Novel Isolate of Halobacteriovorax Capable of Killing Multi-Drug-Resistant Escherichia coli and Salmonella
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Halobacteriovorax Against E7 Detection
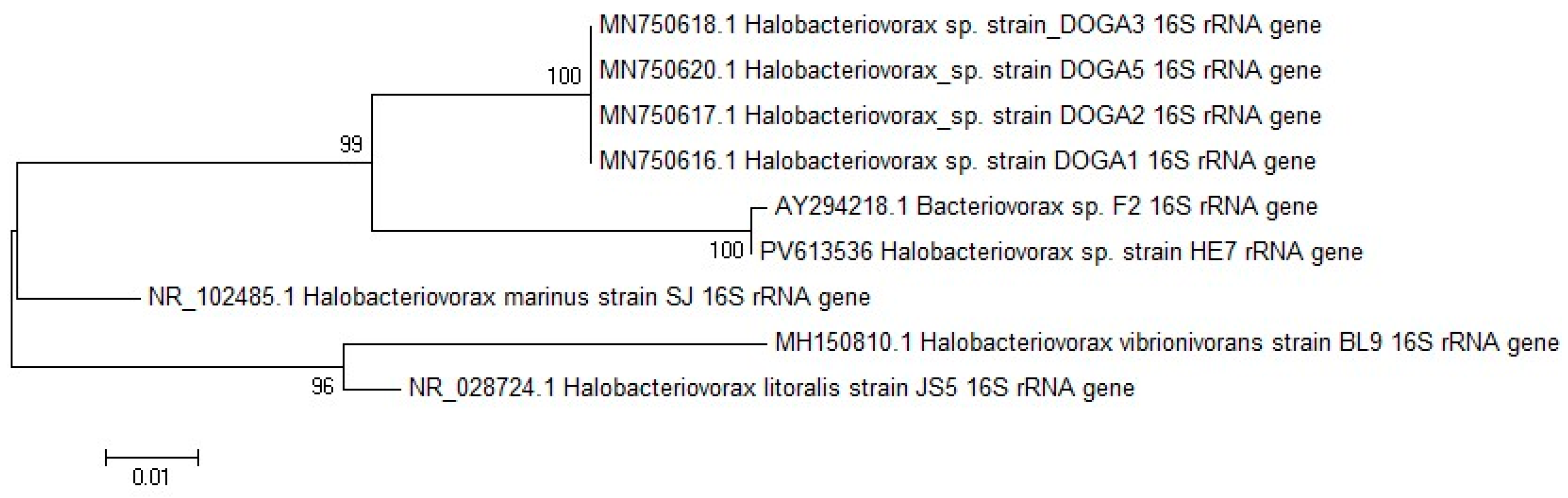
2.2. Halobacteriovorax Molecular Identification and Sequencing Analysis
2.3. Prey Specificity and Predatory Efficiency of HE7 Against Other MDR E. coli and Salmonella Preys
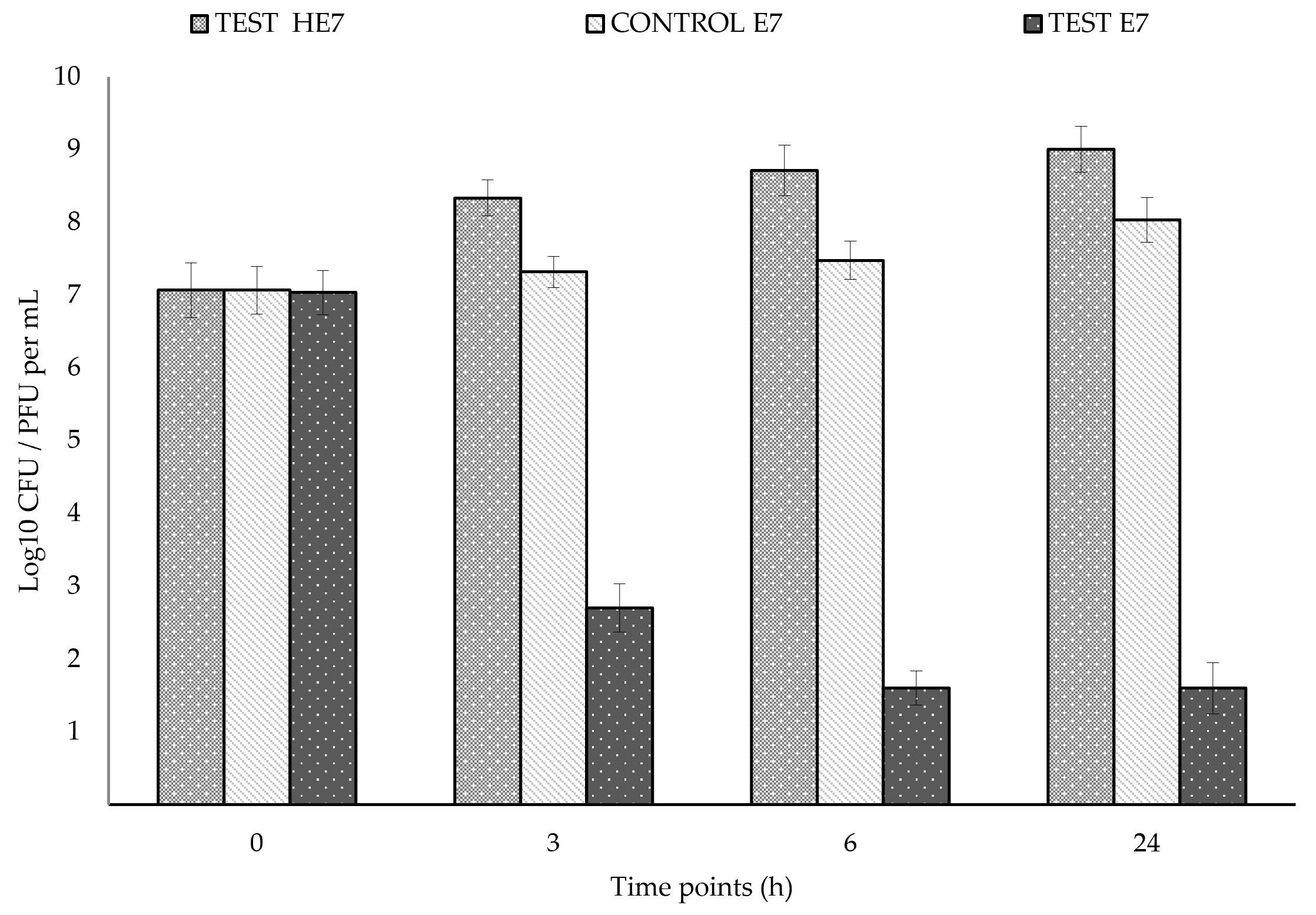
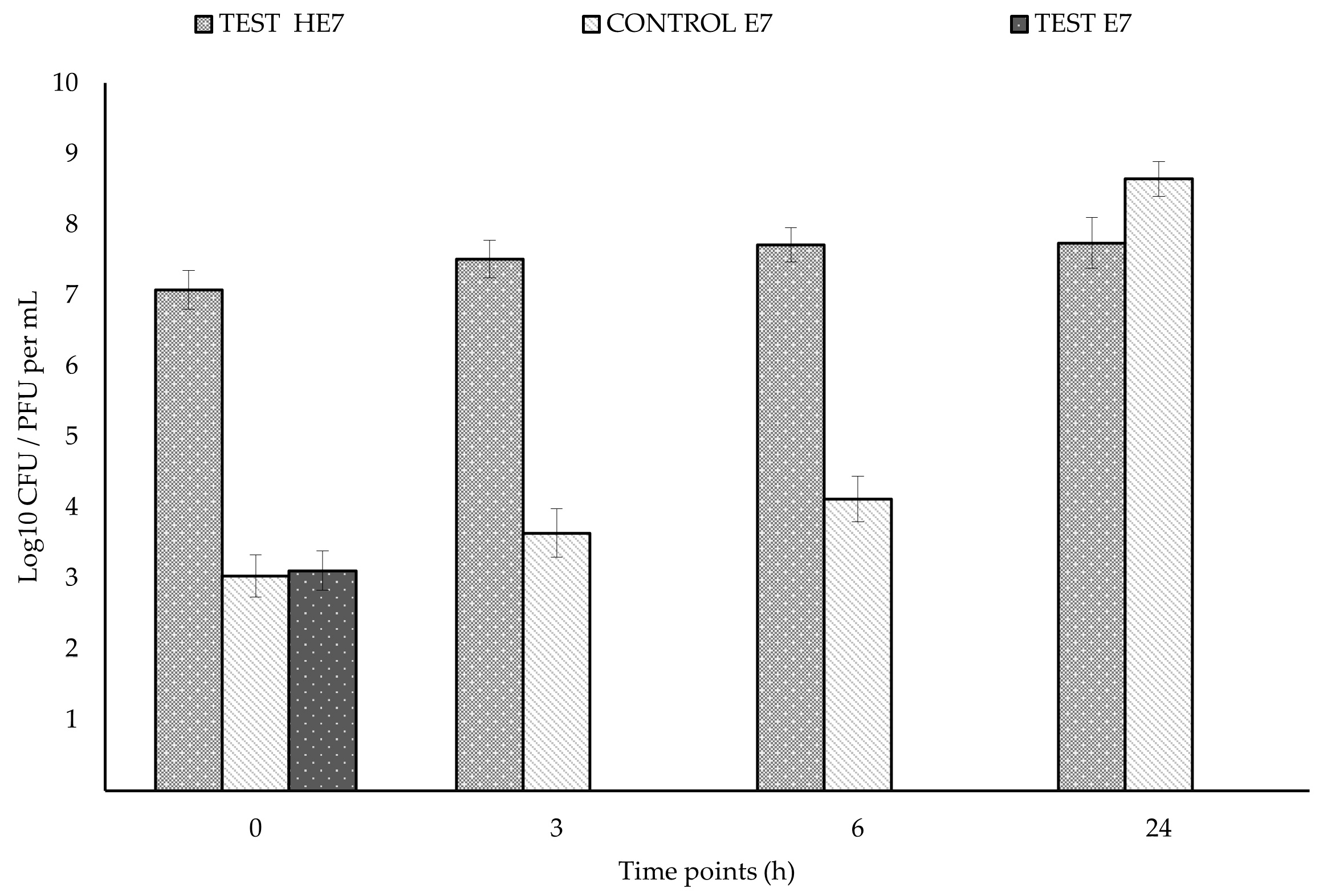
2.4. Challenging HE7/E7
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sampling Site
4.2. Prey Strains
4.3. Halobacteriovorax Against E7 Detection
4.4. Halobacteriovorax Molecular Identification and Sequencing Analysis
