Abstract
Background/Objectives: Campylobacteriosis in human populations is an ongoing issue in both developed and developing countries. Poultry production is recognized as a reservoir for antimicrobial resistance and main source of human Campylobacter infection. Methods: In this study, sixty-five Campylobacter isolates were cultured from fecal samples collected from 17 flocks of broiler chickens in Alberta, Canada over two years (2015–2016). Susceptibility assays and PCR assays were performed to characterize resistance phenotypes and resistance genes. Conjugation assays were used to examine the mobility of AMR phenotypes. Results: Campylobacter jejuni was the predominant species recovered during both years of sampling. There were no Campylobacter coli isolates found in 2015; however, approximately 33% (8/24) of isolates collected in 2016 were Campylobacter coli. The two most frequent antimicrobial resistance patterns in C. jejuni collected in 2015 were tetracycline (39%) and azithromycin/clindamycin/erythromycin/telithromycin resistance (29%). One isolate collected in 2015 has resistance pattern ciprofloxacin/nalidixic acid/tetracycline. The tetO gene was detected in all tetracycline resistant isolates from 2015. The cmeB gene was detected in all species isolates with resistance to azithromycin/clindamycin/erythromycin/telithromycin, and from two isolates with tetracycline resistance. Alignment of the nucleotide sequences of the cmeB gene from C. jejuni isolates with different resistance patterns revealed several single nucleotide polymorphisms. A variety of multi-drug resistance patterns were observed through conjugation experiments. Conclusions: These data suggest that poultry production may serve as a potential reservoir for and source of transmission of multi-drug resistant Campylobacter jejuni and supports the need for continued surveillance.
1. Introduction
Campylobacter spp. are Gram-negative bacteria varying in morphology from rod-, comma- or s-shape, having a single polar flagellum, bipolar flagella, or no flagellum [1]. Most species require microaerophilic conditions (5% O2, 10% CO2, 85% N2) for optimal growth. Some Campylobacter spp. can grow either in microaerophilic or anaerobic conditions [1]. Some species, such as Campylobacter concisus, Campylobacter curvus, Campylobacter rectus, Campylobacter mucosalis, Campylobacter showae, Campylobacter gracilis, and to a certain extent, Campylobacter hyointestinalis, require the presence of hydrogen or formate in culture media.
Campylobacter species, especially C. jejuni and C. coli are the most common cause of diarrheal illness in humans [2,3]. The number of campylobacteriosis cases reported in people in Canada was roughly ten thousand each year during 2006–2015, a rate of approximately 27 cases per 100,000 population [4]. In Europe, there was an estimate of 230,000 cases annually [5], while globally approximately 96 million cases was estimated annually [5]. C. jejuni appears to cause 95% of diagnosed campylobacteriosis cases in people [6]. Most Campylobacter infections are mild and self-limiting with symptoms of acute watery or bloody diarrhea, fever, abdominal cramps and weight loss [1]. However, infections may become severe and prolonged especially in patients whose immune systems are compromised [7].
Campylobacter spp. is transmitted to human from various sources such as untreated drinking water, contaminated meat products or direct contact with live animals [8]. Poultry production is recognized as a reservoir for antimicrobial resistance and main source of human Campylobacter infection, especially infection caused by C. jejuni [9,10]. C. jejuni is a common commensal species in chicken gut microbiome [9]. Broiler meat caused 20–30% of human infections while 50–80% was presumably from chicken reservoir as a whole [8]. Chicken litter is known to be a reservoir for multidrug resistant bacteria due to the misuse of antimicrobials in poultry production [10,11]. In poultry Alberta, 23.5% (48/204) of chicken samples and 14.2% (8/110) of turkey samples were positive with Campylobacter spp., most of which showed resistance to tetracycline [12]. Pig production is also another Campylobacter reservoir and mainly associated with C. coli [13].
Erythromycin (macrolide) is the drug of choice for C. jejuni campylobacteriosis in people because of high effectiveness, low toxicity and ease of administration. Fluoroquinolones (e.g., ciprofloxacin) are the second choice for treatment because of broad spectrum activity [14]. Alternative antibiotic choices such as chloramphenicol, clindamycin, aminoglycosides and carbapenems are effective against Campylobacter spp. Despite effective treatments the prevalence of resistant strains may complicate empirical treatment of campylobacteriosis [15]. All antimicrobials used to treat campylobacteriosis are considered to be of very high importance (Category I) or high importance (Category II) for human medicine [16]. The use of Category I and II antimicrobials is now prohibited in poultry for preventive treatment [17].
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) is considered as a key mechanism for not only driving genetic diversification but also facilitating the dissemination of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) genes. There are three HGT routes: natural transformation, conjugation and bacteriophage transduction, which were previously described, specifically in Campylobacter spp. [18]. HGT via conjugative plasmids is the most well-studied mechanism for the spread of AMR genes in resistant bacteria [18,19,20]. The most prevalent plasmid found in both C. jejuni and C. coli was type-1 plasmid (pTet) harboring tetO gene [18]. However, HGT via natural transformation appears to be more efficient for genetic exchange in Campylobacter spp. The CmeABC efflux pump in C. jejuni comprises a periplasmic fusion protein (CmeA), an inner membrane efflux transporter (CmeB), and an outer membrane protein (CmeC) [21,22]. This predominant efflux pump was shown to actively expel multiple antimicrobials such as fluoroquinolones, macrolides, and tetracycline [21,23]. A recent study demonstrated mutations in RE-CmeB (CmeB in a functionally potent variant of CmeABC), but not in RE-CmeA or RE-CmeC, were responsible for the functional gain of the multidrug efflux pump [24].
