Impact of Antibiotic Therapy with Ceftazidime Avibactam vs. Best Available Therapy in Adult Patients with Bacteremia Caused by Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacterales
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Sociodemographic Characteristics
2.2. Microbiological Data
2.3. Antimicrobial Therapy and Non-Adjusted Outcomes
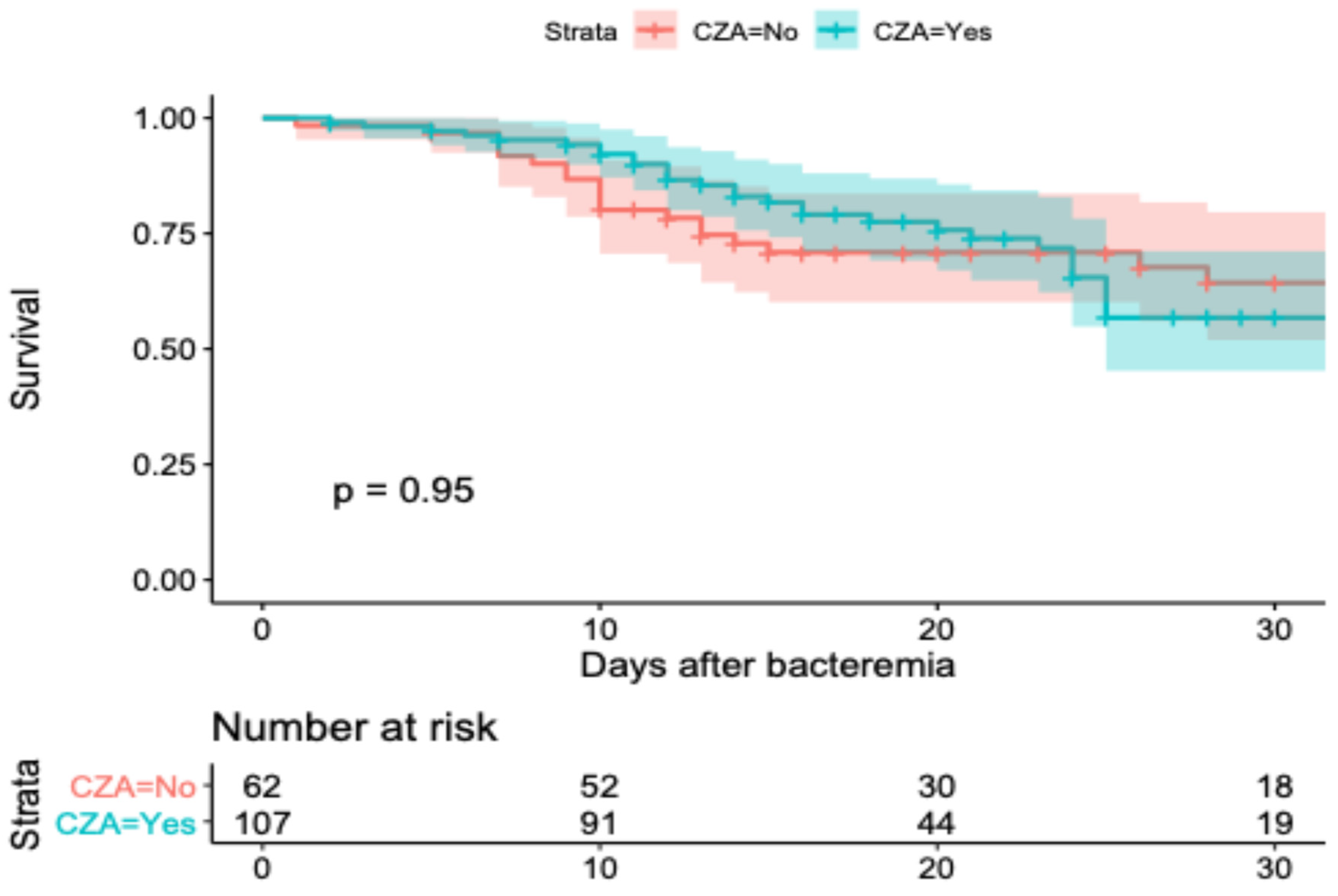
2.4. Survival Model and Adjusted Outcomes
2.5. Sensibility Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
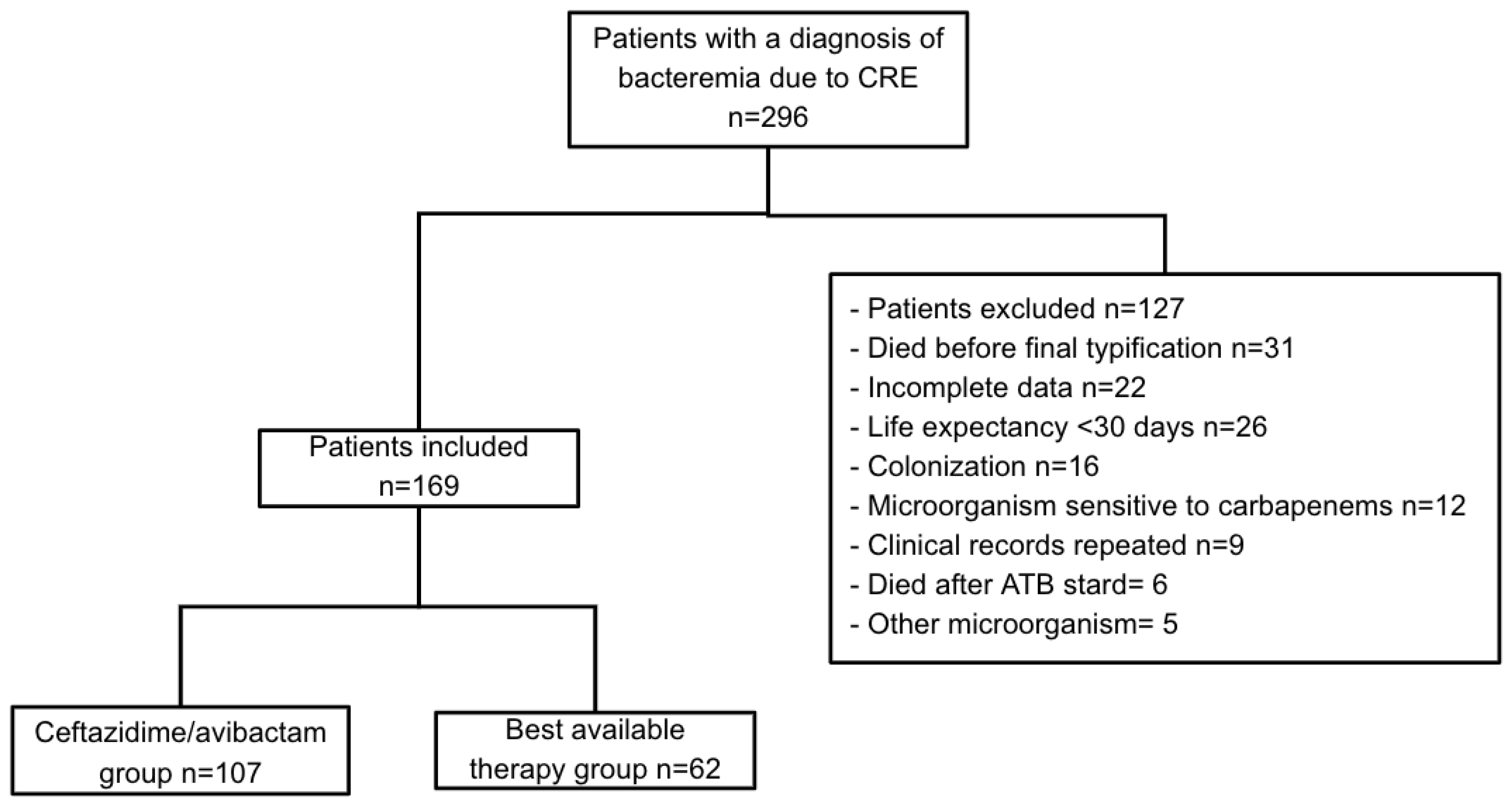
4.1. Study Design and Population
4.2. Study Participants
4.3. Endpoints
4.4. Definitions and Covariations
4.5. Microbiology
4.6. Statistical Analysis
4.7. Ethics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CRE | Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales |
| CZA | Ceftazidime/avibactam |
| BAT | Best available therapy |
| ATM | Aztreonam |
| SMD | Standardized mean difference |
| SD | Standard deviation |
References
- Murray, C.J.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Aguilar, G.R.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logan, L.K.; Weinstein, R.A. The Epidemiology of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae: The Impact and Evolution of a Global Menace. