Abstract
In recent years, the widespread application of antibiotics has raised global concerns, posing a severe threat to ecological health. In this study, the occurrence, source, and ecological risks of 39 antibiotics belonging to 5 classes in mangrove sediments from Lianzhou Bay, China, were assessed. The total concentrations of the antibiotics (∑39 antibiotics) ranged from 65.45 to 202.24 ng/g dry weight (dw), with an average of 142.73 ± 36.76 ng/g dw. The concentrations of these five classes of antibiotics were as follows: Sulfonamides (SAs) > Tetracyclines (TCs) > Fluoroquinolones (QUs) > Penicillin (PCs) > Macrolides (MLs). The spatial distribution of antibiotics varied as high tidal zone > middle tidal zone > low tidal zone. The total organic carbon (TOC), pH, nitrate (NO3−-N), and nitrite (NO2−-N) of the sediment significantly influenced the distribution of antibiotics (p < 0.05). A source analysis identified untreated sewage from aquaculture as the primary source of antibiotics in the local mangrove. A risk assessment revealed that ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin, ofloxacin of QUs, and tetracycline of TCs exhibited medium risks to algae in certain sampling sites, while other antibiotics exhibited low or no risks to all organisms. Nevertheless, the total risk of all the detected antibiotics to algae was medium in 95% of the sites. The overall ecological risk level of antibiotics in the middle tidal zone was slightly lower than in the high tidal zone and the lowest in the low tidal zone. In summary, the experimental results provided insights into the fate and transport behaviors of antibiotics in mangrove sediments from Lianzhou Bay.
1. Introduction
Antibiotics, classified as antibacterial and bactericidal drugs, are commonly used to treat or prevent bacterial infections in humans and animals [1]. Over the years 2000 to 2015, global antibiotic consumption has increased by 65% from 21.1 to 34.8 billion defined daily doses (DDDs) [2]. In 2013, China utilized a total of 36 commonly used antibiotics, accounting for 92,700 tons, with 48% used for human health and the rest for animals [3]. Predictions indicate that the consumption of veterinary antibiotics in China will double by 2030 [2]. Antibiotics have been widely detected in various environments, including sewage treatment plants, aquatic ecosystems, and livestock waste due to their widespread use, incomplete breakdown, and insufficient wastewater treatment [4,5,6]. In coastal areas, antibiotics can have long-term effects on aquatic organisms [1]. The toxic effects of antibiotics on green algae are mainly attributed to the inhibition of chloroplast metabolisms, such as protein synthesis and photosynthesis, which affect cell growth [7]. The effects of antibiotics on ecological functions can lead to changes in nitrogen transformation, methanogenesis, sulfate reduction, nutrient cycling, and organic matter degradation [8]. Moreover, the excessive use of antibiotics can increase the abundance of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) among bacteria, especially harmful pathogens threatening human health [9]. Antibiotics are increasingly recognized as an emerging environmental pollutant [10]. Therefore, understanding the environmental impacts associated with antibiotic use is crucial.
Mangroves, composed of highly coordinated mangrove plants, animals, and microorganisms, are aquatic ecosystems distributed in tropical and subtropical areas [11]. As a type of intertidal zone [12], mangrove wetlands are renowned for their high biological productivity and abundant total organic carbon (TOC) [13], facilitating pollutant decomposition and nutrient cycling by effectively processing and utilizing terrestrial anthropogenic emissions before they reach the ocean [14]. However, mangroves face multiple threats, including sea-level rise [15], deforestation [16], hyper-salination, and contamination by wastewater containing trace metals, various persistent organic pollutants [17], and pharmaceuticals such as antibiotics [18,19,20]. These pollutants significantly impact the microbial diversity of mangroves [21], which play crucial roles in ecosystem productivity [22], nutrient cycling [23], and the synthesis of various metabolites such as antimicrobial compounds [24]. A study by Liu et al. [11] on the coastal mangroves in southern China revealed that the total antibiotic concentrations were higher (>250 ng/g dw) in the mangrove sediment of Fangchenggang (mean, 501 ng/g dw), Hong Kong (mean, 368 ng/g dw), Zhanjiang (mean, 311 ng/g dw), and Shenzhen (mean, 268 ng/g dw). Therefore, mangrove sediments are considered suitable indicators of past human activity in the study area [25]. However, reports on the occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in the mangrove wetlands area are scarce. Furthermore, the source and potential ecological risks posed by these antibiotics to the surrounding ecosystems remain largely unexplored.
With the rapid development of the Beibu Gulf Economic Rim, the increased industrialization and population have significantly impacted the environmental quality of this region [25,26,27]. The advantageous geographical location renders the Beibu Gulf an ideal area for the aquaculture industry. In 2017, the total farmed seafood production in this region was 1.3 million tons [28], inevitably leading to the contamination of antibiotics. Lianzhou Bay is located on the northern margin of Beibu Gulf and is mostly characterized as a faulted estuarine bay, receiving inflow from the Nanliu River, Fengfeng River, Lianzhou River, and Qixing River, collectively forming an estuarine delta [29]. The tide in Lianzhou Bay is moderate, with a flow rate of high tide being lower than that of low tide. Consequently, sediment, debris, and other materials carried by the sea tide and river inflows are deposited on the beach. These soil conditions are conducive to the growth of mangroves, thereby establishing Lianzhou Bay as one of the principal bays for mangrove distribution in Guangxi [30]. Tidal patterns play a vital role in the spatial distribution of antibiotics [31]. Zhang et al. [32] showed that antibiotic concentrations in the East River estuary were influenced by tidal fluctuations. The moderate tidal velocity in Lianzhou Bay may facilitate the deposition of antibiotics in mangrove sediments, posing ecological risks. Therefore, this study has selected mangrove wetlands in Lianzhou Bay as a representative area and 39 commonly used antibotics belonging to 5 different classes. It aims to (1) analyze the occurrence and spatial distribution of antibiotics in mangrove sediments collected from the high, middle, and low tidal zones in Lianzhou Bay, China; (2) determine the main factors influencing the distribution of target antibiotics in the sediments and explore the potential sources, and (3) evaluate the ecologic risks of detected antibiotic residues in mangrove sediments to various organisms.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Occurrence and Distribution of Antibiotics in Mangrove Sediments from Lianzhou Bay
In this study, 28 out of 39 target antibiotics were detected in mangrove sediments. The detection frequencies of Norfloxacin (NOR), Ciprofloxacin (CIP), Enrofloxacin (ERX), Azithromycin (AZM), Roxithromycin (ROX), Ofloxacin (OFX), Erythromycin (ERY), Sulfapyridine (SPD), Sulfadiazine (SA), Sulfamethoxazole (SMX), Sulfamerazine (SMZ), Sulfamethoxine (SMM), Oxytetracycline (OXY), Chlortetracyelin (CTE), Tetracycline (TC), and Doxycycline (DOX) were >90%, revealing the widespread existence of target antibiotics in the mangrove sediments of Lianzhou Bay. The total antibiotic concentrations (∑39 antibiotics) at 21 sites ranged from 65.45 to 202.24 ng/g dry weight (dw), with an average value of 142.73 ± 36.76 ng/g dw (Table S1). The mean antibiotic concentration in this study was lower than that observed in mangrove sediments from Fangcheng Bay (mean, 501 ng/g dw), Hong Kong (mean, 368 ng/g dw), Zhanjiang province (mean, 311 ng/g dw), and Shenzhen (mean, 268 ng/g dw) [11]. On average, the concentration of the SAs (15.25–100.07 ng/g dw), TCs (20.74–65.33 ng/g dw), QUs (18.53–51.10 ng/g dw), PCs (0.00–7.40 ng/g dw), and MLs (0.58–2.89 ng/g dw) accounted for 46%, 27%, 25%, 0.9%, and 0.6% of the total antibiotics, respectively. The SAs, TCs, and QUs were the main detected antibiotics, which was consistent with those reported in the sediments from the Gaoqiao mangroves in Zhanjiang, China [33,34]. SAs are frequently used in human medicine, livestock agriculture, and aquaculture, as well as growth enhancers [35]. Qiu et al. [36] found high concentrations of SAs in the sediments of the Shenzhen River estuary. Zhang et al. [37] observed that high concentrations of SAs could hinder microbial activity, thus retarding the degradation of SAs in sediments. TCs are the second most widely used antibiotics due to their advantages of low cost and broad spectrum and high antimicrobial activity [38]. Currently, TCs have been detected in various water environments and sediments [9,11]. QUs were the third most abundant antibiotics, with mean values of 36.29 ± 9.59 ng/g dw, which was much lower than that in coastal mangrove sediments of Fangchenggang (mean, 227.7 ng/g dw), Zhanjiang (mean, 108.8 ng/g dw), Shenzhen (mean, 119.2 ng/g dw), Hong Kong (mean, 126.6 ng/g dw), and Yunxiao (mean, 93.0 ng/g dw) in China [11]. Studies have indicated that QUs have a high chelating capacity towards cations and can bind with particulate matter, making them easily adsorbed in the sediments [39,40].