In this retrospective study, antimicrobial resistance phenotypes and genotypes of Campylobacter strains isolated from commercial broiler chicken production in Alberta during the period of 2015–2016 were characterized. Our study also performed conjugation assays to show the mobility of AMR phenotypes among Campylobacter spp. strains.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Flock Characteristics
Management practices, including methods used to clean barn and water lines, and antimicrobials used in flocks were collected and summarized (Table S1). The most commonly used antibiotics were bacitracin (n = 14), salinomycin (n = 9) and monensin (n = 5).
2.2. Bacterial Isolation and Speciation
Four pooled fecal samples, representing one per floor quadrant with at least 10 fecal droppings were collected from randomly selected barns and floors (if multiple level/pen barn) in 2015 and 2016, as part of the Canadian Integrated Program for Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance program–CIPARS [25]. Using a sterile sponge, 2 environmental barn surface samples and 3 meconium samples were collected. In total, 68 fecal samples per year were collected from 17 flocks of broiler chickens in Alberta, Canada (Table S1). Pooled fecal samples were sent on ice in coolers to Alberta Agriculture and Forestry for bacterial isolation and speciation on the same day.
Campylobacter was isolated using the standard CIPARS methodology, which is as follows: 25 g portion of each composite fecal sample was mixed with 225 mL of buffered peptone water (BPW) and incubated at 35 ± 1 °C for 24 h. The BPW mixture was serially diluted with Bolton broth (BB) in the ratios of 1:100 and 1:1000, then incubated in a microaerophilic atmosphere at 37 °C for 4 h. After that, they were incubated at 42 °C for 20 to 24 h. The BB tube contents were next streaked on modified Charcoal Cefoperazone Deoxycholate Agar (mCCDA) plates, followed by microaerophilic incubation at 42 °C for 72 h. Finally, presumptive Campylobacter colonies were identified using biochemical tests (Gram stain, catalase test, oxidase test) and multiplex PCR for speciation [25].
The multiplex PCR speciation of C. jejuni and C. coli was performed as previously described [26]. Three pairs of oligo primers were added into the PCR mix (Table 1).

Table 1.
Primers used in the study.
The bacterial isolates were then shipped to University of Calgary for further characterization. Mueller-Hinton agar/broth (MHA/MHB) (Becton Dickinson-BD, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) was used to recover these isolates. Campylobacter was cultured under microaerophilic condition at 37 °C for 3 days or at 42 °C for 2 days. Microaerophilic conditions were achieved by placing activated sachets in a BD BBL GasPakTM jar (BD GasPakTM EZ Campy Container System, BD, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) with inoculated growth medium.
2.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Assays
The minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) values for Campylobacter were determined by broth microdilution assay as part of the CIPARS program and was performed by Public Health Agency Canada (PHAC). The detailed procedure was previously described in a previous report by PHAC [25]. Briefly, the CAMPY plates designed by NARMS and containing 9 dehydrated antimicrobials were used. The list of these antimicrobials was presented in Table 2 with the testing concentration range for each antimicrobial indicated in clear areas. After incubation period, plates were read using the Sensititre Vizion System. The MIC values obtained were compared with those of CLSI standards [30]. Isolates resistant to at least three drug classes were considered as multiclass resistant (MDR) isolates.

Table 2.
Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC)’s distributions for resistance to each drug in Campylobacter isolates from Alberta poultry farms in year 2015 (n = 41) and in year 2016 (n = 24).
The MIC values for transconjugants (see protocol for transconjugants selection) were also determined using a broth microdilution method. Sensititre™ Campylobacter MIC plates (Trek Diagnostic Systems, Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Mississauga, ON, Canada). Strains were streaked on Mueller-Hinton agar plates and incubated in microaerophilic conditions at 37 °C for 72 h or 42 °C for 48 h. Several colonies were selected and inoculated into 5 mL Sensititre™ cation-adjusted Mueller-Hinton broth with TES buffer–CAMHBT (Trek Diagnostic Systems, Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Mississauga, ON, Canada) and adjusted to a 0.5 McFarland Standard using a Sensititre™ nephelometer. The inoculated CAMHBT was then mixed well, and subsequently 100 µL was transferred into Sensititre cation adjusted Mueller-Hinton broth with TES buffer and lysed horse blood–CAMHBT+ LHB (Trek Diagnostic Systems, Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Mississauga, ON, Canada). The inoculated CAMHBT + LHB was mixed, and 100 µL was inoculated into each well on MIC plate using Sensititre™ Auto-Inoculator. The microtiter plate was incubated in microaerophilic conditions at 37 °C for 48 h before reading results using the Sensititre™ Manual Viewer. For interpretation of manually read results we followed MIC Interpretive guidelines as provided by the CLSI [30].
