Isavuconazole-Amphotericin B and Isavuconazole-Caspofungin In Vitro Synergic Activity Against Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis Molds Isolates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Information and Isolates Collection
4.2. Isolates Identification and Susceptibility Testing
4.3. Synergy Assays
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ledoux, M.P.; Herbrecht, R. Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, M.; Fortún, J.; Muñoz, P. Invasive aspergillosis: A comprehensive review. Med. Clin. 2024, 163, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamoth, F.; Calandra, T. Pulmonary aspergillosis: Diagnosis and treatment. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2022, 31, 220114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Patterson, T.F.; Thompson, G.R.; Denning, D.W.; Fishman, J.A.; Hadley, S.; Herbrecht, R.; Kontoyiannis, D.P.; Marr, K.A.; Morrison, V.A.; Nguyen, M.H.; et al. Practice Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Aspergillosis: 2016 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, e1–e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AMCLI ETS. Percorso Diagnostico “MICOSI PROFONDE E SISTEMICHE”—Rif. 2023-16, rev. 2023. Available online: https://amcli.it/percorsi-diagnostici-218/ (accessed on 6 September 2025).
- Schwarz, M.C.R.; Moskaluk, A.E.; Daniels, J.B.; VandeWoude, S.; Reynolds, M.M. Current Analytical Methods and Challenges for the Clinical Diagnosis of Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis Infection. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Francesco, M.A. Drug-Resistant Aspergillus spp.: A Literature Review of Its Resistance Mechanisms and Its Prevalence in Europe. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffetin, A.; Courbin, V.; Jullien, V.; Dannaoui, E. In Vitro Combination of Isavuconazole with Echinocandins against Azole-Susceptible and -Resistant Aspergillus spp. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katragkou, A.; McCarthy, M.; Meletiadis, J.; Petraitis, V.; Moradi, P.W.; Strauss, G.E.; Fouant, M.M.; Kovanda, L.L.; Petraitiene, R.; Roilides, E.; et al. In vitro combination of isavuconazole with micafungin or amphotericin B deoxycholate against medically important molds. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 6934–6937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of Filamentous Fungi, 3rd ed.; CLSI supplement M38M51S; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters. Version 15.0. 2025. Available online: https://www.eucast.org (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- Ortalli, G.; Oliva, E.; Lo Cascio, G.; on behalf of the Medical Mycology Committee (CoSM)—Italian Association of Clinical Microbiologists (AMCLI); Farina, C. In Vitro Activity of Isavuconazole and Amphotericin B in Association against Mucorales. Pathogens 2023, 12, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Calvo, M.; Lauricella, F.; Mellini, A.M.; Scalia, G.; Trovato, L. Isavuconazole and Amphotericin B Synergic Antifungal Activity: In Vitro Evaluation on Pulmonary Aspergillosis Molds Isolates. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, A.P.; Smibert, O.C.; Bajel, A.; Halliday, C.L.; Lavee, O.; McMullan, B.; Yong, M.K.; van Hal, S.J.; Chen, S.C.-A.; the Australasian Antifungal Guidelines Steering Committee. Consensus guidelines for the diagnosis and management of invasive aspergillosis, 2021. Intern. Med. J. 2021, 51 (Suppl. S7), 143–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagenais, T.R.T.; Keller, N.P. Pathogenesis of Aspergillus fumigatus in Invasive Aspergillosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 22, 447–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franconi, I.; Rizzato, C.; Ghelardi, E.; Lupetti, A. Hospital distribution, seasonality, time trends and antifungal susceptibility profiles of all Aspergillus species isolated from clinical samples from 2015 to 2022 in a tertiary care hospital. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, A.; Tiseo, G.; Falcone, M.; Menichetti, F. Pulmonary Aspergillosis: An Evo5. Russo A, Tiseo G, Falcone M, Menichetti F. Pulmonary Aspergillosis: An Evolving Challenge for Diagnosis and Treatment. Infect Dis Ther. 2020; 9:511-524lving Challenge for Diagnosis and Treatment. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2020, 9, 511–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, M.; Xu, Y. Epidemiology, drug susceptibility, and clinical risk factors in patients with invasive aspergillosis. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 835092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhapery, A.; Fatima, M.; Soubani, A.O. Emerging Risk Factors for Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis: A Narrative Review. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassetti, M.; Azoulay, E.; Kullberg, B.-J.; Ruhnke, M.; Shoham, S.; Vazquez, J.; Giacobbe, D.R.; Calandra, T. EORTC/MSGERC Definitions of Invasive Fungal Diseases: Summary of Activities of the Intensive Care Unit Working Group. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 72 (Suppl. S2), S121–S127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenks, J.D.; Hoenigl, M. Treatment of Aspergillosis. J. Fungi 2018, 4, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovato, L.; Scalia, G.; Domina, M.; Oliveri, S. Environmental Isolates of Multi-Azole-Resistant Aspergillus spp. in Southern Italy. J. Fungi 2018, 4, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovato, L.; Calvo, M.; Palermo, C.I.; Scalia, G. The Role of Quantitative Real-Time PCR in the Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis Diagnosis: A Retrospective Study. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buil, J.B.; Brüggemann, R.J.M.; E Wasmann, R.; Zoll, J.; Meis, J.F.; Melchers, W.J.G.; Mouton, J.W.; E Verweij, P. Isavuconazole susceptibility of clinical Aspergillus fumigatus isolates and feasibility of isavuconazole dose escalation to treat isolates with elevated MICs. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, J.S.; Wiederhold, N.P.; Hakki, M.; Thompson, G.R. New Perspectives on Antimicrobial Agents: Isavuconazole. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2022, 66, e00177-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakhim, H.; Badali, H.; Dannaoui, E.; Nasirian, M.; Jahangiri, F.; Raei, M.; Vaseghi, N.; Ahmadikia, K.; Vaezi, A. Trends in the Prevalence of Amphotericin B-Resistance (AmBR) among Clinical Isolates of Aspergillus Species. J. Mycol. Med. 2022, 32, 101310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahedi-Shahandashti, R.; Dietl, A.M.; Binder, U.; Nagl, M.; Würzner, R.; Lass-Flörl, C. Aspergillus terreus and the Interplay with Amphotericin B: From Resistance to Tolerance? Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2022, 66, e0227421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockhart, S.R.; Zimbeck, A.J.; Baddley, J.W.; Marr, K.A.; Andes, D.R.; Walsh, T.J.; Kauffman, C.A.; Kontoyiannis, D.P.; Ito, J.I.; Pappas, P.G.; et al. In vitro echinocandin susceptibility of Aspergillus isolates from patients enrolled in the Transplant-Associated Infection Surveillance Network. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 3944–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheven, M.; Schwegler, F. Antagonistic interactions between azoles and amphotericin B with yeasts depend on azole lipophilia for special test conditions in vitro. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1995, 39, 1779–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geißel, B.; Loiko, V.; Klugherz, I.; Zhu, Z.; Wagener, N.; Kurzai, O.; Hondel, C.A.M.J.J.v.D.; Wagener, J. Azole-induced cell wall carbohydrate patches kill Aspergillus fumigatus. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://c.peervoice.com/programs/140200557/downloads/PV_practiceaids_QVJ.pdf (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- Donnelly, J.P.; Chen, S.C.; Kauffman, C.A.; Steinbach, W.J.; Baddley, J.W.; Verweij, P.E.; Clancy, C.J.; Wingard, J.R.; Lockhart, S.R.; Groll, A.H.; et al. Revision and Update of the Consensus Definitions of Invasive Fungal Disease from the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer and the Mycoses Study Group Education and Research Consortium. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Koehler, P.; Bassetti, M.; Chakrabarti, A.; Chen, S.C.; Colombo, A.L.; Hoenigl, M.; Klimko, N.; Lass-Flörl, C.; Oladele, R.O.; Vinh, D.C.; et al. Defining and managing COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis: The 2020 ECMM/ISHAM consensus criteria for research and clinical guidance. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, e149–e162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.liofilchem.net/login.area.mic/technical_sheets/MTS40.pdf (accessed on 3 January 2025).