The numbers of detected antibiotics in high, middle, and low tidal zones were 25, 25, and 22, respectively (Figure 1A). There was no significant difference between the number of antibiotics among the three tidal zones. The mean antibiotic concentration in the high tidal zone was the highest (157.54 ± 33.84 ng/g dw), followed by that in the middle tidal zone (141.77 ± 35.39 ng/g dw), and the low tidal zone (129.36 ± 40.52 ng/g dw) (Figure 1B). Nevertheless, there were no significant differences between the mean antibiotic concentration among the three tidal zones. The difference in the distribution of antibiotics in the mangroves of Lianzhou Bay may be due to the direct discharge of wastewater from the local aquaculture pond with high antibiotic concentrations into the mangrove environment [11]. Additionally, the mangrove ecosystem has the capacity to accumulate or degrade various pollutants (antibiotics, trace metals, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, etc.) from the land area [19,34]. Therefore, the mangrove ecosystem close to sewage outlets plays a crucial role in degrading significant amounts of antibiotics in sediments.
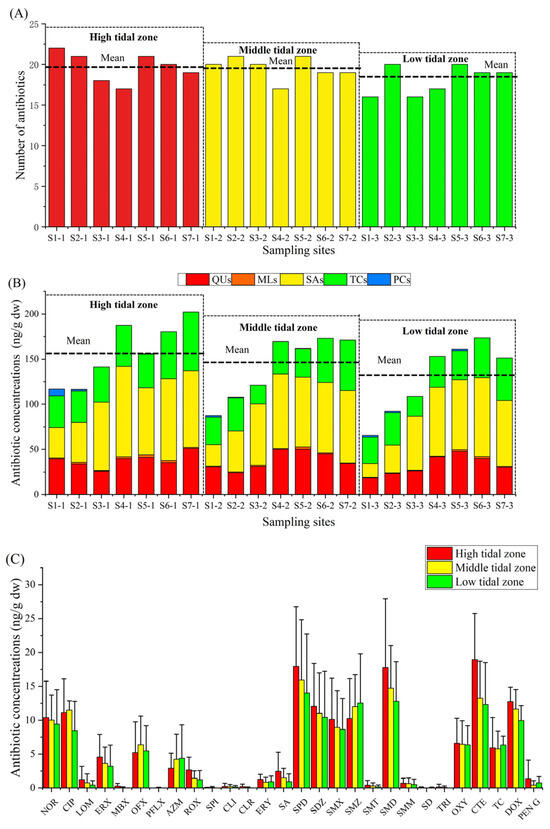
Figure 1.
Presence (A), concentration composition (B), and regional distribution (C) of antibiotics in mangrove sediments.
The mean concentration of each antibiotic distributed in each tidal zone is shown in Figure 1C. Chemicals with a low concentration (>5%) were not included in the following analysis of this paragraph. SMM, SDZ, SMX, SMD, NOR, CTE, and DOX was high tidal zone > middle tidal zone > low tidal zone. These antibiotics are frequently used in human medicine, aquaculture, and animal husbandry [35,41,42], and were preferentially discharged to the high tidal zone through sewage outflows, resulting in this distribution trend. The mean concentration of SMZ and TC in the low tidal zone were the highest among the three tidal zones. Han et al. [43] found that the main source of SMZ in the seawater of Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea, was surrounding marine aquaculture. Another study had shown that SMZ in the seawater of the Beibu Gulf coastal area mainly originates from river discharges from livestock and poultry farming upstream [44]. Thus, tidal action and river inputs may lead to a large accumulation of SMZ carried by seawater and rivers in low-tide sediments. Some researchers have indicated that the TC concentration of the river water in the wet season was higher than that in the dry season [45]. As the survey time of this study was the wet season, the flowing of river water carried with a higher TC content may lead to TC accumulation in sediments of the low tidal zone. Moreover, the mean concentration of CIP and OFX in the middle tidal zone were the highest among the three tidal zones. Furthermore, the TOC and sediment particle size in the middle tidal zone were also the highest. Some studies have proved that a higher TOC and larger sediment particle size contribute to the significant accumulation of antibiotics [33,34,39,46], which may lead to a higher content of CIP and OFX in the middle tidal zone. In addition, it has been reported that antibiotics with logKow of less than 1 cannot be easily adsorbed by the root epidermis or actively pass through the plant cell membrane due to their strong hydrophilic effects [47,48,49]. Herein, the logKow values of the CIP and OFX were both less than 1, indicating that they were not easily absorbed and cleansed by the mangrove plants and were stored in the sediments.
2.2. Correlation between Environmental Factors and Antibiotic Concentrations
Several environmental factors, such as TOC, particle size, pH, and nutrient composition, have been identified as influential factors affecting the distribution and persistence of antibiotics [46,50,51]. In this study, the physicochemical properties of mangrove sediments were analyzed and are shown in Table 1. The pH of the high tidal zone was significantly lower than that of the middle and low tidal zones (p < 0.05), while the pH of the low tidal zone was the highest. The order of NO3−-N concentration was as follows: high tidal zone > middle tidal zone > low tidal zone, and there were significant differences between every two tidal zones (p < 0.05). The TOC concentration was the highest in the high tidal zone, followed by the middle and low tidal zones. Additionally, the NO2−-N, NH4+-N, and sediment particle size were the highest in the middle tidal zone, followed by the low and high tidal zones.

