Elephant Cathelicidin-Derived Peptides Inhibit Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Design of Cathelicidin EM and Its Derivative Peptides
2.2. Safety Evaluation of Cathelicidin EM and Its Derivative Peptides
2.3. The Peptide EM-1 Inhibits HSV-1 Infection In Vitro
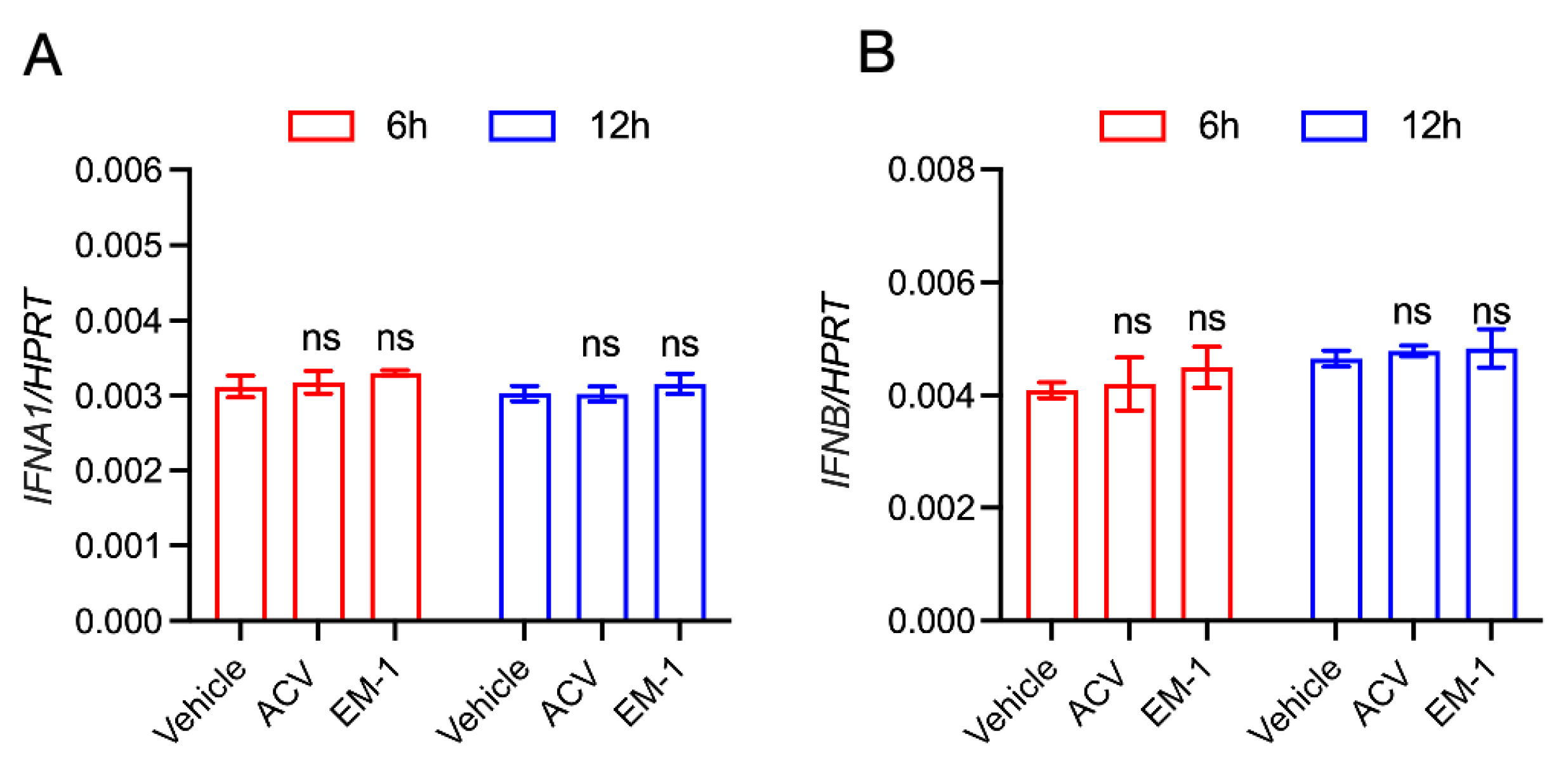
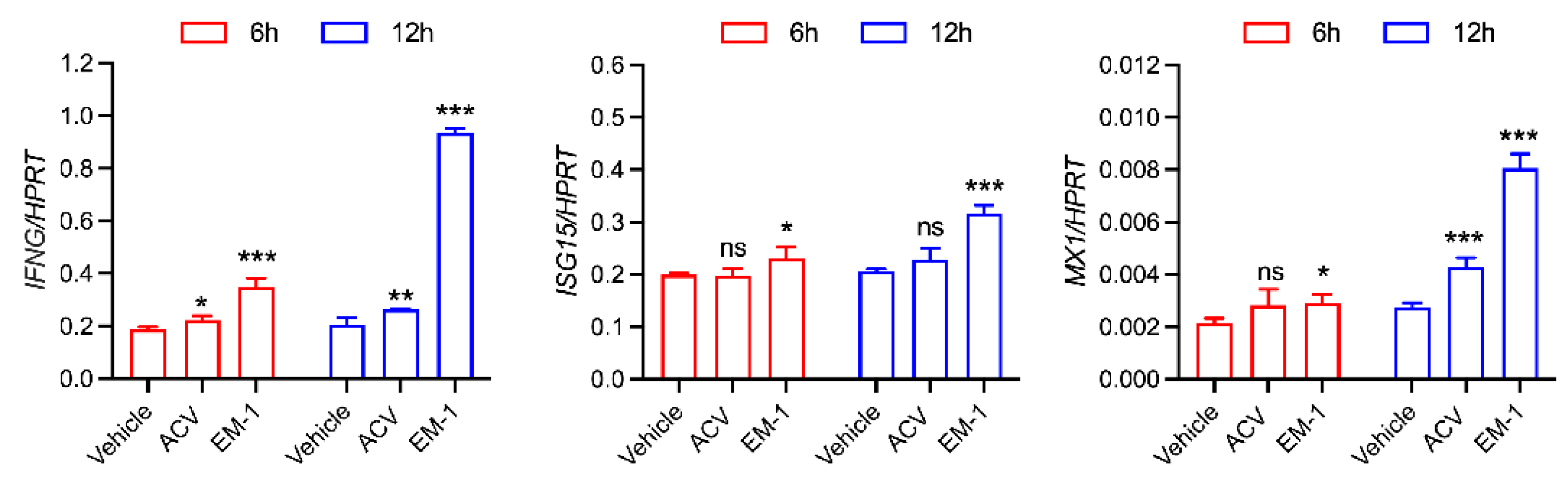
2.4. The Peptide EM-1 Induces Type Ⅱ Interferon and Its Downstream Gene Expression
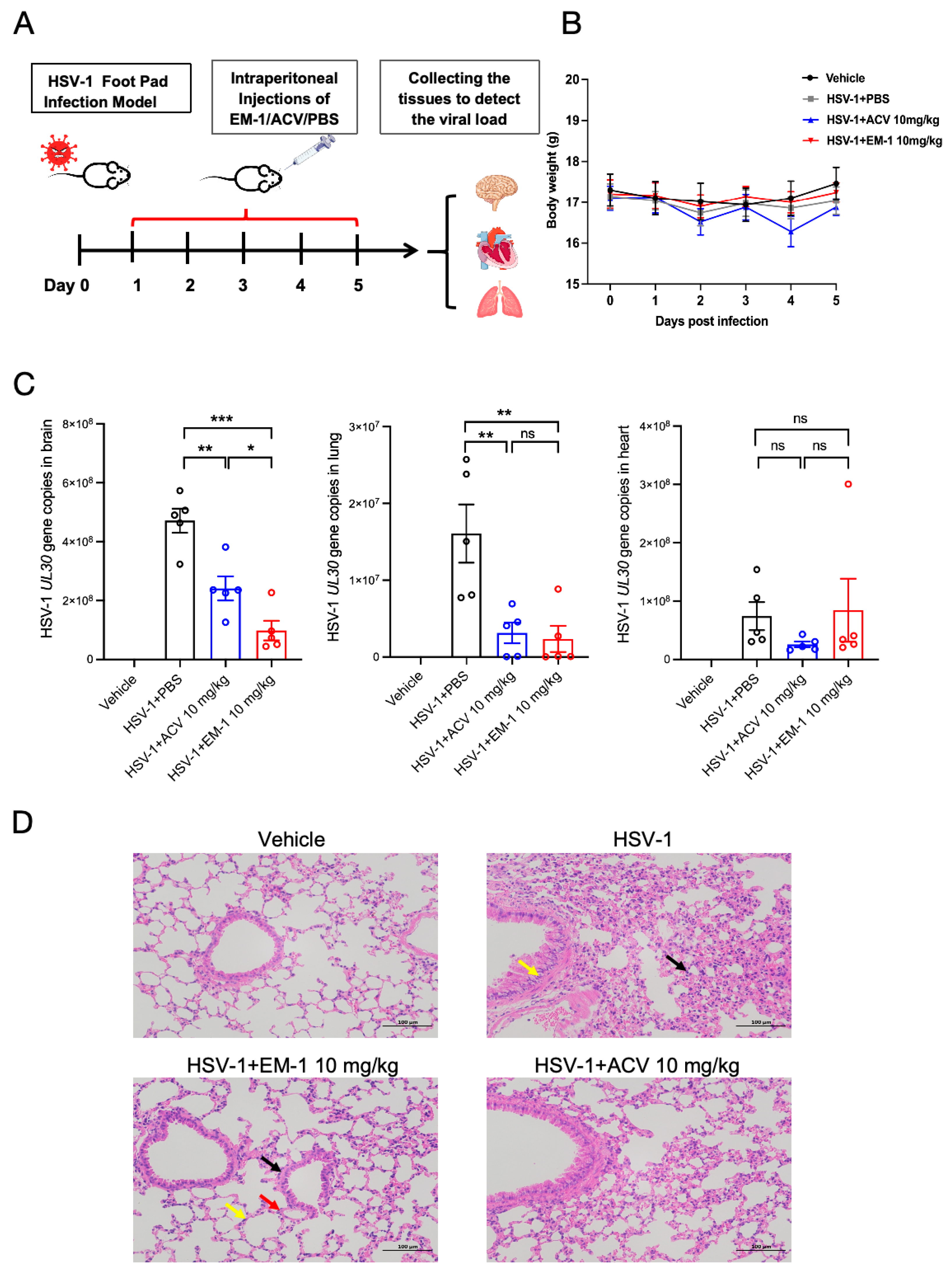
2.5. The Peptide EM-1 Inhibits Viral Load and Reduces Inflammatory Responses in Mice Lungs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cells and Virues
4.2. Peptides Design and Synthesis
4.3. Prediction of Physicochemical Properties of Peptides
- (1)
- Physicochemical properties including molecular weight, theoretical isoelectric point, and grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY) were predicted using the ProtParam tool (https://web.expasy.org/protparam/, 29 December 2022).
- (2)
- Transmembrane helix domains were analyzed through TMHMM (https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM-2.0/, 29 December 2022).
- (3)
- Subcellular localization prediction was performed with Cell-PLoc 2.0 (http://www.csbio.sjtu.edu.cn/bioinf/Cell-PLoc-2/, 29 December 2022).
4.4. Cytotoxicity Assay
4.5. Hemolysis Analysis
4.6. Isolation DNA and RNA for qPCR and RT-qPCR Analyses
4.7. Animal Experiment
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Physicochemical Property | EM | EM-1 | EM-2 | EM-3 | EM-4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sequence | RPRHVRRIRGLRKFFRKSKEKLKKVGRRVKGFFRDVLRRVPYLPGPRFSYAF-NH2 | RRIRGLRKFFRKSKEKLKKV-NH2 | GRRVKGFFRDVLRRVPYLPGPR-NH2 | RVIRVLKKFFKKIKKILKKV-NH2 | VRKVKKFFKKVLKKVKKLVRVI-NH2 |
| Length | 52 | 20 | 22 | 20 | 22 |
| Charge | +18 | +10 | +6 | +10 | +11 |
| Theoretical MW | 6459.80 | 2574.21 | 2642.15 | 2513.33 | 2712.58 |
| Measured MW | 6458.72 | 2573.19 | 2641.13 | 2512.31 | 2711.56 |
| Isoelectric point | 12.21 | 12.19 | 12.01 | 12.06 | 12.07 |
| Molecular formula | C299H488N100O61 | C117H209N41O24 | C121H197N41O26 | C123H222N34O21 | C132H239N37O23 |
| Hydrophilia | Hydrophilic | Hydrophilic | Hydrophilic | Hydrophilic | Hydrophilic |
| Stability | Unstable | Stable | Unstable | Stable | Stable |
| Subcellular localization | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm |
| Gene | Primer Sequences (5′→3′) |
|---|---|
| HSV-1 UL30 | F: TGTTTCGCGTGTGGGACATA |
| R: TTGTCCTTCAGGACGGCTTC | |
| 18S rRNA | F: GTAACCCGTTGAACCCCATT |
