Effects of Antibiotic De-Escalation on Outcomes in Severe Community-Acquired Pneumonia: An Inverse Propensity Score-Weighted Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
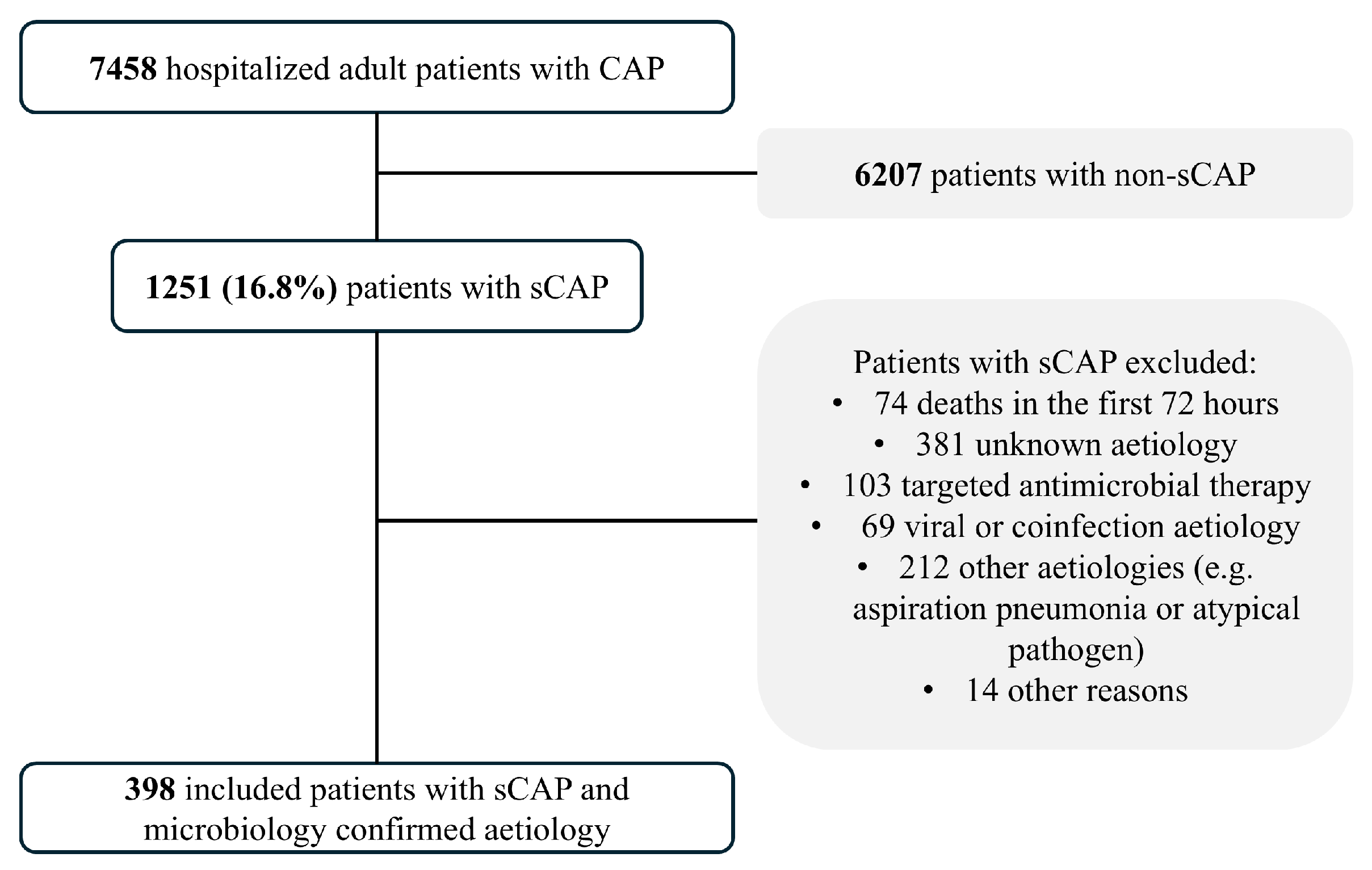
4.1. Study Population
4.2. Study Outcomes
4.3. Definitions
4.4. Microbiological Evaluation
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| aOR | Adjusted odds ratio |
| ATS | American Thoracic Society |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| ICU | Intensive care unit |
| IDSA | Infectious Diseases Society of America |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| IV | Intravenous |
| LOS | Length of hospital stay |
| sCAP | Severe community-acquired pneumonia |
References
- Niederman, M.S.; Torres, A. Severe community-acquired pneumonia. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2022, 31, 220123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Loeches, I.; Torres, A.; Nagavci, B.; Aliberti, S.; Antonelli, M.; Bassetti, M.; Bos, L.D.; Chalmers, J.D.; Derde, L.; de Waele, J.; et al. ERS/ESICM/ESCMID/ALAT guidelines for the management of severe community-acquired pneumonia. Intensive Care Med. 2023, 49, 615–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandell, L.A.; Wunderink, R.G.; Anzueto, A.; Bartlett, J.G.; Campbell, G.D.; Dean, N.C.; Dowell, S.F.; File, T.M., Jr.; Musher, D.M.; Niederman, M.S.; et al. Infectious Diseases Society of America; American Thoracic Society. Infectious Diseases Society of America/American Thoracic Society consensus guidelines on the management of community-acquired pneumonia in adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 44 (Suppl. 2), S27–S72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallazzi, R.; Furmanek, S.; Arnold, F.W.; Beavin, L.A.; Wunderink, R.G.; Niederman, M.S.; Ramirez, J.A. The Burden of Community-Acquired Pneumonia Requiring Admission to ICU in the United States. Chest 2020, 158, 1008–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, D.; Chiong, F.; Secombe, P.; Hnin, K.M.; Stewart, P.; Goud, R.; Woodman, R.; Lipman, J.; Roberts, J.; Hewagama, S. Epidemiology and microbiology of severe community-acquired pneumonia in Central Australia: A retrospective study. Intern. Med. J. 2022, 52, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viasus, D.; Vecino-Moreno, M.; De La Hoz, J.M.; Carratalà, J. Antibiotic stewardship in community-acquired pneumonia. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2017, 15, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, T.M.; Juang, P.; Weaver, K.; Kollef, M.H.; Betthauser, K.D. Outcomes of Macrolide Deescalation in Severe Community-acquired Pneumonia. Clin. Ther. 2019, 41, 2540–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez-Pizarraya, A.; Leone, M.; Garnacho-Montero, J.; Martin, C.; Martin-Loeches, I. Collaborative approach of individual participant data of prospective studies of de-escalation in non-immunosuppressed critically ill patients with sepsis. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 10, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, A.; Sibila, O.; Ferrer, M.; Polverino, E.; Menendez, R.; Mensa, J.; Gabarrús, A.; Sellarés, J.; Restrepo, M.I.; Anzueto, A.; et al. Effect of corticosteroids on treatment failure among hospitalized patients with severe community-acquired pneumonia and high inflammatory response: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2015, 313, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metlay, J.P.; Waterer, G.W.; Long, A.C.; Anzueto, A.; Brozek, J.; Crothers, K.; Cooley, L.A.; Dean, N.C.; Fine, M.J.; Flanders, S.A.; et al. Diagnosis and Treatment of Adults with Community-acquired Pneumonia. An Official Clinical Practice Guideline of the American Thoracic Society and Infectious Diseases Society of America. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, e45–e67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Restrepo, M.I.; Mortensen, E.M.; Waterer, G.W.; Wunderink, R.G.; Coalson, J.J.; Anzueto, A. Impact of macrolide therapy on mortality for patients with severe sepsis due to pneumonia. Eur. Respir. J. 2009, 33, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akinosoglou, K.; Leventogiannis, K.; Tasouli, E.; Kakavoulis, N.; Niotis, G.; Doulou, S.; Skorda, L.; Iliopoulou, K.; Papailiou, A.; Katsaounou, P.; et al. Clarithromycin for improved clinical outcomes in community-acquired pneumonia: A subgroup analysis of the ACCESS trial. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2025, 65, 107406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viasus, D.; Simonetti, A.F.; Garcia-Vidal, C.; Niubó, J.; Dorca, J.; Carratalà, J. Impact of antibiotic de-escalation on clinical outcomes in community-acquired pneumococcal pneumonia. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 547–5553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carugati, M.; Franzetti, F.; Wiemken, T.; Kelly, R.; Peyrani, P.; Blasi, F.; Ramirez, J.; Aliberti, S. De-escalation therapy among bacteraemic patients with community-acquired pneumonia. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 936.e11–936.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamana, H.; Matsui, H.; Tagami, T.; Hirashima, J.; Fushimi, K.; Yasunaga, H. De-escalation versus continuation of empirical antimicrobial therapy in community-acquired pneumonia. J. Infect. 2016, 73, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshpande, A.; Richter, S.S.; Haessler, S.; Lindenauer, P.K.; Yu, P.-C.; Zilberberg, M.D.; Imrey, P.B.; Higgins, T.; Rothberg, M.B. De-escalation of Empiric Antibiotics Following Negative Cultures in Hospitalized Patients with Pneumonia: Rates and Outcomes. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 72, 1314–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cawcutt, K.A.; Kalil, A.C. Is Antibiotic Deescalation Safe and Beneficial to Patients with Sepsis? Clin. Infect. Dis. 2025, 80, 118–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abelenda-Alonso, G.; Rombauts, A.; Gudiol, C.; García-Lerma, E.; Pallarés, N.; Ardanuy, C.; Calatayud, L.; Niubó, J.; Tebé, C.; Carratalà, J. Effect of positive microbiological testing on antibiotic de-escalation and outcomes in community-acquired pneumonia: A propensity score analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2022, 28, 1602–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Heijl, I.; Schweitzer, V.A.; Boel, C.H.E.; Oosterheert, J.J.; Huijts, S.M.; Dorigo-Zetsma, W.; van der Linden, P.D.; Bonten, M.J.M.; van Werkhoven, C.H.; Ehrman, R. Confounding by indication of the safety of de-escalation in community-acquired pneumonia: A simulation study embedded in a prospective cohort. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2008, 61, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halm, E.A.; Fine, M.J.; Marrie, T.J.; Coley, C.M.; Kapoor, W.N.; Obrosky, D.S.; Singer, D.E. Time to clinical stability in patients hospitalized with community-acquired pneumonia: Implications for practice guidelines. JAMA 1998, 279, 1452–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabor, E.C.; Assel, M. On the need for landmark analysis or time-dependent covariates. J. Urol. 2023, 209, 1060–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| All Patients | De-Escalation on Day 3 | De-Escalation on Day 6 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| De-Escalation Group | Non-De-Escalation Group | De-Escalation Group | Non-De-Escalation Group | ||
| (n = 398) | (n = 39) | (n = 359) | (n = 96) | (n = 302) | |
| Demographic data | |||||
| Age (years), median (IQR) | 66 (53–77) | 68 (55.5–77) | 66 (53–77) | 69 (55.5–77.5) | 65 (53–77) |
| Male sex | 255 (64.1) | 25 (64.1) | 230 (64.1) | 67 (69.8) | 188 (62.3) |
| Current/former smoker | 274 (68.8) | 30 (76.9) | 244 (68) | 73 (76) | 201 (66.6) |
| Pneumococcal vaccine within last 5 years | 59 (14.8) | 11 (31.4) | 48 (15.4) | 19 (22.1) | 40 (15.4) |
| Comorbid conditions | |||||
| Chronic pulmonary disease | 114 (28.6) | 12 (30.8) | 102 (28.4) | 31 (32.3) | 83 (27.5) |
| Chronic heart disease | 92 (23.1) | 9 (23.1) | 83 (23.19 | 27 (28.1) | 65 (21.5) |
| Diabetes mellitus | 91 (22.9) | 10 (25.6) | 81 (22.6) | 26 (27.1) | 65 (21.5) |
| Clinical features | |||||
| Hypothermia | 37 (9.3) | 4 (10.3) | 33 (9.2) | 12 (12.5) | 25 (8.3) |
| Tachycardia (≥100 beats/min) | 276 (69.3) | 24 (61.5) | 252 (72.8) | 67 (69.8) | 209 (72.3) |
| Tachypnea (≥24 breaths/min) | 288 (72.4) | 31 (79.5) | 257 (71.6) | 72 (75) | 216 (71.5) |
| Impaired consciousness | 132 (33.2) | 12 (30.8) | 120 (33.4) | 28 (29.2) | 104 (34.4) |
| Septic shock | 47 (11.8) | 3 (7.7) | 44 (12.3) | 11 (11.5) | 36 (11.9) |
| Empyema | 24 (6) | 0 (0) | 24 (6.7) | 1 (1) | 23 (7.6) * |
| Laboratory and radiographic findings | |||||
| Leukopenia | 54 (13.6) | 1 (2.6) | 53 (14.8) * | 13 (13.5) | 41 (13.6) |
| Respiratory failure (PaO2/FiO2 < 250) | 222 (55.8) | 25 (64.1) | 197 (54.9) | 51 (53.1) | 171 (56.6) |
| Multilobar pneumonia | 270 (67.8) | 26 (66.7) | 244 (68) | 59 (61.5) | 211 (69.9) |
| Bacteremia | 123 (30.9) | 6 (16.2) | 117 (34.8) * | 24 (26.4) | 99 (35.1) |
| Pneumococcal pneumonia | 328 (82.4) | 19 (48.7) | 309 (86.1) * | 64 (66.7) | 264 (87.4) * |
| Empiric antibiotic therapy | |||||
| Ceftriaxone | 307 (77.1) | 31 (79.5) | 276 (76.9) | 73 (76) | 234 (77.5) |