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215, S28–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, J.P., 3rd; Clark, N.M.; Zhanel, G.G. Escalating antimicrobial resistance among Enterobacteriaceae: Focus on carbapenemases. Expert. Opin. Pharmacother. 2021, 22, 1455–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasko, M.J.; Nicolau, D.P. Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacterales: Considerations for Treatment in the Era of New Antimicrobials and Evolving Enzymology. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2020, 22, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Baño, J.; Gutiérrez-Gutiérrez, B.; Machuca, I.; Pascual, A. Treatment of Infections Caused by Extended-Spectrum-Beta-Lactamase-, AmpC-, and Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, e00079-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castón, J.J.; Cano, A.; Pérez-Camacho, I.; Aguado, J.M.; Carratalá, J.; Ramasco, F.; Soriano, A.; Pintado, V.; Castelo-Corral, L.; Sousa, A.; et al. Impact of ceftazidime/avibactam versus best available therapy on mortality from infections caused by carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales (CAVICOR study). J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2022, 77, 1452–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abril, D.; Vergara, E.; Palacios, D.; Leal, A.L.; Marquez-Ortiz, R.A.; Madroñero, J.; Corredor Rozo, Z.L.; De La Rosa, Z.; Nieto, C.A.; Vanegas, N.; et al. Within patient genetic diversity of bla(KPC) harboring Klebsiella pneumoniae in a Colombian hospital and identification of a new NTE(KPC) platform. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saavedra, S.Y.; Bernal, J.F.; Montilla-Escudero, E.; Arevalo, S.A.; Prada, D.A.; Valencia, M.F.; Moreno, J.; Hidalgo, A.M.; Garcia-Vega, A.S.; Abrudan, M.; et al. Complexity of Genomic Epidemiology of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates in Colombia Urges the Reinforcement of Whole Genome Sequencing-Based Surveillance Programs. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, S290–S299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacterales. 2024. Available online: https://arpsp.cdc.gov/profile/arln/cre (accessed on 24 June 2024).
