Abstract
Background: Salmonella enterica and Escherichia coli are common foodborne pathogens of global concern, particularly due to their antimicrobial resistance, notably to cephalosporins. Objective: This study aimed to evaluate a polymerase chain reaction-based lateral flow strip (PCR-LFS) assay for the detection of Salmonella spp. and E. coli harboring the blaCTX-M gene, which confers resistance to third-generation cephalosporins. Methods: Two duplex PCRs (dPCR) were established to detect E. coli-harboring blaCTX-M (set 1) and Salmonella-harboring blaCTX-M (set 2). 600 bacterial isolates and raw pork mince spiked with blaCTX-M-harboring E. coli and Salmonella were used to evaluated. Results: Both dPCR assays successfully detected blaCTX-M-positive E. coli or Salmonella strains, while strains lacking the gene showed no amplification. Non-E. coli and non-Salmonella strains were PCR-negative unless they carried blaCTX-M. The dPCR-LFS showed 100% validity including accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value for both E. coli or Salmonella spp. harboring or lacking blaCTX-M. The assay accurately detected target strains without cross-reactivity with other bacteria or antimicrobial resistance genes. Cohen’s Kappa coefficient indicated perfect agreement (κ = 1), reflecting the high reliability of the dPCR-LFS. The assay could detect as low as 25 CFU/mL for blaCTX-M-positive E. coli and 40 CFU/mL for blaCTX-M-positive Salmonella in spiked raw pork mince. Conclusions: This assay is rapid, easy to interpret, and suitable for large-scale screening in surveillance programs.
1. Introduction
Foodborne pathogens in contaminated food are a significant concern in food safety and require close monitoring. These pathogens include viruses, bacteria, fungi, and protozoa [1]. Generally, infection occurs through the consumption of food or water contaminated with foodborne pathogens or their toxins. Detection and control of foodborne pathogens are prerequisites for protecting human and animal health and maintaining international trade. Rapid detection of foodborne pathogens is key to effective surveillance systems, ensuring a safe food supply, and preventing foodborne diseases [2,3,4].
Among these foodborne pathogens, Salmonella enterica and Escherichia coli have been implicated in numerous foodborne diseases associated with the consumption of contaminated food and water [1]. These bacterial pathogens are critical targets for the monitoring and surveillance of both phenotypic and genotypic antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in food-producing animals, fresh and processed meat, vegetables, and drinking water. Additionally, Salmonella, E. coli, Campylobacter spp., and Enterococcus spp. are recommended as indicators for AMR surveillance in human and non-human sectors (i.e., food supply chains, animals, and the environment) [5,6,7].
The emergence of extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)-producing bacteria has conferred resistance to penicillin and third- and fourth-generation cephalosporins, which are critically important antibiotics in both human and veterinary medicine [8]. These pathogens are recognized by the World Health Organization (WHO) as among the most challenging to treat [9]. Infections caused by ESBL-producing bacteria in humans and animals have been widely reported, with documented transmission routes including food, water, and contact with contaminated environments [10]. Thus, monitoring ESBL-producing Salmonella spp. and E. coli is essential for public health.
ESBL has been classified into three main groups, including Ambler class A ESBL, miscellaneous ESBL, and ESBL that degrade carbapenems [11]. Most ESBLs belong to Ambler class A, which includes sulfhydryl reagent variable (SHV), Temoniera (TEM), and cefotaxime-M (CTX-M) types [11]. Among these, CTX-M-type ESBLs are the most widely distributed globally [12,13,14]. CTX-M type-ESBLs have increased in prevalence since 2000, and this is an important mechanism for developing resistance to cephalosporins, posing a major difficulty in clinical treatment, with restricted options to treat infections caused by CTX-M-producing bacteria [12,14]. This trend has led to increased reliance on carbapenems [12]. CTX-M-producing bacteria are now frequently detected in Europe, Asia, and the Americas [14]. Over 80 CTX-M variants have been reported across hospitals, communities, food animals, fresh produce, water, and the environment [15].
Routine screening and rapid detection of ESBL-producing bacteria in clinical laboratory settings are critical for infection control and therapeutic decision-making. The Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) recommends a two-step approach for ESBL detection [16]. Initial screening methods include the Kirby–Bauer disk diffusion test and automated systems such as Vitek. Confirmatory tests involve the double-disk synergy test (DDST), combination disk methods, or E-test ESBL strips. In addition to phenotypic confirmatory methods, genotypic assays such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and nucleotide sequencing are employed to detect specific ESBL-encoding genes and their variants [11]. Other molecular methods include isoelectric point determination, DNA probes, oligotyping, PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP), PCR-single-strand conformational polymorphism (PCR-SSCP), real-time PCR, matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization–time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF), and the NG-Test CTX-M MULTI, a rapid immunochromatographic lateral flow strip assay (LFS) [11].
