Precision Dosing of Meropenem in Adults with Normal Renal Function: Insights from a Population Pharmacokinetic and Monte Carlo Simulation Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Participants
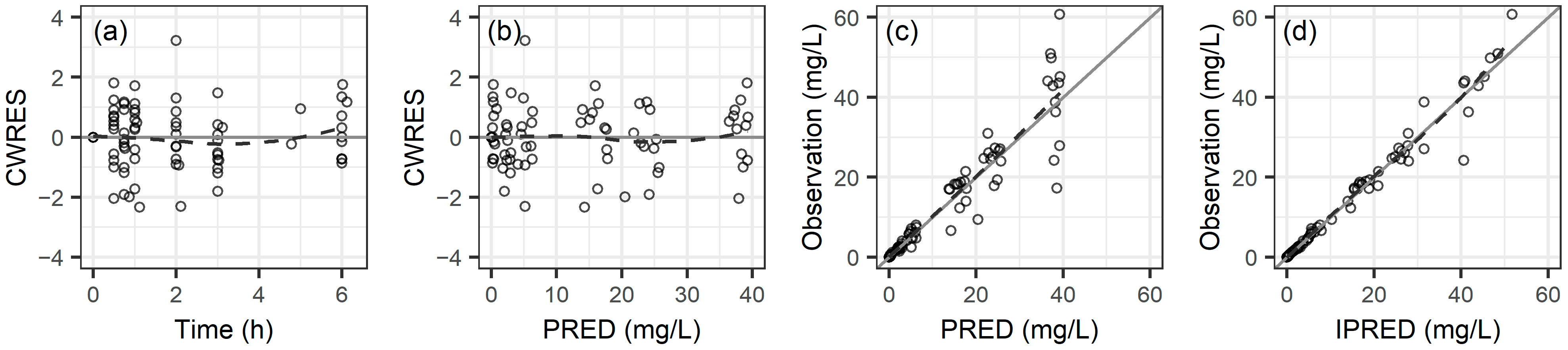
2.2. Population Pharmacokinetic Analysis
2.3. Comparing Noncompartmental Analysis and Population Pharmacokinetics Results
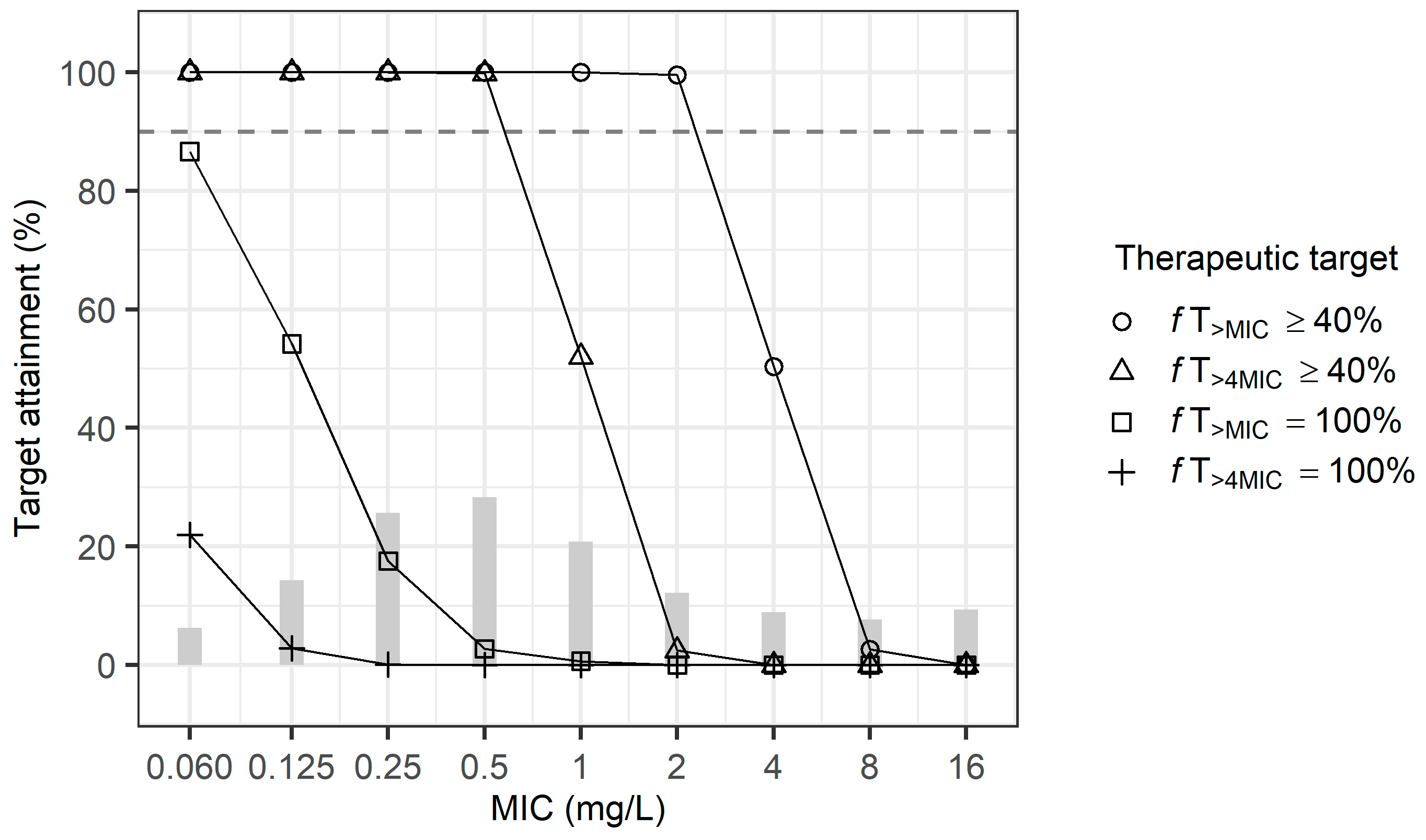
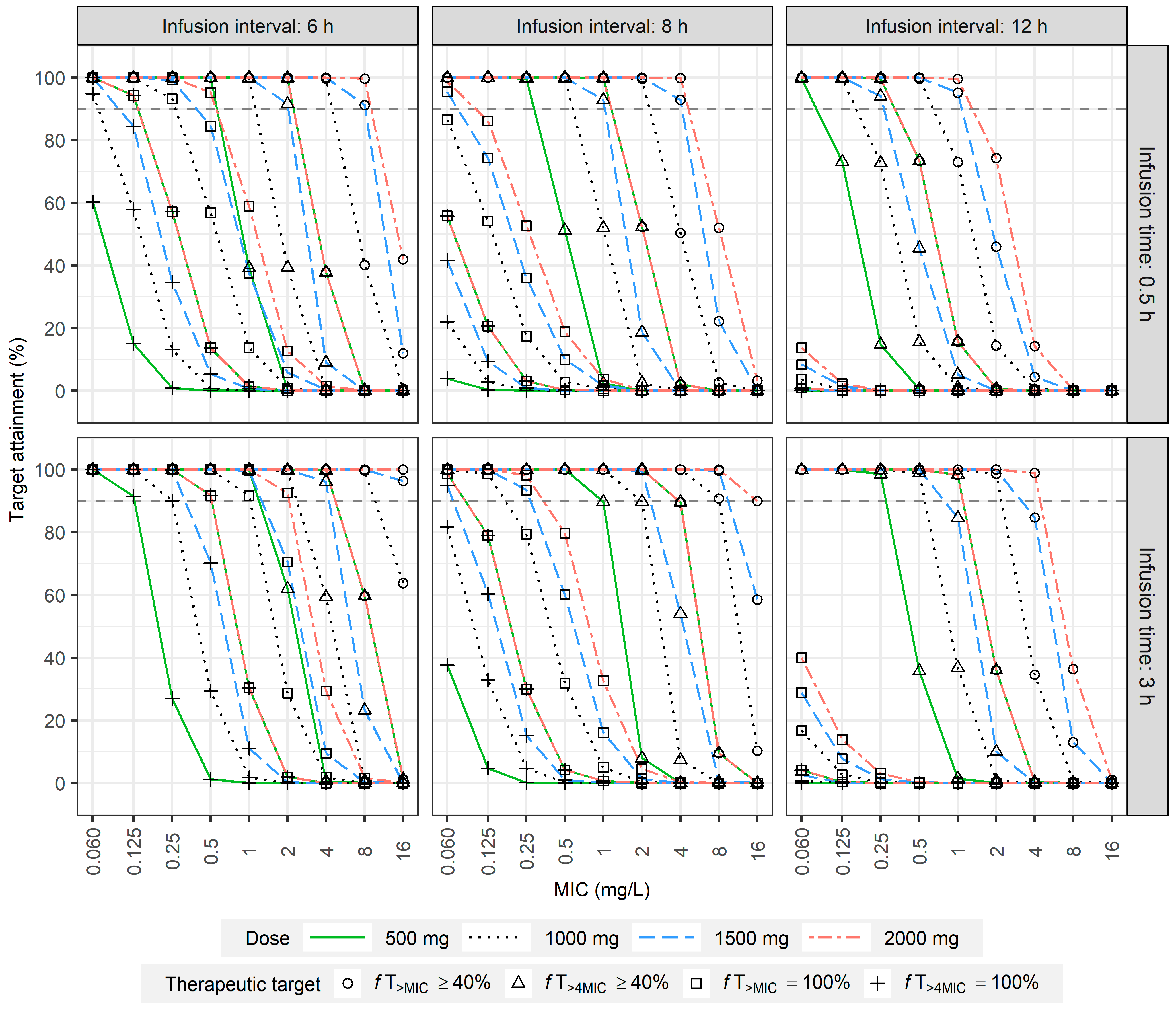
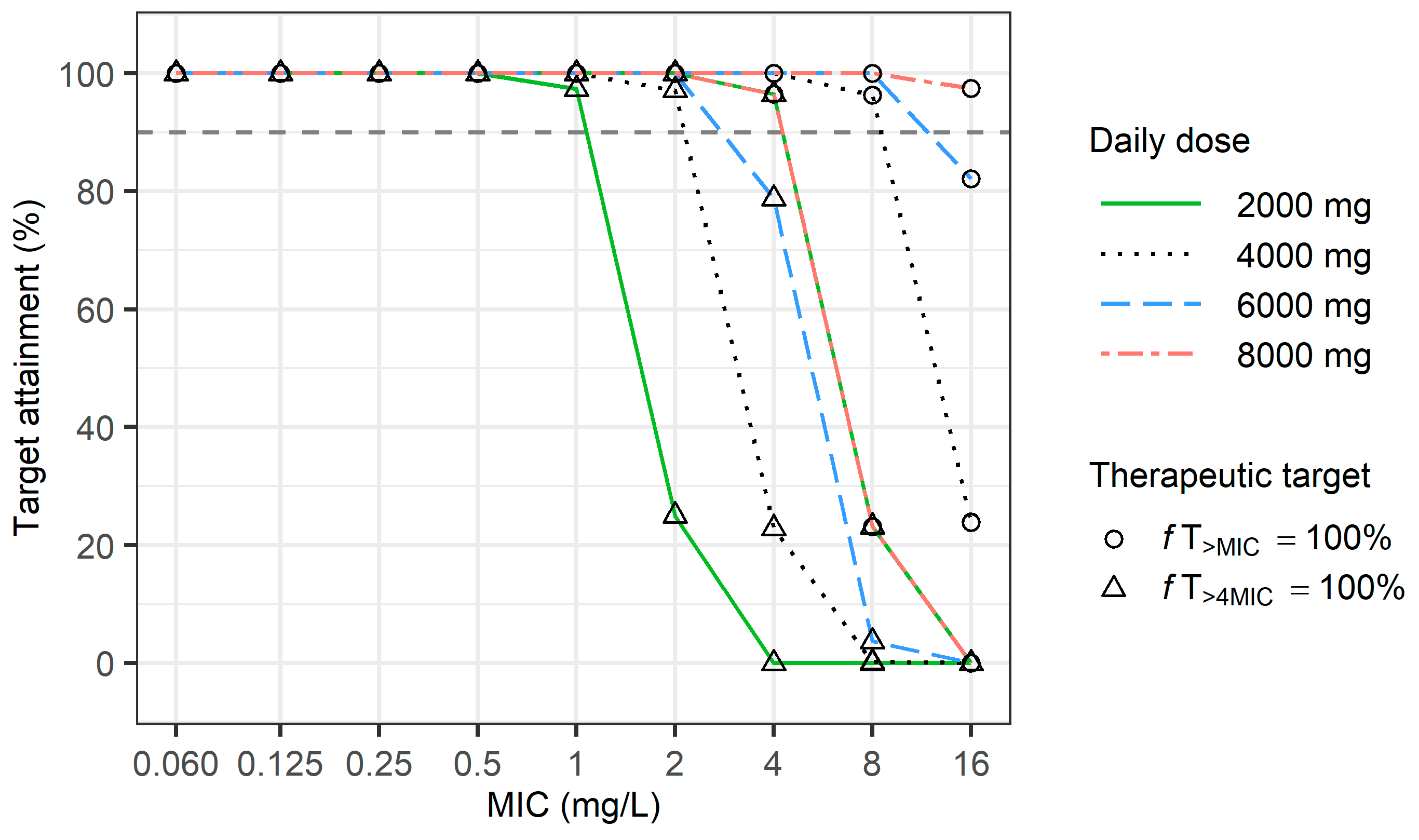
2.4. Dosage Simulation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Participants
4.2. Study Design
4.3. Population Pharmacokinetic Analysis
4.4. Noncompartmental Analysis
4.5. Dosage Simulation