- Available online: https://www.liofilchem.com/images/brochure/mic_test_strip_patent/MTS06.pdf (accessed on 3 January 2025).
- Guinea, J.; Meletiadis, J.; Arikan-Akdagli, S.; Muehlethaler, K.; Kahlmeter, G.; Arendrup, M.C. the Subcommittee on Antifungal Susceptibility Testing (AFST) of the ESCMID European Committee for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) EUCAST DEFINITIVE DOCUMENT E.DEF 9.4 Method for the Determination of Broth Dilution Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations of Antifungal Agents for Conidia Forming Moulds. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/fileadmin/src/media/PDFs/EUCAST_files/AFST/Files/EUCAST_EDef_9.4_method_for_susceptibility_testing_of_moulds.pdf (accessed on 20 September 2023).
- The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs for Antifungal Agents, Version 10.0. 2020. Available online: http://www.eucast.org/astoffungi/clinicalbreakpointsforantifungals/ (accessed on 20 September 2023).
- The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing EUCAST Development Laboratories. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/fileadmin/src/media/PDFs/EUCAST_files/Network_labs/EDL/EUCAST_Development_Laboratories.pdf (accessed on 20 September 2023).
- Available online: https://www.liofilchem.net/login.area.mic/technical_sheets/MTS31.pdf (accessed on 24 September 2023).
- Roell, K.R.; Reif, D.M.; Motsinger-Reif, A.A. An Introduction to Terminology and Methodology of Chemical Synergy-Perspectives from Across Disciplines. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, A.; Kaya, S.Y.; Balkan, I.I.; Alkan, S.; Kurt, A.F.; Elverdi, T.; Urkmez, S.; Ongoren, S.; Aygun, G. Amphotericin B Resistant Aspergillus spp.: Report of Two Cases. Infect. Dis. Clin. Microbiol. 2024, 6, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovato, L.; Scalia, G.; Palermo, C.I.; Costanzo, C.M.; Oliveri, S. Evaluation of isavuconazole MIC strips for susceptibility testing of Aspergillus and Scedosporium species. Med. Mycol. 2019, 57, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.idsociety.org/practice-guideline/Diagnosis-and-Management-of-Cryptococcosis/ (accessed on 27 September 2025).
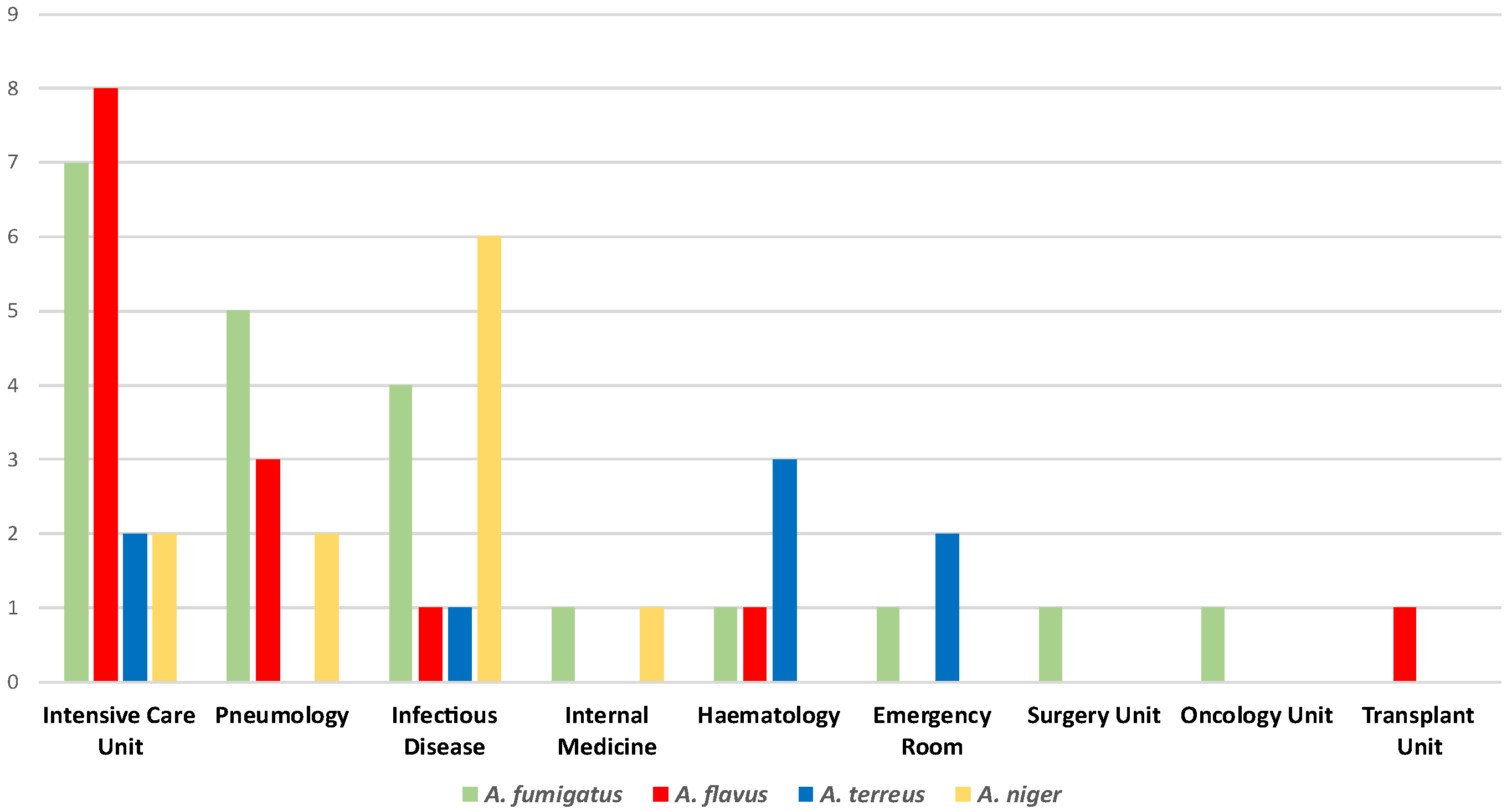