| Macrolides or quinolones | 250 (62.8) | 23 (59) | 227 (63.2) | 58 (60.4) | 192 (63.6) |
| Complications | |||||
| Mechanical ventilation | 103 (25.9) | 4 (10.3) | 99 (27.7) * | 11 (11.6) | 92 (30.5) * |
| ICU admission | 170 (42.7) | 9 (23.1) | 161 (44.8) * | 23 (24) | 147 (48.7) * |
| Time to clinical stability (days), median (IQR) | 6 (4–12) | 5.5 (3–9) | 6 (4–14) | 5 (3–8) | 7 (4–14.5) * |
| Clinical stability | 8 (25.8) | 49 (19.4) | 47 (60.3) | 74 (36.5) * | |
| De-Escalation on Day 3 | De-Escalation on Day 6 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Patients | De-Escalation Group | Non-De-Escalation Group | De-Escalation Group | Non-De-Escalation Group | |
| (n = 398) | (n = 39) | (n = 359) | (n = 96) | (n = 302) | |
| Primary outcome | |||||
| All-cause 30-day mortality | 49 (12.3) | 3 (7.7) | 46 (12.8) | 7 (7.3) | 42 (13.9) |
| Secondary outcomes | |||||
| LOS (days), median (IQR) | 11 (8–19) | 10 (5.5–13.5) | 12 (8–20) | 8 (5.5–13.5) | 13 (8–21) * |
| LOS above the median | 196 (49.2) | 17 (43.6) | 179 (50.6) | 31 (32.3) | 165 (55.6) * |
| IV antibiotic therapy (days), median (IQR) | 7 (4–11) | 3 (2–5) | 7 (5–13) * | 4 (3–6) | 8 (5–13) * |
| IV antibiotic therapy above the median | 175 (44) | 6 (15.8) | 169 (49) * | 17 (18.3) | 158 (54.5) * |
| Adverse drug reactions ** | 32 (8) | 1 (2.6) | 31 (8.6) | 4 (4.2) | 28 (9.3) |
| De-Escalation on Day 3 | De-Escalation on Day 6 * | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| aOR | CI 95% | p-Value | aOR | CI 95% | p-Value | |
| Primary outcome | ||||||
| All-cause 30-day mortality | 1.48 | (0.29–7.40) | 0.63 | 0.57 | (0.14–2.31) | 0.43 |
| Secondary outcomes | ||||||
| LOS above the median | 0.75 | (0.38–1.47) | 0.41 | 0.65 | (0.32–1.33) | 0.24 |
| IV antibiotic therapy above the median ** | 0.22 | (0.06–0.74) | 0.01 | 0.39 | (0.17–0.85) | 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Viasus, D.; Abelenda-Alonso, G.; Bolivar-Areiza, J.; Gudiol, C.; Carratalà, J. Effects of Antibiotic De-Escalation on Outcomes in Severe Community-Acquired Pneumonia: An Inverse Propensity Score-Weighted Analysis. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14070716
Viasus D, Abelenda-Alonso G, Bolivar-Areiza J, Gudiol C, Carratalà J. Effects of Antibiotic De-Escalation on Outcomes in Severe Community-Acquired Pneumonia: An Inverse Propensity Score-Weighted Analysis. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(7):716. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14070716
Chicago/Turabian StyleViasus, Diego, Gabriela Abelenda-Alonso, Juan Bolivar-Areiza, Carlota Gudiol, and Jordi Carratalà. 2025. "Effects of Antibiotic De-Escalation on Outcomes in Severe Community-Acquired Pneumonia: An Inverse Propensity Score-Weighted Analysis" Antibiotics 14, no. 7: 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14070716
APA StyleViasus, D., Abelenda-Alonso, G., Bolivar-Areiza, J., Gudiol, C., & Carratalà, J. (2025). Effects of Antibiotic De-Escalation on Outcomes in Severe Community-Acquired Pneumonia: An Inverse Propensity Score-Weighted Analysis. Antibiotics, 14(7), 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14070716






