Prevalence, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Virulence Potential of Staphylococcus aureus in Donkeys from Nigeria
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
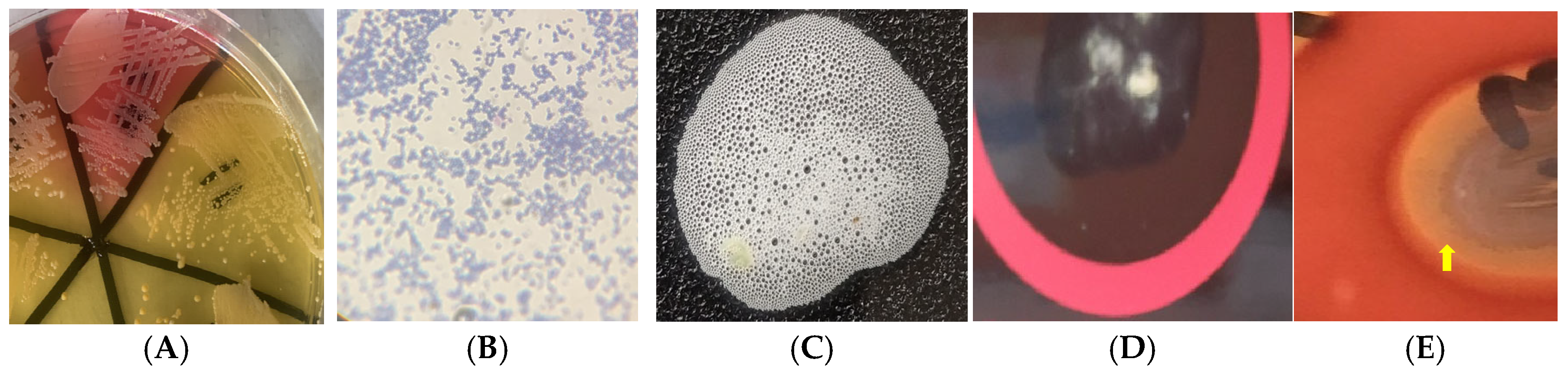
2.1. Occurrence of S. aureus in Donkeys
2.2. Antimicrobial Resistance Profile of the Isolates
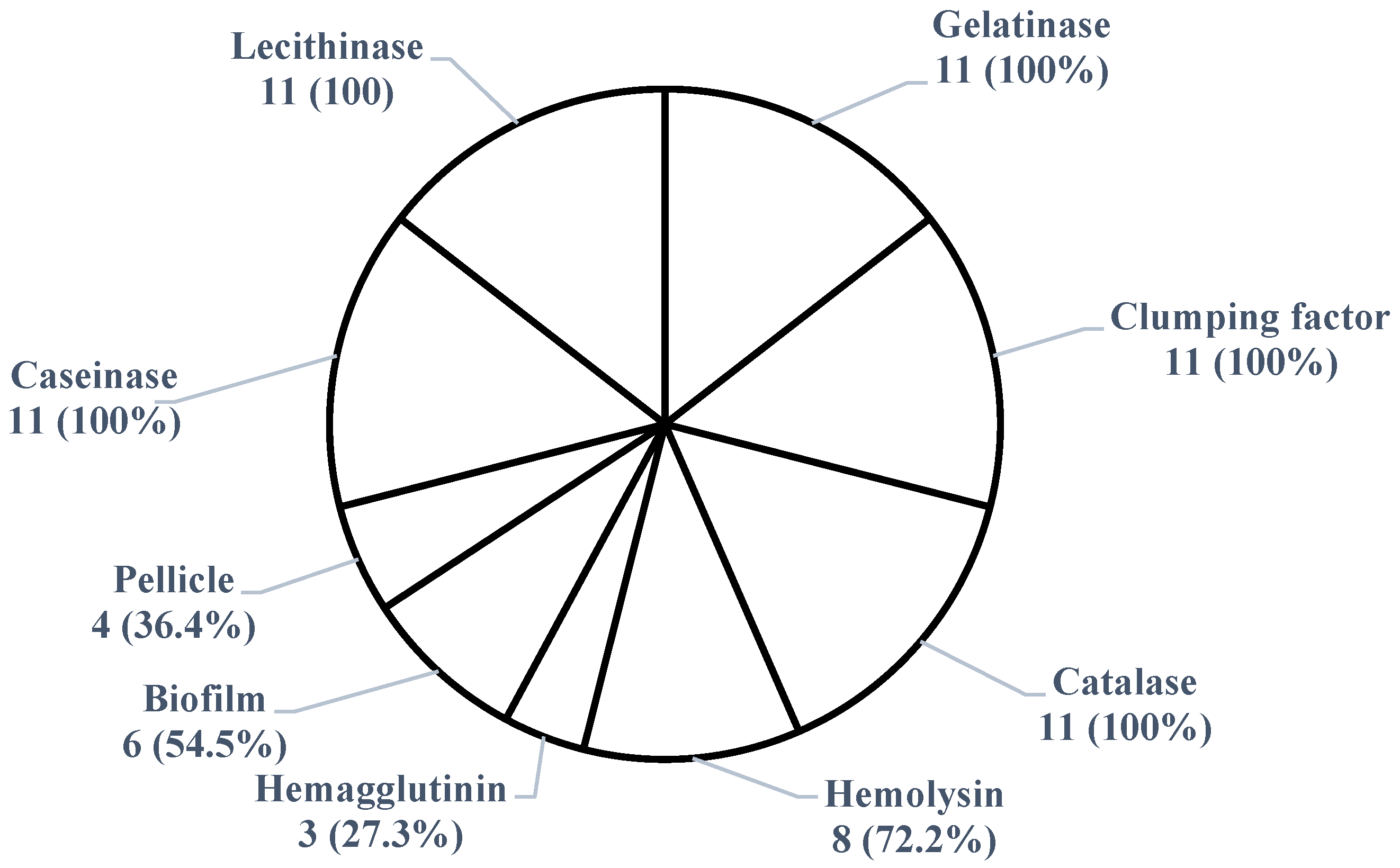
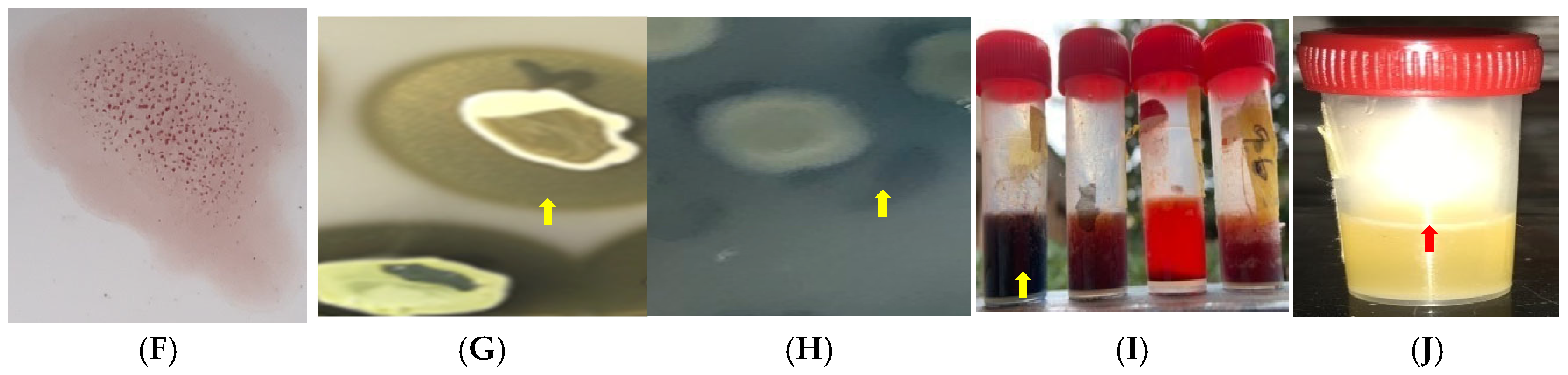
2.3. Virulence Potential of S. aureus Isolates
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethical Approval
4.2. Study Area
4.3. Sample Collection, Bacterial Isolation, and Identification
4.4. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
4.4.1. Detection of Phenotypic Methicillin Resistance
4.4.2. Detection of β-Lactamase Production
4.4.3. Phenotypic Vancomycin Resistance Assay
4.4.4. Inducible Clindamycin Resistance Assay
4.5. Detection of Virulence Potential of S. aureus Isolates
4.5.1. Catalase Activity
4.5.2. Pellicle Formation
4.5.3. Biofilm Production
4.5.4. Hemolysin Production
4.5.5. Hemagglutinin Expression
4.5.6. Gelatinase Activity
4.5.7. Caseinase Activity
4.5.8. Lipase and Esterase Activity
4.5.9. Amylase Activity
4.6. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bertelloni, F.; Cagnoli, G.; Ebani, V.V. Virulence and Antimicrobial Resistance in Canine Staphylococcus spp. Isolates. Microorg. 2021, 9, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, S.; Blasi, F.; Curtis, N.; Kaplan, S.; Lazzarotto, T.; Meschiari, M.; Mussini, C.; Peghin, M.; Rodrigo, C.; Vena, A.; et al. New Antibiotics for Staphylococcus aureus Infection: An Update from the World Association of Infectious Diseases and Immunological Disorders (WAidid) and the Italian Society of Anti-Infective Therapy (SITA). Antibiotics 2023, 12, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derdak, R.; Quinteiro, J.; Sakoui, S.; Addoum, B.; Rodríguez Castro, J.; Rey Méndez, M.; Soukri, A.; El Khalfi, B. Isolation and Identification of Dominant Bacteria from Raw Donkey Milk Produced in a Region of Morocco by QIIME 2 and Evaluation of Their Antibacterial Activity. Sci. World J. 2021, 2021, 6664636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad-Mansour, N.; Loubet, P.; Pouget, C.; Dunyach-Remy, C.; Sotto, A.; Lavigne, J.P.; Molle, V. Staphylococcus aureus Toxins: An Update on Their Pathogenic Properties and Potential Treatments. Toxins 2021, 13, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, K.; Torres, V.J. Staphylococcus aureus Secreted Toxins and Extracellular Enzymes. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillay, S.; Zishiri, O.T.; Adeleke, M.A. Prevalence of Virulence Genes in Enterococcus Species Isolated from Companion Animals and Livestock. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2018, 85, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsin, S.; Amin, M.N. Superbugs: A Constraint to Achieving the Sustainable Development Goals. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2023, 47, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsen, N.; Vollset, S.E.; Ikuta, K.S. Global Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance 1990–2021: A Systematic Analysis with Forecasts to 2050. Lancet 2024, 404, 1199–1226. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, C.J.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance in 2019: A Systematic Analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikuta, K.S.; Swetschinski, L.R.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Sharara, F.; Mestrovic, T.; Gray, A.P.; Davis Weaver, N.; Wool, E.E.; Han, C.; Gershberg Hayoon, A.; et al. Global Mortality Associated with 33 Bacterial Pathogens in 2019: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2022, 400, 2221–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, D.M.P.; Forde, B.M.; Kidd, T.J.; Harris, P.N.A.; Schembri, M.A.; Beatson, S.A.; Paterson, D.L.; Walker, M.J. Antimicrobial Resistance in ESKAPE Pathogens. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aloke, C.; Achilonu, I. Coping with the ESKAPE Pathogens: Evolving Strategies, Challenges and Future Prospects. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 175, 105963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OPS Group. WHO Bacterial Priority Pathogens List, 2024: Bacterial Pathogens of Public Health Importance to Guide Research, Development and Strategies to Prevent and Control Antimicrobial Resistance; World Health Organization: Geneva, German, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, G. Assessing Antimicrobial Use and Practices in Equids. Vet. Rec. 2022, 191, 442–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, S.L.; Little, H.A.; Ryding, J.; Raw, Z. Global Donkey and Mule Populations: Figures and Trends. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.R.; Steenstra, F.A.; Udo, H.M.J. Benefits of Donkeys in Rural and Urban Areas in Northwest Nigeria. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2013, 8, 6202–6212. [Google Scholar]
- Maigari, M.A.; Dantani, U.; Yelwa, M.M.; Ibrahim, A. Scavenging for Ejiao’s Raw Material and the Extinction of Donkeys in Nigeria. Glob. J. Sociol. Curr. Issues 2020, 10, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodrum, F.; Theuri, S.; Mutua, E.; Carder, G. The Donkey Skin Trade: Challenges and Opportunities for Policy Change. Glob. Policy 2022, 13, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.; Alfarela, C.; Caniça, M.; Manageiro, V.; Nóvoa, M.; Leiva, B.; Kress, M.; Capelo, J.L.; Poeta, P.; Igrejas, G. A One Health Approach Molecular Analysis of Staphylococcus aureus Reveals Distinct Lineages in Isolates from Miranda Donkeys (Equus asinus) and Their Handlers. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ituma, O.E. Acceptability and Consumption of Donkey Meat in Ebonyi State. Glob. J. Bio-Sci. Technol. 2014, 3, 128–220. [Google Scholar]