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Craig, W.A. The pharmacology of meropenem, a new carbapenem antibiotic. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1997, 24 (Suppl S2), S266–S275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fish, D.N.; Singletary, T.J. Meropenem, a new carbapenem antibiotic. Pharmacotherapy 1997, 17, 644–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrier, J.; Timsit, J.F. Carbapenem use in critically ill patients. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 33, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolau, D.P. Carbapenems: A potent class of antibiotics. Expert. Opin. Pharmacother. 2008, 9, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Versporten, A.; Zarb, P.; Caniaux, I.; Gros, M.F.; Drapier, N.; Miller, M.; Jarlier, V.; Nathwani, D.; Goossens, H.; Koraqi, A.; et al. Antimicrobial consumption and resistance in adult hospital inpatients in 53 countries: Results of an internet-based global point prevalence survey. Lancet Glob. Health 2018, 6, e619–e629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antimicrobial Resistance, C. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.A.; Kruger, P.; Paterson, D.L.; Lipman, J. Antibiotic resistance—What’s dosing got to do with it? Crit. Care Med. 2008, 36, 2433–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelini, J.; Giuliano, S.; Flammini, S.; Pagotto, A.; Lo Re, F.; Tascini, C.; Baraldo, M. Meropenem PK/PD Variability and Renal Function: “We Go Together”. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Zhang, M.; Ma, S.Q.; Cong, R.N.; Li, J.F. Application of Monte Carlo simulation to optimise the dosage regimen of meropenem in patients with augmented renal clearance for Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. Heliyon 2024, 10, e32600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Shen, Y.; Fu, Y.; Li, Y.; Gao, M.; Zhang, D. Changes of PK/PD of Meropenem in patients with abdominal septic shock and exploration of clinical rational administration plan: A prospective exploratory study. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Antimicrobial Wild Type Distributions of Microorganisms. Available online: https://mic.eucast.org/ (accessed on 18 June 2024).
