Detection of Delafloxacin Resistance Mechanisms in Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
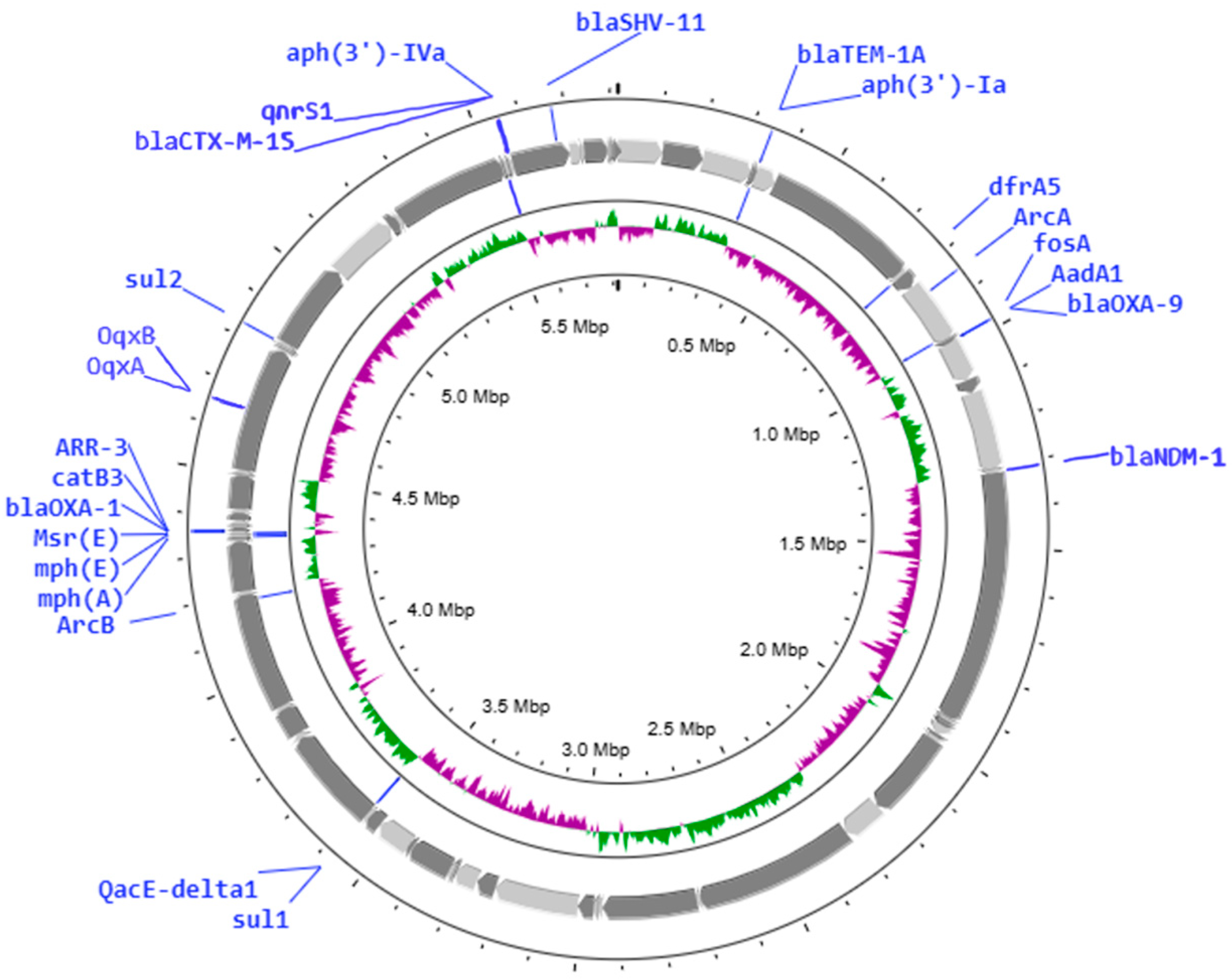
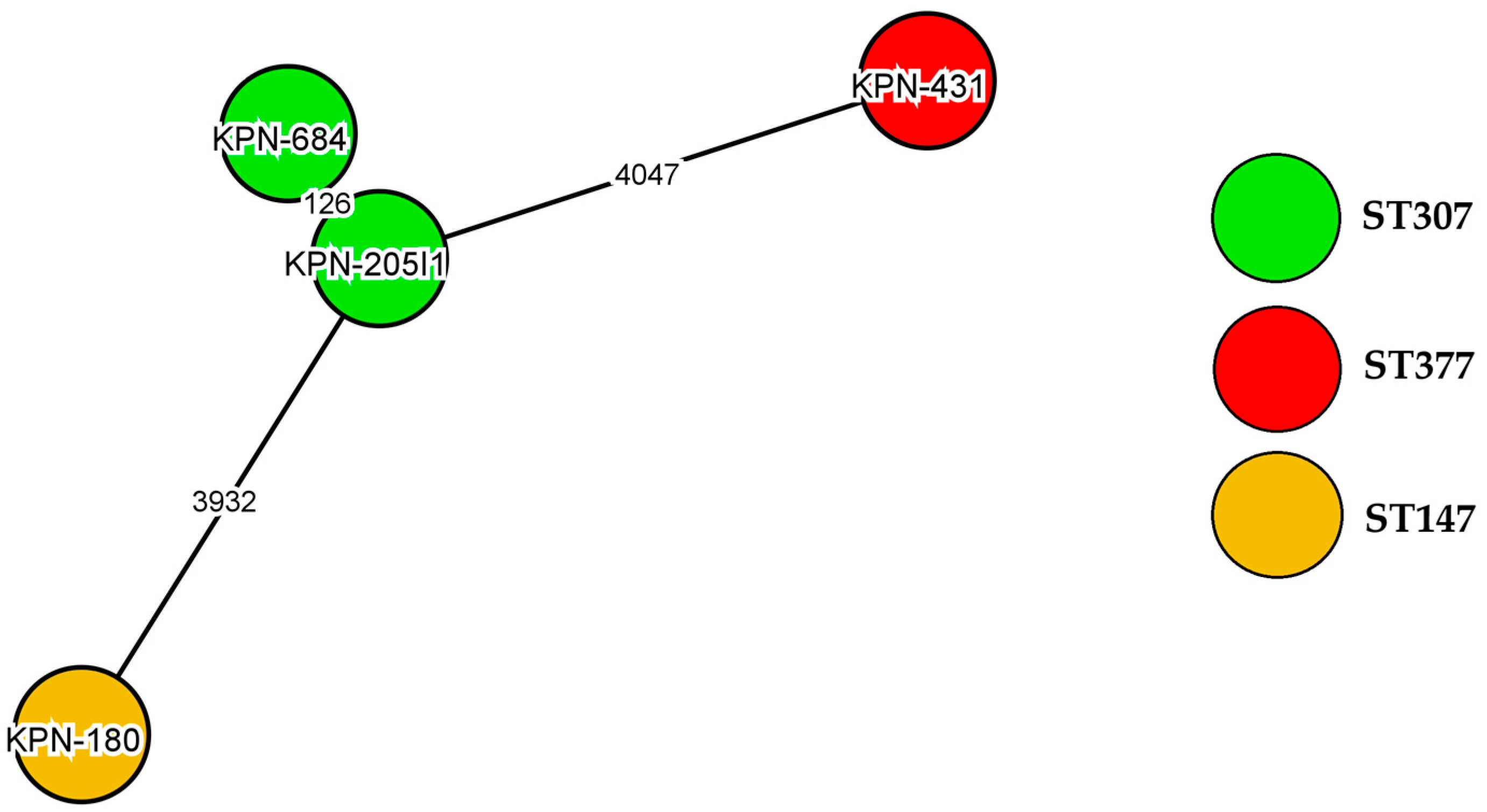
2.2. Genome Sequencing
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Strains
4.2. Detection of the Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
4.3. Whole-Genome Sequencing (WGS)
4.4. Analysis of Genome Sequence
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Navon-Venezia, S.; Kondratyeva, K.; Carattoli, A. Klebsiella pneumoniae: A major worldwide source and shuttle for antibiotic resistance. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 252–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paczosa, M.K.; Mecsas, J. Klebsiella pneumoniae: Going on the offense with a strong defense. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventura, A.; Addis, E.; Bertoncelli, A.; Mazzariol, A. Multiple detection of hypermucoviscous and hypervirulent strains of Klebsiella pneumoniae: An emergent health care threat. Acta Microbiol. Immunol. Hung. 2022, 69, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.R.; Lee, J.H.; Park, K.S.; Jeon, J.H.; Kim, Y.B.; Cha, C.J.; Jeong, B.C.; Lee, S.H. Antimicrobial resistance of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: Epidemiology, hypervirulence-associated determinants, and resistance mechanisms. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shon, A.S.; Bajwa, R.P.; Russo, T.A. Hypervirulent (hypermucoviscous) Klebsiella pneumoniae: A new and dangerous breed. Virulence 2013, 4, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.A.; Marr, C.M. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00001-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, V.L.; Hansen, D.S.; Ko, W.C.; Sagnimeni, A.; Klugman, K.P.; von Gottberg, A.; Gossens, H.; Wagener, M.M.; Benedi, V.J.; International Klebseilla Study Group. Virulence characteristics of Klebsiella and clinical manifestations of K. pneumoniae bloodstream infections. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 986–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Gu, D.; Fang, Y.; Chan, E.W.; Chen, S.; Zhang, R. Rapid detection of K1 hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae by MALDI-TOF MS. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belouad, E.M.; Benaissa, E.; El Mrimar, N.; Eddair, Y.; Maleb, A.; Elouennass, M. Investigations of carbapenem resistant and hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Acta Microbiol. Immunol. Hung. 2024, 71, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, K.-M.; Lin, J.C.; Yin, F.Y.; Fung, C.P.; Hung, H.C.; Siu, L.K.; Chang, F.Y. Revisiting the importance of virulence determinant magA and its surrounding genes in Klebsiella pneumoniae causing pyogenic liver abscesses: Exact role in serotype K1 capsule formation. