Evaluating Tuberculosis and Drug Resistance in Serbia: A Ten-Year Experience from a Tertiary Center
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
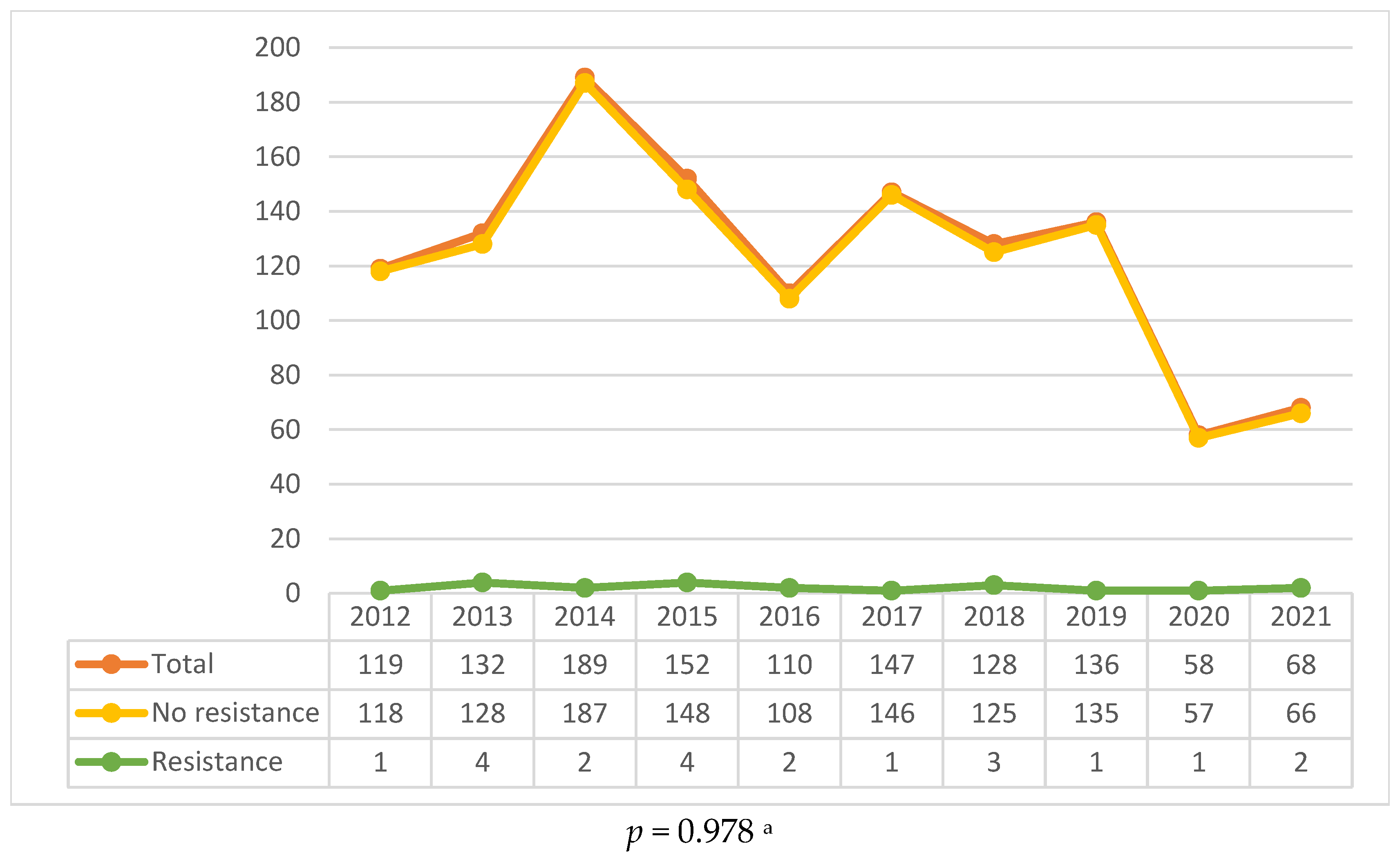
2.1. General Epidemiological Trends
2.2. Drug Resistance
2.3. Patient Characteristics
2.4. Comorbidities and Risk Factors
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population
4.2. Laboratory Methods
4.3. Resistance
4.4. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DM | diabetes mellitus |
| DST | drug susceptibility testing |
| EMB | ethambutol |
| HIV | human immunodeficiency virus |
| INH | isoniazid |
| LTBI | latent tuberculosis infection |
| MDR/RR-TB | multidrug-resistant/rifampicin-resistant tuberculosis |
| MDR-TB | multidrug-resistant tuberculosis |
| MTB/RPM | Mycobacterium tuberculosis/Rifampicin |
| PZA | pyrazinamide |
| RMP | rifampicin |
| RR-TB | rifampicin-resistant tuberculosis |
| STM | streptomycin |
| TB | tuberculosis |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- WHO. Global Tuberculosis Report 2023; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/373828/9789240083851-eng.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 29 September 2024).
