Borderline Oxacillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (BORSA) Bacteremia—Case Report
Abstract
1. Introduction
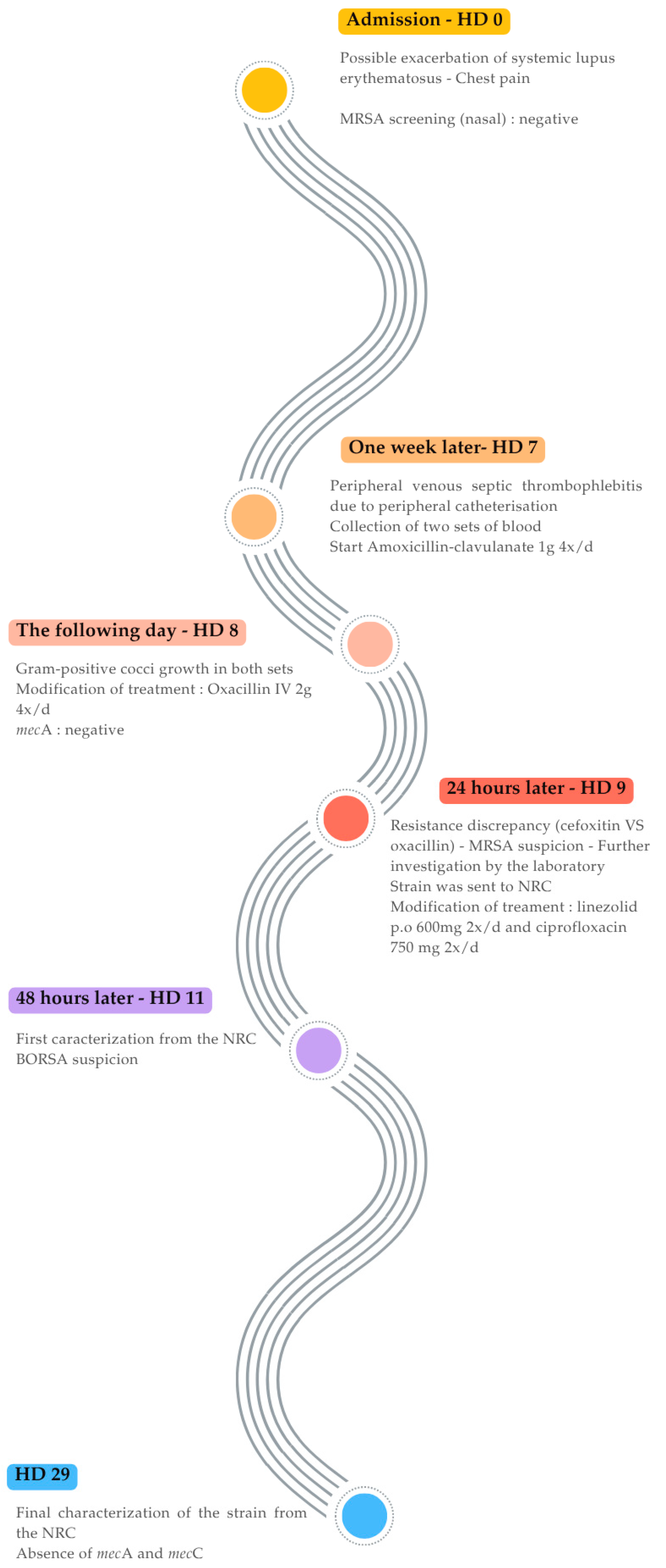
2. Case Presentation and Results
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Howden, B.P.; Giulieri, S.G.; Wong Fok Lung, T.; Baines, S.L.; Sharkey, L.K.; Lee, J.Y.H.; Hachani, A.; Monk, I.R.; Stinear, T.P. Staphylococcus aureus host interactions and adaptation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 380–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peacock, S.J.; Paterson, G.K. Mechanisms of Methicillin Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2015, 84, 577–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montanari, M.P.; Tonin, E.; Biavasco, F.; Varaldo, P.E. Further characterization of borderline methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and analysis of penicillin-binding proteins. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1990, 34, 911–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, X.; Harrison, E.M.; Edwards, G.F.; Holden, M.T.G.; Larsen, A.R.; Petersen, A.; Skov, R.L.; Peacock, S.J.; Parkhill, J.; Paterson, G.K.; et al. Novel mutations in penicillin-binding protein genes in clinical Staphylococcus aureus isolates that are methicillin resistant on susceptibility testing, but lack the mec gene. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 594–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoint Tables for Interpreta-Tion of MICs and Zone Diameters. Version 15.0. 2025. Available online: https://www.eucast.org (accessed on 18 January 2024).
