Selective Antimicrobial Chitosan Films Incorporating Green-Synthesized Silver and Copper Oxide Nanoparticles for Acne Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of CuONPs and AgNPs Synthesized by Green Tea
2.2. Characterization CHI Films, CuONPs@CHI Films, and AgNPs@CHI Films
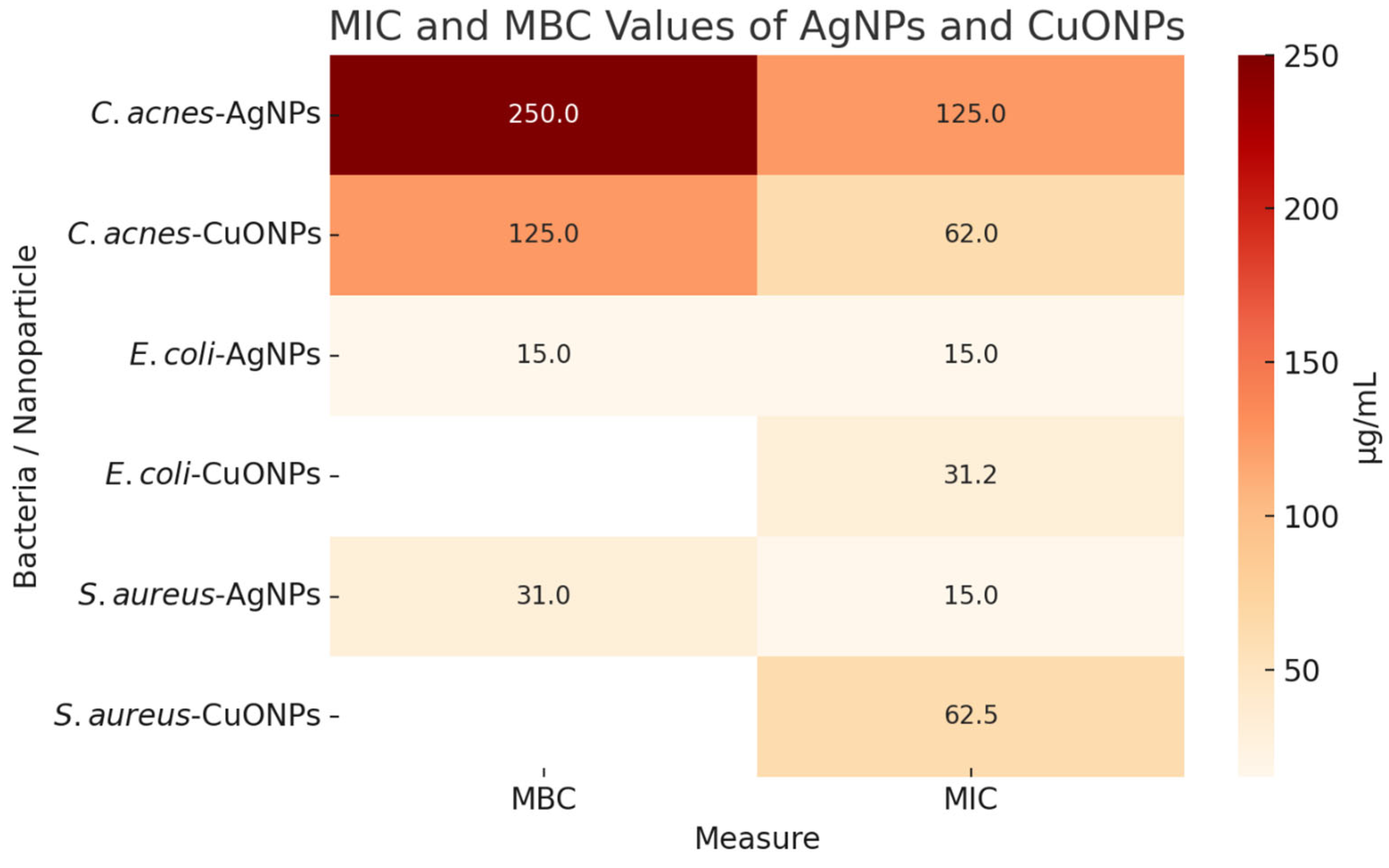
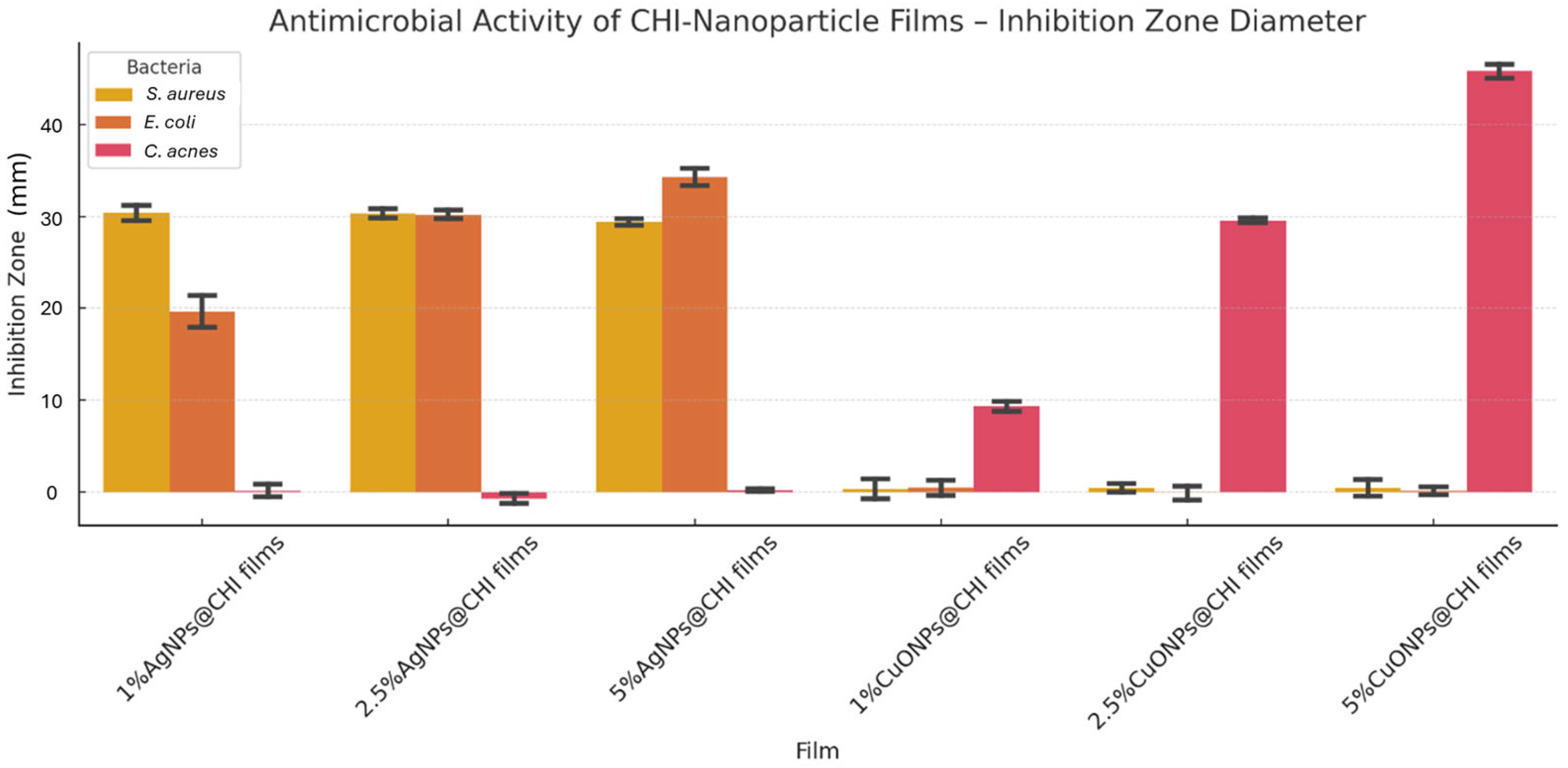
2.3. Biological Essays
3. Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of CuONPs and AgNPs Synthesized by Green Tea
3.2. Characterization of CHI Films, CuONPs@CHI Films, and AgNPs@CHI Films
3.3. Antimicrobial Effects
3.3.1. MIC and MBC Results for AgNPs and CuONPs
3.3.2. Agar Diffusion (Halo) Assay in Chitosan Films
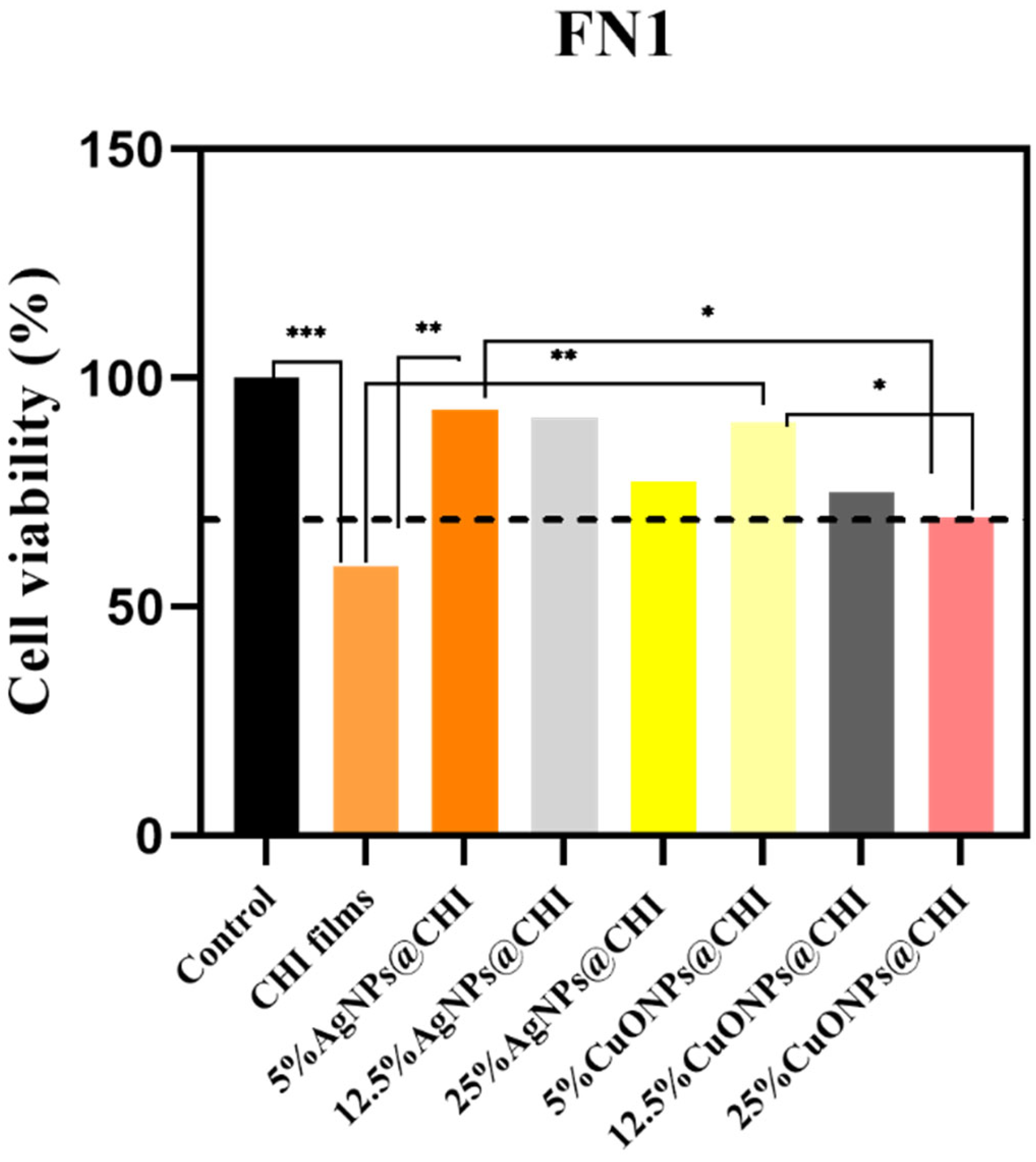
3.4. Cytotoxicity Assay
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. AgNPs and CuONPs Synthesized by Green Tea
4.3. Solvent Cast Chitosan Film Production
4.4. Characterization of CuONPs and AgNPs Synthesized by Green Tea
4.5. Characterization of CHI Film, CuONPs@CHI Films, and AgNPs@CHI Films
4.6. Antimicrobial Activity
4.6.1. Determination of MIC and MBC Values for AgNPs and CuONPs
4.6.2. Agar Diffusion Test for Films
4.7. Cytotoxicity Assay of CHI Film, AgNPs@CHI Films, and AgNPs@CHI Films
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Meaning |
| AgNPs | Silver nanoparticles |
| AgNPs@CHI film(s) | Chitosan film(s) containing silver nanoparticles |
| ATR | Attenuated Total Reflectance |
| ATCC | American Type Culture Collection |
| CHI films | Chitosan films |
| CFU | Colony-Forming Unit |
| CuONPs | Copper oxide nanoparticles |
| CuONPs@CHI film(s) | Chitosan film(s) containing copper oxide nanoparticles |
| DLS | Dynamic Light Scattering |
| FTIR | Fourier Transform Infrared |
| HRTEM | High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| ISO | International Organization for Standardization |
| MBC | Minimum Bactericidal Concentration |
| MIC | Minimum Inhibitory Concentration |
| PBS | Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| PDI | Polydispersity Index |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| TEM | Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| TGA | Thermogravimetric Analysis |
References