| Species | Ward | Sample | IVU MIC (mg/L) | AMB MIC (mg/L) | CAS MIC (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. fumigatus | Internal Medicine | BAL | 0.125 | 0.19 | 0.19 |
| A. fumigatus | Intensive Care | BAS | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.19 |
| A. fumigatus | Infectious Diseases | BAL | 0.125 | 0.19 | 0.25 |
| A. fumigatus | Intensive Care | BAL | 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.094 |
| A. fumigatus | Intensive Care | BAL | 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| A. fumigatus | Surgery Unit | BAL | 0.064 | 0.25 | 0.19 |
| A. fumigatus | Pneumology | Sputum | 0.19 | 0.25 | 0.38 |
| A. fumigatus | Infectious Diseases | BAL | 0.094 | 0.25 | 0.5 |
| A. fumigatus | Intensive Care | BAL | 0.19 | 0.25 | 0.19 |
| A. fumigatus | Pneumology | BAL | 0.125 | 0.25 | 64 |
| A. fumigatus | Infectious Diseases | BAL | 0.19 | 0.38 | 0.064 |
| A. fumigatus | Intensive Care | BAL | 0.25 | 0.38 | 0.19 |
| A. fumigatus | Intensive Care | BAL | 0.19 | 0.38 | 0.19 |
| A. fumigatus | Intensive Care | BAS | 0.19 | 0.38 | 0.094 |
| A. fumigatus | Infectious Diseases | Sputum | 0.19 | 0.38 | 0.25 |
| A. fumigatus | Pneumology | BAS | 0.19 | 0.5 | 0.094 |
| A. fumigatus | Pneumology | Sputum | 0.38 | 0.5 | 0.125 |
| A. fumigatus | Pneumology | BAL | 0.19 | 0.75 | 0.064 |
| A. fumigatus | Oncology | BAL | 0.19 | 0.75 | 0.19 |
| A. fumigatus | Intensive Care | BAS | 0.38 | 2 | 0.064 |
| A. fumigatus | Emergency Room | BAL | 0.19 | 4 | 0.19 |
| A. fumigatus | Hematology | Sputum | 0.38 | >32 | 0.125 |
| A. flavus | Pneumology | Sputum | 0.094 | 0.002 | 0.25 |
| A. flavus | Transplants unit | Sputum | 0.047 | 0.002 | 0.19 |
| A. flavus | Intensive Care | BAS | 0.012 | 0.06 | 0.25 |
| A. flavus | Intensive Care | Sputum | 0.047 | 0.38 | 0.125 |
| A. flavus | Intensive Care | BAL | 0.25 | 0.75 | 0.38 |
| A. flavus | Intensive Care | BAS | 0.25 | 1.5 | 0.25 |
| A. flavus | Intensive Care | BAS | 0.25 | 8 | 0.064 |
| A. flavus | Intensive Care | BAS | 0.38 | 1 | 0.38 |
| A. flavus | Pneumology | BAL | 0.19 | 0.75 | 0.25 |
| A. flavus | Pneumology | Sputum | 0.19 | 0.5 | 0.125 |
| A. flavus | Infectious Diseases | BAS | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.25 |
| A. flavus | Intensive Care | BAS | 0.25 | 0.75 | 0.25 |
