Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus T144: A Hypervirulent Model Strain for Infection Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Analysis of Antibiotic Susceptibility and Pathogenicity
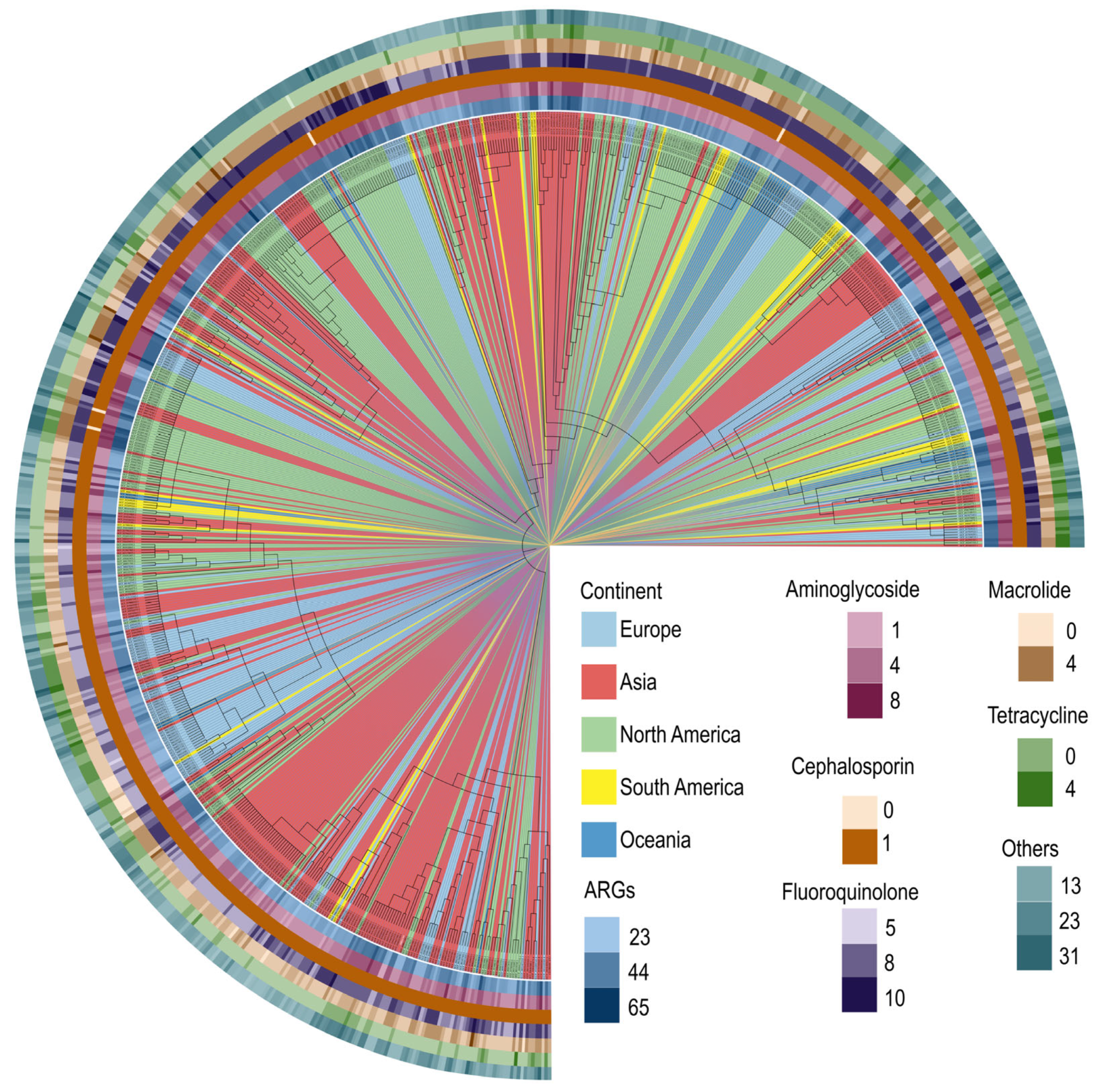
2.2. Antimicrobial Resistance Profiling and Phylogenetic Analysis of MRSA T144
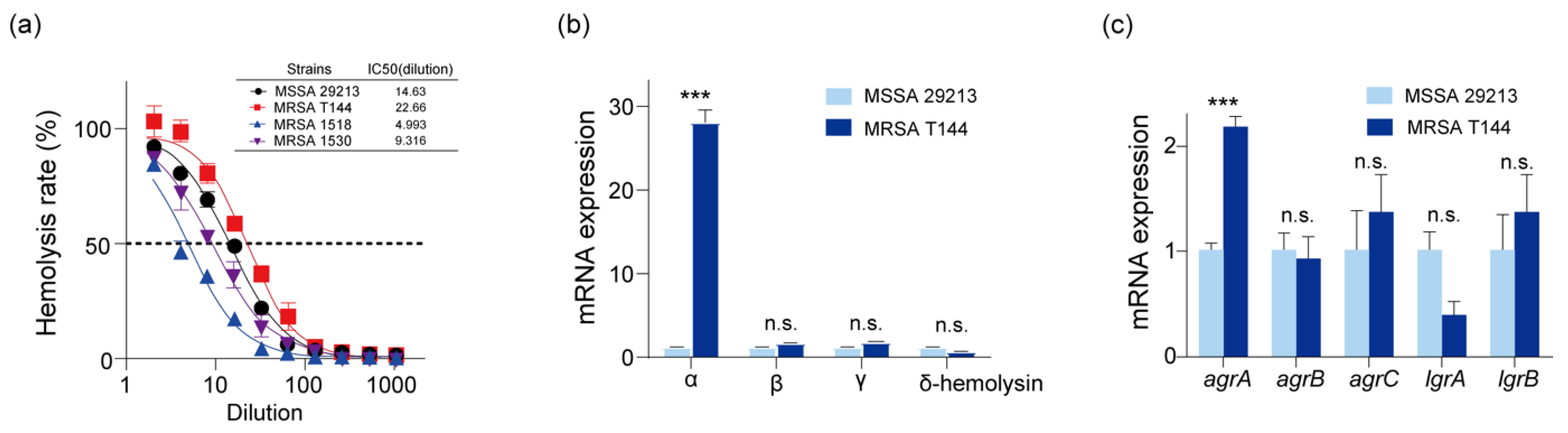
2.3. Virulence Gene Characterization and Virulence Determinants of MRSA T144
2.4. Construction of Mouse Lung Infection Models
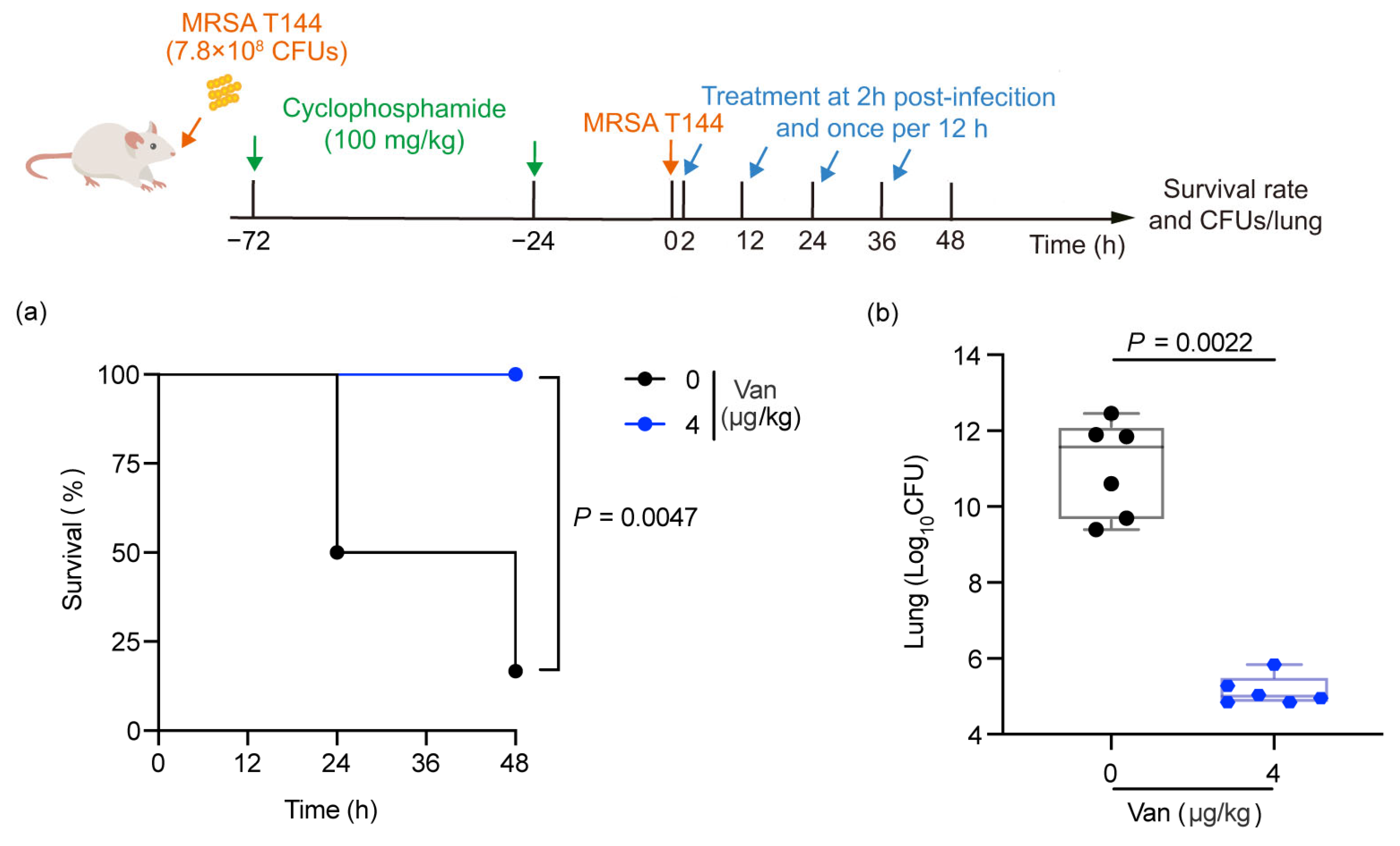
2.5. Efficacy Evaluation of Vancomycin in the MRSA T144-Infected Mouse Model
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Test
4.3. Virulence Evaluation in Galleria Mellonella and Mice
4.4. LD50 Determination
- Xm represents the logarithmic value of the dose in the highest-dose group.
- i is the logarithmic ratio of the doses between adjacent high- and low-dose groups.
- ΣP is the cumulative sum of the mortality rates across all groups.
4.5. Whole-Genome Sequencing
4.6. Bioinformatics
4.7. Hemolysis Assay
4.8. RT-PCR Analysis
4.9. Mouse Lung Infection Model
4.10. Dynamic Analysis of MRSA T144 in Mouse Lungs
4.11. Immunofluorescence
4.12. Determination of Inflammatory Factors in MRSA T144 Infection
4.13. Rescue of Infected Mice with Vancomycin
4.14. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MRSA | methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus |
| VRSA | vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus |
| QA-AuNCs | quaternary ammonium-capped gold nanoclusters |
| MDR | multidrug-resistant |
| MICs | minimum inhibitory concentrations |
| MSSA | methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus |
| PVL | Panton–Valentine leukocidin |
| RBCs | red blood cells |
| CBC | complete blood count |
| LA-MRSA | livestock-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus |
| CA-MRSA | community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus |
| HA-MRSA | hospital-associated MRSA |
| SPF | specific pathogen-free |
| MHB | Mueller–Hinton Broth |
| MHA | Mueller–Hinton Agar |
| BHI | Brain Heart Infusion |
| VFDB | Virulence Factor Database |
References
- Hennekinne, J.A.; De Buyser, M.L.; Dragacci, S. Staphylococcus aureus and its food poisoning toxins: Characterization and outbreak investigation. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 36, 815–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlio, J.-P. Staphylococcus aureus and Sézary syndrome. Blood 2024, 143, 1436–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossop, M.; Ish-Horowicz, J.; Hughes, D.; Dobra, R.; Cunanan, A.G.; Rosenthal, M.; Carr, S.B.; Ramadan, N.; Nolan, L.M.; Davies, J.C. Chronicity Counts: The Impact of P. aeruginosa, S. aureus, and Co-Infection in Cystic Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2024, 210, 240–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.Y.; Davis, J.S.; Eichenberger, E.; Holland, T.L.; Fowler, V.G., Jr. Staphylococcus aureus infections: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and management. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 603–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, Y.; Yang, S.; Rao, X. Vancomycin resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections: A review of case updating and clinical features. J. Adv. Res. 2020, 21, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, M.Z.; Daum, R.S. Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Epidemiology and clinical consequences of an emerging epidemic. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 616–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhundi, S.; Zhang, K. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Molecular Characterization, Evolution, and Epidemiology. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, H.F.; Deleo, F.R. Waves of resistance: Staphylococcus aureus in the antibiotic era. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, H.F.; Fowler, V.G. Intertwining clonality and resistance: Staphylococcus aureus in the antibiotic era. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 134, e185824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaborators, A.R. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, N.A.; Sharma-Kuinkel, B.K.; Maskarinec, S.A.; Eichenberger, E.M.; Shah, P.P.; Carugati, M.; Holland, T.L.; Fowler, V.G., Jr. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: An overview of basic and clinical research. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLeo, F.R.; Chambers, H.F. Reemergence of antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in the genomics era. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 2464–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, E.; Smith, D.L.; Laxminarayan, R. Hospitalizations and deaths caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, United States, 1999-2005. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 1840–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Zhou, M.; Qian, Y.; Cong, Z.; Chen, S.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, W.; Dai, C.; Shao, N.; Ji, Z.; et al. Addressing MRSA infection and antibacterial resistance with peptoid polymers. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lou, W.; Liu, J.; Ding, B.; Fan, W.; Hong, J. A novel antimicrobial polymer efficiently treats multidrug-resistant MRSA-induced bloodstream infection. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20192354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, Y.; Chen, T.; Yang, Z.; Xiang, G.; Xu, K.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, N.; He, L.; Liu, Q.; Li, M. Small regulatory RNA RSaX28 promotes virulence by reinforcing the stability of RNAIII in community-associated ST398 clonotype Staphylococcus aureus. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2024, 13, 2341972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Pan, Z.; Liao, X.; Zhong, Y.; Guo, J.; Pang, R.; Chen, X.; Ye, G.; Su, Y. Uracil restores susceptibility of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus to aminoglycosides through metabolic reprogramming. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1133685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helaine, S.; Conlon, B.P.; Davis, K.M.; Russell, D.G. Host stress drives tolerance and persistence: The bane of anti-microbial therapeutics. Cell Host Microbe 2024, 32, 852–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, G.J.; Mendonça, N. Association between antimicrobial resistance and virulence in Escherichia coli. Virulence 2012, 3, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Li, M.; Spiller, O.B.; Andrey, D.O.; Hinchliffe, P.; Li, H.; MacLean, C.; Niumsup, P.; Powell, L.; Pritchard, M.; et al. Balancing mcr-1 expression and bacterial survival is a delicate equilibrium between essential cellular defence mechanisms. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ding, S.; Dietrich, R.; Märtlbauer, E.; Zhu, K. A Biosurfactant-Inspired Heptapeptide with Improved Specificity to Kill MRSA. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2017, 56, 1486–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, Y.; Hu, F.; Zhu, K.; Jiang, X. Gold Nanoclusters for Targeting Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus In Vivo. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2018, 57, 3958–3962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Dong, N.; Zheng, Z.; Lin, D.; Huang, M.; Wang, L.; Chan, E.W.; Shu, L.; Yu, J.; Zhang, R.; et al. A fatal outbreak of ST11 carbapenem-resistant hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae in a Chinese hospital: A molecular epidemiological study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinges, M.M.; Orwin, P.M.; Schlievert, P.M. Exotoxins of Staphylococcus aureus. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 13, 16–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Song, G.; Sun, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y. Prevalence and Therapies of Antibiotic-Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassini, A.; Högberg, L.D.; Plachouras, D.; Quattrocchi, A.; Hoxha, A.; Simonsen, G.S.; Colomb-Cotinat, M.; Kretzschmar, M.E.; Devleesschauwer, B.; Cecchini, M.; et al. Attributable deaths and disability-adjusted life-years caused by infections with antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the EU and the European Economic Area in 2015: A population-level modelling analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadashi, M.; Nasiri, M.J.; Fallah, F.; Owlia, P.; Hajikhani, B.; Emaneini, M.; Mirpour, M. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Iran: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2018, 12, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Sun, H.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Hu, B.; Yu, Y.; Sun, Z.; Chu, Y.; Cao, B.; Liao, K.; et al. Antimicrobial resistance trends among 5608 clinical Gram-positive isolates in China: Results from the Gram-Positive Cocci Resistance Surveillance program (2005-2010). Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 73, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huijsdens, X.W.; van Dijke, B.J.; Spalburg, E.; van Santen-Verheuvel, M.G.; Heck, M.E.; Pluister, G.N.; Voss, A.; Wannet, W.J.; de Neeling, A.J. Community-acquired MRSA and pig-farming. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2006, 5, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ballhausen, B.; Jung, P.; Kriegeskorte, A.; Makgotlho, P.E.; Ruffing, U.; von Müller, L.; Köck, R.; Peters, G.; Herrmann, M.; Ziebuhr, W.; et al. LA-MRSA CC398 differ from classical community acquired-MRSA and hospital acquired-MRSA lineages: Functional analysis of infection and colonization processes. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 304, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Nunez-Garcia, J.; Kearns, A.M.; Doumith, M.; Butaye, P.R.; Argudín, M.A.; Lahuerta-Marin, A.; Pichon, B.; AbuOun, M.; Rogers, J.; et al. Livestock-Associated Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (LA-MRSA) Clonal Complex (CC) 398 Isolated from UK Animals belong to European Lineages. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Alen, S.; Ballhausen, B.; Peters, G.; Friedrich, A.W.; Mellmann, A.; Köck, R.; Becker, K. In the centre of an epidemic: Fifteen years of LA-MRSA CC398 at the University Hospital Münster. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 200, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, D.A.; Bakker, S.; Coombs, G.W.; Tan, H.; Monecke, S.; Heffernan, H. Emergence and molecular characterization of clonal complex 398 (CC398) methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in New Zealand. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 1428–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wagenaar, J.A.; Yue, H.; Pritchard, J.; Broekhuizen-Stins, M.; Huijsdens, X.; Mevius, D.J.; Bosch, T.; Van Duijkeren, E. Unexpected sequence types in livestock associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA): MRSA ST9 and a single locus variant of ST9 in pig farming in China. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 139, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Du, N.; Shen, E.; Chen, H.; Niu, J.; Ye, H.; Chen, M. Molecular evidence for spread of two major methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clones with a unique geographic distribution in Chinese hospitals. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J.; Lauderdale, T.Y.; Lu, C.T.; Chuang, Y.Y.; Yang, C.C.; Wu, T.S.; Lee, C.Y.; Lu, M.C.; Ko, W.C.; Huang, Y.C. Clinical and molecular features of MDR livestock-associated MRSA ST9 with staphylococcal cassette chromosome mecXII in humans. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.W.; Chiang, P.H.; Huang, Y.C. Livestock-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus ST9 in pigs and related personnel in Taiwan. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrel, M.; Perencevich, E.N.; David, M.Z. USA300 Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus, United States, 2000-2013. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 1973–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurlow, L.R.; Joshi, G.S.; Richardson, A.R. Virulence strategies of the dominant USA300 lineage of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA). FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 65, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, K.Y.; Monk, I.R.; Lin, Y.H.; Seemann, T.; Tuck, K.L.; Porter, J.L.; Stepnell, J.; Coombs, G.W.; Davies, J.K.; Stinear, T.P.; et al. Hyperexpression of α-hemolysin explains enhanced virulence of sequence type 93 community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, M. MRSA virulence and spread. Cell Microbiol. 2012, 14, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.D.; Malachowa, N.; Whitney, A.R.; Braughton, K.R.; Gardner, D.J.; Long, D.; Bubeck Wardenburg, J.; Schneewind, O.; Otto, M.; Deleo, F.R. Comparative analysis of USA300 virulence determinants in a rabbit model of skin and soft tissue infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 204, 937–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinska, U.; Hermans, K.; Meulemans, L.; Dumitrescu, O.; Badiou, C.; Duchateau, L.; Haesebrouck, F.; Etienne, J.; Lina, G. Panton-Valentine leukocidin does play a role in the early stage of Staphylococcus aureus skin infections: A rabbit model. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhakdi, S.; Tranum-Jensen, J. Alpha-toxin of Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiol. Rev. 1991, 55, 733–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Hobaugh, M.R.; Shustak, C.; Cheley, S.; Bayley, H.; Gouaux, J.E. Structure of staphylococcal alpha-hemolysin, a heptameric transmembrane pore. Science 1996, 274, 1859–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, T.S.; Hilliard, J.J.; Jones-Nelson, O.; Keller, A.E.; O’Day, T.; Tkaczyk, C.; DiGiandomenico, A.; Hamilton, M.; Pelletier, M.; Wang, Q.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus α toxin potentiates opportunistic bacterial lung infections. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 329ra331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, T.; Zou, X.; Wu, S.; Zhu, J. Panton-valentine leucocidin carrying Staphylococcus aureus causing necrotizing pneumonia inactivates the JAK/STAT signaling pathway and increases the expression of inflammatory cytokines. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 86, 104582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKelvey, M.; Uddin, M.B.; Palani, S.; Shao, S.; Sun, K. IL-10 Counteracts IFN-γ to Alleviate Acute Lung Injury in a Viral-Bacterial Superinfection Model. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2024, 71, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Guideline M100, 34th ed.; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, H.J.; Lee, E.H.; Yoon, Y.; Chua, B.; Son, A. Portable lysis apparatus for rapid single-step DNA extraction of Bacillus subtilis. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 120, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.Y.; Chang, H.Y.; Lu, J.K.; Huang, Y.C.; Harroun, S.G.; Tseng, Y.T.; Li, Y.J.; Huang, C.C.; Chang, H.T. Self-assembly of antimicrobial peptides on gold nanodots: Against multidrug-resistant bacteria and wound-healing application. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 7189–7199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Antibiotics | MIC (µg/mL) | Antibiotics | Inhibition Zone Diameter (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amoxicillin | 16 | Penicillin G (10 units) | 6 |
| Ceftiofur | 8 | Quinupristin/dalfopristin | 17 |
| Cefoxitin | 8 | Tetracycline (30 µg) | 8 |
| Clindamycin | >128 | Fusidic acid (10 µg) | 25 |
| Doxycycline | 16 | Gentamicin (10 µg) | 12 |
| Enrofloxacin | 2 | Ciprofloxacin (5 µg) | 16 |
| Erythromycin | >128 | Rifampicin (5 µg) | 29 |
| Chloramphenicol | 32 | ||
| Florfenicol | 64 | ||
| Linezolid | 1 | ||
| Vancomycin | 0.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mao, C.; Liu, Y.; Song, M.; Shen, J.; Zhu, K. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus T144: A Hypervirulent Model Strain for Infection Models. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14030270
Mao C, Liu Y, Song M, Shen J, Zhu K. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus T144: A Hypervirulent Model Strain for Infection Models. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(3):270. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14030270
Chicago/Turabian StyleMao, Changsi, Yuan Liu, Meirong Song, Jianzhong Shen, and Kui Zhu. 2025. "Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus T144: A Hypervirulent Model Strain for Infection Models" Antibiotics 14, no. 3: 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14030270
APA StyleMao, C., Liu, Y., Song, M., Shen, J., & Zhu, K. (2025). Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus T144: A Hypervirulent Model Strain for Infection Models. Antibiotics, 14(3), 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14030270







