Biofilm-Forming Lactic Acid Bacteria in Sausages: Isolation, Characterization, and Inhibition Using Eisenia bicyclis-Based Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Identification of the Biofilm-Forming LAB Isolated from Meat Products
2.2. Growth and Hemolytic Characteristics of Isolated LAB
2.3. Fermentation Profile of Carbohydrate in LAB Isolates
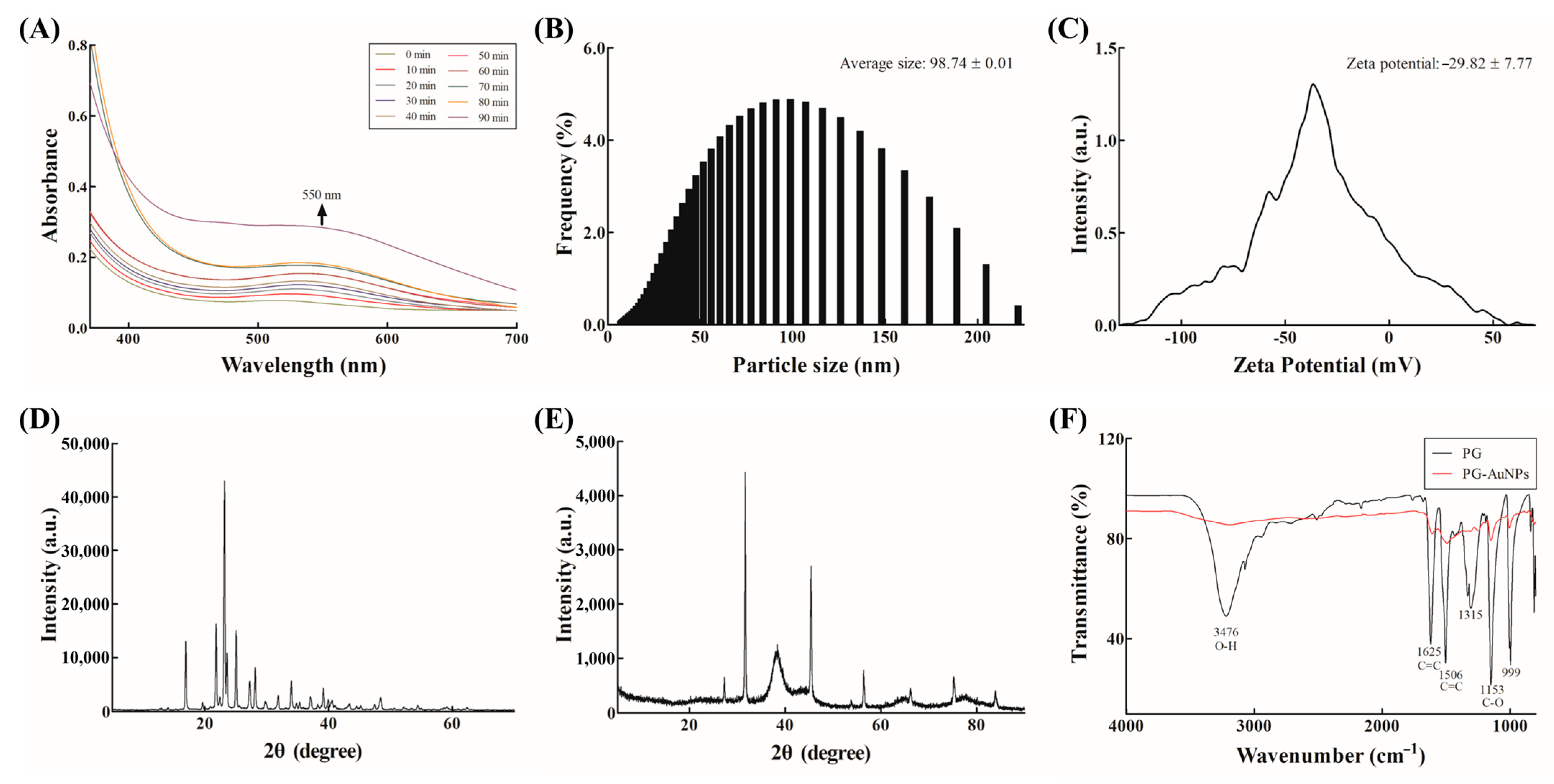
2.4. Synthesis and Characterization of PG-AuNPs
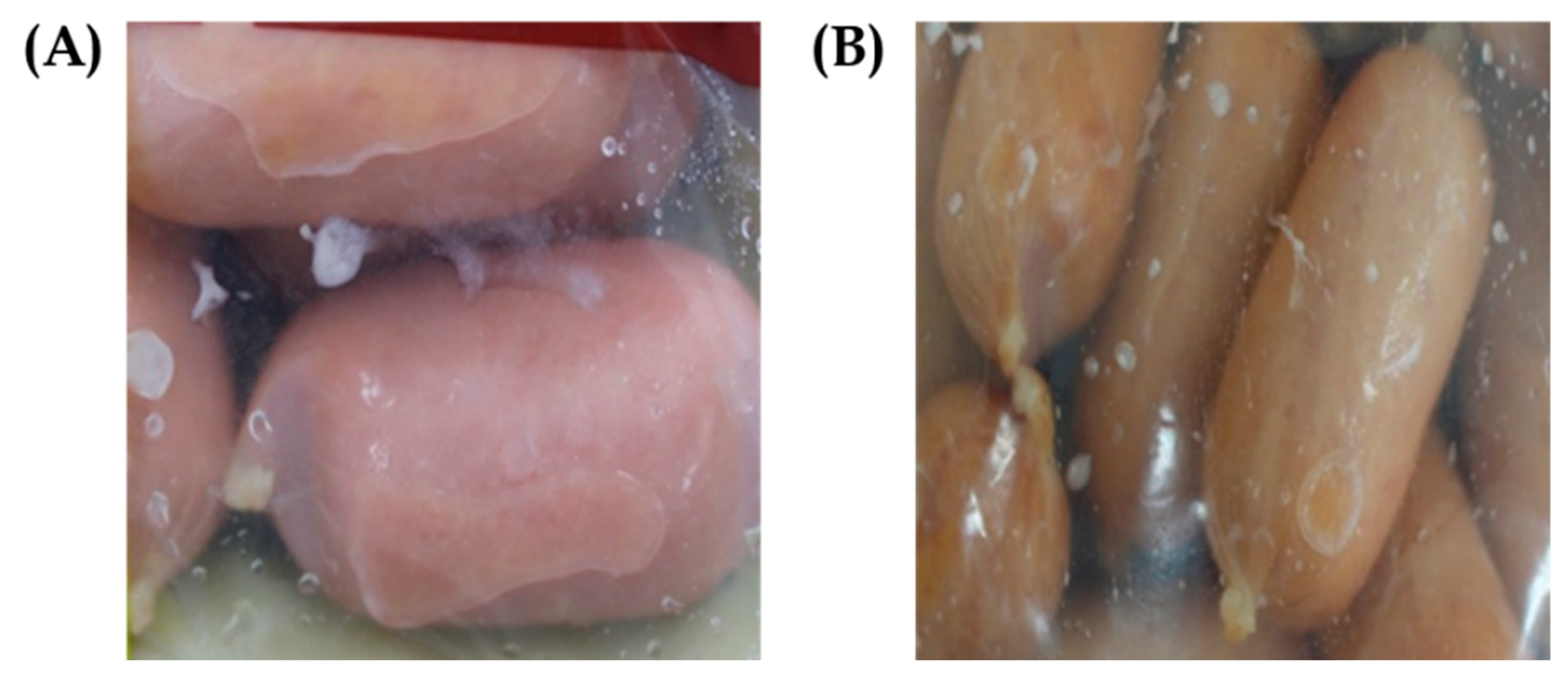
2.5. Assessment of Biofilm Control In Situ Against Pathogens and Biofilm-Forming LAB
3. Limitations of the Present Study
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Isolation of LAB
4.2. Taxonomic Identification of LAB Isolates
4.3. Characterization of Isolated LAB
4.4. Biochemical Characterization of LAB Isolates
4.5. Preparation and Characterization of AuNPs
4.6. Biofilm-Inhibitory Activity of LAB Isolates
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holzapfel, W.H.; Wood, B.J. Lactic Acid Bacteria: Biodiversity and Taxonomy; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- De Vuyst, L.; Leroy, F. Bacteriocins from lactic acid bacteria: Production, purification, and food applications. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 13, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipilkina, T.A.; Xu, C.; Barbosa, M.d.S.; Khramova, V.N.; Shebeko, S.K.; Ermakov, A.M.; Ivanova, I.V.; Todorov, S.D. Beneficial and Safety Properties of a Bacteriocinogenic and Putative Probiotic