Among these techniques, nucleic acid amplification followed by LFS, such as PCR-LFS and recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA)-LFS, is simple and widely applied for detecting various pathogens and antimicrobial resistance genes [17,18,19,20,21,22]. LFS is a paper-based device that uses colloidal gold nanoparticles as signal labels [23]. Combining PCR or RPA with LFS improves laboratory efficiency and enables rapid visualization of target genes, eliminating the need for gel electrophoresis and staining, thereby reducing detection time and processing complexity. The principles of PCR-LFS or RPA-LFS involve labeling the 5′ end of the forward primer with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) and the 5′ end of the reverse primer with biotin or digoxigenin, followed by amplification using PCR or RPA [21,24]. The labeled amplicons bind to specific antibodies on the test line of the colloidal gold strip, producing a visual colorimetric signal interpretable by the naked eye.
Salmonella spp. and E. coli are important indicator organisms for pathogen and AMR surveillance, particularly in relation to cephalosporin nonsusceptibility due to blaCTX-M. Although many PCR assays have been developed to detect Salmonella spp. and E. coli harboring antimicrobial resistance genes such as blaCTX-M [25,26], neither PCR-LFS nor RPA-LFS currently allow simultaneous detection of both bacterial species and resistance genes in a single assay [18,27,28,29]. In this study, we evaluated a polymerase chain reaction-based lateral flow strip (PCR-LFS) assay for detecting Salmonella spp. and E. coli harboring blaCTX-M, aimed at infection control and surveillance in environmental, livestock, food, or feed contamination, particularly in resource-limited laboratories. This assay is rapid, easy to perform and interpret, and suitable for high-throughput screening in AMR surveillance programs.
2. Results
Two duplex PCR (dPCR) assays were established to detect E. coli harboring blaCTX-M (set 1) and Salmonella harboring blaCTX-M (set 2). Both assays successfully detected blaCTX-M-positive E. coli and Salmonella strains, while E. coli and Salmonella strains lacking blaCTX-M showed no blaCTX-M amplification, and the negative control (Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC13883) did not show any bands (Figure 1 and Figure 2). Non-E. coli and non-Salmonella strains tested negative in the dPCR assays unless they carried blaCTX-M, in which case only the blaCTX-M band was detected. For bacterial species other than E. coli, Salmonella, or Enterobacterales that do not harbor blaCTX-M, the PCR-LFS produced negative results for both target bands, while the internal strip-control band remained positive. These results confirm the high specificity of the duplex PCR-LFS for E. coli and Salmonella.
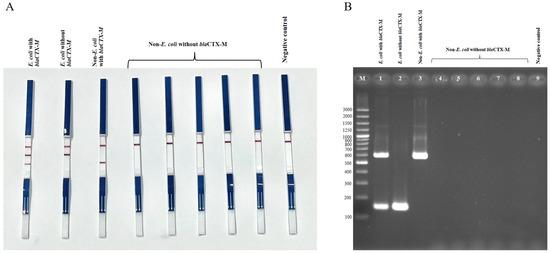
Figure 1.
Duplex PCR-LFS (A) and duplex PCR–gel electrophoresis (B) detection of E. coli with and without blaCTX-M, and non-E. coli with and without blaCTX-M. (A) Top line = control line; middle line = E. coli; bottom line = blaCTX-M. E. coli carrying blaCTX-M shows two bands (species-specific and blaCTX-M) (first strip from left). E. coli lacking blaCTX-M shows only the E. coli line (second strip). Non-E. coli strains carrying blaCTX-M show only the blaCTX-M line (third strip). Non-E. coli strains without blaCTX-M show no target lines (strips 4–8). Negative control = Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 13883. (B) Lane M = 100 bp DNA ladder; Lane 1 = E. coli with blaCTX-M; Lane 2 = E. coli without blaCTX-M; Lane 3 = non-E. coli with blaCTX-M; Lanes 4–8 = non-E. coli without blaCTX-M; Lane 9 = negative control (Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 13883).
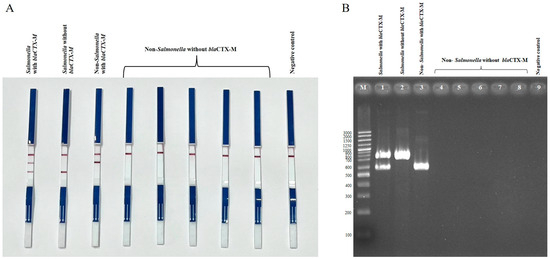
Figure 2.
Duplex PCR-LFS (A) and duplex PCR-gel electrophoresis; (B) detection of Salmonella spp. with and without blaCTX-M, and non-Salmonella spp. with and without blaCTX-M. (A) Top line = control line; middle line = blaCTX-M; bottom line = Salmonella. Salmonella carrying blaCTX-M shows two lines (first strip). Salmonella without blaCTX-M shows only the species-specific line (second strip). Non-Salmonella carrying blaCTX-M shows the blaCTX-M line (third strip). Non-Salmonella without blaCTX-M shows no target lines (strips 4–8). Negative control = Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 13883. (B) Lane M = 100 bp DNA ladder; Lane 1 = Salmonella with blaCTX-M; Lane 2 = Salmonella without blaCTX-M; Lane 3 = non-Salmonella with blaCTX-M; Lanes 4–8 = non-Salmonella without blaCTX-M; Lane 9 = negative control (Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 13883).