- Hryniewicz, M.M.; Garbacz, K. Borderline oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (BORSA)—A more common problem than expected? J. Med. Microbiol. 2017, 66, 1367–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, L.; Cockram, C.; Lui, G.; Lam, R.; Lam, E.; Lai, R.; Ip, M. Community Case of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infection. Emerg. Infect. Dis. J. 2006, 12, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, S.; Murray, M.; Walus, T.; Karlowsky, J.A. Failure of Cloxacillin in Treatment of a Patient with Borderline Oxacillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Endocarditis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 859–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steensels, D.; Reynders, M.; Descheemaeker, P.; Curran, M.D.; Jacobs, F.; Denis, O.; Delforge, M.-L.; Montesinos, I. Clinical evaluation of a multi-parameter customized respiratory TaqMan® array card compared to conventional methods in immunocompromised patients. J. Clin. Virol. 2015, 72, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 33rd ed.; CLSI Supplement M100; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Malvern, PA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Maes, N.; Magdalena, J.; Rottiers, S.; De Gheldre, Y.; Struelens, M.J. Evaluation of a triplex PCR assay to discriminate Staphylococcus aureus from coagulase-negative Staphylococci and determine methicillin resistance from blood cultures. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 1514–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegger, M.; Andersen, P.S.; Kearns, A.; Pichon, B.; Holmes, M.A.; Edwards, G.; Laurent, F.; Teale, C.; Skov, R.; Larsen, A.R. Rapid detection, differentiation and typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus harbouring either mecA or the new mecA homologue mecALGA251. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsubakishita, S.; Kuwahara-Arai, K.; Baba, T.; Hiramatsu, K. Staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec-like element in Macrococcus caseolyticus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 1469–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolaia, V.; Kaas, R.S.; Ruppe, E.; Roberts, M.C.; Schwarz, S.; Cattoir, V.; Philippon, A.; Allesoe, R.L.; Rebelo, A.R.; Florensa, A.F.; et al. ResFinder 4.0 for predictions of phenotypes from genotypes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 3491–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinovski, M.M.; Veldkamp, K.E.; Lavrijsen, A.P.M.; Bosch, T.; Kraakman, M.E.M.; Nooij, S.; Claas, E.C.J.; Gooskens, J. Hospital transmission of borderline oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus evaluated by whole-genome sequencing. J. Med. Microbiol. 2021, 70, 001384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balslev, U.; Bremmelgaard, A.; Svejgaard, E.; Havstreym, J.; Westh, H. An Outbreak of Borderline Oxacillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (BORSA) in a Dermatological Unit. Microb. Drug Resist. 2005, 11, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maalej, S.M.; Rhimi, F.M.; Fines, M.; Mnif, B.; Leclercq, R.; Hammami, A. Analysis of Borderline Oxacillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (BORSA) Strains Isolated in Tunisia. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 3345–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, M.; Rasmussen, M.; Fuursted, K.; Westh, H.; Pedersen, L.; Deleuran, M.; Møller, J. Clonal Spread of Staphylococcus aureus with Reduced Susceptibility to Oxacillin in a Dermatological Hospital Unit. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2006, 86, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samsudin, N.; Chuan, C.W.; Hasan, H.; Hassan, S.A.; Deris, Z. Underdiagnosis of Borderline oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (BORSA)-Case series. Malays. J. Pathol. 