- Jassim, S.A.; Kandala, N.J. Molecular Detection of Enterotoxin Genes of Multiresistant Staphylococcus aureus Isolates from Different Sources of Food. Iraqi J. Sci. 2021, 62, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debelu, T.; Aklilu, N.; Sisay, T.; Desissa, F. Isolation and Identification of Aerobic Bacterial Flora from the Upper Respiratory Tract of Donkeys in Central Ethiopia. J. Veterainry Med. Anim. Health 2014, 6, 181–189. [Google Scholar]
- Tahoun, A.; Elnafarawy, H.K.; El-Sharkawy, H.; Rizk, A.M.; Alorabi, M.; El-Shehawi, A.M.; Youssef, M.A.; Ibrahim, H.M.M.; El-Khodery, S. The Prevalence and Molecular Biology of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Healthy and Diseased Equine Eyes in Egypt. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharsa, H.; Ben Sallem, R.; Ben Slama, K.; Gómez-Sanz, E.; Lozano, C.; Jouini, A.; Klibi, N.; Zarazaga, M.; Boudabous, A.; Torres, C. High Diversity of Genetic Lineages and Virulence Genes. in Nasal Staphylococcus aureus Isolates from Donkeys Destined to Food Consumption in Tunisia with Predominance of the Ruminant Associated CC133 Lineage. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharsa, H.; Slama, K.B.; Gómez-Sanz, E.; Gómez, P.; Klibi, N.; Zarazaga, M.; Boudabous, A.; Torres, C. Characterisation of Nasal Staphylococcus delphini and Staphylococcus pseudintermedius Isolates from Healthy Donkeys in Tunisia. Equine Vet. J. 2015, 47, 463–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilla, R.; Daprà, V.; Zecconi, A.; Piccinini, R. Hygienic and Health Characteristics of Donkey Milk during a Follow-up Study. J. Dairy. Res. 2010, 77, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foti, M.; Fisichella, V.; Giacopello, C. Detection of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) in the Microbial Flora from the Conjunctiva of Healthy Donkeys from Sicily (Italy). Vet. Ophthalmol. 2013, 16, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, S.V.; Hillhouse, A.E.; Lawhon, S.D.; Bryan, L.K.; Fey, P.D. Analysis of Virulence and Antimicrobial Resistance Gene Carriage in Staphylococcus aureus Infections in Equids Using Whole-Genome Sequencing. Msphere 2021, 6, e0019620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, P.; García, P.; Miles, J.; Isla, D.; Yáñez, C.; Santibáñez, R.; Núñez, A.; Flores-Yáñez, C.; Del Río, C.; Cuadra, F. Isolation and Identification of Staphylococcus Species Obtained from Healthy Companion Animals and Humans. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwobi, O.C.; Anyanwu, M.U.; Jaja, I.F.; Nwankwo, I.O.; Okolo, C.C.; Nwobi, C.A.; Ezenduka, E.V.; Oguttu, J.W. Staphylococcus aureus in Horses in Nigeria: Occurrence, Antimicrobial, Methicillin and Heavy Metal Resistance and Virulence Potentials. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argudín, M.