Distribution and Clinical Impact of Helicobacter pylori Virulence Factors in Epstein–Barr-Virus-Associated Gastric Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinicopathologic Characteristics According to EBV Infection Status
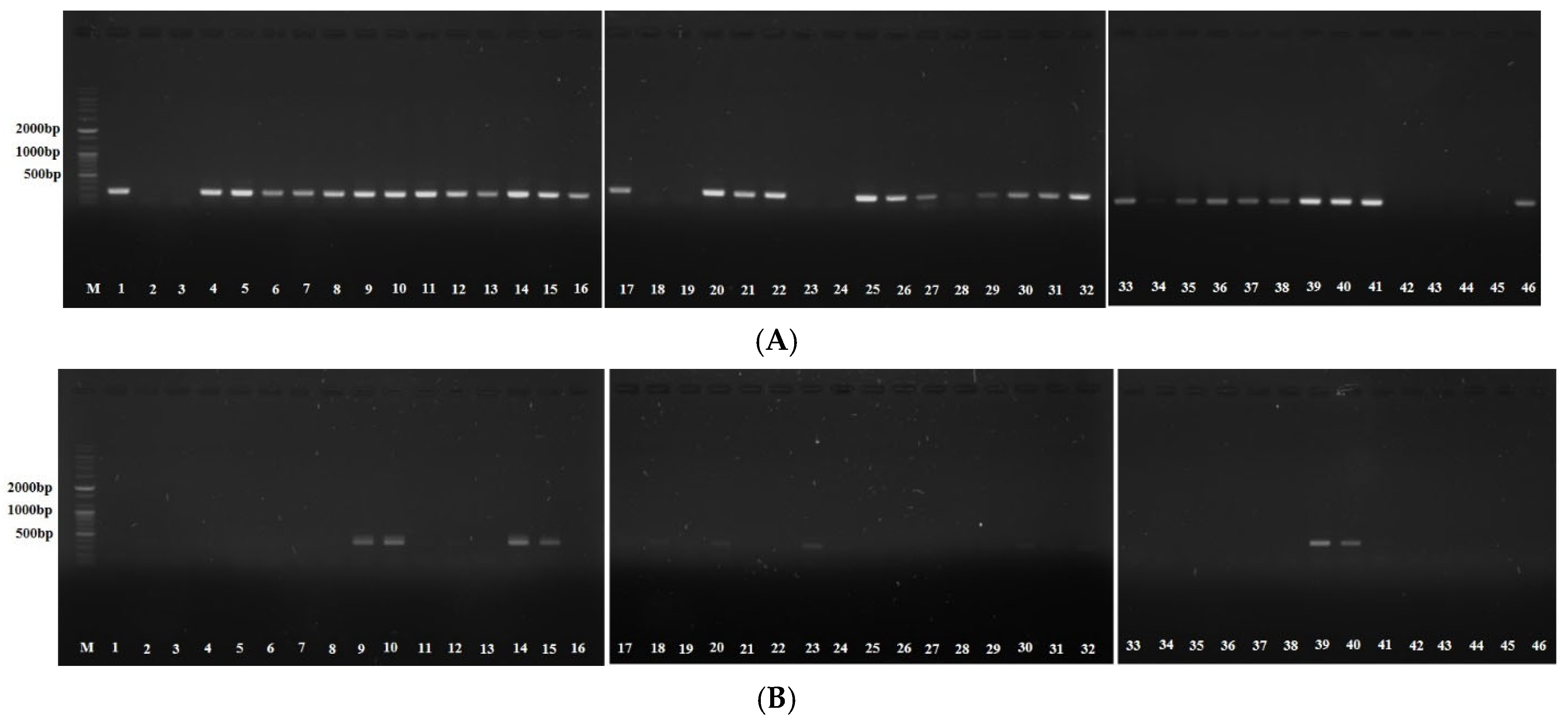
2.2. Positivity of Virulence Factors According to EBV Infection Status
2.3. Clinical Outcomes According to Virulence Factors in EBV-Associated Gastric Cancer
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population
4.2. H. pylori Culture
4.3. Genomic DNA Extraction
4.4. PCR Amplification
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomceli, I.; Demiriz, B.; Tez, M. Gastric carcinogenesis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 5164–5170. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Salvatori, S.; Marafini, I.; Laudisi, F.; Monteleone, G.; Stolfi, C. Helicobacter pylori and Gastric Cancer: Pathogenetic Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schistosomes, liver flukes and Helicobacter pylori. In IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; IARC: Lyon, France, 1994; Volume 61, pp. 1–241.
