Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance of Enterobacteriaceae in Wild Birds Across Europe: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
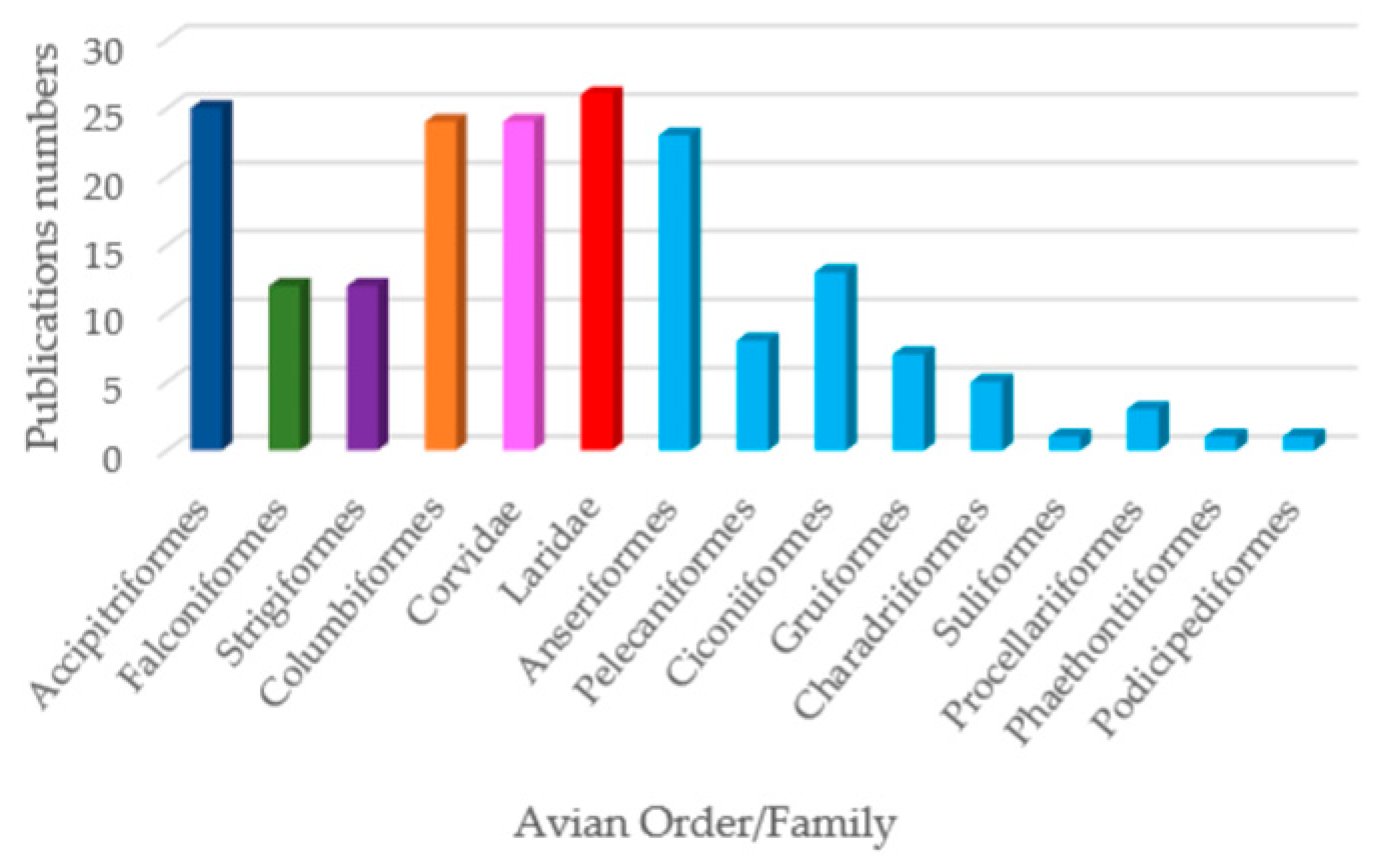
2. Results
2.1. Accipitriformes
2.2. Falconiformes
2.3. Strigiformes
2.4. Columbiformes
2.5. Passeriformes (Corvidae)
2.6. Charadriiformes (Laridae)
2.7. Aquatic Birds
2.7.1. Anseriformes
2.7.2. Pelecaniformes
2.7.3. Ciconiiformes
2.7.4. Gruiformes
2.7.5. Charadriiformes
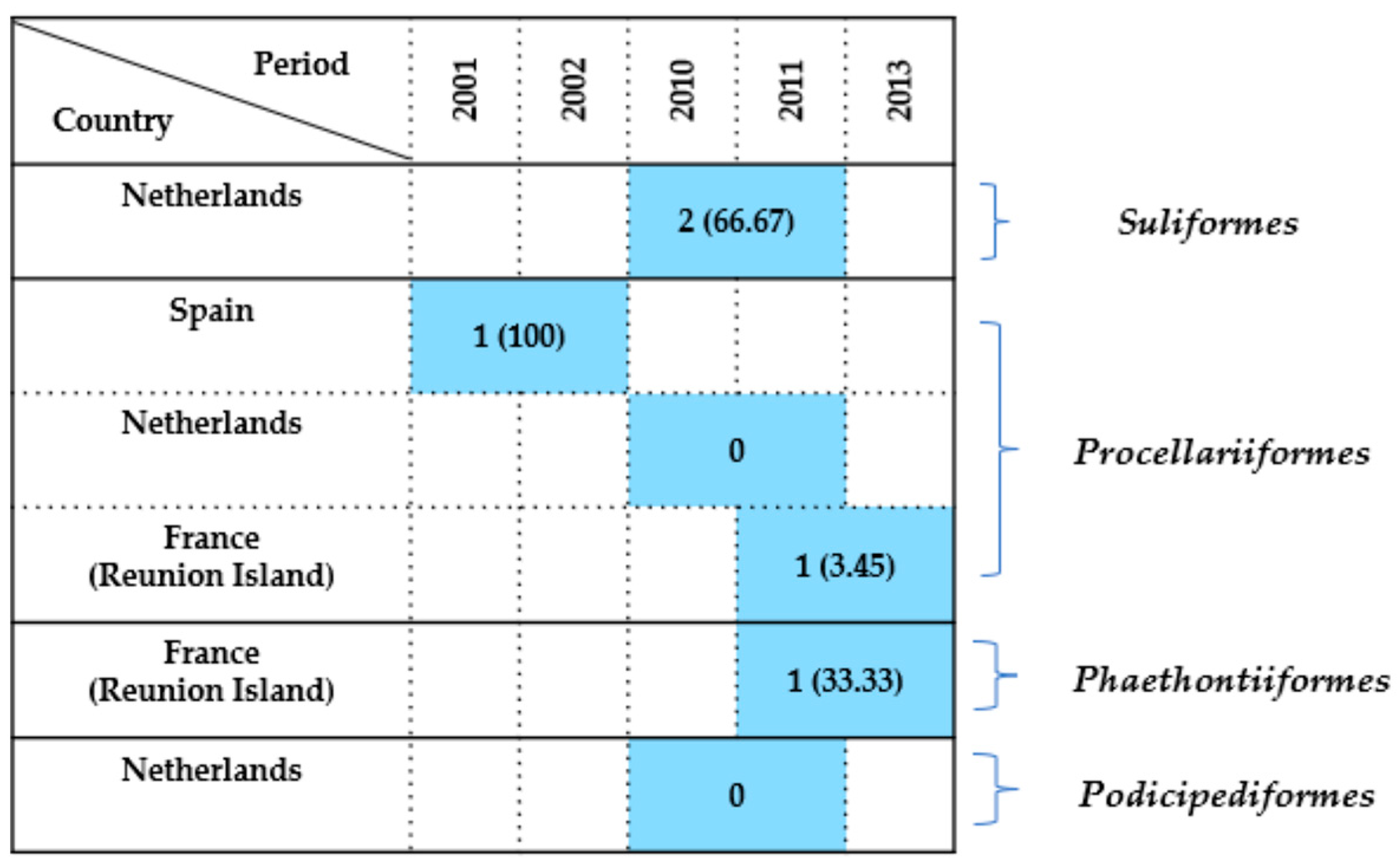
2.7.6. Other Seabird Orders
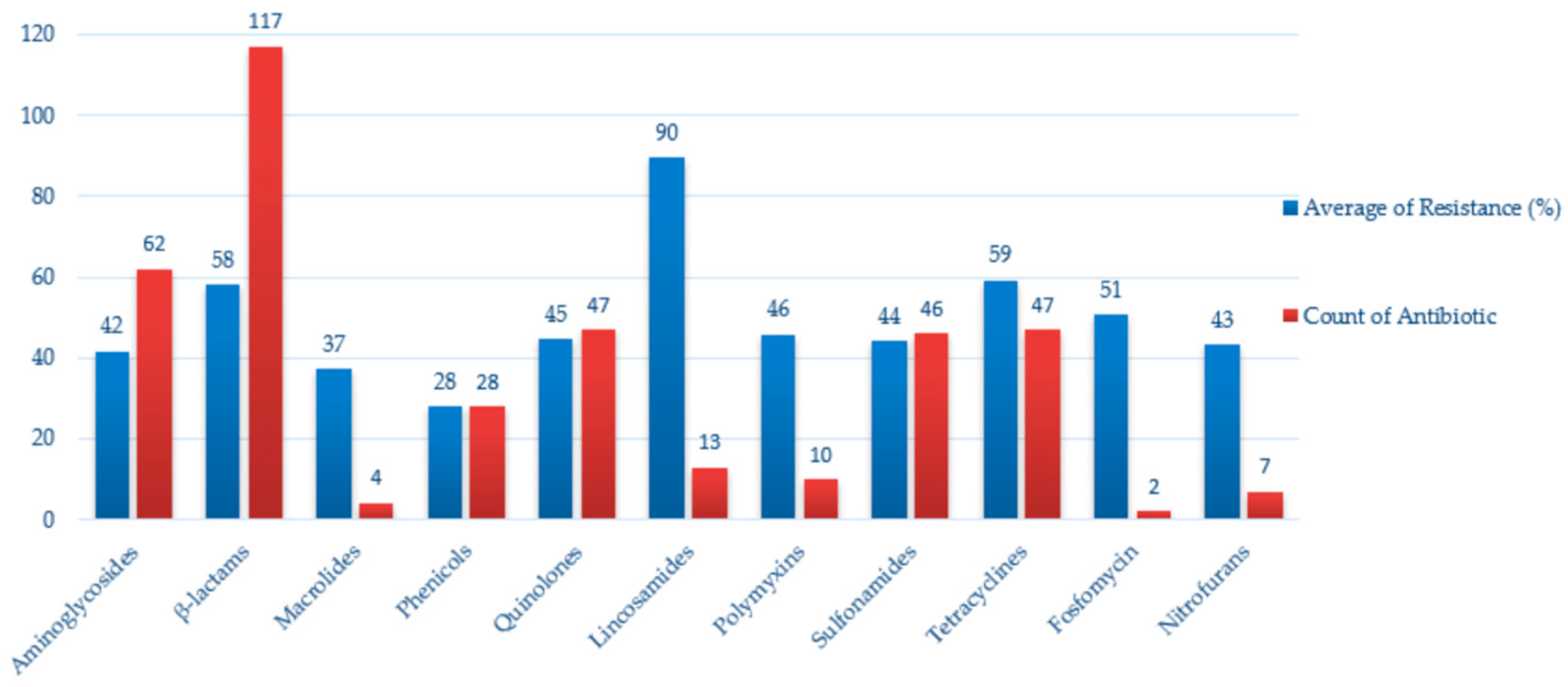
2.8. Antimicrobial Resistance in Enterobacteriaceae Isolated from Wild Birds
3. Discussion
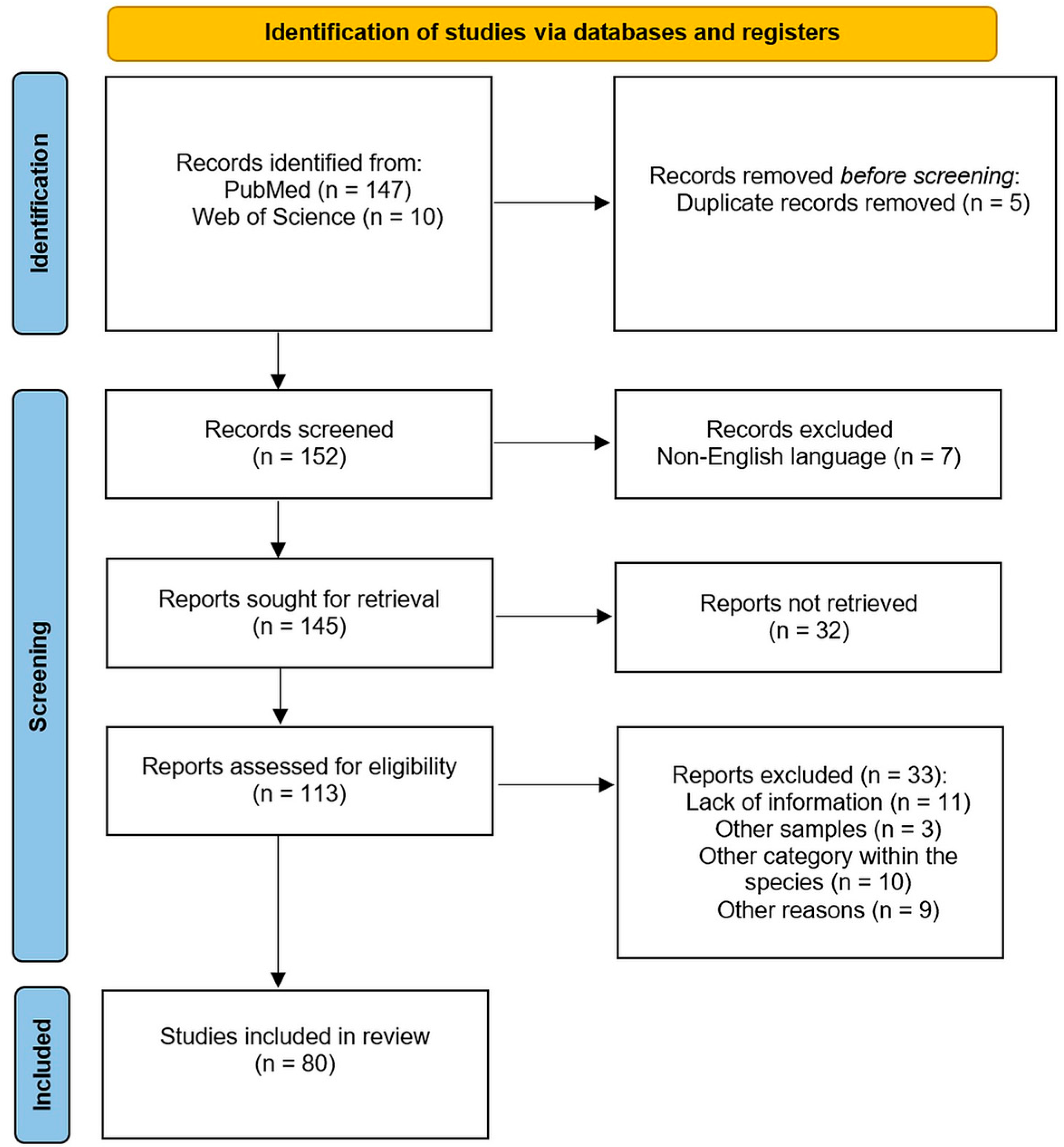
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramey, A.M.; Ahlstrom, C.A. Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria in Wildlife: Perspectives on Trends, Acquisition and Dissemination, Data Gaps, and Future Directions. J. Wildl. Dis. 2019, 56, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadimpalli, M.L.; Chan, C.W.; Doron, S. Antibiotic Resistance: A Call to Action to Prevent the next Epidemic of Inequality. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 187–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO Regional Office for Europe/European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance in Europe 2022—2020 Data; Publications Office: Luxembourg, 2022; Available online: https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2900/112339 (accessed on 15 July 2025).
- Oliveira, M.; Antunes, W.; Mota, S.; Madureira-Carvalho, Á.; Dinis-Oliveira, R.J.; Dias da Silva, D. An Overview of the Recent Advances in Antimicrobial Resistance. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnedahl, J.; Järhult, J.D. Antibiotic Resistance in Wild Birds. Upsala J. Med. Sci. 2014, 119, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacopello, C.; Foti, M.; Mascetti, A. Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns of Enterobacteriaceae in European Wild Bird Species Admitted in a Wildlife Rescue Centre. Vet. Ital. 2016, 52, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handrova, L.; Kmet, V. Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence Factors of Escherichia coli from Eagles and Goshawks. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2019, 54, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pătrînjan, R.-T.; Morar, A.; Ban-Cucerzan, A.; Popa, S.A.; Imre, M.; Morar, D.; Imre, K. Systematic Review of the Occurrence and Antimicrobial Resistance Profile of Foodborne Pathogens from Enterobacteriaceae in Wild Ungulates Within the European Countries. Pathogens 2024, 13, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Sánchez, S.; Sánchez, S.; Ewers, C.; Höfle, U. Occurrence of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli and Antimicrobial-Resistant E. coli in Red-Legged Partridges (Alectoris rufa): Sanitary Concerns of Farming. Avian Pathol. 2012, 41, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority); ECDC (European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control). The European Union Summary Report on Antimicrobial Resistance in Zoonotic and Indicator Bacteria from Humans, Animals and Food in 2021/2022. Annex C—Data Reported on Antimicrobial Resistance in Indicator Commensal Escherichia coli from Foodproducing Animals and Imported Fresh Meat. EFSA J. 2024, 22, e8583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, B.M.C.; Bennett, M.; Waller, K.; Dodd, C.; Murray, A.; Gomes, R.L.; Humphreys, B.; Hobman, J.L.; Jones, M.A.; Whitlock, S.E.; et al. Anthropogenic Environmental Drivers of Antimicrobial Resistance in Wildlife. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guitart-Matas, J.; Espunyes, J.; Illera, L.; Gonzalez-Escalona, N.; Ribas, M.P.; Marco, I.; Migura-Garcia, L. High-Risk Lineages of Extended Spectrum Cephalosporinase Producing Escherichia coli from Eurasian Griffon Vultures (Gyps fulvus) Foraging in Landfills in North-Eastern Spain. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 909, 168625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnedahl, J.; Drobni, M.; Gauthier-Clerc, M.; Hernandez, J.; Granholm, S.; Kayser, Y.; Melhus, A.; Kahlmeter, G.; Waldenström, J.; Johansson, A.; et al. Dissemination of Escherichia coli with CTX-M Type ESBL between Humans and Yellow-Legged Gulls in the South of France. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guenther, S.; Grobbel, M.; Lübke-Becker, A.; Goedecke, A.; Friedrich, N.D.; Wieler, L.H.; Ewers, C. Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles of Escherichia coli from Common European Wild Bird Species. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 144, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furmanek-Blaszk, B.; Sektas, M.; Rybak, B. High Prevalence of Plasmid-Mediated Quinolone Resistance among ESBL/AmpC-Producing Enterobacterales from Free-Living Birds in Poland. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; Pohjanvirta, T.; Pelkonen, S. Prevalence and Characteristics of Intimin- and Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli from Gulls, Pigeons and Broilers in Finland. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2002, 64, 1071–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refsum, T.; Handeland, K.; Baggesen, D.L.; Holstad, G.; Kapperud, G. Salmonellae in Avian Wildlife in Norway from 1969 to 2000. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 5595–5599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlstrom, C.A.; Ramey, A.M.; Woksepp, H.; Bonnedahl, J. Early Emergence of Mcr-1-Positive Enterobacteriaceae in Gulls from Spain and Portugal. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2019, 11, 669–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brassó, D.L.; Knop, R.; Várszegi, Z.; Bársony, P.; Komlósi, I.; Bacsadi, Á.; Bistyák, A. Assessment of the Microbiological Status of Two Hungarian Ostrich Farms. Acta Vet. Hung. 2023, 71, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwaśna, N.; Majewska, M.; Karwańska, M.; Siedlecka, M.; Pałucki, A.; Piasecki, T. Occurrence and Molecular Characterization of Escherichia coli Strains Isolated from Black Grouse (Lyrurus tetrix) from the Karkonosze National Park in Poland. BMC Vet. Res. 2024, 20, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millán, J.; Aduriz, G.; Moreno, B.; Juste, R.A.; Barral, M. Salmonella Isolates from Wild Birds and Mammals in the Basque Country (Spain). Rev. Sci. Tech. 2004, 23, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasyl, D.; Hasman, H.; Cavaco, L.M.; Aarestrup, F.M. Prevalence and Characterization of Cephalosporin Resistance in Nonpathogenic Escherichia coli from Food-Producing Animals Slaughtered in Poland. Microb. Drug Resist. 2012, 18, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atterby, C.; Börjesson, S.; Ny, S.; Järhult, J.D.; Byfors, S.; Bonnedahl, J. ESBL-Producing Escherichia coli in Swedish Gulls—A Case of Environmental Pollution from Humans? PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0190380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köck, R.; Daniels-Haardt, I.; Becker, K.; Mellmann, A.; Friedrich, A.W.; Mevius, D.; Schwarz, S.; Jurke, A. Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae in Wildlife, Food-Producing, and Companion Animals: A Systematic Review. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 1241–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, G.A.; Salah-Eldein, A.M.; Al-Zaban, M.I.; El-Oksh, A.S.A.; Ahmed, E.M.; Farid, D.S.; Saad, E.M. Monitoring the Genetic Variation of Some Escherichia coli Strains in Wild Birds and Cattle. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2023, 90, e1–e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skov, M.N.; Madsen, J.J.; Rahbek, C.; Lodal, J.; Jespersen, J.B.; Jørgensen, J.C.; Dietz, H.H.; Chriél, M.; Baggesen, D.L. Transmission of Salmonella between Wildlife and Meat-Production Animals in Denmark. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 105, 1558–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reche, M.P.; Jiménez, P.A.; Alvarez, F.; García de los Rios, J.E.; Rojas, A.M.; de Pedro, P. Incidence of Salmonellae in Captive and Wild Free-Living Raptorial Birds in Central Spain. J. Vet. Med. B Infect. Dis. Vet. Public Health 2003, 50, 42–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, C.; Palomeque, M.-D.; Marco-Jiménez, F.; Vega, S. Wild Griffon Vultures (Gyps fulvus) as a Source of Salmonella and Campylobacter in Eastern Spain. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcalá, L.; Alonso, C.A.; Simón, C.; González-Esteban, C.; Orós, J.; Rezusta, A.; Ortega, C.; Torres, C. Wild Birds, Frequent Carriers of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase (ESBL) Producing Escherichia coli of CTX-M and SHV-12 Types. Microb. Ecol. 2016, 72, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado-Tarifa, E.; Torralbo, A.; Borge, C.; Cerdà-Cuéllar, M.; Ayats, T.; Carbonero, A.; García-Bocanegra, I. Genetic Diversity and Antimicrobial Resistance of Campylobacter and Salmonella Strains Isolated from Decoys and Raptors. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 48, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-López, R.A.; Vidal, A.; Obón, E.; Martín, M.; Darwich, L. Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Monophasic Variant 4,12:I:- Isolated from Asymptomatic Wildlife in a Catalonian Wildlife Rehabilitation Center, Spain. J. Wildl. Dis. 2015, 51, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, G. Supplementary Feeding as a Source of Multiresistant Salmonella in Endangered Egyptian Vultures. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 806–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin, C.; Torres, C.; Marco-Jiménez, F.; Cerdà-Cuéllar, M.; Sevilla, S.; Ayats, T.; Vega, S. Supplementary Feeding Stations for Conservation of Vultures Could Be an Important Source of Monophasic Salmonella typhimurium 1,4,[5],12:I:. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Maldonado, B.; Montoro-Dasi, L.; Pérez-Gracia, M.T.; Jordá, J.; Vega, S.; Marco-Jiménez, F.; Marin, C. Wild Bonelli’s Eagles (Aquila fasciata) as Carrier of Antimicrobial Resistant Salmonella and Campylobacter in Eastern Spain. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 67, 101372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oteo, J.; Mencia, A.; Bautista, V.; Pastor, N.; Lara, N.; Gonzalez-Gonzalez, F.; Javier Garcia-Pena, F.; Campos, J. Colonization with Enterobacteriaceae-Producing ESBLs, AmpCs, and OXA-48 in Wild Avian Species, Spain 2015-2016. Microb. Drug Resist. 