2024, 46, 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Hess, K.A.; Kooda, K.; Shirley, J.D.; Schuetz, A.N.; Abu Saleh, O.; Stevens, R.W. Failure of mecA/mecC PCR Testing to Accurately Predict Oxacillin Resistance in a Patient with Staphylococcus aureus Infective Endocarditis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2023, 67, e00437-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argudín, M.A.; Roisin, S.; Nienhaus, L.; Dodémont, M.; De Mendonça, R.; Nonhoff, C.; Deplano, A.; Denis, O. Genetic Diversity among Staphylococcus aureus Isolates Showing Oxacillin and/or Cefoxitin Resistance Not Linked to the Presence of mec Genes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e00091-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchan, B.W.; Ledeboer, N.A. Identification of Two Borderline Oxacillin-Resistant Strains of Staphylococcus aureus From Routine Nares Swab Specimens by One of Three Chromogenic Agars Evaluated for the Detection of MRSA. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2010, 134, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Njenga, J.; Nyasinga, J.; Munshi, Z.; Muraya, A.; Omuse, G.; Ngugi, C.; Revathi, G. Genomic characterization of two community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus with novel sequence types in Kenya. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 966283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotz, J.F.; Staudacher, M.; Schefberger, K.; Spettel, K.; Schmid, K.; Kriz, R.; Schneider, L.; Hagemann, J.B.; Cyran, N.; Schmidt, K.; et al. Unraveling novel mutation patterns and morphological variations in two dalbavancin-resistant MRSA strains in Austria using whole genome sequencing and transmission electron microscopy. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakthavatchalam, Y.D.; Babu, P.; Munusamy, E.; Dwarakanathan, H.T.; Rupali, P.; Zervos, M.; John Victor, P.; Veeraraghavan, B. Genomic insights on heterogeneous resistance to vancomycin and teicoplanin in Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: A first report from South India. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0227009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackbarth, C.J.; Kocagoz, T.; Kocagoz, S.; Chambers, H.F. Point mutations in Staphylococcus aureus PBP 2 gene affect penicillin-binding kinetics and are associated with resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1995, 39, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Bayer, A.; Cosgrove, S.E.; Daum, R.S.; Fridkin, S.K.; Gorwitz, R.J.; Kaplan, S.L.; Karchmer, A.W.; Levine, D.P.; Murray, B.E.; et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America for the Treatment of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infections in Adults and Children. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52, e18–e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Antibiotics | Susceptible (S)/Susceptible, Increased Exposure (I)/Resistant (R) | Vitek-2®-Derived MIC Values (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|
| Oxacillin | S | ≥4 |
| Ciprofloxacin | I | ≤0.5 |
| Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole | R | 160 |
| Tobramycin | S | ≤1 |
| Gentamycin | S | ≤0.5 |
| Erythromycin | S | 0.5 |
| Clindamycin | S | 0.25 |
| Minocycline | S | ≤0.5 |
| Tetracycline | R | ≥16 |
| Linezolid | S | 2 |
| Rifampicin | S | ≤0.03 |
| Fusidic acid | S | ≤0.5 |
| Vancomycin | S | 1 |
| Kanamycin | S | ≤4 |
| Teicoplanin | S | ≤0.5 |
| Mupirocin | S | ≤1 |
| Clinical Sample | Diagnosis–Origin of Infection–Other Pathological Condition | Cefoxitin Screen (mm) | Oxacillin MIC (mg/L) | Treatment | Outcome | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Blood | Endocarditis–involvement of prosthetic material | / | ≥4 a 2–4 b | High-dose flucloxacillin and then vancomycin | Death | [15] |
| 2 | Blood | Bacteremia and possible endocarditis–infected venous line–kidney transplantation | / | ≥4 a 4 b | Unknown | Unknown | [15] |
| 3 | Blood | Bacteremia and infective endocarditis complicated with septic arthritis and pneumonia | 27 (S) e | ≥4 a | IV vancomycin 1 g B.I.D. and oral TMP-SMX 1440 mg BD for 42 days | Recovery | [19] |
| 4 | Synovial | 29 (S) e | ≥4 a | [19] | |||
| 5 | Blood | Abscess and bacteremia | 27 (S) e | ≥4 a | IV cloxacillin 2 g QID for 1 day; then, IV vancomycin 1 g BD for 13 days | Recovery | [19] |
| 6 | Pus | 26 (S) e | ≥4 a | [19] | |||
| 7 | Blood | Pneumonia and bacteremia | 27 (S) e | ≥4 a | IV vancomycin 1 g loading dose, 750 mg/day (renal adjusted dosing) for 5 days, then IV ceftaroline 300 mg TDS for 11 days | Recovery | [19] |
| 8 | Blood | Catheter-related bloodstream infection and bacteremia | 28 (S) e | ≥4 a | IV vancomycin 1 g loading dose; then, 750 mg/day for 14 days | Recovery | [19] |