| A. flavus | Intensive Care | BAS | 0.25 | 0.75 | 0.094 |
| A. flavus | Hematology | BAS | 0.125 | 0.064 | 0.125 |
| A. niger | Internal Medicine | BAL | 0.5 | 0.047 | 64 |
| A. niger | Infectious Diseases | BAL | 0.19 | 0.25 | 0.064 |
| A. niger | Infectious Diseases | BAL | 0.19 | 0.25 | 0.064 |
| A. niger | Infectious Diseases | BAS | 0.19 | 0.25 | 0.064 |
| A. niger | Pneumology | BAL | 0.19 | 0.25 | 0.19 |
| A. niger | Pneumology | BAL | 0.19 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| A. niger | Intensive Care | BAL | 0.19 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| A. niger | Infectious Diseases | BAL | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.5 |
| A. niger | Infectious Diseases | BAS | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.5 |
| A. niger | Intensive Care | BAL | 0.19 | 0.38 | 0.25 |
| A. niger | Infectious Diseases | BAL | 0.19 | 8 | 0.064 |
| A. terreus | Infectious Diseases | BAL | 0.5 | 0.047 | 64 |
| A. terreus | Hematology | Sputum | 0.064 | 0.38 | 64 |
| A. terreus | Hematology | Sputum | 0.064 | 4 | 64 |
| A. terreus | Hematology | BAS | 0.064 | 4 | 64 |
| A. terreus | Emergency Room | BAS | 0.064 | 32 | 64 |
| A. terreus | Intensive Care | BAL | 0.125 | 32 | 0.19 |
| A. terreus | Emergency Room | BAL | 0.25 | 32 | 64 |
| A. terreus | Intensive Care | BAS | 0.25 | 32 | 0.19 |
| Aspergillus spp. | MIC Range (mg/L) | % >ECOFF/BP | S/R | MIC90 | ECOFF/BP/HC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. fumigatus (22) | |||||
| Amphotericin B | 0.125–64 | 13.6 | 19/3 | 2 | 1 |
| Caspofungin ** | 0.064–64 | 4.5 | 21/1 | 0.38 | 32 |
| Isavuconazole | 0.064–0.38 | 0 | 22/0 | 0.38 | 2 |
| A. flavus (14) | |||||
| Amphotericin B * | 0.002–8 | 7.1 | 13/1 | 1.5 | 4 |
| Caspofungin ** | 0.064–0.38 | 0 | 14/0 | 0.38 | 32 |
| Isavuconazole | 0.012–0.38 | 0 | 14/0 | 0.25 | 2 |
| A. niger (11) | |||||
| Amphotericin B | 0.047–0.38 | 9.1 | 10/1 | 0.38 | 1 |
| Caspofungin ** | 0.064–64 | 9.1 | 10/1 | 0.5 | 32 |
| Isavuconazole * | 0.19–0.5 | 0 | 11/0 | 0.5 | 4 |
| A. terreus (8) | |||||
| Amphotericin B * | 0.094–64 | 87.5 | 1/7 | 32 | 8 |
| Caspofungin ** | 0.19–64 | 62.5 | 3/5 | 64 | 32 |
| Isavuconazole | 0.064–0.38 | 0 | 8/0 | 0.25 | 1 |
| TOTAL (55) |