2.4. Genomic DNA Extraction
Genomic DNA extraction was performed using a previously published method with modifications [31]. Briefly, overnight culture was harvested, re-suspended in 500 μL TES (10 mM Tris, 25 mM EDTA, pH 8.0) and lysed using lysis solution (20 μL of 25% SDS, 50 μL of 5 mg/mL of predigested Pronase E and 50 μL of 5 M NaCl) at 68 °C for 30 min. Proteins were precipitated by adding 260 μL of 7.5 M ammonium acetate to the lysate kept on ice for 20 min. Precipitated protein was separated from the lysate by centrifuging at 13,000 rpm for 15 min. DNA was extracted from the lysate supernatant by adding chloroform of the same volume and subsequent centrifugation at 13,000 rpm for 15 min. After this centrifugation step, the top layer was transferred to a new tube containing 780 μL of isopropanol and the mixture was incubated on ice for 30 min to precipitate DNA. DNA was pelleted by being centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 1 min, then washed with 500 μL of 70% ethanol and pelleted again. After the supernatant was discarded, the tube was air-dried to remove traces of ethanol and then DNA was dissolved in 50 μL of TE buffer.
2.5. PCR Assay to Detect AMR Genes
A PCR assay was performed on genomic DNA prep to determine the presence of tetA, tetO and cmeB genes with previously published primers (Table 1).
Two tetO PCR products from isolates 96.3 and 13.3 were sent for Sanger sequencing (https://cumming.ucalgary.ca/research/cat/health-genomics, accessed on 13 April 2025) to confirm their sequences. Four cmeB PCR products from isolates 13.3, 14.3 85.3 and 86.3 were also sent for Sanger sequencing (https://cumming.ucalgary.ca/research/cat/health-genomics, accessed on 13 April 2025) to confirm their sequences. Multiple sequence alignment was done using online tool (http://multalin.toulouse.inra.fr/multalin/, accessed on 13 April 2025).
2.6. Conjugation Assay
All C. jejuni isolates displaying various resistance patterns selected for conjugation assays were from the 2015 sampling. The C. jejuni isolate number 13.3, with MDR phenotype: azithromycin/clindamycin/erythromycin/telithromycin (AzClErTl) was used for mating assays with four randomly picked C. jejuni isolates (6.3, 33.3, 85.3, 96.3) that displayed resistance to tetracycline (Te) but susceptible to macrolides. The donor and recipient strains were mated in the ratio of 1:1 on MHA plates [32]. After 3-day incubation at 37 °C, conjugation spots were transferred to selective media: MHA plates supplemented with erythromycin (5 µg/mL) and tetracycline (5 µg/mL), to select for transconjugants. Conjugation spots were also spotted individually onto MHA plates and then transferred to selective media (MHA plates supplemented with erythromycin (5 µg/mL) and tetracycline (5 µg/mL)), as negative controls.
In a second conjugation experiment, the C. jejuni isolate number 96.3 which had a ciprofloxacin/nalidixic acid/tetracycline resistance phenotype (CiNaTe) was used as the donor in a mating assay with three isolates (no. 13.3, 113.3, 117.3) which had the AzClErTl resistance phenotype. The conjugation protocol was similar to the protocol mentioned above, except for the use of different selective media. In this conjugation experiment, the selective medium was MHA supplemented with erythromycin (5 µg/mL) and nalidixic acid (15 µg/mL).
A third conjugation experiment was performed similarly as described in the second conjugation using the same donors and recipients, except for selective media. In the third conjugation, selective media were MHA supplemented with erythromycin (5 µg/mL), tetracycline (5 µg/mL) and nalidixic acid (15 µg/mL).
2.7. Statistical Analyses
All analysis was completed in Stata 15 (StataCorp LLC: College Station, TX, USA).
Fisher’s exact test was used to assess resistance to different antimicrobials between 2015 and 2016.
3. Results
3.1. Distribution Frequency and Minimum Inhibition Concentration (MIC) for Campylobacter spp. Isolates from 2015 and 2016
Resistance to one or more drugs was detected in 9/17 flocks. Two flocks had isolates that were either susceptible or intermediate to all drugs, and isolates from the remaining six flocks were susceptible to all drugs tested. Chicks originated from three different hatcheries; however, 80% were from the same hatchery. Two flocks reported no use of antibiotics, the remaining 15 flocks were conventionally raised (i.e., reported using antibiotics).
Forty-one and twenty-four Campylobacter isolates were isolated from fecal samples in 17 flocks in 2015 and 2016, respectively. All 2015 isolates (100%, 41/41) were C. jejuni, while in 2016 there were 66.7% C. jejuni (16/24) and 33.3% C. coli (8/24). Twenty nine percent of Campylobacter isolates from 2015 (12/41) had MDR isolates, but no MDR isolates were identified in 2016 (Figure 1).
