Epidemiology of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae Co-Producing MBL and OXA-48-Like in a Romanian Tertiary Hospital: A Call to Action
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
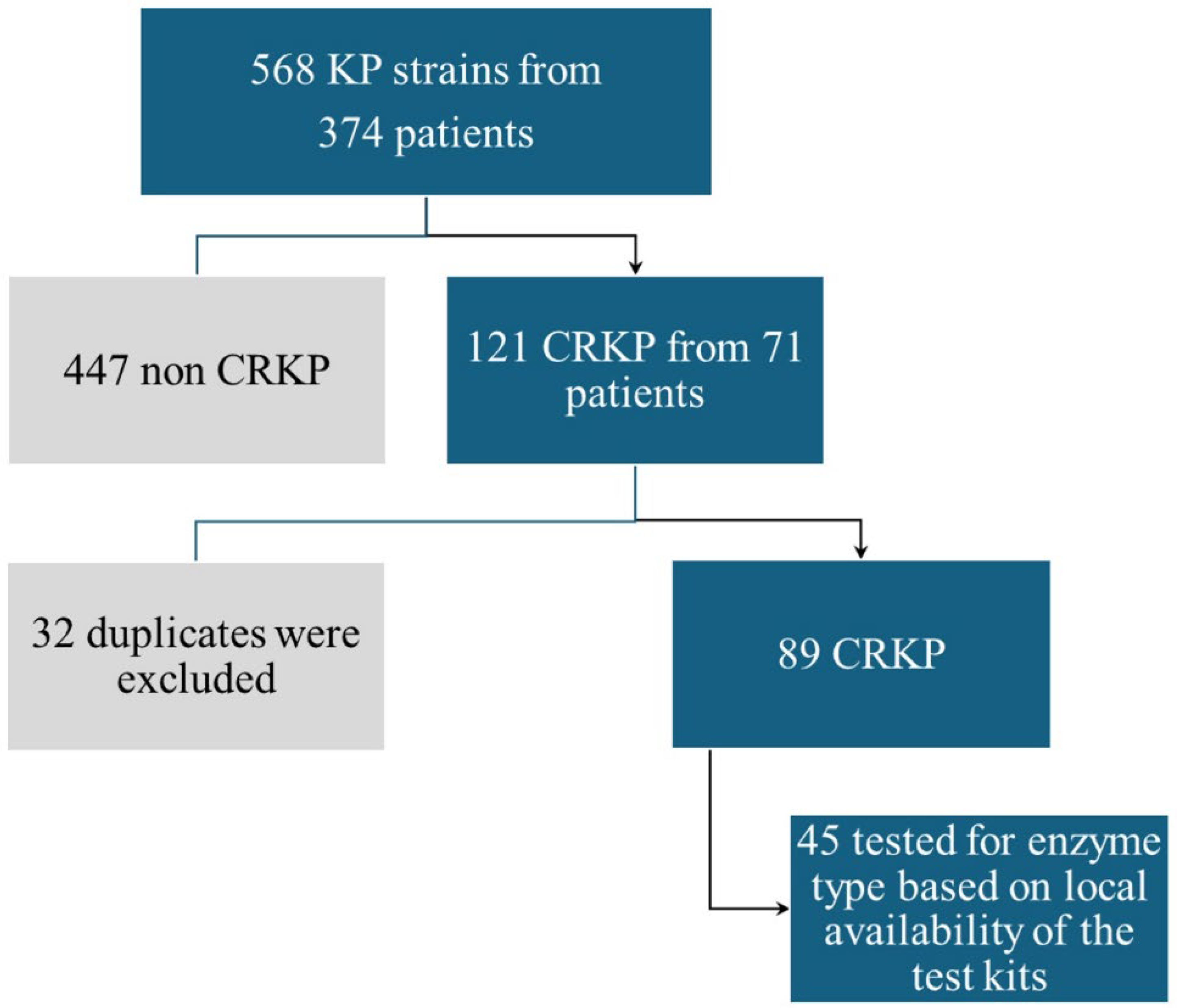
2.1. Main Sample Description
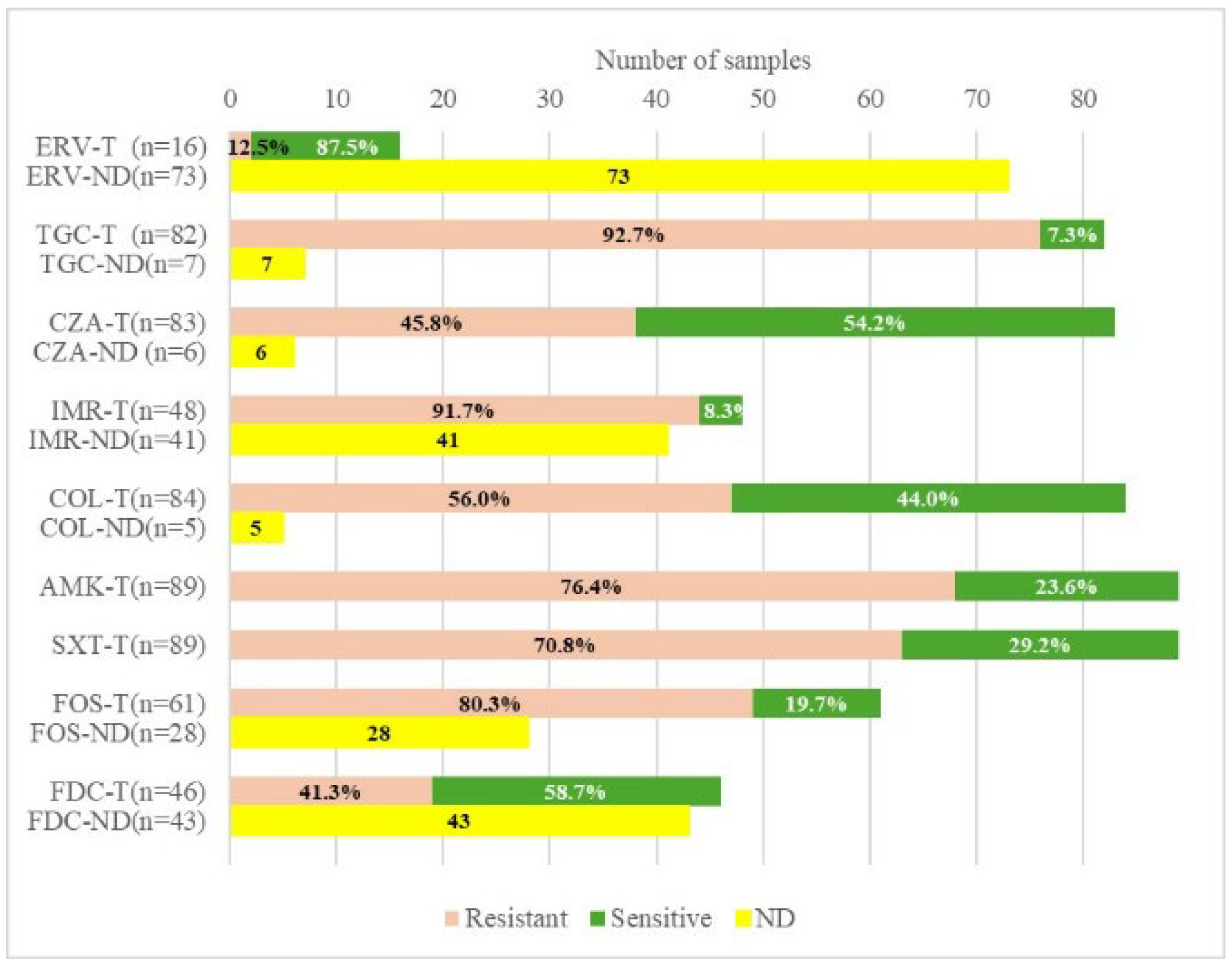
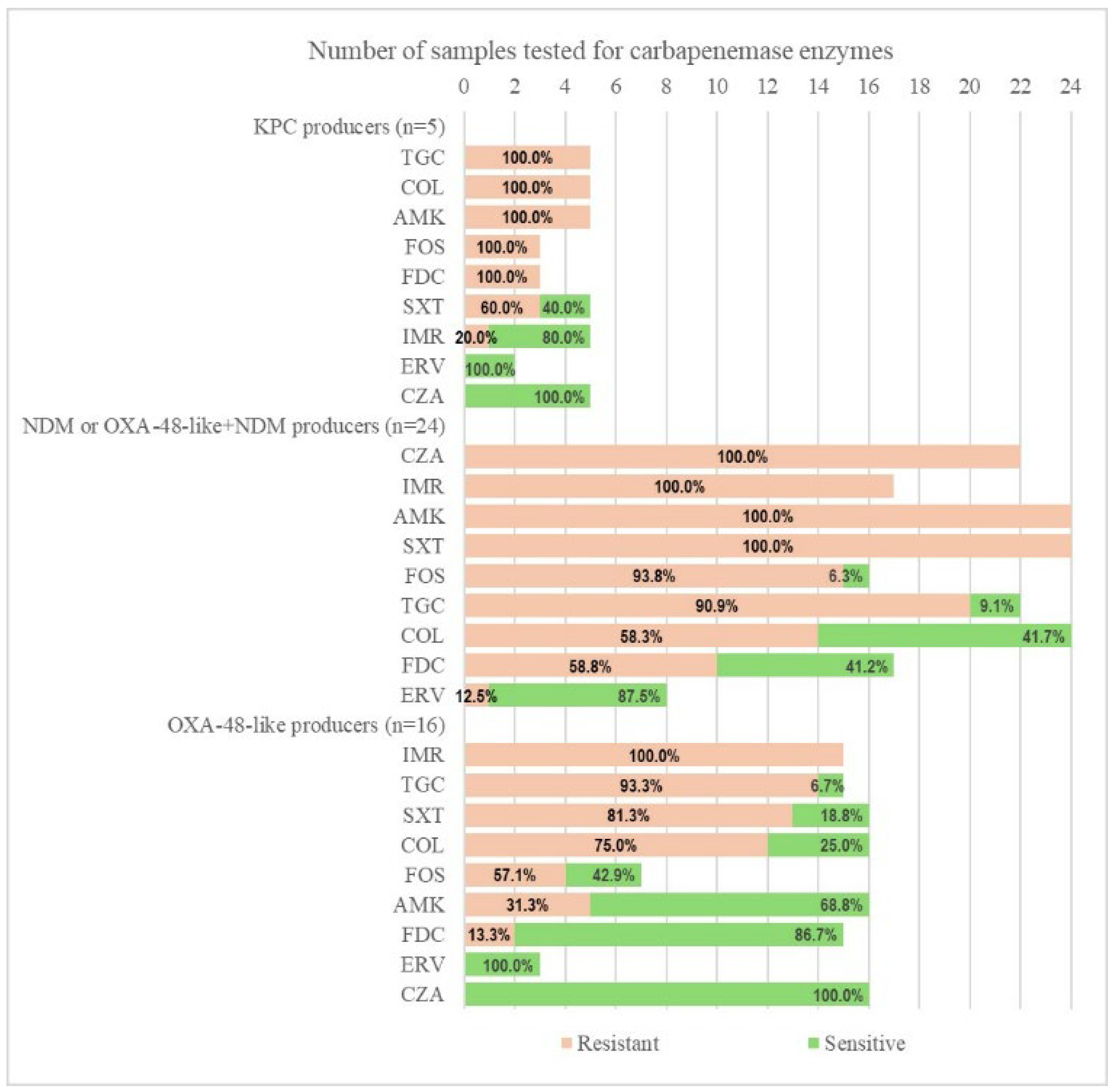
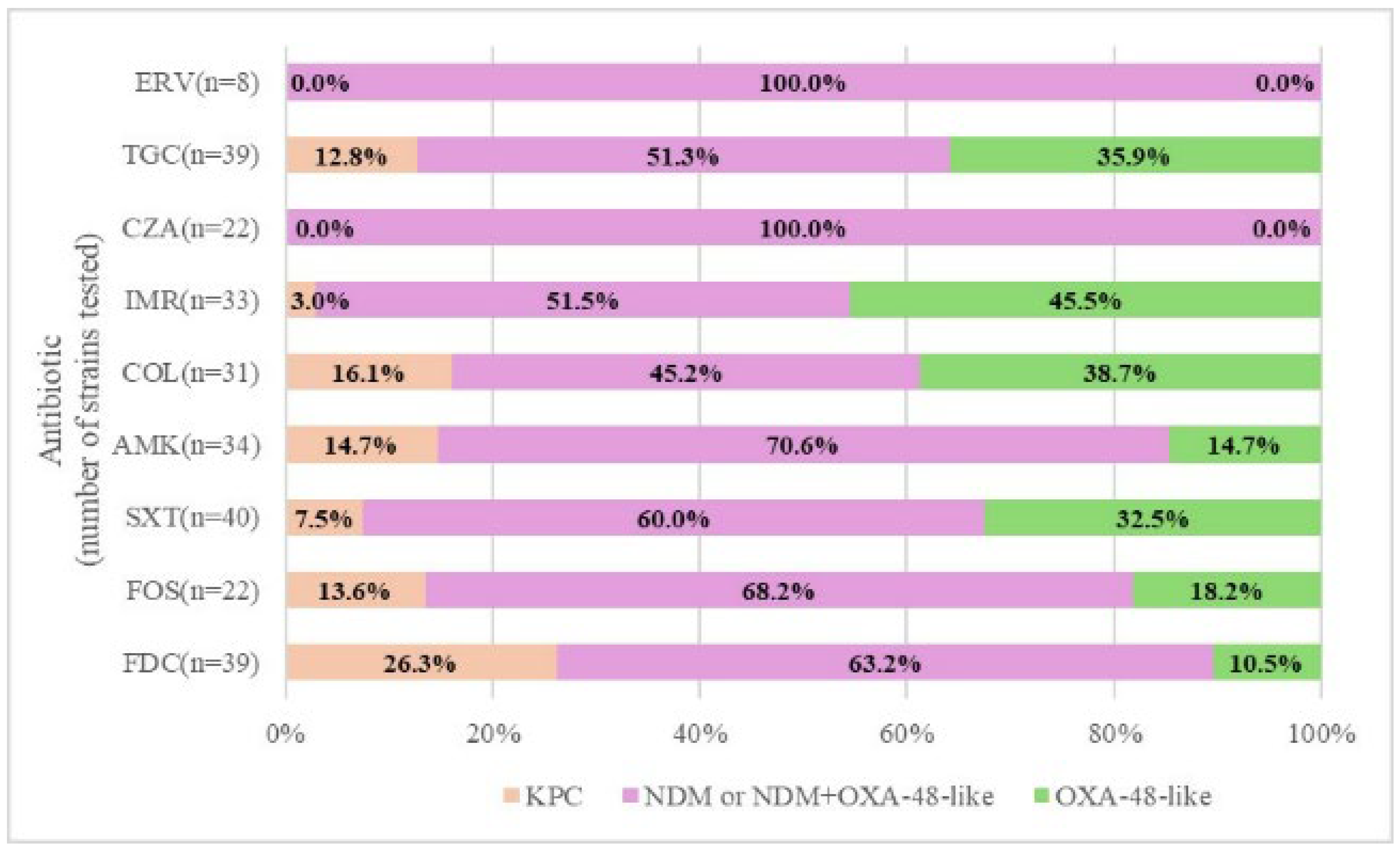
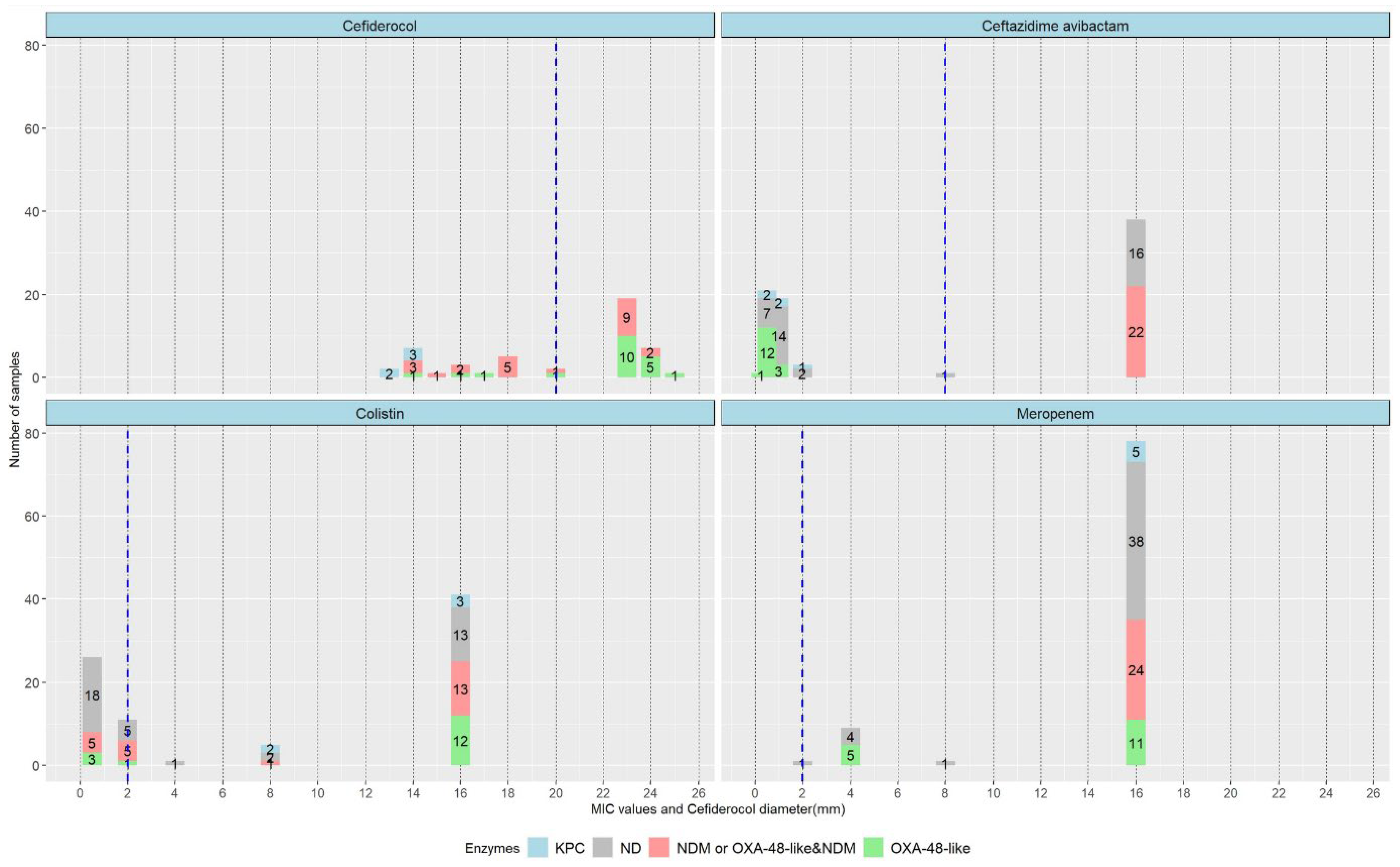
2.2. Carbapenemase Type and Susceptibility Profile
2.3. Patient Risks and Outcomes
3. Discussion
3.1. CRE (MBL) Epidemiology
3.2. Risk Factors
3.3. FDC Resistance
3.4. Carriage/Sepsis
3.5. Aztreonam Plus Ceftazidime–Avibactam Synergy
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Main Aspects
4.2. Bacteriology
4.3. Statistical Methods
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wareth, G.; Neubauer, H. The animal-foods-environment interface of klebsiella pneumoniae in Germany: An observational study on pathogenicity, resistance development and the current situation. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junaid, K.; Ejaz, H.; Younas, S.; Alanazi, A.; Yasmeen, H.; Rehman, A. Detection of Klebsiella pneumoniae antibiotic-resistant genes: An impending source of multidrug resistance dissemination through raw food. Saudi. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 3347–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paczosa, M.K.; Mecsas, J. Klebsiella pneumoniae: Going on the offensive with a strong defense. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.M.; Bachman, M.A. Colonization, infection, and the accessory genome of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Point Prevalence Survey of Healthcare Associated Infections and Antimicrobial use in European Acute Care Hospitals; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Bush, K. Past and Present Perspectives on β-Lactamases. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e01076-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kumar, S.; Zhang, L.; Wu, H.; Wu, H. Characteristics of antibiotic resistance mechanisms and genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Open Med. 2023, 18, 20230707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Emergence of Hypervirulent Klebsiella Pneumoniae ST23 Carrying Carbapenemase Genes in EU/EEA Countries; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Pan American Health Organisation Public Health Rapid Risk Assessment Related to Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae Carrying Carbapenemase Genes in the Region of the Americas-20 March 2024. Available online: https://www.paho.org/en/documents/public-health-rapid-risk-assessment-related-hypervirulent-klebsiella-pneumoniae-carrying (accessed on 20 March 2024).
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (2019) Surveillance Atlas of Infectious Diseases. Available online: https://atlas.ecdc.europa.eu/public/index.aspx?Dataset=27&HealthTopic=4 (accessed on 22 May 2024).