- Correa, P.; Piazuelo, M.B. The gastric precancerous cascade. J. Dig. Dis. 2012, 13, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Y.; Liu, X.F.; Gao, X.Z. Helicobacter pylori virulence factors in development of gastric carcinoma. Future Microbiol. 2015, 10, 1505–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pormohammad, A.; Ghotaslou, R.; Leylabadlo, H.E.; Nasiri, M.J.; Dabiri, H.; Hashemi, A. Risk of gastric cancer in association with Helicobacter pylori different virulence factors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 118, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Z.; Chen, H.; Castro, F.A.; Hu, J.K.; Brenner, H. Epstein-Barr virus infection and gastric cancer: A systematic review. Medicine 2015, 94, e792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas-Mondragón, M.G.; Torres, J.; Flores-Luna, L.; Camorlinga-Ponce, M.; Carreón-Talavera, R.; Gomez-Delgado, A.; Kasamatsu, E.; Fuentes-Pananá, E.M. Case–control study of Epstein–Barr virus and Helicobacter pylori serology in Latin American patients with gastric disease. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 1866–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Gan, R. Signaling pathways of EBV-induced oncogenesis. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Jha, H.C. Status of Epstein-Barr Virus Coinfection with Helicobacter pylori in Gastric Cancer. J. Oncol. 2017, 2017, 3456264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsusaka, K.; Funata, S.; Fukayama, M.; Kaneda, A. DNA methylation in gastric cancer, related to Helicobacter pylori and Epstein-Barr virus. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 3916–3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dávila-Collado, R.; Jarquín-Durán, O.; Dong, L.T.; Espinoza, J.L. Epstein-Barr Virus and Helicobacter pylori Co-Infection in Non-Malignant Gastroduodenal Disorders. Pathogens 2020, 9, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, J.H.; Shin, J.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Park, Y.S.; Lee, I.S.; Kim, G.H.; Na, H.K.; Ahn, J.Y.; Jung, K.W.; Kim, D.H.; et al. Clinical Significance of Epstein-Barr Virus and Helicobacter pylori Infection in Gastric Carcinoma. Gut Liver 2023, 17, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naseem, M.; Barzi, A.; Brezden-Masley, C.; Puccini, A.; Berger, M.D.; Tokunaga, R.; Battaglin, F.; Soni, S.; McSkane, M.; Zhang, W.; et al. Outlooks on Epstein-Barr virus associated gastric cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2018, 66, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, S.; Jha, H.C.; Shukla, S.K.; Shirley, M.K.; Robertson, E.S. Epigenetic Regulation of Tumor Suppressors by Helicobacter pylori Enhances EBV-Induced Proliferation of Gastric Epithelial Cells. mBio 2018, 9, e00649-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, X.; Tang, B.; Li, B.S.; Xie, R.; Hu, C.J.; Luo, G.; Qin, Y.; Dong, H.; Yang, S.