Veillonella parvula as a Causative Agent of Discitis: Insights from a Clinical Case and Literature Overview
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Case Report
2.1. Medical History
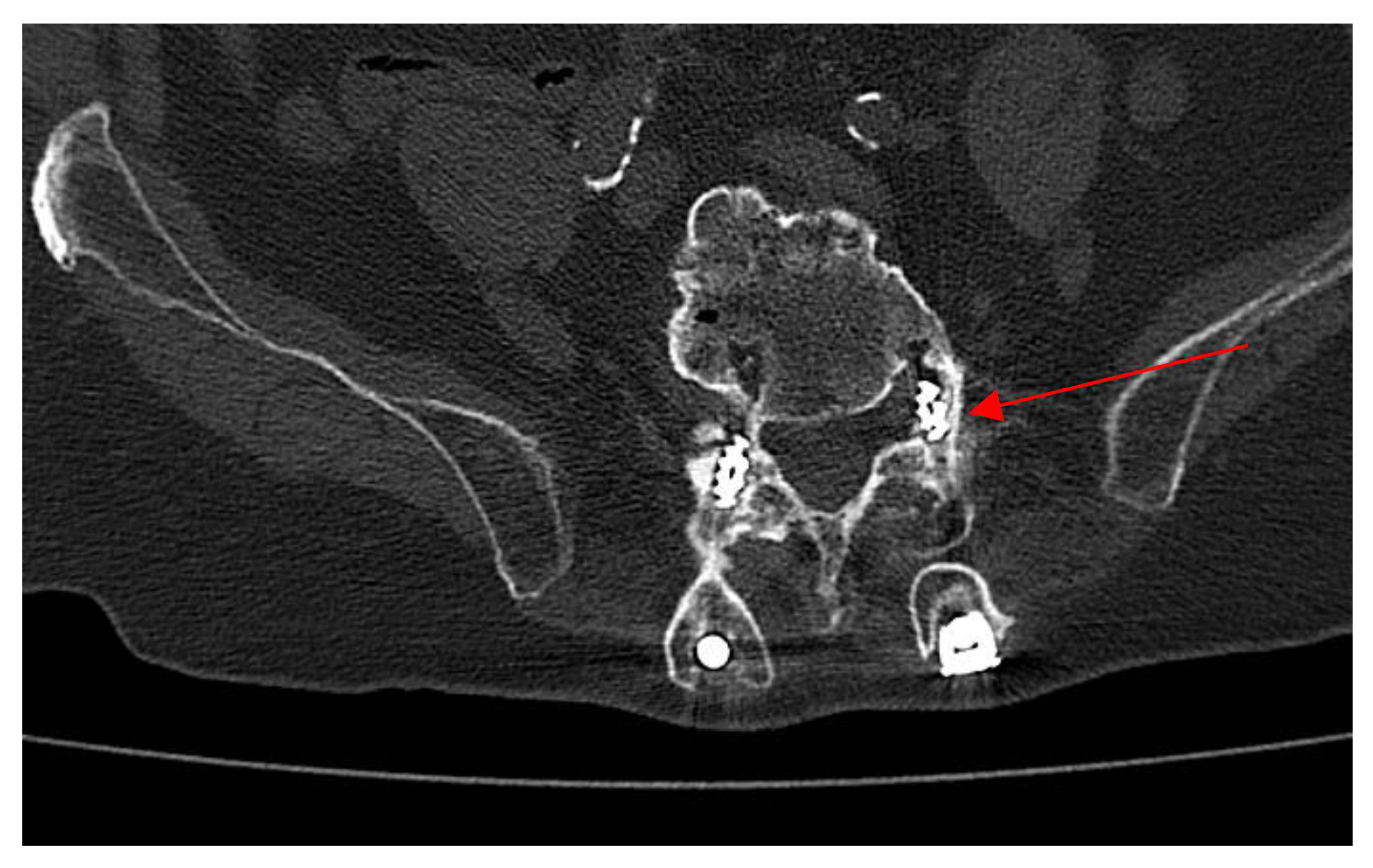
2.2. Previous Spinal Surgeries
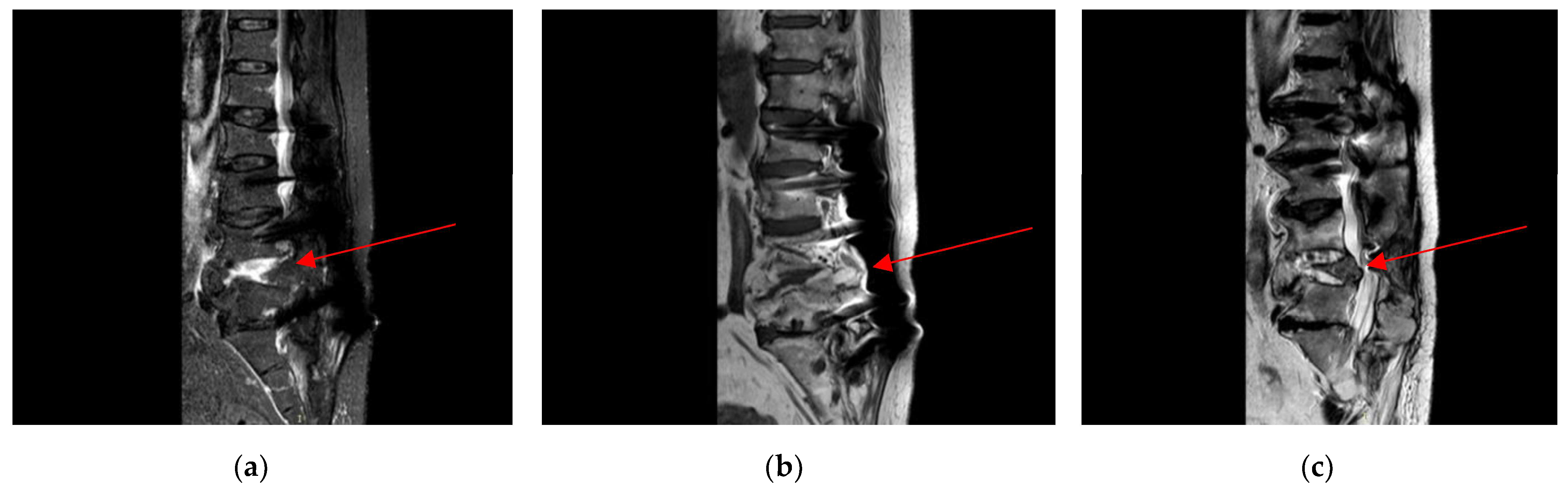
2.3. Admission to Infectious Diseases Unit
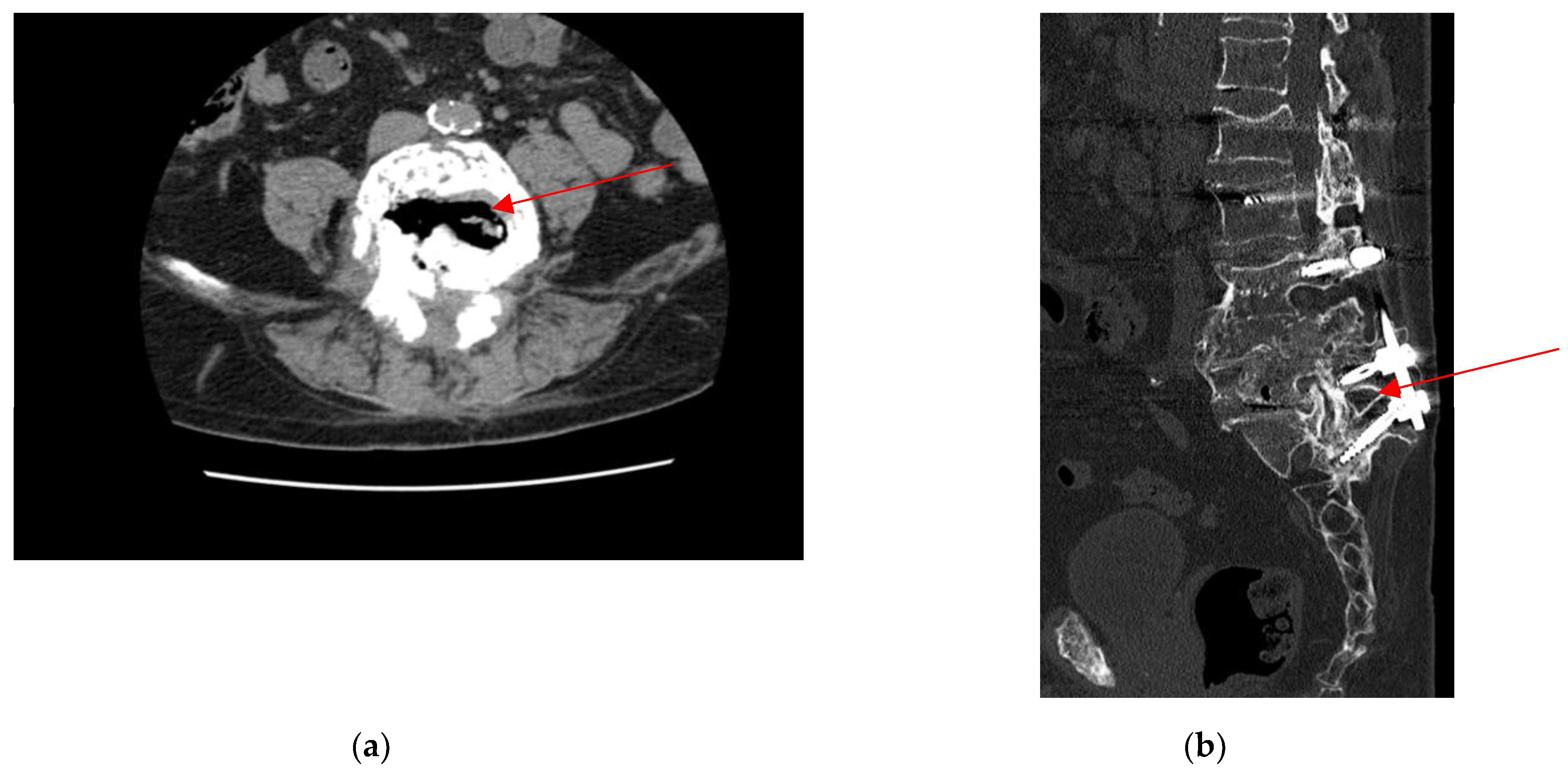
2.4. Neurosurgery Evaluation
2.5. Microbiological Analysis
2.6. Treatment and Follow-Up
3. Literature Review and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| LPB | Low pain back |
| w | Weeks |
| S | Susceptibility |
| R | Resistance |
| IV | Intravenous |
| PO | Per os/oral administration |
References
- Mays, T.O.; Holdeman, L.V.; Moore, W.E.C.; Rogosa, M.; Johnson, J.L. Taxonomy of the genus Veillonella prevot. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1982, 32, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouze, H.; Noussair, L.; Padovano, I.; Salomon, E.; de Laroche, M.; Duran, C.; Felter, A.; Carlier, R.; Breban, M.; Dinh, A. Veillonella parvula spondylodiscitis. Med. Mal. Infect. 2019, 49, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziga, M.; Gianoli, D.; Waldeck, F.; Dennler, C.; Schlichtherle, R.; Forster, T.; Martens, B.; Schwizer, R. Spondylodiscitis due to anaerobic bacteria Veillonella parvula: Case report and literature review. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2021, 12, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashima, I.; Nakazawa, F. The interaction between Streptococcus spp. and Veillonella tobetsuensis in the early stages of oral biofilm formation. J. Bacteriol. 2015, 197, 2104–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marriott, D.; Stark, D.; Harkness, J. Veillonella parvula discitis and secondary bacteremia: A rare infection complicating endoscopy and colonoscopy? J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 672–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, S.; Allyn, R. Lytic lesions: Looking lethal but leaving room for a simple cure? A case of Veillonella spinal osteomyelitis. JMM Case Rep. 2017, 4, e005108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arif, N.; Sheehy, E.C.; Do, T.; Beighton, D. Diversity