Pathogenomic Characterization of Multidrug-Resistant Escherichia coli Strains Carrying Wide Efflux-Associated and Virulence Genes from the Dairy Farm Environment in Xinjiang, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Cluster of Orthologous Genes (COG) Functional Classification of MDR E. coli
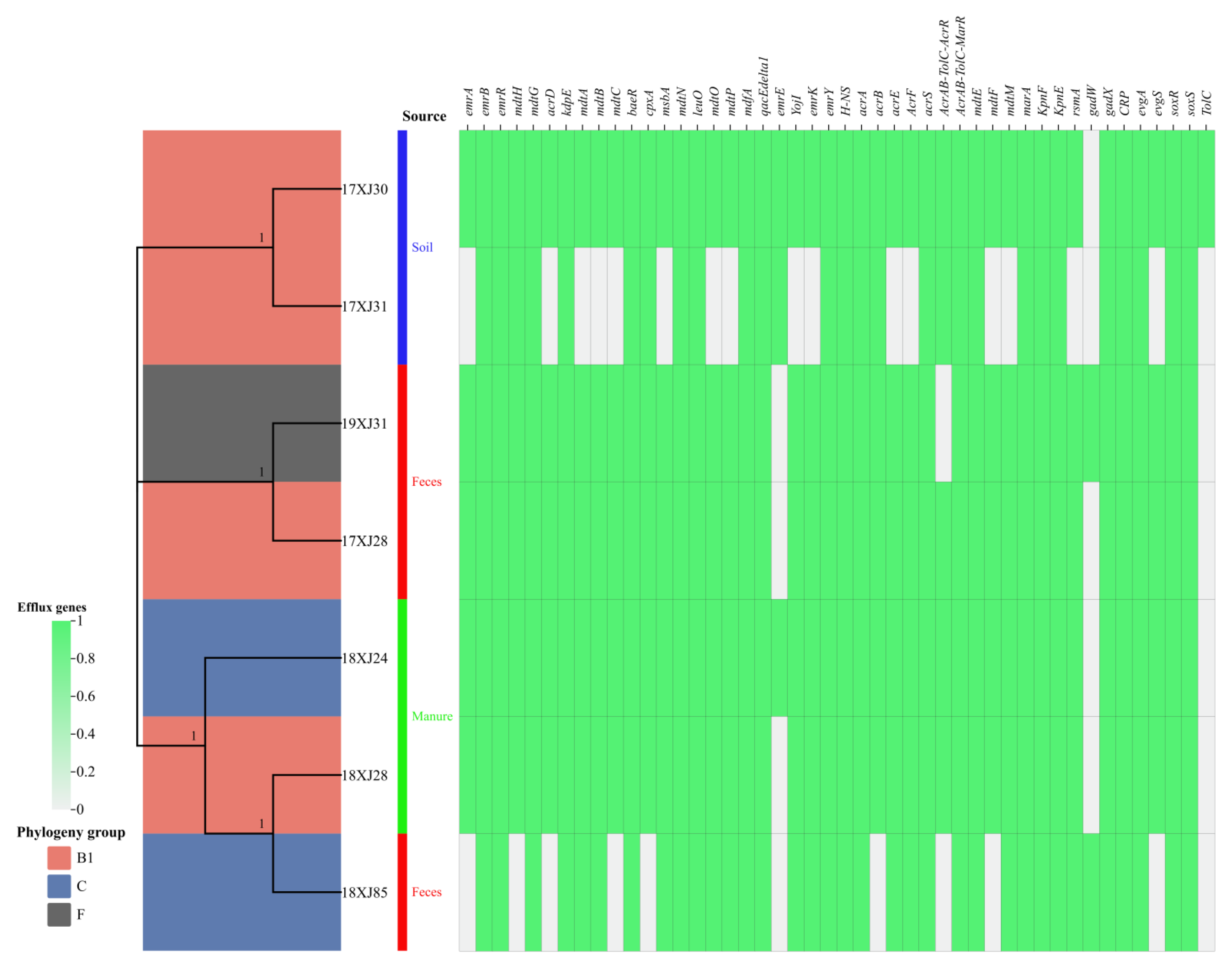
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis and Distribution of Antibiotic Efflux-Associated Genes
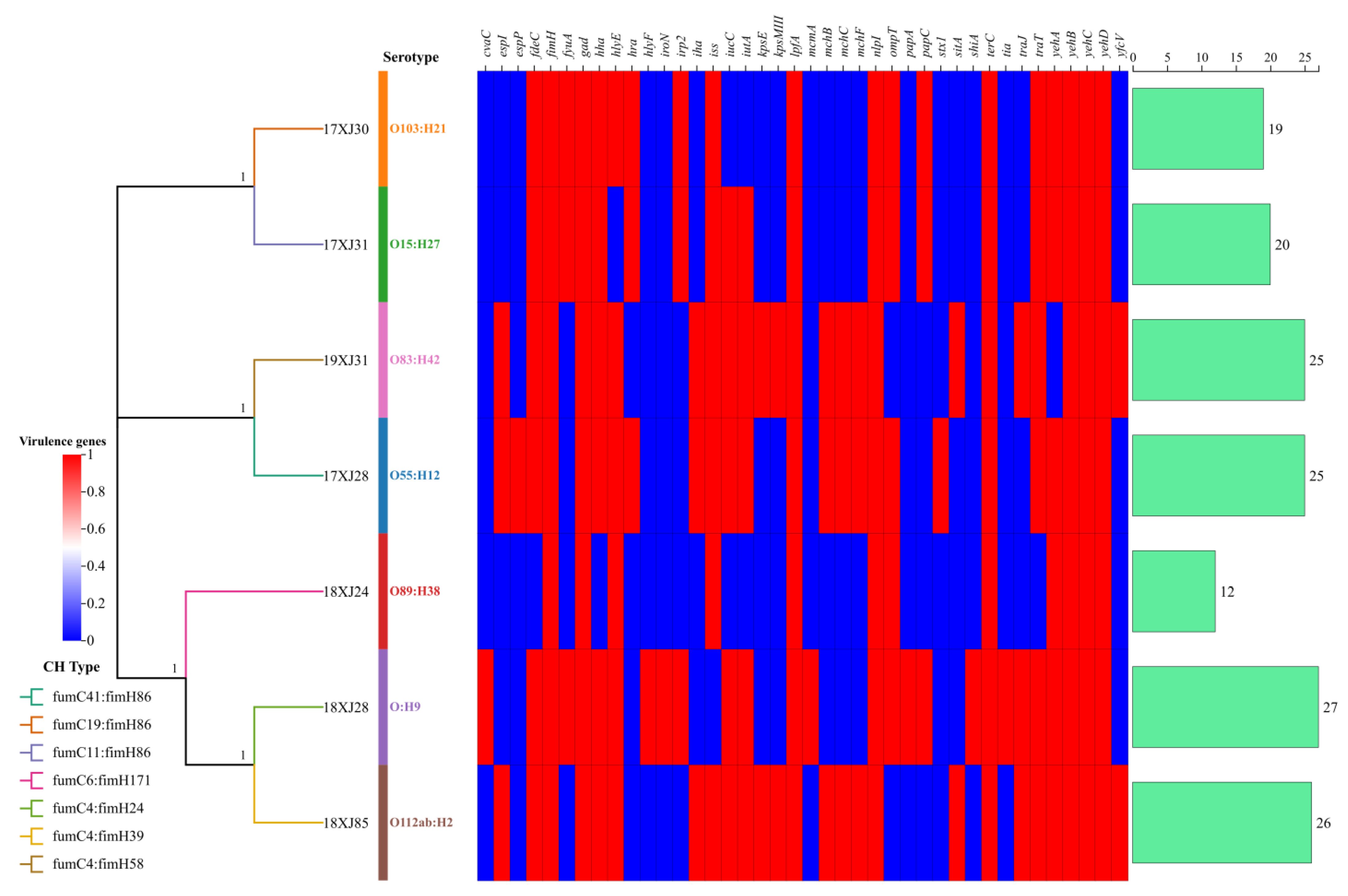
2.3. Serotyping, CH-Typing, and Virulence Determinants Acquired by MDR E. coli
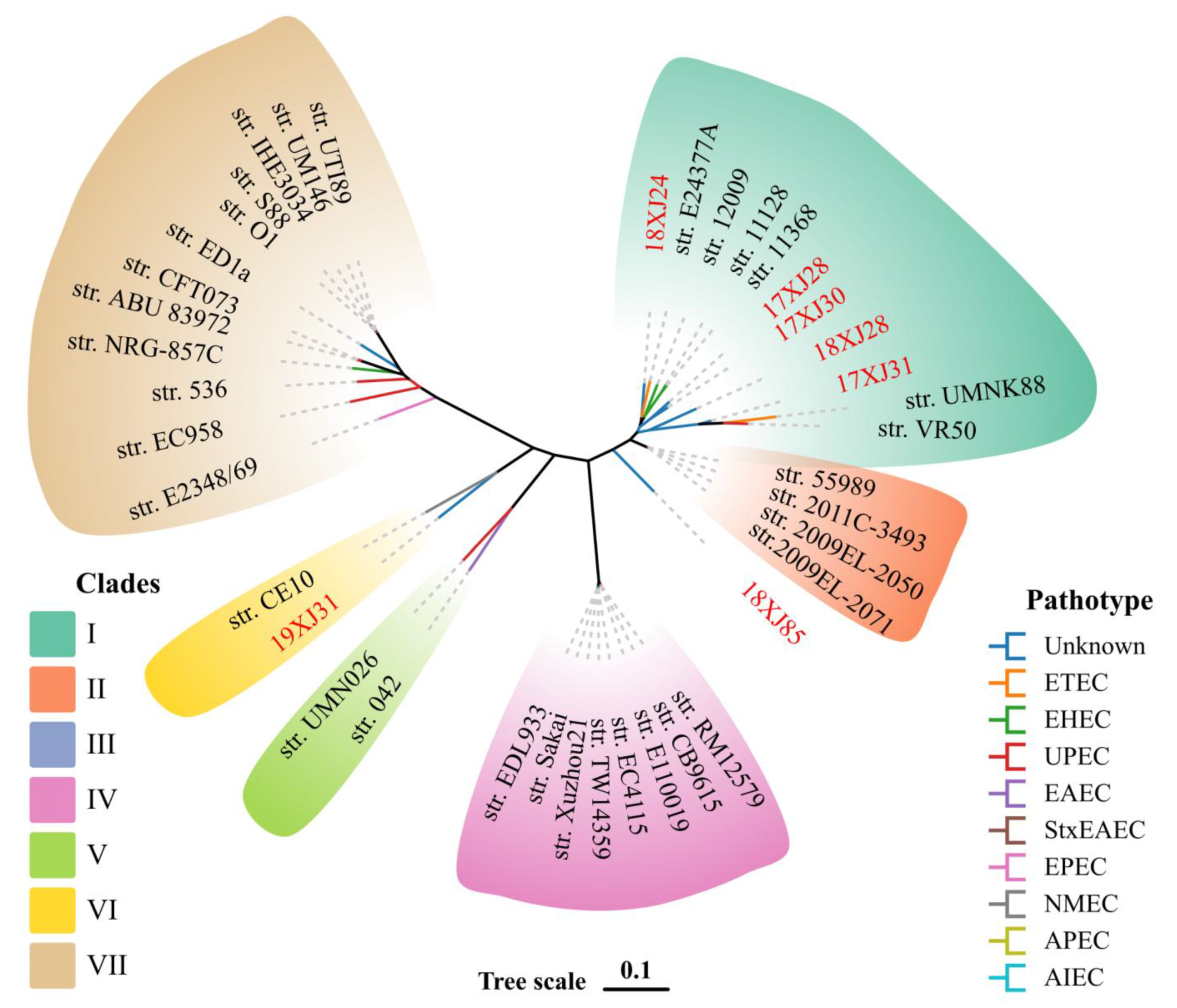
2.4. Phylogenetic Relationship of E. coli Strains with Verified E. coli Pathotypes
2.5. Prophage and Genomic Island-Associated Virulence Genes (VGs)
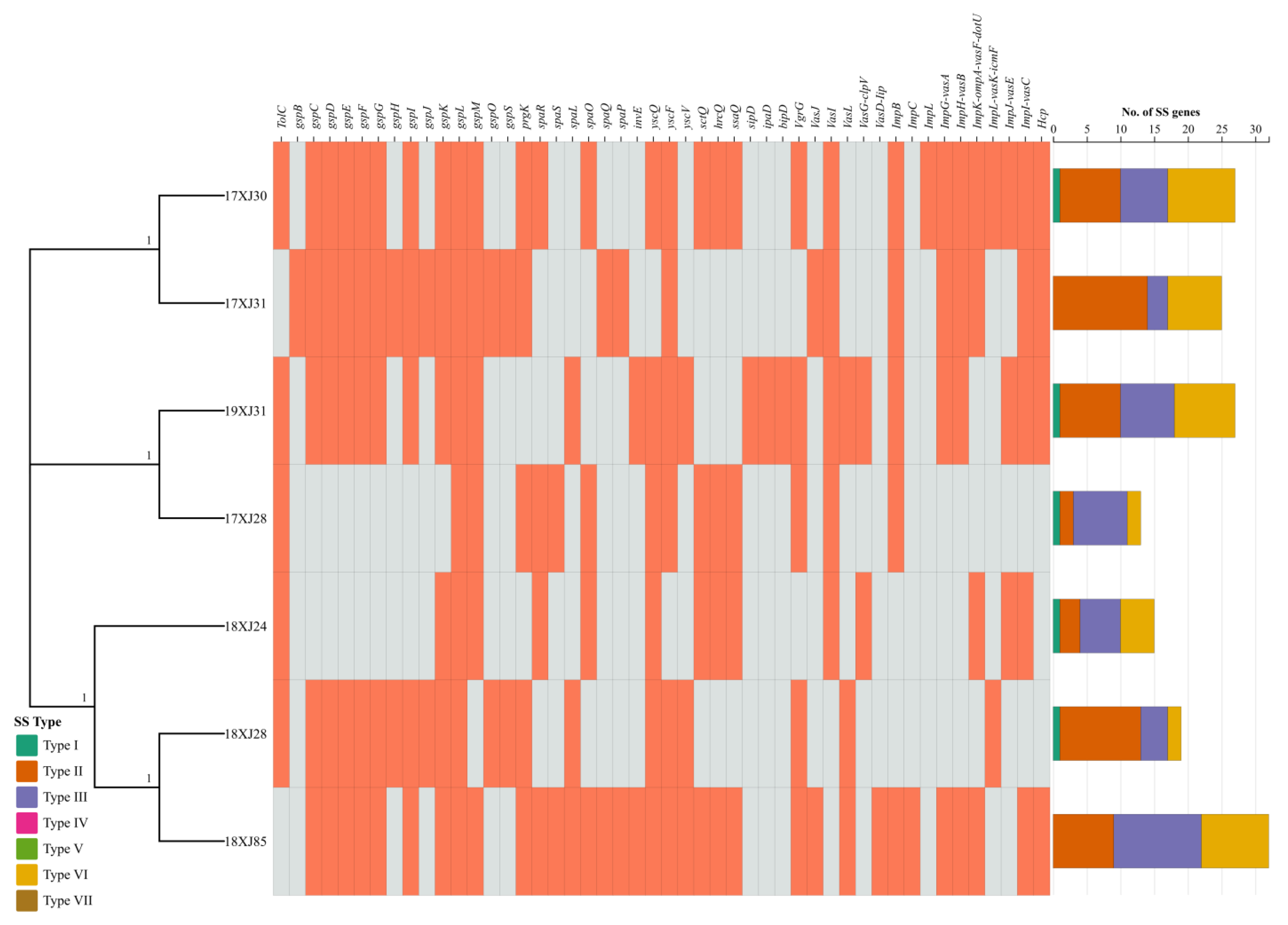
2.6. Bacterial Secretions Systems Related Genes Acquired by MDR E. coli Strains
2.7. Biofilm-Associated Genes Acquired by MDR E. coli Strains
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Origin and Background Information of E. coli Strains
4.2. DNA Extraction, Library Construction, and Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS)
4.3. Data Processing and Genome Assembly
4.4. Pangenome and Bioinformatics Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TNSS | Type N secretion systems |
| CGE | Center for Genomic Epidemiology |
| WGS | Whole Genome Sequencing |
| COG | Cluster of Orthologous Genes |
| EMB | Eosin Methylene Blue |
| VGs | Virulence genes |
| MDR | Multidrug resistance |
| STEC | Shiga toxin-producing E. coli |
| CCCP | Carbonyl-cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone |
| VTEC | Verotoxigenic E. coli |
| APEC | Avian pathogenic E. coli |
| ETEC | Enterotoxigenic E. coli |
| EHEC | Enterohemorrhagic E. coli |
| NMEC | Neonatal meningitis E. coli |
| UPEC | Uropathogenic E. coli |
| EAEC | Enteroaggregative E. coli |
| Ex-PEC | Extraintestinal pathogenic E. coli |
| DEC | Diarrheagenic E. coli |
| MGE | Mobile genetic elements |
| E. coli | Escherichia coli |
| GIs | Genomic islands |
| ARGs | Antibiotic resistance genes |
References
- Shoaib, M.; He, Z.; Geng, X.; Tang, M.; Hao, R.; Wang, S.; Shang, R.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Pu, W. The Emergence of Multidrug Resistant and Virulence Gene Carrying Escherichia coli Strains in the Dairy Environment: A Rising Threat to the Environment, Animal, and Public Health. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1197579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Essendoubi, S.; Keenliside, J.; Reuter, T.; Stanford, K.; King, R.; Lu, P.; Yang, X. Genomic analysis of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O157:H7 from cattle and pork-production related environments. npj Sci. Food 2021, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, R.; Singh, P. Prevalence and Implications of Shiga Toxin-Producing E. coli in Farm and Wild Ruminants. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Yang, X. Genetic Characteristics of the Transmissible Locus of Stress Tolerance (TLST) and TLST Harboring Escherichia coli as Revealed by Large-Scale Genomic Analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 88, e02185-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vangchhia, B.; Abraham, S.; Bell, J.M.; Collignon, P.; Gibson, J.S.; Ingram, P.R.; Johnson, J.R.; Kennedy, K.; Trott, D.J.; Turnidge, J.D.; et al. Phylogenetic Diversity, Antimicrobial Susceptibility and Virulence Characteristics of Phylogroup F Escherichia coli in Australia. Microbiology 2016, 162, 1904–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlos, C.; Pires, M.M.; Stoppe, N.C.; Hachich, E.M.; Sato, M.I.Z.; Gomes, T.A.T.; Amaral, L.A.; Ottoboni, L.M.M. Escherichia coli Phylogenetic Group Determination and Its Application in the Identification of the Major Animal Source of Fecal Contamination. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedict, K.M.; Gow, S.P.; McAllister, T.A.; Booker, C.W.; Hannon, S.J.; Checkley, S.L.; Noyes, N.R.; Morley, P.S. Antimicrobial Resistance in Escherichia coli Recovered from Feedlot Cattle and Associations with Antimicrobial Use. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wepking, C.; Avera, B.; Badgley, B.; Barrett, J.E.; Franklin, J.; Knowlton, K.F.; Ray, P.P.; Smitherman, C.; Strickland, M.S. Exposure to Dairy Manure Leads to Greater Antibiotic Resistance and Increased Mass-Specific Respiration in Soil Microbial Communities. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 284, 20162233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, M.; Tang, M.; Awan, F.; Aqib, A.I.; Hao, R.; Ahmad, S.; Wang, S.; Shang, R.; Pu, W. Genomic Characterization of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase (ESBL) Producing E. coli Harboring blaOXA−1-catB3-arr-3 Genes Isolated from Dairy Farm Environment in China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2024, 2024, 3526395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjölund, M.; Bonnedahl, J.; Hernandez, J.; Bengtsson, S.; Cederbrant, G.; Pinhassi, J.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsen, B. Dissemination of Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria into the Arctic. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, R.K.; Hayyan, M.; AlSaadi, M.A.; Hayyan, A.; Ibrahim, S. Environmental Application of Nanotechnology: Air, Soil, and Water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 13754–13788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amézquita-López, B.A.; Quiñones, B.; Soto-Beltrán, M.; Lee, B.G.; Yambao, J.C.; Lugo-Melchor, O.Y.; Chaidez, C. Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli O157 and Non-O157 Recovered from Domestic Farm Animals in Rural Communities in Northwestern Mexico. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2016, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manyi-Loh, C.; Mamphweli, S.; Meyer, E.; Okoh, A. Antibiotic Use in Agriculture and Its Consequential Resistance in Environmental Sources: Potential Public Health Implications. Molecules 2018, 23, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, M.A.; Yin, X.; Lepp, D.; Laing, C.; Ziebell, K.; Talbot, G.; Topp, E.; Diarra, M.S. Genomic Analysis of Third Generation Cephalosporin Resistant Escherichia coli from Dairy Cow Manure. Vet. Sci. 2017, 4, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidoo, N.; Zishiri, O.T. Comparative Genomics Analysis and Characterization of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli O157:H7 Strains Reveal Virulence Genes, Resistance Genes, Prophages and Plasmids. BMC Genom. 2023, 24, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Forster, T.; Mayer, O.; Curtin, J.J.; Lehman, S.M.; Donlan, R.M. Bacteriophage Cocktail for the Prevention of Biofilm Formation by Pseudomonas Aeruginosa on Catheters in an in Vitro Model System. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Li, Y.; Hui, M.; Lu, Z.; Li, H.; Tian, H. Metagenomic Insights into Quorum Sensing in Membrane-Aerated Biofilm Reactors for Phenolic Wastewater Treatment. Environ. Technol. 2022, 43, 1318–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, H.; Hrycauk, S.; Holman, D.B.; Ells, T.C. Microbial Dynamics in Mixed-Culture Biofilms of Salmonella Typhimurium and Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Bacteria Surviving Sanitation of Conveyor Belts of Meat Processing Plants. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, F.-J.; Martinez-Freijo, P.; Theis, S.; Fluit, A.C.; Verhoef, J.; Heinz, H.-P.; Jones, M.E. Class I Integrons: Prevalence and Impact on Antibiotic Susceptibility in 278 Consecutive Unrelated Gram-Negative Blood Isolates. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Off. Publ. Eur. Soc. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1999, 5, 496–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, C.M.; Zhao, C.; DebRoy, C.; Torcolini, J.; Zhao, S.; White, D.G.; Wagner, D.D.; McDermott, P.F.; Walker, R.D.; Meng, J. Antimicrobial Resistance of Escherichia coli O157 Isolated from Humans, Cattle, Swine, and Food. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beghain, J.; Bridier-Nahmias, A.; Le Nagard, H.; Denamur, E.; Clermont, O. ClermonTyping: An Easy-to-Use and Accurate in Silico Method for Escherichia Genus Strain Phylotyping. Microb. Genom. 2018, 4, e000192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, R.; Shoaib, M.; Tang, M.; Cao, Z.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Shang, R.; Zhang, H.; Pu, W. Genomic insights into resistome, virulome, and mobilome as organic contaminants of ESKAPE pathogens and E. coli recovered from milk, farm workers, and environmental settings in Hainan, China. Emerg. Contam. 2024, 10, 100385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergholz, P.W.; Noar, J.D.; Buckley, D.H. Environmental Patterns Are Imposed on the Population Structure of Escherichia coli after Fecal Deposition. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, M.; Tang, M.; Aqib, A.I.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Z.; Wen, Y.; Hou, X.; Xu, J.; Hao, R.; Wang, S.; et al. Dairy Farm Waste: A Potential Reservoir of Diverse Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence Genes in Aminoglycoside- and Beta-Lactam-Resistant Escherichia coli in Gansu Province, China. Environ. Res. 2024, 263, 120190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandakafle, G.; Seale, T.; Flint, T.; Nepal, M.; Venter, S.N.; Brözel, V.S. Distribution of Diverse Escherichia coli between Cattle and Pasture. Microbes Environ. 2017, 32, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coura, F.M.; Diniz, S.D.A.; Silva, M.X.; Mussi, J.M.S.; Barbosa, S.M.; Lage, A.P.; Heinemann, M.B. Phylogenetic Group Determination of Escherichia coli Isolated from Animals Samples. Sci. World J. 2015, 2015, 258424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Walk, S.T.; Gordon, D.M.; Feldgarden, M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Konstantinidis, K.T. Genome Sequencing of Environmental Escherichia coli Expands Understanding of the Ecology and Speciation of the Model Bacterial Species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 7200–7205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teelucksingh, T.; Thompson, L.K.; Cox, G. The Evolutionary Conservation of Escherichia coli Drug Efflux Pumps Supports Physiological Functions. J. Bacteriol. 