- Bax, R.P.; Bastain, W.; Featherstone, A.; Wilkinson, D.M.; Hutchison, M.; Haworth, S.J. The pharmacokinetics of meropenem in volunteers. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1989, 24, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wise, R.; Logan, M.; Cooper, M.; Ashby, J.P.; Andrews, J.M. Meropenem pharmacokinetics and penetration into an inflammatory exudate. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1990, 34, 1515–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burman, L.A.; Nilsson-Ehle, I.; Hutchison, M.; Haworth, S.J.; Norrby, S.R. Pharmacokinetics of meropenem and its metabolite ICI 213,689 in healthy subjects with known renal metabolism of imipenem. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1991, 27, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson-Ehle, I.; Hutchison, M.; Haworth, S.J.; Norrby, S.R. Pharmacokinetics of meropenem compared to imipenem-cilastatin in young, healthy males. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1991, 10, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensson, B.A.; Nilsson-Ehle, I.; Hutchison, M.; Haworth, S.J.; Oqvist, B.; Norrby, S.R. Pharmacokinetics of meropenem in subjects with various degrees of renal impairment. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1992, 36, 1532–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, A.; Fillastre, J.P.; Borsa-Lebas, F.; Etienne, I.; Humbert, G. Pharmacokinetics of meropenem (ICI 194,660) and its metabolite (ICI 213,689) in healthy subjects and in patients with renal impairment. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1992, 36, 2794–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ljungberg, B.; Nilsson-Ehle, I. Pharmacokinetics of meropenem and its metabolite in young and elderly healthy men. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1992, 36, 1437–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, L.; Sassen, S.D.T.; Ewoldt, T.M.J.; Abdulla, A.; Hunfeld, N.G.M.; Muller, A.E.; de Winter, B.C.M.; Endeman, H.; Koch, B.C.P. Meropenem Model-Informed Precision Dosing in the Treatment of Critically Ill Patients: Can We Use It? Antibiotics 2023, 12, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.A.; Abdul-Aziz, M.H.; Lipman, J.; Mouton, J.W.; Vinks, A.A.; Felton, T.W.; Hope, W.W.; Farkas, A.; Neely, M.N.; Schentag, J.J.; et al. Individualised antibiotic dosing for patients who are critically ill: Challenges and potential solutions. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gijsen, M.; Elkayal, O.; Annaert, P.; Van Daele, R.; Meersseman, P.; Debaveye, Y.; Wauters, J.; Dreesen, E.; Spriet, I. Meropenem Target Attainment and Population Pharmacokinetics in Critically Ill Septic Patients with Preserved or Increased Renal Function. Infect. Drug Resist. 2022, 15, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udy, A.A.; Varghese, J.M.; Altukroni, M.; Briscoe, S.; McWhinney, B.C.; Ungerer, J.P.; Lipman, J.; Roberts, J.A. Subtherapeutic initial beta-lactam concentrations in select critically ill patients: Association between augmented renal clearance and low trough drug concentrations. Chest 2012, 142, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilbao-Meseguer, I.; Rodriguez-Gascon, A.; Barrasa, H.; Isla, A.; Solinis, M.A. Augmented Renal Clearance in Critically Ill Patients: A Systematic Review. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2018, 57, 1107–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamatsukuri, T.; Ohbayashi, M.; Kohyama, N.; Kobayashi, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Fukuda, K.; Nakamura, S.; Miyake, Y.; Dohi, K.; Kogo, M. The exploration of population pharmacokinetic model for meropenem in augmented renal clearance and investigation of optimum setting of dose. J. Infect. Chemother. 2018, 24, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrie, C.; Chadefaux, G.; Sauvage, N.; de Courson, H.; Petit, L.; Nouette-Gaulain, K.; Pereira, B.; Biais, M. Increased beta-Lactams dosing regimens improve clinical outcome in critically ill patients with augmented renal clearance treated for a first episode of hospital or ventilator-acquired pneumonia: A before and after study. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agyeman, A.A.; Rogers, K.E.; Tait, J.R.; Bergen, P.J.; Kirkpatrick, C.M.; Wallis, S.C.; Bulitta, J.B.; Paterson, D.L.; Lipman, J.; Nation, R.L.; et al. Evaluation of Meropenem-Ciprofloxacin Combination Dosage Regimens for the Pharmacokinetics of Critically Ill Patients With Augmented Renal Clearance. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 109, 1104–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, W.A. Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic parameters: Rationale for antibacterial dosing of mice and men. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1998, 26, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drusano, G.L. Antimicrobial pharmacodynamics: Critical interactions of ‘bug and drug’. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delattre, I.K.; Taccone, F.S.; Jacobs, F.; Hites, M.; Dugernier, T.; Spapen, H.; Laterre, P.F.; Wallemacq, P.E.; Van Bambeke, F.; Tulkens, P.M. Optimizing beta-lactams treatment in critically-ill patients using pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics targets: Are first conventional doses effective? Expert. Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2017, 15, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.A.; Paul, S.K.; Akova, M.; Bassetti, M.; De Waele, J.J.; Dimopoulos, G.; Kaukonen, K.M.; Koulenti, D.; Martin, C.; Montravers, P.; et al. DALI: Defining antibiotic levels in intensive care unit patients: Are current beta-lactam antibiotic doses sufficient for critically ill patients? Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 58, 1072–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Bono, V.; Giacobbe, D.R.; Marchese, A.; Parisini, A.; Fucile, C.; Coppo, E.; Marini, V.; Arena, A.; Molin, A.; Martelli, A.; et al. Meropenem for treating KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae bloodstream infections: Should we get to the PK/PD root of the paradox? Virulence 2017, 8, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothekar, A.T.; Divatia, J.V.; Myatra, S.N.; Patil, A.; Nookala Krishnamurthy, M.; Maheshwarappa, H.M.; Siddiqui, S.S.; Gurjar, M.; Biswas, S.; Gota, V. Clinical pharmacokinetics of 3-h extended infusion of meropenem in adult patients with severe sepsis and septic shock: Implications for empirical therapy against Gram-negative bacteria. Ann. Intensive Care 2020, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharf, C.; Liebchen, U.; Paal, M.; Taubert, M.; Vogeser, M.; Irlbeck, M.; Zoller, M.; Schroeder, I. The higher the better? Defining the optimal beta-lactam target for critically ill patients to reach infection resolution and improve outcome. J. Intensive Care 2020, 8, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonpeng, A.; Jaruratanasirikul, S.; Jullangkoon, M.; Samaeng, M.; Wattanavijitkul, T.; Bhurayanontachai, R.; Pattharachayakul, S. Population Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics and Clinical Outcomes of Meropenem in Critically Ill Patients. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2022, 66, e0084522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, S.J.; Mueller, B.A. Antibiotic dosing recommendations in critically ill patients receiving new innovative kidney replacement therapy. BMC Nephrol. 2024, 25, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razzazzadeh, S.; Darazam, I.A.; Hajiesmaeili, M.; Salamzadeh, J.; Mahboubi, A.; Sadeghnezhad, E.; Sahraei, Z. Investigation of pharmacokinetic and clinical outcomes of various meropenem regimens in patients with ventilator-associated pneumonia and augmented renal clearance. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 78, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sistanizad, M.; Hassanpour, R.; Pourheidar, E. Are Antibiotics Appropriately Dosed in Critically Ill Patients with Augmented Renal Clearance? A Narrative Review. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2022, 2022, 1867674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.H.; Kim, H.S.; Park, S.; Kim, H.I.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, Y.K. Population Pharmacokinetics of Meropenem in Critically Ill Korean Patients and Effects of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters | Mean (CV%) | Median (IQR) |
|---|---|---|
| Demographic characteristics | ||
| Age, years | 36.8 (19.9%) | 36.0 (31.5–39.3) |
| Height, cm | 168 (4.29%) | 168 (163–173) |
| Weight, kg | 65.7 (20.8%) | 61.7 (56.7–73.3) |
| Body surface area, m2 | 1.74 (11.6%) | 1.71 (1.61–1.88) |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 23.0 (13.9%) | 21.5 (21.4–24.0) |
| Laboratory characteristics | ||
| Protein, g/dL | 7.48 (4.64%) | 7.45 (7.28–7.63) |
| Albumin, g/dL | 4.88 (4.35%) | 4.80 (4.78–5.03) |
| Cystatin C, mg/dL | 0.790 (15.9%) | 0.765 (0.705–0.873) |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 0.863 (19.0%) | 0.860 (0.738–1.02) |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.558 (62.2%) | 0.470 (0.328–0.720) |
| Blood urea nitrogen, mg/dL | 15.1 (30.0%) | 14.1 (12.1–17.9) |
| Alanine aminotransferase, U/L | 21.8 (85.3%) | 17.0 (10.8–23.3) |
| Aspartate aminotransferase, U/L | 25.0 (38.7%) | 21.0 (19.8–27.5) |
| Gamma-glutamyl transferase, U/L | 27.3 (68.1%) | 17.0 (14.5–38.3) |
| Renal functions | ||
| CLCR, CG (mL/min) a | 105 (21.2%) | 105 (84.3–118) |
| CLCR, normalized CG (mL/min/1.73m2) b | 93.8 (16.4%) | 93.2 (80.5–106) |
| eGFR, MDRD (mL/min/1.73m2) c | 108 (13.9%) | 108 (96.6–116) |
| eGFR, CKD-EPICR (mL/min/1.73m2) d | 111 (15.4%) | 110 (102–120) |
| eGFR, CKD-EPICC (mL/min/1.73m2) e | 112 (14.9%) | 111 (102–122) |
| eGFR, CKD-EPICR-CC (mL/min/1.73m2) f | 93.3 (14.4%) | 93.1 (82.9–98.8) |
| eGFR, adjusted MDRD (mL/min) g | 107 (11.5%) | 111 (98.0–116) |
| eGFR, adjusted CKD-EPICR (mL/min) g | 110 (12.6%) | 116 (102–121) |
| eGFR, adjusted CKD-EPICC (mL/min) g | 112 (12.3%) | 116 (100–120) |
| eGFR, adjusted CKD-EPICR-CC(mL/min/1.73m2) g | 101 (15.8%) | 100 (90.7–112) |
| Parameter | Estimate | RSE (%) [Shrinkage, %] | Bootstrap Median (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structural model | |||
| CL = θ1 × (CR/0.86)θ2 | |||
| θ1 (L/h) | 12.4 | 7.87 | 12.3 (10.8–14.7) |
| θ2 | −0.392 | 19.2 | −0.378 (−0.579–−0.115) |
| V1 (L) | 8.26 | 12.5 | 8.31 (6.56–11.0) |
