Immunomodulatory Effect of Phage Depolymerase Dep_kpv74 with Therapeutic Potential Against K2-Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
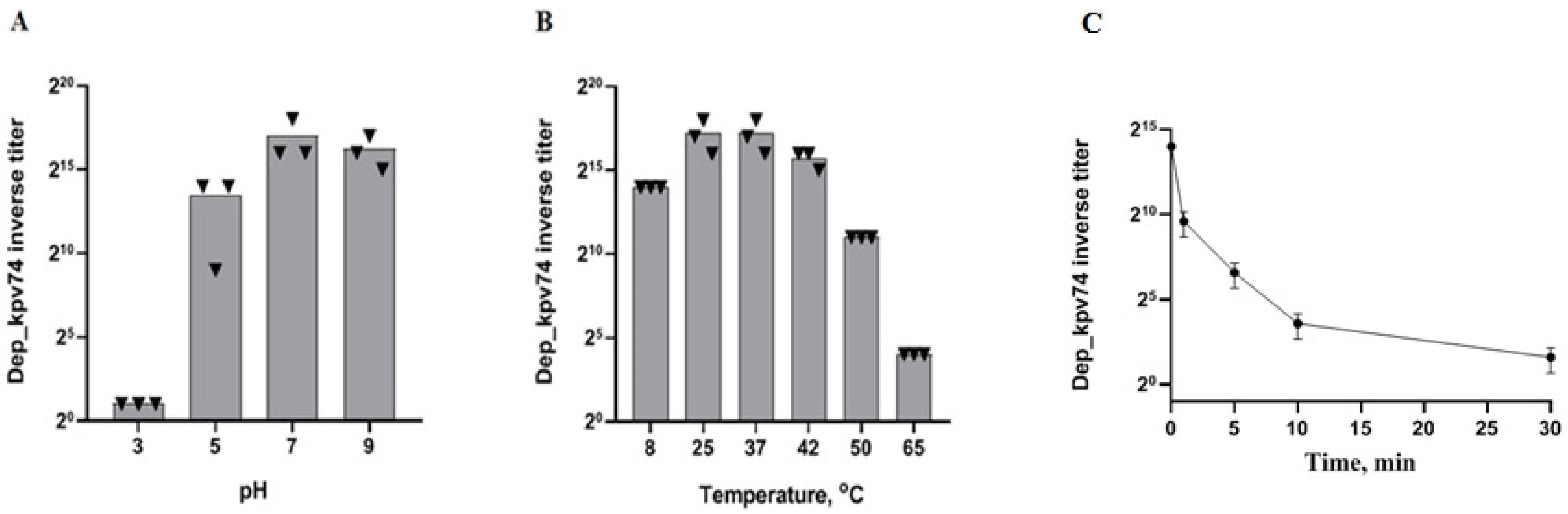
2.1. Depolymerase Dep_kpv74 Activity and Stability
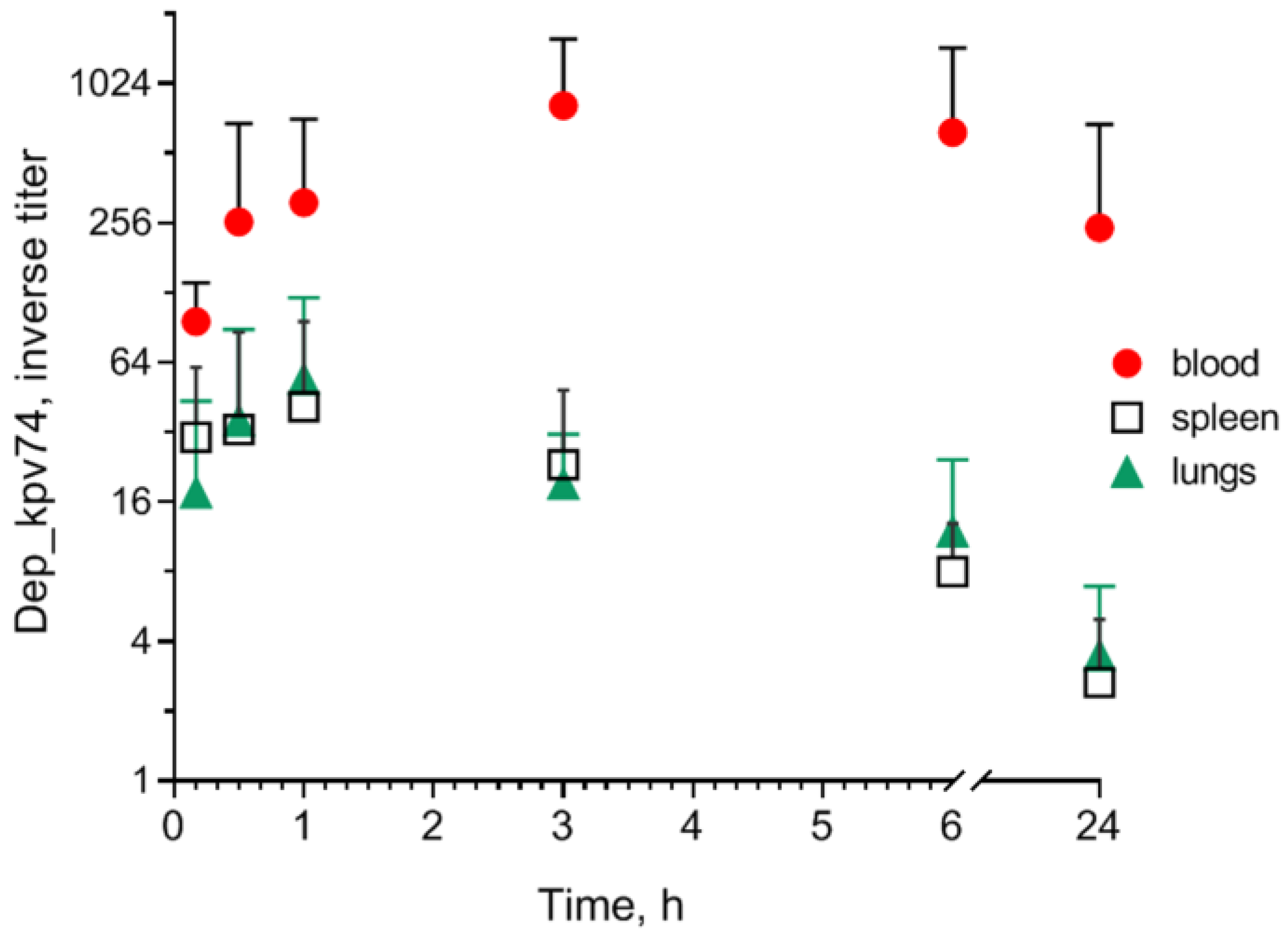
2.2. Effect of Depolymerase Dep_kpv74 on Blood Parameters in Mice
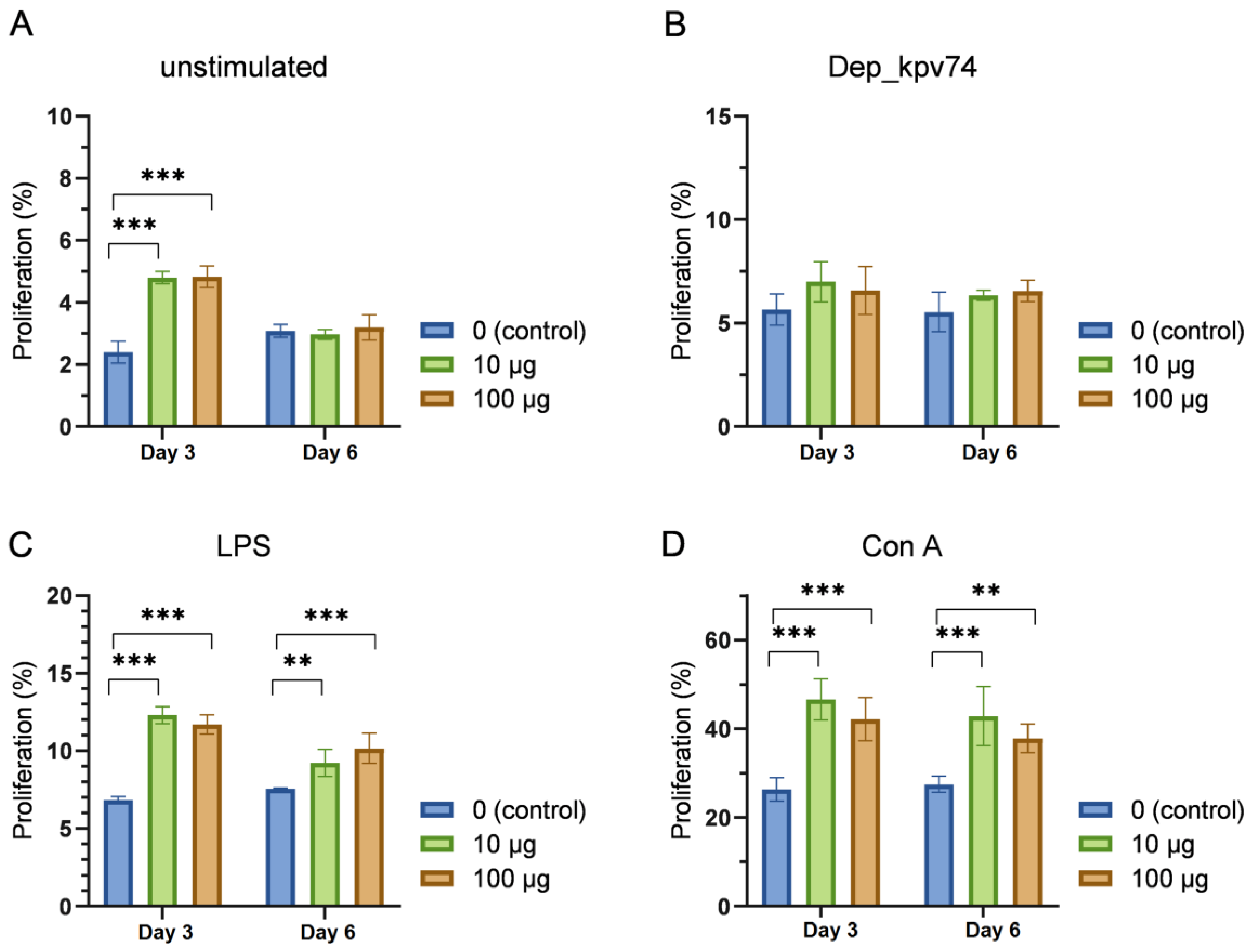
2.3. Effect of Depolymerase Dep_kpv74 on the Proliferation and Subpopulation Composition of Lymphocytes
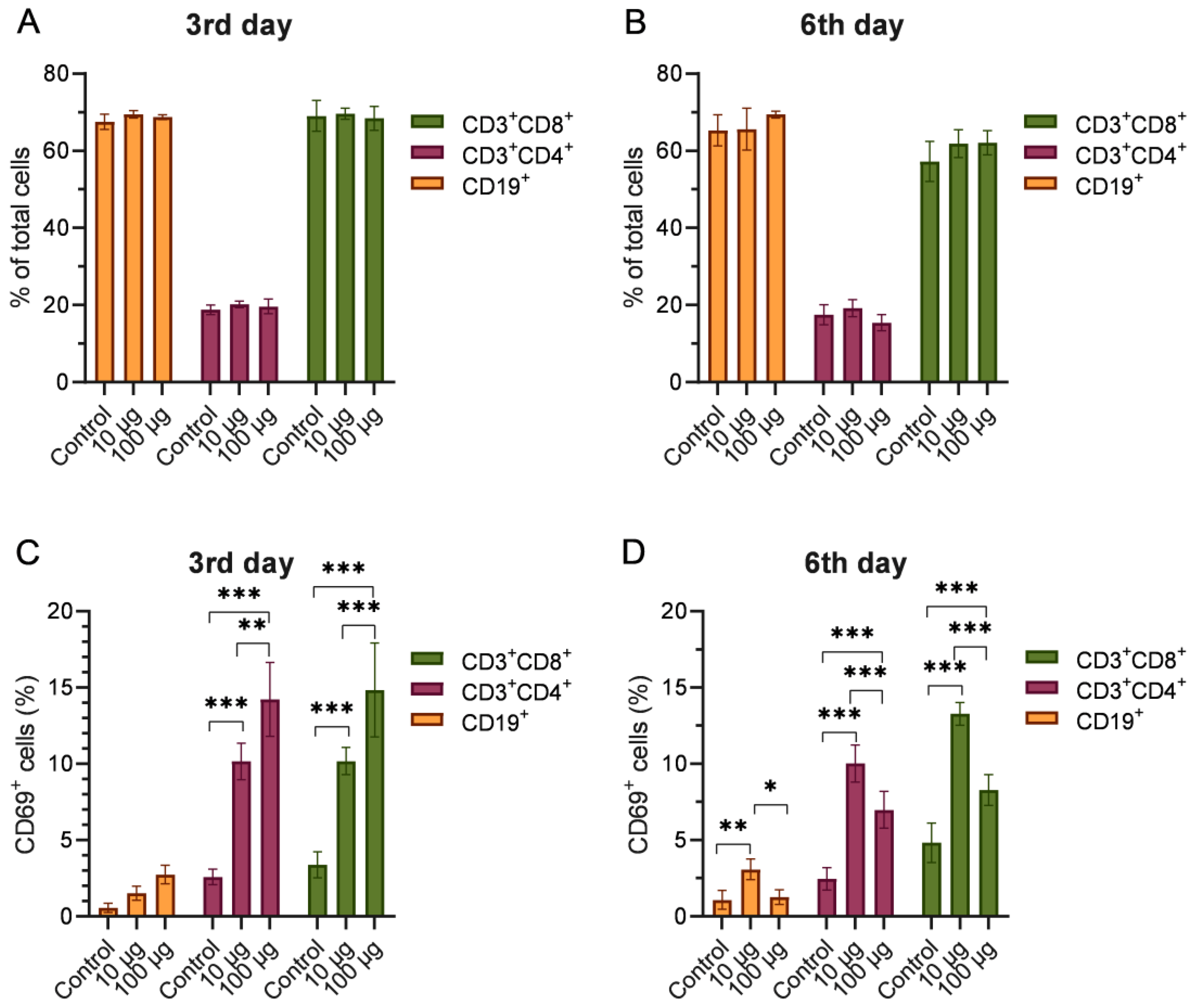
2.4. Phenotyping of Splenocytes from Mice Injected with Depolymerase Dep_kpv74
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains
4.2. Recombinant CPS Depolymerase Preparation
4.3. Determination of Dep_kpv74 Activity and Stability
4.4. Determination of Depolymerase in Mouse Blood and Organs
4.5. Blood Parameter Tests
4.6. Preparation and Stimulation of Splenocytes
4.7. Lymphocyte Proliferation Assay
4.8. Flow Cytometry Analysis of Surface Markers
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shon, A.S.; Bajwa, R.P.; Russo, T.A. Hypervirulent (hypermucoviscous) Klebsiella pneumoniae: A new and dangerous breed. Virulence 2013, 4, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choby, J.E.; Howard-Anderson, J.; Weiss, D.S. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae-clinical and molecular perspectives. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 287, 283–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadasy, K.A.; Domiati-Saad, R.; Tribble, M.A. Invasive Klebsiella pneumoniae syndrome in North America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 45, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turton, J.F.; Englender, H.; Gabriel, S.N.; Turton, S.E.; Kaufmann, M.E.; Pitt, T.L. Genetically similar isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae serotype K1 causing liver abscesses in three continents. J. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 56, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, F.; Li, S.; Wang, R.; Wang, H. High Prevalence of Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae Infection in China: Geographic Distribution, Clinical Characteristics, and Antimicrobial Resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 6115–6120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.R.; Lee, J.H.; Park, K.S.; Jeon, J.H.; Kim, Y.B.; Cha, C.J.; Jeong, B.C.; Lee, S.H. Antimicrobial resistance of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: Epidemiology, hypervirulence-associated determinants, and resistance mechanisms. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 21, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paczosa, M.K.; Mecsas, J. Klebsiella pneumoniae: Going on the Offense with a Strong Defense. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, G.; Borrell, N.; Ãstorza, B.; Gómez, C.; Sauleda, J.; Albertí, S. Molecular analysis of the contribution of the capsular polysaccharide and the lipopolysaccharide O side chain to the virulence of Klebsiella pneumoniae in a murine model of pneumonia. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 2583–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenico, P.; Salo, R.J.; Cross, A.S.; Cunha, B.A. Polysaccharide capsule-mediated resistance to opsonophagocytosis in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 4495–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latka, A.; Maciejewska, B.; Majkowska-Skrobek, G.; Briers, Y.; Drulis-Kawa, Z. Bacteriophage-encoded virion associated enzymes to overcome the carbohydrate barriers during the infection process. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 3103–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, D.P.; Oliveira, H.; Melo, L.D.R.; Sillankorva, S.; Azeredo, J. Bacteriophage-encoded depolymerases: Their diversity and biotechnological applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 2141–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzozowska, E.; Pyra, A.; Pawlik, K.; Janik, M.; Górska, S.; Urbanska, N.; Drulis-Kawa, Z.; Gamian, A. Hydrolytic activity determination of Tail Tubular Protein A of Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteriophages towards saccharide substrates. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 18048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.L.; Hsieh, P.F.; Huang, Y.T.; Lee, W.C.; Tsai, Y.T.; Su, P.A.; Pan, Y.J.; Hsu, C.R.; Wu, M.C.; Wang, J.T. Isolation of a bacteriophage and its depolymerase specific for K1 capsule of Klebsiella pneumoniae: Implication in typing and treatment. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 210, 1734–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majkowska-Skrobek, G.; Łątka, A.; Berisio, R.; Maciejewska, B.; Squeglia, F.; Romano, M.; Lavigne, R.; Struve, C.; Drulis-Kawa, Z. Capsule-Targeting Depolymerase, Derived from Klebsiella KP36 Phage, as a Tool for the Development of Anti-Virulent Strategy. Viruses 2016, 8, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majkowska-Skrobek, G.; Latka, A.; Berisio, R.; Squeglia, F.; Maciejewska, B.; Briers, Y.; Drulis-Kawa, Z. Phage-Borne depolymerases decrease Klebsiella pneumoniae resistance to innate defense mechanisms. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 23, 2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, P.F.; Lin, H.; Lin, T.L.; Chen, Y.Y.; Wang, J.T. Two T7-like Bacteriophages, K5-2 and K5-4, Each Encodes Two Capsule Depolymerases: Isolation and Functional Characterization. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volozhantsev, N.V.; Shpirt, A.M.; Borzilov, A.I.; Komisarova, E.V.; Krasilnikova, V.M.; Shashkov, A.S.; Verevkin, V.V.; Knirel, Y.A. Characterization and Therapeutic Potential of Bacteriophage-Encoded Polysaccharide Depolymerases with β Galactosidase Activity against Klebsiella pneumoniae K57 Capsular Type. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volozhantsev, N.V.; Borzilov, A.I.; Shpirt, A.M.; Krasilnikova, V.M.; Verevkin, V.V.; Denisenko, E.A.; Kombarova, T.I.; Shashkov, A.S.; Knirel, Y.A.; Dyatlov, I.A. Comparison of the therapeutic potential of bacteriophage KpV74 and phage-derived depolymerase (β-glucosidase) against Klebsiella pneumoniae capsular type K2. Virus Res. 2022, 322, 198951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorodnichev, R.B.; Volozhantsev, N.V.; Krasilnikova, V.M.; Bodoev, I.N.; Kornienko, M.A.; Kuptsov, N.S.; Popova, A.V.; Makarenko, G.I.; Manolov, A.I.; Slukin, P.V.; et al. Novel Klebsiella pneumoniae K23-Specific Bacteriophages From Different Families: Similarity of Depolymerases and Their Therapeutic Potential. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 669618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessler, W.; Freund-Mölbert, E.; Knüfermann, H.; Rudolph, C.; Thurow, H.; Stirm, S. A bacteriophage-induced depolymerase active on Klebsiella K11 capsular polysaccharide. Virology 1973, 56, 134–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, R.; Xu, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Qiu, J.; Liu, Q.; He, P.; Li, Q. A Novel Polysaccharide Depolymerase Encoded by the Phage SH-KP152226 Confers Specific Activity Against Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae via Biofilm Degradation. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 3, 2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, S.; Kumar, V.; Das, R.; Sharma, V.; Mehta, D.K. Biomarkers of Hepatic Toxicity: An Overview. Curr. Ther. Res. Clin. Exp. 2024, 26, 100737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, Y.; Yasuoka, C.; Mishima, T.; Ikematsu, T.; Uede, T.; Matsunaga, T.; Inobe, M. Concanavalin A-mediated T cell proliferation is regulated by herpes virus entry mediator costimulatory molecule. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. Anim. 2014, 50, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Liew, L.N.; Kuo, I.C.; Huang, C.H.; Goh, D.L.; Chua, K.Y. The modulatory effects of lipopolysaccharide-stimulated B cells on differential T-cell polarization. Immunology 2008, 125, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cibrián, D.; Sánchez-Madrid, F. CD69: From activation marker to metabolic gatekeeper. Eur. J. Immunol. 2017, 47, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solovieva, E.V.; Myakinina, V.P.; Kislichkina, A.A.; Krasilnikova, V.M.; Verevkin, V.V.; Mochalov, V.V.; Lev, A.I.; Fursova, N.K.; Volozhantsev, N.V. Comparative genome analysis of novel Podoviruses lytic for hypermucoviscous Klebsiella pneumoniae of K1, K2, and K57 capsular types. Virus Res. 2018, 243, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameters (Unit) | Intact Mice | 3 Days | 6 Days | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 µg | 100 µg | 10 µg | 100 µg | ||
| Leukocytes (×109/L) | 5.8 ± 2.3 | 5.5 ± 2.7 | 4.9 ± 0.8 | 5.9 ± 0.8 | 4.8 ± 1.4 |
| Lymphocytes (×109/L) | 3.9 ± 1.2 | 3.3 ± 2.0 | 2.3 ± 1.0 | 5.2 ± 1.5 | 3.1 ± 0.7 |
| Monocytes (×109/L) | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 |
| Granulocytes (×109/L) | 1.7 ± 1.0 | 2.0 ± 0.6 | 2.4 ± 0.5 | 3.3 ± 0.7 | 1.5 ± 0.7 |
| Lymphocytes (%) | 68.1 ± 6.1 | 58.1 ± 6.5 | 46.4 ± 14.7 | 58.0 ± 11.3 | 64.8 ± 6.0 |
| Monocytes (%) | 3.8 ± 0.9 | 3.0 ± 0.2 | 4.0 ± 1.0 | 5.5 ± 2.4 | 4.0 ± 0.7 |
| Granulocytes (%) | 28.2 ± 5.2 | 38.9 ± 6.6 | 49.6 ± 13.9 | 36.5 ± 8.9 | 31.2 ± 5.3 |
| RBC (×1012/L) | 9.58 ± 0.31 | 9.66 ± 0.27 | 9.42 ± 0.57 | 9.17 ± 0.14 | 9.95 ± 0.66 |