Latilactobacillus sakei subsp. sakei 2a Strain. Foods 2024, 13, 3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iulietto, M.F.; Sechi, P.; Borgogni, E.; Cenci-Goga, B.T. Meat spoilage: A critical review of a neglected alteration due to ropy slime producing bacteria. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 14, 4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dušková, M.; Kameník, J.; Karpíšková, R. Weissella viridescens in meat products–A review. Acta Vet. Brno 2013, 82, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, E.; Adamsen, A.; Feilberg, A.; Schäfer, A.; Løkke, M.M.; Petersen, M. Quality changes during storage of cooked and sliced meat products measured with PTR-MS and HS-GC–MS. Meat Sci. 2013, 95, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankar, C.R.; Lalitha, K.; Jose, L.; Manju, S.; Gopal, T. Effect of packaging atmosphere on the microbial attributes of pearlspot (Etroplus suratensis Bloch) stored at 0–2 °C. Food Microbiol. 2008, 25, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsafrakidou, P.; Sameli, N.; Kakouri, A.; Bosnea, L.; Samelis, J. Assessment of the spoilage microbiota and the growth potential of Listeria monocytogenes in minced free-range chicken meat stored at 4 C in vacuum: Comparison with the spoilage community of resultant retail modified atmosphere packaged products. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 3, 1277–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R. Biofilms and meat safety: A mini-review. J. Food Prot. 2019, 82, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaev, Y.; Yushina, Y.; Mardanov, A.; Gruzdev, E.; Tikhonova, E.; El-Registan, G.; Beletskiy, A.; Semenova, A.; Zaiko, E.; Bataeva, D. Microbial biofilms at meat-processing plant as possible places of bacteria survival. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridier, A.; Briandet, R.; Thomas, V.; Dubois-Brissonnet, F. Resistance of bacterial biofilms to disinfectants: A review. Biofouling 2011, 27, 1017–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlan, L.M.; Cotter, P.D.; Hill, C.; Alvarez-Ordóñez, A. New weapons to fight old enemies: Novel strategies for the (bio) control of bacterial biofilms in the food industry. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Ciccio, P.; Rubiola, S.; Panebianco, F.; Lomonaco, S.; Allard, M.; Bianchi, D.M.; Civera, T.; Chiesa, F. Biofilm formation and genomic features of Listeria monocytogenes strains isolated from meat and dairy industries located in Piedmont (Italy). Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 378, 109784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Gu, N.; Huang, T.Y.; Zhong, F.; Peng, G. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A typical biofilm forming pathogen and an emerging but underestimated pathogen in food processing. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1114199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MFDS. Food Code; MFDS: Cheongju, Republic of Korea, 2024.