| Aspergillus Species | Additivity (%) | Indifference (%) | Antagonism (%) | Synergy (%) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. fumigatus (22) | 6 (27.7) | 8 (36,4) | 6 (27.7) | 2 (9.1) | 0.218 |
| A. flavus (14) | 1 (7.14) | 3 (21.4) | 10 (71.4) | 0 | 0.089 |
| A. niger (11) | 2 (18.2) | 2 (18.2) | 6 (54.5) | 1 (9.1) | 0.763 |
| A. terreus (8) | 1 (12.5) | 4 (50.0) | 2 (25.0) | 1 (12.5) | 0.499 |
| Total (55) | 10 (18.2) | 17 (30.9) | 24 (43.6) | 4 (7.8) |
| Aspergillus Species | Additivity (%) | Indifference (%) | Antagonism (%) | Synergy (%) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. fumigatus (22) | 8 (36.4) | 10 (45.4) | 3 (13.6) | 1 (4.5) | 0.729 |
| A. flavus (14) | 0 | 7 (50) | 5 (35.7) | 1 (7.1) | 0.011 |
| A. niger (11) | 6 (54.5) | 1 (9.1) | 0 | 1 (9.2) | 0.012 |
| A. terreus (8) | 1 (12.5) | 6 (75) | 0 | 1 (12.5) | 0.235 |
| Total (55) | 15 (27.3) | 24 (43.6) | 8 (14.8) | 4 (7.8) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Calvo, M.; Caruso, M.; Tempesta, A.A.; Trovato, L. Isavuconazole-Amphotericin B and Isavuconazole-Caspofungin In Vitro Synergic Activity Against Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis Molds Isolates. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 993. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14100993
Calvo M, Caruso M, Tempesta AA, Trovato L. Isavuconazole-Amphotericin B and Isavuconazole-Caspofungin In Vitro Synergic Activity Against Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis Molds Isolates. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(10):993. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14100993
Chicago/Turabian StyleCalvo, Maddalena, Michelangelo Caruso, Adriana Antonina Tempesta, and Laura Trovato. 2025. "Isavuconazole-Amphotericin B and Isavuconazole-Caspofungin In Vitro Synergic Activity Against Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis Molds Isolates" Antibiotics 14, no. 10: 993. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14100993
APA StyleCalvo, M., Caruso, M., Tempesta, A. A., & Trovato, L. (2025). Isavuconazole-Amphotericin B and Isavuconazole-Caspofungin In Vitro Synergic Activity Against Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis Molds Isolates. Antibiotics, 14(10), 993. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14100993