of Veillonella spp. from sound and carious sites in children. J. Dent. Res. 2008, 87, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurihara, M.; Tamaki, I.; Tokuda, Y. Epidural abscess and spondylitis caused by Veillonella parvula in a man on hemodialysis. Clin. Case Rep. 2021, 9, e04660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boo, T.W.; Cryan, B.; O’Donnell, A.; Fahy, G. Prosthetic valve endocarditis caused by Veillonella parvula. J. Infect. 2005, 50, 81–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borchardt, K.A.; Baker, M.; Gelber, R. Veillonella parvula septicemia and osteomyelitis. Ann. Intern. Med. 1977, 86, 63–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Otaibi, F.E.; Al-Mohizea, M.M. Non-vertebral Veillonella species septicemia and osteomyelitis in a patient with diabetes: A case report and review of the literature. J. Med. Case Rep. 2014, 8, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatti, M.A.; Frank, M.O. Veillonella parvula meningitis: Case report and review of Veillonella infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2000, 31, 839–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malkoc, A.; Mamoun, L.; Cremat, D.; Barmanwalla, A.; Phan, A.; Daoud, A.; Perez, K.; Woodward, B. Emerging liver infection of Veillonella parvula associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome: A case report. Ann. Med. Surg. 2024, 86, 4870–4874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobo, F.; Aguilera-Franco, M.; Pérez-Carrasco, V.; García-Salcedo, J.A.; Navarro-Marí, J.M. Bacteremia caused by Veillonella parvula: Two case reports and a review of the literature. Anaerobe 2024, 88, 102879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahara, S.; Kinoshita, T.; Amano, T.; Ishida, M.; Yamakita, T.; Takimoto, N.; Oka, K. Decubitus ulcer infection and bacteremia due to tazobactam/piperacillin-resistant Veillonella parvula. Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 2024, 86, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaninetti-Schaerer, A.; Van Delden, C.; Genevay, S.; Gabay, C. Total hip prosthetic joint infection due to Veillonella species. Jt. Bone Spine 2004, 71, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchandin, H.; Jean-Pierre, H.; Carrière, C.; Canovas, F.; Darbas, H.; Jumas-Bilak, E. Prosthetic joint infection due to Veillonella dispar. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2001, 20, 340–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.W.; Wu, J.J.; Wang, L.R.; Teng, L.J.; Huang, T.C. Two fatal cases of Veillonella bacteremia. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1998, 17, 62–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirai, J.; Yamagishi, Y.; Kinjo, T.; Hagihara, M.; Sakanashi, D.; Suematsu, H.; Fujita, J.; Mikamo, H. Osteomyelitis caused by Veillonella species: Case report and review of the literature. J. Infect. Chemother. 2016, 22, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyfors, S.; Könönen, E.; Bryk, A.; Syrjänen, R.; Jousimies-Somer, H. Age-related frequency of penicillin resistance of oral Veillonella. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2003, 46, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Antibiotics | Zone of Inhibition Diameter |
|---|---|
| Ampicillin/Sulbactam | 30.0 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 18.0 |
| Gentamicin | 18.0 |
| Penicillin G | 14.0 |
| Vancomycin | 15.0 |
| Author | Age (Year)/Sex | Symptoms (Weeks) | Risk Factors | Discitis/Spondylodiscitis | Other Sites of Infection | (1) Blood and (2) Bone/Disc Cultures | Susceptibility | Therapy (Weeks) | Surgery | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | 35/F | LPB (20 w) | Chronic pulpitis and periapical cyst | Spondylodiscitis L4-L5 | No | (1) Negative (2) V. parvula | S: Amoxicillin Cefotaxime Rifampicin Fluoroquinolones Clindamycin Metronidazole. R: Amikacin Macrolides | Amoxicillin PO (6 w) | No | Cure |
| (2) | 76/F | Thoracolumbar junction pain (12 w) | No | Spondylodiscitis L1-L2 | No | (1) Negative (2) Veillonella spp. | Not reported | Ceftriaxone IV +metronidazolo IV (4 w), then amoxicillina/ clavulanic acid PO + metronidazolo PO (6 w) | Yes | Cure |
| (3) | 55/M | LPB + Fever (1 w) | Small bowel biopsy and a rectal biopsy | Spondylodiscitis L3-L4-L5 | No | (1) Negative (2) Negative V. parvula confirmed by PCR rRNA 16S | Not performed | Ceftriaxone IV (6 w), then amoxicillin/ clavulanic acid PO (6 w) | No | Cure |