- Chenoll, E.; Macián, M.; Elizaquivel, P.; Aznar, R. Lactic acid bacteria associated with vacuum-packed cooked meat product spoilage: Population analysis by rDNA-based methods. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 102, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, R.; Alam, M.; Sarkar, A.; Haque, M.I.; Hasan, M.M.; Hoque, M. Application of nanotechnology in food: Processing, preservation, packaging and safety assessment. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behzadnia, A.; Moosavi-Nasab, M.; Oliyaei, N. Anti-biofilm activity of marine algae-derived bioactive compounds. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1270174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-K.; Wijesekara, I. Development and biological activities of marine-derived bioactive peptides: A review. J. Funct. Foods 2010, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.A.; Jin, S.E.; Ahn, B.R.; Lee, C.M.; Choi, J.S. Anti-inflammatory activity of edible brown alga Eisenia bicyclis and its constituents fucosterol and phlorotannins in LPS-stimulated RAW264. 7 macrophages. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 59, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Eom, S.-H.; Lee, E.-H.; Jung, Y.-J.; Kim, H.-J.; Jo, M.-R.; Son, K.-T.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, M.-S. In vitro antibacterial and synergistic effect of phlorotannins isolated from edible brown seaweed Eisenia bicyclis against acne-related bacteria. Algae 2014, 29, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, M.G.; Singh, A.; Singh, S.V.; Kamble, M.G.; Sagar, N.A.; Rani, N. Nanotechnology for encapsulation of bioactive components: A review. Discov. Food 2025, 5, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, M.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, J. Development of gold nanoparticles coated with silica containing the antibiofilm drug cinnamaldehyde and their effects on pathogenic bacteria. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 2813–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Hu, Z.; Ma, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Yuan, Z. The systematic evaluation of size-dependent toxicity and multi-time biodistribution of gold nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 167, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-S.; Hung, Y.-C.; Liau, I.; Huang, G.S. Assessment of the in vivo toxicity of gold nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2009, 4, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Ilan, O.; Albrecht, R.M.; Fako, V.E.; Furgeson, D.Y. Toxicity assessments of multisized gold and silver nanoparticles in zebrafish embryos. Small 2009, 5, 1897–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, C.M.; McCusker, C.D.; Yilmaz, T.; Rotello, V.M. Toxicity of Gold Nanoparticles Functionalized with Cationic and Anionic Side Chains. Bioconjugate Chem. 2004, 15, 897–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zawrah, M.; El-Moez, S.; Center, D. Antimicrobial activities of gold nanoparticles against major foodborne pathogens. Life Sci. J. 2011, 8, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayan, S.R.; Santhiyagu, P.; Singamuthu, M.; Kumari Ahila, N.; Jayaraman, R.; Ethiraj, K. Synthesis and characterization of silver and gold nanoparticles using aqueous extract of seaweed, Turbinaria conoides, and their antimicrofouling activity. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 938272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menna, P.M.; Barcellos, F.G.; Hungria, M. Phylogeny and taxonomy of a diverse collection of Bradyrhizobium strains based on multilocus sequence analysis of the 16S rRNA gene, ITS region and glnII, recA, atpD and dnaK genes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 2934–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla-Frausto, J.; Cepeda-Marquez, L.; Salgado, L.; Iturriaga, M.; Arvizu-Medrano, S. Detection and genotyping of Leuconostoc spp. in a sausage processing plant. J. Food Prot. 2015, 78, 2170–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pothakos, V.; Devlieghere, F.; Villani, F.; Björkroth, J.; Ercolini, D. Lactic acid bacteria and their controversial role in fresh meat spoilage. Meat Sci. 2015, 109, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, I.; Molchanova, N.; Holmedal, E.; Jenssen, H.; Hummel, B.D.; Watts, J.L.; Håkansson, J.; Hansen, P.R.; Svenson, J. Correlation between hemolytic activity, cytotoxicity and systemic in vivo toxicity of synthetic antimicrobial peptides. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buxton, R. Blood agar plates and hemolysis protocols. Am. Soc. Microbiol. 