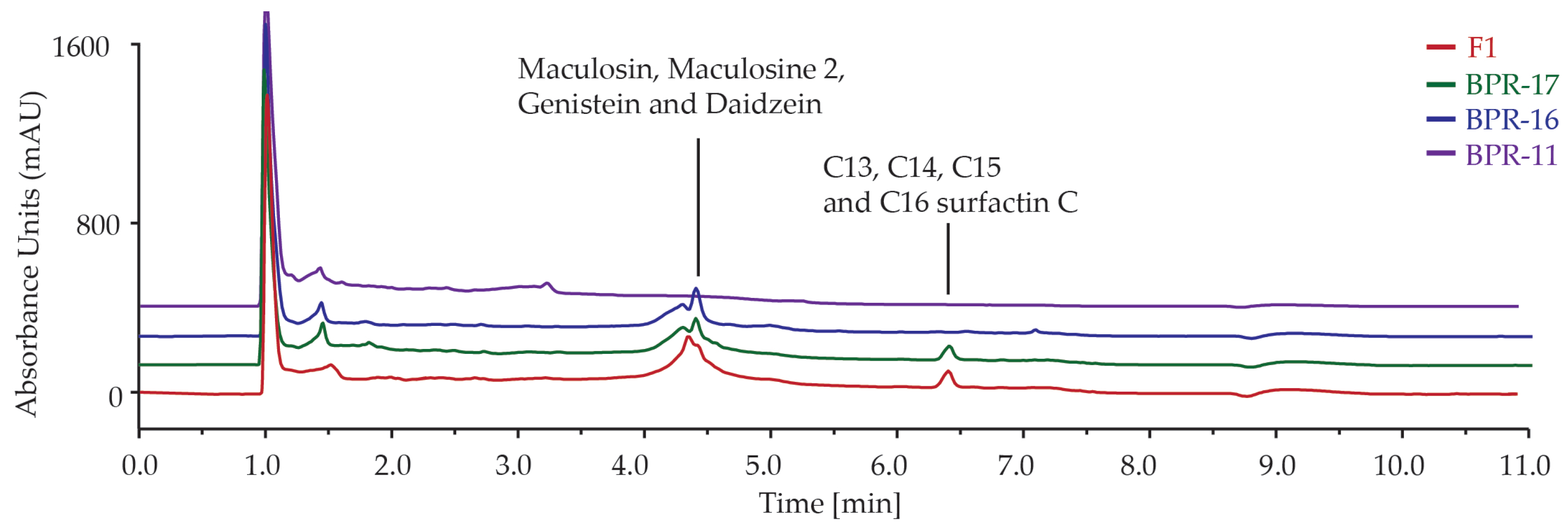
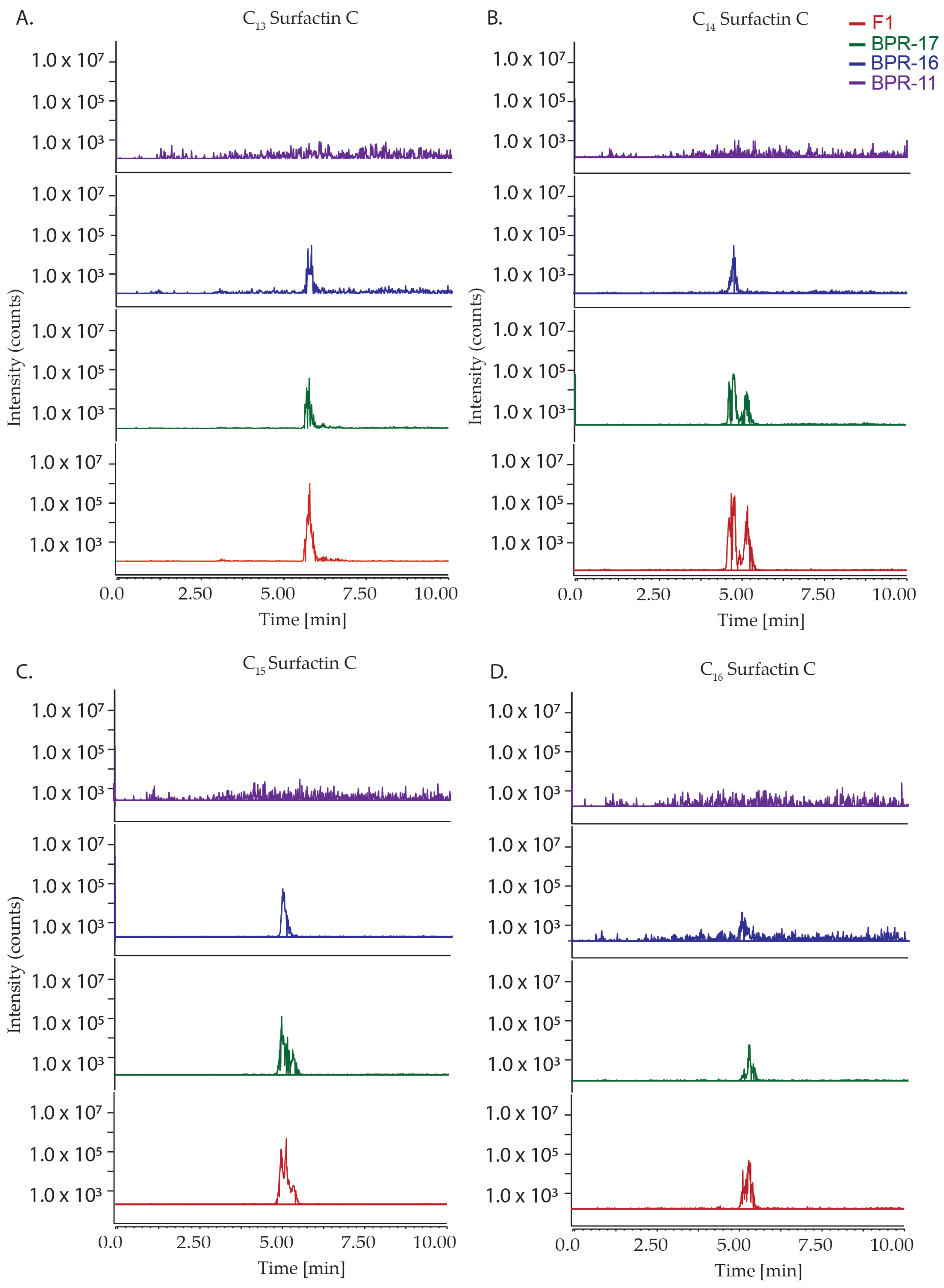
2.3. Metabolite Profiling by HPLC
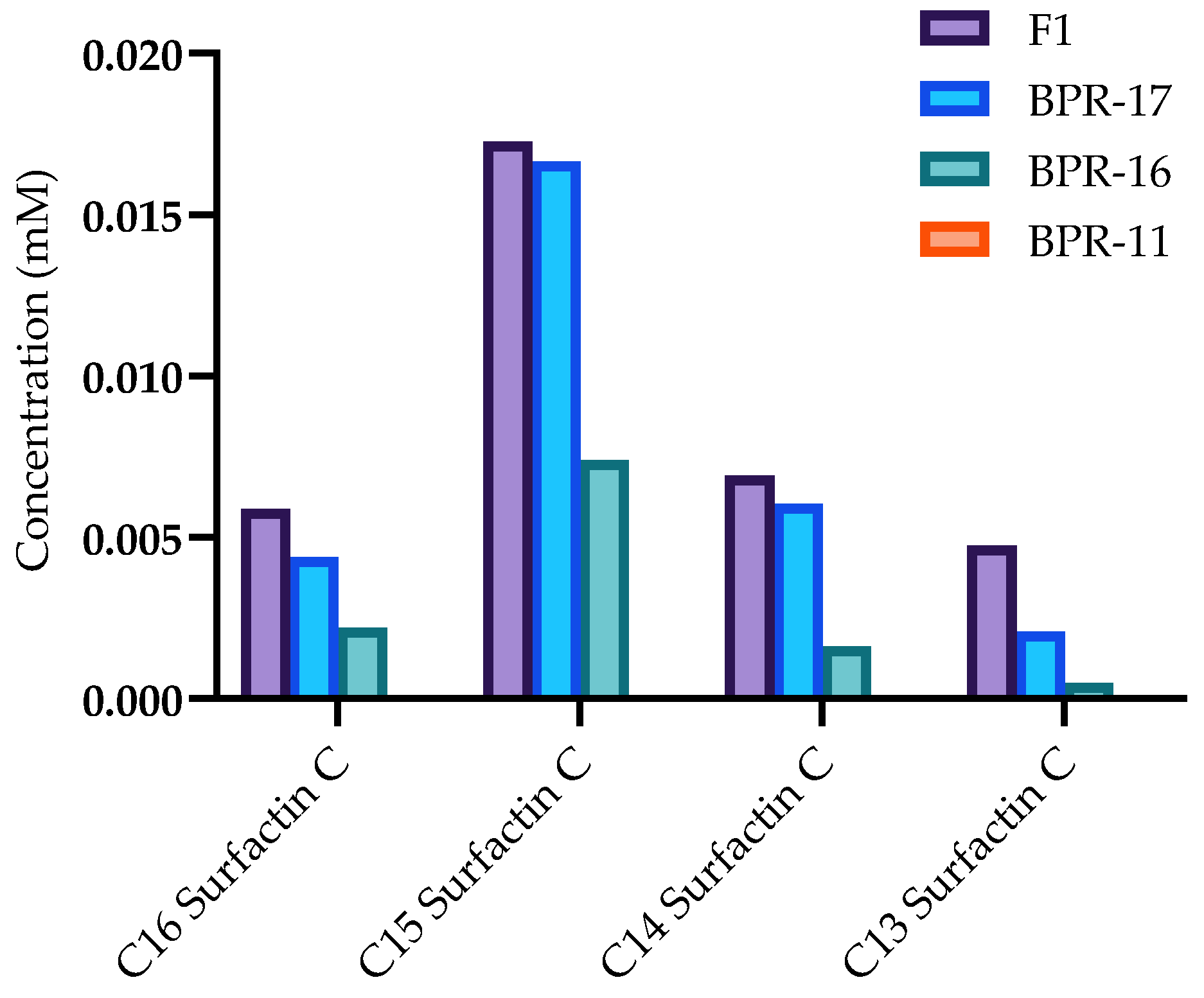
2.4. Quantification of Surfactin C Metabolites
2.5. Surfactin C Stability Study
3. Discussion
3.1. Elevated Microorganism Growth
3.2. Increase Production of Antimicrobial Metabolites
3.3. Stability Experiment
3.4. Limitations
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Experimental Procedure
4.2. Bacillus Strains and Fermentation
4.3. Extraction
4.4. Antimicrobial Assay
4.5. Chemical Profile by LC Analysis
4.6. Surfactin C Quantification by LC-MS Analysis
4.7. Microsome Preparation
4.8. Surfactin C Metabolism Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Selegato, D.M.; Castro-Gamboa, I. Enhancing chemical and biological diversity by co-cultivation. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1117559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwoji, I.D.; Aiyegoro, O.A.; Okpeku, M.; Adeleke, M.A. Multi-Strain Probiotics: Synergy among Isolates Enhances Biological Activities. Biology 2021, 10, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, S.A.; Ahmadi, H.; Karimi Torshizi, M.A. Evaluating two multistrain probiotics on growth performance, intestinal morphology, lipid oxidation and ileal microflora in chickens. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2019, 103, 1399–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicault, M.; Zaiter, A.; Dumarcay, S.; Chaimbault, P.; Gelhaye, E.; Leblond, P.; Bontemps, C. Elicitation of Antimicrobial Active Compounds by Streptomyces-Fungus Co-Cultures. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oana, K.; Shimizu, K.; Takada, T.; Makino, H.; Yamazaki, M.; Katto, M.; Ando, M.; Kurakawa, T.; Oishi, K. Manipulating the growth environment through co-culture to enhance stress tolerance and viability of probiotic strains in the gastrointestinal tract. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 89, e0150223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hifnawy, S.M.; Hassan, H.M.; Mohammed, R.; Fouda, M.M.; Sayed, A.M.; Hamed, A.A.; AbouZid, F.S.; Rateb, M.E.; Alhadrami, H.A.; Abdelmohsen, U.R. Induction of Antibacterial Metabolites by Co-Cultivation of Two Red-Sea-Sponge-Associated Actinomycetes Micromonospora sp. UR56 and Actinokinespora sp. EG49. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riazi, S.; Wirawan, R.E.; Badmaev, V.; Chikindas, M.L. Characterization of lactosporin, a novel antimicrobial protein produced by Bacillus coagulans ATCC 7050. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 106, 1370–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alayande, K.A.; Aiyegoro, O.A.; Ateba, C.N. Probiotics in Animal Husbandry: Applicability and Associated Risk Factors. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.-R.; Wei, S.-Y.; Ding, M.-Z.; Hou, Z.-J.; Wang, D.-J.; Xu, Q.-M.; Cheng, J.-S.; Yuan, Y.-J. Enhancing fengycin production in the co-culture of Bacillus subtilis and Corynebacterium glutamicum by engineering proline transporter. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 383, 129229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosero-Chasoy, G.; Rodríguez-Jasso, R.M.; Aguilar, C.N.; Buitrón, G.; Chairez, I.; Ruiz, H.A. Microbial co-culturing strategies for the production high value compounds, a reliable framework towards sustainable biorefinery implementation—An overview. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 321, 124458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Li, G.; Gao, P.; Han, X. Optimizing Culture Conditions by Statistical Approach to Enhance Production of Pectinase from Bacillus sp. Y1. Biomed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 8146948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wu, R.; Zhou, J.; He, A.; Xu, J.; Xin, F.; Zhang, W.; Jiangfeng, M.; Jiang, M.; Weiliang, D. Recent advances of biofuels and biochemicals production from sustainable resources using co-cultivation systems. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2019, 12, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, C.D.; Yagi, S.; Ijima, M.; Nashimoto, T.; Sawada, M.; Ikeda, S.; Asano, K.; Orikasa, Y.; Ohwada, T. Bacterial Compatibility in Combined Inoculations Enhances the Growth of Potato Seedlings. Microbes Environ. 2017, 32, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriksson, P.J.G.; Troell, M.; Banks, L.K.; Belton, B.; Beveridge, M.C.M.; Klinger, D.H.; Pelletier, N.; Phillips, M.J.; Tran, N. Interventions for improving the productivity and environmental performance of global aquaculture for future food security. One Earth 2021, 4, 1220–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shini, S.; Bryden, W.L. Probiotics and gut health: Linking gut homeostasis and poultry productivity. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2022, 62, 1090–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caudal, F.; Tapissier-Bontemps, N.; Edrada-Ebel, R.A. Impact of Co-Culture on the Metabolism of Marine Microorganisms. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, L.; Zhang, H. Utilizing cross-species co-cultures for discovery of novel natural products. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2021, 69, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz Ramos, H.; Hoffmann, T.; Marino, M.; Nedjari, H.; Presecan-Siedel, E.; Dreesen, O.; Glaser, P.; Jahn, D. Fermentative metabolism of Bacillus subtilis: Physiology and regulation of gene expression. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 3072–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Yang, F.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, X.; Feng, D.; Ye, S. Batch fermentation kinetics study of biosynthesis lipopeptides by Bacillus altitudinis Q7 in 5 L fermenter. Process Biochem. 2024, 140, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azi, F.; Tu, C.; Meng, L.; Zhiyu, L.; Cherinet, M.T.; Ahmadullah, Z.; Dong, M. Metabolite dynamics and phytochemistry of a soy whey-based beverage bio-transformed by water kefir consortium. Food Chem. 2021, 342, 128225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, J.; Yasmin, S.; Kamal, G.M.; Asmari, M.; Saqib, M.; Chen, H. Changes in Metabolite Profiles of Chinese Soy Sauce at Different Time Durations of Fermentation Studied by 1H-NMR-Based Metabolomics. Metabolites 2024, 14, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurva, U.; Sandinge, A.S.; Baek, J.M.; Avanthay, M.; Thomson, R.E.S.; D’Cunha, S.A.; Andersson, S.; Hayes, M.A.; Gillam, E.M.J. Biocatalysis using Thermostable Cytochrome P450 Enzymes in Bacterial Membranes—Comparison of Metabolic Pathways with Human Liver Microsomes and Recombinant Human Enzymes. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2024, 52, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, C.; Horyanto, D.; Stanley, D.; Cock, I.E.; Chen, X.; Feng, Y. Antimicrobial Properties of Bacillus Probiotics as Animal Growth Promoters. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bromfield, J.I.; Niknafs, S.; Chen, X.; von Hellens, J.; Horyanto, D.; Sun, B.; Yu, L.; Tran, V.H.; Navarro, M.; Roura, E. The evaluation of next-generation probiotics on broiler growth performance, gut morphology, gut microbiome, nutrient digestibility, in addition to enzyme production of Bacillus spp. in vitro. Anim. Nutr. 2024, 18, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charman, S.A.; Andreu, A.; Barker, H.; Blundell, S.; Campbell, A.; Campbell, M.; Chen, G.; Chiu, F.C.K.; Crighton, E.; Katneni, K.; et