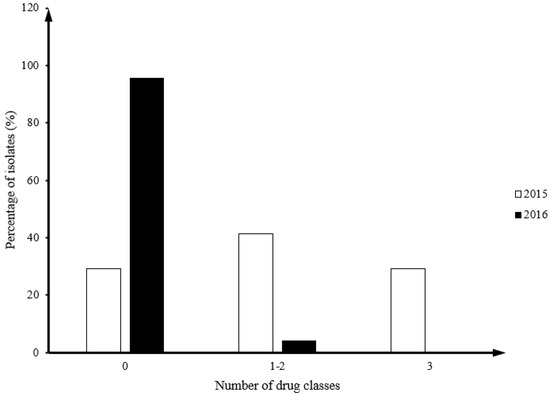
Figure 1.
Comparison of distribution frequency by the number of drug classes between Campylobacter in year 2015 and 2016.
The distribution of MICs around the resistance breakpoint for each antimicrobial showed that some isolates in 2015 had MICs larger than the maximum value of the tested range (Table 2): TEL (12/12), NAL (1/41), ERY (12/41), AZM (12/41). All 2016 isolates had MIC of all antimicrobials falling within the tested range (Table 2).
The association between resistance to individual drugs and year of isolation was examined in C. jejuni using Fisher’s exact test. A significant difference in the number of resistant isolates from 2015 (17/41, 41%) to 2016 (1/24, 4%) was detected for tetracycline (p = 0.011), and the pattern of telithromycin, erythromycin, clindamycin and azithromycin resistance (p = 0.013).
3.2. Resistance Patterns of Campylobacter Isolates from 2015 and 2016
Two main resistance patterns found in Campylobacter isolates from 2015 were azithromycin/clindamycin/erythromycin/telithromycin resistance (AzClErTlR–pattern 1, drug classes: macrolide-lincosamide-ketolide) and tetracycline resistance (TeR–pattern 2, drug classes: tetracyclines). In 2015, 39% (16/41) exhibited TeR pattern, and 29% (12/41) exhibited the AzClErTlR pattern. There was only one isolate 96.3 which displayed resistance to ciprofloxacin/nalidixic acid/tetracycline resistance (CiNaTeR, drug classes: quinolone-tetracycline).
C. jejuni isolates with the resistance pattern AzClErTlR were identified in three flocks in 2015. All three flocks obtained their chicks from the same hatchery, and all three farms used salinomycin for treatment of coccidiosis. These farms had the same floor space area (8000 ft2) and stocking density (0.54 ft2 per bird), used Ross 308 birds, and were all multi-age facilities [25]. Sanitation on these three farms was done using a hot water wash between productions periods, with chlorine in a pressurized form used as the disinfectant of choice. These three farms did not disinfect their water lines between flocks but did use chlorine to treat the water lines during the production cycle [25].
Out of 16 C. jejuni isolates collected in 2016, there was only one isolate which had resistance to Tetracycline (TeR). The rest 15 C. jejuni and 8 C. coli isolates in 2016 were pan-sensitive.
3.3. Detection of AMR Genes
All TeR isolates from the 2015 batch (n = 17) harbored tetO gene as determined by PCR assay and sequence analysis. The tetO nucleotide sequence had 99% agreement with the sequence encoding TetM/TetW/TetO/TetS family tetracycline resistance protein published in the GenBank database (Accession No. CP023546.1). The tetA gene sequence was not detected in any of our Te resistant isolates. For the PCR assays, C. jejuni isolate 13.3 with the AzClErTlR pattern was included as a negative control as no tetO gene was amplified from this tetracycline sensitive isolate.
The cmeB gene was detected in all C. jejuni strains collected in 2015 which had the AzClErTlR pattern (n = 12). In addition, out of five C. jejuni isolates which had other resistance patterns (TeR and CiNaTeR), the cmeB gene was detected in two TeR C. jejuni isolates. Alignment of the cmeB nucleotide sequence obtained by PCR revealed that isolates with the same resistance pattern (AzClErTlR or TeR) shared the same nucleotide sequence and single-nucleotide polymorphisms of the cmeB gene (Figure 2). The cmeB gene was not detected in a C. jejuni isolate with the CiNaTeR pattern nor in two C. jejuni isolates with TeR pattern.
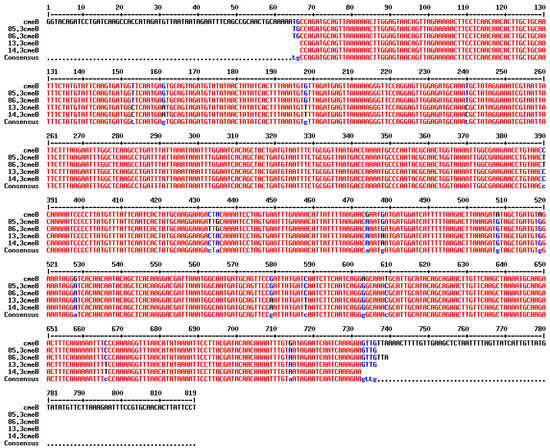
Figure 2.