Table 1.
Physicochemical properties of mangrove sediments in Lianzhou Bay.
To explore the correlation between the antibiotic concentrations and environmental factors of mangrove sediments, a Pearson analysis was conducted and the results are shown in Figure 2. The TOC, NO3−-N, NO2−-N, and pH accounted for 39% (p = 0.01), 32% (p = 0.03), 35% (p = 0.01), and 30% (p = 0.04) of the factors, revealing that the concentration distribution of antibiotics was strongly affected by these four environmental factors. TOC is a key environmental factor affecting antibiotic concentrations in sediments, and a higher TOC content can facilitate antibiotic absorption, leading to increased accumulation of antibiotics [34,39]. Previous studies have indicated that some antibiotics (SMX, TC, NOR, and CIP) can reduce the denitrification and anammox reactions by eliminating the denitrifying bacteria and decreasing their abundance, resulting in an increase in NO3−-N and NO2−-N levels [52,53,54]. Therefore, higher concentrations of NO3−-N and NO2−-N are associated with higher antibiotic concentrations in the antibiotic polluted areas [50]. Similarly, pH can affect the adsorption and biodegradability of antibiotics in sediments [55,56,57,58]. Herein, the antibiotic concentrations were significantly positively correlated (p < 0.01) with the TOC, NO3−-N, and NO2−-N in the high and middle tidal zones. Additionally, pH was significantly correlated with the antibiotic concentrations in the middle tidal zone (p < 0.05). Li et al. [59] also found a significant positive correlation (p < 0.05) between TOC and antibiotic concentrations in the sediments of the Pearl River estuary, China. Similarly, Chen et al. [60] found a significant positive correlation (p < 0.05) between NO3−-N and antibiotic concentrations in the sediments of Hailing Bay, China. The antibiotic concentrations in the low-tide zone were significantly positively correlated with the pH (p < 0.01). A previous study has reported a significant positive correlation between the pH and antibiotic concentrations (p < 0.05) in the sediments of typical bays of the East China Sea [51].
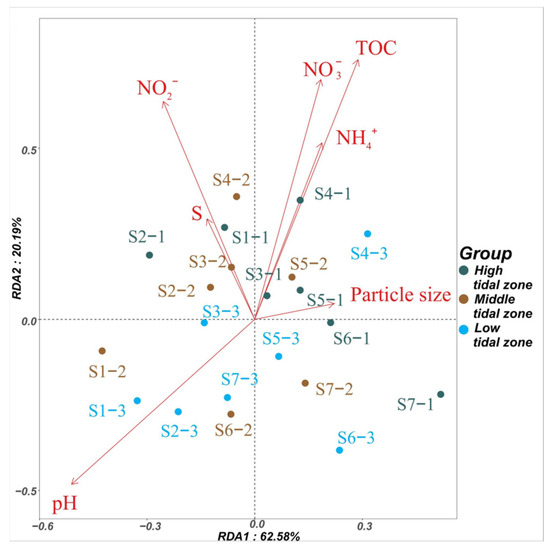
Figure 2.
Redundancy analysis of the antibiotic concentrations and environmental factors in the sediment samples. The RDA1 and RDA2 explained 63% and 20% of the total variance, respectively.
2.3. Potential Sources of Antibiotics in the Sediment of Lianzhou Bay
The sources of antibiotics in the sediment samples were identified using the varimax-rotated component matrix following PCA (Table 2). Chemicals with a low detection frequency (<10%) were not included in this study. Five principal components (PC1, PC2, PC3, PC4, and PC5), accounting for 25%, 17%, 17%, 15%, and 9% of the total variance, respectively, were identified. PC1 was highly associated with CIP, LOM, OFX, ROX, SPD, SMX, OXY, CTE, and TC. Studies have found that TCs, QUs, and SAs are the most frequently utilized antibiotics in aquaculture, with QUs displaying a significant and positive correlation with factors related to human healthcare (p < 0.05) [61]. CIP is also a commonly used antibiotic in aquaculture and has been detected in rivers in Italy and in major rivers in China [6,11,62]. TC is a commonly used antibiotic as a growth promoter in aquaculture to improve nutrient absorption capacity and enhance the body weight of aquatic organisms [63]. The presence of SMX and TC in mangrove sediments is probably due to the difficulty of their removal by conventional wastewater treatment plants [64,65]. Meanwhile, most of these antibiotic concentrations were significantly correlated with each other at the 0.01 level (Table S2), indicating that they may come from the same source or have the same environmental behaviors [66,67]. Thus, PC1 suggested that the source of antibiotics in the study area was the combined discharge of aquaculture and hospital wastewater. PC2 was highly associated with AZM, ERY, SA, SMZ, and SMM. Studies have reported that ERY is difficult to remove through conventional sewage treatment, with a removal rate below 20% [68,69]. Additionally, SMM is significantly positively correlated with the aquaculture (p < 0.05) [61]. Thus, PC2 suggested that the source of antibiotics in the study area was probably the combined sewage of human domestic and aquaculture. PC3 was highly associated with SDZ, SMZ, and SPD. PC3 suggested that the source of the SAs was aquaculture industry emissions [66]. PC4 was highly associated with ERX, AZM, SDZ, and SMD, and PC5 was highly associated with CTE and DOX. The detected antibiotics are commonly used in aquaculture, indicating that aquaculture activities are the main sources of the studied antibiotics in the mangrove sediments of Lianzhou Bay.

Table 2.
Varimax-rotated component matrix following PCA of all sediment samples.
2.4. Risk Assessment
With the widespread use of antibiotics, risk assessments of antibiotics in the environment have attracted considerable attention [4,70,71]. In this study, the ecological risks of the detected antibiotics to aquatic organisms at three trophic levels (including algae, fish, and invertebrates) were evaluated (Table S3). Without considering the combined toxicological contamination of each antibiotic, the RQ values of the antibiotics against the three categories of aquatic organisms (algae, fish, and invertebrate) were separately summed to obtain the RQsum-algae, RQsum-invertebrates, and RQsum-fish. The RQsum-algae was significantly higher than the RQsum-invertebrate (p < 0.01) and RQsum-fish (p < 0.01). This result implied that the algae was the most sensitive species to the detected antibiotics, and these antibiotics were not likely to pose risks to invertebrates and fish due to their low RQsum values. Similar results were observed in the sediments of the Beibu Gulf of China [1], Baiyangdian Lake of China [72], and the Hong Kong River of China [73]. Algae are important flora in mangrove ecosystems. As the high plant productivity in mangroves is only possible due to interactions with microorganisms, for example, cyanobacteria may contribute to these ecosystems by providing fixed nitrogen, carbon, and plant defense molecules, biosorption and bioremediation of xenobiotics, and secretion of substances that promote plant growth [74]. Thus, the high ecological risk of antibiotics to algae affects the ecological stability of mangroves.
