Identification and Antibiotic Resistance of Isolates from Poultry Meat and Poultry Meat By-Products Exhibiting Characteristic Salmonella Morphology on Chromogenic Agar
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
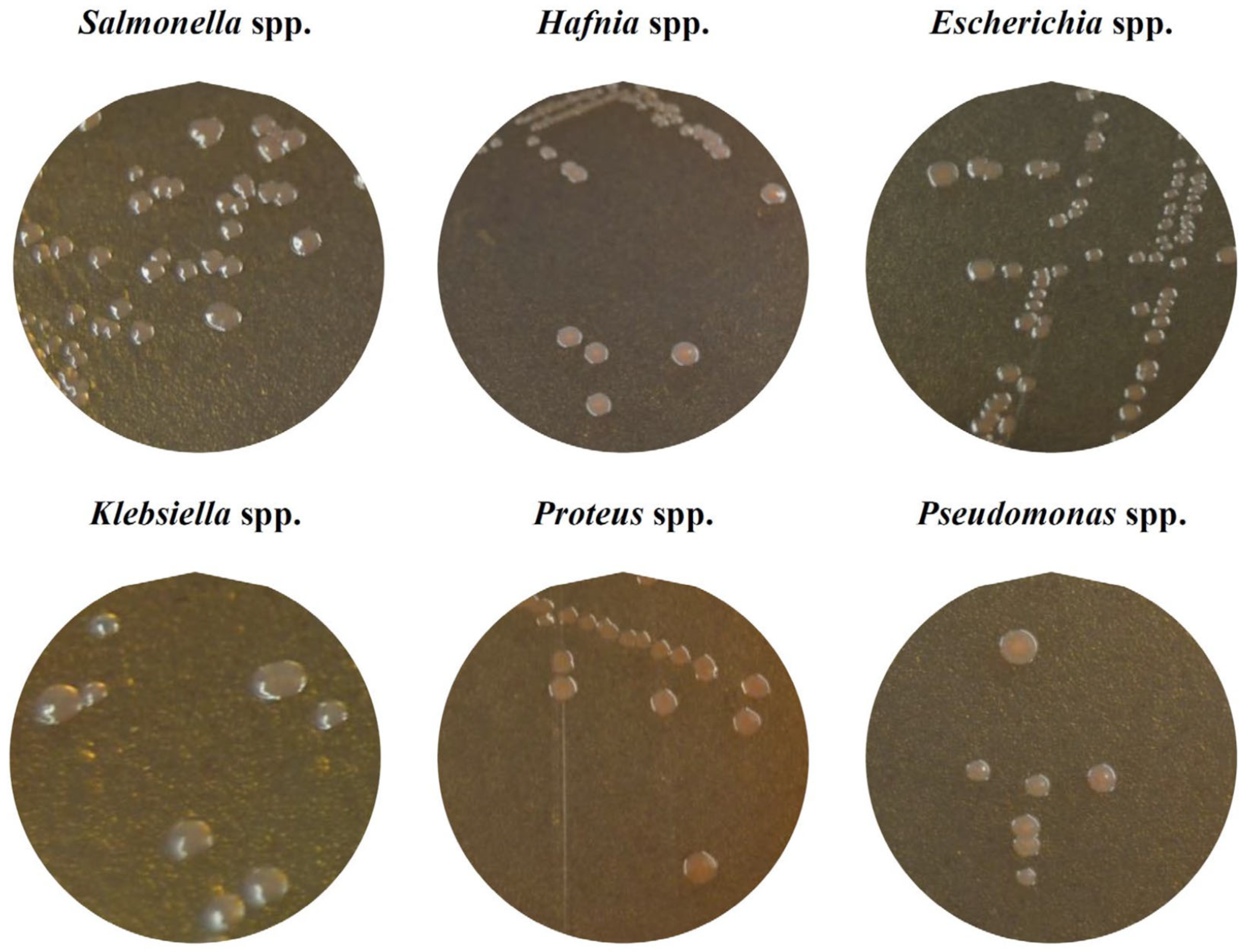
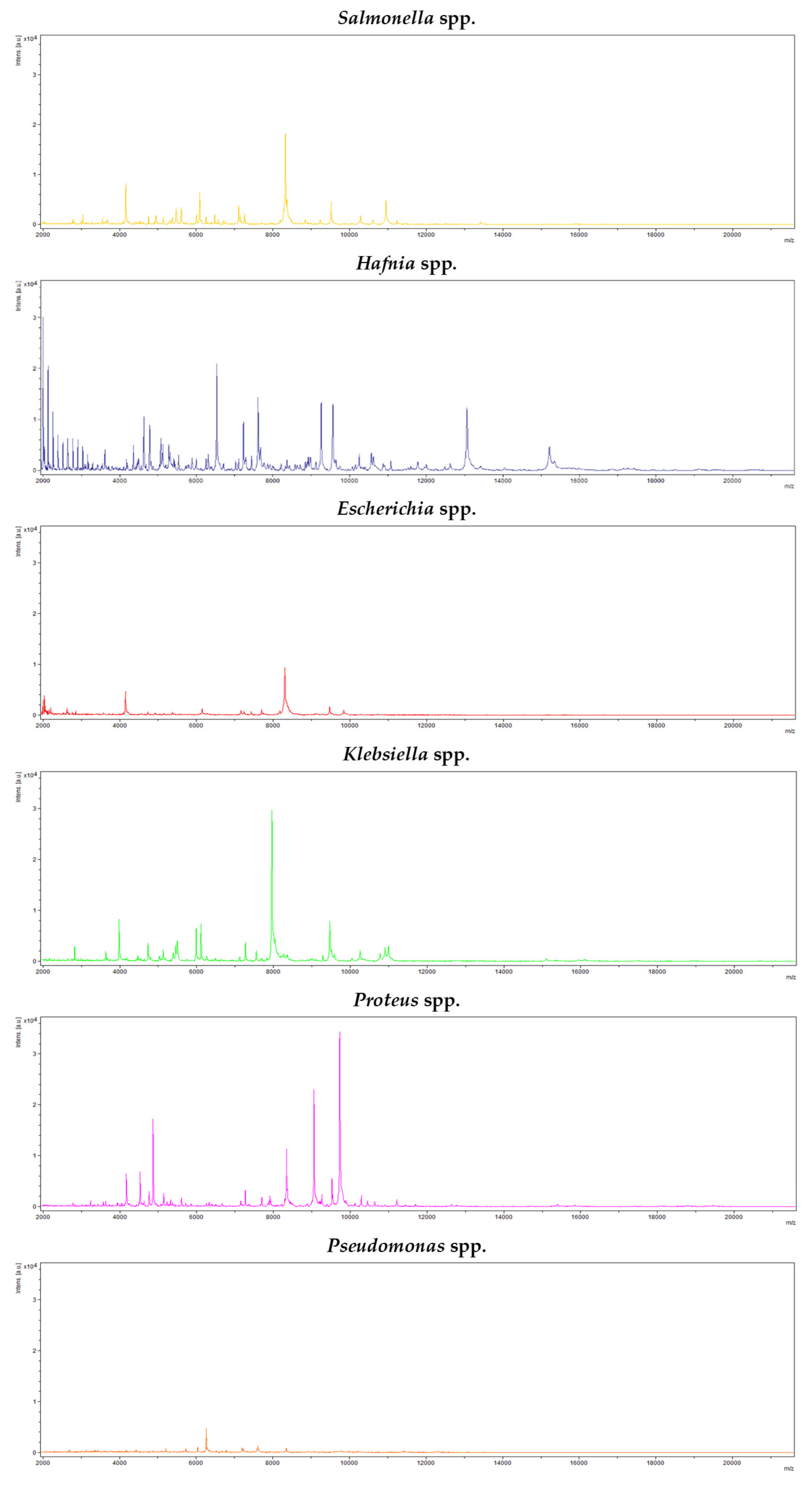
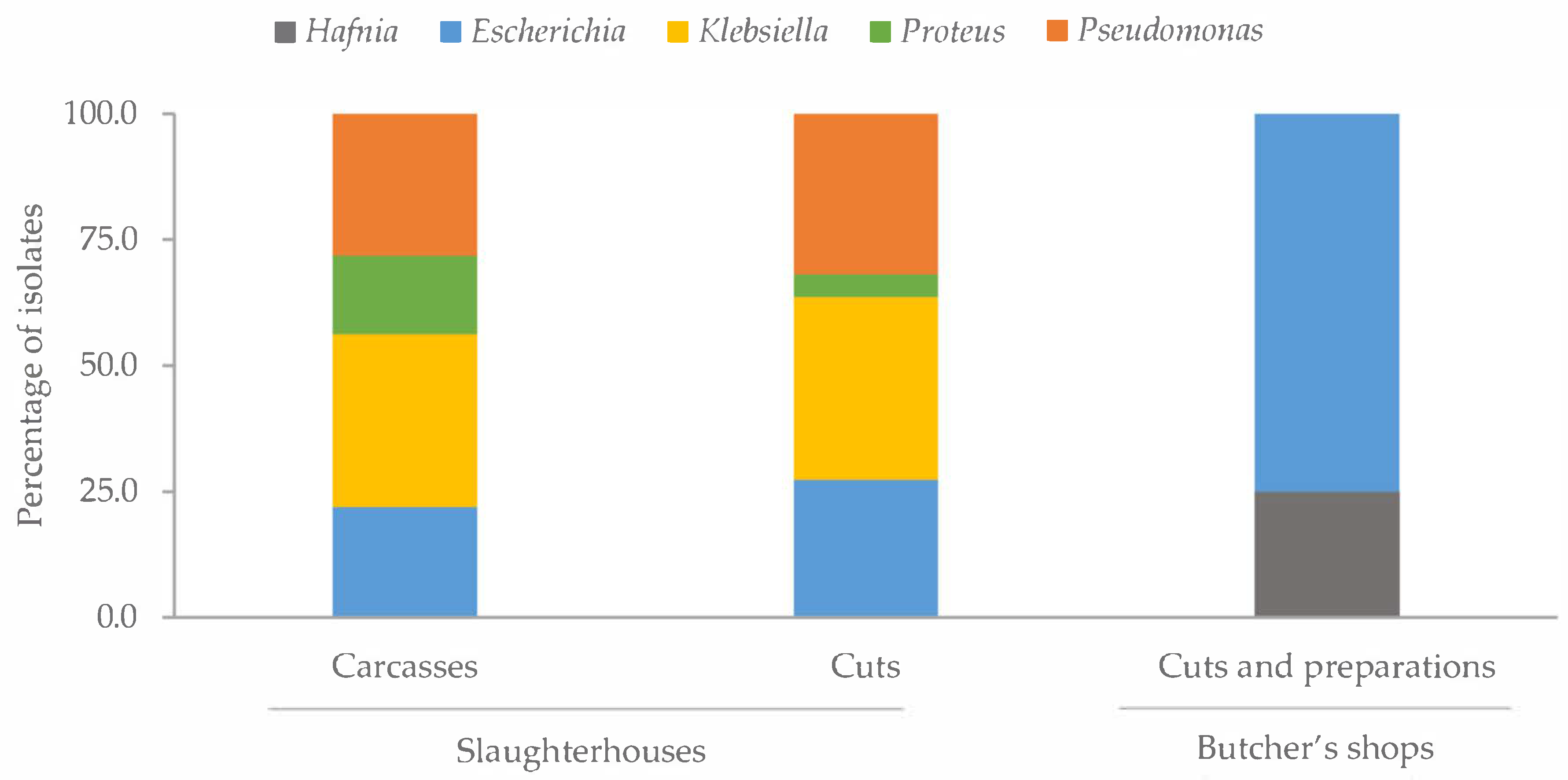
2.1. Identification of Colonies with Characteristic Morphology of Salmonella
