Antimicrobial Susceptibility Profiles of Escherichia coli Isolates from Clinical Cases of Geese in Hungary Between 2022 and 2023
Abstract
:1. Introduction
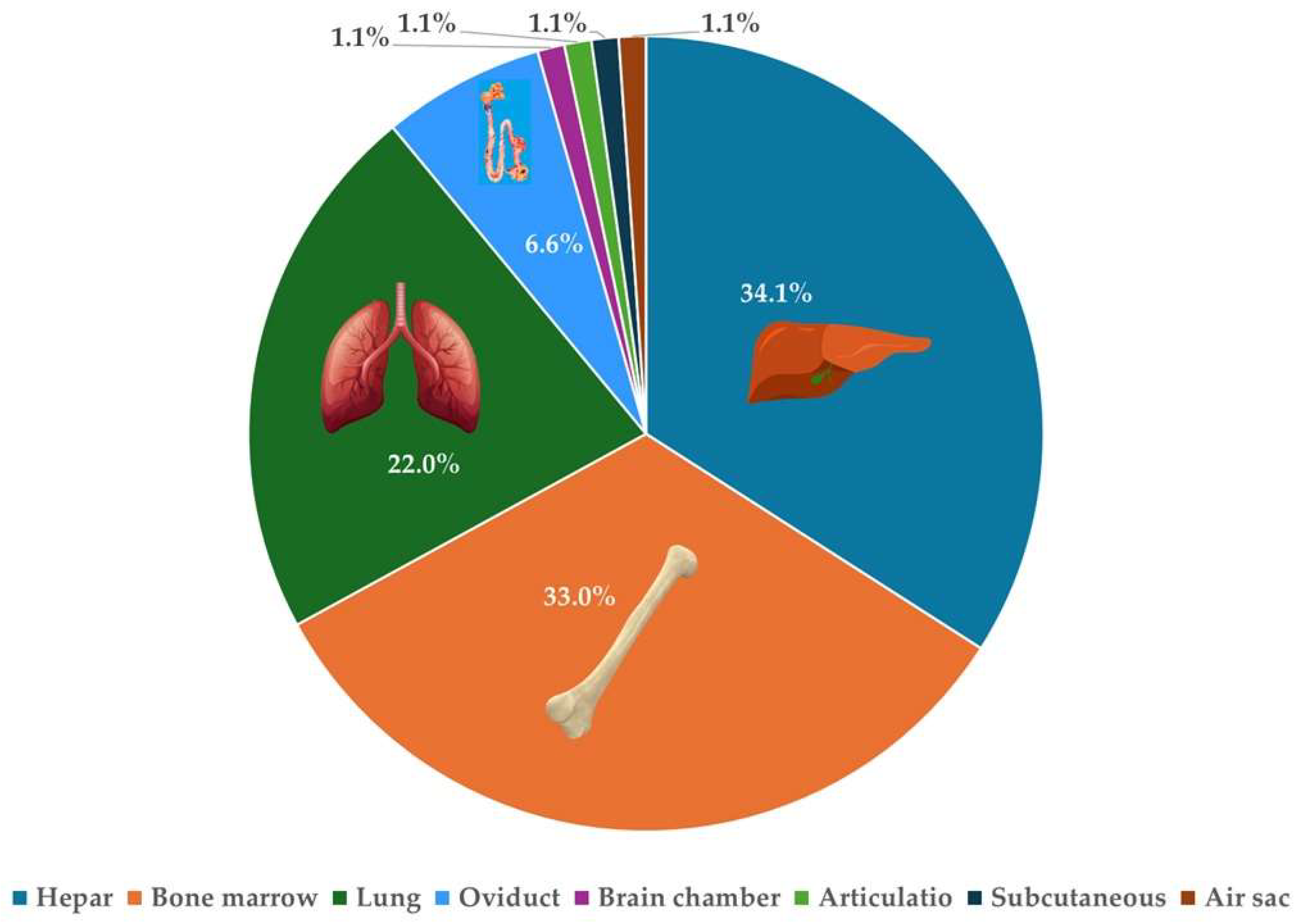
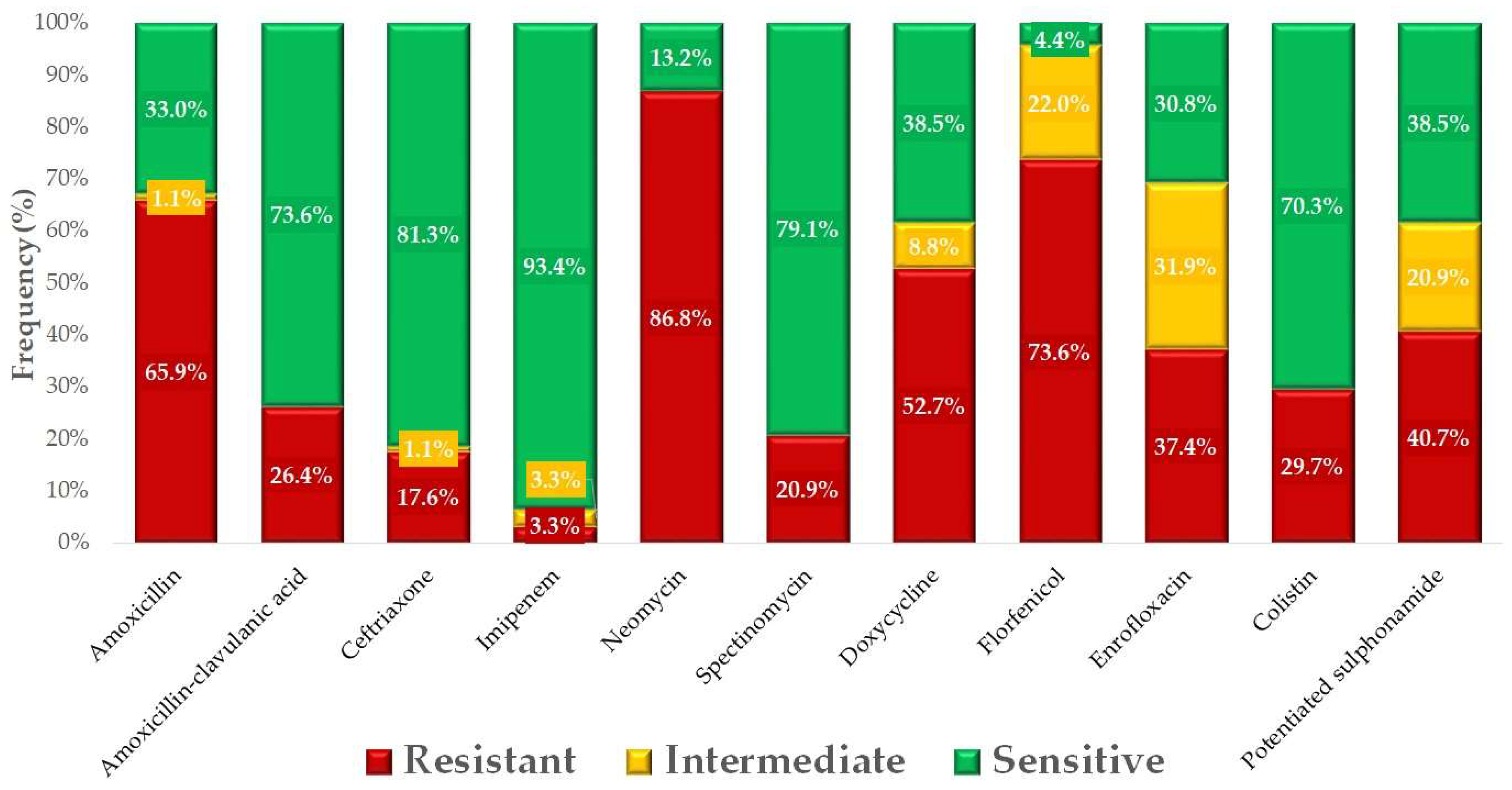
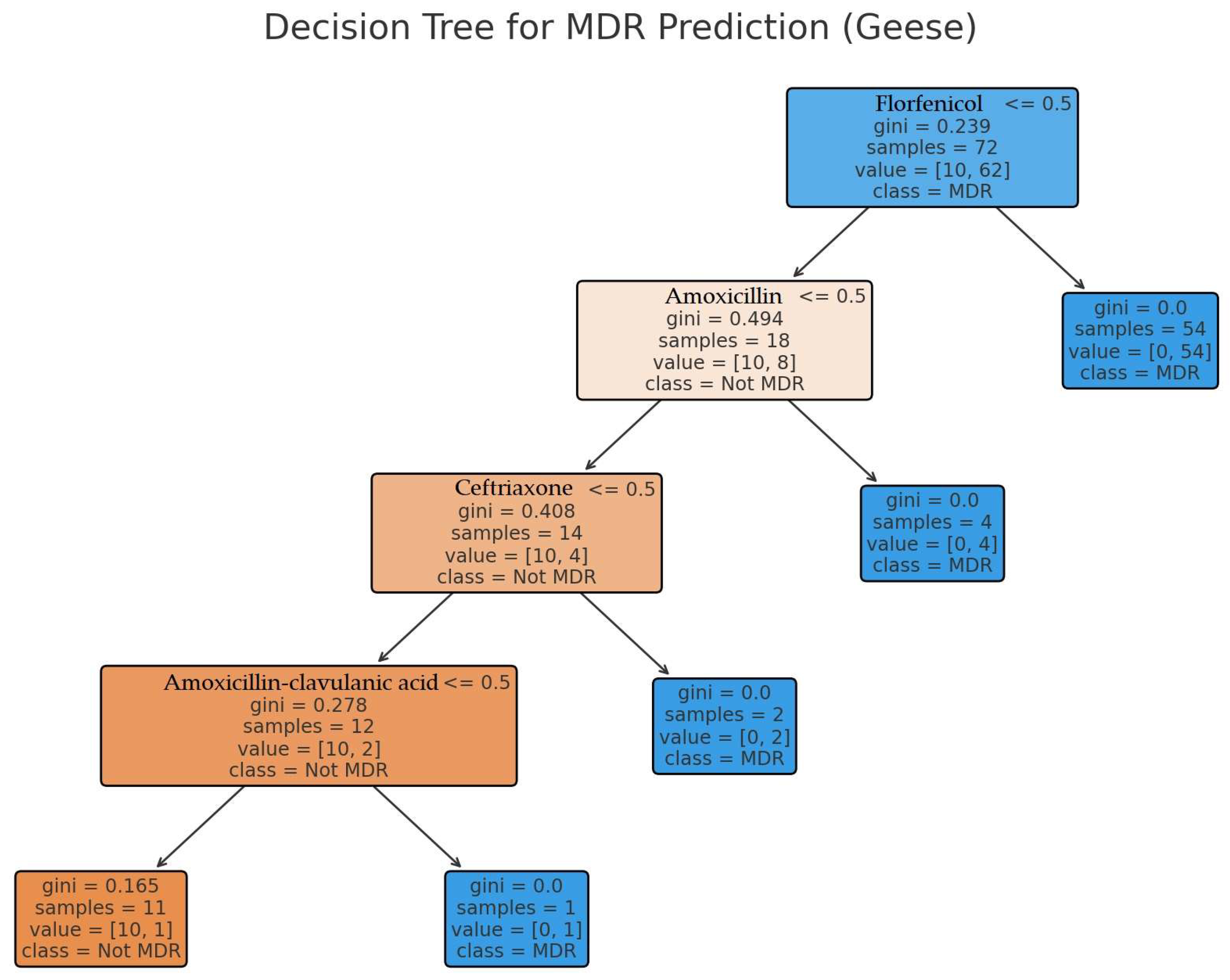
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Origin of the Strains and Human Data
4.2. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Determination
4.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMR | Antimicrobial resistance |
| CAMHB | Cation-adjusted Mueller Hinton Broth |
| CLSI | Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute |
| ECOFF | Epidemiological cutoff values |
| EUCAST | European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing |
| ESBL | Extended spectrum beta-lactamases |
| MDR | Multidrug-resistant |
| MIC | Minimum inhibitory concentration |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| XDR | Extensively drug-resistant |
References
- Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Machalaba, C.C.; Tang, H.; Chmura, A.A.; Fielder, M.D.; Daszak, P. Wild Animal and Zoonotic Disease Risk Management and Regulation in China: Examining Gaps and One Health Opportunities in Scope, Mandates, and Monitoring Systems. One Health 2021, 13, 100301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.T.; Sobur, M.A.; Islam, M.S.; Ievy, S.; Hossain, M.J.; El Zowalaty, M.E.; Rahman, A.T.; Ashour, H.M. Zoonotic Diseases: Etiology, Impact, and Control. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirel, L.; Madec, J.-Y.; Lupo, A.; Schink, A.-K.; Kieffer, N.; Nordmann, P.; Schwarz, S. Antimicrobial Resistance in Escherichia coli. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, O.M.; Snyder, W.E.; Owen, J.P. Are We Overestimating Risk of Enteric Pathogen Spillover from Wild Birds to Humans? Biol. Rev. 2020, 95, 652–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Bogaard, A.E.; Stobberingh, E.E. Epidemiology of Resistance to Antibiotics: Links between Animals and Humans. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2000, 14, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darwich, L.; Vidal, A.; Seminati, C.; Albamonte, A.; Casado, A.; López, F.; Molina-López, R.A.; Migura-Garcia, L. High Prevalence and Diversity of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase and Emergence of OXA-48 Producing Enterobacterales in Wildlife in Catalonia. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodewes, R.; Kuiken, T. Chapter Twelve—Changing Role of Wild Birds in the Epidemiology of Avian Influenza A Viruses. In Advances in Virus Research; Kielian, M., Mettenleiter, T.C., Roossinck, M.J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; Volume 100, pp. 279–307. [Google Scholar]
- Apun, K.; Kho, K.L.; Chong, Y.L.; Hashimatul, F.H.; Abdullah, M.T.; Rahman, M.A.; Lesley, M.B.; Samuel, L. Detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in Wildlife from Disturbed Habitats in Sarawak, Malaysia. Res. J. Microbiol. 2010, 6, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benmazouz, I.; Kövér, L.; Kardos, G. The Rise of Antimicrobial Resistance in Wild Birds: Potential AMR Sources and Wild Birds as AMR Reservoirs and Disseminators: Literature Review. Magy. Állatorvosok Lapja 2024, 146, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, D.; Palkovicsné Pézsa, N.; Farkas, O.; Jerzsele, Á. Usage of Antibiotic Alternatives in Pig Farming: Literature Review. Magy. Állatorvosok Lapja 2021, 143, 281–282. [Google Scholar]
- Essősy, M.; Fodor, I.; Ihnáth, Z.; Karancsi, Z.; Kovács, D.; Szalai, K.V.; Szentmiklósi, D.; Jerzsele, Á. The Possibilities of Antibiotic-Free Broiler-Hen Fattening, with Special Reference to the Use of Pre- and Probiotics. Magy. Állatorvosok Lapja 2020, 142, 397–407. [Google Scholar]
- Van Boeckel, T.P.; Brower, C.; Gilbert, M.; Grenfell, B.T.; Levin, S.A.; Robinson, T.P.; Teillant, A.; Laxminarayan, R. Global Trends in Antimicrobial Use in Food Animals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5649–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Zheng, J.; Liu, C.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Fan, H. Removal of Antibiotics and Resistance Genes from Swine Wastewater Using Vertical Flow Constructed Wetlands: Effect of Hydraulic Flow Direction and Substrate Type. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 308, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manyi-Loh, C.; Mamphweli, S.; Meyer, E.; Okoh, A. Antibiotic Use in Agriculture and Its Consequential Resistance in Environmental Sources: Potential Public Health Implications. Molecules 2018, 23, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, M.; Ying, G.-G.; Singer, A.C.; Zhu, Y.-G. Review of Antibiotic Resistance in China and Its Environment. Environ. Int. 2018, 110, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olasz, Á.; Jerzsele, Á.; Balta, L.; Dobra, P.F.; Kerek, Á. In Vivo Efficacy of Different Extracts of Propolis in Broiler Salmonellosis. Magy. Állatorvosok Lapja 2023, 145, 461–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerek, Á.; Csanády, P.; Jerzsele, Á. Antibacterial Efficiency of Propolis—Part 1. Magy. Állatorvosok Lapja 2022, 144, 285–298. [Google Scholar]
- Kerek, Á.; Csanády, P.; Jerzsele, Á. Antiprotozoal and Antifungal Efficiency of Propolis—Part 2. Magy. Állatorvosok Lapja 2022, 144, 691–704. [Google Scholar]
- Sebők, C.; Márton, R.A.; Meckei, M.; Neogrády, Z.; Mátis, G. Antimicrobial Peptides as New Tools to Combat Infectious Diseases. Magy. Állatorvosok Lapja 2024, 146, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetényi, N.; Bersényi, A.; Hullár, I. Physiological Effects of Medium-Chain Fatty Acids and Triglycerides, and Their Potential Use in Poultry and Swine Nutrition: A Literature Review. Magy. Állatorvosok Lapja 2024, 146, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jócsák, G.; Schilling-Tóth, B.; Bartha, T.; Tóth, I.; Ondrašovičová, S.; Kiss, D.S. Metal Nanoparticles—Immersion in the „tiny” World of Medicine. Magy. Állatorvosok Lapja 2025, 147, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, L.; Hejel, P.; Farkas, M.; László, L. Könyves László Study Report on the Effect of a Litter Treatment Product Containing Bacillus Licheniformis and Zeolite in Male Fattening Turkey Flock. Magy. Állatorvosok Lapja 2024, 146, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, M.; Könyves, L.; Csorba, S.; Farkas, Z.; Józwiák, Á.; Süth, M.; Kovács, L. Biosecurity