| Q (L/h) | 5.22 | 16.1 | 5.05 (3.34–7.33) |
| V2 (L) | 4.06 | 11.1 | 4.01 (3.00–5.07) |
| Interindividual variability | |||
| CL (%) | 26.2 | 30.4 [1.82] | 25.4 (7.8–38.3) |
| V1 a | 1.53 | 4.80 | 1.53 (1.07–2.43) |
| Q (%) b | 14.4 | [49.1] | |
| V2 (%) b | 17.9 | [11.2] | |
| Residual variability | |||
| Proportional error (%) | 10.9 | 20.4 | 10.4 (6.50–14.0) |
| Parameters | Unit | Mean (CV%) | Median (IQR) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NCA results | |||
| Cmax | mg/L | 40.2 (30.1%) | 43.3 (34.2–46.3) |
| Clast | h | 0.393 (71.4%) | 0.289 (0.231–0.484) |
| Tlast | mg/L | 5.83 (7.56%) | 6.00 (6.00–6.00) |
| AUClast | mg·h/L | 39.8 (22.7%) | 41.4 (35.9–44.9) |
| AUCinf | mg·h/L | 40.4 (22.8%) | 42.3 (36.2–45.2) |
| AUMClast | mg·h2/L | 49.8 (22.1%) | 51.0 (42.9–54.3) |
| AUMCinf | mg·h2/L | 53.9 (24.1%) | 54.2 (46.2–58.9) |
| MRTinf | h | 1.09 (13.3%) | 1.07 (0.989–1.22) |
| CLNCA | L/h/kg | 0.201 (21.1%) | 0.193 (0.174–0.218) |
| VzZNCA | L/kg | 0.280 (25.7%) | 0.260 (0.236–0.296) |
| VssNCA | L/kg | 0.219 (25.8%) | 0.210 (0.187–0.228) |
| t1/2λz | h | 0.967 (15.3%) | 0.908 (0.870–1.08) |
| Population PK results | |||
| CL | L/h/kg | 0.197 (20.8%) | 0.189 (0.169–0.215) |
| VC | L/kg | 0.134 (37.7%) | 0.118 (0.108–0.137) |
| Vss | L/kg | 0.197 (25.4%) | 0.184 (0.165–0.209) |
| AUC | mg·h/L | 41.3 (21.7%) | 43.5 (37.1–45.2) |
| t1/2α | h | 0.260 (26.9%) | 0.229 (0.214–0.277) |
| t1/2β | h | 0.985 (14.5%) | 0.923 (0.893–1.10) |
| Study | n | Age (Years) | Weight (kg) | Height (cm) | BSA (m2) | CL (L/h) | Vss (L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bax et al. [12] | 12 | 26 (19–45) | 74 (68–87) | 179 (170–184) | 1.92 * | 16.7 (1.2) | 19.1 (1.6) |
| Wise et al. [13] | 6 | 23.6 (23–31) | 69.9 (63–80) | 180 (169–187) | 1.89 * | 15.2 (3.09) | 20.6 (5.90) |
| Burman et al. [14] | 6 | 35 (30–40) | 83 (68–93) | – | – | 16.6 (0.6) | 20.4 (0.7) |
| Nilsson-Ehle et al. [15] | 8 | 33 (22–38) | 74 (66–86) | – | – | 11.3 (1.86) | 12.5 (1.50) |
| Christensson et al. [16] | 6 | 34 (13.4) | 79 (8.4) | – | 1.96 (0.09) | 11.2 (1.68) | 14.7 (0.21) |
| Leroy et al. [17] | 6 | 33.8 (9.0) | 66.9 (12.4) | – | – | 19.7 (5.7) | 27.4 (7.0) |
| Ljunberg et al. [18] | 8 | 28 (5.2) | 69 (7.7) | – | 1.88 (7.3) | 11.7 (1.7) | 11.7 (1.2) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.K.; Kang, G.; Zang, D.Y.; Lee, D.H. Precision Dosing of Meropenem in Adults with Normal Renal Function: Insights from a Population Pharmacokinetic and Monte Carlo Simulation Study. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13090849
Kim YK, Kang G, Zang DY, Lee DH. Precision Dosing of Meropenem in Adults with Normal Renal Function: Insights from a Population Pharmacokinetic and Monte Carlo Simulation Study. Antibiotics. 2024; 13(9):849. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13090849
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Yong Kyun, Gaeun Kang, Dae Young Zang, and Dong Hwan Lee. 2024. "Precision Dosing of Meropenem in Adults with Normal Renal Function: Insights from a Population Pharmacokinetic and Monte Carlo Simulation Study" Antibiotics 13, no. 9: 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13090849
APA StyleKim, Y. K., Kang, G., Zang, D. Y., & Lee, D. H. (2024). Precision Dosing of Meropenem in Adults with Normal Renal Function: Insights from a Population Pharmacokinetic and Monte Carlo Simulation Study. Antibiotics, 13(9), 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13090849