al. An in vitro toolbox to accelerate anti-malarial drug discovery and development. Malar. J. 2020, 19, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerdijk Fungal Biodiversity Institute, Utrecht, The Netherlands. Available online: https://wi.knaw.nl/ (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- Ulenberg, S.; Belka, M.; Król, M.; Herold, F.; Hewelt-Belka, W.; Kot-Wasik, A.; Bączek, T. Prediction of overall in vitro microsomal stability of drug candidates based on molecular modeling and support vector machines. Case study of novel arylpiperazines derivatives. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, L.; Naved, T.; Grover, P.; Bhardwaj, M.; Mukherjee, D. LC and LC–MS/MS studies for identification and characterization of new degradation products of ibrutinib and elucidation of their degradation pathway. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 194, 113768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakibe, U.; Tiwari, R.; Mahajan, A.; Rane, V.; Wakte, P. LC and LC-MS/MS studies for the identification and characterization of degradation products of acebutolol. J. Pharm. Anal. 2018, 8, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Huang, W.; Sha, Y.; Yin, H.; Liang, Y.; Wang, X.; Shen, Y.; Wu, X.; Wu, D.; Wang, J. Co-Cultivation of Two Bacillus Strains for Improved Cell Growth and Enzyme Production to Enhance the Degradation of Aflatoxin B(1). Toxins 2021, 13, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Shi, X.; Xing, Y.; Ren, X.X.; Zhang, D.Y.; Li, X.; Xiu, Z.L.; Dong, Y.S. Co-culture of Aspergillus sydowii and Bacillus subtilis induces the production of antibacterial metabolites. Fungal Biol. 2022, 126, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Wu, C.; Liang, Y.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Song, G. Bacillus Co-culture Inhibits Quorum Sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Curr. Microbiol. 2023, 80, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hao, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, J. Approaches for the establishment of optimized co-culture system of multiple Trichoderma strains for culture metabolites highly effective in cucumber growth promotion. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1020077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oslizlo, A.; Stefanic, P.; Dogsa, I.; Mandic-Mulec, I. Private link between signal and response in Bacillus subtilis quorum sensing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 1586–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, A.A.; Gromek, S.M.; Balunas, M.J. Upregulation and Identification of Antibiotic Activity of a Marine-Derived Streptomyces sp. via Co-Cultures with Human Pathogens. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sansinenea, E.; Ortiz, A. Secondary metabolites of soil Bacillus spp. Biotechnol. Lett. 2011, 33, 1523–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atolia, E.; Cesar, S.; Arjes, H.A.; Rajendram, M.; Shi, H.; Knapp, B.D.; Khare, S.; Aranda-Díaz, A.; Lenski, R.E.; Huang, K.C. Environmental and Physiological Factors Affecting High-Throughput Measurements of Bacterial Growth. mBio 2020, 11, 10-1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purwasena, I.A.; Astuti, D.I.; Syukron, M.; Amaniyah, M.; Sugai, Y. Stability test of biosurfactant produced by Bacillus licheniformis DS1 using experimental design and its application for MEOR. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 183, 106383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, C.; Ge, X.F.; Lu, Y.T.; Liu, W.Z. Chemical structure, properties and potential applications of surfactin, as well as advanced strategies for improving its microbial production. AIMS Microbiol. 2023, 9, 195–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, H.Z.; Liu, J.F.; Mu, B.Z. Molecular dynamics study of surfactin monolayer at the air/water interface. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 12770–12777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumi, C.D.; Yang, B.W.; Yeo, I.-C.; Hahm, Y.T. Antimicrobial peptides of the genus Bacillus: A new era for antibiotics. Can. J. Microbiol. 2015, 61, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Xu, B. Inspiration from the mirror: D-amino acid containing peptides in biomedical approaches. Biomol. Concepts 2016, 7, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beers, M.F.; Kim, C.Y.; Dodia, C.; Fisher, A.B. Localization, synthesis, and processing of surfactant protein SP-C in rat lung analyzed by epitope-specific antipeptide antibodies. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 20318–20328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, K.R.; Kanwar, S.S. Lipopeptides as the Antifungal and Antibacterial Agents: Applications in Food Safety and Therapeutics. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 473050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knights, K.M.; Stresser, D.M.; Miners, J.O.; Crespi, C.L. In Vitro Drug Metabolism Using Liver Microsomes. Curr. Protoc. Pharmacol. 2016, 74, 7.8.1–7.8.24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Strains | Strain Type | Origin | CBS Number * |