The QUs and TCs showed the highest ecological risk, followed by SAs, while PCs and MLs showed the lowest ecological risk (Figure 3). Some studies have found that QUs and TCs in the sediments of Wangyang River [75], Laizhou Bay [76], and Beibu Gulf [77] have high ecological risks to algae. Furthermore, the QUs and TCs are easily accumulated by mangrove sediments due to their low solubility, bioavailability, and biodegradability [78,79]. In the study area, 11 kinds of antibiotics (NOR, OFX, SDZ, SMZ, CIP, ERX, SA, LOM, SMD, SMX, AZM, OXY, TC, and PEN G) with potential ecological risks to current algae were identified. The proportion of risk sites for CIP, TC, NOR, and OFX was 100%, 95%, 95%, and 81%, respectively, while the proportions of risk sites for other antibiotics were all less than 40% (Figure 3). This implied that CIP, TC, NOR, and OFX exhibited a higher risk to algae than the other kinds of antibiotics. The mangrove sediments could absorb large amounts of antibiotics due to their high organic carbon properties [13,80]. This result implied that the mangrove sediments with a high TOC concentration are more likely to accumulate antibiotics. CLI, ERY, SMM, and TRI had the lowest ecological risk among the 25 detected antibiotics. Although these antibiotics did not show high ecological risks, the degradation rates of these antibiotics were relatively low [81,82,83], resulting in their long-term existence in the mangrove environment.
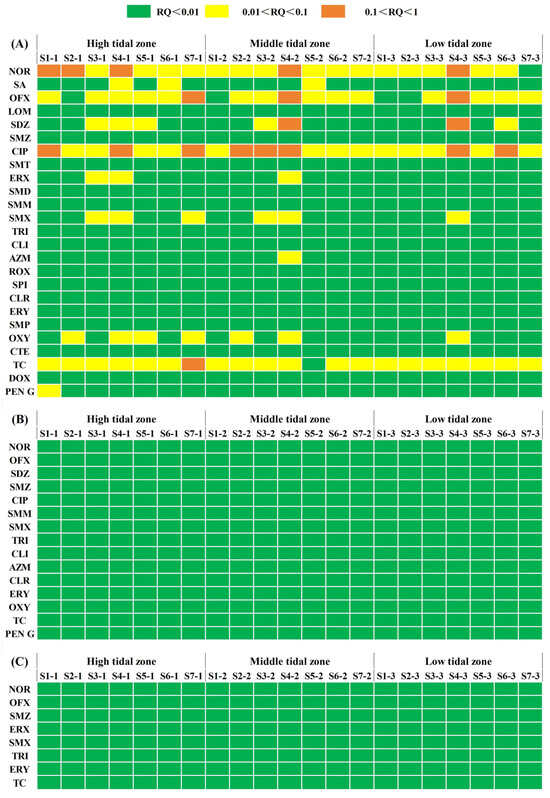
Figure 3.
Risk quotients (RQs) of antibiotics in the sediment of Lianzhou Bay to algae (A), invertebrates (B), and fish (C).
Additionally, the combined risk of multiple antibiotics can increase via synergistic effects, which need more attention [84]. The RQsum-algae values were selected as the indicator of ecological risk in this study due to its greater sensitivity to antibiotics than fish and invertebrates. The RQsum-algae varied from 0.09 to 0.98 (Figure S1), indicating that 95% of the sites were categorized as intermediate risk, with only site S5-2 being classified as low risk. These results imply that the ecological risk posed by antibiotics to the mangrove area is generally at a medium risk level. The mean value of RQsum-algae in the high tidal zone was slightly higher than that in the middle tidal zone, and the mean value of RQsum-algae in the low tidal zone was the lowest. The Spearman correlation analysis between logarithmic transformed RQsum-algae and environmental factors showed that only pH was significantly negatively correlated with RQsum-algae (p < 0.01), while the TOC, NO3−-N, NO2−-N, NH4+-N, and particle size were significantly positively correlated with RQsum-algae (p < 0.01) (Table S4). The RQsum-algae in the high tidal zone was slightly higher than that in the middle tidal zone, and the lowest in the low tidal zone. The high tidal zone impacted by land-based pollution exhibited the highest ecological risk, primarily due to significant antibiotic settlement. Previous studies have suggested that higher TOC and larger sediment particle size might contribute to the significant accumulation of antibiotics [33,34,39,46]. Therefore, the middle tidal zone characterized by higher levels of TOC and larger particle sizes showed ecological risk levels comparable to those in the high tidal zone. It is reported that the frequent tidal inundation in the low tidal zone could lead to a certain dilution effect on the concentration of some antibiotics in mangrove sediments [31], resulting in a low ecological risk of antibiotics in this zone. Notably, the higher the antibiotic risk level, the greater the probability of the generation and spread of drug-resistant bacteria and drug-resistant genetic elements, eventually leading to ARG pollution. However, the relatively stable ARGs could rapidly migrate and spread in the marine environment, posing a great potential threat to marine ecology and human health [9].
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sampling Sites and Sample Collection
The sediment samples were collected from 21 sites (3 parallel samples were collected from each site) in the high tidal zone, middle tidal zone, and low tidal zone in the mangrove area of Lianzhou Bay (108°58′00″–109°02′35″ E, 21°26′20″–21°37′00″ N), China, in April 2023 (Figure 4). The sites in the high tidal zone were all located near the effluent outlet of the aquaculture area (Figure S2). The surface sediment samples (depth < 5 cm) were obtained using a stainless-steel grab and stored in sterile polyethylene (PE) bags. These samples were immediately transported on ice via a portable refrigerator to the laboratory. Once back in the laboratory, the sediments were immediately freeze-dried by CHRIST Alpha 1-4 LSCbasic (Osterode, Germany), and then grounded and homogenized. Finally, the homogenized sediments were stored at −20 °C until analysis.
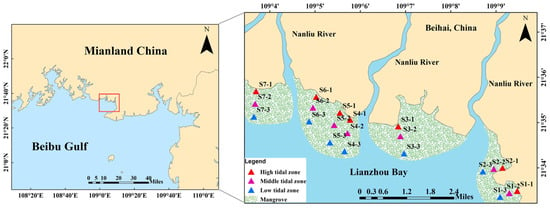
Figure 4.
Location of sampling sites in the mangrove sediments of Lianzhou Bay, China.
3.2. Materials and Solvents
A total of 39 antibiotics belonging to 5 classes, including 16 Sulfonamides (SAs), 11 Fluoroquinolones (QUs), 5 Tetracyclines (TCs), 6 Macrolides (MLs), and 1 Penicillin (PCs) were analyzed in this study. Trimethyl-13C3 caffeine was used as a surrogate standard to evaluate the antibiotic recoveries in sediments and simetone was used as an internal standard to calculate the possible interference of sediment matrix and instrumental analysis. All the antibiotic standards, Citrate buffer (pH 5), and EDTA buffer were purchased from Aladdin (Shanghai, China), and the trimethyl-13C3 caffeine and simetone standards were purchased from Dr. Ehrenstorfer GmbH (Oakville, ON, Canada) and Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA), respectively. HPLC grade methanol and acetonitrile were obtained from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany). Formic acid was supplied by CNW (Dusseldorf, Germany). Disodium edetate dihydrate (Na2EDTA) was acquired from J&K® (Beijing, China). Detailed information about the antibiotics, reagents, and solvents is provided in Text S1 and Table S5.