- El-Araby, A.; Janati, W.; Ullah, R.; Ercisli, S.; Errachidi, F. Chitosan, chitosan derivatives, and chitosan-based nanocomposites: Eco-friendly materials for advanced applications (a review). Front. Chem. 2024, 11, 1327426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonciarz, W.; Balcerczak, E.; Brzeziński, M.; Jeleń, A.; Pietrzyk-Brzezińska, A.J.; Narayanan, V.H.B.; Chmiela, M. Chitosan-based formulations for therapeutic applications. A recent overview. J. Biomed. Sci. 2025, 32, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kean, T.; Thanou, M. Biodegradation, biodistribution and toxicity of chitosan. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Tang, B.; Wang, Z.; Feng, F.; Wang, G.; Zhao, Z.; Xue, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, W. Solution blow spun bilayer chitosan/polylactic acid nanofibrous patch with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties for accelerating acne healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 326, 121618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganotti, A.; de Freitas, C.C.; Pereira, R.H.; Vital, V.G.; Paiva, G.S.; de Lima, L.F.; da Silva, L.L.; Teodorov, E.; da Silva, R.A.G.; de Vasconcellos, S.P.; et al. Biogenic CuO nanoparticles from Camellia sinensis and Pimpinella anisum plant extracts and their role as antimicrobial agents. Plant Nano Biol. 2025, 11, 100138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wusigale; Kuttappan, D.; Amalaradjou, M.A.; Luo, Y.; Luo, Y. Polydopamine-coated chitosan hydrogel beads for synthesis and immobilization of silver nanoparticles to simultaneously enhance antimicrobial activity and adsorption kinetics. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2021, 4, 696–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouhan, D.; Mandal, P. Applications of chitosan and chitosan based metallic nanoparticles in agrosciences-A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 166, 1554–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alven, S.; Aderibigbe, B.A. Chitosan-Based Scaffolds Incorporated with Silver Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Infected Wounds. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bumbudsanpharoke, N.; Harnkarnsujarit, N.; Chongcharoenyanon, B.; Kwon, S.; Ko, S. Enhanced properties of PBAT/TPS biopolymer blend with CuO nanoparticles for promising active packaging. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2023, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolim, W.R.; Pelegrino, M.T.; Lima, B.d.A.; Ferraz, L.S.; Costa, F.N.; Bernardes, J.S.; Rodigues, T.; Brocchi, M.; Seabra, A.B. Green tea extract mediated biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Characterization, cytotoxicity evaluation and antibacterial activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 463, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, T.R.; Efthimiou, J.; Dréno, B. Systematic review of antibiotic resistance in acne: An increasing topical and oral threat. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, e23–e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, I.; Fleischer, A.; Feldman, S. Emerging drugs for the treatment of acne. Expert Opin. Emerg. Drugs 2015, 20, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzubaidi, A.K.; Al-Kaabi, W.J.; Al Ali, A.; Albukhaty, S.; Al-Karagoly, H.; Sulaiman, G.M.; Asiri, M.; Khane, Y. Green Synthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles Using Flaxseed Extract and Evaluation of Their Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activities. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahluwalia, V.; Elumalai, S.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, S.; Sangwan, R.S. Nano silver particle synthesis using Swertia paniculata herbal extract and its antimicrobial activity. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 114, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheung, J.Y.; Ge, P.; Lim, S.J.; Lee, S.H.; Smith, A.M.; Selvin, P.R. Structural Contributions to Hydrodynamic Diameter for Quantum Dots Optimized for Live-Cell Single-Molecule Tracking. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 17406–17412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krueger, K.M.; Al-Somali, A.M.; Mejia, M.; Colvin, V.L. The hydrodynamic size of polymer stabilized nanocrystals. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 475709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuhrotun, A.; Oktaviani, D.J.; Hasanah, A.N. Biosynthesis of Gold and Silver Nanoparticles Using Phytochemical Compounds. Molecules 2023, 28, 3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.M.-T.; Huynh, T.T.-T.; Dang, C.-H.; Mai, D.-T.; Nguyen, T.T.-N.; Nguyen, D.-T.; Dang, V.-S. Novel biogenic silver nanoparticles used for antibacterial effect and catalytic degradation of contaminants. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2020, 46, 1975–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busi, S.; Rajkumari, J.; Ranjan, B.; Karuganti, S. Green rapid biogenic synthesis of bioactive silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) using Pseudomonas aeruginosa. IET Nanobiotechnology 2014, 8, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biliuta, G.; Gherman, S.P.; Baron, R.I.; Bargan, A.; Ochiuz, L.; Tuchilus, C.G.; Spac, A.F.; Zavastin, D.E. Development and Characterization of Polymeric Films Loaded with Terbinafine for Fungal Infection Treatment. Polymers 2025, 17, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, G.D.; Sing, S.L.; Lim, Y.F.; Thong, J.L.J.; Peh, Z.K.; Mogali, S.R.; Yeong, W.Y. Machine learning for 3D printed multi-materials tissue-mimicking anatomical models. Mater. Des. 2021, 211, 110125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, D.; Momin, B.; Palamthodi, S.; Lele, S. Physicochemical and functional properties of chitosan-based nano-composite films incorporated with biogenic silver nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 211, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, C.; Ma, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, L. Structure and properties of chitosan films: Effect of the type of solvent acid. LWT 2021, 135, 109984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Mirza, A. Facile one pot green synthesis of Chitosan-Iron oxide (CS-Fe2O3) nanocomposite: Removal of Pb(II) and Cd(II) from synthetic and industrial wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 186, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, S.; Wang, L.-F.; Rhim, J.-W. Preparation and properties of carbohydrate-based composite films incorporated with CuO nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 169, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordianu-Antochi, I.E.; Olaru, M.; Cotofana, C. Novel hybrid formulations based on chitosan and a siloxane compound intended for biomedical applications. React. Funct. Polym. 2017, 114, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, L.; Moldovan, B. Green Synthesis of Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles for Efficient Catalytic Removal of Harmful Organic Dyes. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Al-Thabaiti, S.A. Biogenic silver nanoparticles: Green synthesis, encapsulation, thermal stability and antimicrobial activities. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 289, 111102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseem, K.; Rehman, M.Z.U.; Ahmad, A.; Dubal, D.; AlGarni, T.S. Plant Extract Induced Biogenic Preparation of Silver Nanoparticles and Their Potential as Catalyst for Degradation of Toxic Dyes. Coatings 2020, 10, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhou, L.; Yang, P.; Pizzo, S.V. Chemical Composition and Anti-Inflammatory, Cytotoxic and Antioxidant Activities of Essential Oil from Leaves of Mentha piperita Grown in China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madian, N.G.; Mohamed, N. Enhancement of the dynamic mechanical properties of chitosan thin films by crosslinking with greenly synthesized silver nanoparticles. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 12970–12975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.S.; Samanta, S.; Dey, S.; Giri, B.; Dash, S.K. Rapid Green Synthesis of Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles Using Cinnamomum tamala Leaf Extract and its Potential Antimicrobial Application Against Clinically Isolated Multidrug-Resistant Bacterial Strains. Biol. Trace Element Res. 2020, 198, 681–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Momani, H.; Massadeh, M.I.; Almasri, M.; Al Balawi, D.; Aolymat, I.; Hamed, S.; Albiss, B.A.; Ibrahim, L.; Al Balawi, H.; Mahmoud, S.A.H. Anti-Bacterial Activity of Green Synthesised Silver and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles against Propionibacterium acnes. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonohara, R.; Muramatsu, N.; Ohshima, H.; Kondo, T. Difference in surface properties between Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus as revealed by electrophoretic mobility measurements. Biophys. Chem. 1995, 55, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ookubo, M.; Tashiro, Y.; Asano, K.; Kamei, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Honda, T.; Yokoyama, T.; Honda, M. “Rich arginine and strong positive charge” antimicrobial protein protamine: From its action on cell membranes to inhibition of bacterial vital functions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Biomembr. 