4.5. Prey Specificity and Predatory Efficiency of Halobacteriovorax Against Other AMR E. coli and Salmonella Preys
4.6. Preliminary Tests to Define the Most Effective Predator/Prey Ratio on Prey Reduction and the Optimal Physical-Chemical Parameters to Be Used in Challenge Experiments
4.7. Challenging Halobacteriovorax/E7
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMC | Antimicrobial-Resistant |
| BALOs | Bdellovibrio And Like Organisms |
| CFU | Colony Forming Unit |
| CTX-M | blaCTX-M genes |
| DNB | Diluted Nutrient Broth |
| ESBL | Extended Spectrum β Lactamase |
| PFU | Plaque Forming Unit |
| Pp | Polypeptone peptone |
| TBX | Tryptone Bile X-GLUC Agar |
References
- Tacconelli, E.; Carrara, E.; Savoldi, A.; Harbarth, S.; Mendelson, M.; Monnet, D.L.; Pulcini, C.; Kahlmeter, G.; Kluytmans, J.; Carmeli, Y.; et al. Discovery, research, and development of new antibiotics: The WHO priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and tuberculosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernando-Amado, S.; Coque, T.M.; Baquero, F.; Martínez, J.L. Defining and combating antibiotic resistance from One Health and Global Health perspectives. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1432–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Critically Important Antimicrobials for Human Medicine, 6th Revision. 2019. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241515528 (accessed on 20 May 2025).