-M. Helicobacter pylori virulence factor CagA promotes tumorigenesis of gastric cancer via multiple signaling pathways. Cell Commun. Signal. CCS 2015, 13, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.Q.; Zheng, G.F.; Sumanac, K.; Irvine, E.J.; Hunt, R.H. Meta-analysis of the relationship between cagA seropositivity and gastric cancer. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 1636–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.R.; Marcus, E.A.; Weeks, D.L.; Sachs, G. Mechanisms of acid resistance due to the urease system of Helicobacter pylori. Gastroenterology 2002, 123, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clyne, M.; Labigne, A.; Drumm, B. Helicobacter pylori requires an acidic environment to survive in the presence of urea. Infect. Immun. 1995, 63, 1669–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.R.; Marcus, E.A.; Wen, Y.; Oh, J.; Sachs, G. Gene expression in vivo shows that Helicobacter pylori colonizes an acidic niche on the gastric surface. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7235–7240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela-Valderrama, M.; Cerda-Opazo, P.; Backert, S.; González, M.F.; Carrasco-Véliz, N.; Jorquera-Cordero, C.; Wehinger, S.; Canales, J.; Bravo, D.; Quest, A.F.G. The Helicobacter pylori Urease Virulence Factor Is Required for the Induction of Hypoxia-Induced Factor-1α in Gastric Cells. Cancers 2019, 11, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wroblewski, L.E.; Peek, R.M., Jr. Clinical Pathogenesis, Molecular Mechanisms of Gastric Cancer Development. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2023, 444, 25–52. [Google Scholar]
- Bui, N.N.; Huang, S.C.; Tran, T.N.L.; Nguyen, N.H.; Do, H.N.; Chiu, Y.F.; Lai, C.-H. Association between Helicobacter pylori and Epstein-Barr virus co-infection and gastric cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. QJM Mon. J. Assoc. Physicians 2025, 118, hcaf092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| EBV+ (n = 28) | EBV− (n = 26) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age at diagnosis, years, mean ± SD | 61.5 ± 9.4 | 60.4 ± 12.8 | 0.310 |
| Male sex, n (%) | 23 (82.1) | 22 (84.6) | 1.000 |
| Serum IgG Ab titer (n = 51), mean ± SD | 4.8 ± 2.1 | 5.4 ± 2.3 | 0.149 |
| Eradication success rate | 15/17 (88.2) | 15/16 (93.8) | 1.000 |
| Tumor size, cm, mean ± SD | 2.9 ± 2.4 | 2.7 ± 1.9 | 0.808 |
| Tumor location, n (%) | 0.034 | ||
| Upper | 8 (28.6) | 2 (7.7) | |
| Middle | 15 (53.6) | 12 (46.2) | |
| Lower | 5 (17.9) | 12 (46.2) | |
| Tumor type, n (%) | 0.604 | ||
| EGC | 27 (96.4) | 24 (92.3) | |
| AGC | 1 (3.6) | 2 (7.7) | |
| Histology, n (%) | <0.001 | ||
| WD/MD | 6 (21.4) | 16 (61.5) | |
| PD/SRC | 7 (25.0) | 10 (38.5) | |
| GCLS | 15 (53.6) | 0 (0.0) | |
| AJCC TNM stage, n (%) | 0.736 | ||
| I | 27 (96.4) | 24 (92.3) | |
| II | 0 (0.0) | 1 (3.8) | |
| III | 1 (3.6) | 1 (3.8) | |
| Lymphovascular invasion, n (%) | 2 (7.1) | 4 (15.4) | 0.413 |