2018, 24, 932–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardón, A.; Bataller, E.; Llobat, L.; Jiménez-Trigos, E. Bacteria and Antibiotic Resistance Detection in Fractures of Wild Birds from Wildlife Rehabilitation Centres in Spain. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 74, 101575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenther, S.; Aschenbrenner, K.; Stamm, I.; Bethe, A.; Semmler, T.; Stubbe, A.; Stubbe, M.; Batsajkhan, N.; Glupczynski, Y.; Wieler, L.H.; et al. Comparable High Rates of Extended-Spectrum-Beta-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli in Birds of Prey from Germany and Mongolia. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e53039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, J.; Schmoger, S.; Jahn, S.; Helmuth, R.; Guerra, B. NDM-1 Carbapenemase-Producing Salmonella enterica Subsp. Enterica Serovar Corvallis Isolated from a Wild Bird in Germany. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 2954–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaufler, K.; Semmler, T.; Wieler, L.H.; Wöhrmann, M.; Baddam, R.; Ahmed, N.; Müller, K.; Kola, A.; Fruth, A.; Ewers, C.; et al. Clonal Spread and Interspecies Transmission of Clinically Relevant ESBL-Producing Escherichia coli of ST410—Another Successful Pandemic Clone? FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2016, 92, fiv155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dipineto, L.; Bossa, L.M.D.L.; Pace, A.; Russo, T.P.; Gargiulo, A.; Ciccarelli, F.; Raia, P.; Caputo, V.; Fioretti, A. Microbiological Survey of Birds of Prey Pellets. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 41, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargiulo, A.; Fioretti, A.; Russo, T.P.; Varriale, L.; Rampa, L.; Paone, S.; De Luca Bossa, L.M.; Raia, P.; Dipineto, L. Occurrence of Enteropathogenic Bacteria in Birds of Prey in Italy. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 66, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botti, V.; Navillod, F.V.; Domenis, L.; Orusa, R.; Pepe, E.; Robetto, S.; Guidetti, C. Salmonella spp. and Antibiotic-Resistant Strains in Wild Mammals and Birds in North-Western Italy from 2002 to 2010. Vet. Ital. 2013, 49, 195–202. [Google Scholar]
- Pennycott, T.W.; Park, A.; Mather, H.A. Isolation of Different Serovars of Salmonella enterica from Wild Birds in Great Britain between 1995 and 2003. Vet. Rec. 2006, 158, 817–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldman, K.; van Tulden, P.; Kant, A.; Testerink, J.; Mevius, D. Characteristics of Cefotaxime-Resistant Escherichia coli from Wild Birds in the Netherlands. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 7556–7561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krawiec, M.; Kuczkowski, M.; Kruszewicz, A.G.; Wieliczko, A. Prevalence and Genetic Characteristics of Salmonella in Free-Living Birds in Poland. BMC Vet. Res. 2015, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konicek, C.; Vodrážka, P.; Barták, P.; Knotek, Z.; Hess, C.; Račka, K.; Hess, M.; Troxler, S. Detection of zoonotic pathogens in wild birds in the cross-border region Austria—Czech republic. J. Wildl. Dis. 2016, 52, 850–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurfluh, K.; Albini, S.; Mattmann, P.; Kindle, P.; Nüesch-Inderbinen, M.; Stephan, R.; Vogler, B.R. Antimicrobial Resistant and Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase Producing Escherichia coli in Common Wild Bird Species in Switzerland. Microbiologyopen 2019, 8, e845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapperud, G.; Rosef, O. Avian Wildlife Reservoir of Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni, Yersinia spp., and Salmonella spp. in Norway. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1983, 45, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillehaug, A.; Monceyron Jonassen, C.; Bergsjø, B.; Hofshagen, M.; Tharaldsen, J.; Nesse, L.L.; Handeland, K. Screening of Feral Pigeon (Colomba livia), Mallard (Anas platyrhynchos) and Graylag Goose (Anser anser) Populations for Campylobacter spp., Salmonella spp., Avian Influenza Virus and Avian Paramyxovirus. Acta Vet. Scand. 2005, 46, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cízek, A.; Literák, I.; Hejlícek, K.; Treml, F.; Smola, J. Salmonella Contamination of the Environment and Its Incidence in Wild Birds. Zentralbl Vet. B 1994, 41, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morabito, S.; Dell’Omo, G.; Agrimi, U.; Schmidt, H.; Karch, H.; Cheasty, T.; Caprioli, A. Detection and Characterization of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli in Feral Pigeons. Vet. Microbiol. 2001, 82, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubini, S.; Ravaioli, C.; Previato, S.; D’Incau, M.; Tassinari, M.; Guidi, E.; Lupi, S.; Merialdi, G.; Bergamini, M. Prevalence of Salmonella Strains in Wild Animals from a Highly Populated Area of North-Eastern Italy. Ann. Ist. Super. Sanita 2016, 52, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, L.A.; Shopland, S.; Wigley, P.; Bradon, H.; Leatherbarrow, A.H.; Williams, N.J.; Bennett, M.; de Pinna, E.; Lawson, B.; Cunningham, A.A.; et al. Characterisation of Salmonella enterica Serotype Typhimurium Isolates from Wild Birds in Northern England from 2005–2006. BMC Vet. Res. 2008, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, L.A.; Wigley, P.; Bennett, M.; Chantrey, J.; Williams, N. Multi-Locus Sequence Typing of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Isolates from Wild Birds in Northern England Suggests Host-Adapted Strain. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 51, 477–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrés, S.; Vico, J.P.; Garrido, V.; Grilló, M.J.; Samper, S.; Gavín, P.; Herrera-León, S.; Mainar-Jaime, R.C. Epidemiology of Subclinical Salmonellosis in Wild Birds from an Area of High Prevalence of Pig Salmonellosis: Phenotypic and Genetic Profiles of Salmonella Isolates. Zoonoses Public Health 2013, 60, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Maldonado, B.; Vega, S.; Mencía-Gutiérrez, A.; Lorenzo-Rebenaque, L.; de Frutos, C.; González, F.; Revuelta, L.; Marin, C. Urban Birds: An Important Source of Antimicrobial Resistant Salmonella Strains in Central Spain. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 72, 101519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurfluh, K.; Nüesch-Inderbinen, M.; Stephan, R.; Hächler, H. Higher-Generation Cephalosporin-Resistant Escherichia coli in Feral Birds in Switzerland. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2013, 41, 296–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawiec, M.; Rusiecki, S.; Kuczkowski, M.; Wieliczko, A. Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Salmonella spp. Strains Isolated from Free-Living Birds. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2017, 20, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, C.; Parama Atiana, L.; Lagadec, E.; Le Minter, G.; Denis, M.; Cardinale, E. Wild Fauna as a Carrier of Salmonella in Reunion Island: Impact on Pig Farms. Acta Trop. 2016, 158, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngaiganam, E.P.; Pagnier, I.; Chaalal, W.; Leangapichart, T.; Chabou, S.; Rolain, J.-M.; Diene, S.M. Investigation of Urban Birds as Source of β-Lactamase-Producing Gram-Negative Bacteria in Marseille City, France. Acta Vet. Scand. 2019, 61, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapperud, G.; Olsvik, O. Isolation of Enterotoxigenic Yersinia Enterocolitica from Birds in Norway. J. Wildl. Dis. 1982, 18, 247–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janecko, N.; Čížek, A.; Halová, D.; Karpíšková, R.; Myšková, P.; Literák, I. Prevalence, Characterization and Antibiotic Resistance of Salmonella Isolates in Large Corvid Species of Europe and North America between 2010 and 2013. Zoonoses Public Health 2015, 62, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łopucki, R.; Stępień-Pyśniak, D.; Christensen, H.; Kubiński, K.; Lenarczyk, E.; Martinez-de-Tejada, G.; Kitowski, I.; Masłyk, M. Interspecies Transmission of Antimicrobial-Resistant Bacteria between Wild Birds and Mammals in Urban Environment. Vet. Microbiol. 2024, 294, 110130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesse, L.L.; Refsum, T.; Heir, E.; Nordby, K.; Vardund, T.; Holstad, G. Molecular Epidemiology of Salmonella spp. Isolates from Gulls, Fish-Meal Factories, Feed Factories, Animals and Humans in Norway Based on Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis. Epidemiol. Infect. 2005, 133, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Literak, I.; Manga, I.; Wojczulanis-Jakubas, K.; Chroma, M.; Jamborova, I.; Dobiasova, H.; Sedlakova, M.H.; Cizek, A. Enterobacter Cloacae with a Novel Variant of ACT AmpC Beta-Lactamase Originating from Glaucous Gull (Larus hyperboreus) in Svalbard. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 171, 432–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lucia, A.; Rabie, A.; Smith, R.P.; Davies, R.; Ostanello, F.; Ajayi, D.; Petrovska, L.; Martelli, F. Role of Wild Birds and Environmental Contamination in the Epidemiology of Salmonella Infection in an Outdoor Pig Farm. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 227, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubálek, Z.; Sixl, W.; Mikuláskova, M.; Sixl-Voigt, B.; Thiel, W.; Halouzka, J.; Juricová, Z.; Rosický, B.; Mátlová, L.; Honza, M. Salmonellae in Gulls and Other Free-Living Birds in the Czech Republic. Cent. Eur. J. Public Health 1995, 3, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Nesporova, K.; Ruzickova, M.; Tarabai, H.; Krejci, S.; Masarikova, M.; Lausova, J.; Literak, I.; Dolejska, M. Changing Dynamics of Antibiotic Resistant Escherichia in Caspian Gulls Shows the Importance of Longitudinal Environmental Studies. Environ. Int. 2024, 186, 108606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmgren, H.; Sellin, M.; Bergström, S.; Olsen, B. Enteropathogenic Bacteria in Migrating Birds Arriving in Sweden. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 1997, 29, 565–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlström, H.; Tysén, E.; Olsson Engvall, E.; Brändström, B.; Eriksson, E.; Mörner, T.; Vågsholm, I. Survey of Campylobacter Species, VTEC O157 and Salmonella Species in Swedish Wildlife. Vet. Rec. 2003, 153, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnedahl, J.; Drobni, P.; Johansson, A.; Hernandez, J.; Melhus, A.; Stedt, J.; Olsen, B.; Drobni, M. Characterization, and Comparison, of Human Clinical and Black-Headed Gull (Larus ridibundus) Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase-Producing Bacterial Isolates from Kalmar, on the Southeast Coast of Sweden. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 1939–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Literak, I.; Dolejska, M.; Janoszowska, D.; Hrusakova, J.; Meissner, W.; Rzyska, H.; Bzoma, S.; Cizek, A. Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia coli Bacteria, Including Strains with Genes Encoding the Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase and QnrS, in Waterbirds on the Baltic Sea Coast of Poland. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 8126–8134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, D.; Wang, J.; Fanning, S.; McMahon, B.J. Antimicrobial Resistance in Wildlife: Implications for Public Health. Zoonoses Public Health 2015, 62, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzanares-Pedrosa, A.; Ayats, T.; Antilles, N.; Sabaté, S.; Planell, R.; González, R.; Montalvo, T.; Cerdà-Cuéllar, M. Urban Yellow-Legged Gull (Larus michahellis) and Peri-Urban Audouin’s Gull (Larus audouinii) as a Source of Campylobacter and Salmonella of Public Health Relevance. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 960, 178227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, T.R.; Ridgwell, T. The Frequency Of Salmonellae In Wild Ducks. J. Med. Microbiol. 1971, 4, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hessman, J.; Atterby, C.; Olsen, B.; Järhult, J.D. High Prevalence and Temporal Variation of Extended Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Bacteria in Urban Swedish Mallards. Microb. Drug Resist. 2018, 24, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antilles, N.; Sanglas, A.; Cerdà-Cuéllar, M. Free-Living Waterfowl as a Source of Zoonotic Bacteria in a Dense Wild Bird Population Area in Northeastern Spain. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2015, 62, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczkowski, M.; Krawiec, M.; Voslamber, B.; Książczyk, M.; Płoskońska-Bugla, G.; Wieliczko, A. Virulence Genes and the Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Escherichia coli, Isolated from Wild Waterbirds, in the Netherlands and Poland. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2016, 16, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wódz, K.; Piechowicz, L.; Tokarska-Pietrzak, E.; Gawor, J.; Gromadka, R.; Bełkot, Z.; Strzałkowska, Z.; Wiśniewski, J.; Nowak, T.; Bogdan, J.; et al. Does Salmonella Diarizonae 58:R:Z53 Isolated from a Mallard Duck Pose a Threat to Human Health? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garmyn, A.; Haesebrouck, F.; Hellebuyck, T.; Smet, A.; Pasmans, F.; Butaye, P.; Martel, A. Presence of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli in Wild Geese. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 66, 1643–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Iannibelli, F.; Troiano, P.; Volterra, L.; Nanni, F.; Chiesa, C. Comparative Isolation of Yersinia spp. from Avian Wildlife by Different Methods. Contrib. Microbiol. Immunol. 1991, 12, 26–31. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Rödiger, S.; Kramer, T.; Frömmel, U.; Weinreich, J.; Roggenbuck, D.; Guenther, S.; Schaufler, K.; Schröder, C.; Schierack, P. Intestinal Escherichia coli Colonization in a Mallard Duck Population over Four Consecutive Winter Seasons. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 3352–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, N.A.; Reynolds, L.J.; Sala-Comorera, L.; Nolan, T.M.; Stephens, J.H.; Gitto, A.; Gao, G.; Corkery, A.; O’Sullivan, J.J.; O’Hare, G.M.P.; et al. Quantitative Source Apportionment of Faecal Indicator Bacteria from Anthropogenic and Zoogenic Sources of Faecal Contamination. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 205, 116591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckenko, R.; Maiboroda, O.; Muzyka, N.; Stegniy, B.; Mezinov, O.; Rula, O.; Muzyka, D. Circulation of Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia coli in Wild and Domestic Waterfowl in Ukraine. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2024, 24, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, L.; Marcheggiani, S.; D’Angelo, A.; Puccinelli, C.; Chiudioni, F.; Rossi, F.; Delibato, E.; De Medici, D.; Dionisi, A.M.; Owczarek, S.; et al. First Isolation of Salmonella enterica Serovar Napoli from Wild Birds in Italy. Ann. Ist. Super. Sanita 2014, 50, 96–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, M.; Hernández, J.M.; Lima-Barbero, J.F.; Höfle, U. Use of Wildlife Rehabilitation Centres in Pathogen Surveillance: A Case Study in White Storks (Ciconia ciconia). Prev. Vet. Med. 2016, 130, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holko, I.; Doležalová, M.; Pavlíčková, S.; Gal, R.; Valenta, T.; Holkova, T. Antimicrobial-Resistance in Escherichia coli Isolatedfrom Wild Pheasants (Phasianus colchicus). Vet. Ital. 2019, 55, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hleba, L.; Hlebová, M.; Kováčik, A.; Šmehýl, P.; Hricáková, N.; Petrová, J.; Shariati, M.A.; Čuboň, J. Escherichia coli as a Carrier of Tetracyclines and Penicillins Resistance in Wild Pheasant (Phasianus colchicus). J. Environ. Sci. Health A Tox Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2020, 55, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowaczek, A.; Dec, M.; Stępień-Pyśniak, D.; Urban-Chmiel, R.; Marek, A.; Różański, P. Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence Profiles of Escherichia coli Strains Isolated from Wild Birds in Poland. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vittecoq, M.; Brazier, L.; Elguero, E.; Bravo, I.G.; Renaud, N.; Manzano-Marín, A.; Prugnolle, F.; Godreuil, S.; Blanchon, T.; Roux, F.; et al. Multiresistant Enterobacteriaceae in Yellow-Legged Gull Chicks in Their First Weeks of Life. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e8974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