2024, 1866, 184323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottet, J.; Oshodi, J.O.; Yebouet, J.; Leang, A.; Furst, A.L.; Buie, C.R. Zeta potential characterization using commercial microfluidic chips. Lab A Chip 2023, 24, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Yahia, L.; Sacher, E. Antimicrobial Properties of the Ag, Cu Nanoparticle System. Biology 2021, 10, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Garg, A.; Pandit, S.; Mokkapati, V.R.S.S.; Mijakovic, I. Antimicrobial Effects of Biogenic Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Mao, S.; Xu, Z.; Ding, W. Various antibacterial mechanisms of biosynthesized copper oxide nanoparticles against soilborne Ralstonia solanacearum. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 3788–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leceta, I.; Guerrero, P.; Ibarburu, I.; Dueñas, M.; de la Caba, K. Characterization and antimicrobial analysis of chitosan-based films. J. Food Eng. 2013, 116, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zou, X.; Zhai, X.; Huang, X.; Jiang, C.; Holmes, M. Preparation of an intelligent pH film based on biodegradable polymers and roselle anthocyanins for monitoring pork freshness. Food Chem. 2019, 272, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khubiev, O.M.; Egorov, A.R.; Kirichuk, A.A.; Khrustalev, V.N.; Tskhovrebov, A.G.; Kritchenkov, A.S. Chitosan-Based Antibacterial Films for Biomedical and Food Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, N.; Rana, D.; Salave, S.; Gupta, R.; Patel, P.; Karunakaran, B.; Sharma, A.; Giri, J.; Benival, D.; Kommineni, N. Chitosan: A Potential Biopolymer in Drug Delivery and Biomedical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khubiev, O.M.; Egorov, A.R.; Lobanov, N.N.; Fortalnova, E.A.; Kirichuk, A.A.; Tskhovrebov, A.G.; Kritchenkov, A.S. Novel Highly Efficient Antibacterial Chitosan-Based Films. BioTech 2023, 12, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christopher, D.; Anbalagan, A.; Govindarajan, V.U.; Muthuraman, M.S. Biofabrication of copper oxide nanoparticles incorporated chitosan/gelatin films for food packaging applications. Biomass- Convers. Biorefinery 2024, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruna, T.; Maldonado-Bravo, F.; Jara, P.; Caro, N. Silver Nanoparticles and Their Antibacterial Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, N. Synthesis and antibacterial effects of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) against multi-drug