| Perineural invasion, n (%) | 1 (3.6) | 1 (3.8) | 1.000 |
| Treatment method, n (%) | 0.821 | ||
| ESD | 17 (60.7) | 15 (57.7) | |
| Surgery | 11 (39.3) | 11 (42.3) | |
| Recurrence-free survival, mean ± SD, median (IQR) | 36.4 ± 17.0, 31.5 (31.0–32.0) | 30.0 ± 5.1, 31.0 (23.3–46.5) | 0.075 |
| Overall survival, mean ± SD, median (IQR) | 37.8 ± 16.1, 32.0 (31.0–32.0) | 32.6 ± 3.7, 32.5 (24.3–46.5) | 0.113 |
| EBV+ (n = 46) | EBV– (n = 50) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| cagA, n (%) | 46 (100.0) | 50 (100.0) | 1.000 |
| dupA, n (%) | 4 (8.7) | 9 (18.0) | 0.183 |
| iceA1, n (%) | 36 (78.3) | 48 (96.0) | 0.009 |
| iceA2, n (%) | 10 (21.7) | 0 (0.0) | <0.001 |
| JHP917, n (%) | 0 (0.0) | 9 (18.0) | 0.003 |
| JHP918, n (%) | 4 (8.7) | 9 (18.0) | 0.183 |
| oipA, n (%) | 7 (15.2) | 3 (6.0) | 0.187 |
| 16srRNA, n (%) | 46 (100.0) | 50 (100.0) | 1.000 |
| ureA, n (%) | 10 (21.7) | 2 (4.0) | 0.009 |
| vacA s1, n (%) | 46 (100.0) | 50 (100.0) | 1.000 |
| s1a, n (%) | 2 (4.3) | 11 (22.0) | 0.012 |
| s1b, n (%) | 46 (100.0) | 50 (100.0) | 1.000 |
| s1c, n (%) | 42 (91.3) | 39 (78.0) | 0.073 |
| vacA m1, n (%) | 46 (100.0) | 50 (100.0) | 1.000 |
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p-Value | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Age | 1.010 (0.962–1.061) | 0.691 | ||
| Sex (male) | 0.836 (0.198–3.526) | 0.808 | ||
| dupA | 0.434 (0.124–1.520) | 0.192 | ||
| iceA1 | 0.150 (0.031–0.727) | 0.018 | 0.163 (0.032–0.819) | 0.028 |
| JHP918 | 0.434 (0.124–1.520) | 0.192 | ||
| oipA | 2.812 (0.681–11.605) | 0.153 | ||
| ureA | 6.667 (1.375–32.317) | 0.018 | 6.148 (1.221–30.958) | 0.028 |
| vacA s1a | 0.161 (0.034–0.772) | 0.022 | ||
| vacA s1c | 2.962 (0.870–10.077) | 0.082 | ||
| ureA+ (n = 10) | ureA− (n = 36) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age at diagnosis, years, mean ± SD | 66.6 ± 6.8 | 60.8 ± 10.1 | 0.114 |
| Male sex, n (%) | 6 (60.0) | 30 (83.3) | 1.189 |
| Eradication success rate | 5/5 (100.0) | 10/12 (83.3) | 0.669 |
| Tumor size, cm, mean ± SD | 2.8 ± 1.6 | 3.0 ± 2.8 | 0.723 |
| Tumor location, n (%) | 1.000 | ||
| Upper | 2 (20.0) | 10 (27.8) | |
| Middle | 6 (60.0) | 20 (55.6) | |
| Lower | 2 (20.0) | 6 (16.7) | |
| Tumor type, n (%) | 1.000 | ||
| EGC | 10 (100.0) | 34 (94.4) | |
| AGC | 0 (0.0) | 2 (5.6) | |
| Histology, n (%) | 0.697 | ||
| WD/MD | 1 (10.0) | 7 (19.4) | |
| PD/SRC | 2 (20.0) | 10 (27.8) | |
| GCLS | 7 (70.0) | 19 (52.8) | |
| AJCC TNM stage, n (%) | 1.000 | ||
| I | 10 (100.0) | 34 (94.4) | |
| II | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| III | 0 (0.0) | 2 (5.6) | |
| Lymphovascular invasion, n (%) | 0 (0.0) | 4 (11.1) | 0.562 |
| Perineural invasion, n (%) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (5.6) | 1.000 |
| Treatment method, n (%) | 0.717 | ||
| ESD | 7 (70.0) | 21 (58.3) | |
| Surgery | 3 (30.0) | 15 (41.7) | |
| Recurrence-free survival, mean ± SD, median (IQR) | 36.2 ± 12.4, 43.0 (28.0–45.0) | 36.4 ± 19.2, 43.0 (28.0–45.0) | 0.423 |