Multiple sequence alignment of cmeB gene amplification from four isolates against cmeB gene from Genbank database (Access No. AB894099.1) using online tool (http://multalin.toulouse.inra.fr/multalin/, accessed on 13 April 2025). Two of them (85.3 and 86.3) were C.jejuni isolates with Te resistance pattern, and the other two (13.3 and 14.3) were C. jejuni isolates with AzClErTl resistance pattern.
3.4. Campylobacter jejuni Antimicrobial Resistance Phenotypes Transferred via In Vitro Conjugation
Three out of four C. jejuni isolates from 2015 with either TeR (isolates 6.3 and 85.3) or CiNaTeR (isolate 96.3) were able to produce transconjugants when mated with the C. jejuni isolate from 2015 with AzClErTlR pattern (isolate 13.3) (Table 3). The combined AMR pattern (AzClErTlTeR) of transconjugants 13.6, 13.85 and 13.96 was then confirmed by antimicrobial susceptibility assay (Table 3). All the transconjugants had the same MICs for nalidixic acid as the parental isolate 13.3 (MIC = 8 µg/mL). However, these MICs were higher than MICs in two isolates 6.3 and 85.3 (MIC ≤ 4 µg/mL), but lower than the MIC of the isolate 96.3 (MIC > 64 µg/mL). As a result, the TeR phenotype was likely transferred from supposed donors (6.3, 85.3, 96.3) to a supposed recipient (13.3). Although all of the transconjugants had phenotypic resistance to clindamycin, their MICs (MIC = 8 µg/mL) were half of the supposed recipient’s original MIC value (MIC = 16 µg/mL).

Table 3.
Minimum inhibition concentration (MIC) and AMR patterns of isolates used in conjugation assays and the resulting transconjugants.
In the second conjugation assay, three isolates (13.3, 113.3 and 117.3) with AzClErTlR pattern were mated with the isolate 96.3 with CiNaTeR pattern (Table 3). All transconjugants displayed the combined patterns CiNaR + AzClErTlR but they were all susceptible to Te; and two of them had an increased MIC (16 µg/mL) for ciprofloxacin as compared to the parental strain (8 µg/mL).
In the third conjugation, the presence of tetracycline in the selective media helped maintain Te resistance in the transconjugants. Presumable C. jejuni donors (13.3, 113.3 and 117.3) with AzClErTlR pattern was mated with the presumable C. jejuni recipient 96.3 with CiNaTeR pattern and selected on medium containing tetracycline. The transconjugants had a combined multi-drug resistance pattern of CiNaTeAzClErTl (Fluoroquinolones–CiNa, Tetracycline–Te, Macrolides–AzEr, Lincosamide–Cl, Ketolide–Tl).
4. Discussion
Campylobacter jejuni was the only Campylobacter species identified in samples from broiler production in Alberta in 2015, while both C. jejuni (66.7%) and C. coli (33.3%) were identified in samples collected in 2016. Overall, C. jejuni was the predominant Campylobacter species isolated, which is similar to other studies [5,33]. This is a clinically grave concern in humans when considering the fact that the majority (95 to 98%) of human cases of Campylobacter gastroenteritis were caused by C. jejuni, followed by C. coli cases (2 to 5%) [2,34]. Our study showed almost 30% of C. jejuni isolates from poultry in 2015 having phenotypic resistance to erythromycin. In addition, while other studies otherwise reported that C. coli was more likely to be associated with macrolide resistance, macrolide resistance phenotype was only found in C. jejuni isolates in our study [35]. All C. jejuni isolates were erythromycin-sensitive, while 9% of C. coli were resistant to erythromycin from Irish broiler neck skin and caeca [36].
Tetracycline-resistant isolates were found to make up 41% of 2015 Campylobacter isolates. The tetO gene was identified in all our 2015 C. jejuni isolates (n = 17) with phenotypic resistance to tetracycline. This result is similar to previous studies where the tetO gene was identified as the most common tetracycline resistance gene in all C. jejuni and C. coli isolates with resistance to tetracycline [27,37,38]. Transmissible plasmids carrying the tetO gene have been found not only in C. jejuni and C. coli but also in other bacteria such Enterococcus faecalis and Streptococcus spp. [39]. These tetO-carrying conjugative plasmids were also associated with genes encoding for different aminoglycoside inactivating enzymes, transposase- like genes, and multiple other genes [40,41]. The tetO gene can also be located on the bacterial chromosome, especially in C. coli [37,38]. The phenotypes of our transconjugants imply that the tetO gene in some of our isolates is plasmid-encoded and transmissible. The isolate that was unable to transfer the tetracycline resistance phenotype to the recipient might carry a chromosomally encoded tetO gene, or the gene may be located on a separate mobile element which was not transferred.