Á.; Mendoza, M.C.; Rodicio, M.R. Food Poisoning and Staphylococcus aureus Enterotoxins. Toxins 2010, 2, 1751–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanda, M.I.; Idris, A. M Nasopharyngeal Carriage of Staphylococcus aureus among Horses and Horse Handlers in Kano Metropolis, Nigeria. UMYU J. Microbiol. Res. (UJMR) 2021, 6, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.; Sah, R.; Sharma, A.; Khanal, B.; Bhattarai, N.R. Evaluation of Latex Agglutination Test for Rapid Identification of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Pyogenic Wound Infections at a Tertiary Care Hospital. Kathmandu Univ. Med. J. 2023, 21, 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Lainhart, W.; Yarbrough, M.L.; Burnham, C.A.D. The Brief Case: Staphylococcus Intermedius Group-Look What the Dog Dragged In. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e00839-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latorre-Fernández, J.; Aspiroz, C.; Abdullahi, I.N.; Campaña-Burguet, A.; Eguizábal, P.; González-Azcona, C.; Tenorio, C.; Zarazaga, M.; Shittu, A.O.; Lozano, C.; et al. Evaluation of the Double-Zone Hemolysis (DZH) Test for the Detection of Livestock-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiol. Spectr. 2025, 13, e0110224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, P.; Nayyar, C.; Tak, V.; Saigal, K. Mannitol-Fermenting and Tube Coagulase-Negative Staphylococcal Isolates: Unraveling the Diagnostic Dilemma. J. Lab. Physicians 2017, 9, 65–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adesokan, H.K.; Akanbi, I.O.; Akanbi, I.M.; Obaweda, R.A. Pattern of Antimicrobial Usage in Livestock Animals in South-Western Nigeria: The Need for Alternative Plans. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2015, 82, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhaji, N.B.; Isola, T.O. Antimicrobial Usage by Pastoralists in Food Animals in North-Central Nigeria: The Associated Socio-Cultural Drivers for Antimicrobials Misuse and Public Health Implications. One Health 2018, 6, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, T.; Basit, A.; Karim, A.M.; Lee, J.H.; Jeon, J.H.; Rehman, S.U.; Lee, S.H. Mutation-Based Antibiotic Resistance Mechanism in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Clinical Isolates. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peacock, S.J.; Paterson, G.K. Mechanisms of Methicillin Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2015, 84, 577–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI VET01S; Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria Isolated from Animals. 7th ed. CLSI Supplement VET01S. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Malvern, PA, USA, 2024.
- Ezeh, C.K.; Eze, C.N.; Dibua, M.E.U.; Emencheta, S.C. A Meta-Analysis on the Prevalence of Resistance of Staphylococcus aureus to Different Antibiotics in Nigeria. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2023, 12, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.F.; Mobashery, S. β-Lactam Resistance Mechanisms: Gram-Positive Bacteria and Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a025221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanichelli, V.; Sharland, M.; Cappello, B.; Moja, L.; Getahun, H.; Pessoa-Silva, C.; Sati, H.; van Weezenbeek, C.; Balkhy, H.; Simão, M.; et al. The WHO AWaRe (Access, Watch, Reserve) Antibiotic Book and Prevention of Antimicrobial Resistance. Bull. World Health Organ. 