resistant bacteria. Bio-Medical Mater. Eng. 2024, 35, 451–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondarenko, O.M.; Sihtmäe, M.; Kuzmičiova, J.; Ragelienė, L.; Kahru, A.; Daugelavičius, R. Plasma membrane is the target of rapid antibacterial action of silver nanoparticles in Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 6779–6790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girma, A.; Alamnie, G.; Bekele, T.; Mebratie, G.; Mekuye, B.; Abera, B.; Workineh, D.; Tabor, A.; Jufar, D. Green-synthesised silver nanoparticles: Antibacterial activity and alternative mechanisms of action to combat multidrug-resistant bacterial pathogens: A systematic literature review. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2024, 17, 2412601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bumgardner, J.D.; Wiser, R.; Gerard, P.D.; Bergin, P.; Chestnutt, B.; Marini, M.; Ramsey, V.; Elder, S.H.; Gilbert, J.A. Chitosan: Potential use as a bioactive coating for orthopaedic and craniofacial/dental implants. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2003, 14, 423–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, R.; Cao, J.; Jiang, X.; Rogachev, A.V. Physicochemical, antibacterial properties and cytocompatibility of starch/chitosan films incorporated with zinc oxide nanoparticles. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 27, 102265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brás, T.; Rosa, D.; Gonçalves, A.C.; Gomes, A.C.; Alves, V.D.; Crespo, J.G.; Duarte, M.F.; Neves, L.A. Development of bioactive films based on chitosan and Cynara cardunculus leaves extracts for wound dressings. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 1707–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
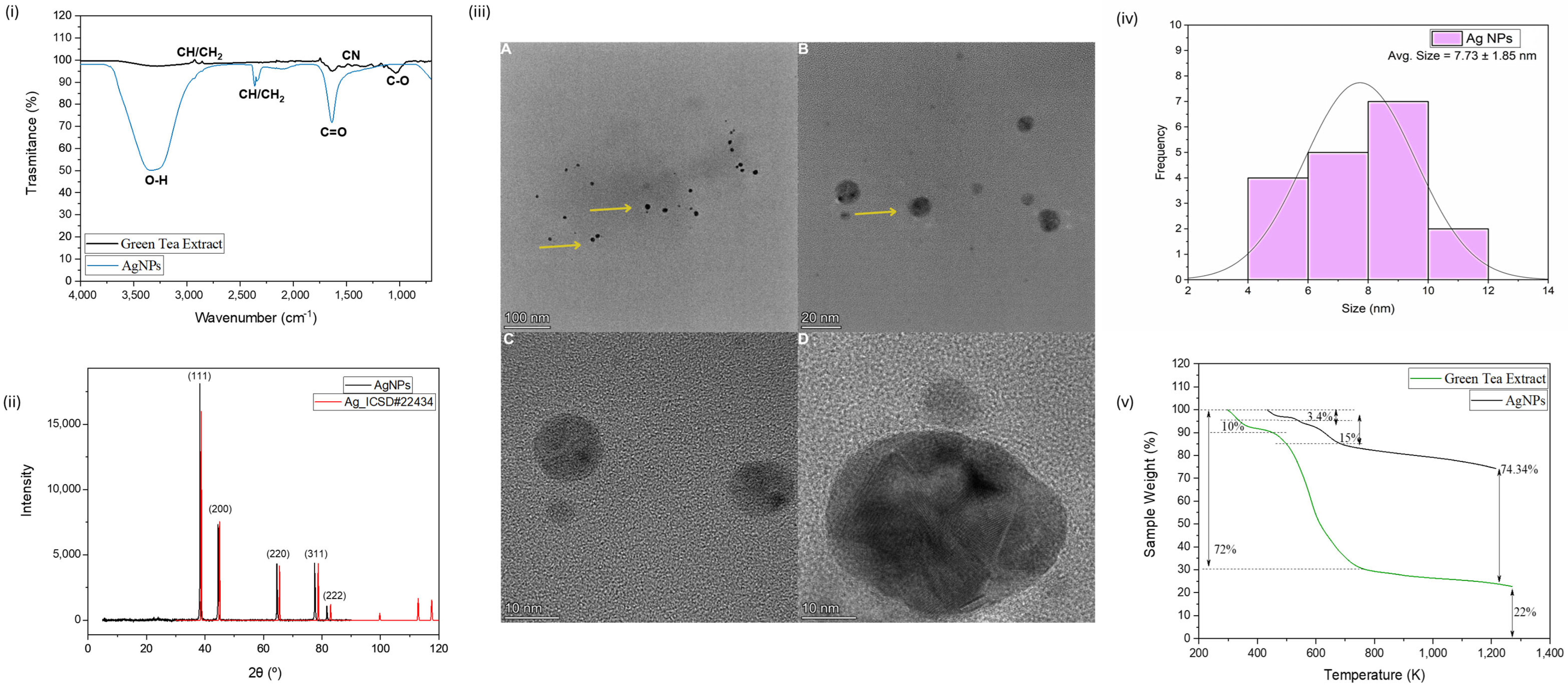
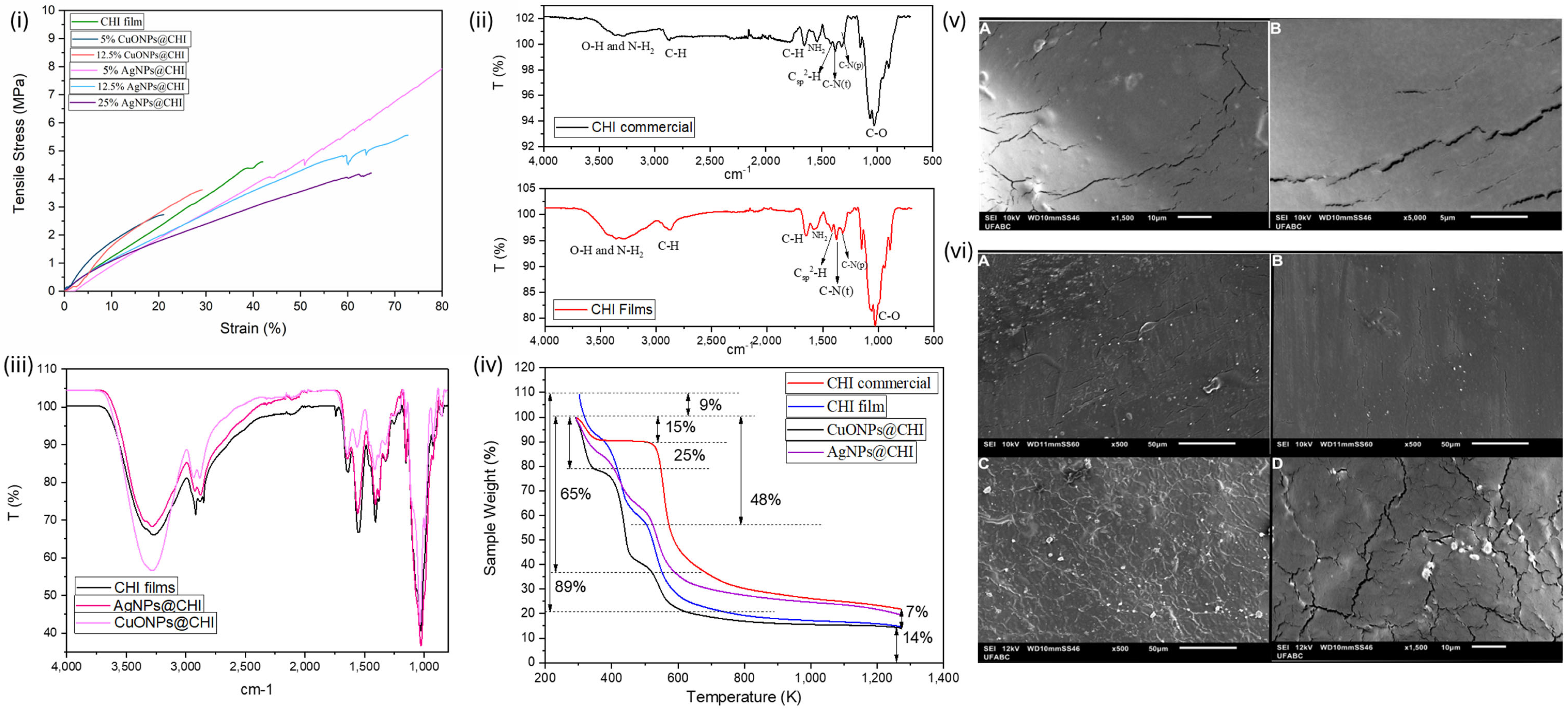
| Parameter | CuONPs * | AgNPs |
|---|---|---|
| Core diameter (TEM)/nm | 9.11 ± 6.72 | 7.73 ± 1.85 |
| Hydrodynamic size (DLS)/nm | 78.0 ± 2.7 | 57.36 ± 3.9 |
| Polydispersity index (PDI) | 0.17 ± 0.04 | 0.32 ± 0.01 |
| Zeta potential (mV) | −26.5 ± 2.7 | −37.5 ± 3.32 |
| Crystalline structure (XRD) | CuO (ICSD #16025) | Ag0 (ICSD #22434) |
| FTIR functional groups | Polyphenols and flavonoids | Polyphenols and flavonoids |
| Morphology (HTEM) | Roughly spherical and slight aggregation | Spherical, with no apparent aggregation |