Situation of Large-Scale Poultry Farms in Hungary According to the Databases of National Food Chain Safety Office Centre for Disease Control and Biosecurity Audit System of Poultry Product Board of Hungary in the Period of 2021–2022. Magy. Állatorvosok Lapja 2024, 146, 723–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mag, P.; Németh, K.; Somogyi, Z.; Jerzsele, Á. Antibacterial therapy based on pharmacokinetic/ pharmacodynamic models in small animal medicine-1. Literature review. Magy. Állatorvosok Lapja 2023, 145, 419–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eda, M.; Itahashi, Y.; Kikuchi, H.; Sun, G.; Hsu, K.-H.; Gakuhari, T.; Yoneda, M.; Jiang, L.; Yang, G.; Nakamura, S. Multiple Lines of Evidence of Early Goose Domestication in a 7,000-y-Old Rice Cultivation Village in the Lower Yangtze River, China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2117064119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albarella, U. Alternate Fortunes? The Role of Domestic Ducks and Geese from Roman to Medieval Times in Britain. Doc. Archaeobiologiae 2005, 3, 249–258. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.; Wang, D.; Yan, S.; Xue, Y. Characterization of Escherichia Coli Strains Isolated from Geese by Detection of Integron-Mediated Antimicrobial Resistance. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2022, 31, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassin, A.K.; Gong, J.; Kelly, P.; Lu, G.; Guardabassi, L.; Wei, L.; Han, X.; Qiu, H.; Price, S.; Cheng, D.; et al. Antimicrobial Resistance in Clinical Escherichia coli Isolates from Poultry and Livestock, China. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, C.; Guerin, M.T.; Brash, M.L.; Slavic, D.; Boerlin, P.; Susta, L. Antimicrobial Resistance in Fecal Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica Isolates: A Two-Year Prospective Study of Small Poultry Flocks in Ontario, Canada. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kang, M.-S.; Lee, H.-J.; Kang, S.-I.; Lee, O.-M.; Kwon, Y.-K.; Kim, J.