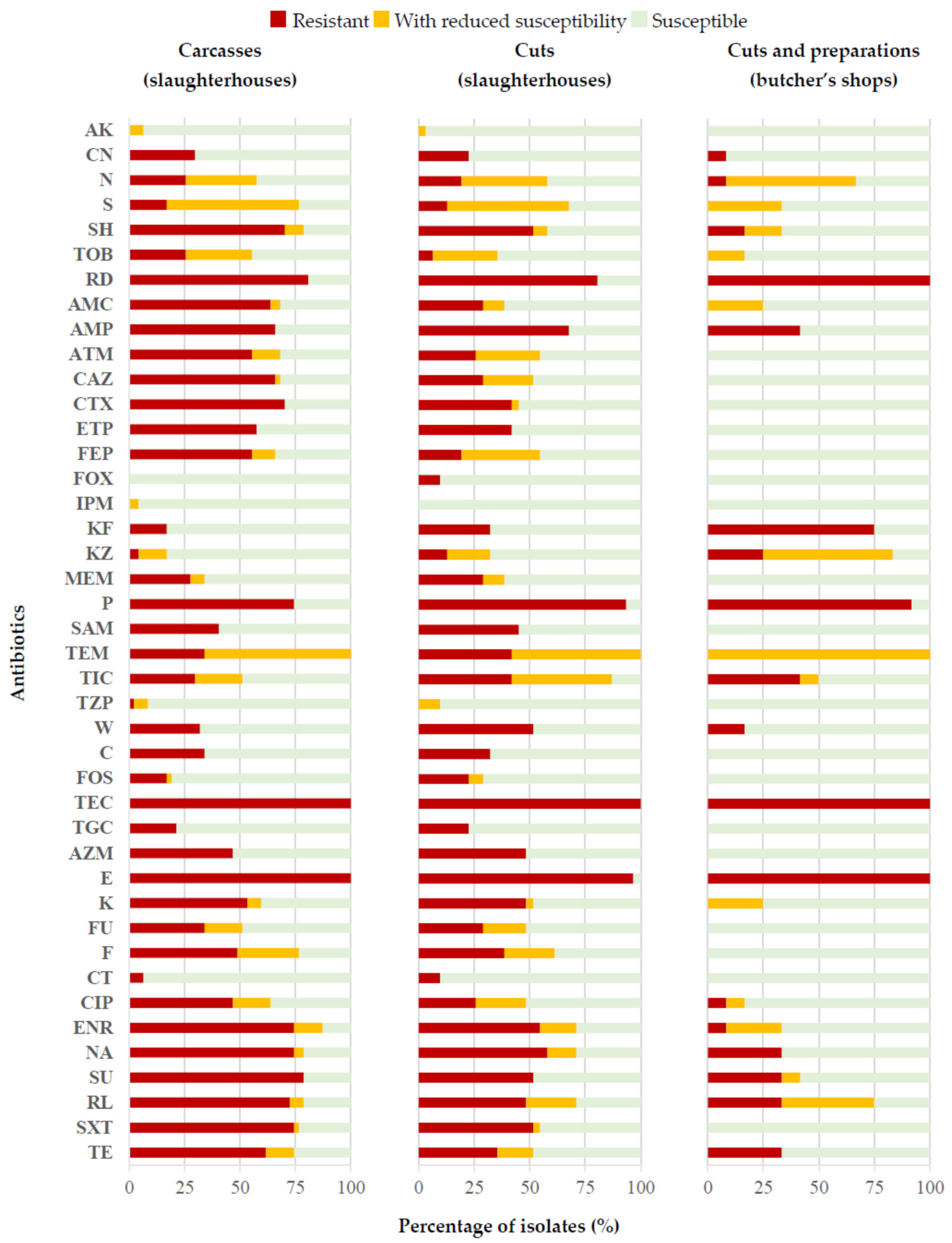
2.2. Antibiotic Susceptibility
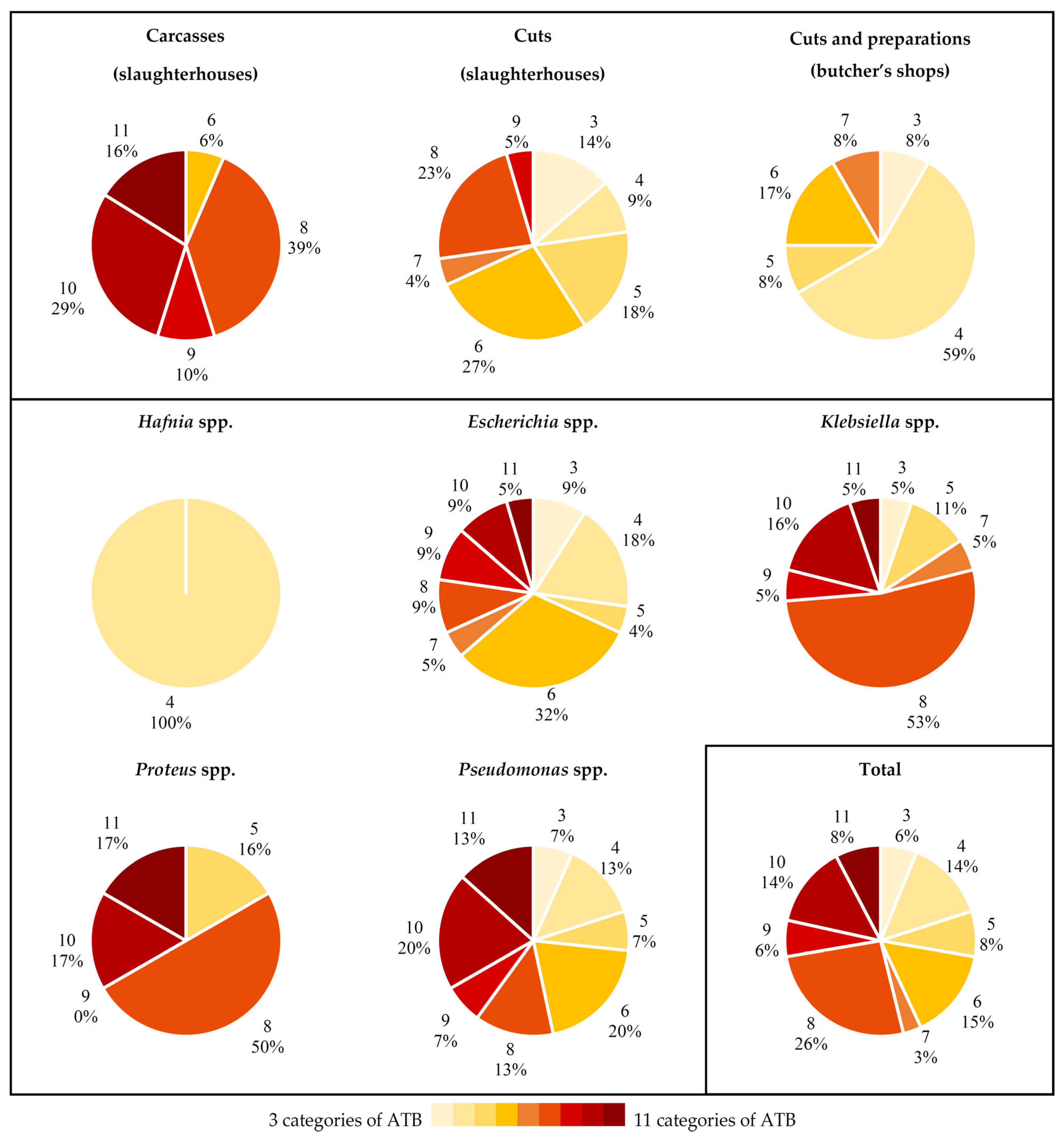
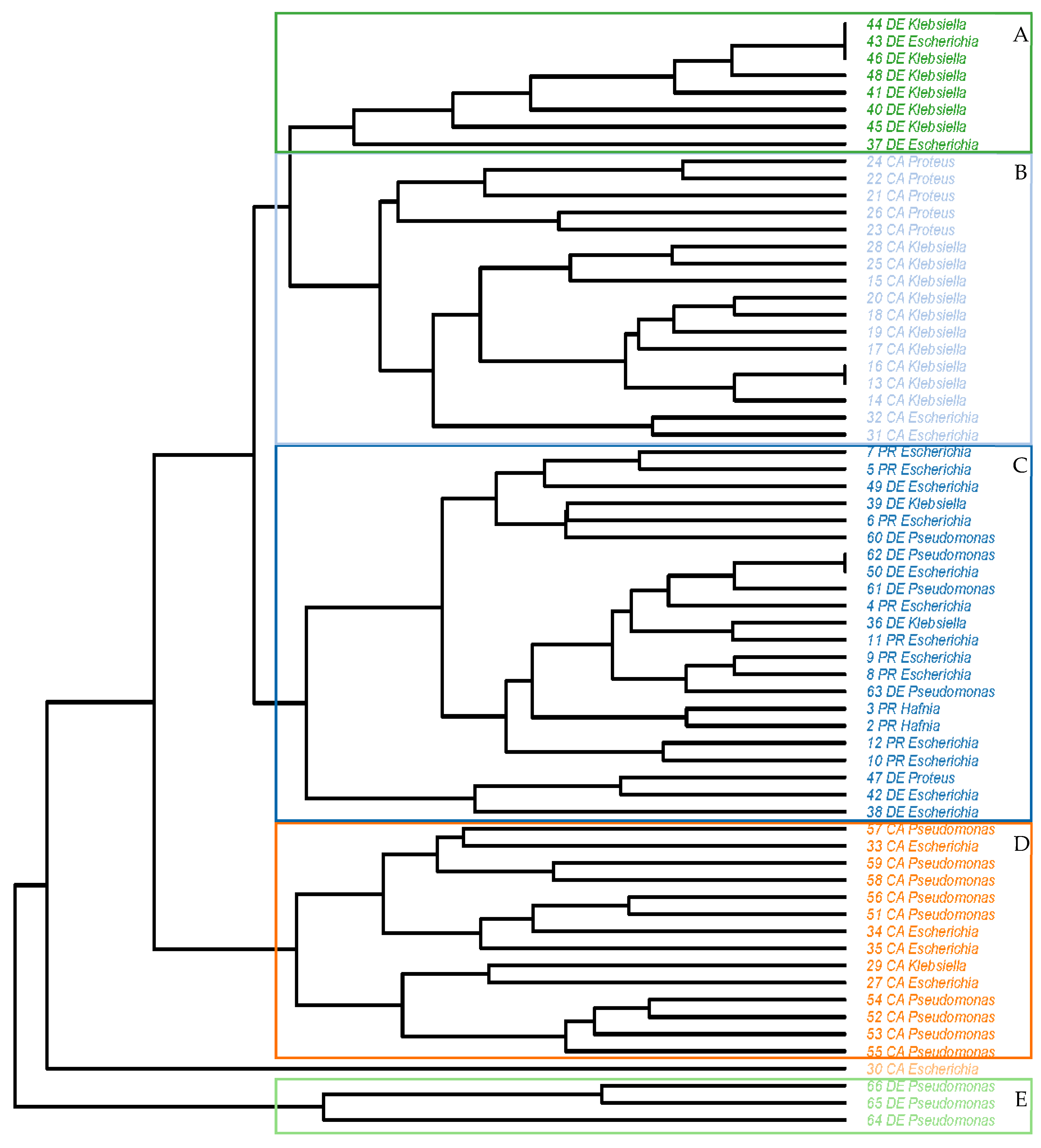
2.3. Antibiotic Resistance Patterns
3. Discussion
3.1. Identification of Colonies with Characteristic Morphology of Salmonella
3.2. Antibiotic Susceptibility
3.3. Antibiotic Resistance Patterns
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Processing
4.2. Isolation and Identification of Strains
4.3. Antibiotic Resistance Determination
4.4. Antibiotic Resistance Patterns
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Farmer, J.J.; Farmer, M.K.; Holmes, B. The Enterobacteriaceae: General characteristics. In Topley & Wilson’s Microbiology and Microbial Infections; Borriello, S.P., Murray, P.R., Funke, G., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 1317–1359. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, H.; De Reu, K.; Gabriël, S.; Mattheus, W.; De Zutter, L.; Rasschaert, G. Salmonella prevalence and persistence in industrialized poultry slaughterhouses. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 100991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzón-Durán, L.; Capita, R.; Alonso-Calleja, C. Microbial loads and antibiotic resistance patterns of Staphylococcus aureus in different types of raw poultry-based meat preparations. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 4046–4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OECD-FAO. Agricultural Outlook 2023–2032. Available online: https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/agriculture-and-food/oecd-fao-agricultural-outlook-2023-2032_08801ab7-en (accessed on 19 April 2025).