| 9 | Blood | Bacteremia and infective endocarditis | 27 (S) e | ≥4 a | IV vancomycin 1 g BD and IV metronidazole 500 mg TDS for 4 days | Unresolved infection—patient requested to be discharged | [19] |
| 10 | Blood | Bacteremia, infective endocarditis, and vertebral osteomyelitis–invasive material: intravenous drug user, tricuspid valve replacement (bioprosthetic valve), and pacemaker insertion | / | ≥4 a 12 c | IV cloxacillin 2 g every 4 h and 600 mg of rifampin orally once daily and then vancomycin | Symptoms resolved—patient requested to be discharged | [8] |
| 11 | Blood | Community-acquired BORSA bacteremia; infective endocarditis and lung abscesses–chronic eczema; cellulitis in the left leg | / | 4 b | IV cloxacillin (2 g every 6 h) was given on days 2–5, and then IV vancomycin + rifampicin on day 5. Treatment switched to ampicillin/sulbactam (3 g every 6 h) on day 10 (and for 6 weeks) with rifampin; vancomycin treatment was stopped | Condition progressively deteriorated from day 2 to day 10 and defervescence occurred 3 days later | [7] |
| 12a | Blood | Sternal wound abscess, bacteremia, and infective endocarditis–bioprosthetic aortic valve replacement? | ≈S a | ≥4 a, and then the MIC was suppressed | Empirical vancomycin (15 mg/kg intravenously, every 24 h [i.v. q24h] at a separate outside institution. Two days later, vancomycin was de-escalated to cefazolin (2 g i.v. q8h). A diagnosis of IE was made: the treatment switched to oxacillin (2 g i.v. q4h) and synergistic gentamicin (1 mg/kg i.v. q12h), with plans to add rifampin. Patient was transitioned from oxacillin to cefazolin due to rising serum creatinine on HD9, then transitioned to daptomycin (8 mg/kg i.v. q24h) and rifampin (300 mg orally [p.o.] q8h) on HD11 and for 6 weeks, and finally, to lifelong suppressive doxycycline (100 mg p.o. q12h) | Recovery | [20] |
| 12b | ≈S a | “S” a (MIC was suppressed) | [20] | ||||
| 12c | 21 (R) e | ≥2 b | [20] | ||||
| 13 | Blood | Unknown | 33 (S) e | 2 d | Not specified for each individual case—treatments were pristinamycin, cefotaxime, or imipenem | Recovery | [17] |
| 14 | Blood | Unknown | 28 (S) e | 4 d | [17] | ||
| 15 | Blood | Unknown | 32 (S) e | 2 d | [17] | ||
| 16 | Blood | Unknown | 30 (S) e | 2 d | [17] | ||
| 17 | Blood | Bacteremia–Dermatitis atopica | / | “Reduced” (disk diffusion) e | Dicloxacillin | Recovery | [18] |
| 18 | Blood | Bacteremia–Mycosis fungoides | / | “Reduced” (disk diffusion) e | [18] | ||
| 19 | Blood | Bacteremia–Mb. Darier | / | “Reduced” (disk diffusion) e | [18] | ||
| 20 | Blood | Bacteremia–Pemphigoides bullosa | / | “Reduced” (disk diffusion) e | [18] |
| Isolates | Cefoxitin Screen | Oxacillin MIC E-test (mg/L) | Vitek-2®-Derived Oxacillin MIC Vitek2 (mg/L) | mec Gene Investigation (mecA and mecC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NRC-1 | 26 mm | 4 | ≥4 | Absence |
| NRC-2 | 26 mm | 4 | ≥4 | Absence |
| NRC-3 | 23 mm | 4 | ≥4 | Absence |
| NRC-4 | 27 mm | 4 | ≥4 | Absence |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buffart, B.; Clevenbergh, P.; Stiuliuc, A.; Raftakis, I.; Hing, M.; Miendje Deyi, V.Y.; Denis, O.; Martiny, D.; Yin, N. Borderline Oxacillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (BORSA) Bacteremia—Case Report. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 809. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14080809
Buffart B, Clevenbergh P, Stiuliuc A, Raftakis I, Hing M, Miendje Deyi VY, Denis O, Martiny D, Yin N. Borderline Oxacillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (BORSA) Bacteremia—Case Report. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(8):809. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14080809
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuffart, Beverly, Philippe Clevenbergh, Alina Stiuliuc, Ioannis Raftakis, Mony Hing, Véronique Yvette Miendje Deyi, Olivier Denis, Delphine Martiny, and Nicolas Yin. 2025. "Borderline Oxacillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (BORSA) Bacteremia—Case Report" Antibiotics 14, no. 8: 809. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14080809
APA StyleBuffart, B., Clevenbergh, P., Stiuliuc, A., Raftakis, I., Hing, M., Miendje Deyi, V. Y., Denis, O., Martiny, D., & Yin, N. (2025). Borderline Oxacillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (BORSA) Bacteremia—Case Report. Antibiotics, 14(8), 809. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14080809