The PCR-LFS assay was evaluated using 200 E. coli isolates and 30 Salmonella isolates harboring blaCTX-M (Table 1). All isolates showed positive results for both the species-specific and blaCTX-M bands. E. coli and Salmonella strains carrying other antimicrobial resistance genes (but not blaCTX-M) showed amplification of only the species-specific band. In contrast, blaCTX-M-harboring strains of other species (e.g., Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter cloacae, Citrobacter freundii) showed positive results only for the blaCTX-M band. Sanger sequencing of representative amplicons confirmed the identities of E. coli, Salmonella, and blaCTX-M. Non-Enterobacterales species tested negative for all targets, indicating no cross-reactivity.

Table 1.
Evaluation of dPCR-LFS for detection of blaCTX-M in E. coli, Salmonella, and other Enterobacterales.
As shown in Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4, the dPCR-LFS assay demonstrated 100% validity, including accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value, for both E. coli and Salmonella strains harboring or lacking blaCTX-M. The assay accurately detected the target species without cross-reactivity with non-target bacteria or other antimicrobial resistance genes. Cohen’s kappa coefficient indicated perfect agreement (κ = 1), confirming the high reliability of the dPCR-LFS. Statistical analysis revealed a significant association (p < 0.01) for true positives. The coefficient of determination (R2) was 0.92952 for simultaneous detection of E. coli and Salmonella with blaCTX-M, and 0.96621 and 0.96642 for detecting either target species or blaCTX-M alone, respectively. A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve confirmed that the assay’s sensitivity and specificity were consistent with theoretical expectations (Figure 3).

Table 2.
Diagnostic performance of dPCR-LFS in detecting E. coli and Salmonella harboring blaCTX-M.

Table 3.
Diagnostic performance of dPCR-LFS in detecting E. coli and Salmonella lacking blaCTX-M.

Table 4.
Diagnostic performance of dPCR-LFS for detection of blaCTX-M among Enterobacterales.
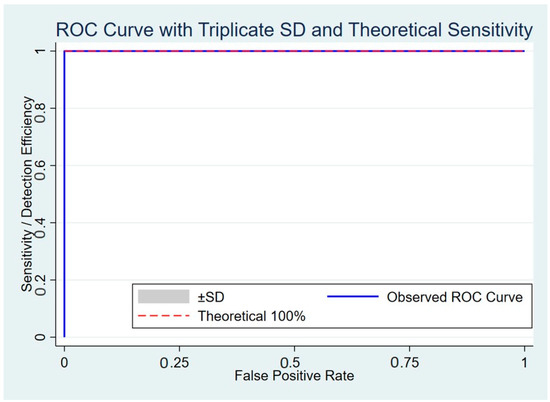
Figure 3.
ROC curve showing triplicate standard deviation and theoretical sensitivity of duplex PCR-LFS detecting E. coli and Salmonella carrying blaCTX-M.
The limit of detection of the duplex PCR-LFS assay was 72 fg and 105 fg of genomic DNA for E. coli and Salmonella, respectively. In the case of blaCTX-M detection, the assay identified as little as 7.2 pg for E. coli carrying blaCTX-M and 105 fg for Salmonella carrying blaCTX-M. When tested in artificially spiked raw pork mince, the assay could detect as low as 25 CFU/mL for blaCTX-M-positive E. coli and 40 CFU/mL for blaCTX-M-positive Salmonella (Figure 4). However, the signal at these lowest concentrations was noticeably weaker compared to 102 CFU/mL. In contrast, dPCR–gel electrophoresis had a detection limit of 103 CFU/mL for both targets. The duplex PCR-LFS assay was more time-efficient than PCR followed by gel electrophoresis. Excluding DNA extraction, the cost per sample for dPCR-LFS was approximately USD 2.25–2.45 per set. The total running time for dPCR-LFS was approximately 60–70 min.
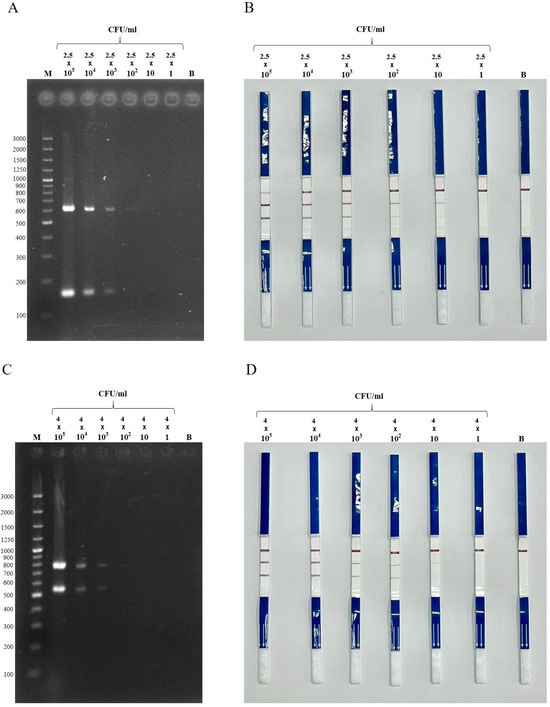
Figure 4.