| (4) | 27/M | LPB (3 w) | No | Discitis L4-L5 | No | (1) Negative (2) Veillonela spp. | Not reported | Amoxicillin IV (3 w), then amoxicillin PO (8 weeks) | No | Lost during the follow-up |
| (5) | 31/M | Odynophagia + Neck pain + Fever (8 w) | Cervical fracture and surgical procedure | Spondylodiscitis C4-C5 | No | (1) Not reported (2) Veillonella spp. and Streptococcus viridans group in the abscess fluid culture | Not reported | Penicillin G IV/IM (6 w) | Yes | Cure |
| (6) | 79/M | LBP (4 w) | No | Spondylodiscitis L3-L4 | No | (1) Negative V. parvula confirmed by PCR rRNA 16S (2) Negative | Not reported | Ceftriaxone IV + metronidazolo IV (4 w), then amoxicillin/clavulanic acid PO (2 w) | Yes | Cure |
| (7) | 74/M | LBP (18 w) | Extensively carious residual dentition | Spondylodiscitis T12-L1 | No | (1) Not reported (2) V. parvula | Not reported | Penicillin G IV/IM (6 w) | No | Cure |
| (8) | 61/F | LBP and paravertebral muscle spasm + Fever (1 w) | Rheumatoid arthritis | Spondylodiscitis L5-S1 | No | (1), (2) V. parvula | Not reported | Ceftriaxone IV (6 w) | No | Cure |
| (9) | 70/M | LPB (4 w) | No | Spondylodiscitis L3-L4 | No | (1) Not performed (2) Veillonela spp. | Not reported | Not reported | No | Cure |
| (10) | 68/M | LPB (3 w) | Bilateral sinusotomy and turbinectomy for carcinoma | Spondylodiscitis L1-L2 | No | (1) Veillonella. spp. (2) V. parvula | S: penicillin, amoxicillin/clavulanic acid, cefoxitin, clindamycin, imipenem, and metronidazole. | Amoxicillin/clavulanic acid IV (2 w) Then amoxicillin/clavulanic acid PO (4 w) | Yes | Cure |
| (11) | 67/M | LPB (2 w) | Dental dislocation following an accidental fall | Spondylodiscitis L1-L5 | No | (1), (2) Veillonella spp. | S: meropenem, ampicillin/sulbactam and piperacillin/tazobactam, and borderline sensitivity to metronidazole and penicillin. | Ceftriaxone IV (6 w) | No | Cure |
| (12) | 82/M | LBP + Fever (2 w) | Decompressive laminectomy at L2–S1 and C4–C5, along with anterior cervical discectomy | Discitis T10-L1 | Right tibial osteomyelitis, tricuspid and mitral valve endocarditis | (1) V. parvula (2) not performed | S: Amoxicillin/clavulanate, Ceftriaxone, Clindamycin, Metronidazole R: Penicillin | Ceftriaxone IV then Amoxicillin/clavulanate PO (27 w) | Yes | Cure |