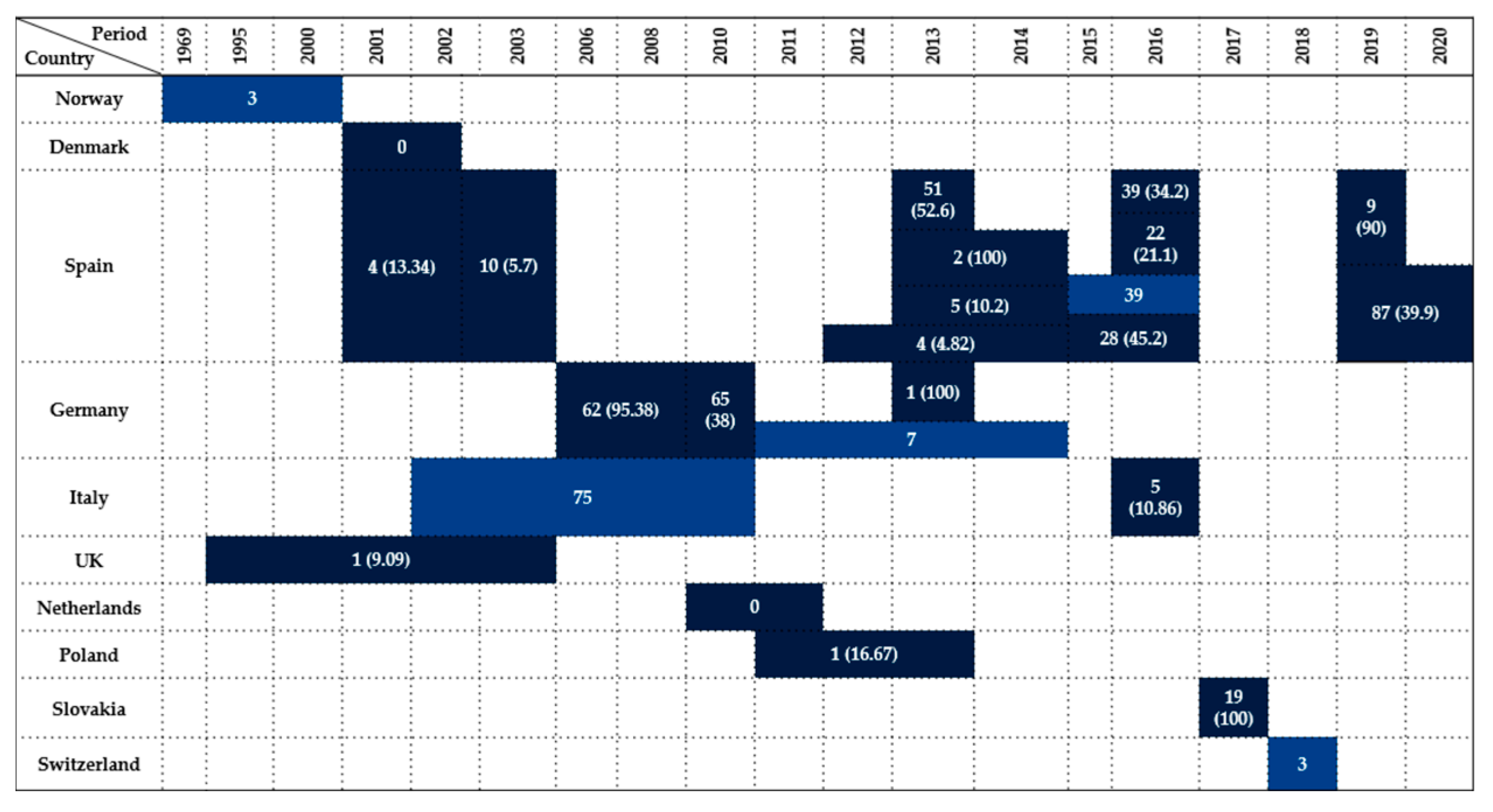
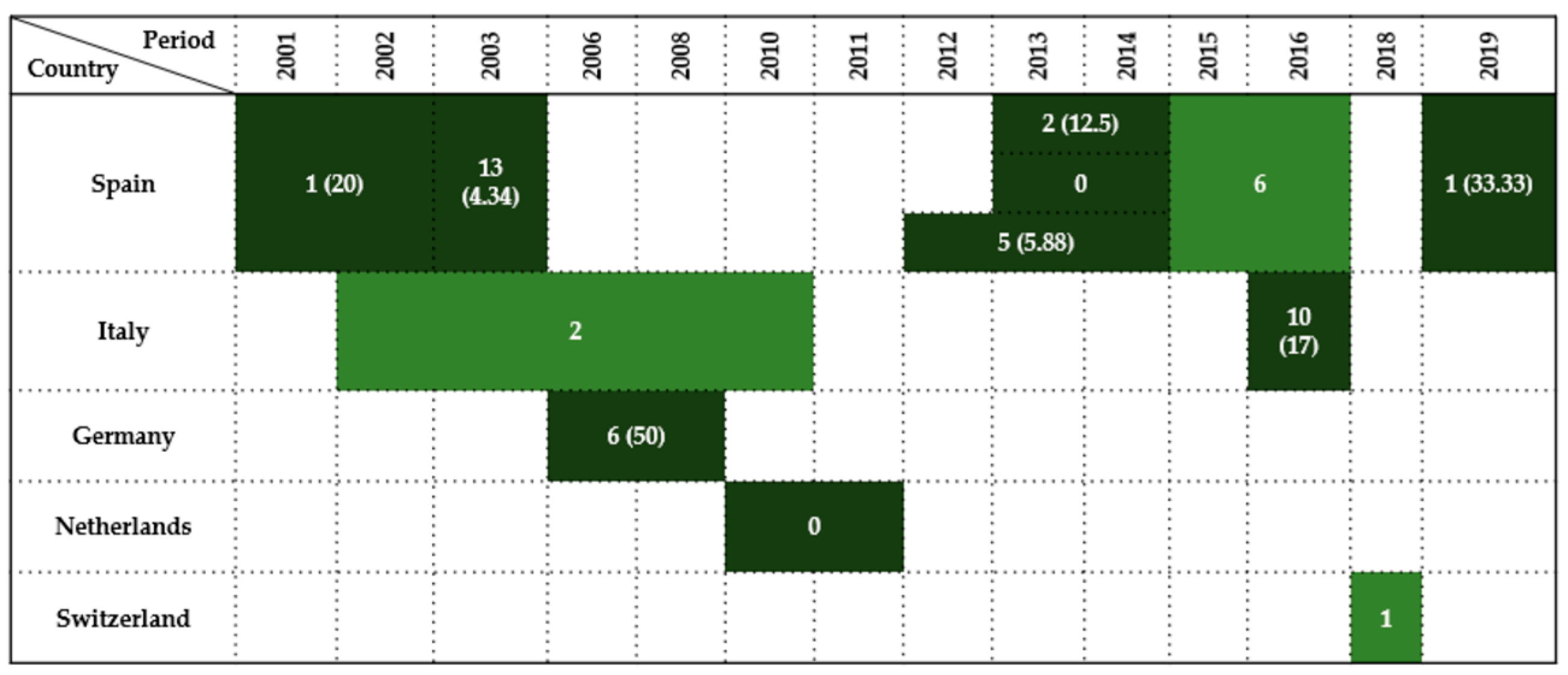
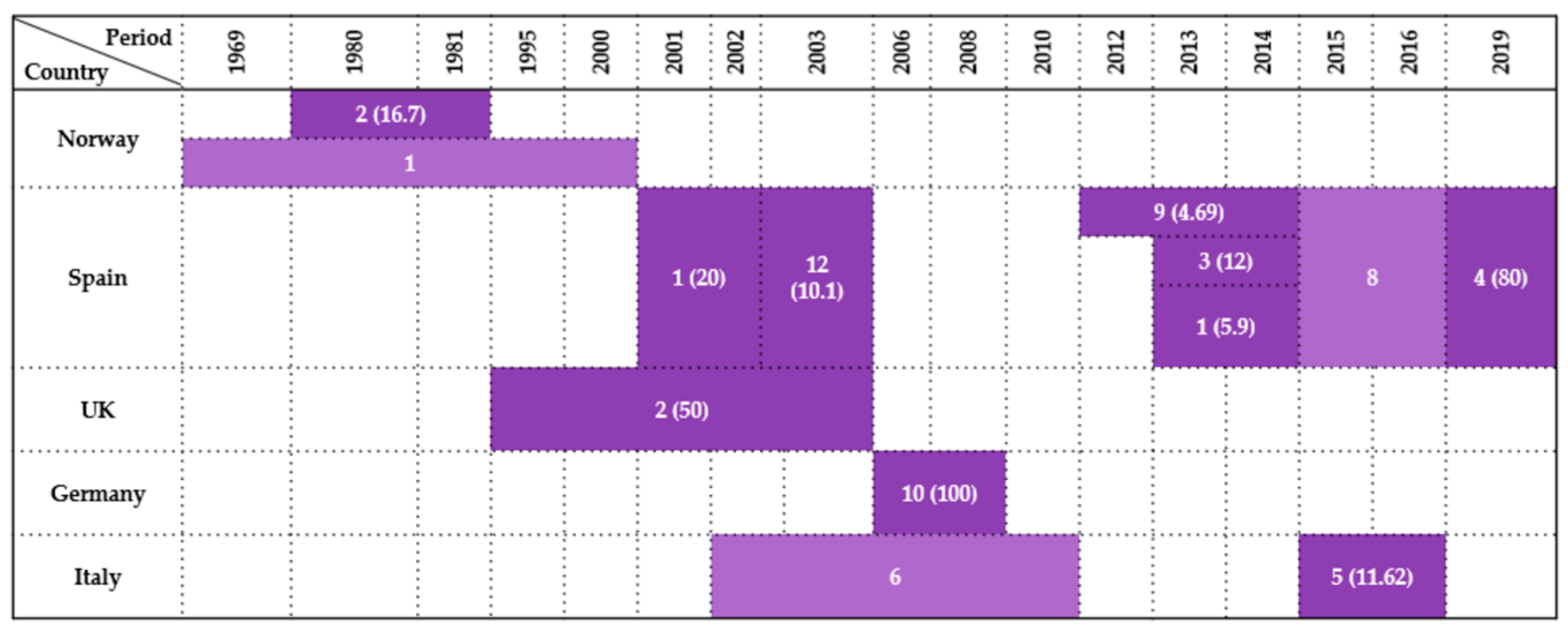


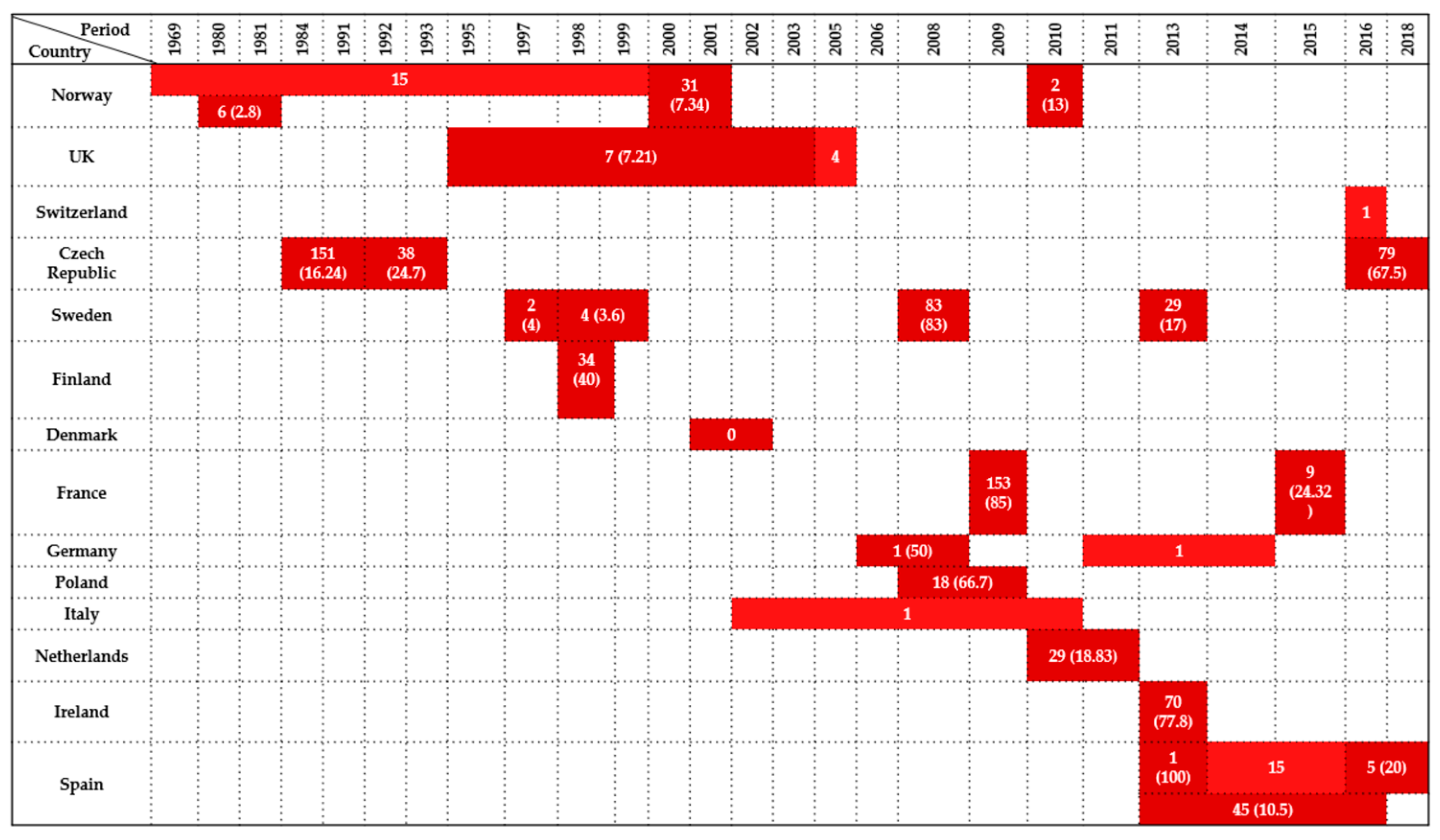
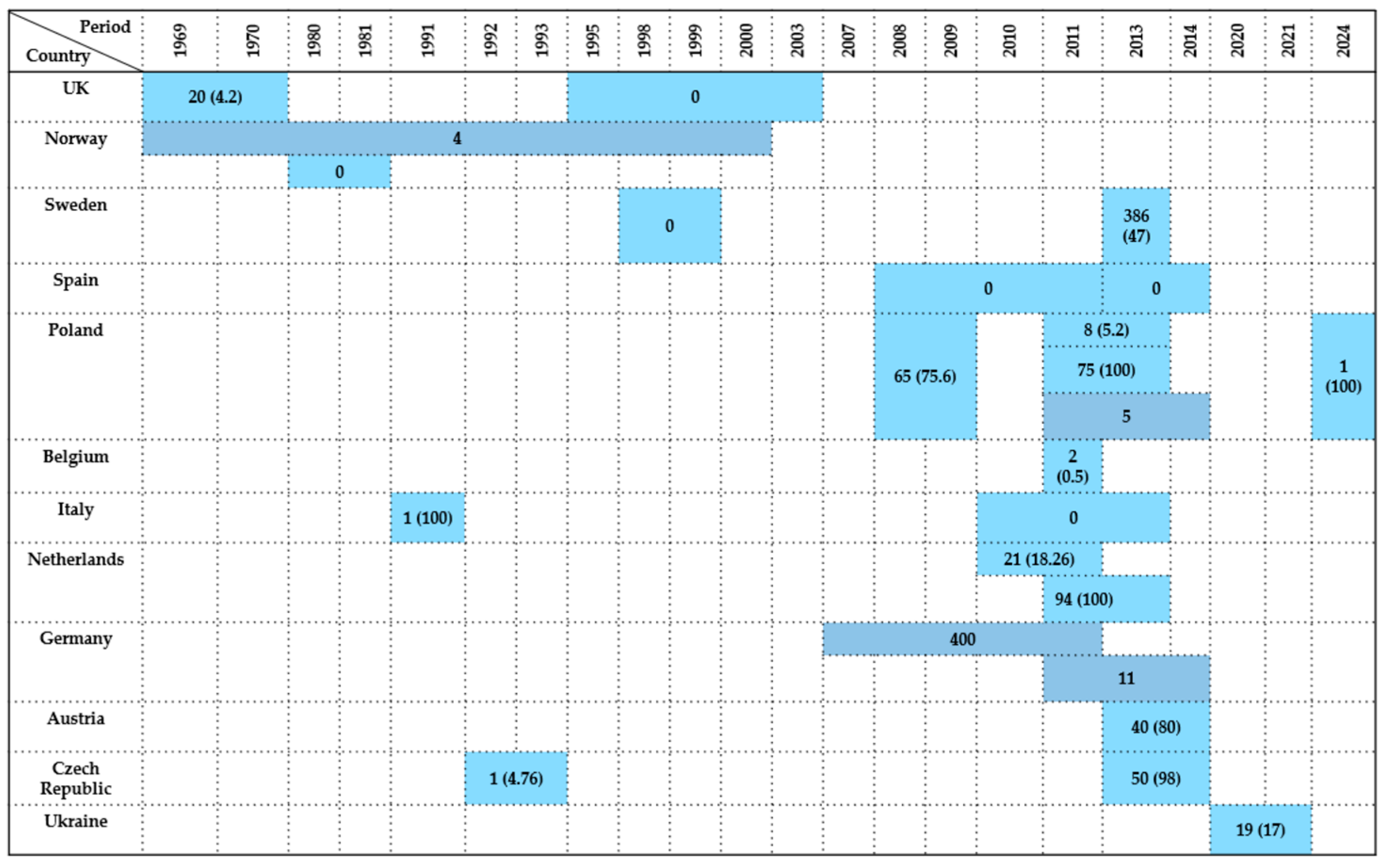
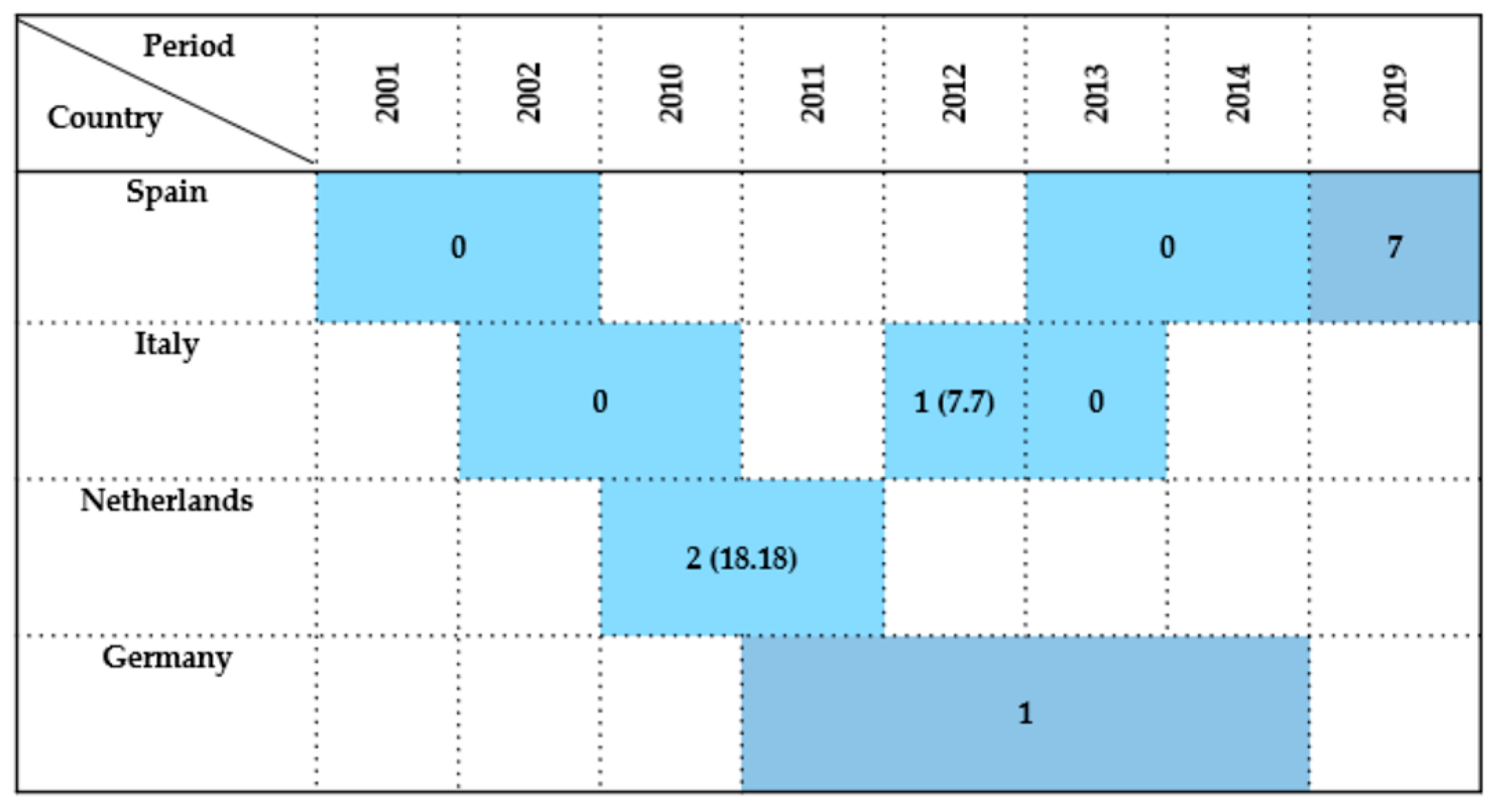

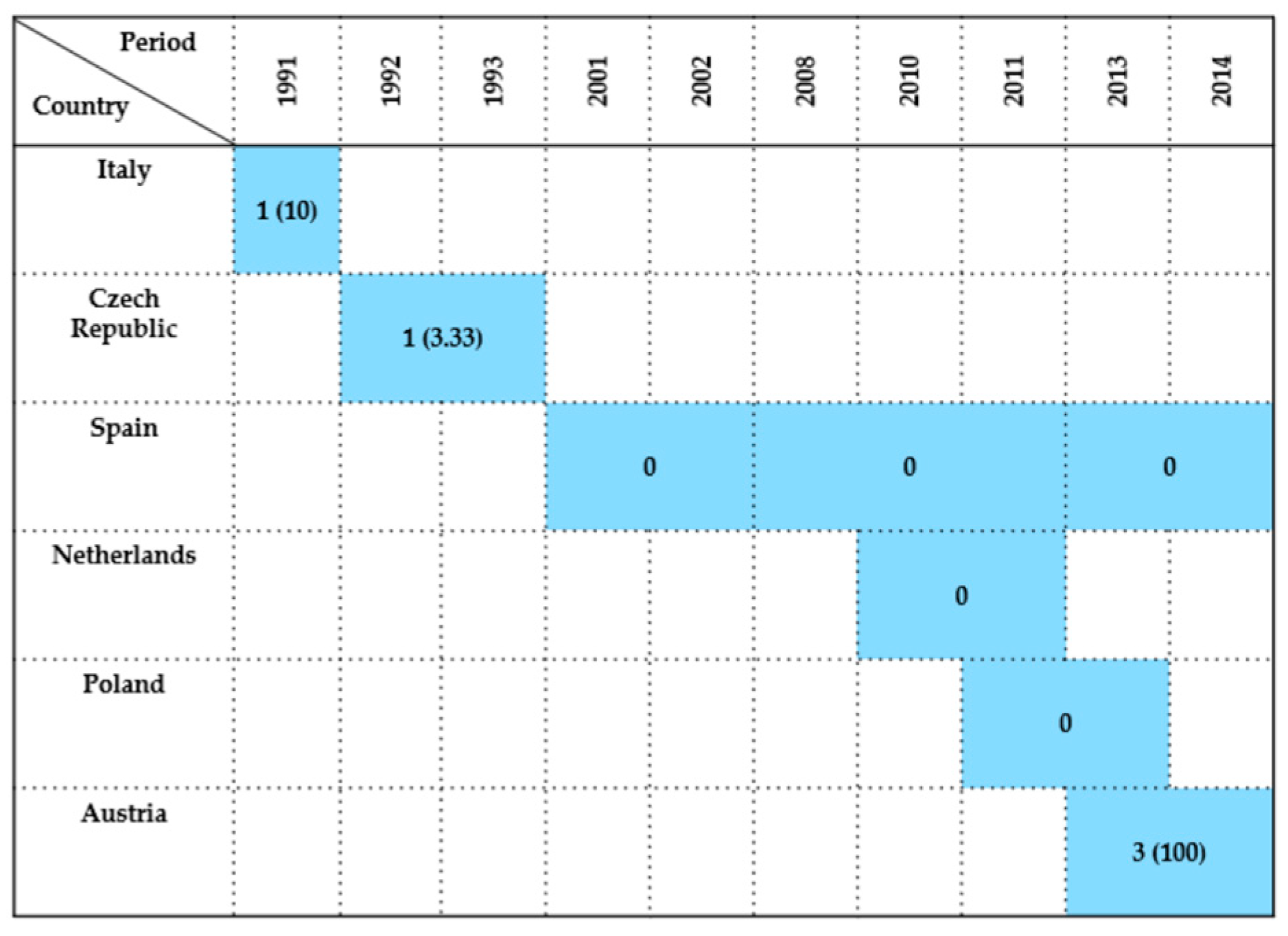
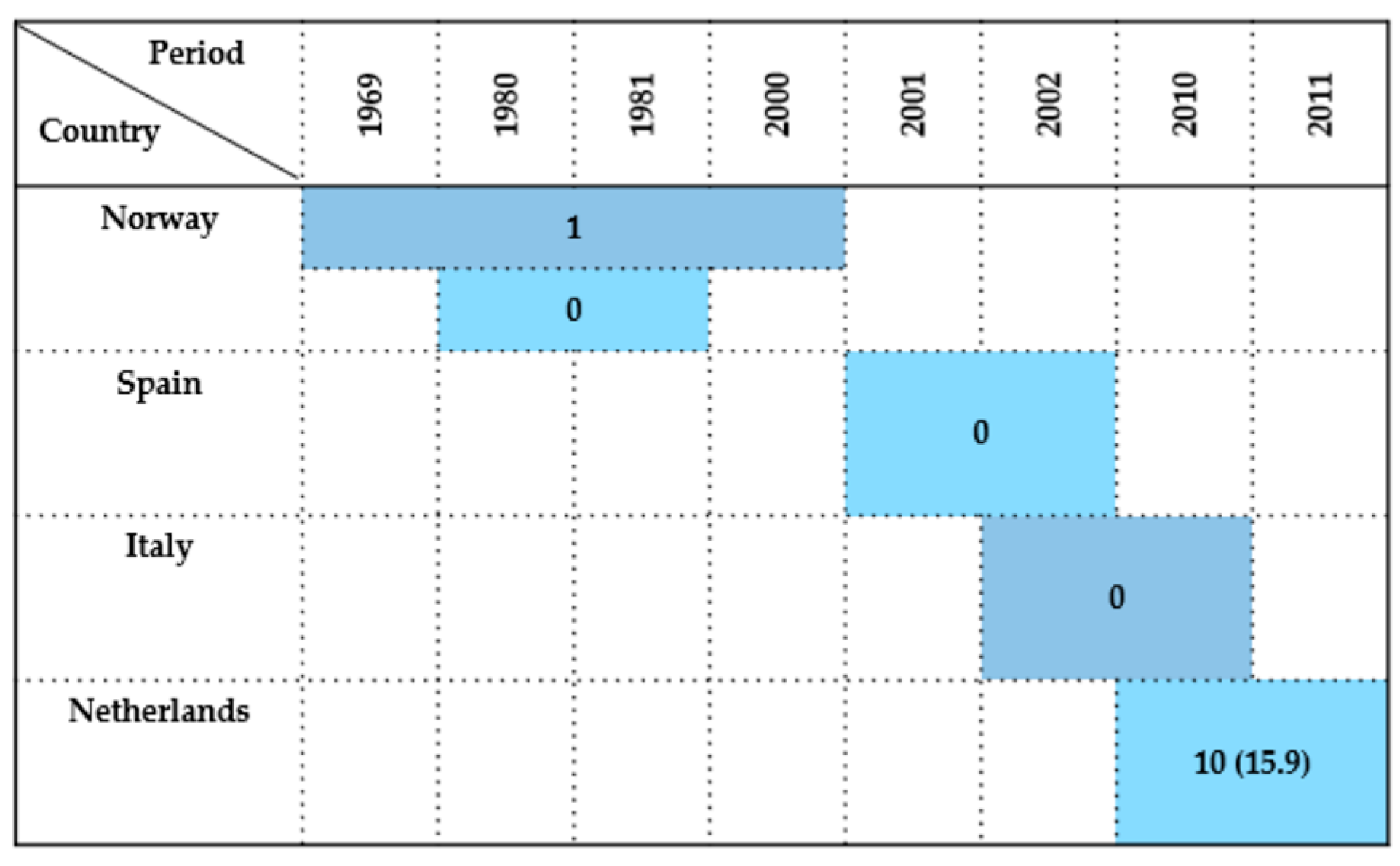

| Country | Sample Type | Period | Wildlife Species Examined | Species (No. of Isolates) | Antimicrobials Tested | Resistance (%) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UK | Post-mortem | 1995–2003 | Accipitriformes | Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium DT104 (1) | n.a. | AMP, CHL, STR, S, TET-(100) | Pennycott et al. [43] |
| France | Cloacal swabs | 2009 | Laridae | Escherichia coli (153) | TET, AMP, STR, CHL, NAL, CFR | TET (39), AMP (25), STR (19), CHL (7), NAL (3), CFR (3) | Bonnedahl et al. [13] |
| Sweden | Cloacal swabs | 2008 | Laridae | Escherichia coli (83) | TET, AMP, STR, CHL, NAL, CFR, SMX, FOS, TGC, TMP, NIT, MEC | TMP (2.4), STR (2.4), CHL (1.2), NIT (1.2), CFR (1.2), FOS (1.2) | Bonnedahl et al. [71] |
| Germany | Cloacal swabs/post-mortem | 2006/2008 | Accipitriformes Falconiformes Strigiformes Columbiformes Laridae Corvidae | Escherichia coli (188) | AMP, CHL, GEN, SP, STR, TET | AMP (7.45), CHL (1.6), GEN (2), SP (8.5), STR (10), TET (8.5) | Guenther et al. [14] |
| Poland | Cloacal swabs/feces | 2008–2009 | Anseriformes Laridae | Escherichia coli (31) | AMC, AMP, KF, CIP, CHL, GEN, NAL, STR, S, SXT, TET | AMP (48.4), GEN (9.7), NAL (38.7), STR (67.7), S (16), TET (22.6), AMC (9.7), KF (13), CIP (13), SXT (13), CHL (3.2) | Literak et al. [72] |
| Norway | Feces | 2010 | Laridae | Enterobacter cloacae (2) | AMP, SAM, CFZ, CXM, FOX, GEN, SXT, COL, OXA, OFX, TET, ATM, PIP, TZP, CFP, CTX, CAZ, FEP, SCF, MER, CIP, TGC, TOB, AMK | AMP, CFZ, FOX-(100) | Literak et al. [65] |
| Belgium | Cloacal swabs | 2011 | Anseriformes | Escherichia coli (2) | AMP, CEF, AMC | CEF (100) | Garmyn et al. [80] |
| Spain | Feces | 2009–2011 | Columbiformes Passeriformes | Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium (15) | NAL, CIP, CTX, AMP, CHL, STR, GEN, SFX, TMP, TET | AMP (20), STR (20), S (13.33), TET (20), NAL (6.66), CHL (6.66) | Andrés et al. [55] |
| Italy | Cloacal swabs | 2002–2010 | Strigidae | Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium DT 193 | AMP, AMC, CTX, KF, OXY, TET, AMK, STR, NEO, GEN, K, NAL, ENR, CIP, CHL, SXT, COL | AMP, AMC, NEO, STR, OXY, TET-(100) | Botti et al. [42] |
| Accipitridae | Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium | AMP, AMC, STR, OXY, TET-(100) | |||||
| Falconidae | Salmonella enterica serovar Brancaster | AMP, AMC, NAL, NEO, STR, K, OXY, TET, SXT-(100) | |||||
| Accipitridae | Salmonella enterica serovar Ohio | AMP, AMC, STR, OXY, TET-(100) | |||||
| Germany | Cloacal swabs | 2013 | Accipitriformes | Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Corvallis | IPM, ERT, MER, CHL, K, TET, TMP, STR, S, FOS | IPM, CHL, K, TET, TMP, STR, S, FOS-(100) | Fischer et al. [38] |
| The Netherlands | Cloacal swabs/postmortem | 2010–2011 | Accipitriformes Falconiformes Columbiformes Anseriformes Pelecaniformes Ciconiiformes Gruiformes Charadriiformes Suliformes Procellariiformes Laridae Corvidae Sturnidae | Escherichia coli (65) | AMP, CTX, CAZ, CIP, CHL, FFC, GEN, K, NAL, STR, SMX, TMP, TET | AMP (100), CEF (100), CAZ (97), CHL (34), CIP (48), FFN (6), GEN (23), NAL (46), STR (57), SUL (66), TET (61.5), TMP (58.5), K (38.5) | Veldman et al. [44] |
| Switzerland | Cloacal swabs | 2011–2012 | Columbiformes Ciconiiformes | Escherichia coli (6) | AMP, KF, CTX, FEP, IPM, AMC, NAL, CIP, STR, TET, SMX, TMP, CHL | AMP (100), KF (100), CTX (50), AMC (50), NAL (66.66), CIP (16.66), STR (66.66), TET (100), SMX (50), TMP (50) | Zurfluh et al. [57] |
| Ireland | Feces | 2013 | Laridae Sturnidae | Escherichia coli (115) | AMC, AMP, CIP, STR, TET, PG, MER | TET (8.7), STR (6), AMP(1.7) | Carroll et al. [73] |
| Czech Republic | Feces | 2010–2013 | Corvidae | S. Typhimurium (2) S. Hadar (1) | AMC, AMP, KF, CAZ, CHL, CIP, GEN, NAL, STR, SXT, S, TET | AMP (33.33), CHL (33.33), STR (66.66), TET (66.66), NAL (33.33), SXT (33.33) | Janecko et al. [62] |
| France | Feces | 2011 | S. Montevideo (2) | TET (100) | |||
| Germany | Feces | 2011 | S. Senftenberg (1) | KF (100) | |||
| Poland | Feces | 2011 | S. Enteritidis (5) | NAL (60) | |||
| Slovakia | Feces | 2013 | S. Infantis (4) | NAL, SXT, TET-(100) | |||
| Spain | Feces | 2011 | S. Oranienburg (2) | SXT (50), NAL (50), S (50) | |||