2020, 202, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S. AcrAB-TolC, a major efflux pump in Gram-negative bacteria: Toward understanding its operation mechanism. BMB Rep. 2023, 56, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramonti, A.; De Canio, M.; De Biase, D. GadX/GadW-Dependent Regulation of the Escherichia coli Acid Fitness Island: Transcriptional Control at the GadY-GadW Divergent Promoters and Identification of Four Novel 42 Bp GadX/GadW-Specific Binding Sites. Mol. Microbiol. 2008, 70, 965–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hung Le, V.; Biggs, P.J.; Wheeler, D.; Davies, I.G.; Rakonjac, J. Novel Mechanisms of TolC-Independent Decreased Bile-Salt Susceptibility in Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2021, 367, fnaa083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manishimwe, R.; Moncada, P.M.; Musanayire, V.; Shyaka, A.; Morgan Scott, H.; Loneragan, G.H. Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia coli and Salmonella from the Feces of Food Animals in the East Province of Rwanda. Animals 2021, 11, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, V.M.; Pinchbeck, G.L.; Nuttall, T.; McEwan, N.; Dawson, S.; Williams, N.J. Antimicrobial Resistance Risk Factors and Characterisation of Faecal E. coli Isolated from Healthy Labrador Retrievers in the United Kingdom. Prev. Vet. Med. 2015, 119, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, S.; Bal, M.; Pati, S.; Rana, R.; Dixit, S.; Ranjit, M. Antibiotic resistance in toxigenic E. coli: A severe threat to global health. Discov. Med. 2024, 1, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Liu, L.; Sheng, H.; Zhang, M.; Wang, T.; Chang, G.; Wang, Y.; Bai, L.; Wang, X. Antibiotic Resistance and Genomic Analysis of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli from Dairy Cattle, Raw Milk, and Farm Environment in Shaanxi Province, China. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2024, 21, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beutin, L.; Delannoy, S.; Fach, P. Genetic Analysis and Detection of fliC H1 and fliC H12 Genes Coding for Serologically Closely Related Flagellar Antigens in Human and Animal Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mare, A.; Man, A.; Ciurea, C.N.; Pintea-Simon, I.A.; Ianoși, E.S.; Gîrbovan, C.E.; Toma, F. Serogroups and Genetic Diversity of Diarrheagenic Strains of Escherichia coli: A Retrospective Study. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2022, 16, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, M.G.; Al-Hindi, R.R.; Esmael, A.; Alotibi, I.A.; Azhari, S.A.; Alseghayer, M.S.; Teklemariam, A.D. The “Big Six”: Hidden Emerging Foodborne Bacterial Pathogens. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 7, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, K.; Osek, J. Identification and Molecular Characteristics of Verotoxin-Producing Escherichia coli (VTEC) from Bovine and Pig Carcasses Isolated in Poland during 2014–2018. Food Microbiol. 2020, 92, 103587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusa, V.; Restovich, V.; Galli, L.; Teitelbaum, D.; Signorini, M.; Brasesco, H.; Londero, A.; García, D.; Padola, N.L.; Superno, V.; et al. Isolation and Characterization of Non-O157 Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli from Beef Carcasses, Cuts and Trimmings of Abattoirs in Argentina. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egervärn, M.; Flink, C. Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli (STEC) in Meat and Leafy Greens Available in the Swedish Retail Market—Occurrence and Diversity of Stx Subtypes and Serotypes. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2024, 408, 110446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galarce, N.; Sánchez, F.; Escobar, B.; Lapierre, L.; Cornejo, J.; Alegría-Morán, R.; Neira, V.; Martínez, V.; Johnson, T.; Fuentes-Castillo, D.; et al. Genomic Epidemiology of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli Isolated from the Livestock-Food-Human Interface in South America. Animals 2021, 11, 1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Overbeek, L.S.; Wichers, J.H.; van Amerongen, A.; van Roermund, H.J.W.; van der Zouwen, P.; Willemsen, P.T.J. Circulation of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli Phylogenetic Group B1 Strains Between Calve Stable Manure and Pasture Land with Grazing Heifers. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libisch, B.; Nagy, G.; Csivincsik, Á.; Keresztény, T.; Papp, P.; Olasz, F.; Fébel, H.; Sándor, Z.J.; Rasschaert, G.; Lambrecht, E.; et al. Detection of Acquired Antibiotic Resistance Determinants in the Intestinal Microbiota of Food Producing Animals in Hungary. In Book of Abstracts, “Antimicrobial Resistance: A Challenge for Public Health, Animal Health and Environment”; Scientific Symposium Bruxelles: Brüsszel, Belgium, 2022; Volume 64, p. 7180. [Google Scholar]
- García, V.; Lestón, L.; Parga, A.; García-Meniño, I.; Fernández, J.; Otero, A.; Olsen, J.E.; Herrero-Fresno, A.; Mora, A. Genomics, Biofilm Formation and Infection of Bladder Epithelial Cells in Potentially Uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC) from Animal Sources and Human Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) Further Support Food-Borne Transmission. One Health 2023, 16, 100558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonyar, L.A.; Sauder, A.B.; Mortensen, L.; Willsey, G.G.; Kendall, M.M. The yad and yeh fimbrial loci influence gene expression and virulence in Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157: H7. Msphere 2024, 9, e00124-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desvaux, M.; Dalmasso, G.; Beyrouthy, R.; Barnich, N.; Delmas, J.; Bonnet, R. Pathogenicity Factors of Genomic Islands in Intestinal and Extraintestinal Escherichia coli. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, K.; Kawano, M.; Sugai, M. Distribution of Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Genes within the Prophage-Associated Regions in Nosocomial Pathogens. mSphere 2021, 6, e0045221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondy-Denomy, J.; Qian, J.; Westra, E.R.; Buckling, A.; Guttman, D.S.; Davidson, A.R.; Maxwell, K.L. Prophages Mediate Defense against Phage Infection through Diverse Mechanisms. ISME J. 2016, 10, 2854–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sváb, D.; Falgenhauer, L.; Mag, T.; Chakraborty, T.; Tóth, I. Genomic Diversity, Virulence Gene, and Prophage Arrays of Bovine and Human Shiga Toxigenic and Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli Strains Isolated in Hungary. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 896296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankhi, S.; Bhattarai, R.; Basnet, H.; Marasine, N.; Luitel, H.; Nayak, M.; Sankhi, S. Identification of Antibiotic Resistance Pattern, and Detection of Virulence Genes Iss, and OmpT in Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli from Broiler Chickens in Chitwan, Nepal. J. Pharm. Res. Int. 2020, 32, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovi, F.; Zhang, L.; Nabors, H.; Jia, L.; Adhikari, P. A Compilation of Virulence-Associated Genes That Are Frequently Reported in Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) Compared to Other E. coli. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 134, lxad014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, A.N.; Chamorro-Veloso, N.; Costa, P.; Cádiz, L.; Del Canto, F.; Venegas, S.A.; López Nitsche, M.; Coloma-Rivero, R.F.; Montero, D.A.; Vidal, R.M. Deciphering Additional Roles for the EF-Tu, l-Asparaginase II and OmpT Proteins of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, L.S.A.; Motta, R.G.; Martinez, A.C.; Orsi, H.; Hernandes, R.T.; Rall, V.L.M.; Pantoja, J.C.F.; Nardi Júnior, G.; Ribeiro, M.G. Virulence-encoding genes related to extraintestinal pathogenic E. coli and multidrug resistant pattern of strains isolated from neonatal calves with different severity scores of umbilical infections. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 174, 105861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadulghani, M.; Ogura, Y.; Ooka, T.; Itoh, T.; Sawaguchi, A.; Iguchi, A.; Nakayama, K.; Hayashi, T. The Defective Prophage Pool of Escherichia coli O157: Prophage-Prophage Interactions Potentiate Horizontal Transfer of Virulence Determinants. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsirigotaki, A.; De Geyter, J.; Šoštaric, N.; Economou, A.; Karamanou, S. Protein Export through the Bacterial Sec Pathway. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, E.R.; Mecsas, J. Bacterial Secretion Systems: An Overview. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.; Andleeb, S.; Ullah, S.R.; Mustafa, Z.; Gul, D.; Mehmood, K. Antibiotic-Mediated Expression Analysis of Shiga Toxin 1 and 2 in Multi-Drug-Resistant Shiga Toxigenic Escherichia coli. Folia Microbiol. 2021, 66, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempf, F.; Slugocki, C.; Blum, S.E.; Leitner, G.; Germon, P. Genomic Comparative Study of Bovine Mastitis Escherichia coli. PLoS ONE. 2016, 11, e0147954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarris, P.F.; Zoumadakis, C.; Panopoulos, N.J.; Scoulica, E.V. Distribution of the Putative Type VI Secretion System Core Genes in Klebsiella spp. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2011, 11, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogasawara, H.; Ishizuka, T.; Hotta, S.; Aoki, M.; Shimada, T.; Ishihama, A. Novel Regulators of the CSGD Gene Encoding the Master Regulator of Biofilm Formation in Escherichia coli K-12. Microbiology 2020, 166, 880–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Siu, G.K.H.; Yeung, A.S.F.; Chen, J.H.K.; Ho, P.L.; Leung, K.W.; Tsang, J.L.Y.; Cheng, V.C.C.; Guo, L.; Yang, J.; et al. Performance of the VITEK MS Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry System for Rapid Bacterial Identification in Two Diagnostic Centres in China. J. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 64, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A Flexible Trimmer for Illumina Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A New Genome Assembly Algorithm and Its Applications to Single-Cell Sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besemer, J.; Lomsadze, A.; Borodovsky, M. GeneMarkS: A Self-Training Method for Prediction of Gene Starts in Microbial Genomes. Implications for Finding Sequence Motifs in Regulatory Regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 2607–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatusov, R.L.; Galperin, M.Y.; Natale, D.A.; Koonin, E.V. The COG database: A tool for genome-scale analysis of protein functions and evolution. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichinger, V.; Nussbaumer, T.; Platzer, A.; Jehl, M.A.; Arnold, R.; Rattei, T. EffectiveDB—Updates and Novel Features for a Better Annotation of Bacterial Secreted Proteins and Type III, IV, VI Secretion Systems. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D669–D674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcock, B.P.; Huynh, W.; Chalil, R.; Smith, K.W.; Raphenya, A.R.; Wlodarski, M.A.; Edalatmand, A.; Petkau, A.; Syed, S.A.; Tsang, K.K.; et al. CARD 2023: Expanded curation, support for machine learning, and resistome prediction at the Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D690–D699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Function Class | Number of Matched Genes, n | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17XJ28 | 17XJ30 | 17XJ31 | 18XJ24 | 18XJ28 | 18XJ85 | 19XJ31 | |
| A | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 |
| B | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| C | 301 | 298 | 217 | 324 | 304 | 285 | 310 |
| D | 43 | 48 | 44 | 49 | 49 | 37 | 53 |
| E | 375 | 372 | 300 | 389 | 374 | 355 | 379 |
| F | 110 | 105 | 84 | 108 | 107 | 103 | 102 |
| G | 415 | 417 | 331 | 444 | 430 | 458 | 452 |
| H | 201 | 195 | 164 | 207 | 197 | 208 | 205 |
| I | 125 | 125 | 105 | 134 | 132 | 128 | 124 |
| J | 250 | 249 | 226 | 261 | 249 | 237 | 249 |
| K | 341 | 349 | 322 | 349 | 350 | 384 | 367 |
| L | 177 | 192 | 187 | 193 | 179 | 172 | 191 |
| M | 286 | 285 | 249 | 292 | 295 | 291 | 291 |
| N | 154 | 134 | 136 | 122 | 139 | 175 | 150 |
| O | 176 | 179 | 161 | 183 | 174 | 164 | 180 |
| P | 260 | 252 | 200 | 264 | 272 | 290 | 291 |
| Q | 84 | 85 | 77 | 85 | 90 | 102 | 84 |
| R | 325 | 312 | 275 | 336 | 320 | 343 | 336 |
| S | 228 | 228 | 209 | 244 | 221 | 272 | 233 |
| T | 232 | 229 | 191 | 234 | 230 | 233 | 236 |
| U | 79 | 98 | 94 | 69 | 92 | 94 | 97 |
| V | 113 | 112 | 111 | 116 | 116 | 138 | 130 |
| W | 44 | 46 | 48 | 39 | 51 | 48 | 42 |
| X | 138 | 142 | 218 | 128 | 111 | 215 | 138 |
| Total | 4460 | 4455 | 3951 | 4572 | 4485 | 4736 | 4647 |
| Strain ID | Prophage-Associated VGs | Genomic Island-Associated VGs |
|---|---|---|
| 17XJ28 | stx1, colE5, hha, iha, iss, ompT | None |
| 17XJ30 | hra, iss, papC | None |
| 17XJ31 | f17G, f17C, nlpI | None |
| 18XJ24 | iss | fimH, ompT |
| 18XJ28 | mcmA | None |
| 18XJ85 | iss | None |
| 19XJ31 | iss, nlpI, terC | afaA, afaB, afaC, afaD, iha, kpsE |
| Strain ID | Biofilm Genes | Biofilm Genes Activated by Environmental Signals | sRNAs Involved in Biofilm Formation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 17XJ28 | crr, cyaA, crp, flhD, flhC, flgM, fliA, fliZ, yhjH, yegE, ycgR, yciR, ydaM, mlrA, rpoS, adrA, adrB, bcsA, csgA, csgB, csgD, luxS, lsrR, wza, BarA, SdiA, uvrY, csrA, glgA, glgC, glgP, pgaA, pgaB, pgaC, pgaD | oxyR, arcB, arcA, flhD, flhC, rcsA, rcsB, rcsC, rcsD, gcvA, gcvR, envZ, ompR, crp, rpoS, ydaM, csgD | None |
| 17XJ30 | crr, cyaA, crp, flhD, flhC, flgM, fliA, fliZ, yhjH, yegE, ycgR, yciR, ydaM, mlrA, rpoS, adrA, adrB, bcsA, csgA, csgB, csgD, luxS, lsrR, wza, BarA, SdiA, uvrY, csrA, glgA, glgC, glgP, pgaA, pgaB, pgaC, pgaD, dksA, ag43 | oxyR, arcB, arcA, flhD, flhC, rcsA, rcsB, rcsC, rcsD, gcvA, gcvR, envZ, ompR, crp, rpoS, ydaM, csgD | None |