2023, 101, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngbede, E.O.; Sy, I.; Akwuobu, C.A.; Nanven, M.A.; Adikwu, A.A.; Abba, P.O.; Adah, M.I.; Becker, S.L. Carriage of Linezolid-Resistant Enterococci (LRE) among Humans and Animals in Nigeria: Coexistence of the Cfr, OptrA, and PoxtA Genes in Enterococcus Faecium of Animal Origin. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2023, 34, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anyanwu, M.U.; Ikenna-Ezeh, N.H.; Okafor, S.C.; Ezemuoka, C.F.; Nwobi, O.C.; Ogunniran, T.M.; Obodoechi, L.O.; Okorie-Kanu, O.J.; Mgbeahuruike, A.C.; Okosi, I.R.; et al. Commercial Day-Old Chicks in Nigeria Are Potential Reservoirs of Colistin- and Tigecycline-Resistant Potentially Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adesoji, A.T.; Call, D.R. Molecular Analysis of Florfenicol-Resistant Bacteria Isolated from Drinking Water Distribution Systems in Southwestern Nigeria. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 23, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdu, A.; Lamikanra, A. Linezolid and Methicillin Resistances in S. aureus Isolated from the Anterior Nares of Apparently Healthy Undergraduates of the Niger Delta University, Nigeria. Br. Microbiol. Res. J. 2016, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Wan, M.; Wang, C.; Gao, X.; Yang, Q.; Partridge, S.R.; Wang, Y.; Zong, Z.; Doi, Y.; Shen, J.; et al. Emergence of a Plasmid-Encoded Resistance-Nodulation- Division Efflux Pump Conferring Resistance to Multiple Drugs, Including Tigecycline, in Klebsiella pneumoniae. mBio 2020, 11, 10-1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidary, M.; Sholeh, M.; Koupaei, M.; Asadi, A.; Khah, S.M.; Kheirabadi, F.; Saeidi, P.; Darbandi, A.; Taheri, B.; Ghanavati, R. Prevalence of Tigecycline Resistance in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2024, 108, 116088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoroafor, O.N.; Aneru, E.; Eze, J.I.; Chukwudi, I.C.; Anagor, T.; Kazeem, H.; Ngene, A.A. Prevalence of Mycotic Agents Isolated from Skin Lesions of Trade Horses in Obollor-Afor, Enugu State, Nigeria. Sokoto J. Vet. Sci. 2020, 18, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, N.M.; Penati, M.; Fusar-Poli, S.; Addis, M.F.; Tola, S. Species Identification by MALDI-TOF MS and Gap PCR-RFLP of Non-Aureus Staphylococcus, Mammaliicoccus, and Streptococcus spp. Associated with Sheep and Goat Mastitis. Vet. Res. 2022, 53, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUCAST The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters. Version 14.0. 2024. Available online: http://www.Eucast.Org (accessed on 15 January 2024).