3.3. Analysis of the Physicochemical Parameters of the Sediments
The sediment was mixed with CO2-free deionized water at a volume ratio of 1:2.5, and the pH of the sediment was measured using a pH meter (Mettler-Toledo, Greifensee, Switzerland) [85]. The TOC in the freeze-dried sediment was analyzed using a TOC analyzer (Vario TOC, Elementar, Langenselbold, Germany) [86]. The particle size of the sediment was measured using a Horiba LA-300 particle sizer (Horiba Group, Edison, NJ, USA). Exchangeable ammonium (NH4+-N), nitrate (NO3−-N) and nitrite (NO2−-N) were extracted from the fresh sediments using 2 M of KCl and quantified spectrophotometrically on a continuous flow analyzer (SAN Plus, Skalar Analytical B.V., Breda, The Netherlands) with detection limits of 0.5 M for NH4+-N and 0.1 M for NO3−-N and NO2−-N [87]. Detailed data about the physicochemical properties of mangrove sediments are shown in Table S6.
3.4. Quantitative Analysis of Antibiotics in Sediments
Various physicochemical properties of the wide family of antibiotics, together with matrix interference, make their reliable analysis in complex environmental samples (e.g., sediment and water) very challenging [88,89]. The preparation of sediment samples was conducted as per the methodology outlined in a previous study. Briefly, 2 g of freeze-dried and homogenized sediment samples was weighted into a PTEE tube (50 mL), and 50 ng of 13C3-caffeine and 0.3 g NaF were spiked as a surrogate and ion exchanger, respectively. Ultrasound-assisted extraction using 30 mL extraction solution, including 15 mL of methanol, 10 mL of citrate buffer (pH 5), and 5 mL of 0.1 M EDTA buffer, was then conducted for 20 min, after which the extract was centrifuged for 10 min at 5000 rpm and the upper supernant was transferred into a clean glass jar. The same extraction process was repeated twice, and all the obtained supernants were combined and diluted to 500 mL with ultrapure water. The diluted extract was acidified to pH 5.0 by adding drops of 6 mol/L HCl, and then 0.8 g of Na2EDTA was added as the chelating agent, after which the adjusted extract was loaded onto pre-conditioned (5 mL methanol) and pre-equilibrated (5 mL ultrapure water) Oasis HLB cartridges (6 mL, 500 mg; Waters), with a flow rate of 5–10 mL/min. Following that, 5 mL methanol and 5 mL dichloromethane were used to elute the antibiotics in the cartridge, and then the eluent was condensed to near dryness under a gentle nitrogen flow at room temperature. Finally, the concentrated eluate was diluted to an equal volume of 1.0 mL with methanol and 20 μL of a simetone (100 μg/L) was added as internal standard.
The target antibiotics were analyzed by the Dionex series high-performance liquid chromatograph system coupled to an AB Science triple quadrupole mass spectrometer (Palo Alto, CA, USA), equipped with an electrospray ionization (ESI) source in a multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode. The selected antibiotics were separated using an Agilent (Santa Clara, CA, USA) ZORBAX Eclipse Plus C18 (150 mm × 2.1 mm, 3.5 μm) column, and the column temperature was at 40 °C. The 0.2% formic acid in ultrapure water (eluent A) and acetonitrile (eluent B) were used as the mobile phase. The elution program was as follows: 1% B (0–5 min), 10% B (5–25 min), 50% B (25–26 min), and 1% B (26–30 min), and the flow rate was at 0.3 mL/min. All the targets were analyzed in the ESI+ mode, the ion source temperature was 550 °C, the ion spray voltage was 500 V, the curtain gas was 35 kPa, and the ion source gas was 60 kPa.
3.5. Quality Assurance and Quality Control (QA/QC)
The experimental procedures were subjected to strict QA/QC procedures. All the glass containers were rinsed three times with ultrapure water and methanol, respectively, and then baked at 450 °C for 4 h in a muffle furnace. The concentrations of the antibiotic were quantified using the internal standard method. Linearity was evaluated using an 8-point calibration curve (1 ppb, 2 ppb, 5 ppb, 10 ppb, 20 ppb, 50 ppb, 100 ppb, and 200 ppb) for each compound (R2 > 0.99). The limit of detection (LOD) (0.02–1.09 ng/g for sediment samples) and limit of quantitation (LOQ) (0.04–1.75 ng/g for sediment samples) were determined as the minimum detectable amount of an analyte with signal-to-noise (S/N) ratios of 3 and 10, respectively. Procedural blanks and standard solutions were included in each batch of 5 samples to evaluate the possible interference or background contamination. The concentrations of all compounds in the procedural blank were below the detection limit. The spiked recoveries of the target antibiotics in sediments ranged from 55 to 94% with relative standard deviations (RSD) lower than 20%. The recovery of 13C3-caffeine surrogate in sediment samples was 74–93%.
3.6. Ecological Risk Assessment
The potential ecological risks associated with target antibiotics were evaluated by risk quotients (RQs), using Equations (1)–(6) [1,90,91,92,93]. The risk levels were divided into four categories, i.e., insignificant risk (RQ < 0.01), low risk (0.01 ≤ RQ < 0.1), medium risk (0.1 ≤ RQ < 1), and high risk (RQ > 1) [94].
where PNECwater denotes the predicted no-effect concentration (PNEC means a concentration that does not normally produce adverse effects) of antibiotics in water, μg/L, EC50 denotes the half-maximal effective mass concentration, and LC50 denotes the half-lethal mass concentration, mg/L. Episodes of toxicity within one day were considered acute and those greater than one day were considered chronic. AF denotes the assessment factor and takes a value of 1000 when using acute toxicity data and 100 when using chronic toxicity data [95]. PNECSediment denotes the predicted non-effect content of antibiotics in soil, mg/kg. Koc means the organic carbon partition coefficient of the antibiotic, and Kd is their sediment-water distribution coefficients. The foc (%) is the TOC concentration in the sediment; Koc can be calculated using an octanol-water partition coefficient (logKow). MECsediment means the measured antibiotic concentrations in sediment, μg/g. The total RQsum in a sediment sample was caculated by summing the RQ of each individual antibiotic together. EC50 or LC50 were obtained from previous literature or the ECOTOX Drugbank Database (https://go.drugbank.com/, accessed on 1 December 2023) (Table S7). SD, MBX, and PFLX were not found EC50 or LC50 data.