| Organic content (TGA) | 59% organic matter | 25% organic matter |
| Thermal stability (TGA) | Less stable than AgNPs; higher organic loss | High thermal stability; ~74% residual mass at 1200 K |
| Bacteria | 5% AgNPs in AgNPs@CHI Film Inhibition Zone (cm) | 5% CuONPs in CuONPs@CHI Film Inhibition Zone (cm) | Statistical Comparison | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | 0.30 ± 0.01 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | AgNPs > CuONPs (p < 0.05) | AgNPs: highly effective against Gram-positive aerobes |
| E. coli | 0.35 ± 0.01 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | AgNPs > CuONPs (p < 0.05) | AgNPs: effective against Gram-negative bacteria |
| C. acnes | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.45 ± 0.01 | CuONPs > AgNPs (p < 0.05) | CuONPs: selectively effective against anaerobic C. acnes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reis, R.A.d.; de Freitas, C.C.; da Silva, L.L.; Monteiro, L.P.; Nakazato, G.; Champeau, M.; da Silva, R.A.G.; Seabra, A.B. Selective Antimicrobial Chitosan Films Incorporating Green-Synthesized Silver and Copper Oxide Nanoparticles for Acne Treatment. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090891
Reis RAd, de Freitas CC, da Silva LL, Monteiro LP, Nakazato G, Champeau M, da Silva RAG, Seabra AB. Selective Antimicrobial Chitosan Films Incorporating Green-Synthesized Silver and Copper Oxide Nanoparticles for Acne Treatment. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(9):891. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090891
Chicago/Turabian StyleReis, Roberta Albino dos, Carolina C. de Freitas, Leonardo Longuini da Silva, Laura Pierobão Monteiro, Gerson Nakazato, Mathilde Champeau, Ricardo A. Galdino da Silva, and Amedea Barozzi Seabra. 2025. "Selective Antimicrobial Chitosan Films Incorporating Green-Synthesized Silver and Copper Oxide Nanoparticles for Acne Treatment" Antibiotics 14, no. 9: 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090891
APA StyleReis, R. A. d., de Freitas, C. C., da Silva, L. L., Monteiro, L. P., Nakazato, G., Champeau, M., da Silva, R. A. G., & Seabra, A. B. (2025). Selective Antimicrobial Chitosan Films Incorporating Green-Synthesized Silver and Copper Oxide Nanoparticles for Acne Treatment. Antibiotics, 14(9), 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090891