- WHO Bacterial Priority Pathogens List, 2024. Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/376776/9789240093461-eng.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 17 May 2024).
- Tesfa, T.; Mitiku, H.; Edae, M.; Assefa, N. Prevalence and incidence of carbapenem-resistant K. pneumoniae colonization: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Syst. Rev. 2022, 11, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Nation, R.L.; Turnidge, J.D.; Milne, R.W.; Coulthard, K.; Rayner, C.R.; Paterson, D.L. Colistin: The re-emerging antibiotic for multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2006, 6, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tompkins, K.; Duin, D.V. Treatment for carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales infections: Recent advances and future directions. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 40, 2053–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassetti, M.; Vena, A.; Larosa, B.; Giacobbe, D.R. New antibiotics in clinical pipeline for treating infections caused by metallo-β-lactamases producing Gram-negative bacteria. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2024, 37, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Pilato, V.; Pollini, S.; Miriagou, V.; Rossolini, G.M.; D’Andrea, M.M. Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: The role of plasmids in emergence, dissemination, and evolution of a major clinical challenge. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2024, 22, 25–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ECDC. Antimicrobial Resistance in the EU/EEA A One Health Response; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Hosmer, D.W.; Lemeshow, S.; Sturdivant, R.X. Wiley series in probability and statistics. In Applied Logistic Regression, 3rd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; Available online: https://dl.icdst.org/pdfs/files4/7751d268eb7358d3ca5bd88968d9227a.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2025)ISBN 978-0-470-58247-3.