| Spain | Cloacal swabs | 2013–2014 | Acipitriformes Falconiformes Strigiformes | S. Typhimurium monophasic 4,12:i:- (6) S. Hadar 6,8:z10:e,n,x (1) S. Enteritidis 9,12:g,m:- (1) | AMP, AMC, APR, CHL, CEF, COL, FFC, FL, GEN, NAL, NEO, STR, SXT, S, TET | AMP (75), AMC (12.5), CHL (37.5), STR (62.5), S (62.5), SXT (37.5), CEF (12.5), GEN (37.5), COL (50), APR (37.5), TET (37.5), FL (12.5), FFC (12.5) | Molina-López et al. [31] |
| Germany | Feces | 2007–2011 | Anseriformes | Escherichia coli (400) | AMK, AMC, AMP, SAM, CZO, CTX, CAZ, FOX, CXM, CHL, CIP, DOX, K, GEN, IPM, LEV, MER, NEO, TZP, STR, S3, SXT, TET, TIC, TOB, TMP | AMC (0.75), AMP (5.75), SAM (2.25), CZO (0.25), FOX (0.25), CXM (0.25), CHL (1.75), CIP (0.75), DOX (4), K (0.5), GEN (0.75), LEV (0.5), NEO (0.25) TZP (0.25), STR (4), S3 (3.25), SXT (1), TET (4.5) TIC (5), TMP (2) | Rödiger et al. [82] |
| Spain | Cloacal swabs | 2013–2014 | Accipitriformes Falconiformes Strigiformes Columbiformes Anseriformes Pelecaniformes Ciconiiformes Gruiformes Laridae Sturnidae | Escherichia coli (16) | AMP, AMC, CTX, CAZ, CRO, FOX, IPM, NAL, CIP, GEN, AMK, TOB, CHL, SXT, TET | CHL (50), NAL (87.5), CIP (75), GEN (25), TOB (25), TET (75), SXT (44), AMC (12.5), FOX (12.5), CAZ (69), CTX (100) | Alcalá et al. [29] |
| Spain | Cloacal swabs | 2013 | Ciconiiformes | Escherichia coli (104) | GEN, CTX, ENR | GEN (47), CTX (27), ENR (41.3) | Camacho et al. [86] |
| Spain | Feces | 2012–2014 | Accipitriformes Falconiformes Strigiformes Anseriformes | Salmonella serovars Anatum (1), Bredeney (1), Enteritidis (4), London (1), Mikawasima (1), Salmonella spp. (2), Typhimurium (5) | TET, GEN, CIP, ERY | ERY (93.33), TET (60) | Jurado-Tarifa et al. [30] |
| Poland | Cloacal swabs | 2011–2013 | Anseriformes Ciconiiformes | Escherichia coli (96) | AMX, ENR, TET | AMX (19.8), ENR (2), TET (8.33) | Kuczkowski et al. [78] |
| The Netherlands | Anseriformes | Escherichia coli (94) | AMX (24.5), TET (1) | ||||
| Italy | Post-mortem | 2010–2013 | Corvidae | S. Bredeney | AMC, CIP, CTX, SXT, CHL, AMP, STR, TET, GEN, NAL, COL, KF | AMP, STR, TET, NAL-(100) | Rubini et al. [52] |
| S. Enteritidis | AMP (100) | ||||||
| S. Typhimurium (5) | AMP (60), STR (20), COL (40), KF (20) | ||||||
| Sweden | Feces | 2013 | Laridae | Escherichia coli (29) | AMP, CIP, NAL, GEN, STR, TET, FFC, COL, SMX, TMP, CHL, K, CTX, CAZ, FOX, TOB, TZP, AMC AMC, TGC, NIT, MER, AMK, AMK, ERT, IPM, FOS | AMC (72.4), AMP (100), CTX (100), CAZ (65.5), TET (62), STR (31), TMP (48.3), SMX (44.8), FFC (7), CIP (69), NAL (55.2), GEN (34.5), CHL (20.7), K (13.8), TOB (17.2), TZP (7) | Atterby et al. [23] |
| Poland | n.a. | 2011–2014 | Columbiformes Anseriformes Ciconiiformes Passeriformes (Turdidae) Apodidae | Salmonella spp. (36) | SMX, GEN, STR, K, CIP, NAL, CTX, CAZ, AMP, TET, FFC, CHL, COL, TMP | SMX (94.44), CIP (8.33), NAL (8.33), COL (22.22), TMP (8.33), TET (8.33), AMP (5.55), STR (11.11), CHL (5.55), FFC (11.11), K (5.55) | Krawiec et al. [58] |
| Spain | Feces | 2016 | Accipitriformes | Salmonella enterica (38) serotypes Typhimurium monophasic 4,12:i:- (1), Typhimurium 4,12:i:1,2 (1) | CIP, CAZ, AMP, AMX, AMC, STR, GEN, NEO, SXT, TET, DOX | AMP (75), AMX (75), AMC (10), STR (77.5), GEN (30), NEO (65), SXT (10), TET (70), DOX (77.5) | Blanco et al. [32] |
| Spain | Cloacal swabs | 2015–2016 | Accipitriformes Falconiformes Strigiformes Laridae Corvidae | Escherichia coli (60), Klebsiella pneumoniae (10), Hafnia alvei (10), Enterobacter spp. (8), Proteus mirabilis (4), Citrobacter freundii (1), Morganella morganii (1) | CTX, AMC, FOX, CLX | CTX (100) | Oteo et al. [35] |
| Slovak Republic | Feces | 2017 | Accipitriformes | Escherichia coli (19) | AMP, SAM, ERT, CEF, CRO, CAZ, CAC, CFQ, GEN, STR, NEO, SPE, NAL, ENR, CIP, CHL, FFC, TET, COL, SXT, COT | AMP (52.6), TET (52.6), NAL (42.1), STR (26.3), ENR (21), CIP (21), COT (21) | Handrova and Kmet [7] |
| Czech Republic | Cloacal swabs | 2010–2013 | Phasianidae | Escherichia coli (180) | AMC, AMP, CEF, SCF, CIP, COL, GEN, CHL, NEO, TZP, STR, SXT, TET | AMP (72.22), CEF (89), CHL (5.55), SXT (5.55), TET (22.22) | Holko et al. [87] |
| Spain | Feces/cloacal swabs | 2015–2016 | Accipitriformes | S. Enteritidis (4) | AMP, CTX, CAZ, GEN, NAL, CIP, COL, CHL, AZM, TGC, SXT, TMP | AMP (50) | Martín-Maldonado et al. [34] |
| S. Typhimurium (4) | AMP (50), TGC (25) | ||||||
| S. Houston (4) | AMP (25) | ||||||
| S. Manhattan (1) | AMP (100) | ||||||
| S. Schleissheim (1) | AMP (100) | ||||||
| France | Feces | 2016 | Laridae Columbifomes | Escherichia coli (5) | AMX, AMC, KF, CRO, FEP, TZP, ERT, IPM, FOS, NIT, SXT, AMK, CIP, COL, GEN | AMX (80), AMC (60), CRO (80), FEP (80), STX (40), CIP (20), KF (20) | Ngaiganam et al. [60] |
| Cronobacter sakazakii (1) | AMX, AMC, CRO, FFC-(100) | ||||||
| Hafnia alvei (8) | AMX (4), AMC (4), KF (6), COL (6), FFC (2), NIT (2) | ||||||
| Proteus hauseri (1) | NIT, COL-(100) | ||||||
| Panteoa ananatis (1) | AMX, AMC, KF, FFC, NIT, COL-(100) | ||||||
| Serratia marcescens (1) | NIT, COL-(100) | ||||||
| UK | Feces | 2016 | Passeriformes Columbiformes | Escherichia coli (27) | AMP, CPD, COL, APR, IPM, TMP, TET, CIP | AMP (51.9), CEF (26), COL (18.5), APR (11.11), IPM (11.11), TMP (18.5), TET (22.22), CIP (11.11) | Swift et al. [11] |