Detection limit of duplex PCR–gel electrophoresis (A,C) and duplex PCR-LFS (B,D) detecting E. coli (A,B) and Salmonella spp. (C,D) harboring blaCTX-M, spiked in raw pork mince. Dilutions: 2.5 × 105 to 2.5 CFU/mL for E. coli, and 4 × 105 to 4 CFU/mL for Salmonella. M = 100 bp DNA ladder; B = blank control (uninoculated).
3. Discussion
In 2017, the WHO released guidance on the integrated surveillance of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in foodborne bacteria, recommending a One Health approach and suggesting the monitoring of Salmonella, Campylobacter spp., E. coli, and Enterococcus spp. as priority organisms [6]. Similarly, in 2019, the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) designated the same bacterial species as targets for AMR surveillance [5]. In 2021, the WHO introduced the Tricycle Surveillance Program, which emphasizes the monitoring of ESBL-producing E. coli across human, food supply chain, and environmental sectors [7]. These organisms serve as key indicators in global AMR surveillance systems.
Rapid diagnostic methods are critical to reducing the spread of antimicrobial-resistant bacteria, enabling timely isolation and appropriate treatment. A variety of rapid detection technologies have been developed, including nucleic acid amplification (NAA) techniques, immunochromatographic tests, electrochemical assays, microarrays, nanoparticle-based systems, and mass spectrometry [30,31,32,33]. Among these, NAA-based methods such as PCR, real-time PCR, loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP), and recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) are particularly favored. These have been applied for the detection of Salmonella spp., E. coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and other Enterobacterales harboring blaCTX-M or other antimicrobial resistance genes [18,34,35,36,37].
In this study, two sets of duplex PCR-based lateral flow strip (dPCR-LFS) assays were evaluated to detect E. coli, Salmonella, and blaCTX-M for use in surveillance of foods, the environment, livestock, and hospital infection control purposes. The method is rapid and user-friendly, with results easily interpreted without the need for gel electrophoresis or specialized visualization instruments. These characteristics make it suitable for application in both human and non-human sectors, especially in the food safety program part of surveillance.
NAA-based lateral flow assays (NAA-LFS) have been developed for detecting various pathogens, including Vibrio parahaemolyticus, E. coli, Salmonella, Bacillus anthracis, Yersinia pestis, Listeria monocytogenes, Staphylococcus aureus, and coliforms [20,38,39,40,41,42,43,44]. For example, mPCR-LFS assays have enabled the simultaneous detection of E. coli O157:H7 and S. Typhimurium [45]. PCR-LFS has also been applied for detecting E. coli, coliform bacteria, and total bacterial load [42]. A lateral flow biosensor based on LAMP-CRISPR/Cas12a has been developed for Salmonella detection in food samples [46]. However, few NAA-LFS assays enable simultaneous detection of both bacterial species and resistance genes, as demonstrated in this study. For example, RPA-LFS assays have detected antimicrobial resistance genes such as blaCTX-M, blaSHV, blaOXA, blaKPC, blaNDM, mcr-1, and tet(X4), but without identifying the bacterial species carrying them [18,37,47,48]. One prior study used mPCR-LFS to detect blaKPC and blaNDM in Enterobacterales [49].
A comparison of detection limits between dPCR-LFS and dPCR–gel electrophoresis, using raw pork mince spiked with E. coli and S. enterica harboring blaCTX-M, showed that dPCR-LFS had a lower detection limit. Our dPCR-LFS assay detected bacterial concentrations as low as 25–40 CFU/mL, consistent with previous findings demonstrating low detection limits for NAA-LFS in food matrices [45,50,51,52]. For instance, a previous study reported that mPCR-LFS detected E. coli O157:H7 and S. Typhimurium in spiked cabbage at limits of 104 CFU/25 g and 103 CFU/25 g, respectively [45]. Zeng et al. (2020) reported a detection limit of 50 CFU/mL for Vibrio parahaemolyticus using PCR-LFS [52]. Another study detected methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus at 200 CFU/100 g of pork products using PCR-LFS [53]. Wang et al. (2020) showed that RPA-LFS detected as low as 1 CFU of Listeria monocytogenes per reaction without DNA purification [51]. LAMP-LFS has also been used to detect Salmonella in milk, pork, beef, and chicken samples at 144 CFU/g or mL, without an enrichment step [50]. These findings collectively demonstrate that NAA-LFS assays, including PCR-LFS, offer highly sensitive detection of target organisms. However, a unique advantage of our PCR-LFS is its ability to detect both the bacterial species (E. coli or Salmonella spp.) and the antimicrobial resistance gene blaCTX-M in a single reaction.