The cmeB gene encodes for an inner membrane efflux transporter and is a part of three-gene operon (designated cmeABC) that contributes to multidrug resistance in C. jejuni [29]. It was shown that mutation of the cmeB gene resulted in decreasing MICs to a wide range of antimicrobial agents (i.e., ciprofloxacin, nalidixic acid, erythromycin, tetracycline), heavy metals and bile salts between 2 and 4000-fold. In these cmeB mutant strains resistance to ciprofloxacin was decreased 8-fold, resistance to nalidixic acid decreased 2-fold, to erythromycin decreased 4-fold, and tetracycline resistance decreased 8-fold, [29]. In our study, the cmeB gene (819 bp) was selected for screening in a subset of Campylobacter isolates, especially the ones with AzClErTl phenotype because the gene was likely to confer resistance to antibiotics of different classes. All isolates with AzClErTl resistance pattern carried the cmeB gene. The cmeB gene was also present in two C. jejuni isolates with Te resistance pattern. However, they did not share the same sequence identity of cmeB genes with C. jejuni isolates of AzClErTl resistance pattern. A significant increase of cmeB mutations in C. jejuni strains carrying cmeB gene compared to those in the CmeB null mutant strains at 10× and 32× the concentration [42]. However, there were no further investigation of these mutations in their study.
In this study, only one C. jejuni isolate was resistant to ciprofloxacin, nalidixic acid and tetracycline. The cmeB gene was not detected in the C. jejuni isolate with the CiNaTe phenotype although this gene was shown to be associated with the resistance to ciprofloxacin, nalidixic acid and tetracycline in several previous studies [29,42,43] We postulate that some mutation in the gyrA gene most likely accounted for the resistance to flouroquinolones (ciprofloxacin and nalixidic acid) in this isolate because these drugs target the DNA gyrase encoded by gyrA gene [44,45].
In the first conjugation assay, the transconjugants with a combined resistance pattern (AzClErTl + Te) can be made by mating isolates of AzClErTl and Te phenotypes. Based on the MICs of transconjugants, isolates with Te phenotypes were likely to be the donors which transferred Te phenotype into the recipient isolate 13.3 with AzClErTl phenotype. In the second conjugation assay, isolate 96.3 with CiNaTe phenotype was used as the recipient and mated it with isolates exhibiting AzClErTl resistance pattern to determine the transferability of AzClErTl phenotype. Interestingly, the transconjugants displayed resistance not only to erythromycin, which was used as a selection marker, but also to azithromycin, clindamycin, and telithromycin. More surprisingly, all transconjugants maintained resistance to CiNa but lost resistance to Te after conjugation. It is well-known that the strains normally suffer a fitness cost to maintain plasmids; therefore, they can easily lose plasmids in antibiotic-free environment [46]. In the last conjugation experiment, we wanted to see if the transconjugants still maintain resistance to Te when we added tetracycline into the media in addition to nalidixic acid and erythromycin. The results suggested that they were able to maintain resistance to all antimicrobials provided that selection pressure was present in the media.
In conclusion, the study isolated and speciated Campylobacter isolates from broiler chickens in Alberta. In both years, C. jejuni was the predominant species isolated, and C. coli was only isolated in 2016. Twenty nine percent of C. jejuni isolates from 2015 (12/41) had multiclass drug resistance (MDR) (≥3 drug classes), but no MDR isolates were identified in 2016. Several single nucleotide polymorphisms were found in the cmeB gene of isolates of different resistance patterns. We also showed the potential for resistance pattern transfer during conjugation. The demonstration of transmission of multi-drug resistance via conjugation between strains supports the importance of continued antimicrobial resistance surveillance in food borne pathogens.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/antibiotics14080759/s1, Table S1: Flock level characteristics including antibiotics given in feed and methods used to disinfect barns.
Author Contributions
S.C., K.L., S.G. and C.M. conceptualized the research idea and obtained research funding from Alberta Agriculture and Forestry (PI: S.C.). S.G. and A.A. developed the CIPARS AMU-AMR farm surveillance framework, farm surveillance tools (questionnaire) and protocols, and validated the recovery and AMR datasets. Bacterial isolation and initial antimicrobial susceptibility testing were performed by T.T.T. and K.L. were responsible for experimental design. T.T.T. conducted research and laboratory analysis. N.C. conducted statistical analysis. T.T.T. and N.C. designed and drafted the manuscript. All authors contributed to manuscript development. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by Alberta Agriculture and Forestry (AAF) [grant number 2015R025R] with significant in a kind support from PHAC and the AAF, Agri-Food Laboratories.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Materials. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the poultry veterinarians and producers who voluntarily participated in the CIPARS farm surveillance program and enabled data and sample collection. We are grateful to the Chicken Farmers of Canada and the Alberta Chicken Producers for their valuable input to the framework development and technical discussions. T.T.T. also wishes to thank Odd-Gunnar Wikmark, Norwegian Environment Agency and the Norwegian Research Council (MARMIB—project number 315812) for their support in finishing this work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