| Hemoglobin (g/L) | 141 ± 5 | 138 ± 3 | 137 ± 9 | 119 ± 3 | 144 ± 9 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 44.9 ± 1.3 | 43.3 ± 0.9 | 43.0 ± 2.7 | 40.5 ± 1.5 | 46.3 ± 2.7 |
| MCV (FL) | 46.9 ± 1.2 | 44.8 ± 0.6 | 45.7 ± 0.1 | 44.2 ± 1.2 | 46.6 ± 1.3 |
| MCH (pg) | 14.6 ± 0.5 | 14.2 ± 0.3 | 14.5 ± 0.1 | 12.9 ± 0.2 | 14.4 ± 0.5 |
| MCHC (g/L) | 313 ± 14 | 318 ± 3 | 319 ± 2 | 293 ± 7 | 311 ± 1 |
| Platelets (×109/L) | 792 ± 121 | 792 ± 225 | 816 ± 96 | 655 ± 87 | 702 ± 319 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Volozhantsev, N.V.; Makarova, M.A.; Kartseva, A.S.; Silkina, M.V.; Krasilnikova, V.M.; Denisenko, E.A.; Borzilov, A.I.; Firstova, V.V. Immunomodulatory Effect of Phage Depolymerase Dep_kpv74 with Therapeutic Potential Against K2-Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14010044
Volozhantsev NV, Makarova MA, Kartseva AS, Silkina MV, Krasilnikova VM, Denisenko EA, Borzilov AI, Firstova VV. Immunomodulatory Effect of Phage Depolymerase Dep_kpv74 with Therapeutic Potential Against K2-Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(1):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14010044
Chicago/Turabian StyleVolozhantsev, Nikolay V., Maria A. Makarova, Alena S. Kartseva, Marina V. Silkina, Valentina M. Krasilnikova, Egor A. Denisenko, Alexander I. Borzilov, and Victoria V. Firstova. 2025. "Immunomodulatory Effect of Phage Depolymerase Dep_kpv74 with Therapeutic Potential Against K2-Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae" Antibiotics 14, no. 1: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14010044
APA StyleVolozhantsev, N. V., Makarova, M. A., Kartseva, A. S., Silkina, M. V., Krasilnikova, V. M., Denisenko, E. A., Borzilov, A. I., & Firstova, V. V. (2025). Immunomodulatory Effect of Phage Depolymerase Dep_kpv74 with Therapeutic Potential Against K2-Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antibiotics, 14(1), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14010044