Our current study demonstrated high validity of the dPCR-LFS assay in terms of accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value when tested with pure bacterial cultures. Although the assay shows promise for direct application to clinical or environmental samples, further validation using reference methods is necessary. One limitation of the current dPCR-LFS is its ability to detect only two targets per reaction, due to constraints in the availability of label molecules such as biotin and digoxigenin. A triplex format that includes E. coli-specific, Salmonella-specific, and blaCTX-M targets with distinct labels would improve efficiency and reduce cost. Therefore, future development is warranted. Moreover, while the assay was validated using pure isolates, its application to direct specimens remains a key challenge for further research.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacteria
E. coli and Salmonella strains harboring blaCTX-M, as well as other Enterobacterales species, are listed in Table 1. The 287 E. coli strains were isolated from humans (n = 162), ready-to-eat foods (n = 50), meats (n = 40), and environmental water (n = 35). A total of 95 Salmonella strains were isolated from humans (n = 50), ready-to-eat foods (n = 15), and meats (n = 30). Other Enterobacterales species (Table 1) were isolated from humans (n = 118) and environmental sources (n = 100). In addition, various non-Enterobacterales species were included to evaluate potential nonspecific reactions. These strains included: Streptococcus pneumoniae ATCC33400, S. anginosus ATCC33397, S. pyogenes SF370, S. agalactiae ATCC 13813, Enterococcus faecalis ATCC29212, E. faecium ATCC10541, Lactiplantibacillus plantarum ATCC 43199, Leuconostoc lactis ATCC19256, Micrococcus luteus ATCC10240, Bacillus subtilis ATCC6633, Staphylococcus aureus ATCC700698, Haemophilus influenzae ATCC10211, Achromobacter xylosoxidans ATCC27061, Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC9027, Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 19606, Burkholderia cepacia LMG0122, Vibrio parahaemolyticus ATCC17802, Aeromonas hydrophila ATCC7966, and Neisseria flavescens ATCC13119. All bacterial strains were kept at −80 °C before used in this study.
4.2. DNA Extraction
DNA was extracted from cultured bacterial colonies using a simple alkaline lysis method [54]. Briefly, one or two colonies (incubated for 18–24 h) were suspended in 20 µL of lysis buffer containing 0.25% (v/v) sodium dodecyl sulfate and 0.05 M NaOH, then heated at 95 °C for 15 min. After lysis, samples were briefly centrifuged, and 180 µL of sterile deionized water was added. The crude DNA supernatant was stored at −20 °C and used as the template for PCR.
4.3. PCR Reaction
The PCR reaction mixture consisted of 1× PCRBIO HS Taq Mix Red (PCR Biosystems, London, UK) and 0.4 µM of each primer (Table 5). The thermal cycling conditions were as follows: initial denaturation at 95 °C for 2 min; 35 cycles of denaturation at 95 °C for 30 s; annealing at 58 °C for 30 s; and extension at 72 °C for 45 s. E. coli ATCC BAA-3303 (carrying blaCTX-M-15) and S. enterica strain SW060-1 (carrying blaCTX-M) were used as positive controls. Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 13883 was used as the negative control. PCR products were analyzed by 2% agarose gel electrophoresis (Mupid-ExU, Takara, Japan) in 0.5× TBE buffer for 30 min. Gels were stained with ethidium bromide and visualized under UV light (GeneGenius Bioimaging System; SynGene, Cambridge, UK). PCR product sizes were determined using a 100 bp Plus DNA ladder (GeneRuler™, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).

Table 5.
Primer used in this study.
4.4. Lateral-Flow Strip (LFS)
LFS devices and reagents (K-AmpDetect 2T) were purchased from K.Bio Sciences (Bangkok, Thailand). Each strip had three lines (C, T1, and T2), with T1 and T2 lines immobilized with anti-biotin and anti-digoxigenin, respectively. The LFS reaction was done according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Briefly, strips were immersed in the PCR product for 10–20 s, after which 100 µL (or three drops) of DNA running buffer was added to the application pad. Results were observed within 2–10 min. The presence of both test lines (T1, T2, or both) and the control line (C) indicated a positive result. The appearance of only the control line indicated a negative result.
4.5. Confirmation of PCR Products by DNA Sequencing
To confirm the dPCR-LFS results, PCR products from strains testing positive for E. coli, Salmonella, or blaCTX-M were subjected to Sanger DNA sequencing using the respective forward and reverse primers without labelling molecules (Table 5). Sequences were analyzed using BLASTN (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi; accessed on 5 June 2025).
4.6. Detection Limit
The detection limit of the duplex PCR was evaluated using blaCTX-M-harboring E. coli and Salmonella strains. Serial 10-fold dilutions were prepared from an initial DNA concentration of 72 ng/µL for E. coli and 105 ng/µL for Salmonella, based on OD260 readings. The detection limit was defined as the highest dilution at which a positive result was observed. Each test was performed in triplicate.
4.7. Artificially Spiked Raw Pork Mince Sample
Raw pork mince confirmed to be free of blaCTX-M-harboring E. coli and Salmonella by conventional culture and PCR methods was used for spiking experiments. Pure colonies of E. coli ATCC BAA-3303 and S. enterica strain SW060-1 were suspended in 1 mL of sterile saline, vortexed for 30 s, and adjusted to a turbidity of 1.00 using a turbidimeter. Serial 10-fold dilutions were prepared. Then, 10 g of pork mince was mixed with 99 mL of buffered peptone water (BPW; Oxoid, Basingstoke, UK) and inoculated with 1 mL of the appropriate dilution. One uninoculated sample served as a negative control. After inoculation, samples were stomached for 1 min. One milliliter of the homogenate was subjected to DNA extraction using ZymoBIOMICS DNA Kits (Zymo Research, Tustin, CA, USA) following the manufacturer’s instructions. Each dilution was tested in duplicate. Colony-forming units (CFU) were determined by plating on MacConkey agar for E. coli and XLD agar for Salmonella (Oxoid, Basingstoke, UK).