- EUCAST Warnings Concerning Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Products or Procedures. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/ast-of-bacteria/warnings (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- WHO Antimicrobial Resistance. 2023. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antimicrobial-resistance (accessed on 29 May 2024).
- Goodman, K.E.; Simner, P.J.; Tamma, P.D.; Milstone, A.M. Infection control implications of heterogeneous resistance mechanisms in carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE). Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2016, 14, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effah, C.Y.; Sun, T.; Liu, S.; Wu, Y. Klebsiella pneumoniae: An increasing threat to public health. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2020, 19, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Kang, J.; Ma, Y.; Yin, D.; Song, Y.; Liu, Y.; Duan, J. Molecular Epidemiology of Carbapenem Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae in Northern China: Clinical Characteristics, Antimicrobial Resistance, Virulence and Geographic Distribution. Infect Drug Resist. 2023, 16, 7289–7304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibik, Y.E.; Ejder, N.; Sevim, E.; Rakici, E.; Tanriverdi, E.S.; Cicek, A.C. Evaluating molecular epidemiology of carbapenem non-susceptible Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates with MLST, MALDI-TOF MS, PFGE. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2023, 22, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Wu, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Xu, J.; He, F. Global emergence of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae co-carrying multiple carbapenemases. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2023, 21, 3557–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianco, G.; Boattini, M.; Comini, S.; Casale, R.; Iannaccone, M.; Cavallo, R.; Costa, C. Occurrence of multi-carbapenemases producers among carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales and in vitro activity of combinations including cefiderocol, ceftazidime-avibactam, meropenem-vaborbactam, and aztreonam in the COVID-19 era. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect Dis. 2022, 41, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simner, P.J.; Mostafa, H.H.; Bergman, Y.; Ante, M.; Tekle, T.; Adebayo, A.; Beisken, S.; Dzintars, K.; Tamma, P.D. Progressive Development of Cefiderocol Resistance in Escherichia coli During Therapy Is Associated with Increased blaNDM-5 Copy Number and Gene Expression. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 75, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tălăpan, D.; Rafila, A. Five-Year Survey of Asymptomatic Colonization with Multidrug-Resistant Organisms in a Romanian Tertiary Care Hospital. Infect. Drug Resist. 2022, 15, 2959–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Albiger, B.; Glasner, C.; Struelens, M.J.; Grundmann, H.; Monnet, D.L. Carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in Europe: Assessment by national experts from 38 countries. Euro. Surveill. 2015, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute of Public Health. Available online: https://insp.gov.ro/centrul-national-de-supraveghere-si-control-al-bolilor-transmisibile-cnscbt/analiza-date-supraveghere/ (accessed on 22 May 2024).
- Tian, X.; Huang, C.; Ye, X.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, R.; Hu, X.; Xu, D. Molecular Epidemiology of and Risk Factors for Extensively Drug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Infections in Southwestern China: A Retrospective Study. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yuan, Y.; Wang, J.; Yao, Z.; Ma, B.; Li, Y.; Yan, W.; Wang, S.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, J.; Xu, J.; et al. Risk Factors for Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Bloodstream Infections and Outcomes. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, T.; Du, X.; Zhang, P.; Shi, Q.; Han, X.; Lan, P.; Yan, R.; Hu, H.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X. Risk factors for infection and mortality caused by carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: A large multicentre case-control and cohort study. J. Infect 2022, 84, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, A.Y.; Chang, H.; Wang, N.Y.; Sun, F.J.; Liu, C.P. Clinical and molecular characteristics and risk factors for patients acquiring carbapenemase-producing and non-carbapenemase-producing carbapenem-nonsusceptible-Enterobacterales bacteremia. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2022, 55 Pt 2, 1229–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, C.; Mesini, A.; Mariani, M.; Tavella, E.; Sette, C.; Ugolotti, E.; Bartalucci, C.; Palmero, C.; Bandettini, R.; Castagnola, E. Reduce susceptibility to cefiderocol in gram negative bacteria in children: Is hope already lost before it’s even arrived? J. Inf. Pub. Health 2024, 17, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Terrier, C.; Nordmann, P.; Buchs, C.; Poirel, L. Effect of modification of penicillin-binding protein 3 on susceptibility to ceftazidime-avibactam, imipenem-relebactam, meropenem-vaborbactam, aztreonam-avibactam, cefepime-taniborbactam, and cefiderocol of Escherichia coli strains producing broad-spectrum β-lactamases. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2024, 68, e0154823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.H.; Huang, E. Cefiderocol Resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae Is Linked to SHV Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase Activities and Functional Loss of the Outer Membrane Porin OmpK35. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0349622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, G.; Boattini, M.; Comini, S.; Iannaccone, M.; Bondi, A.; Cavallo, R.; Costa, C. In vitro activity of cefiderocol against ceftazidime-avibactam susceptible and resistant KPC-producing Enterobacterales: Cross-resistance and synergistic effects. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect Dis. 2022, 41, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temkin, E.; Solter, E.; Lugassy, C.; Chen, D.; Cohen, A.; Schwaber, M.J.; Carmeli, Y. CPE Working Group. The Natural History of Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacterales: Progression from Carriage of Various Carbapenemases to Bloodstream Infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2024, 79, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karampatakis, T.; Tsergouli, K.; Behzadi, P. Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: Virulence Factors, Molecular Epidemiology and Latest Updates in Treatment Options. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yusuf, E.; Bax, H.I.; Verkaik, N.J.; van Westreenen, M. An Update on Eight “New” Antibiotics against Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Xia, J.; Zong, Z.; Shi, Y.; Ni, Y.; Hu, F.; Chen, Y.; Zhuo, C.; Hu, B.; Lv, X.; et al. Society of Bacterial Infection and Resistance of Chinese Medical Association; Expert Committee on Clinical Use of Antimicrobial Agents and Evaluation of Antimicrobial Resistance of the National Health Commission; Infectious Diseases Society of Chinese Medical Education Association. Guidelines for the diagnosis, treatment, prevention and control of infections caused by carbapenem-resistant gram-negative bacilli. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2023, 56, 653–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cismaru, I.M.; Văcăroiu, M.C.; Soium, E.; Holban, T.; Radu, A.M.; Melinte, V.; Gheorghiță, V. Synergistic Combination of Aztreonam and Ceftazidime—Avibactam—A Promising Defense Strategy against OXA-48 + NDM Klebsiella pneumoniae in Romania. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Fu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, L.; Long, W.; Yu, K.; Li, X.; Wei, C.; Liang, X.; et al. In vitro and in vivo activity of ceftazidime/avibactam and aztreonam alone or in combination against mcr-9, serine- and metallo-β-lactamases-co-producing carbapenem-resistant Enterobacter cloacae complex. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2024, 43, 1309–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Luo, Q.; Shen, P.; Chen, Y.; Xu, H.; Xiao, Y.; Qiu, Y. New options for bloodstream infections caused by colistin- or ceftazidime/avibactam-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2021, 58, 106458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/search?search_api_fulltext=Emblaveo (accessed on 22 May 2024).
- Huy, T.X.N. Overcoming Klebsiella pneumoniae antibiotic resistance: New insights into mechanisms and drug discovery. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2024, 13, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, M.; Carrara, E.; Retamar, P.; Tängdén, T.; Bitterman, R.; Bonomo, R.A.; deWaele, J.; Daikos, G.L.; Akova, M.; Harbarth, S.; et al. European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID) guidelines for the treatment of infections caused by multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacilli (endorsed by European society of intensive care medicine). Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2022, 28, 521–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamma, P.D.; Aitken, S.L.; Bonomo, R.A.; Mathers, A.J.; van Duin, D.; Clancy, C.J. Infectious Diseases Society of America 2023 Guidance on the Treatment of Antimicrobial Resistant Gram-Negative Infections. Clin Infect Dis. 2023, 18, ciad428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Factors | Values | Samples | Hospital Events (Discharges) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 89 | % of Total Valid Cases | n = 77 | % of Total Valid Cases | ||