| Overall survival, mean ± SD, median (IQR) | 37.9 ± 8.7, 27.5 (23.0–49.5) | 38.3 ± 18.3, 29.5 (23.3–49.5) | 0.503 |
| Primer | Sequence (5′-3′) | Annealing Temperature | Size (bp) of PCR Product |
|---|---|---|---|
| cagA | GAT AAC AGG CAA GCT TTT GAG G | 55 | 349 |
| CTG CAA AAG ATT GTT TGG CAG A | |||
| vacA s1 | ATG GAA ATA CAA CAA ACA CAC | 55 | 259 |
| CTG CTT GAA TGC GCC AAA C | |||
| vacA s1a | TCT YGC TTT AGT AGG AGC | 55 | 212 |
| CTG CTT GAA TGC GCC AAA C | |||
| vacA s1b | AGC GCC ATA CCC CAA GAG | 55 | 187 |
| CTG CTT GAA TGC GCC AAA C | |||
| vacA s1c | CTY GCT TTA GTR GGG YTA | 55 | 213 |
| CTG CTT GAA TGC GCC AAA C | |||
| VAG (vacA m1) | CAA TCT GTC CAA TCA AGC GAG | 50 | 570 |
| GCG TCT AAA TAA TTC CAA GG | |||
| VA3 | GGT CAA AAT GCG GTC ATG G | 55 | |
| CCA TTG GTA CCT GTA GAA AC | |||
| VA4 | GGA GCC CCA GGA AAC ATT G | 55 | |
| CAT AAC TAG CGC CTT GCA C | |||
| ureA | GCC AAT GGT AAA TTA GTT | 50 | |
| CTC CTT AAT TGT TTT TAC | |||
| 16s rDNA | CTG GAG AGA CTA AGC CCT CC | 55 | |
| AGG ATC AAG GTT TAA GGA TT | |||
| iceA1 | GTG TTT TTA ACC AAA GTA TC | 50 | 247 |
| CTA TAC CCA STY TCT TTG CA | |||
| iceA2 | GTT GGG TAT ATC ACA ATT TAT | 50 | 229 or 334 |
| TTR CCC TAT TTT CTA GTA GGT | |||
| OipA | CAA GCG CTT AGA TAG GC | 50 | 427 |
| AAG GCA TTT TCT GCT GAA | |||
| JHP917 | TGG TTT CTA CTG ACA GAG CGC | 55 | 307 |
| AAC ACG CTG ACA GGA CAA TCT CCC | |||
| JHP918 | CCCT ATA TCG CTA ACG CGC TCG | 55 | 276 |
| AAG CTG AAG CGT TTG TAA CG | |||
| dupA | TAA GCG TGA TCA CTC TGG AT | 55 | 350 |
| TGG AAC GCC GCA TTC TAT TA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Noh, J.H.; Ahn, J.Y.; Na, H.K.; Lee, J.H.; Jung, K.W.; Kim, D.H.; Choi, K.D.; Song, H.J.; Lee, G.H.; Jung, H.-Y. Distribution and Clinical Impact of Helicobacter pylori Virulence Factors in Epstein–Barr-Virus-Associated Gastric Cancer. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14060580
Noh JH, Ahn JY, Na HK, Lee JH, Jung KW, Kim DH, Choi KD, Song HJ, Lee GH, Jung H-Y. Distribution and Clinical Impact of Helicobacter pylori Virulence Factors in Epstein–Barr-Virus-Associated Gastric Cancer. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(6):580. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14060580
Chicago/Turabian StyleNoh, Jin Hee, Ji Yong Ahn, Hee Kyong Na, Jeong Hoon Lee, Kee Wook Jung, Do Hoon Kim, Kee Don Choi, Ho June Song, Gin Hyug Lee, and Hwoon-Yong Jung. 2025. "Distribution and Clinical Impact of Helicobacter pylori Virulence Factors in Epstein–Barr-Virus-Associated Gastric Cancer" Antibiotics 14, no. 6: 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14060580
APA StyleNoh, J. H., Ahn, J. Y., Na, H. K., Lee, J. H., Jung, K. W., Kim, D. H., Choi, K. D., Song, H. J., Lee, G. H., & Jung, H.-Y. (2025). Distribution and Clinical Impact of Helicobacter pylori Virulence Factors in Epstein–Barr-Virus-Associated Gastric Cancer. Antibiotics, 14(6), 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14060580