-H. Comparative Characteristics and Zoonotic Potential of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) Isolates from Chicken and Duck in South Korea. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afayibo, D.J.A.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, B.; Yao, L.; Abdelgawad, H.A.; Tian, M.; Qi, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S. Isolation, Molecular Characterization, and Antibiotic Resistance of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli in Eastern China. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, D.-J.; Sun, R.-Y.; Mai, J.-L.; Jiang, Y.-W.; Wang, D.; Guo, W.-Y.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.-F.; Zhang, R.-M.; et al. Occurrence and Transmission of blaNDM-Carrying Enterobacteriaceae from Geese and the Surrounding Environment on a Commercial Goose Farm. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e00087-e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adiguzel, M.C.; Baran, A.; Wu, Z.; Cengiz, S.; Dai, L.; Oz, C.; Ozmenli, E.; Goulart, D.B.; Sahin, O. Prevalence of Colistin Resistance in Escherichia coli in Eastern Turkey and Genomic Characterization of an mcr-1 Positive Strain from Retail Chicken Meat. Microb. Drug Resist. 2021, 27, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, S.; Sultana, S.A.; Prova, S.R.; Uddin, T.M.; Islam, F.; Das, R.; Nainu, F.; Sartini, S.; Chidambaram, K.; Alhumaydhi, F.A.; et al. Investigating Forthcoming Strategies to Tackle Deadly Superbugs: Current Status and Future Vision. Expert. Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2022, 20, 1309–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEwen, S.A.; Collignon, P.J. Antimicrobial Resistance: A One Health Perspective. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6, 521–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collineau, L.; Bourély, C.; Rousset, L.; Berger-Carbonne, A.; Ploy, M.-C.; Pulcini, C.; Colomb-Cotinat, M. Towards One Health Surveillance of Antibiotic Resistance: Characterisation and Mapping of Existing Programmes in Humans, Animals, Food and the Environment in France, 2021. Euro Surveill. 