|---|---|---|---|
| BPR-11 | B. amyloliquefaciens | Soil and vegetation | 141,692 |
| BPR-16 | B. amyloliquefaciens ** | Soil and vegetation | 148,295 |
| BPR-17 | B. amyloliquefaciens | Soil and vegetation | 148,296 |
| Strain | C. perfringens | E. coli | P. aeruginosa | S. aureus | S. enterica |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BPR-11 EtOAc | 100 | 100 | NA | 100 | NA |
| BPR-16 EtOAc | 50 | 50 | 100 | 50 | 100 |
| BPR-17 EtOAc | 50 | 50 | 100 | 50 | 100 |
| F1 EtOAc | 25 | 25 | 50 | 25 | 50 |
| BPR-11 crude | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| BPR-16 crude | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| BPR-17 crude | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| F1 crude | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Target (Analyte) | Molecular Weight | Scan Range (m/z) | Quantitative Ion (m/z) |
|---|---|---|---|
| C13 surfactin C | 1008.3 | 100–1500 | 1007.3 |
| C14 surfactin C | 1022.3 | 100–1500 | 1021.3 |
| C15 surfactin C | 1036.3 | 100–1500 | 1035.3 |
| plemeC16 surfactin C | 1050.3 | 100–1500 | 1049.3 |
| Target (Analyte) | Molecular Weight | k | t1/2 (Mins) |
|---|---|---|---|
| C13 surfactin C | 1008.3 | 0.0006 | 1155 |
| C14 surfactin C | 1022.3 | 0.0018 | 378 |
| C15 surfactin C | 1036.3 | 0.0008 | 866.25 |
| C16 surfactin C | 1050.3 | 0.0007 | 990 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tran, C.; Addison, R.S.; Cock, I.E.; Chen, X.; Feng, Y. Co-Culturing Bacillus Strains for Enhanced Antimicrobial Activity. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 908. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090908
Tran C, Addison RS, Cock IE, Chen X, Feng Y. Co-Culturing Bacillus Strains for Enhanced Antimicrobial Activity. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(9):908. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090908
Chicago/Turabian StyleTran, Charlie, Russell S. Addison, Ian E. Cock, Xiaojing Chen, and Yunjiang Feng. 2025. "Co-Culturing Bacillus Strains for Enhanced Antimicrobial Activity" Antibiotics 14, no. 9: 908. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090908
APA StyleTran, C., Addison, R. S., Cock, I. E., Chen, X., & Feng, Y. (2025). Co-Culturing Bacillus Strains for Enhanced Antimicrobial Activity. Antibiotics, 14(9), 908. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090908