| (13) | 72/M | LBP (7 w) | periodontitis and dental caries | Spondylodiscitis L2-L3 | No | (1) Negative (2) V. parvula | Not reported | Ceftriaxone IV + Metronidazole IV (6 w) | No | Not reported |
| (14) | 52/M | LBP (1 w) | No | Spondylitis L5/S1 | No | (1), (2) V. parvula | Ampicillin, ceftazidime, levofloxacin | Ampicillin IV (8 w) | No | Cure |
| Present case | 80/M | Neuropathic metatarsalgia (8 w) | Permanent dental prosthesis | Discitis L3-L5 | No | (1) V. parvula (2) Not performed | S: Penicillin G, ampicillin/sulbactam, ceftriaxone, ciprofloxacin, gentamicin, vancomycin R: Piperacillin, ceftriaxone, azithromycin | Amoxicillin/clavulanic acid (6 w) | No | Cure |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
D’Agati, G.; Mignone, L.; Bartolone, A.; Sciortino, G.; Fasciana, T.M.A.; Calà, C.; Bonura, S.; Carini, F.; Pipitò, L.; Cascio, A. Veillonella parvula as a Causative Agent of Discitis: Insights from a Clinical Case and Literature Overview. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 854. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090854
D’Agati G, Mignone L, Bartolone A, Sciortino G, Fasciana TMA, Calà C, Bonura S, Carini F, Pipitò L, Cascio A. Veillonella parvula as a Causative Agent of Discitis: Insights from a Clinical Case and Literature Overview. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(9):854. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090854
Chicago/Turabian StyleD’Agati, Giulio, Lorena Mignone, Antonella Bartolone, Giuseppa Sciortino, Teresa Maria Assunta Fasciana, Cinzia Calà, Silvia Bonura, Francesco Carini, Luca Pipitò, and Antonio Cascio. 2025. "Veillonella parvula as a Causative Agent of Discitis: Insights from a Clinical Case and Literature Overview" Antibiotics 14, no. 9: 854. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090854
APA StyleD’Agati, G., Mignone, L., Bartolone, A., Sciortino, G., Fasciana, T. M. A., Calà, C., Bonura, S., Carini, F., Pipitò, L., & Cascio, A. (2025). Veillonella parvula as a Causative Agent of Discitis: Insights from a Clinical Case and Literature Overview. Antibiotics, 14(9), 854. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090854