| Switzerland | Cloacal swabs | 2018 | Accipitriformes Anseriformes Falconiformes Columbiformes Laridae Passeriformes Corvidae | Escherichia coli (256) | AMP, AMC, AZM, CHL, CIP, CZS, NIT, GEN, K, NAL, STR, SXT, TET, CTX, FEP | AMP (5), NAL (4), TET (5.5), CHL (2.3), CIP (2.3), CZS (3.5), STR (2.3), SXT (3.1), AMC (0.4), AZM (1.2), NIT (0.4), GEN (1.2), K (1.6), FEP (0.4), CTX (2) | Zurfluh et al. [47] |
| Slovacia | Contents of the appendix | 2020 | Phasianidae | Escherichia coli (70) | AMP, TET, CTX, CAZ | CTX (100), CAZ (100), AMP (100), TET (87) | Hleba et al. [88] |
| Spain | Cloacal swabs | 2018–2019 | Columbiformes Ciconiiformes Laridae Passeriformes Sturnidae | Salmonella spp. (37) | CIP, NAL, AMP, FOX, CAZ, MER, CHL, SMX, COL, AZM, TGC, GEN, TMP, TET | CIP (30), NAL (30), AMP (10.8), COL (21.6), TET (13.5) | Martín-Maldonado et al. [56] |
| Poland | Cloacal swabs | 2017 | Accipitriformes Falconiformes Anseriformes Passeriformes Strigiformes | Escherichia coli (32) | TET, GEN, K, CIP, AMP, CHL, SXT | TET (50), GEN (34.4), CIP (47), AMP (28), K (18.75), CHL (6.25), SXT (34.4) | Nowaczek et al. [89] |
| Spain | Buffers on the bone surface of fractures | 2019 | Accipitriformes, Falconiformes, Charadriiformes, Strigiformes, Ciconiiformes, Pelecaniformes, Apodiformes, Passeriformes | Escherichia fergusonii (9) | CL, CZS, CEF, ENR, CTX | CL (77.8), CZS (33.33) | Tardón et al. [36] |
| Escherichia marmotae (1) | CL (100) | ||||||
| Enterobacter cloacae (1) | CL, CZS-(100) | ||||||
| Enterobacter kobei (1) | CL (100) | ||||||
| Enterobacter ludwigii (1) | CL, CZS-(100) | ||||||
| Enterobacter faecalis (4) | CL (50), CZS (100), CEF (100), CTX (100) | ||||||
| Hafnia alvei (2) | CL, CZS-(100) | ||||||
| Leclercia adecarboxylata (1) | CL (100) | ||||||
| Pantoea agglomerans (5) | CL (60) | ||||||
| Proteus mirabilis (1) | CL (100) | ||||||
| Shigella boydii (1) | CL (100) | ||||||
| Shigella flexneri (5) | CL (80) | ||||||
| Shigella sonnei (1) | CL (100) | ||||||
| France | Cloacal swabs | 2016 | Laridae | Escherichia coli (51) Enterobacter cloacae (1) Klebsiella pneumoniae (4) Proteus mirabilis (2) Citrobacter freundii (1) Enterobacter kobei (1) Escherichia albertii (1) Escherichia fergusonii (1) Hafnia alvei (1) Klebsiella aerogenes (1) | CTX, CAZ | CTX, CAZ-(100) | Vittecoq et al. [90] |
| Spain | Cloacal swabs | 2019–2020 | Accipitriformes | Escherichia coli (87) | AMP, CTX, CAZ, MER, NAL, CIP, GEN, TET, TGC, AZM, CHL, COL, SMX, TMP | AMP (100), CTX (100), CAZ (100), CIP (95.4), TET (87.35), SMX (85), TMP (84), NAL (71.3), CHL (69), GEN (41.4), AZM (35.6) | Guitart-Matas et al. [12] |
| Poland | Feces | 2017–2018 | Phasianidae | Escherichia coli (27) | AMC, CIP, TET, SMX, GEN, AMP, NAL, COL | AMC (7.4), SMX (52) | Kwaśna et al. [20] |
| Poland | Cloacal swabs | n.a. | Corvidae | Escherichia coli (31) | AMP, AMC, CTX, MER, IPM, GEN, K, STR, TET, CIP, S, SXT, TMP, CHL, CTX/C | TET (29), AMP (26), AMC (3.2), S (13), TMP (13), SXT (13), CHL (6.45) | Łopucki et al. [63] |
| Czech Republic | Cloacal swabs | 2018–2019 | Laridae | Escherichia coli (141) | AMP, STR, S, S3, TET, SXT, CHL, CZS, NAL, CAZ, CAZ, GEN, AMC, CIP, ERT, IPM, ATM, NIT, AZM, COL | AMP (89.4), STR (18), S (25), TET (32), SXT (17), CHL (10.6), CZS (61), NAL (31.2), CAZ (49.6), GEN (34), AMC (59), CIP (23), ERT (33), ATM (61), NIT (0.7), AZM (19), COL (0.7) | Nesporova et al. [68] |
| Spain | Cloacal swabs | 2009–2018 | Laridae | Salmonella Typhimurium and monophasic S. Typhimurium (Typhimurium m.) (23) | AMP, AZM, CTX, TAZ, CHL, NAL, CIP, COL, GEN, MER, TET, TGC, SMX, TMP | AMP (39), NAL (4.3), CIP (4.3), TET (26), TMP (8.7) | Manzanares-Pedrosa et al. [74] |
| Bredeney (4) | AMP (50), CTX (50), TAZ (50), CHL (50), TET (100), TMP (50) | ||||||
| Infantis (2) | NAL, CIP, TMP, TET (100) | ||||||
| London | TMP, TET-(100) | ||||||
| Mons | NAL, CIP-(100) | ||||||
| Virchow | NAL, CIP, TMP, TET-(100) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cocoș, D.-I.; Dumitrescu, E.; Muselin, F.; Brezovan, D.; Degi, J.; Boldura, O.-M.; Cristina, R.T. Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance of Enterobacteriaceae in Wild Birds Across Europe: A Systematic Review. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 905. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090905
Cocoș D-I, Dumitrescu E, Muselin F, Brezovan D, Degi J, Boldura O-M, Cristina RT. Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance of Enterobacteriaceae in Wild Birds Across Europe: A Systematic Review. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(9):905. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090905
Chicago/Turabian StyleCocoș, Daiana-Ionela, Eugenia Dumitrescu, Florin Muselin, Diana Brezovan, János Degi, Oana-Maria Boldura, and Romeo T. Cristina. 2025. "Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance of Enterobacteriaceae in Wild Birds Across Europe: A Systematic Review" Antibiotics 14, no. 9: 905. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090905
APA StyleCocoș, D.-I., Dumitrescu, E., Muselin, F., Brezovan, D., Degi, J., Boldura, O.-M., & Cristina, R. T. (2025). Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance of Enterobacteriaceae in Wild Birds Across Europe: A Systematic Review. Antibiotics, 14(9), 905. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090905