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Diagnostic performance measures—including sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy—were calculated [58]. The kappa statistic was used to evaluate interrater agreement [59]. Fisher’s exact test (p < 0.01 considered significant) was performed using GraphPad tools (https://www.graphpad.com/quickcalcs/, accessed on 5 June 2025) [60,61]. McFadden’s R2 was used to estimate model fit [62]. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was performed using a 2 × 2 contingency table comparing PCR results with genotypic/phenotypic data [63]. Sensitivity and 1 − specificity were plotted to generate the ROC curve. All measurements were done in triplicate. A fixed SD of 0.02 was applied to illustrate variability, similar to approaches used in simulations or illustrative ROC analyses. A dotted reference line indicating ideal performance (100% sensitivity and specificity) was added as a benchmark. All analyses and visualizations were performed using Stata version 17.0.
4.9. Data Availability
Nucleotide sequence of blaCTX-M is available in the GenBank databases under the accession numbers PV809620-PV809640.
5. Conclusions
The dPCR-LFS assay in this study demonstrated high diagnostic performance for detecting E. coli and Salmonella strains harboring blaCTX-M from pure cultures. However, its application to direct specimens requires further validation. This method is rapid and user-friendly, offering simple interpretation without the need for gel electrophoresis. It holds significant potential for application in AMR surveillance across both human and non-human sectors.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.H., P.C., P.B. and A.K.; methodology, R.H., R.U., K.S., P.C., P.B. and S.C.; validation, R.H., P.C., P.B. and A.K.; formal analysis, R.H., R.U., P.B., P.C. and K.S.; investigation, R.H., S.C., P.C. and P.B.; resources, A.K.; writing—original draft preparation, R.H. and A.K.; writing—review and editing, R.H. and A.K.; visualization, R.H.; supervision, A.K.; funding acquisition, A.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by Kasetsart University Research and Development Institute (KURDI) under Grant No. FF(KU-SRIU)16.67.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable because this study did not involve humans or animals.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Bintsis, T. Foodborne pathogens. AIMS Microbiol. 2017, 3, 529–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, J.W.; Ab Mutalib, N.S.; Chan, K.G.; Lee, L.H. Rapid methods for the detection of foodborne bacterial pathogens: Principles, applications, advantages and limitations. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 5, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangal, M.; Bansal, S.; Sharma, S.K.; Gupta, R.K. Molecular detection of foodborne pathogens: A rapid and accurate answer to food safety. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 1568–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umesha, S.; Manukumar, H.M. Advanced molecular diagnostic techniques for detection of food-borne pathogens: Current applications and future challenges. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 84–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization. Monitoring and surveillance of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria from healthy food animals intended for consumption. In Regional Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring and Surveillance Guidelines—Volume 1; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Integrated Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance in Foodborne Bacteria: Application of a One Health Approach; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. WHO Integrated Global Surveillance on ESBL-Producing E. coli Using a “One Health” Approach: Implementation and Opportunities; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Paterson, D.L.; Bonomo, R.A. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases: A clinical update. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 18, 657–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talebi Bezmin Abadi, A.; Rizvanov, A.A.; Haertlé, T.; Blatt, N.L. World health organization report: Current crisis of antibiotic resistance. BioNanoSci 2019, 9, 778–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saechue, B.; Atwill, E.R.; Jeamsripong, S. Occurrence and molecular characteristics of antimicrobial resistance, virulence factors, and extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL) producing Salmonella enterica and Escherichia coli isolated from the retail produce commodities in Bangkok, Thailand. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husna, A.; Rahman, M.M.; Badruzzaman, A.T.M.; Sikder, M.H.; Islam, M.R.; Rahman, M.T.; Alam, J.; Ashour, H.M. Extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBL): Challenges and opportunities. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevan, E.R.; Jones, A.M.; Hawkey, P.M. Global epidemiology of CTX-M β-lactamases: Temporal and geographical shifts in genotype. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 2145–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossolini, G.M.; D’Andrea, M.M.; Mugnaioli, C. The spread of CTX-M-type extended-spectrum beta-lactamases. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2008, 14, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Huang, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Gao, H.; Bai, X.; Wang, D. Global spread characteristics of CTX-M-type extended-spectrum β-lactamases: A genomic epidemiology analysis. Drug Resist. Updat. 2024, 73, 101036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amelia, A.; Nugroho, A.; Harijanto, P.N. Diagnosis and management of infections caused by Enterobacteriaceae producing extended-spectrum β -lactamase. Acta Med. Indones. 2016, 48, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- CLSI M100; Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2012.