References
- Kaakoush, N.O.; Castaño-Rodríguez, N.; Mitchell, H.M.; Man, S.M. Global epidemiology of campylobacter infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 687–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luber, P.; Wagner, J.; Hahn, H.; Bartelt, E. Antimicrobial Resistance in Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli Strains Isolated in 1991 and 2001–2002 from Poultry and Humans in Berlin, Germany. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 3825–3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Nelson, J.M.; Barrett, T.J.; Tauxe, R.V.; Rossiter, S.P.; Friedman, C.R.; Joyce, K.W.; Smith, K.E.; Jones, T.F.; Hawkins, M.A.; et al. Antimicrobial resistance among Campylobacter strains, United States, 1997–2001. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 1102–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC). Canadian Notifiable Disease Section 2015. Available online: http://diseases.canada.ca/notifiable/charts?c=pl (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- Hansson, I.; Sandberg, M.; Habib, I.; Lowman, R.; Engvall, E.O. Knowledge gaps in control of Campylobacter for prevention of campylobacteriosis. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 30–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butzler, J. Campylobacter, from obscurity to celebrity. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2004, 10, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luangtongkum, T.; Jeon, B.; Han, J.; Plummer, P.; Logue, C.M.; Zhang, Q. Antibiotic resistance in Campylobacter: Emergence, transmission and persistence. Future Microbiol. 2010, 4, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giannatale, E.; Calistri, P.; Di Donato, G.; Decastelli, L.; Goffredo, E.; Adriano, D.; Mancini, M.E.; Galleggiante, A.; Neri, D.; Antoci, S.; et al. Thermotolerant Campylobacter spp. in chicken and bovine meat in Italy: Prevalence, level of contamination and molecular characterization of isolates. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakeem, M.J.; Lu, X. Survival and Control of Campylobacter in Poultry Production Environment. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 10, 615049. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/cellular-and-infection-microbiology/articles/10.3389/fcimb.2020.615049 (accessed on 13 April 2025). [CrossRef]
- Ngogang, M.P.; Ernest, T.; Kariuki, J.; Mouliom Mouiche, M.M.; Ngogang, J.; Wade, A.; van der Sande, M.A.B. Microbial Contamination of Chicken Litter Manure and Antimicrobial Resistance Threat in an Urban Area Setting in Cameroon. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, C.L.; Blum, S.E.; Kattusamy, K.; Daniel, T.; Druyan, S.; Shapira, R.; Krifucks, O.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Zhou, X.-Y.; Su, J.-Q.; et al. Longitudinal study on the effects of growth-promoting and therapeutic antibiotics on the dynamics of chicken cloacal and litter microbiomes and resistomes. Microbiome 2021, 9, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narvaez-Bravo, C.; Taboada, E.N.; Mutschall, S.K.; Aslam, M. Epidemiology of antimicrobial resistant Campylobacter spp. isolated from retail meats in Canada. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 253, 43–47. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0168160517301782 (accessed on 17 April 2025). [CrossRef]
- Rath, A.; Rautenschlein, S.; Rzeznitzeck, J.; Breves, G.; Hewicker-Trautwein, M.; Waldmann, K.H.; von Altrock, A. Impact of Campylobacter spp. on the Integrity of the Porcine Gut. Animals 2021, 11, 2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altekruse, S.F.; Stern, N.J.; Fields, P.I.; Swerdlow, D.L. Campylobacter jejuni—An emerging foodborne pathogen. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1999, 5, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehtopolku, M.; Kotilainen, P.; Puukka, P.; Nakari, U.M.; Siitonen, A.; Eerola, E.; Huovinen, P.; Hakanen, A.J. Inaccuracy of the disk diffusion method compared with the agar dilution method for susceptibility testing of Campylobacter spp. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Government of Canada. Categorization of Antimicrobial Drugs Based on Importance in Human Medicine. 2009. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/drugs-health-products/veterinary-drugs/antimicrobial-resistance/categorization-antimicrobial-drugs-based-importance-human-medicine.html (accessed on 17 April 2025).
- Chicken Farmers of Canada. 2016 Annual Report. 2016. Available online: https://epe.lac-bac.gc.ca/100/201/300/ar_chicken_farmers/2016.pdf?nodisclaimer=1 (accessed on 17 April 2025).