PNECwater = EC50(LC50)/AF
PNECSediment = PNECwater × Kd
Koc = Kd × 100/foc
logKoc = 0.529logKow + 1.082
RQi = MECsediment/PNECSediment
RQsum = ƩRQi
3.7. Statistical Analysis
The averages and standard deviations were computed using Excel 2016 (Microsoft, Redmond, WA, USA), and the data were visualized using Origin 2018 (OriginLab, Northampton, MA, USA). The relationship between the spatial distribution of antibiotics and various environmental factors was assessed through a multivariate analysis, including a detrended correspondence analysis (DCA) and a redundancy analysis (RDA), using R 4.2.2 (R Development Core Team, Vienna, Austria) [96]. The length of the first ordination gradient was determined using DCA, and if the calculated value was less than 3, RDA was selected for further analysis of the dataset. Additionally, the sources of the antibiotics in the sediment samples were identified through a varimax-rotated component matrix analysis using SPSS 26 (IBM Analytics, Armonk, NY, USA) [97].
4. Conclusions
In this study, the occurrence, distribution, potential source, and risk assessment of 39 antibiotics in mangrove sediments from Lianzhou Bay, China, were investigated. The concentrations of these five classes of antibiotics were as follows: SAs > TCs > QUs > PCs > MLs. The spatial distribution of the antibiotic concentrations varied as high tidal zone > middle tidal zone > low tidal zone. Additionally, the spatial distribution of antibiotics in mangrove sediments was significantly correlated (p < 0.05) with TOC, pH, NO3−-N, and NO2−-N. The source analysis indicated that untreated sewage from aquaculture activities constituted the primary source of antibiotics in the local mangrove environment. The risk assessment indicated that low to medium risks posed by an individual antibiotic were only found for algae, among which CIP, TC, NOR, and OFX could pose relatively higher risks to algae. Based on the RQsum-algae results, 95% of the sites were classified as at the intermediate risk level. The overall ecological risk level of antibiotics in the middle tidal zone was slightly lower than that in the high tidal zone, and the lowest in the low tidal zone. Effective regulation of discharges, particularly from aquaculture, is pivotal for managing antibiotic risks in Lianzhou Bay.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/antibiotics13090820/s1. Refs. [98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124] are cited in Supplementary Materials. Text S1: Materials and solvents; Table S1: The antibiotic concentrations and detection frequencies in sediments (ng/g dw); Table S2: Pearson analysis of antibiotics (Detection frequency >10 %); Table S3: Estimated RQsum values of algae, invertebrate, and fish in mangrove sediments of Lianzhou Bay; Table S4: The correlation between antibiotics, RQsum, and environmental factors in mangrove sediments; Table S5: Basic information on tested antibiotics; Table S6: Physicochemical properties of mangrove sediments in Lianzhou Bay; Table S7: The parameters of detected antibiotics for ecological risk assessment; Figure S1: Estimated RQsum-algae values of target antibiotics in mangrove sediments of Lianzhou Bay; Figure S2: Location of sampling sites and the aquaculture area in the mangrove sediments of Lianzhou Bay, China.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.S.; methodology, P.S. and L.Z., investigation, P.S. and Y.T.; software, P.S. and Y.T.; original draft preparation, P.S.; data curation and editing, L.Z., Y.T. and P.S.; supervision, P.S., T.Y., Z.Z. and S.T.; project administration, P.S. and S.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the Special Project of the China-APEC Cooperation Fund Project (OFWG 03 2021S), the Key R&D Program of Guangxi (Nos. Guike AB22080099), the Guangxi Science and Technology Base and Talent (No. GUIKE AD20297065), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. U20A20103), and the Scientific Research Fund of the Fourth Institute of Oceanography (No. 202003).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wu, Q.; Xiao, S.; Pan, C.; Yin, C.; Wang, Y.; Yu, K.F. Occurrence, source apportionment and risk assessment of antibiotics in water and sediment from the subtropical Beibu Gulf, South China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, E.Y.; Van Boeckel, T.P.; Martinez, E.M.; Pant, S.; Gandra, S.; Levin, S.A.; Goossens, H.; Laxminarayan, R. Global increase and geographic convergence in antibiotic consumption between 2000 and 2015. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E3463–E3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.Q.; Ying, G.G.; Pan, C.G.; Liu, Y.S.; Zhao, J.L. Comprehensive evaluation of antibiotics emission and fate in the river basins of China: Source analysis, multimedia modeling, and linkage to bacterial resistance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 6772–6782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, I.T.; Santos, L. Antibiotics in the aquatic environments: A review of the European scenario. Environ. Int. 2016, 94, 736–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, M.; Ying, G.G.; Singer, A.C.; Zhu, Y.G. Review of antibiotic resistance in China and its environment. Environ. Int. 2017, 110, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colzani, L.; Forni, C.; Clerici, L.; Barreca, S.; Dellavedova, P. Determination of pollutants, antibiotics, and drugs in surface water in Italy as required by the third EU Water Framework Directive Watch List: Method development, validation, and assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 14791–14803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalakova, P.; Cizmas, L.; McDonald, T.J.; Marsalek, B.; Feng, M.; Sharma, V.K. Occurrence and toxicity of antibiotics in the aquatic environment: A review. Chemosphere 2020, 251, 126351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grenni, P.; Ancona, V.; Caracciolo, A.B. Ecological effects of antibiotics on natural ecosystems: A review. Microchem. J. 2018, 136, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Y.; Xiao, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, J. Tetracyclines, sulfonamides and quinolones and their corresponding resistance genes in coastal areas of Beibu Gulf, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, N.; Madhavan, J.; Selvi, A.; Das, D. An overview of cephalosporin antibiotics as emerging contaminants: A serious environmental concern. 3 Biotech 2019, 9, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Lun, J.; Zheng, P.; Feng, J.; Meng, S.; Peng, T.; Hu, Z. Diversity and distribution of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in seven national mangrove nature reserves, South China. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 2020, 153, 105000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Zhang, H.; Singh, N.; Tang, Y.; Cai, Z. Intertidal zone effects on occurrence, fate and potential risks of microplastics with perspectives under COVID-19 pandemic. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hu, Y.; Sun, Y.; De Silva, A.O.; Muir, D.C.; Wang, W.; Mai, B. Bioaccumulation and translocation of tetrabromobisphenol A and hexabromocyclododecanes in mangrove plants from a national nature reserve of Shenzhen City, South China. Environ. Int. 2019, 129, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Heo, Y.M.; Kwon, S.L.; Yoo, Y.; Kim, D.; Lee, J.; Kwon, B.O.; Khim, J.S.; Kim, J.J. Environmental drivers affecting the bacterial community of intertidal sediments in the Yellow Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saintilan, N.; Khan, N.S.; Ashe, E.; Kelleway, J.J.; Rogers, K.; Woodroffe, C.D.; Horton, B.P. Thresholds of mangrove survival under rapid sea level rise. Science 2020, 368, 1118–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, N.C.; Meynecke, J.O.; Dittmann, S.; Ellison, A.M.; Anger, K.; Berger, U.; Cannicci, S.; Diele, K.; Ewel, K.C.; Field, C.D.; et al. A world without mangroves? Science 2007, 317, 41–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayen, S. Occurrence, bioavailability and toxic effects of trace metals and organic contaminants in mangrove ecosystems: A review. Environ. Int. 2012, 1, 84–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, X.; Guo, F. Paradigms of mangroves in treatment of anthropogenic wastewater pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 544, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, L.; Lagomasino, D.; Thomas, N.; Fatoyinbo, T. Global decline in human-driven mangrove loss. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 5844–5855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigonato, J.; Kent, A.D.; Gumiere, T.; Branco, L.H.Z.; Andreote, F.D.; Fiore, M.F. Temporal assessment of microbial communities in soils of two contrasting mangroves. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2018, 49, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palit, K.; Rath, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Das, S. Microbial diversity and ecological interactions of microorganisms in the mangrove ecosystem: Threats, vulnerability, and adaptations. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 32467–32512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Flandes, S.; Gonz´alez, B.; Ulloa, O. Redox traits characterize the organization of global microbial communities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 3630–3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passari, A.K.; Leo, V.V.; Chandra, P.; Kumar, B.; Nayak, C.; Hashem, A.; Singh, B.P. Bioprospection of actinobacteria derived from freshwater sediments for their potential to produce antimicrobial compounds. Microb. Cell Factories 2018, 17, 68. [Google Scholar]