2005, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Amenu, D.; Bacha, K. Probiotic potential and safety analysis of lactic acid bacteria isolated from Ethiopian traditional fermented foods and beverages. Ann. Microbiol. 2023, 73, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, F.S.; Duarte, W.F.; Santos, M.R.R.M.; Ramos, E.M.; Schwan, R.F. Screening of Lactobacillus isolated from pork sausages for potential probiotic use and evaluation of the microbiological safety of fermented products. J. Food Prot. 2013, 76, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaillou, S.; Champomier-Vergès, M.-C.; Cornet, M.; Crutz-Le Coq, A.-M.; Dudez, A.-M.; Martin, V.; Beaufils, S.; Darbon-Rongère, E.; Bossy, R.; Loux, V. The complete genome sequence of the meat-borne lactic acid bacterium Lactobacillus sakei 23K. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 1527–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.; Khan, F.; Park, S.-K.; Jo, D.-M.; Kim, N.-G.; Jung, W.-K.; Kim, Y.-M. Antimicrobial, antibiofilm, and antivirulence properties of Eisenia bicyclis-extracts and Eisenia bicyclis-gold nanoparticles towards microbial pathogens. Microb. Pathog. 2024, 188, 106546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, D.K.; Jo, D.-M.; Kim, N.-G.; Cho, K.-J.; Jeong, G.-J.; Tabassum, N.; Jung, W.-K.; Khan, F.; Kim, Y.-M. Eisenia bicyclis-Mediated Gold Nanoparticles Exhibit Antibiofilm and Antivirulence Activities Against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, K.; Okuyama, Y.; Hirano, R.; Okabe, S.; Takahashi, M.; Satoh, H. Development of a simple analytical method to determine arsenite using a DNA aptamer and gold nanoparticles. Chemosphere 2019, 224, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Ballesteros, N.; Rodríguez-Argüelles, M.; Lastra-Valdor, M.; González-Mediero, G.; Rey-Cao, S.; Grimaldi, M.; Cavazza, A.; Bigi, F. Synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles by Sargassum muticum biomolecules and evaluation of their antioxidant activity and antibacterial properties. J. Nanostructure Chem. 2020, 10, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindaraj, M.; Suresh, M.; Palaniyandi, T.; Viswanathan, S.; Wahab, M.R.A.; Baskar, G.; Surendran, H.; Ravi, M.; Sivaji, A. Bio-fabrication of gold nanoparticles from brown seaweeds for anticancer activity against glioblastoma through in vitro and molecular docking approaches. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1281, 135178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, S.; Rajkumar, P.; Thirunavukkarasu, K.; Gunasekaran, S.; Kumaresan, S. Vibrational (FT-IR and FT-Raman), electronic (UV–vis) and quantum chemical investigations on pyrogallol: A study on benzenetriol dimers. Vib. Spectrosc. 2018, 95, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Senthamilselvi, S.; Govindaraju, M. Phloroglucinol-encapsulated starch biopolymer: Preparation, antioxidant and cytotoxic effects on HepG2 liver cancer cell lines. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 26787–26795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Batal, A.; Al Tamie, M. Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles using marine Streptomyces cyaneus and their antimicrobial, antioxidant and antitumor (in vitro) activities. J. Chem. Pharm. Res 2015, 7, 1020–1036. [Google Scholar]
- Hammami, I.; Alabdallah, N.M. Gold nanoparticles: Synthesis properties and applications. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2021, 33, 101560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Park, S.-K.; Jo, D.-M.; Cho, K.-J.; Jeong, G.-J.; Sim, Y.-J.; Choi, J.M.; Woon, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-M. Inhibition of Food-derived Lactic Acid Bacterial Biofilm Formation Using Eisenia bicyclis-derived Nanoparticles. Korean J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2024, 57, 129–136. [Google Scholar]
- Tabassum, N.; Jeong, G.-J.; Jo, D.-M.; Khan, F.; Kim, Y.-M. Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus and Candida albicans polymicrobial biofilms by phloroglucinol-gold nanoparticles. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 185, 106416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lima, A.L.; Guerra, C.A.; Costa, L.M.; de Oliveira, V.S.; Lemos Junior, W.J.F.; Luchese, R.H.; Guerra, A.F. A natural technology for vacuum-packaged cooked sausage preservation with potentially postbiotic-containing preservative. Fermentation 2022, 8, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, P.; Aguirre, J.; Troncoso, M.; Figueroa, G. Comparison of in vitro and in situ antagonism assays as tools for the selection of bio-preservative lactic acid bacteria (LAB) in poultry meat. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 118, 108846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahar, S.; Jeong, H.L.; Cho, A.J.; Park, J.-H.; Han, S.; Kim, Y.; Park, S.-H.; Ha, S.-D. Efficacy of ficin and peroxyacetic acid against Salmonella enterica serovar Thompson biofilm on plastic, eggshell, and chicken skin. Food Microbiol. 2022, 104, 103997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinoj, G.; Pati, R.; Sonawane, A.; Vaseeharan, B. In Vitro Cytotoxic Effects of Gold Nanoparticles Coated with Functional Acyl Homoserine Lactone Lactonase Protein from Bacillus licheniformis and Their Antibiofilm Activity against Proteus Species. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, P.P.; Rai, A.; Baruah, P.K. Recent Advances in the Development of Antibiotics-Coated Gold Nanoparticles to Combat Antimicrobial Resistance. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faegheh, F.; Samira, E.; Sousan Torabi, P.; Tannaz, J.; Eric, G.; Amirhossein, S. Polyphenolic Nano-formulations: A New Avenue against Bacterial Infection. Curr. Med. Chem. 2024, 31, 6154–6171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhalifa, M.E.M.; Muhammad, A.; Alshebli, A.; Assad, U.; Hamdoon, A.A.; Elawad, M.A.; Almalki, M.G.; Mosa, O.F.; Niyazov, L.N.; Ayaz, M. Polyphenols and Their Nanoformulations as Potential Antibiofilm Agents Against Multidrug-Resistant Pathogens. Future Microbiol. 2024, 19, 255–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Dong, S.; Wang, X.; Xu, H.; Liu, C.; Yang, X.; Wu, S.; Jiang, X.; Kan, M.; Xu, C. Research progress of polyphenols in nanoformulations for antibacterial application. Mater. Today Bio 2023, 21, 100729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, S.; Wagh, H.; Liang, Y.; Yang, S.; Boyer, C. Enhancing the antimicrobial and antibiofilm effectiveness of silver nanoparticles prepared by green synthesis. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 4124–4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Sun, Q.; Wu, F.-G.; Dai, Y.; Chen, X. Polyphenol-Containing Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Properties, and Therapeutic Delivery. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2007356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byun, K.-H.; Na, K.W.; Ashrafudoulla, M.; Choi, M.W.; Han, S.H.; Kang, I.; Park, S.H.; Ha, S.-D. Combination treatment of peroxyacetic acid or lactic acid with UV-C to control Salmonella Enteritidis biofilms on food contact surface and chicken skin. Food Microbiol. 2022, 102, 103906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, Y.J.; Myung, G.E.; Min, S.C. In-package cold plasma treatment enhances the antimicrobial efficacy of malic acid-incorporated whey protein edible coating against Salmonella and Listeria monocytogenes in steamed fish paste. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 33, 100905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Samples | Treated Concentration (μg/mL) | Cell Growth of the Biofilm (Log CFU/g) |
|---|---|---|
| S10 strain (control) | - | 6.38 ± 0.01 |
| EA-AuNPs | 1024 | 5.23 ± 0.11 |
| PG | 1024 | 4.60 ± 0.60 |
| PG-AuNPs | 1024 | 5.00 ± 0.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, D.K.; Jo, D.-M.; Kim, M.; Jo, J.-B.; Choi, J.-H.; Choi, J.M.; Jeong, G.-J.; Jeong, S.Y.; Khan, F.; Kim, Y.-M. Biofilm-Forming Lactic Acid Bacteria in Sausages: Isolation, Characterization, and Inhibition Using Eisenia bicyclis-Based Nanoparticles. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 637. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14070637
Oh DK, Jo D-M, Kim M, Jo J-B, Choi J-H, Choi JM, Jeong G-J, Jeong SY, Khan F, Kim Y-M. Biofilm-Forming Lactic Acid Bacteria in Sausages: Isolation, Characterization, and Inhibition Using Eisenia bicyclis-Based Nanoparticles. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(7):637. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14070637
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Do Kyung, Du-Min Jo, Minji Kim, Jeong-Bin Jo, Ji-Hwan Choi, Jeong Mi Choi, Geum-Jae Jeong, Se Yun Jeong, Fazlurrahman Khan, and Young-Mog Kim. 2025. "Biofilm-Forming Lactic Acid Bacteria in Sausages: Isolation, Characterization, and Inhibition Using Eisenia bicyclis-Based Nanoparticles" Antibiotics 14, no. 7: 637. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14070637
APA StyleOh, D. K., Jo, D.-M., Kim, M., Jo, J.-B., Choi, J.-H., Choi, J. M., Jeong, G.-J., Jeong, S. Y., Khan, F., & Kim, Y.-M. (2025). Biofilm-Forming Lactic Acid Bacteria in Sausages: Isolation, Characterization, and Inhibition Using Eisenia bicyclis-Based Nanoparticles. Antibiotics, 14(7), 637. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14070637