- World Health Organization. Global Antimicrobial Resistance and Surveillance System (GLASS) Report. 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240027336 (accessed on 20 May 2025).
- Pitout, J.D.; Laupland, K.B. Extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae: An emerging public-health concern. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2008, 8, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Y.; Shimoda, S.; Shimono, N. Current epidemiology, genetic evolution and clinical impact of extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infect. Genet Evol. 2018, 61, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezabih, Y.M.; Sabiiti, W.; Alamneh, E.; Bezabih, A.; Peterson, G.M.; Bezabhe, W.M.; Roujeinikova, A. The global prevalence and trend of human intestinal carriage of ESBL-producing Escherichia coli in the community. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezabih, Y.M.; Bezabih, A.; Dion, M.; Batard, E.; Teka, S.; Obole, A.; Dessalegn, N.; Enyew, A.; Roujeinikova, A.; Alamneh, E.; et al. Comparison of the global prevalence and trend of human intestinal carriage of ESBL-producing Escherichia coli between healthcare and community settings: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAC Antimicrob. Resist. 2022, 4, dlac048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratanis, E.; Andersson, T.; Lood, R.; Bukowska-Faniband, E. Biotechnological Potential of Bdellovibrio and Like Organisms and Their Secreted Enzymes. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallo, F.M.; Jordana, L.; Friedrich, A.W.; Glasner, C.; van Dijl, J.M. Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus: A potential ‘living antibiotic’ to control bacterial pathogens. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 47, 630–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, J.; Contreras-Moreno, F.J.; Marcos-Torres, F.J.; Moraleda-Muñoz, A.; Muñoz-Dorado, J. The antibiotic crisis: How bacterial predators can help. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 2547–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMA (European Medicines Agency); EFSA (European Food Safety Authority). EMA and EFSA Joint Scientific Opinion on measures to reduce the need to use antimicrobial agents in animal husbandry in the European Union, and the resulting impacts on food safety (RONAFA). [EMA/CVMP/570771/2015]. EFSA J. 2017, 15, e04666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. The European Union Summary Report on Antimicrobial Resistance in Zoonotic and Indicator Bacteria from Humans, Animals and Food in 2018/2019. EFSA J. 2021, 19, e06490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, C.M.; Fleitas Martínez, O.; Morales Duque, H.; Franco, O.L. Expanding therapeutic potential of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus against multidrug-resistant pathogens. Drug Discov. Today 2023, 28, 103595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvaraj, S.; Gayathri, S.; Varalakshmi, P.; Nagarajan, N.; Palaniswami, R.; Ashokkumar, B. Predatory potentials of novel Bdellovibrio isolates against multidrug-resistant and extremely drug-resistant bacterial pathogens of animals and plants. 3 Biotech 2025, 15, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Koval, S.F.; Williams, H.N.; Stine, O.C. Reclassification of Bacteriovorax marinus as Halobacteriovorax marinus gen. nov., comb. nov. and Bacteriovorax litoralis as Halobacteriovorax litoralis comb. nov.; description of Halobacteriovoraceae fam. nov. in the class Deltaproteobacteria. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Paix, B.; Ezzedine, J.A.; Jacquet, S. Diversity, Dynamics, and Distribution of Bdellovibrio and Like Organisms in Perialpine Lakes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e02494-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Williams, H.N.; Chen, H. Environmental Regulation of the Distribution and Ecology of Bdellovibrio and Like Organisms. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 545070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Davidov, Y.; Jurkevitch, E. Diversity and evolution of Bdellovibrio-and-like organisms (BALOs), reclassification of Bacteriovorax starrii as Peredibacter starrii gen. nov., comb. nov., and description of the Bacteriovorax-Peredibacter clade as Bacteriovoracaceae fam. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 1439–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidov, Y.; Friedjung, A.; Jurkevitch, E. Structure analysis of a soil community of predatory bacteria using culture dependent and culture-independent methods reveals a hitherto undetected diversity of Bdellovibrio-and like organisms. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 1667–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pineiro, S.A.; Stine, O.C.; Chauhan, A.; Steyert, S.R.; Smith, R.; Williams, H.N. Global survey of diversity among environmental saltwater Bacteriovoracaceae. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 2441–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, H.; Choi, S.Y.; Son, S.; Mitchell, R.J. Combined Application of Bacterial Predation and Violacein to Kill Polymicrobial Pathogenic Communities. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, H.; Choi, S.Y.; Mun, W.; Jeong, S.H.; Mitchell, R.J. Predation of colistin- and carbapenem-resistant bacterial pathogenic populations and their antibiotic resistance genes in simulated microgravity. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 255, 126941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexakis, K.; Baliou, S.; Ioannou, P. Predatory Bacteria in the Treatment of Infectious Diseases and Beyond. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2024, 16, 684–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottaviani, D.; Pieralisi, S.; Rocchegiani, E.; Latini, M.; Leoni, F.; Mosca, F.; Pallavicini, A.; Tiscar, P.G.; Angelico, G. Vibrio parahaemolyticus-specific Halobacteriovorax from seawater of a mussel harvesting area in the Adriatic Sea: Abundance, diversity, efficiency and relationship with the prey natural level. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieralisi, S.; Hattab, J.; Mosca, F.; Angelico, G.; Lanci, L.; Ottaviani, D.; Rocchegiani, E.; Giorgio Tiscar, P. Halobacteriovorax isolated from the Adriatic Sea to challenge Salmonella. Ital. J. Food Sci. 2024, 36, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primeau, C.A.; Bharat, A.; Janecko, N.; Carson, C.A.; Mulvey, M.; Reid-Smith, R.; McEwen, S.; McWhirter, J.E.; Parmley, E.J. Integrated surveillance of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Salmonella and Escherichia coli from humans and animal species raised for human consumption in Canada from 2012 to 2017. Epidemiol. Infect. 2023, 151, e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, I.; Bencardino, D.; Napoleoni, M.; Andreoni, F.; Schiavano, G.F.; Baldelli, G.; Brandi, G.; Amagliani, G. Prevalence, Antibiotic-Resistance, and Replicon-Typing of Salmonella Strains among Serovars Mainly Isolated from Food Chain in Marche Region, Italy. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Guo, L.; Cui, Z.; Ju, F. Exploiting Predatory Bacteria as Biocontrol Agents across Ecosystems. Trends Microbiol. 2024, 32, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, M.; Negus, D.; Raghunathan, D.; Radford, P.; Moore, C.; Clark, G.; Diggle, M.; Tyson, J.; Twycross, J.; Sockett, R.E. Measuring and modelling the response of Klebsiella pneumoniae KPC prey to Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus predation, in human serum and defined buffer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dharani, S.; Kim, D.H.; Shanks, R.M.Q.; Doi, Y.; Kadouri, D.E. Susceptibility of colistin-resistant pathogens to predatory bacteria. Res. Microbiol. 2018, 169, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ottaviani, D.; Chierichetti, S.; Angelico, G.; Forte, C.; Rocchegiani, E.; Manuali, E.; Leoni, F. Halobacteriovorax isolated from marine water of the Adriatic Sea, Italy, as an effective predator of Vibrio parahaemolyticus, non-O1/O139 V. cholerae, V. vulnificus. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 4, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, G.P.; Fay, J.P.; Uknalis, J.; Olanya, O.M.; Watson, M.A. Purification and host specificity of predatory Halobacteriovorax isolates from seawater. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Enos, B.G.; Anthony, M.K.; De Giorgis, J.A.; Williams, L.E. Prey Range and Genome Evolution of Halobacteriovorax marinus Predatory Bacteria from an Estuary. mSphere 2018, 3, e00508-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Patini, R.; Cattani, P.; Marchetti, S.; Isola, G.; Quaranta, G.; Gallenzi, P. Evaluation of Predation Capability of Periodontopathogens Bacteria by Bdellovibrio Bacteriovorus HD100. An In Vitro Study. Materials 2019, 12, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, G.P.; Fay, J.P.; Dickens, K.A.; Parent, M.A.; Soroka, D.S.; Boyd, E.F. Predatory bacteria as natural modulators of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio vulnificus in seawater and oysters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 7455–7466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Richards, G.P.; Watson, M.A.; Boyd, E.F.; Burkhardt, W., III; Lau, R.; Uknalis, J.; Fay, J.P. Seasonal levels of the Vibrio predator Bacteriovorax in Atlantic, Pacific and Gulf Coast seawater. Int. J. Microbiol. 2013, 2013, 375371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rekadwad, B.N.; Gonzalez, J.M.; Khobragade, C.N. Genomic Analysis of a Marine Bacterium: Bioinformatics for Comparison, Evaluation, and Interpretation of DNA Sequences. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 7215379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Laboratory Identification | Species | Origin | MDR Patterns |
|---|---|---|---|
| E7 (primary prey) | E. coli | Chamelea gallina | ESBL blaCTX-M-55 AMP FOT CIP CHL NAL TMP TET SMX FEP |
| E3 | E. coli | Chamelea gallina | ESBL blaCTX-M-1 AMP FOT TMP TET SMX FEP |
| S3 | Salmonella Infantis | Human urine | ESBL blaCTX-M-1 AMP FOT KAN NAL TET SMX SXT |
| S9 | Salmonella Havana | Ring test | AmpC-phenotype FOX TAZ |
| PFU Predator/CFU Prey per mL | Log Prey Reduction in Test Respect to Control | |
|---|---|---|
| 26–30 °C 0–30 ppt aer/ma/ana Conditions | 37 °C 0–30 ppt aer/ma/ana Conditions | |
| 107/107 | 6 | 4 |
| 107/103 | 4 | 2 |
| 106/106 | 3.5 | 2 |
| 106/103 | 3 | 2 |
| 105/105 | 1 | 0.5 |
| 105/103 | 1 | 1 |
| 104/104 | 1 | 1 |
| 103/103 | 1 | 0.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Lullo, S.; Pieralisi, S.; Talevi, G.; Angelico, G.; Rocchegiani, E.; Leoni, F.; Napoleoni, M.; Maiolatesi, D.; Barchiesi, F.; Nardi, S.; et al. Novel Isolate of Halobacteriovorax Capable of Killing Multi-Drug-Resistant Escherichia coli and Salmonella. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111133
Di Lullo S, Pieralisi S, Talevi G, Angelico G, Rocchegiani E, Leoni F, Napoleoni M, Maiolatesi D, Barchiesi F, Nardi S, et al. Novel Isolate of Halobacteriovorax Capable of Killing Multi-Drug-Resistant Escherichia coli and Salmonella. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(11):1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111133
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Lullo, Stefania, Silvia Pieralisi, Giulia Talevi, Gabriele Angelico, Elena Rocchegiani, Francesca Leoni, Maira Napoleoni, Diego Maiolatesi, Francesca Barchiesi, Sara Nardi, and et al. 2025. "Novel Isolate of Halobacteriovorax Capable of Killing Multi-Drug-Resistant Escherichia coli and Salmonella" Antibiotics 14, no. 11: 1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111133
APA StyleDi Lullo, S., Pieralisi, S., Talevi, G., Angelico, G., Rocchegiani, E., Leoni, F., Napoleoni, M., Maiolatesi, D., Barchiesi, F., Nardi, S., Petruzzelli, A., Gabucci, C., Conti, A., Cardinali, G., & Ottaviani, D. (2025). Novel Isolate of Halobacteriovorax Capable of Killing Multi-Drug-Resistant Escherichia coli and Salmonella. Antibiotics, 14(11), 1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111133