| 17XJ31 | crr, cyaA, crp, flhD, flhC, flgM, fliA, fliZ, yhjH, yegE, ycgR, yciR, ydaM, mlrA, rpoS, adrA, adrB, bcsA, csgA, csgB, csgD, luxS, lsrR, wza, BarA, SdiA, uvrY, csrA, glgA, glgC, glgP, pgaA, pgaB, pgaC, pgaD, dksA, ag43 | oxyR, arcB, arcA, flhD, flhC, rcsA, rcsB, rcsC, rcsD, gcvA, gcvR, envZ, ompR, crp, rpoS, ydaM, csgD | None |
| 18XJ24 | crr, cyaA, crp, flhD, flhC, flgM, fliA, fliZ, yhjH, yegE, ycgR, yciR, ydaM, mlrA, rpoS, adrA, adrB, bcsA, csgA, csgB, csgD, luxS, lsrR, wza, BarA, SdiA, uvrY, csrA, glgA, glgC, glgP, pgaA, pgaB, pgaC, pgaD | oxyR, arcB, arcA, flhD, flhC, rcsA, rcsB, rcsC, rcsD, gcvA, gcvR, envZ, ompR, crp, rpoS, ydaM, csgD | None |
| 18XJ28 | crr, cyaA, crp, flhD, flhC, flgM, fliA, fliZ, yhjH, yegE, ycgR, yciR, ydaM, mlrA, rpoS, adrA, adrB, bcsA, csgA, csgB, csgD, luxS, lsrR, wza, BarA, SdiA, uvrY, csrA, glgA, glgC, glgP, pgaA, pgaB, pgaC, pgaD, dksA, ag43 | oxyR, arcB, arcA, flhD, flhC, rcsA, rcsB, rcsC, rcsD, gcvA, gcvR, envZ, ompR, crp, rpoS, ydaM, csgD | None |
| 18XJ85 | crr, cyaA, crp, flhD, flhC, flgM, fliA, fliZ, yhjH, yegE, ycgR, yciR, ydaM, mlrA, rpoS, adrA, adrB, bcsA, csgA, csgB, csgD, luxS, lsrR, wza, BarA, SdiA, uvrY, csrA, glgA, glgC, glgP, pgaA, pgaB, pgaC, pgaD, dksA, ag43 | oxyR, arcB, arcA, flhD, flhC, rcsA, rcsB, rcsC, rcsD, gcvA, gcvR, envZ, ompR, crp, rpoS, ydaM, csgD | None |
| 19XJ31 | crr, cyaA, crp, flhD, flhC, flgM, fliA, fliZ, yhjH, yegE, ycgR, yciR, ydaM, mlrA, rpoS, adrA, adrB, bcsA, csgA, csgB, csgD, luxS, lsrR, wza, BarA, SdiA, uvrY, csrA, glgA, glgC, glgP, pgaA, pgaB, pgaC, pgaD | oxyR, arcB, arcA, flhD, flhC, rcsA, rcsB, rcsC, rcsD, gcvA, gcvR, envZ, ompR, crp, rpoS, ydaM, csgD | None |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shoaib, M.; Gul, S.; Majeed, S.; He, Z.; Hao, B.; Tang, M.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Z.; Wang, S.; Pu, W. Pathogenomic Characterization of Multidrug-Resistant Escherichia coli Strains Carrying Wide Efflux-Associated and Virulence Genes from the Dairy Farm Environment in Xinjiang, China. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 511. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050511
Shoaib M, Gul S, Majeed S, He Z, Hao B, Tang M, Zhang X, Wu Z, Wang S, Pu W. Pathogenomic Characterization of Multidrug-Resistant Escherichia coli Strains Carrying Wide Efflux-Associated and Virulence Genes from the Dairy Farm Environment in Xinjiang, China. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(5):511. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050511
Chicago/Turabian StyleShoaib, Muhammad, Sehrish Gul, Sana Majeed, Zhuolin He, Baocheng Hao, Minjia Tang, Xunjing Zhang, Zhongyong Wu, Shengyi Wang, and Wanxia Pu. 2025. "Pathogenomic Characterization of Multidrug-Resistant Escherichia coli Strains Carrying Wide Efflux-Associated and Virulence Genes from the Dairy Farm Environment in Xinjiang, China" Antibiotics 14, no. 5: 511. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050511
APA StyleShoaib, M., Gul, S., Majeed, S., He, Z., Hao, B., Tang, M., Zhang, X., Wu, Z., Wang, S., & Pu, W. (2025). Pathogenomic Characterization of Multidrug-Resistant Escherichia coli Strains Carrying Wide Efflux-Associated and Virulence Genes from the Dairy Farm Environment in Xinjiang, China. Antibiotics, 14(5), 511. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050511