- Ma, J.; Song, X.; Li, M.; Yu, Z.; Cheng, W.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, A.; Sun, H.; et al. Global spread of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae: Epidemiological features, resistance mechanisms, detection and therapy. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 266, 127249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Jin, L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Chen, F.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, C.; Chen, H.; Cao, B.; Wang, H. Bloodstream Infections Caused by Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacterales: Risk Factors for Mortality, Antimicrobial Therapy and Treatment Outcomes from a Prospective Multicenter Study. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasina, E.; Haidich, A.B.; Kokkali, S.; Arvanitidou, M. Efficacy and safety of tigecycline for the treatment of infectious diseases: A meta-analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2011, 11, 834–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satlin, M.J.; Chen, L.; Gomez-Simmonds, A.; Marino, J.; Weston, G.; Bhowmick, T.; Seo, S.K.; Sperber, S.J.; Kim, A.C.; Eilertson, B.; et al. Impact of a Rapid Molecular Test for Klebsiella pneumoniae Carbapenemase and Ceftazidime-Avibactam Use on Outcomes After Bacteremia Caused by Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacterales. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 75, 2066–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcone, M.; Daikos, G.L.; Tiseo, G.; Bassoulis, D.; Giordano, C.; Galfo, V.; Leonildi, A.; Tagliaferri, E.; Barnini, S.; Sani, S.; et al. Efficacy of Ceftazidime-avibactam Plus Aztreonam in Patients With Bloodstream Infections Caused by Metallo-β-lactamase-Producing Enterobacterales. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 72, 1871–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, V.H.; Rogers, C.A.; Chang, K.T.; Weston, J.S.; Caeiro, J.P.; Garey, K.W. Impact of multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteremia on patient outcomes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 3717–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- So-Ngern, A.; Osaithai, N.; Meesing, A.; Chumpangern, W. Mortality rate and factors associated with mortality of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae infection. Drug Target. Insights 2023, 17, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, G.; Cai, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, D.; Wang, L.; Qiu, Y.; Deng, H.; Bai, H.; Bian, X.; He, J. Ceftazidime/Avibactam-Based Versus Polymyxin B-Based Therapeutic Regimens for the Treatment of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Infection in Critically Ill Patients: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2022, 11, 1917–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Hu, Q.; Zhou, P.; Deng, S. Ceftazidime-avibactam versus polymyxins in treating patients with carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Infection 2024, 52, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Gutierrez, B.; Salamanca, E.; de Cueto, M.; Hsueh, P.R.; Viale, P.; Pano-Pardo, J.R.; Venditti, M.; Tumbarello, M.; Daikos, G.; Canton, R.; et al. Effect of appropriate combination therapy on mortality of patients with bloodstream infections due to carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae (INCREMENT): A retrospective cohort study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojica, M.F.; De La Cadena, E.; Garcia-Betancur, J.C.; Porras, J.; Novoa-Caicedo, I.; Paez-Zamora, L.; Pallares, C.; Appel, T.M.; Radice, M.A.; Castaneda-Mendez, P.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms of Resistance to Ceftazidime/Avibactam in Clinical Isolates of Enterobacterales and Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Latin American Hospitals. mSphere 2023, 8, e0065122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Guo, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Dong, D.; Zhu, D.; He, P.; Hu, F. In vitro and in vivo bactericidal activity of ceftazidime-avibactam against Carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2018, 7, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Boodman, C.; Prayag, P.; Manesh, A.; Kumar, T.P. Ceftazidime-avibactam and aztreonam combination for Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales bloodstream infections with presumed Metallo-beta-lactamase production: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert. Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2024, 22, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Sun, X.; Ma, X. Systematic review and meta-analysis of mortality of patients infected with carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2017, 16, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Han, X.; Li, Y.; Li, M. Assessment of Mortality-Related Risk Factors and Effective Antimicrobial Regimens for Treatment of Bloodstream Infections Caused by Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacterales. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, e0069821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests, 29th ed.; M200; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Caliskan-Aydogan, O.; Alocilja, E.C. A Review of Carbapenem Resistance in Enterobacterales and Its Detection Techniques. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austin, P.C.; Stuart, E.A. Moving towards best practice when using inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) using the propensity score to estimate causal treatment effects in observational studies. Stat. Med. 2015, 34, 3661–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
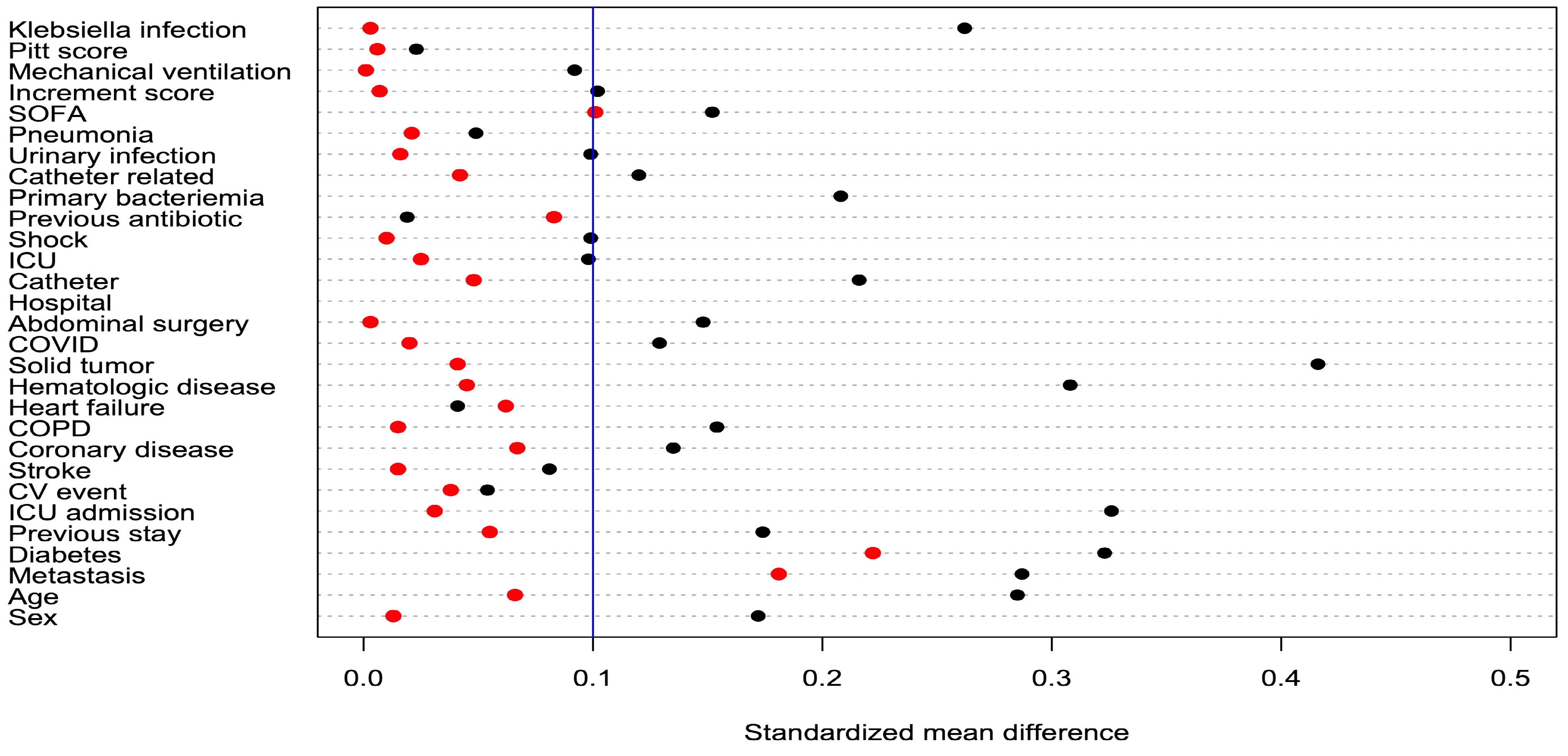
| Original Cohort (N = 169) | Post-IPWT | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CZA (n = 107) | BAT (n = 62) | SMD | CZA | BAT | SMD | |