| Gender | Males | 67 | 75.3 | 59 | 76.6 |
| Females | 22 | 24.7 | 18 | 23.4 | |
| Ward | Surgical | 44 | 49.4 | 41 | 53.3 |
| Medical | 45 | 50.6 | 36 | 46.7 | |
| Origin | Community | 22 | 24.7 | 21 | 27.3 |
| Hospital | 67 | 75.3 | 56 | 72.7 | |
| Charlson score | Below 5 | 36 | 41.9 | 28 | 37.8 |
| At least 5 | 50 | 58.1 | 46 | 62.2 | |
| Events with Intensive Care Unit (ICU) stay | Yes | - | - | 45 | 58.4 |
| No | - | - | 32 | 41.6 | |
| Surgical intervention | Yes | - | - | 43 | 55.8 |
| No | - | - | 34 | 44.2 | |
| Sepsis | Yes | 32 | 36.0 | 24 | 31.2 |
| No | 57 | 64.0 | 53 | 68.8 | |
| Sample site | Abdominal | 3 | 3.4 | 3 | 3.9 |
| Blood culture | 5 | 5.6 | 5 | 6.5 | |
| Wound | 8 | 9.0 | 8 | 10.4 | |
| Respiratory tract | 13 | 14.6 | 13 | 16.9 | |
| Urinary tract | 32 | 36.0 | 32 | 41.6 | |
| Others | 13 | 14.5 | 13 | 16.8 | |
| Active treatment | Yes | 50 | 56.2 | 46 | 59.7 |
| No | 39 | 43.8 | 31 | 40.3 | |
| Patients with active treatment | Yes | 50 | 56.2 | 46 | 59.7 |
| No | 39 | 43.8 | 31 | 40.3 | |
| Current portage | Yes | - | - | 34 | 44.7 |
| No | - | - | 42 | 55.3 | |
| Portage and sepsis | Yes | - | - | 15 | 19.7 |
| Fatality during hosp. stay | Yes | - | - | 15 | 19.5 |
| No | - | - | 62 | 81.5 | |
| Covariates | Statistics | Samples (days) | Hospital Events (Discharges) (days) | ||
| Age in years | mean (s.d.) | 62.5 (14.0) | 63.7 (13.8) | ||
| Length of hospital stay (LoS) | mean (s.d.) | - | 23.2 (19.1) | ||
| ICU stay, excluding non-ICU cases | mean (s.d.) | - | 12.2 (11.1) | ||
| Active treatment | mean (s.d.) | - | 13.6 (13.4) | ||
| Time from admission to sample collection | mean (s.d.) | 9.1 (12.4) | - | ||
| ICU Stay | Charlson Group | Surgical Intervention | Sepsis | Active Treatment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICU stay | 1 | 0.200 (p = 0.087) | 0.144 (p = 0.210) | 0.407 (p < 0.001) | 0.160 (p = 0.164) |
| Charlson group | 1 | 0.163 (p = 0.162) | 0.064 (p = 0.580) | −0.034 (p = 0.769) | |
| Surgical intervention | 1 | −0.079 (p = 0.487) | 0.283 (p = 0.013) | ||
| Sepsis | 1 | 0.267 (p = 0.019) | |||
| Active treatment | 1 |
| Covariates (Factors) | Model | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mortality | Sepsis | |||
| aOR (95% CI) | p-Value | aOR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| LoS (days) | 1.00 (0.95–1.05) | 0.919 | 1.03(1.00–1.07) | 0.048 |
| ICU stay (ref = no stay) | 40.8(3.5–473.3) | p < 0.01 | 10.0(2.4–41.0) | p < 0.01 |
| Surgical intervention (ref = no intervention) | 0.05(0.01–0.33) | p < 0.01 | 0.26(0.07–0.97) | 0.045 |
| Charlson group (ref = below 5) | 4.8(0.74–30.9) | 0.101 | 1.4(0.39–4.8) | 0.617 |
| Constant | 0.02 | p < 0.01 | 0.07 | p < 0.01 |
| Sample size | 73 | 73 | ||
| Nagelkerke R squared | 0.47 | 0.33 | ||
| HL-test | p = 0.93 | p = 0.79 | ||
| Overall correct classification | 84.9% | 76.7% | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Melinte, V.; Radu, M.A.; Văcăroiu, M.C.; Mîrzan, L.; Holban, T.S.; Ileanu, B.V.; Cismaru, I.M.; Gheorghiță, V. Epidemiology of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae Co-Producing MBL and OXA-48-Like in a Romanian Tertiary Hospital: A Call to Action. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 783. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14080783
Melinte V, Radu MA, Văcăroiu MC, Mîrzan L, Holban TS, Ileanu BV, Cismaru IM, Gheorghiță V. Epidemiology of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae Co-Producing MBL and OXA-48-Like in a Romanian Tertiary Hospital: A Call to Action. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(8):783. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14080783
Chicago/Turabian StyleMelinte, Violeta, Maria Adelina Radu, Maria Cristina Văcăroiu, Luminița Mîrzan, Tiberiu Sebastian Holban, Bogdan Vasile Ileanu, Ioana Miriana Cismaru, and Valeriu Gheorghiță. 2025. "Epidemiology of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae Co-Producing MBL and OXA-48-Like in a Romanian Tertiary Hospital: A Call to Action" Antibiotics 14, no. 8: 783. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14080783
APA StyleMelinte, V., Radu, M. A., Văcăroiu, M. C., Mîrzan, L., Holban, T. S., Ileanu, B. V., Cismaru, I. M., & Gheorghiță, V. (2025). Epidemiology of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae Co-Producing MBL and OXA-48-Like in a Romanian Tertiary Hospital: A Call to Action. Antibiotics, 14(8), 783. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14080783