- Capita, R.; Castaño-Arriba, A.; Rodríguez-Melcón, C.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P.; Alonso-Calleja, C. Diversity, antibiotic resistance, and biofilm-forming ability of enterobacteria isolated from red meat and poultry preparations. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.M.; Runyon, M.; Herrman, T.J.; Phillips, R.; Hsieh, J. Review of Salmonella detection and identification methods: Aspects of rapid emergency response and food safety. Food Control 2015, 47, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 6579-1:2017; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Detection, Enumeration and Serotyping of Salmonella—Part 1: Detection of Salmonella spp. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Lauer, W.F.; Martinez, F.L.; Hammack, T. RAPID’ Salmonella Chromogenic Medium. J. AOAC Int. 2009, 92, 1871–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruzzese, E.; Giannattasio, A.; Guarino, A. Antibiotic treatment of acute gastroenteritis in children. Food Res. 2018, 7, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozwandowicz, M.; Brouwer, M.S.M.; Fischer, J.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Gonzalez-Zorn, B.; Guerra, B.; Mevius, D.J.; Hordijk, J. Plasmids carrying antimicrobial resistance genes in Enterobacteriaceae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 1121–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrill, H.J.; Pogue, J.M.; Kaye, K.S.; LaPlante, K.L. Treatment options for carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae infections. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2015, 2, ofv050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, C.; Silva, V.; Capita, R.; Alonso-Calleja, C.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P. Implications of antibiotics use during the COVID-19 pandemic: Present and future. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 3413–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capita, R.; Alonso-Calleja, C. Antibiotic-resistant bacteria: A challenge for the food industry. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 53, 11–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Jiménez, D.; García-Meniño, I.; Fernández, J.; García, V.; Mora, A. Chicken and turkey meat: Consumer exposure to multidrug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae including mcr-carriers, uropathogenic E. coli and high-risk lineages such as ST131. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 331, 108750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzeh, R.E.; Adewumi, F.; Odumosu, B.T. Antibiotic resistance and plasmid analysis of Enterobacteriaceae isolated from retail meat in Lagos Nigeria. One Health Outlook 2021, 3, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregová, G.; Kmetova, M.; Kmet, V.; Venglovsky, J.; Feher, A. Antibiotic resistance of Escherichia coli isolated from a poultry slaughterhouse. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2012, 19, 75–79. [Google Scholar]
- Manal, A.H.; Saad, S.F.; Zahraa, A.J.; Saba, T.H. Chromogenic agar media for rapid detection of Enterobacteriaceae in food samples. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2015, 9, 2354–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelopoulou, G.; Burriel, A.R.; Solomakos, N. Distinctive culture expressions of enterobacteria interfering with isolation of Salmonella spp. during the application of the recommended ISO 6579-1: 2017. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pławińska-Czarnak, J.; Wódz, K.; Kizerwetter-Świda, M.; Nowak, T.; Bogdan, J.; Kwieciński, P.; Kwieciński, A.; Anusz, K. Citrobacter braakii yield false-positive identification as Salmonella, a note of caution. Foods 2021, 10, 2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrique-Mas, J.J.; Barnes, S.; McLaren, I.; Davies, R. Comparison of three plating media for the isolation of Salmonella from poultry environmental samples in Great Britain using ISO 6579: 2002 (Annex D). J. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 107, 1976–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, B.C.; Rostagno, M.H. Comparison of five culture methods for Salmonella isolation from swine fecal samples of known infection status. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2008, 20, 620–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yhiler, N.Y.; Bassey, E.B.; Useh, M.F. Evaluation of the performance of two selective enrichment media and two selective plating media for the detection of Salmonella from primary poultry production, according to ISO 6579: 2002. Open J. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 5, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iredell, J.; Brown, J.; Tagg, K. Antibiotic resistance in Enterobacteriaceae: Mechanisms and clinical implications. BMJ 2016, 352, h6420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgül, Ö.; Körkoca, H.; Bora, G. Analysis of antibiotic resistance of KPC-2-positive Klebsiella pneumoniae strains isolated from blood cultures in Van, Turkey. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2024, 28, 1272–1281. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nada, H.G.; El-Tahan, A.S.; El-Didamony, G.; Askora, A. Detection of multidrug-resistant Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in some food products and cattle feces in Al-Sharkia, Egypt: One health menace. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panera-Martínez, S.; Rodríguez-Melcón, C.; Rodríguez-Campos, D.; Pérez-Estébanez, N.; Capita, R.; Alonso-Calleja, C. Levels of different microbial groups on inert surfaces of poultry slaughterhouses: Identification using matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight and detection of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-and carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteria. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barka, M.S.; Cherif-Anntar, A.; Benamar, I. Antimicrobial resistance patterns and transferable traits in Enterobacteriaceae isolates from poultry in Tlemcen, Algeria. Afr. J. Clin. Experimental Microbiol. 2021, 22, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushen, A.; Tekalign, E.; Abayneh, M. Drug-and multidrug-resistance pattern of Enterobacteriaceae isolated from droppings of healthy chickens on a poultry farm in Southwest Ethiopia. Infect. Drug Res. 2021, 2021, 2051–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elabbasy, M.T.; Hussein, M.A.; Algahtani, F.D.; Abd El-Rahman, G.I.; Morshdy, A.E.; Elkafrawy, I.A.; Adeboye, A.A. MALDI-TOF MS based typing for rapid screening of multiple antibiotic resistance E. coli and virulent non-O157 shiga toxin-producing E. coli isolated from the slaughterhouse settings and beef carcasses. Foods 2021, 10, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savin, M.; Bierbaum, G.; Mutters, N.T.; Schmithausen, R.M.; Kreyenschmidt, J.; García-Meniño, I.; Schmoger, S.; Käsbohrer, A.; Hammerl, J.A. Genetic characterization of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella spp. from municipal and slaughterhouse wastewater. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puangseree, J.; Jeamsripong, S.; Prathan, R.; Pungpian, C.; Chuanchuen, R. Resistance to widely-used disinfectants and heavy metals and cross resistance to antibiotics in Escherichia coli isolated from pigs, pork and pig carcass. Food Control 2021, 124, 107892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizi, K.S.; Hasanzade, S.; Soleimanpour, S.; Youssefi, M.; Jamehdar, S.A.; Ghazvini, K.; Safdari, H.; Farsiani, H. Phenotypic and molecular characterization of antimicrobial resistance in clinical species of Enterobacter, Serratia, and Hafnia in Northeast Iran. Gene Rep. 2021, 25, 101352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmonir, W.; Abd El-Aziz, N.K.; Tartor, Y.H.; Moustafa, S.M.; Abo Remela, E.M.; Eissa, R.; Saad, H.A.; Tawab, A.A. Emergence of colistin and carbapenem resistance in extended-spectrum β-lactamase producing Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from chickens and humans in Egypt. Biology 2021, 10, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xin, L.; Peng, C.; Liu, C.; Wang, P.; Yu, L.; Liu, M.; Wang, F. Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility profiles of ESBL-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae from broiler chicken farms in Shandong Province, China. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 102002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Permatasari, D.A.; Witaningrum, A.M.; Wibisono, F.J.; Effendi, M.H. Detection and prevalence of multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae strains isolated from poultry farms in Blitar, Indonesia. Biodivers. J. Biol. Divers. 2000, 21, 4642–4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veloo, Y.; Thahir, S.S.; Rajendiran, S.; Hock, L.K.; Ahmad, N.; Muthu, V.; Shaharudin, R. Multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacteria and extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae from the poultry farm environment. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e02694-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishaq, K.; Ahmad, A.; Rafique, A.; Aslam, R.; Ali, S.; Shahid, M.A.; Sarwar, N.; Aslam, M.A.; Aslam, B.; Arshad, M.I. Occurrence and antimicrobial susceptibility of Proteus mirabilis from chicken carcass. Pak. Vet. J. 2022, 42, 576–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Peng, C.; Zhang, G.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, M.; Wang, F. Prevalence and characteristics of multidrug-resistant Proteus mirabilis from broiler farms in Shandong Province, China. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owoseni, M.C.; Oyigye, O.; Sani, B.; Lamin, J.; Chere, A. Antimicrobial resistance and virulence genes profiling of Proteus species from poultry farms in Lafia, Nigeria. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Ghany, W.A. Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection of avian origin: Zoonosis and one health implications. Vet. World 2021, 14, 2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marouf, S.; Li, X.; Salem, H.M.; Ahmed, Z.S.; Nader, S.M.; Shaalan, M.; Awad, F.H.; Zhou, H.; Cheang, T. Molecular detection of multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa of different avian sources with pathogenicity testing and in vitro evaluation of antibacterial efficacy of silver nanoparticles against multidrug-resistant P. aeruginosa. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odoi, H.; Boamah, V.E.; Boakye, Y.D.; Agyare, C. Prevalence and phenotypic and genotypic resistance mechanisms of multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from clinical, environmental, and poultry litter samples from the Ashanti region of Ghana. J. Environ. Public Health 2021, 2021, 9976064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaya, E.; Reyes, D.; Paniagua, M.; Calderón, S.; Rashid, M.U.; Colque, P.; Kühn, I.; Möllby, R.; Weintraub, A.; Nord, C.E. Antibiotic resistance patterns of Escherichia coli isolates from different aquatic environmental sources in Leon, Nicaragua. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, R.G.; Festivo, M.L.; Araujo, M.S.; Reis, E.M.; Lázaro, N.S.; Rodrigues, D.P. Antimicrobial susceptibility and serovars of Salmonella circulating in commercial poultry carcasses and poultry products in Brazil. J. Food Prot. 2013, 76, 2011–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 33rd ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- EUCAST. The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters. Version 13.1. Available online: http://www.eucast.org (accessed on 19 April 2025).
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R. Available online: http://www.rstudio.com/ (accessed on 19 April 2025).
- Tang, D.; Chen, M.; Huang, X.; Zhang, G.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, G.; Wu, S.; Wang, Y. Rplot: A free online platform for data visualization and graphing. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0294236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample Type/Microbial Genera | Resistance * | Reduced Susceptibility * | Susceptibility * | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number ATB | % | Number ATB | % | Number ATB | % | |
| Carcasses 1 | 18.89 ± 7.13 | 45.0 | 3.91 ± 1.54 | 9.3 | 19.19 ± 5.84 | 45.7 |
| Cuts 2 | 15.81 ± 7.13 | 37.6 | 5.19 ± 2.30 | 12.4 | 12.37 ± 6.93 | 50.0 |
| Cuts and Preparations 3 | 7.75 ± 2.38 | 18.5 | 4.25 ± 2.09 | 10.1 | 30.00 ± 3.50 | 71.4 |
| Hafnia | 7.33 ± 1.15 | 17.5 | 2.33 ± 1.53 | 5.6 | 32.33 ± 0.58 | 77.0 |
| Escherichia | 13.41 ± 7.31 | 31.9 | 4.27 ± 4.23 | 10.2 | 24.32 ± 7.09 | 57.9 |
| Klebsiella | 17.89 ± 4.63 | 42.6 | 3.42 ± 1.30 | 8.1 | 20.68 ± 4.32 | 49.2 |
| Proteus | 19.17 ± 4.79 | 45.6 | 4.17 ± 2.14 | 9.9 | 18.67 ± 4.97 | 44.4 |
| Pseudomonas | 17.06 ± 8.39 | 40.6 | 6.44 ± 2.25 | 15.3 | 18.50 ± 7.19 | 44.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Panera-Martínez, S.; Rodríguez-Melcón, C.; González-Machado, C.; Alonso-Calleja, C.; Capita, R. Identification and Antibiotic Resistance of Isolates from Poultry Meat and Poultry Meat By-Products Exhibiting Characteristic Salmonella Morphology on Chromogenic Agar. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 540. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14060540
Panera-Martínez S, Rodríguez-Melcón C, González-Machado C, Alonso-Calleja C, Capita R. Identification and Antibiotic Resistance of Isolates from Poultry Meat and Poultry Meat By-Products Exhibiting Characteristic Salmonella Morphology on Chromogenic Agar. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(6):540. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14060540
Chicago/Turabian StylePanera-Martínez, Sarah, Cristina Rodríguez-Melcón, Camino González-Machado, Carlos Alonso-Calleja, and Rosa Capita. 2025. "Identification and Antibiotic Resistance of Isolates from Poultry Meat and Poultry Meat By-Products Exhibiting Characteristic Salmonella Morphology on Chromogenic Agar" Antibiotics 14, no. 6: 540. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14060540
APA StylePanera-Martínez, S., Rodríguez-Melcón, C., González-Machado, C., Alonso-Calleja, C., & Capita, R. (2025). Identification and Antibiotic Resistance of Isolates from Poultry Meat and Poultry Meat By-Products Exhibiting Characteristic Salmonella Morphology on Chromogenic Agar. Antibiotics, 14(6), 540. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14060540