2023, 28, 2200804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulingam, T.; Parumasivam, T.; Gazzali, A.M.; Sulaiman, A.M.; Chee, J.Y.; Lakshmanan, M.; Chin, C.F.; Sudesh, K. Antimicrobial Resistance: Prevalence, Economic Burden, Mechanisms of Resistance and Strategies to Overcome. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 170, 106103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coculescu, B.-I. Antimicrobial Resistance Induced by Genetic Changes. J. Med. Life 2009, 2, 114–123. [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker, A.; Do, T.T.; Davis, M.D.M.; Barr, J. AMR Survivors? Chronic Living with Antimicrobial Resistant Infections. Glob. Public Health 2023, 18, 2217445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, M.; Ranucci, E.; Romagnoli, P.; Giaccone, V. Antimicrobial Resistance: A Global Emerging Threat to Public Health Systems. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 2857–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmberg, J.; Berg, C.; Lerner, H.; Waldenström, J.; Hessel, R. Potential Disease Transmission from Wild Geese and Swans to Livestock, Poultry and Humans: A Review of the Scientific Literature from a One Health Perspective. Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2017, 7, 1300450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.-F.; Li, H.-Q.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, F.-F.; Tan, J.; Zeng, Y.-B.; Wei, Q.-P.; Huang, J.-N.; Wu, C.-C.; Li, N.; et al. Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance Profile of Bacterial Pathogens Isolated from Poultry in Jiangxi Province, China from 2020 to 2022. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasnim, Y.; Rahman, M.K.; Abdul-Hamid, C.; Awosile, B. Beta-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli in Migratory Geese at West Texas Recreational Parks. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2025, 118, 102320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA. The European Union Summary Report on Antimicrobial Resistance in Zoonotic and Indicator Bacteria from Humans, Animals and Food in 2022–2023. Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/pub/9237 (accessed on 19 April 2025).