| Male sex, n (%) | 66 (61.7) | 33 (53.2) | 0.172 | 62.3 (59.6) | 36.8 (58.9) | 0.013 |
| Age, years; mean (SD) | 53.5 (16.5) | 58.2 (16.7) | 0.285 | 54.7 (16.5) | 53.6 (17.2) | 0.066 |
| Charlson score, mean (SD) | 4.0 (2.5) | 4.2 (3.0) | 0.057 | 3.9 (2.4) | 3.7 (2.9) | 0.083 |
| Comorbidities, n (%) | ||||||
| Acute heart attack | 15 (14.0) | 6 (9.7) | 0.135 | 13.3 (12.7) | 6.6 (10.5) | 0.067 |
| COPD | 6 (5.6) | 6 (9.7) | 0.154 | 7.2 (6.9) | 4.5 (7.2) | 0.015 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 25 (23.4) | 7 (11.3) | 0.323 | 19.2 (18.3) | 6.6 (10.6) | 0.222 |
| Chronic kidney failure | 23 (21.5) | 8 (12.9) | 0.229 | 19.1 (18.3) | 7.0 (11.3) | 0.199 |
| Heart failure | 19 (17.8) | 12 (19.4) | 0.041 | 17.6 (16.8) | 9.1 (14.6) | 0.062 |
| Hematology tumor | 41 (38.3) | 15 (24.2) | 0.308 | 35.6 (34.0) | 22.5 (36.1) | 0.045 |
| Solid tumor | 16 (15.0) | 20 (32.3) | 0.416 | 22.5 (21.5) | 14.5 (23.2) | 0.041 |
| COVID-19 | 14 (13.1) | 11 (17.7) | 0.129 | 15.8 (15.1) | 9.0 (14.4) | 0.020 |
| Immunosuppression | 40 (37.4) | 19 (30.6) | 0.143 | 36.1 (34.5) | 28.3 (45.4) | 0.224 |
| Abdominal surgery | 21 (19.6) | 16 (25.8) | 0.148 | 22.8 (21.8) | 13.7 (22.0) | 0.003 |
| Surgical disease | 27 (25.2) | 25 (40.3) | 0.326 | 30.4 (29.1) | 17.3 (27.7) | 0.031 |
| Previous CRE infection | 8 (7.5) | 3 (4.8) | 0.098 | 8.3 (7.9) | 8.9 (14.2) | 0.202 |
| Previous antibiotic treatment | 82 (76.6) | 47 (75.8) | 0.019 | 81.8 (78.2) | 50.8 (81.5) | 0.083 |
| Previous hospital stay in days, mean (SD) | 17.7 (16.8) | 21.5 (25.4) | 0.174 | 17.8 (17.7) | 18.8 (20.6) | 0.055 |
| Urinary catheter | 7 (6.5) | 8 (12.9) | 0.216 | 9.2 (8.8) | 6.4 (10.2) | 0.048 |
| Severity of the disease, n (%) | ||||||
| Critical care stay | 57 (53.3) | 31 (48.4) | 0.098 | 53.5 (51.2) | 31.2 (50.0) | 0.025 |
| Septic shock | 38 (35.5) | 25 (40.3) | 0.099 | 38.2 (36.6) | 23.1 (37.0) | 0.010 |
| SOFA, mean (SD) | 5.8 (3.1) | 5.3 (3.4) | 0.152 | 5.6 (3.14) | 5.3 (3.56) | 0.101 |
| INCREMENT, mean (SD) | 7.4 (3.8) | 7.02 (3.9) | 0.102 | 7.3 (3.8) | 7.3 (3.9) | 0.007 |
| Pitt score, mean (SD) | 2.1 (2.5) | 2.1 (2.6) | 0.023 | 2.1 (2.5) | 2.1 (2.6) | 0.006 |
| Invasive mechanical ventilation | 35 (32.7) | 23 (37.1) | 0.092 | 36.0 (34.4) | 21.4 (34.3) | 0.001 |
| Treatment Option | N (%) |
|---|---|
| Monotherapy | 5 (7.2) |
| Combined antimicrobial therapy | 57 (82.6) |
| Based on carbapenems | 42 (60.9) |
| Doble carbapenem | 14 (20.3) |
| Based on colistin/polymyxin | 24 (34.8) |
| Tigecycline use | 16 (23.2) |
| Aminoglycoside use | 9 (13.0) |
| Quinolone use | 8 (11.6) |
| Fosfomycin use | 6 (8.6) |
| Total N = 169 | CAZ/AVI (n = 107) | BAT (n = 62) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Length of hospitalization, days (SD) | 41.5 (27.8) | 40.9 (26.8) | 43.7 (26.2) |
| Length of antibiotic therapy, days (SD) | 13.7 (11.3) | 13.3 (10.8) | 12.9 (9.8) |
| Length of post-antibiotic treatment, days (SD) | 22.4 (17.2) | 21.3 (16.4) | 21.07 (15.1) |