- Zhang, S.-X.; Miao, F.-Y.; Yang, J.; Zhou, W.-T.; Lv, S.; Wei, F.-N.; Wang, Y.; Hu, X.-J.; Yin, P.; Zheng, P.-Y.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of HIV-negative tuberculosis, 1990–2021: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2024, 13, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- World Health Organization. Tuberculosis Incidence (per 100,000 Population). 2025. Available online: https://data.who.int/indicators/i/13B4226/C288D13 (accessed on 29 January 2025).
- Churchyard, G.; Kim, P.; Shah, N.S.; Rustomjee, R.; Gandhi, N.; Mathema, B.; Dowdy, D.; Kasmar, A.; Cardenas, V. What We Know About Tuberculosis Transmission: An Overview. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 216, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, P.; Meena, L.S. Factors affecting susceptibility to Mycobacterium tuberculosis: A close view of immunological defence mechanism. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 174, 2663–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufariello, J.M.; Chan, J.; Flynn, J.L. Latent tuberculosis: Mechanisms of host and bacillus that contribute to persistent infection. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2003, 3, 578–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houben, R.M.; Dodd, P.J. The Global Burden of Latent Tuberculosis Infection: A Re-estimation Using Mathematical Modelling. PLoS Med. 2016, 13, 1002152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Tuberculosis. Available online: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/tuberculosis (accessed on 20 September 2024).
- Osei, E.; Der, J.; Owusu, R.; Kofie, P.; Axame, W.K. The burden of HIV on Tuberculosis patients in the Volta region of Ghana from 2012 to 2015: Implication for Tuberculosis control. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, N.; Shemko, M.; Vaz, M.; D’Souza, G. An epidemiological evaluation of risk factors for tuberculosis in South India: A matched case control study. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2006, 10, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dong, B.; Ge, N.; Liu, G. Social economical status, behaviors and environment as the risk factors of tuberculosis in Chengdu China. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2001, 22, 102–104. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hassmiller, K.M. The association between smoking and tuberculosis. Salud Publica Mex. 2006, 48, S201–S216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamebo, T.; Mekesha, S.; Getahun, M.; Gumi, B.; Petros, B.; Ameni, G. Prevalence of pulmonary tuberculosis in homeless individuals in the Addis Ababa City, Ethiopia. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1128525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojo, T.; Ruan, C.; Hameed, T.; Malburg, C.; Thunga, S.; Smith, J.; Vieira, D.; Snyder, A.; Tampubolon, S.J.; Gyamfi, J.; et al. HIV, Tuberculosis, and Food Insecurity in Africa—A Syndemics-Based Scoping Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Yuan, S.Y.; Li, Q.G.; Li, J.X.; Yin, X.Y.; Liu, N.N. Prevalence and risk factors of malnutrition in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1173619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dianatinasab, M.; Joulaei, H.; Ghorbani, M.; Zarei, N.; Rezaeian, S.; Fararouei, M.; Greenwald, Z.R. Prevalence of Tuberculosis in HIV-positive Prisoners: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. AIDS Rev. 2018, 20, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niazi, A.K.; Kalra, S. Diabetes and tuberculosis: A review of the role of optimal glycemic control. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2012, 11, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munisankar, S.; Rajamanickam, A.; Balasubramanian, S.; Muthusamy, S.; Menon, P.A.; Ahamed, S.F.; Whalen, C.; Gumne, P.; Kaur, I.; Nadimpalli, V.; et al. Prevalence of proximate risk factors of active tuberculosis in latent tuberculosis infection: A cross-sectional study from South India. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 1011388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Global Lists of High Burden Countries for TB, Multidrug/Rifampicin-Resistant TB (MDR/RR-TB) and TB/HIV, 2021–2025; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; Available online: https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/hq-tuberculosis/who_globalhbcliststb_2021-2025_backgrounddocument.pdf?sfvrsn=f6b854c2_9 (accessed on 15 August 2024).