- CLSI M100-ED35; Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. 35th ed. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Malvern, PA, USA, 2025.
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-Resistant, Extensively Drug-Resistant and Pandrug-Resistant Bacteria: An International Expert Proposal for Interim Standard Definitions for Acquired Resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawadi, P.; Khanal, S.; Prasai Joshi, T.; KC, S.; Tuladhar, R.; Maharjan, B.L.; Darai, A.; Joshi, D.R. Antibiotic Resistance, Biofilm Formation and Sub-Inhibitory Hydrogen Peroxide Stimulation in Uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Microbiol. Insights 2022, 15, 11786361221135224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Bae, Y.M.; Han, A.; Lee, S.Y. Development of Congo Red Broth Method for the Detection of Biofilm-Forming or Slime-Producing Staphylococcus sp. LWT 2016, 73, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagos, D.G.; Mezgebo, T.A.; Berhane, S.; Medhanyie, A.A. Biofilm and Hemagglutinin Formation: A Hallmark for Drug Resistant Uropathogenic Escherichia coli. BMC Res. Notes 2019, 12, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramnath, L.; Sithole, B.; Govinden, R. Identification of Lipolytic Enzymes Isolated from Bacteria Indigenous to Eucalyptus Wood Species for Application in the Pulping Industry. Biotechnol. Rep. 2017, 15, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Esmail, G.A.; Ghilan, A.K.M.; Arasu, M.V.; Duraipandiyan, V.; Ponmurugan, K. Isolation and Purification of Starch Hydrolysing Amylase from Streptomyces sp. Al-Dhabi-46 Obtained from the Jazan Region of Saudi Arabia with Industrial Applications. J. King Saud. Univ. Sci. 2020, 32, 1226–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preda, M.; Mihai, M.M.; Popa, L.I.; Diţu, L.M.; Holban, A.M.; Manolescu, L.S.C.; Popa, G.L.; Muntean, A.A.; Gheorghe, I.; Chifiriuc, C.M.; et al. Phenotypic and Genotypic Virulence Features of Staphylococcal Strains Isolated from Difficult-to-Treat Skin and Soft Tissue Infections. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Organism | Number of Positive Samples (n = 250) | Percentage | 95% Confidence Interval | Odds Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | 11 | 4.4 | 1.86–6.94 | 0.0021 |
| Other Staphylococcus species | 239 | 95.6 | 93.06–98.14 | 0.0021 |
| Antimicrobial Class | Antimicrobial Agent | Number (%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resistant | Susceptible | |||
| β-lactams | Penicillin | 8 (66.7) | 4 (33.3) | 0.1984 |
| Cefoxitin | 3 (27.3) | 8 (72.7) | 0.0861 | |
| Tetracyclines | Doxycycline | 0 (0.0) | 11 (100) | 0.00000284 * |
| Tigecycline | 6 (54.5) | 6 (45.5) | 1.0000 | |
| Glycopeptides | Vancomycin | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | NA |
| Oxazolidinones | Linezolid | 4 (36.4) | 7 (63.6) | 0.3949 |
| Lincosamides | Clindamycin | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | NA |