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 201, 1259–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritsotakis, E.I.; Lagoutari, D.; Michailellis, E.; Georgakakis, I.; Gikas, A. Burden of multidrug and extensively drug-resistant ESKAPEE pathogens in a secondary hospital care setting in Greece. Epidemiol. Infect. 2022, 150, e170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, D.M.P.; Forde, B.M.; Kidd, T.J.; Harris, P.N.A.; Schembri, M.A.; Beatson, S.A.; Paterson, D.L.; Walker, M.J. Antimicrobial resistance in ESKAPE pathogens. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33, e00181-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.R.; Lee, J.H.; Park, K.S.; Kim, Y.B.; Jeong, B.C.; Lee, S.H. Global dissemination of carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae: Epidemiology, genetic context, treatment options, and detection methods. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Bacterial Priority Pathogens List, 2024: Bacterial Pathogens of Public Health Importance to Guide Research, Development and Strategies to Prevent and Control Antimicrobial Resistance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Bush, K.; Bradford, P.A. Interplay between β-lactamases and new β-lactamase inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orosz, L.; Lengyel, G.; Ánosi, N.; Lakatos, L.; Burián, K. Changes in resistance pattern of ESKAPE pathogens between 2010 and 2020 in the clinical center of University of Szeged, Hungary. Acta Microbiol. Immunol. Hung. 2022, 69, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitout, J.D.; Nordmann, P.; Poirel, L. Carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae, a key pathogen set for global nosocomial dominance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 5873–5884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleg, A.Y.; Hooper, D.C. Hospital-acquired infections due to gram-negative bacteria. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1804–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocsis, B.; Gulyás, D.; Szabó, D. Delafloxacin, Finafloxacin, and Zabofloxacin: Novel Fluoroquinolones in the Antibiotic Pipeline. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocsis, B.; Domokos, J.; Szabo, D. Chemical structure and pharmacokinetics of novel quinolone agents represented by avarofloxacin, delafloxacin, finafloxacin, zabofloxacin and nemonoxacin. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2016, 15, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, A.; Munteanu, A.C.; Arbănași, E.M.; Uivarosi, V. Overview of Side-Effects of Antibacterial Fluoroquinolones: New Drugs versus Old Drugs, a Step Forward in the Safety Profile? Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogle, B.T.; Steele, J.M.; Thomas, S.J.; Bohan, K.H.; Kufel, W.D. Clinical review of delafloxacin: A novel anionic fluoroquinolone. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 1439–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaller, M.A.; Sader, H.S.; Rhomberg, P.R.; Flamm, R.K. In vitro activity of delafloxacin against contemporary bacterial pathogens from the United States and Europe, 2014. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e02803-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soge, O.O.; Salipante, S.J.; No, D.; Duffy, E.; Roberts, M.C. In vitro activity of delafloxacin against clinical Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates and selection of gonococcal delafloxacin resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 3106–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyanova, L.; Markovska, R.; Medeiros, J.; Gergova, G.; Mitov, I. Delafloxacin against Helicobacter pylori, a potential option for improving eradication success? Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 96, 114980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, J.; Siala, W.; Tulkens, P.M.; Bambeke, V.F. A combined pharmacodynamic quantitative and qualitative model reveals the potent activity of daptomycin and delafloxacin against Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 2726–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocheretyaner, E.R.; Park, T.E. Delafloxacin: A novel fluoroquinolone with activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Expert. Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2018, 16, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, Y.S.; Cho, S.Y.; Yang, H.Y.; Park, K.S.; Jang, J.H.; Kim, Y.T.; Jeong, J.W.; Suh, J.T.; Lee, H.J. Investigation of mutation distribution in DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV genes in ciprofloxacin-non-susceptible Enterobacteriaceae isolated from blood cultures in a tertiary care university hospital in South Korea, 2005–2010. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2013, 41, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinue, L.; Corcoran, M.A.; Hooper, D.C.; Jacoby, G.A. Mutations That Enhance the Ciprofloxacin Resistance of Escherichia coli with qnrA1. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 60, 1537–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravey, F.; Michel, A.; Langlois, B.; Gerard, M.; Galopin, S.; Gakuba, C.; Du Cheyron, D.; Fazilleu, L.; Brossier, D.; Guerin, F.; et al. Central role of the ramAR locus in the multidrug resistance in ESBL–Enterobacterales. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0354823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Martínez, L.; Pascual, A.; Jacoby, G.A. Quinolone resistance from a transferable plasmid. Lancet. 1998, 351, 797–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacoby, G.A.; Strahilevitz, J.; Hooper, D.C. Plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance. Microbiol. Spectr. 