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute CLSI. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically, 11th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2018; Volume CLSI standards M07. [Google Scholar]
- EUCAST: MIC and Zone Distributions and ECOFFs. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/mic_distributions_and_ecoffs/ (accessed on 1 May 2022).
- Boulianne, M.; Arsenault, J.; Daignault, D.; Archambault, M.; Letellier, A.; Dutil, L. Drug Use and Antimicrobial Resistance among Escherichia coli and Enterococcus spp. Isolates from Chicken and Turkey Flocks Slaughtered in Quebec, Canada. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2016, 80, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lima-Filho, J.V.; Martins, L.V.; de Oliveira Nascimento, D.C.; Ventura, R.F.; Batista, J.E.C.; Silva, A.F.B.; Ralph, M.T.; Vaz, R.V.; Rabello, C.B.-V.; da Silva, I.D.M.M.; et al. Zoonotic Potential of Multidrug-Resistant Extraintestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli Obtained from Healthy Poultry Carcasses in Salvador, Brazil. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 17, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesp, A.; van Schaik, G.; Wiegel, J.; Heuvelink, A.; Mevius, D.; Veldman, K. Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring in Commensal and Clinical Escherichia coli from Broiler Chickens: Differences and Similarities. Prev. Vet. Med. 2022, 204, 105663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brian, V.L. VET01SEd5 | Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria Isolated From Animals, 5th ed.; CLSI: Malvern, PA, USA, 2019; Available online: https://clsi.org/standards/products/veterinary-medicine/documents/vet01s/ (accessed on 8 May 2022).
- R Core Team, R. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kruskal, W.H.; Wallis, W.A. Use of Ranks in One-Criterion Variance Analysis. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1952, 47, 583–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fay, M.P.; Proschan, M.A. Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney or t-Test? On Assumptions for Hypothesis Tests and Multiple Interpretations of Decision Rules. Stat. Surv. 2010, 4, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, O.J. Multiple Comparisons among Means. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1961, 56, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradigaravand, D.; Palm, M.; Farewell, A.; Mustonen, V.; Warringer, J.; Parts, L. Prediction of Antibiotic Resistance in Escherichia coli from Large-Scale Pan-Genome Data. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2018, 14, e1006258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; He, Z.; Wang, C. Monte Carlo Simulation to Optimize Polymyxin B Dosing Regimens for the Treatment of Gram-Negative Bacteremia. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2025, 15, 1533177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkwitz-Bedford, S.; Palm, M.; Demirtas, T.Y.; Mustonen, V.; Farewell, A.; Warringer, J.; Parts, L.; Moradigaravand, D. Machine Learning Prediction of Resistance to Subinhibitory Antimicrobial Concentrations from Escherichia coli Genomes. mSystems 2021, 6, e0034621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Antibiotics | Break-Point | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.008 | 0.016 | 0.031 | 0.063 | 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 32 | 64 | 128 | 256 | 512 | 1024 | MIC50 | MIC90 | ECOFF 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (µg/mL) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amoxicillin | 32 | 2 | 1 | 8 | 14 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 29 | 6 | 3 | 5 | 17 | 64 | 1024 | 8 | |||||||||
| 2.2% | 1.1% | 8.8% | 15.4% | 5.5% | 1.1% | 0.0% | 31.9% | 6.6% | 3.3% | 5.5% | 18.7% | ||||||||||||||