| Phenicols | Chloramphenicol | 2 (18.1) | 9 (81.9) | 0.0089 * |
| Aminoglycosides | Gentamicin | 5 (45.5) | 6 (54.5) | 1.0000 |
| Macrolides | Erythromycin | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | NA |
| Number of Antimicrobial Agents | Number (%) of Resistant Isolates (n = 11) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0 (0.0) |
| 1 | 0 (0.0) |
| 2 | 6 (54.5) |
| 3 | 2 (18.2) |
| 4 | 2 (18.2) |
| 5 | 1 (9.1) |
| SN | No. of Antimicrobials (MARIs) | Antimicrobial Resistance Pattern | Total (n = 11) | No. of Antimicrobial Classes | No. (%) of MDR Strains |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 (0.2) | TIG–GEN | 1 | 2 | 5 (45.5) |
| 2 | LZD–GEN | 1 | |||
| 3 | PEN–LZD | 3 | |||
| 4 | PEN–TIG | 1 | |||
| 5 | 3 (0.3) | PEN–TIG–CHL | 2 | 3 | |
| 6 | 4 (0.4) | PEN–FOX–TIG–GEN | 2 | ||
| 7 | 5 (0.5) | PEN–FOX–TIG–GEN–CHL | 1 | 4 |
| S/N | Virulence Pattern | Number of Isolates | % Frequency (n = 11) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cat–Lec–Clf–Gel–Cas–Bfm–Hgl–Hml | 2 | 18.2 |
| 2 | Cat–Lec–Clf–Gel–Cas–Hml | 2 | 18.2 |
| 3 | Cat–Lec–Clf–Gel–Cas–Hgl–Pel–Hml | 1 | 9.1 |
| 4 | Cat–Lec–Clf–Gel–Cas–Pel | 2 | 18.2 |
| 5 | Cat–Lec–Clf–Gel–Cas–Bfm–Pel | 1 | 9.1 |
| 6 | Cat–Lec–Clf–Gel–Cas–Bfm–Hml | 3 | 27.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Okorie-Kanu, O.J.; Anyanwu, M.U.; Nwobi, O.C.; Tambe-Ebot, R.Y.; Ikenna-Ezeh, N.H.; Okolo, C.C.; Obodoechi, L.O.; Ugwu, P.C.; Okosi, I.R.; Jaja, I.F.; et al. Prevalence, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Virulence Potential of Staphylococcus aureus in Donkeys from Nigeria. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050453
Okorie-Kanu OJ, Anyanwu MU, Nwobi OC, Tambe-Ebot RY, Ikenna-Ezeh NH, Okolo CC, Obodoechi LO, Ugwu PC, Okosi IR, Jaja IF, et al. Prevalence, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Virulence Potential of Staphylococcus aureus in Donkeys from Nigeria. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(5):453. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050453
Chicago/Turabian StyleOkorie-Kanu, Onyinye Josephine, Madubuike Umunna Anyanwu, Obichukwu Chisom Nwobi, Regina Yaya Tambe-Ebot, Nkechi Harriet Ikenna-Ezeh, Chukwuemeka Calistus Okolo, Lynda Onyinyechi Obodoechi, Patience Chinasa Ugwu, Ifeyinwa Riona Okosi, Ishmael Festus Jaja, and et al. 2025. "Prevalence, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Virulence Potential of Staphylococcus aureus in Donkeys from Nigeria" Antibiotics 14, no. 5: 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050453
APA StyleOkorie-Kanu, O. J., Anyanwu, M. U., Nwobi, O. C., Tambe-Ebot, R. Y., Ikenna-Ezeh, N. H., Okolo, C. C., Obodoechi, L. O., Ugwu, P. C., Okosi, I. R., Jaja, I. F., & Oguttu, J. W. (2025). Prevalence, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Virulence Potential of Staphylococcus aureus in Donkeys from Nigeria. Antibiotics, 14(5), 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050453