| R: CCATCCAATCGGTAGTAGCG | |
| HPRT | F: GCTATAAATTCTTTGCTGACCTGCTG |
| R: AATTACTTTTATGTCCCCTGTTGACTGG | |
| IFNG | F: CCAGAGCATCCAAAAGAGTGTG |
| R: TCAGCTTTTCGAAGTCATCTCGTT | |
| MX1 | F: GTTTCCGAAGTGGACATCGCA |
| R: CTGCACAGGTTGTTCTCAGC | |
| ISG15 | F: CGCAGATCACCCAGAAGATCG |
| R: TTCGTCGCATTTGTCCACCA | |
| IFNA1 | F: CTCATACACCAGGTCACGCT |
| R: AGTGTAAAGGTGCACATGACG | |
| IFNB | F: AGCTGAAGCAGTTCCAGAAG |
| R: AGTCTCATTCCAGCCAGTGC |
References
- Farooq, A.V.; Shukla, D. Herpes simplex epithelial and stromal keratitis: An epidemiologic update. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2012, 57, 448–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, T.; Shan, T.; Ye, J.; Jia, J.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, K.; Ren, Z. Viral ul8 is involved in the antiviral activity of oleanolic acid against hsv-1 infection. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 689607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedetti, J.; Corey, L.; Ashley, R. Recurrence rates in genital herpes after symptomatic first-episode infection. Ann. Intern. Med. 1994, 121, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reusser, P. Herpesvirus resistance to antiviral drugs: A review of the mechanisms, clinical importance and therapeutic options. J. Hosp. Infect. 1996, 33, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukhanova, M.K.; Korovina, A.N.; Kochetkov, S.N. Human herpes simplex virus: Life cycle and development of inhibitors. Biochemistry 2014, 79, 1635–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Clercq, E. Selective anti-herpesvirus agents. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 2013, 23, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheenstra, M.R.; van Harten, R.M.; Veldhuizen, E.J.A.; Haagsman, H.P.; Coorens, M. Cathelicidins modulate tlr-activation and inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, K.; Ma, X.; Liu, Y.; Qiao, S.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, G. Dietary modulation of endogenous host defense peptide synthesis as an alternative approach to in-feed antibiotics. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 4, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhai, Z.; Long, H.; Yang, G.; Deng, B.; Deng, J. Inducible expression of defensins and cathelicidins by nutrients and associated regulatory mechanisms. Peptides 2020, 123, 170177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, M.D.; Wollenberg, A.; Gallo, R.L.; Flaig, M.; Streib, J.E.; Wong, C.; Pavicic, T.; Boguniewicz, M.; Leung, D.Y. Cathelicidin deficiency predisposes to eczema herpeticum. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 117, 836–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, M.D.; Jones, J.F.; Kisich, K.O.; Streib, J.E.; Gallo, R.L.; Leung, D.Y. Selective killing of vaccinia virus by LL-37: Implications for eczema vaccinatum. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 1763–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.J.; Buznyk, O.; Kuffova, L.; Rajendran, V.; Forrester, J.V.; Phopase, J.; Islam, M.M.; Skog, M.; Ahlqvist, J.; Griffith, M. Cathelicidin ll-37 and hsv-1 corneal infection: Peptide versus Gene therapy. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2014, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Chen, S.; Jin, J.; Ma, L.; Guo, M.; Zhou, C.; Dou, J. Inhibition of peptide bf-30 on influenza a virus infection in vitro/vivo by causing virion membrane fusion. Peptides 2019, 112, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasin, B.; Wang, W.; Pang, M.; Cheshenko, N.; Hong, T.; Waring, A.J.; Herold, B.C.; Wagar, E.A.; Lehrer, R.I. Theta defensins protect cells from infection by herpes simplex virus by inhibiting viral adhesion and entry. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 5147–5156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, W.; Li, T.; Song, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zeng, Z.; Han, S.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, W.; Cao, Z. Inhibitory activity and mechanism of two scorpion venom peptides against herpes simplex virus type 1. Antivir. Res. 2014, 102, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birteksoz-Tan, A.S.; Zeybek, Z.; Hacioglu, M.; Savage, P.B.; Bozkurt-Guzel, C. In vitro activities of antimicrobial peptides and ceragenins against legionella pneumophila. J. Antibiot. 2019, 72, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moravej, H.; Moravej, Z.; Yazdanparast, M.; Heiat, M.; Mirhosseini, A.; Moosazadeh Moghaddam, M.; Mirnejad, R. Antimicrobial peptides: Features, action, and their resistance mechanisms in bacteria. Microb. Drug Resist. 2018, 24, 747–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Gu, X.; Song, D.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, N.; Chen, W.; Ji, S.; Qi, Y.; Ma, S. Rational design and synthesis of oreoch-2 analogues as efficient broad-spectrum antimicrobial peptides. Bioorgan. Chem. 2022, 119, 105583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, J.; Geng, M.; Lu, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, M.; et al. Rational design of hjh antimicrobial peptides to improve antimicrobial activity. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. Lett. 2023, 83, 129176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabizadeh, S.; Rahbarnia, L.; Nowrozi, J.; Farajnia, S.; Hosseini, F. Rational design of hybrid peptide with high antimicrobial property derived from melittin and lasioglossin. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2024, 42, 13091–13099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Yang, J.; Chen, C.; Li, R.; Chen, S.; Weng, Y.; Lin, Y.; Chen, Z.; Yu, F.; Lü, X.; et al. Rational design of abhisin-like peptides enables generation of potent antimicrobial activity against pathogens. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 6621–6640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Wu, P.; Weng, Y.; Lin, Y.; Chen, Z.; Yu, F.; Lv, X.; Ni, L.; Han, J. Rational design and antimicrobial potency assessment of abaecin analogues. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 9, 6698–6714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangpromma, N.; Konkchaiyaphum, M.; Punpad, A.; Sosiangdi, S.; Daduang, S.; Klaynongsruang, S.; Tankrathok, A. Rational design of rn15m4 cathelin domain-based peptides from siamese crocodile cathelicidin improves antimicrobial activity. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2023, 195, 1096–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosiangdi, S.; Taemaitree, L.; Tankrathok, A.; Daduang, S.; Boonlue, S.; Klaynongsruang, S.; Jangpromma, N. Rational design and characterization of cell-selective antimicrobial peptides based on a bioactive peptide from crocodylus siamensis hemoglobin. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadowski, L.A.; Upadhyay, R.; Greeley, Z.W.; Margulies, B.J. Current drugs to treat infections with herpes simplex viruses-1 and -2. Viruses 2021, 13, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, R.E.; Sahl, H.G. Antimicrobial and host-defense peptides as new anti-infective therapeutic strategies. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, K. Control of cell selectivity of antimicrobial peptides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1788, 1687–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damour, A.; Garcia, M.; Cho, H.S.; Larivière, A.; Lévêque, N.; Park, C.; Bodet, C. Characterisation of antiviral activity of cathelicidins from naked mole rat and python bivittatus on human herpes simplex virus 1. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; An, Y.; Tan, W.; Ma, L.; Wang, M.; Li, J.; Li, B.; Hou, W.; Wu, L. Cathelicidin-derived antiviral peptide inhibits herpes simplex virus 1 infection. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1201505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roizman, B.; Taddeo, B. The strategy of herpes simplex virus replication and takeover of the host cell. In Human Herpesviruses: Biology, Therapy, and Immunoprophylaxis; Arvin, A., Campadelli-Fiume, G., Mocarski, E., Moore, P.S., Roizman, B., Whitley, R., Yamanishi, K., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, S.T.; Masarčíková, R.; Berchová, K. Bioactive natural products with anti-herpes simplex virus properties. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2015, 67, 1325–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valyi-Nagy, T.; Olson, S.J.; Valyi-Nagy, K.; Montine, T.J.; Dermody, T.S. Herpes simplex virus type 1 latency in the murine nervous system is associated with oxidative damage to neurons. Virology 2000, 278, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, P.; Fu, H.; Ma, X. Design, optimization, and nanotechnology of antimicrobial peptides: From exploration to applications. Nano Today 2021, 39, 101229. [Google Scholar]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yisihaer, H.; Dong, P.; Li, P.; Deng, E.; Meng, R.; Jin, L.; Li, G. Elephant Cathelicidin-Derived Peptides Inhibit Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Infection. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 655. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14070655
Yisihaer H, Dong P, Li P, Deng E, Meng R, Jin L, Li G. Elephant Cathelicidin-Derived Peptides Inhibit Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Infection. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(7):655. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14070655
Chicago/Turabian StyleYisihaer, Haiche, Peng Dong, Pengpeng Li, Enjie Deng, Rui Meng, Lin Jin, and Guilan Li. 2025. "Elephant Cathelicidin-Derived Peptides Inhibit Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Infection" Antibiotics 14, no. 7: 655. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14070655
APA StyleYisihaer, H., Dong, P., Li, P., Deng, E., Meng, R., Jin, L., & Li, G. (2025). Elephant Cathelicidin-Derived Peptides Inhibit Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Infection. Antibiotics, 14(7), 655. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14070655