- Falzon, D.; Mirzayev, F.; Wares, F.; Baena, I.G.; Zignol, M.; Linh, N.; Weyer, K.; Jaramillo, E.; Floyd, K.; Raviglione, M. Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis around the world: What progress has been made? Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 45, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montiel Quezel-Guerraz, N.; Sánchez-Porto, A.; Ortega Torres, M.; Pérez Santos, M.J.; Acosta, F.; Guzman, A.; Correa Ruiz, A.; Bérmudez Ruiz, P. Antituberculosis drug resistance in isolates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in southeast Spain. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 20, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez del Molino Bernal, M.L.; Túñez, V.; Cruz-Ferro, E.; Fernández-Villar, A.; Vázquez-Gallardo, R.; Díaz-Cabanela, D.; Anibarro, L.; Grupo Gale de Estudio de Resistencias de, M. tuberculosis. Study of Mycobacterium tuberculosis drug resistance in the region of Galicia, Spain. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2005, 9, 1230–1235. [Google Scholar]
- Perdigão, J.; Macedo, R.; João, I.; Fernandes, E.; Brum, L.; Portugal, I. Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in Lisbon, Portugal: A molecular epidemiological perspective. Microb. Drug Resist. 2008, 14, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Public Health of Serbia “Dr. Milan Jovanović Batut”. Annual Report on Infectious Diseases, Serbia 2022; Institute of Public Health of Serbia “Dr. Milan Jovanović Batut”: Belgrade, Serbia, 2023; Available online: https://www.batut.org.rs/download/izvestaji/GodisnjiIzvestajZarazneBolestiSrbija2022.pdf (accessed on 6 June 2024).
- Zmak, L.; Obrovac, M.; Katalinic-Jankovic, V. A Snapshot of Drug-Resistant M. tuberculosis Strains in Croatia. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 901, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yordanova, S.; Bachiyska, E.; Tagliani, E.; Baykova, A.; Atanasova, Y.; Spitaleri, A.; Cirillo, D.M. Whole genome sequencing of Bulgarian rifampicin resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains. Folia Medica 2022, 64, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khawbung, J.L.; Nath, D.; Chakraborty, S. Drug resistant Tuberculosis: A review. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 74, 101574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsueh, P.R.; Liu, Y.C.; So, J.; Liu, C.Y.; Yang, P.C.; Luh, K.T. Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Taiwan. J. Infect. 2006, 52, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migliori, G.; Sotgiu, G.; D’ambrosio, L.; Centis, R.; Lange, C.; Bothamley, G.; Cirillo, D.; De Lorenzo, S.; Guenther, G.; Kliiman, K.; et al. TB and MDR/XDR-TB in European Union and European Economic Area countries: Managed or mismanaged? Eur. Respir. J. 2012, 39, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, N.R.; Nunn, P.; Dheda, K.; Schaaf, H.S.; Zignol, M.; van Soolingen, D.; Jensen, P.; Bayona, J. Multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis: A threat to global control of tuberculosis. Lancet 2010, 375, 1830–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, V.; Kadam, V.; Narang, P.; Singh, V. Prevalence of drug-resistant pulmonary tuberculosis in India: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradipta, I.S.; Forsman, L.D.; Bruchfeld, J.; Hak, E.; Alffenaar, J.W. Risk factors of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: A global systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Infect. 