- Hemwaranon, P.; Srisrattakarn, A.; Lulitanond, A.; Tippayawat, P.; Tavichakorntrakool, R.; Wonglakorn, L.; Daduang, J.; Chanawong, A. Recombinase polymerase amplification combined with lateral flow strip for rapid detection of OXA-48-like carbapenemase genes in Enterobacterales. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanokudom, S.; Assawakongkarat, T.; Akeda, Y.; Ratthawongjirakul, P.; Chuanchuen, R.; Chaichanawongsaroj, N. Rapid detection of extended spectrum β-lactamase producing Escherichia coli isolated from fresh pork meat and pig cecum samples using multiplex recombinase polymerase amplification and lateral flow strip analysis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najomtien, P.; Phoksawat, W.; Khammanthoon, S.; Klasuk, W.; Srisurat, N.; Chattagul, S.; Photisap, C.; Pipattanaboon, C.; Sermswan, R.W.; Wongratanacheewin, S. PCR combined with lateral flow dipstick assay (PCR-LFD) for a rapid diagnosis of melioidosis. Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol 2024. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saetang, J.; Sukkapat, P.; Palamae, S.; Singh, P.; Senathipathi, D.N.; Buatong, J.; Benjakul, S. Multiplex PCR-lateral flow dipstick method for detection of thermostable direct hemolysin (TDH) producing V. parahaemolyticus. Biosensors 2023, 13, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, A.; Fu, M.; Guo, J.; Wang, L.; Zuo, X.; Ma, F. Establishment and clinical application of a RPA-LFS assay for detection of capsulated and non-capsulated Haemophilus influenzae. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 878813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Sun, Y.; Wang, K.; Feng, N.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, M. Development of a PCR-based lateral flow strip assay for the simple, rapid, and accurate detection of pork in meat and meat products. Food Chem. 2020, 318, 126541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Xu, X.; Guo, L.; Xu, L.; Sun, M.; Hu, S.; Kuang, H.; Xu, C.; Li, A. An overview for the nanoparticles-based quantitative lateral flow assay. Small Methods 2022, 6, e2101143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nihonyanagi, S.; Kanoh, Y.; Okada, K.; Uozumi, T.; Kazuyama, Y.; Yamaguchi, T.; Nakazaki, N.; Sakurai, K.; Hirata, Y.; Munekata, S.; et al. Clinical usefulness of multiplex PCR lateral flow in MRSA detection: A novel, rapid genetic testing method. Inflammation 2012, 35, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalzampuia, H.; Dutta, T.K.; Warjri, I.; Chandra, R. PCR-based detection of extended-spectrum β-lactamases (bla CTX-M-1 and bla TEM) in Escherichia coli, Salmonella spp. and Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from pigs in North Eastern India (Mizoram). Indian J. Microbiol. 2013, 53, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wittum, T.E.; Mollenkopf, D.F.; Erdman, M.M. Detection of Salmonella enterica isolates producing CTX-M Cephalosporinase in U.S. livestock populations. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 7487–7491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Z.; Liu, W.; Jin, J.; Hao, Y.; Jiang, L.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, H. Development of a recombinase polymerase amplification assay with lateral flow dipstick (RPA-LFD) for rapid detection of Shigella spp. and enteroinvasive Escherichia coli. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0278869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutal, H.; Vogel, A.; Bernabeu, S.; Devilliers, K.; Creton, E.; Cotellon, G.; Plaisance, M.; Oueslati, S.; Dortet, L.; Jousset, A.; et al. A multiplex lateral flow immunoassay for the rapid identification of NDM-, KPC-, IMP- and VIM-type and OXA-48-like carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Ma, B.; Fang, J.; Zhi, A.; Chen, E.; Xu, Y.; Yu, X.; Sun, C.; Zhang, M. Recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) combined with lateral flow immunoassay for rapid detection of Salmonella in food. Foods 2019, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjum, M.F.; Zankari, E.; Hasman, H. Molecular methods for detection of antimicrobial resistance. Microbiol. Spectr. 2017, 5, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guliy, O.I.; Evstigneeva, S.S.; Karavaeva, O.A. Antimicrobial resistance and current methods for its detection. Front. Biosci. (Elite Ed). 2023, 15, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, J.H.; Ferraro, M.J. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing: A review of general principles and contemporary practices. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 49, 1749–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasala, A.; Hytönen, V.P.; Laitinen, O.H. Modern tools for rapid diagnostics of antimicrobial resistance. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallenne, C.; Da Costa, A.; Decré, D.; Favier, C.; Arlet, G. Development of a set of multiplex PCR assays for the detection of genes encoding important beta-lactamases in Enterobacteriaceae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monstein, H.J.; Ostholm-Balkhed, A.; Nilsson, M.V.; Nilsson, M.; Dornbusch, K.; Nilsson, L.E. Multiplex PCR amplification assay for the detection of blaSHV, blaTEM and blaCTX-M genes in Enterobacteriaceae. APMIS 2007, 115, 1400–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roschanski, N.; Fischer, J.; Guerra, B.; Roesler, U. Development of a multiplex real-time PCR for the rapid detection of the predominant beta-lactamase genes CTX-M, SHV, TEM and CIT-type AmpCs in Enterobacteriaceae. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, N.; Assawakongkarat, T.; Akeda, Y.; Chaichanawongsaroj, N. Detection of extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli isolates by isothermal amplification and association of their virulence genes and phylogroups with extraintestinal infection. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 12022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amalina, Z.N.; Khalid, M.F.; Rahman, S.F.; Ahmad, M.N.; Ahmad Najib, M.; Ismail, A.; Aziah, I. Nucleic acid-based lateral flow biosensor for Salmonella typhi and Salmonella paratyphi: A detection in stool samples of suspected carriers. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banger, S.; Pal, V.; Tripathi, N.K.; Goel, A.K. Development of a PCR lateral flow assay for rapid detection of Bacillus anthracis, the causative agent of anthrax. Mol. Biotechnol. 2021, 63, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Huang, R.; Sun, Y.; Wei, X.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, C.; Geng, Y.; Sun, X.; Jing, J.; Gao, H.; et al. Sensitive and rapid visual detection of Salmonella Typhimurium in milk based on recombinase polymerase amplification with lateral flow dipsticks. J. Microbiol. Methods 2019, 158, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, B.; Ma, B.; Li, J.; Hong, Y.; Zhang, M. Simultaneous detection of five foodborne pathogens using a mini automatic nucleic acid extractor combined with recombinase polymerase amplification and lateral flow immunoassay. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.M.; Park, J.S.; Yoon, T.H.; Park, J.; Park, K.S. Nucleic acid lateral flow assay for simultaneous detection of hygiene indicator bacteria. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 5003–5011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, K.; Kim, H.Y.; Oh, M.H.; Kim, Y.R. Paper-based lateral flow strip assay for the detection of foodborne pathogens: Principles, applications, technological challenges and opportunities. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Pal, V.; Kumar, M.; Tripathi, N.K.; Goel, A.K. Development of a PCR-lateral flow assay for rapid detection of Yersinia pestis, the causative agent of plague. Acta Trop. 2021, 220, 105958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Oh, S.W. A colorimetric lateral flow assay based on multiplex PCR for the rapid detection of viable Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella typhimurium without enrichment. LWT 2021, 152, 112242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Oh, S.W. Lateral flow biosensor based on LAMP-CRISPR/Cas12a for sensitive and visualized detection of Salmonella spp. Food Control. 2023, 145, 109494. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.; Wang, J.; Pan, L.; Gu, X.; Lu, W.; Chen, D.; Zhang, C.; Ye, Q.; Xiao, C.; Liu, P.; et al. Rapid detection of multiple resistance genes to last-resort antibiotics in Enterobacteriaceae pathogens by recombinase polymerase amplification combined with lateral flow dipstick. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1062577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.W.; Kim, H.; Hyeon, L.S.; Yoo, J.S.; Kang, S. Development of a recombinase polymerase amplification-coupled CRISPR/Cas12a platform for rapid detection of antimicrobial-resistant genes in carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales. Biosensors 2024, 14, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, W.; Xu, Y.; Liu, L.; Cao, H.; Yang, B.; Luo, J.; Fei, Y. Simultaneous and visual detection of KPC and NDM carbapenemase-encoding genes using asymmetric PCR and multiplex lateral flow strip. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2023, 2023, 9975620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, X.; Zhai, X.; Lei, C.; Ye, X.; Kang, Z.; Wu, X.; Xiang, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H. Development and application of a visual loop-mediated isothermal amplification combined with lateral flow dipstick (LAMP-LFD) method for rapid detection of Salmonella strains in food samples. Food Control 2019, 104, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, P.; Si, X.; Li, J.; Dai, X.; Zhang, K.; Gao, S.; Dong, J. Rapid and specific detection of Listeria monocytogenes with an isothermal amplification and lateral flow strip combined method that eliminates false-positive signals from primer-dimers. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.; Chen, S.; Jiang, L.; Ren, J.; Ling, N.; Su, J.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Xue, F.; Tang, F.; et al. A polymerase chain reaction based lateral flow test strip with propidium monoazide for detection of viable Vibrio parahaemolyticus in codfish. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ma, L.; Ma, L.; Hua, M.Z.; Wang, S.; Lu, X. Rapid detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in pork using a nucleic acid-based lateral flow immunoassay. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 243, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Coenye, T.; Burns, J.L.; Whitby, P.W.; Stull, T.L.; LiPuma, J.J. Ribosomal DNA-directed PCR for identification of Achromobacter (Alcaligenes) xylosoxidans recovered from sputum samples from cystic fibrosis patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 1210–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.L.; Palmer, C.J.; Sangermano, L.R. Detection of Escherichia coli in sewage and sludge by polymerase chain reaction. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhika, M.; Saugata, M.; Murali, H.S.; Batra, H.V. A novel multiplex PCR for the simultaneous detection of Salmonella enterica and Shigella species. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2014, 45, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelstein, M.; Pimkin, M.; Palagin, I.; Edelstein, I.; Stratchounski, L. Prevalence and molecular epidemiology of CTX-M extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae in Russian hospitals. Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother. 2003, 47, 3724–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimundić, A.M. Measures of diagnostic accuracy: Basic definitions. EJIFCC 2009, 19, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McHugh, M.L. Interrater reliability: The kappa statistic. Biochem. Med. 2012, 22, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodge, Y. Coefficient of Determination. In The Concise Encyclopedia of Statistics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, G.B. The coefficient of determination: Understanding r2 and R2. Math. Teach. 2000, 93, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFadden, D. Conditional logit analysis of qualitative choice behavior. In Frontiers in Econometrics; Zarembka, P., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1974; pp. 105–142. [Google Scholar]
- Zweig, M.H.; Campbell, G. Receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) plots: A fundamental evaluation tool in clinical medicine. Clin. Chem. 1993, 39, 561–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).