| Amoxicillin–clavulanic acid 1 | 32 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 6 | 16 | 22 | 18 | 14 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | 64 | 8 | ||||
| 1.1% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 3.3% | 1.1% | 6.6% | 17.6% | 24.2% | 19.8% | 15.4% | 6.6% | 1.1% | 1.1% | 1.1% | 1.1% | |||||||||
| Ceftriaxone | 4 | 3 | 10 | 19 | 17 | 12 | 9 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0.06 | 16 | 0.125 | |||
| 3.3% | 11.0% | 20.9% | 18.7% | 13.2% | 9.9% | 1.1% | 3.3% | 1.1% | 2.2% | 1.1% | 4.4% | 6.6% | 1.1% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 2.2% | ||||||||
| Colistin | 2 | 9 | 1 | 7 | 10 | 11 | 16 | 10 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 0.5 | 32 | 2 | ||||
| 9.9% | 1.1% | 7.7% | 11.0% | 12.1% | 17.6% | 11.0% | 2.2% | 2.2% | 1.1% | 2.2% | 16.5% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 1.1% | 4.4% | |||||||||
| Doxycycline | 16 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 16 | 12 | 8 | 16 | 20 | 9 | 3 | 16 | 64 | 8 | ||||||||||
| 1.1% | 3.3% | 0.0% | 3.3% | 17.6% | 13.2% | 8.8% | 17.6% | 22.0% | 9.9% | 3.3% | |||||||||||||||
| Enrofloxacin | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 12 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 11 | 18 | 9 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 7 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 32 | 0.125 |
| 1.1% | 1.1% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 4.4% | 13.2% | 4.4% | 2.2% | 4.4% | 12.1% | 19.8% | 9.9% | 4.4% | 4.4% | 3.3% | 7.7% | 4.4% | 2.2% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 1.1% | |||||
| Florfenicol | 16 | 1 | 3 | 20 | 24 | 8 | 3 | 13 | 10 | 9 | 16 | 256 | 16 | ||||||||||||
| 1.1% | 3.3% | 22.0% | 26.4% | 8.8% | 3.3% | 14.3% | 11.0% | 9.9% | |||||||||||||||||
| Imipenem | 4 | 15 | 9 | 16 | 16 | 29 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.5 | ||||||||||||
| 16.5% | 9.9% | 17.6% | 17.6% | 31.9% | 3.3% | 1.1% | 1.1% | 1.1% | |||||||||||||||||
| Neomycin | 32 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 10 | 31 | 41 | 4 | 3 | 64 | 64 | 8 | |||||||||||||
| 1.1% | 1.1% | 0.0% | 11.0% | 34.1% | 45.1% | 4.4% | 3.3% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Spectinomycin | 128 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 11 | 59 | 10 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 64 | 128 | 64 | |||||||||||
| 1.1% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 1.1% | 12.1% | 64.8% | 11.0% | 2.2% | 4.4% | 3.3% | ||||||||||||||||
| Potentiated sulphonamide 2 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 6 | 13 | 15 | 16 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 13 | 2 | 19 | 16 | 1024 | 0.5 | |||||||||
| 1.1% | 0.0% | 6.6% | 14.3% | 16.5% | 17.6% | 3.3% | 1.1% | 2.2% | 14.3% | 2.2% | 20.9% | ||||||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kerek, Á.; Szabó, Á.; Jerzsele, Á. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Profiles of Escherichia coli Isolates from Clinical Cases of Geese in Hungary Between 2022 and 2023. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050450
Kerek Á, Szabó Á, Jerzsele Á. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Profiles of Escherichia coli Isolates from Clinical Cases of Geese in Hungary Between 2022 and 2023. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(5):450. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050450
Chicago/Turabian StyleKerek, Ádám, Ábel Szabó, and Ákos Jerzsele. 2025. "Antimicrobial Susceptibility Profiles of Escherichia coli Isolates from Clinical Cases of Geese in Hungary Between 2022 and 2023" Antibiotics 14, no. 5: 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050450
APA StyleKerek, Á., Szabó, Á., & Jerzsele, Á. (2025). Antimicrobial Susceptibility Profiles of Escherichia coli Isolates from Clinical Cases of Geese in Hungary Between 2022 and 2023. Antibiotics, 14(5), 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050450