2014, 2, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Martínez, J.M.; Machuca, J.; Cano, M.E.; Calvo, J.; Martínez-Martínez, L.; Pascual, A. Plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance: Two decades on. Drug Resist. Update 2016, 29, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocsis, B.; Szmolka, A.; Szabo, O.; Gulyas, D.; Kristof, K.; Göczö, I.; Szabo, D. Ciprofloxacin Promoted qnrD Expression and Phylogenetic Analysis of qnrD Harboring Plasmids. Microb. Drug Resist. 2019, 25, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albornoz, E.; Tijet, N.; De Belder, D.; Gomez, S.; Martino, F.; Corso, A.; Melano, R.G.; Petroni, A. qnrE1, a Member of a New Family of Plasmid-Located Quinolone Resistance Genes, Originated from the Chromosome of Enterobacter Species. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e02555-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yin, M.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Q.; Wang, M. Identification of qnrE3 and qnrE4, New Transferable Quinolone Resistance qnrE Family Genes Originating from Enterobacter mori and Enterobacter asburiae, Respectively. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, e0045621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.H.; Chan, E.W.; Chen, S. Evolution and dissemination of OqxAB-like efflux pumps, an emerging quinolone resistance determinant among members of Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 3290–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, M.P.V.; Davies, Y.M.; Cerdeira, L.; Dropa, M.; Lincopan, N.; Knöbl, T. Complete DNA sequence of an IncM1 plasmid bearing the novel qnrE1 plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance variant and blaCTX-M-8 from Klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type 147. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e00592-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okeke, I.N.; de Kraker, M.E.A.; Van Boeckel, T.P.; Kumar, C.K.; Schmitt, H.; Gales, A.C.; Bertagnolio, S.; Sharland, M.; Laxminarayan, R. The scope of the antimicrobial resistance challenge. Lancet 2024, 403, 2426–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M.S.; Paterson, D.L. Antibiotics in the clinical pipeline in October 2019. J. Antibiot. 2020, 73, 329–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolaños, S.; Acebes, C.; Martínez-Expósito, Ó.; Boga, J.A.; Fernández, J.; Rodríguez-Lucas, C. Role of parC Mutations at Position 84 on High-Level Delafloxacin Resistance in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iregui, A.; Khan, Z.; Malik, S.; Landman, D.; Quale, J. Emergence of delafloxacin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Brooklyn, New York. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 70, 1758–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzarraga, V.; Cremniter, J.; Plouzeau, C.; Michaud, A.; Broutin, L.; Burucoa, C.; Pichon, M. In vitro activity of delafloxacin against clinical levofloxacin-resistant Helicobacter pylori isolates. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2024, 79, 2633–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulyás, D.; Kamotsay, K.; Szabó, D.; Kocsis, B. Investigation of Delafloxacin Resistance in Multidrug-Resistant Escherichia coli Strains and the Detection of E. coli ST43 International High-Risk Clone. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubicskó, A.; Kamotsay, K.; Szabó, D.; Kocsis, B. Analysis of molecular mechanisms of delafloxacin resistance in Escherichia coli. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 26423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoudabadi, S.; Goudarzi, H.; Goudarzi, M.; Ardebili, A.; Faghihloo, E.; Sharahi, J.Y.; Hashemi, A. Detection of extensively drug-resistant and hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae ST15, ST147, ST377 and ST442 in Iran. Acta Microbiol. Immunol. Hung. 2022, 69, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelenkov, A.; Mikhaylova, Y.; Yanushevich, Y.; Samoilov, A.; Petrova, L.; Fomina, V.; Gusarov, V.; Zamyatin, M.; Shagin, D.; Akimkin, V. Molecular Typing, Characterization of Antimicrobial Resistance, Virulence Profiling and Analysis of Whole-Genome Sequence of Clinical Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibik, Y.E.; Ejder, N.; Sevim, E.; Rakici, E.; Tanriverdi, E.S.; Cicek, A.C. Evaluating molecular epidemiology of carbapenem non-susceptible Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates with MLST, MALDI-TOF MS, PFGE. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2023, 22, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mataseje, L.F.; Chen, L.; Peirano, G.; Fakharuddin, K.; Kreiswith, B.; Mulvey, M.; Pitout, J.D.D. Klebsiella pneumoniae ST147: And then there were three carbapenemases. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2022, 41, 1467–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damjanova, I.; Tóth, A.; Pászti, J.; Hajbel-Vékony, G.; Jakab, M.; Berta, J.; Milch, H.; Füzi, M. Expansion and countrywide dissemination of ST11, ST15 and ST147 ciprofloxacin-resistant CTX-M-15-type beta-lactamase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae epidemic clones in Hungary in 2005--the new ’MRSAs’? J Antimicrob Chemother. 2008, 62, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocsis, B.; Kocsis, E.; Fontana, R.; Cornaglia, G.; Mazzariol, A. Identification of blaLAP-2 and qnrS1 genes in the internationally successful Klebsiella pneumoniae ST147 clone. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 62, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peirano, G.; Chen, L.; Kreiswirth, B.N.; Pitout, J.D.D. Emerging antimicrobial-resistant high-risk Klebsiella pneumoniae clones ST307 and ST147. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e01148-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Gaur, M.; Sykes, E.M.E.; Prusty, M.; Elangovan, S.; Dixit, S.; Pati, S.; Kumar, A.; Subudhi, E. Unravelling the Evolutionary Dynamics of High-Risk Klebsiella pneumoniae ST147 Clones: Insights from Comparative Pangenome Analysis. Genes 2023, 14, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofosu-Appiah, F.; Acquah, E.E.; Mohammed, J.; Sakyi Addo, C.; Agbodzi, B.; Ofosu, D.A.S.; Myers, C.J.; Mohktar, Q.; Ampomah, O.; Ablordey, A.; et al. Klebsiella pneumoniae ST147 harboring blaNDM-1, multidrug resistance and hypervirulence plasmids. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e03017-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domokos, J.; Damjanova, I.; Kristof, K.; Ligeti, B.; Kocsis, B.; Szabo, D. Multiple Benefits of Plasmid-Mediated Quinolone Resistance Determinants in Klebsiella pneumoniae ST11 High-Risk Clone and Recently Emerging ST307 Clone. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador-Oke, K.T.; Pitout, J.D.D.; Peirano, G.; Strydom, K.A.; Kingsburgh, C.; Ehlers, M.M.; Ismail, A.; Takawira, F.T.; Kock, M.M. Molecular epidemiology of carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in Gauteng South Africa. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 27337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Gao, K.; Li, M.; Zhou, J.; Song, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Yu, Z.; Cheng, W.; Zhang, W.; et al. Epidemiological and molecular characteristics of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae from pediatric patients in Henan, China. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2024, 23, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, V.; Mangioni, D.; Renica, S.; Comelli, A.; Teri, A.; Zatelli, M.; Orena, B.S.; Scuderi, C.; Cavallero, A.; Rossi, M.; et al. Genomic characterization of Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae (KPC-Kp) strains circulating in three university hospitals in Northern Italy over three years. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2024, 13, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budia-Silva, M.; Kostyanev, T.; Ayala-Montaño, S.; Bravo-Ferrer Acosta, J.; Garcia-Castillo, M.; Cantón, R.; Goossens, H.; Rodriguez-Baño, J.; Grundmann, H.; Reuter, S. International and regional spread of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in Europe. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, R.O.; Dadzie, I.; Le-Viet, T.; Baker, D.J.; Addy, H.P.K.; Akwetey, S.A.; Donkoh, I.E.; Quansah, E.; Semanshia, P.S.; Morgan, J.; et al. Genomic diversity and antimicrobial resistance in clinical Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from tertiary hospitals in Southern Ghana. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2024, 79, 1529–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, Á.; Kocsis, B.; Damjanova, I.; Kristof, K.; Jánvári, L.; Pászti, J.; Csercsik, R.; Topf, J.; Szabo, D.; Hamar, P.; et al. Fitness cost associated with resistance to fluoroquinolones is diverse across clones of Klebsiella pneumoniae and may select for CTX M-15 type extended-spectrum β-lactamase. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 33, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuzi, M.; Szabo, D.; Csercsik, R. Double-Serine Fluoroquinolone Resistance Mutations Advance Major International Clones and Lineages of Various Multi-Drug Resistant Bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diancourt, L.; Passet, V.; Verhoef, J.; Grimont, P.A.; Brisse, S. Multilocus Sequence Typing of Klebsiella pneumoniae nosocomial isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 4178–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bialek-Davenet, S.; Criscuolo, A.; Ailloud, F.; Passet, V.; Jones, L.; Delannoy-Vieillard, A.S.; Garin, B.; Le Hello, S.; Arlet, G.; Nicolas-Chanoine, M.H.; et al. Genomic definition of Hypervirulent and Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Clonal Groups. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1812–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.J.; Lin, T.L.; Chen, Y.H.; Hsu, C.R.; Hsieh, P.F.; Wu, M.C.; Wang, J.T. Capsular types of Klebsiella pneumoniae revisited by wzc sequencing. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisse, S.; Passet, V.; Haugaard, A.B.; Babosan, A.; Kassis-Chikhani, N.; Struve, C.; Decré, D. wzi gene sequencing, a rapid method to determine the capsular type of Klebsiella strains. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 4073–4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, J.R.; Enns, E.; Marinier, E.; Mandal, A.; Herman, E.K.; Chen, C.Y.; Graham, M.; Domselaar, D.V.; Stothard, P. Proksee: In-depth characterization and visualization of bacterial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W484–W494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, R.K.; Bartels, D.; Best, A.A.; DeJongh, M.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Formsma, K.; Gerdes, S.; Glass, E.M.; Kubal, M.; et al. The RAST Server: Rapid Annotations using Subsystems Technology. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overbeek, R.; Olson, R.; Pusch, G.D.; Olsen, G.J.; Davis, J.J.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Gerdes, S.; Parrello, B.; Shukla, M.; et al. The SEED and the Rapid Annotation of microbial genomes using Subsystems Technology (RAST). Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D206-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
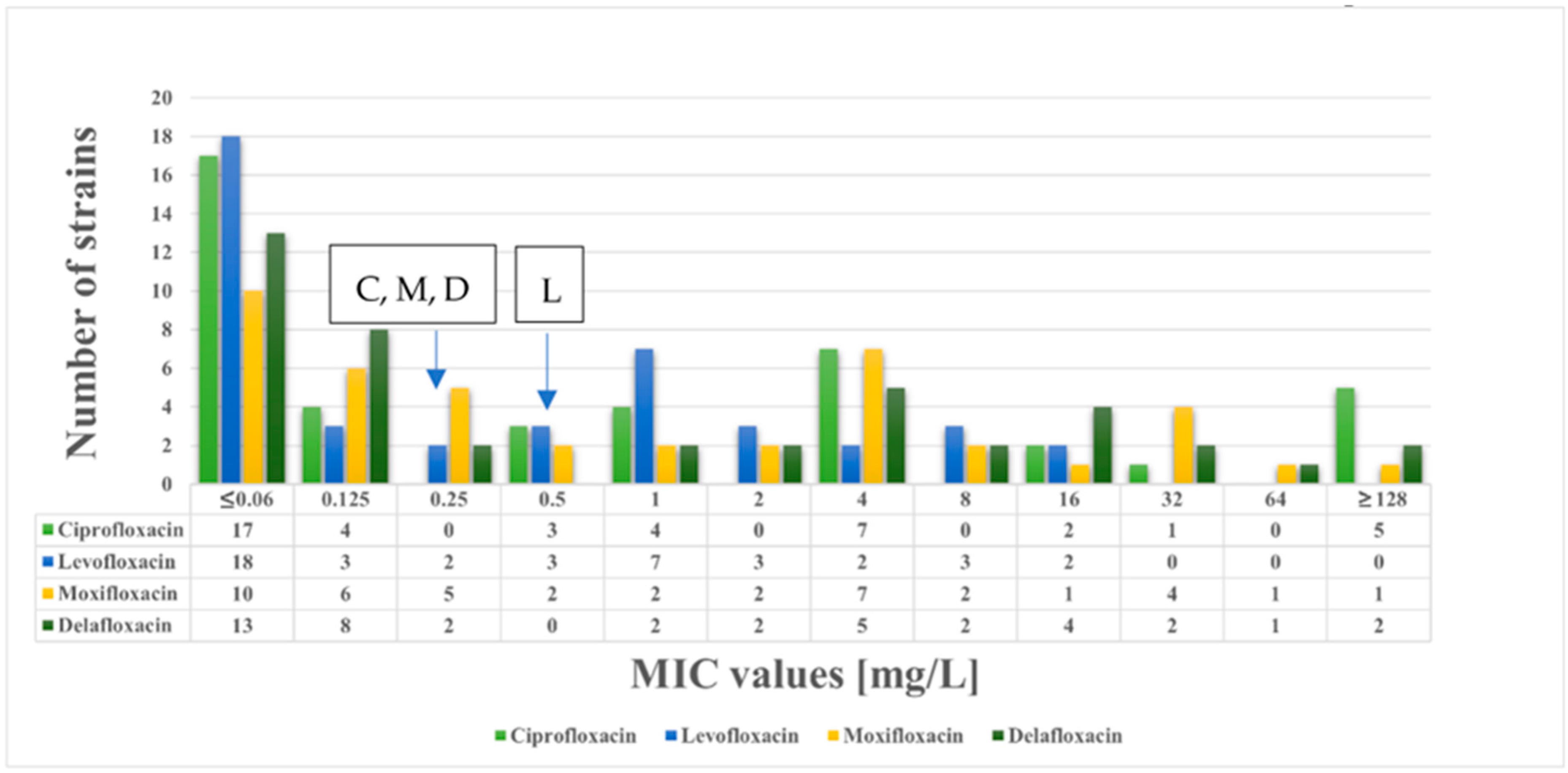
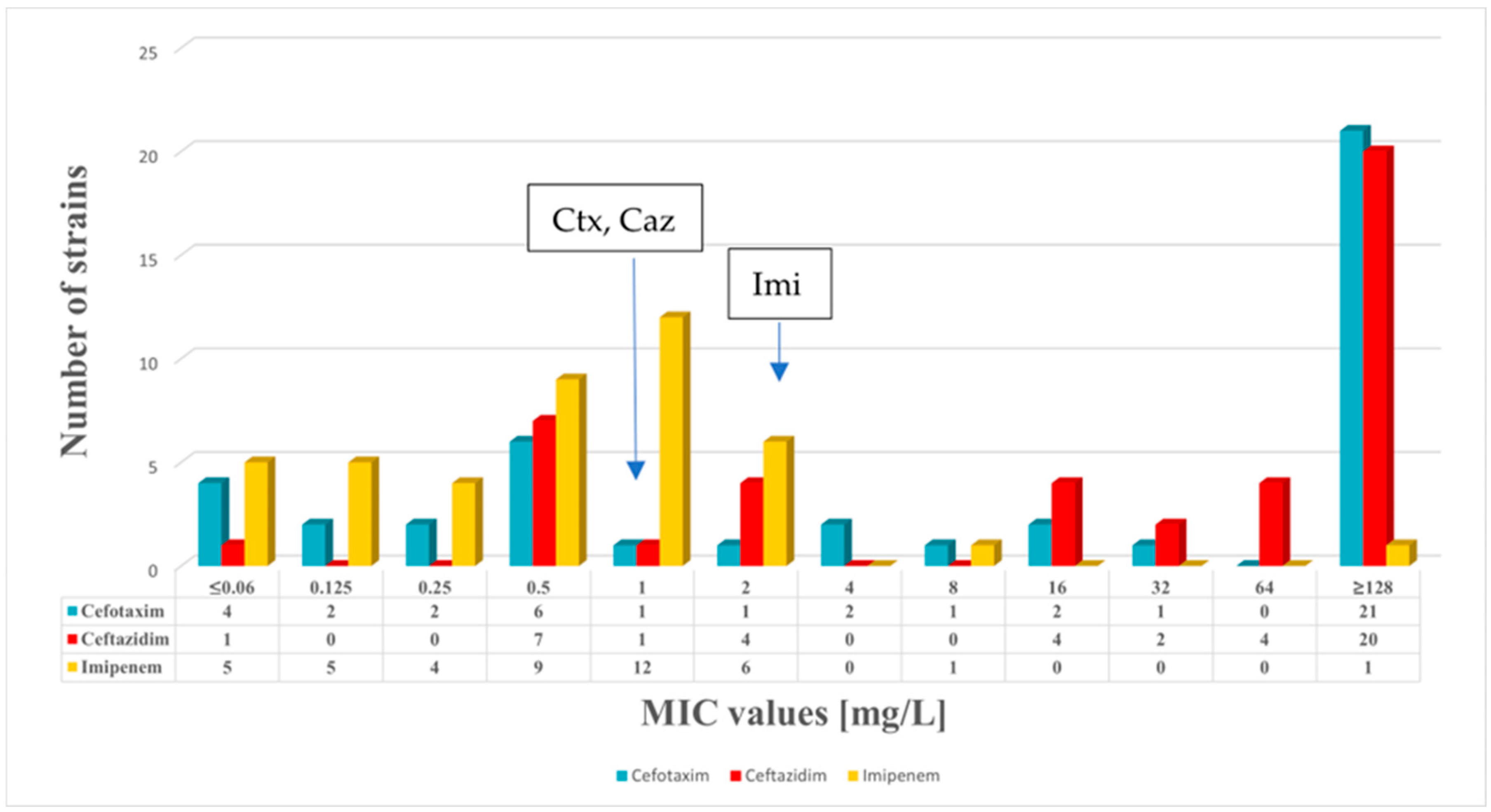