| Acute kidney injury, n (%) | 17 (10.0) | 7.0 (6.6) | 10.0 (15.4) |
| In-hospital mortality, n (%) | 57 (34.0) | 36 (34.5) | 21 (33.2) |
| In-hospital death caused by the infection, n (%) | 44 (76.4) | 25 (68.9) | 19 (90.7) |
| Infection relapse, n (%) | 21 (13.0) | 14 (12.8) | 7 (10.5) |
| Clinical response, n (%) | 106 (62.7) | 66 (61.8) | 40 (61.6) |
| Microbiological cure | |||
| Yes, n (%) | 14 (8.3) | 6.0 (5.6) | 8.0 (12.3) |
| No, n (%) | 24 (14.4) | 22 (20.6) | 2 (2.8) |
| Not applicable | 131 (77.3) | 78 (73.8) | 53 (48.9) |
| Measure of Association | Value | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CZA in-hospital mortality | HR | 0.86 | 0.40 | 1.83 |
| ATM in-hospital mortality | HR | 1.23 | 0.52 | 2.91 |
| Microbiological cure | OR | 1.31 | 0.46 | 3.67 |
| Clinical response | OR | 1.39 | 0.35 | 5.43 |
| Acute kidney injury | OR | 0.56 | 0.11 | 2.80 |
| Relapse | OR | 0.99 | 0.17 | 5.51 |
| Variable | OR | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ceftazidime/avibactam use | 0.65 | 0.26 | 1.62 | 0.362 |
| Aztreonam use | 2.48 | 0.86 | 7.12 | 0.090 |
| Charlson score | 1.27 | 1.08 | 1.50 | 0.004 |
| Urinary infection | 0.08 | 0.008 | 0.91 | 0.042 |
| SOFA | 1.55 | 1.31 | 1.84 | 0.000 |
| Previous stay before bacteremia | 1.02 | 1.00 | 1.04 | 0.003 |
| Bacteremia time before definitive antibiotic therapy (per day) | 1.15 | 1.00 | 1.33 | 0.042 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arboleda, D.; Buitrago, C.; Vergara, E.P.; Nocua-Báez, L.C.; Saavedra, C.H.; Cortés, J.A. Impact of Antibiotic Therapy with Ceftazidime Avibactam vs. Best Available Therapy in Adult Patients with Bacteremia Caused by Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacterales. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14030226
Arboleda D, Buitrago C, Vergara EP, Nocua-Báez LC, Saavedra CH, Cortés JA. Impact of Antibiotic Therapy with Ceftazidime Avibactam vs. Best Available Therapy in Adult Patients with Bacteremia Caused by Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacterales. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(3):226. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14030226
Chicago/Turabian StyleArboleda, Daniel, Camilo Buitrago, Erika Paola Vergara, Laura Cristina Nocua-Báez, Carlos Humberto Saavedra, and Jorge Alberto Cortés. 2025. "Impact of Antibiotic Therapy with Ceftazidime Avibactam vs. Best Available Therapy in Adult Patients with Bacteremia Caused by Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacterales" Antibiotics 14, no. 3: 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14030226
APA StyleArboleda, D., Buitrago, C., Vergara, E. P., Nocua-Báez, L. C., Saavedra, C. H., & Cortés, J. A. (2025). Impact of Antibiotic Therapy with Ceftazidime Avibactam vs. Best Available Therapy in Adult Patients with Bacteremia Caused by Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacterales. Antibiotics, 14(3), 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14030226