- Golz, J.C.; Stingl, K. Natural Competence and Horizontal Gene Transfer in Campylobacter BT—Fighting Campylobacter Infections: Towards a One Health Approach; Backert, S., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 431, pp. 265–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsdottir, I.; Given, C.; Penttinen, R.; Jalasvuori, M. Preceding Host History of Conjugative Resistance Plasmids Affects Intra- and Interspecific Transfer Potential from Biofilm. mSphere 2023, 8, e0010723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-del Valle, A.; Toribio-Celestino, L.; Quirant, A.; Pi, C.T.; DelaFuente, J.; Canton, R.; Rocha, E.P.; Ubeda, C.; Peña-Miller, R.; San Millan, A. Antimicrobial resistance level and conjugation permissiveness shape plasmid distribution in clinical enterobacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2314135120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Wang, X.; Zheng, L.; Zhu, Y. Genomic analysis and antimicrobial resistance in human- and poultry-derived Campylobacter jejuni isolates from Hangzhou, China. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1599555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iovine, N.M. Resistance mechanisms in Campylobacter jejuni. Virulence 2013, 4, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Fang, L.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Q. Antibiotic resistance trends and mechanisms in the foodborne pathogen, Campylobacter. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2017, 18, 87–98. Available online: https://www.cambridge.org/core/product/3CA9C0DA6FA8AE1F0EE12AB80D372380 (accessed on 12 January 2025). [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Wu, Z.; Sahin, O.; Zhao, S.; Yu, E.W.; Zhang, Q. Mutation-based mechanism and evolution of the potent multidrug efflux pump RE-CmeABC in Campylobacter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2415823121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Public Health Agency of Canada. Canadian Integrated Program for Antimicrobial (CIPARS) Annual Report 2015. 2015. Available online: http://publications.gc.ca/collections/collection_2017/aspc-phac/HP2-4-2015-eng.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Persson, S.; Olsen, K.E.P. Multiplex PCR for identification of Campylobacter coli and Campylobacter jejuni from pure cultures and directly on stool samples. J. Med. Microbiol. 2005, 54, 1043–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi-Hachesoo, B.; Khoshbakht, R.; Sharifiyazdi, H.; Tabatabaei, M.; Hosseinzadeh, S.; Asasi, K. Tetracycline resistance genes in Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli isolated from poultry carcasses. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2014, 7, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacon, D.J.; Alm, R.; Burr, D.H.; Hu, L.; Kopecko, D.J.; Ewing, C.P.; Trust, T.J.; Guerry, P.; Barbieri, J.T. Involvement of a plasmid in virulence of Campylobacter jejuni 81–176. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 4384–4390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Michel, L.O.; Zhang, Q. CmeABC Functions as a Multidrug Efflux System in Campylobacter jejuni. Society 2002, 46, 2124–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M45-A2; Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI): Wayne, PL, USA, 2017.
- Meade, H.M.; Long, S.R.; Ruvkun, G.B.; Brown, S.E.; Ausubel, M. Physical and Genetic Characterization of Symbiotic and Auxotrophic Mutants of Rhizobium meliloti Induced by Transposon Tn5 Mutagenesis. J. Bacteriol. 1982, 149, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.; Checkley, S.; Caffrey, N.; Mainali, C.; Gow, S. Genetic Characterization of AmpC and Extended-Spectrum Beta- Lactamase Phenotypes in Escherichia coli and Salmonella From Alberta Broiler Chickens. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 622195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, W.; Adelumola, O.; Dinku, E.; Timothy, S.; Jodie, P.L.; Zaid, A. Virulence factors and antimicrobial resistance profiles of Campylobacter isolates recovered from consecutively reused broiler litter. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e03223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emberland, K.E.; Wensaas, K.A.; Litleskare, S.; Iversen, A.; Hanevik, K.; Langeland, N.; Rortveit, G. Clinical features of gastroenteritis during a large waterborne Campylobacter outbreak in Askøy, Norway. Infection 2022, 50, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolinger, H.; Kathariou, S. The Current State of Macrolide Resistance in Campylobacter spp.: Trends and Impacts of Resistance Mechanisms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e00416–e00417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, C.T.; Lynch, H.; Egan, J.; Whyte, P.; Bolton, D.; Coffey, A.; Lucey, B. Antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter isolates recovered from broilers in the Republic of Ireland in 2017 and 2018, an update. Br. Poult. Sci. 2020, 61, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasti, J.I.; Groß, U.; Pohl, S.; Lugert, R.; Weig, M.; Schmidt-Ott, R. Role of the plasmid-encoded tet(O) gene in tetracycline-resistant clinical isolates of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. J. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 56, 833–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, A.; Korolik, V. Tetracycline resistance of Australian Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli isolates. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2005, 55, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilhao, R.; Papadopoulou, B.; Courvalin, P. Occurrence of the Campylobacter resistance gene tetO in Enterococcus and Streptococcus spp. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1988, 32, 1793–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nirdnoy, W.; Mason, C.J.; Guerry, P. Mosaic structure of a multiple-drug-resistant, conjugative plasmid from Campylobacter jejuni. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 2454–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marasini, D.; Karki, A.B.; Bryant, J.M.; Sheaff, R.J.; Fakhr, M.K. Molecular characterization of megaplasmids encoding the type VI secretion system in Campylobacter jejuni isolated from chicken livers and gizzards. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.; Sahin, O.; Lin, J.; Zhang, Q. Role of the CmeABC efflux pump in the emergence of fluoroquinolone-resistant Campylobacter under selection pressure. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 58, 1154–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, B.; Mcdermott, P.F.; White, D.G.; Meng, J. Role of Efflux Pumps and Topoisomerase Mutations in Fluoroquinolone Resistance in Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 3347–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksomaitiene, J.; Ramonaite, S.; Olsen, J.E.; Malakauskas, M. Prevalence of Genetic Determinants and Phenotypic Resistance to Ciprofloxacin in Campylobacter jejuni from Lithuania. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanen, A.; Jalava, J.; Kotilainen, P.; Jousimies-somer, H.; Siitonen, A.; Huovinen, P. gyrA Polymorphism in Campylobacter jejuni: Detection of gyrA Mutations in 162 C. jejuni Isolates by Single-Strand Conformation Polymorphism and DNA Sequencing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 2644–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Millan, A.; Maclean, R.C. Fitness Costs of Plasmids: A Limit to Plasmid Transmission. Microbiol. Spectr. 2017, 5, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).