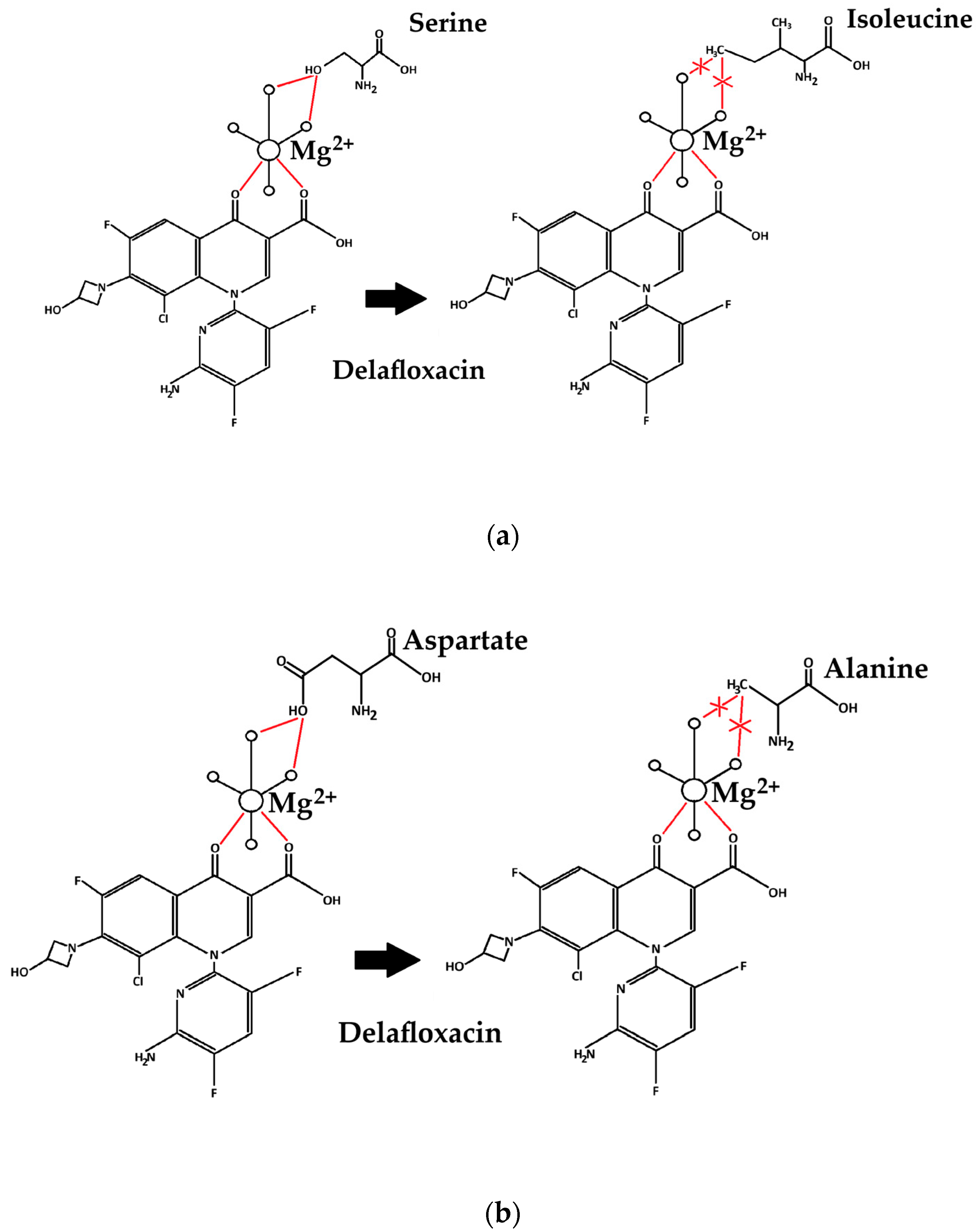
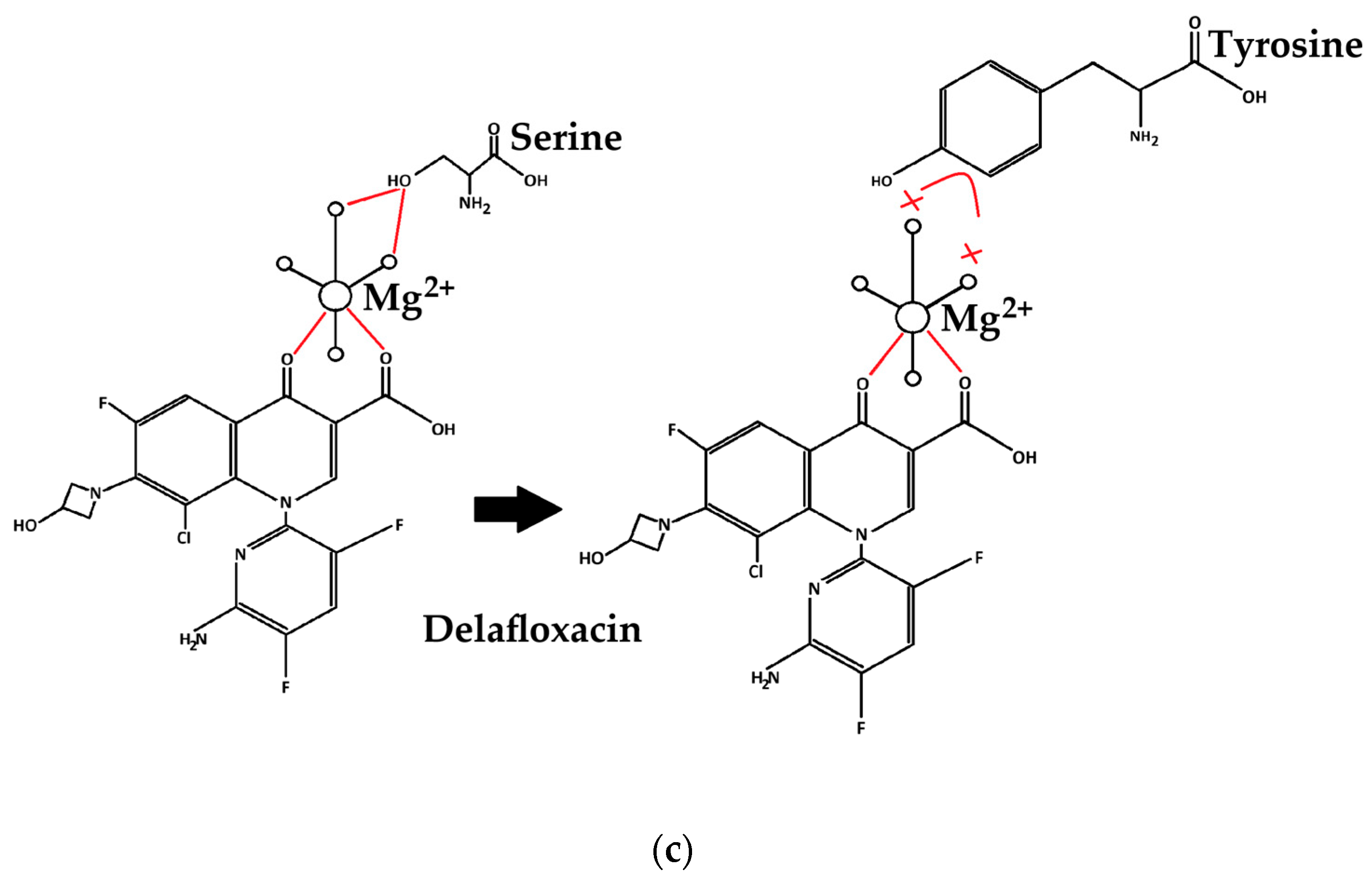
| MLST | PMQR | Beta-Lactamases | Cip | Lev | Mox | Del | Caz | Ctx | Imi | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K. pneumoniae 180 | ST147 | qnrS1, oqxA, oqxB | blaNDM-1, blaSHV-11, blaOXA-1, blaOXA-9, blaTEM-1A, blaCTX-M-15 | 128 | 16 | 128 | 128 | 128 | 128 | 128 |
| K. pneumoniae 205/1 | ST307 | qnrB1, aac(6′)-Ib-cr, oqxA, oqxB | blaSHV-28, blaOXA-1, blaTEM-1B, blaCTX-M-15 | 128 | 8 | 32 | 64 | 128 | 128 | 1 |
| K. pneumoniae 431 | ST377 | aac(6′)-Ib-cr, oqxA, oqxB | blaSHV-110, blaOXA-1, blaCTX-M-15 | 128 | 8 | 32 | 4 | 128 | 128 | 1 |
| K. pneumoniae 684 | ST307 | qnrB1, aac(6′)-Ib-cr, oqxA, oqxB | blaSHV-28, blaOXA-1, blaTEM-1B, blaCTX-M-15 | 128 | 8 | 32 | 32 | 128 | 128 | 0.5 |
| ST | ST377 | ST307 | ST307 | ST147 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PMQR | aac(6′)-Ib-cr, oqxA, oqxB | qnrB1, aac(6′)-Ib-cr, oqxA, oqxB | qnrB1, aac(6′)-Ib-cr, oqxA, oqxB | qnrS1, oqxA, oqxB |
| QRDR | gyrA: Ser83Tyr, Asp87Ala parC: Ser80Ile, Pro402Ala | gyrA: Ser83Ile parC: Ser80Ile, Asn304Ser, Pro402Ala | gyrA: Ser83Ile parC: Ser80Ile, Asn304Ser, Pro402Ala | gyrA: Ser83Ile parC: Ser80Ile, Asn304Ser, Pro402Ala |
| Efflux system | AcrAB/TolC | AcrAB/TolC | AcrAB/TolC | AcrAB/TolC |
| delafloxacin MIC (mg/L) | 4 | 32 | 64 | 128 |
| ST147 | ST307 | ST307 | ST377 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Siderophores fyu, iucB, ybtA, ybtE, ybtP, ybtQ, ybtS, ybtT, ybtU, ybtX | Siderophores fyuA, irp1, irp2, ybtA, ybtE, ybtP, ybtQ, ybtS, ybtT, ybtU, ybtX | ||
| Type III fimbriae mrkA, mrkC, mrkD, mrkF, mrkH, mrkI, mrkJ | Type III fimbriae mrkA, mrkC, mrkD, mrkF, mrkH, mrkI, mrkJ | Type III fimbriae mrkA, mrkC, mrkD, mrkF, mrkH, mrkI, mrkJ | Type III fimbriae mrkA, mrkC, mrkD, mrkF, mrkH, mrkI |
| Mucus regulator rmpA rmpA2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kubicskó, A.; Juhász, J.; Kamotsay, K.; Szabo, D.; Kocsis, B. Detection of Delafloxacin Resistance Mechanisms in Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14010062
Kubicskó A, Juhász J, Kamotsay K, Szabo D, Kocsis B. Detection of Delafloxacin Resistance Mechanisms in Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(1):62. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14010062
Chicago/Turabian StyleKubicskó, András, János Juhász, Katalin Kamotsay, Dora Szabo, and Béla Kocsis. 2025. "Detection of Delafloxacin Resistance Mechanisms in Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae" Antibiotics 14, no. 1: 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14010062
APA StyleKubicskó, A., Juhász, J., Kamotsay, K., Szabo, D., & Kocsis, B. (2025). Detection of Delafloxacin Resistance Mechanisms in Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antibiotics, 14(1), 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14010062