2018, 77, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, L.; Shen, Y.; Mupere, E.; Kizza, A.; Hill, P.C.; Whalen, C.C. Transmission of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Households and the Community: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 185, 1327–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotgiu, G.; Tiberi, S.; D’Ambrosio, L.; Centis, R.; Alffenaar, J.W.; Caminero, J.A.; Arbex, M.A.; Guizado, V.A.; Aleksa, A.; Dore, S.; et al. Faster for less: The new “shorter” regimen for multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 48, 1503–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dheda, K.; Gumbo, T.; Gandhi, N.R.; Murray, M.; Theron, G.; Udwadia, Z.; Migliori, G.B.; Warren, R. Global control of tuberculosis: From extensively drug-resistant to untreatable tuberculosis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2014, 2, 321–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dooley, K.E.; Tang, T.; Golub, J.E.; Dorman, S.E.; Cronin, W. Impact of diabetes mellitus on treatment outcomes of patients with active tuberculosis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 80, 634–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dooley, K.E.; Chaisson, R.E. Tuberculosis and diabetes mellitus: Convergence of two epidemics. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2009, 9, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Restrepo, B.I.; Scordo, J.M.; Aguillón-Durán, G.P.; Ayala, D.; Quirino-Cerrillo, A.P.; Loera-Salazar, R.; Cruz-González, A.; Caso, J.A.; Joya-Ayala, M.; García-Oropesa, E.M.; et al. Differential Role of Type 2 Diabetes as a Risk Factor for Tuberculosis in the Elderly versus Younger Adults. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.A.; Harries, A.D.; Jeon, C.Y.; Hart, J.E.; Kapur, A.; Lönnroth, K.; Ottmani, S.E.; Goonesekera, S.D.; Murray, M.B. The impact of diabetes on tuberculosis treatment outcomes: A systematic review. BMC Med. 2011, 9, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.L.; Wang, L.X.; Chen, M.T. Mutual Impact of Diabetes Mellitus and Tuberculosis in China. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2017, 30, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xiao, H.; Sugawara, I. Tuberculosis complicated by diabetes mellitus at shanghai pulmonary hospital, China. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 62, 390–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaishya, R.; Misra, A.; Vaish, A.; Singh, S.K. Diabetes and tuberculosis syndemic in India: A narrative review of facts, gaps in care and challenges. J. Diabetes 2024, 16, 13427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, U.; Masood, K.I.; Khan, A.; Irfan, M.; Saifullah, N.; Jamil, B.; Hasan, Z. Tuberculosis and diabetes mellitus: Relating immune impact of co-morbidity with challenges in disease management in high burden countries. J. Clin. Tuberc. Other Mycobact. Dis. 2022, 29, 100343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gao, W.; Li, M.; Luo, Q.; Xiang, Y.; Bao, K. The impact of COVID-19 pandemic on reported tuberculosis incidence and mortality in China: An interrupted time series analysis. J. Glob. Health 2023, 13, 06043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsch-Feldman, M.; Pratt, R.H.; Price, S.F.; Tsang, C.A.; Self, J.L. Tuberculosis—United States, 2020. MMWR-Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2021, 70, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soko, R.N.; Burke, R.M.; Feasey, H.R.; Sibande, W.; Nliwasa, M.; Henrion, M.Y.; Khundi, M.; Dodd, P.J.; Ku, C.C.; Kawalazira, G.; et al. Effects of Coronavirus Disease Pandemic on Tuberculosis Notifications, Malawi. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 1831–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniel, O.J.; Bamidele, J.O.; Alabi, A.D.; Tijani, M.A.; Akinleye, C.A.; Oritogun, K.S.; Soyinka, F.O.; Adejumo, O.A. The effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on Tuberculosis (TB) case notification in Ogun State, Nigeria. Afr. Health Sci. 2023, 23, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belic, S.; Ivanovic, A.; Todorovic, A.; Maric, N.; Milic, S.; Perić, J.; Stjepanović, M.; Krajisnik, S.; Milosevic, I.; Jankovic, J. Correlation of the severity of the clinical presentation of SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia with respiratory function parameters in the post-COVID period. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2024, 18, 1347–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington, K.R.; Gandhi, N.R.; Shah, N.S.; Naidoo, K.; Auld, S.C.; Andrews, J.R.; Brust, J.C.; Lutchminarain, K.; Coe, M.; Willis, F.; et al. The impact of COVID-19 national lockdowns on drug-resistant tuberculosis in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa: A spatial analysis. Ann. Epidemiol. 2024, 97, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, T.; Morden, E.; Smith, M.; von Delft, A.; Kassanjee, R.; Mudaly, V.; Boulle, A.; Davies, M.A. Severe outcomes among adults with TB during COVID-19. IJTLD Open 2024, 1, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | Total | Resistance | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (%) | No (n = 1218) | Yes (n = 21) | p Value | |
| Age | 53.4 ± 18.4 | 53.6 ± 18.4 | 46.4 ± 19.1 | 0.079 a |
| Form of TB | ||||
| Lung | 1080 (87.2%) | 1059 (86.9%) | 21 (100%) | 0.341 b |
| Non-lung | 14 (1.1%) | 14 (1.1%) | 0 | |
| Both | 145 (11.7%) | 145 (11.9%) | 0 | |
| Previous TB | 86 (6.9%) | 82 (95.3%) | 4 (4.7%) | 0.052 b |
| Age of previous TB | 37.5 ± 12.6 | 37.8 ± 12.3 | 30.5 ± 17.3 | 0.256 a |
| Sample | ||||
| Sputum | 938 (75.8%) | 920 (75.6%) | 18 (85.7%) | 0.165 b |
| Aspirate | 113 (9.1%) | 110 (9.0%) | 3 (14.3%) | |
| Biopsy | 180 (14.5%) | 180 (14.8%) | 0 | |
| Other | 7 (0.6%) | 7 (0.6%) | 0 | |
| Known contact | 97 (7.8%) | 95 (7.8%) | 2 (9.5%) | 0.677 b |
| Previous lung disease | 128 (10.3%) | 124 (10.2%) | 4 (19.0%) | 0.263 b |
| COPD, asthma | 78 (60.9%) | 76 (61.3%) | 2 (50%) | 0.643 b |
| Carcinoma | 33 (25.8%) | 31 (25%) | 2 (50%) | 0.273 b |
| Risk factors and comorbidities | 296 (23.9%) | 294 (24.1%) | 2 (9.5%) | 0.119 c |
| Methodology | Positive N (%) | Negative N (%) | Not Done N (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct microscopy | 696 (56.2%) | 532 (43%) | 10 (0.8%) |
| GeneXpert Mycobacterium tuberculosis/rifampicin (MTB/RPM) | 132 (10.7%) | 9 (0.7%) | 1097 (88.6%) |
| BACTEC™ MGIT™ 960 | 198 (16%) | 7 (0.6%) | 1033 (83.4%) |
| Lowenstein Jensen cultivation | 1004 (81.1%) | 172 (13.9%) | 62 (5%) |
| Pathologic conformation | 192 (15.5%) | 12 (1%) | 1034 (83.5%) |
| One diagnostic method | 457 (36.9%) | ||
| Two diagnostic methods | 591 (47.7%) | ||
| Three diagnostic methods | 174 (14.0%) | ||
| Four diagnostic methods | 17 (1.4%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stjepanovic, M.; Mijatovic, S.; Nikolic, N.; Maric, N.; Stevanovic, G.; Soldatovic, I.; Barac, A. Evaluating Tuberculosis and Drug Resistance in Serbia: A Ten-Year Experience from a Tertiary Center. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14030320
Stjepanovic M, Mijatovic S, Nikolic N, Maric N, Stevanovic G, Soldatovic I, Barac A. Evaluating Tuberculosis and Drug Resistance in Serbia: A Ten-Year Experience from a Tertiary Center. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(3):320. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14030320
Chicago/Turabian StyleStjepanovic, Mihailo, Snjezana Mijatovic, Nikola Nikolic, Nikola Maric, Goran Stevanovic, Ivan Soldatovic, and Aleksandra Barac. 2025. "Evaluating Tuberculosis and Drug Resistance in Serbia: A Ten-Year Experience from a Tertiary Center" Antibiotics 14, no. 3: 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14030320
APA StyleStjepanovic, M., Mijatovic, S., Nikolic, N., Maric, N., Stevanovic, G., Soldatovic, I., & Barac, A. (2025). Evaluating Tuberculosis and Drug Resistance in Serbia: A Ten-Year Experience from a Tertiary Center. Antibiotics, 14(3), 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14030320