- Costa-Böddeker, S.; Hoelzmann, P.; de Stigter, H.C.; van Gaever, P.; Huy, H.Đ.; Smol, J.P.; Schwalb, A. Heavy metal pollution in a reforested mangrove ecosystem (Can Gio Biosphere Reserve, Southern Vietnam): Effects of natural and anthropogenic stressors over a thirty-year history. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 137035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Wang, Y.; Pan, C.; Li, R.; Xue, R.; Guo, J.; Zhang, R. Spatiotemporal distributions, source apportionment and potential risks of 15 pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in Qinzhou Bay, South China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 141, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, C.G.; Xiao, S.K.; Yu, K.F.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Y.H. Legacy and alternative per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in a subtropical marine food web from the Beibu Gulf, South China: Fate, trophic transfer and health risk assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 403, 123618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.K.; Wu, Q.; Pan, C.G.; Yin, C.; Wang, Y.H.; Yu, K.F. Distribution, partitioning behavior and potential source of legacy and alternative per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in water and sediments from a subtropical Gulf, South China Sea. Environ. Res. 2021, 201, 111485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.M.; Zhang, L.L.; Li, R.L.; Wang, Y.H.; Guo, J.; Yu, K.F.; Wang, S.P. Underestimated microplastic pollution derived from fishery activities and “hidden” in deep sediment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 2210–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Lai, T.; Wang, X.; Pan, L.; Cao, Q. Secondary productivity of benthic macrofaunal community in intertidal zone of Lianzhou Bay, China. Chin. J. Ecol. 2013, 32, 2104–2112. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Liang, Y.; Wei, J.; Zhang, C.; Wei, C. Reshaping of coastal zone terrain deformation monitoring discussion: Taking the Lianzhou Bay of Beihai east coast remediation rehabilitation as an example. Geomat. Spat. Infor. Technol. 2017, 40, 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Cui, M.; Zhang, H. Spatial and temporal variations of antibiotics in a tidal river. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, R.; Li, J.; Cheng, Z.; Luo, C.; Wang, Y.; Yu, K.; Zhang, G. Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in multiple environmental media of the East River (Dongjiang) catchment, South China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 9690–9701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhou, K.; Sun, X.L.; Zhao, L.R.; Zhang, Y.B. Occurrence and distribution of the environmental pollutant antibiotics in Gaoqiao mangrove area, China. Chemosphere 2016, 147, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Xu, J.R.; Ren, K.J.; Meng, X.Z. Tracking aquaculture-derived fluoroquinolones in a mangrove wetland, South China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurwadkar, S.T.; Adams, C.D.; Meyer, M.T.; Kolpin, D.W. Effects of sorbate speciation on sorption of selected sulfonamides in three loamy soils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 1370–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, W.; Sun, J.; Fang, M.; Luo, S.; Tian, Y.; Dong, P.; Xu, B.; Zheng, C. Occurrence of antibiotics in the main rivers of Shenzhen, China: Association with antibiotic resistance genes and microbial community. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhong, Z.; Guo, C.; Li, L.; He, Y.; Fan, W.; Chen, Y. Degradation of sulfonamides antibiotics in lake water and sediment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 2372–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamad, T.; Naushad, M.; Al-Shahrani, T.; Al-Hokbany, N.; Alshehri, S.M. Preparation ochitosan based magnetic nanocomposite for tetracycline adsorption: Kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 147, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Chen, B.; Nie, X.; Shi, Z.; Huang, X.; Li, X. The distribution and partitioning of common antibiotics in water and sediment of the Pearl River Estuary, South China. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 1410–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhou, J.L. Occurrence and behavior of antibiotics in water and sediments from the Huangpu River, Shanghai, China. Chemosphere 2014, 95, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, A.D.; Todd, D.; Hershey, A.E. The seasonal distribution and concentration of antibiotics in rural streams and drinking wells in the piedmont of North Carolina. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Cui, Y.; Wang, H.; Ye, Q.; Duo, X.; Lu, Y.; Cui, X.; Dong, W. Ofloxacin and norfloxacin simultaneous detection by ERGO/GCE and its application in medicine and aquaculture wastewater. Res. Chem. Intermediat. 2023, 49, 741–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.F.; Zhang, X.R.; Xu, X.Y.; Wang, X.L.; Yuan, X.Z.; Ding, Z.J.; Zhao, S.; Wang, S.G. Antibiotics in marine aquaculture farms surrounding Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea: Distribution characteristics considering various culture modes and organism species. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 760, 143863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Z.E.; Wang, J.; Yu, K. Spatiotemporal distribution and potential risks of antibiotics in coastal water of Beibu Gulf, South China Sea: Livestock and poultry emissions play essential effect. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 466, 133550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Cai, J.; Yan, H.; Chen, C. Effects of rainfall events on behavior of tetracycline antibiotics in a receiving river: Seasonal differences in dominant processes and mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 692, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, B.V.; Ren, Y.L. Biodegradation of three tetracyclines in river sediment. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 75, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dettenmaier, E.M.; Doucette, W.J.; Bugbee, B. Chemical hydrophobicity and uptake by plant roots. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonsaner, M.; Hawker, D.W. Accumulation of oxytetracycline and norfloxacin from saline soil by soybeans. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 408, 1731–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herklotz, P.A.; Gurung, P.; Heuvel, B.V.; Kinney, C.A. Uptake of human pharmaceuticals by plants grown under hydroponic conditions. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 1416–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.L.; Cheng, R.; Chen, F.; Lin, X.Q.; Yao, X.J.; Liang, B.; Huang, C.; Sun, K.; Wang, A.J. Selective stress of antibiotics on microbial denitrification: Inhibitory effects, dynamics of microbial community structure and function. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 405, 124366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wen, D.; Bao, Y.; Huang, B.; Mu, Q.; Chen, L. Insights into the distribution, partitioning and influencing factors of antibiotics concentration and ecological risk in typical bays of the East China Sea. Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, K.; Wang, D.; Li, X.; Chen, H.; Sun, J.; An, H.; Wang, L.; Deng, Y.; Liu, J.; Zeng, G. Effect of ciprofloxacin on biological nitrogen and phosphorus removal from wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 605, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, T.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, S.; Chen, Z.; Ma, Y. Performance of the nitrogen removal, bioactivity and microbial community responded to elevated norfloxacin antibiotic in an Anammox biofilm system. Chemosphere 2018, 210, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, N.S.; Bai, Y.H.; Chen, Q.Q.; Shen, Y.Y.; Huang, B.C.; Jin, R.C. Deciphering the toxic effects of antibiotics on denitrification: Process performance, microbial community and antibiotic resistance genes. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 262, 110375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.R.; Li, X.Y. Sorption and desorption of antibiotic tetracycline on marine sediments. Chemosphere 2009, 78, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, X.; Sun, K.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, C. Sorption of tetracycline to sediments and soils: Assessing the roles of pH, the presence of cadmium and properties of sediments and soils. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2010, 4, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Huwe, B. Effect of pH and soil structure on transport of sulfonamide antibiotics in agricultural soils. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 213, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, D.; Yang, D.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; He, Y.; Luo, L.; Zhou, Y. Current progress in the adsorption, transport and biodegradation of antibiotics in soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 251, 109598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Shi, W.; Li, H.; Xu, N.; Zhang, R.; Chen, X.; Sun, W.; Wen, D.; He, S.; Pan, J.; et al. Antibiotics in water and sediments of rivers and coastal area of Zhuhai City, Pearl River estuary, south China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 1009–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, S.; Xu, X.R.; Zhou, G.J.; Liu, S.S.; Yue, W.Z.; Sun, K.F.; Ying, G.G. Antibiotics in the coastal environment of the Hailing Bay region, South China Sea: Spatial distribution, source analysis and ecological risks. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 95, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, J.; Yang, L.; Zhang, L.; Ye, B.; Wang, L. Antibiotics in soil and water in China—A systematic review and source analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wu, Y.; Li, S.; Hu, J.; Sun, W.; Ni, J. Profiles, drivers, and prioritization of antibiotics in China’s major rivers. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 477, 135399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daghrir, R.; Drogui, P. Tetracycline antibiotics in the environment: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2013, 11, 209–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosal, R.; Rodríguez, A.; Perdigón-Melón, J.A.; Petre, A.; García-Calvo, E.; Gómez, M.J.; Agüera, A.; Fernández-Alba, A.R. Occurrence of emerging pollutants in urban wastewater and their removal through biological treatment followed by ozonation. Water Res. 2009, 44, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, H.; Xiong, P.; Zhu, Q.; Liao, C.; Jiang, G. Occurrence, fate, and risk assessment of typical tetracycline antibiotics in the aquatic environment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 753, 141975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Tang, J.; Li, J.; Cheng, Z.; Chaemfa, C.; Liu, D.; Zheng, Q.; Song, M.; Luo, C.; Zhang, G. Occurrence and risks of antibiotics in the coastal aquatic environment of the Yellow Sea, North China. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 450, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Tang, J.; Li, J.; Zheng, Q.; Liu, D.; Chen, Y.; Zou, Y.; Chen, X.; Luo, C.; Zhang, G. Antibiotics in the offshore waters of the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea in China: Occurrence, distribution and ecological risks. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 174, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, S.K.; Kim, H.W.; Oh, J.E.; Park, H.S. Occurrence and removal of antibiotics, hormones and several other pharmaceuticals in wastewater treatment plants of the largest industrial city of Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 4351–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, H.W.; Minh, T.B.; Murphy, M.B.; Lam, J.C.; So, M.K.; Martin, M.; Lam, P.K.; Richardson, B.J. Distribution, fate and risk assessment of antibiotics in sewage treatment plants in Hong Kong, South China. Environ. Int. 2012, 42, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, J.; Wang, J.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, T. Spatial distribution, mass flux, and ecological risk of antibiotics in Taiwan and Luzon Straits: A case in the West Pacific Region. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 201, 16238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.T.; Shao, S.; Fan, S.D.; Tang, W.Q.; Miao, J.W.; Wang, S.; Cao, X.C.; Liu, C.; Ying, G.G.; Chen, Z.B.; et al. Occurrence, distribution, and risk assessment of antibiotics in a typical aquaculture area around the Dongzhai Harbor mangrove forest on Hainan Island. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 920, 170558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Shi, Y.; Gao, L.; Liu, J.; Cai, Y. Occurrence of antibiotics in water, sediments, aquatic plants, and animals from Baiyangdian Lake in North China. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.J.; Li, N.; Ying, G.G. Antibiotic distribution, risk assessment, and microbial diversity in river water and sediment in Hong Kong. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 2191–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarenga, D.O.; Rigonato, J.; Branco, L.H.Z.; Fiore, M.F. Cyanobacteria in mangrove ecosystems. Biodivers. Conserv. 2015, 24, 799–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, M.; Guo, C.; An, D.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xi, B. Distribution and ecological risk of antibiotics in a typical effluent–receiving river (Wangyang River) in north China. Chemosphere 2014, 112, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, G.; Zheng, Q.; Tang, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, W.; Zou, Y.; Chen, X. Occurrence and risks of antibiotics in the Laizhou Bay, China: Impacts of river discharge. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 80, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Pan, X.; Tang, J.; Zhang, G. Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in the Beibu Gulf, China: Impacts of river discharge and aquaculture activities. Mar. Environ. Res. 2012, 78, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifrtová, M.; Nováková, L.; Lino, C.; Pena, A.; Solich, P. An overview of analytical methodologies for the determination of antibiotics in environmental waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 649, 158–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Xu, L.; Rysz, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Alvarez, P.J. Occurrence and transport of tetracycline, sulfonamide, quinolone, and macrolide antibiotics in the Haihe River Basin, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1827–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, L.; Fu, C.; Tu, C.; Huang, Y.; Wu, L.; Tang, J.; Luo, Y.; Christie, P. Levels, distributions and sources of veterinary antibiotics in the sediments of the Bohai Sea in China and surrounding estuaries. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 109, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, A.; Liu, G.; Yousaf, B.; Arif, M.; Ahmed, R.; Irshad, S.; Cheema, A.I.; Rashid, A.; Gulzaman, H. Recent trends in advanced oxidation process-based degradation of erythromycin: Pollution status, eco-toxicity and degradation mechanism in aquatic ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 145389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabilan, A.; Ledesma, D.G.B.; Horn, H.; Borowska, E. Mesocosm experiment to determine the contribution of adsorption, biodegradation, hydrolysis and photodegradation in the attenuation of antibiotics at the water sediment interface. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 866, 161385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Shi, Y.; Ying, G.; Li, M.; He, Z.; Shu, L. Cooperation among nitrifying microorganisms promotes the irreversible biotransformation of sulfamonomethoxine. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 923, 171395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.L.; Wong, M.H. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs): A review on environmental contamination in China. Environ. Int. 2013, 59, 208–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Hou, L.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Zheng, Y.; Yin, G.; Gao, J.; Jiang, X. Nitrogen mineralization and immobilization in sediments of the East China Sea: Spatiotemporal variations and environmental implications. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2016, 121, 2842–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, J.I.; Turin, H.J.; Ertel, J.R. Sources and distributions of sedimentary organic matter in the Columbia River drainage basin, Washington and Oregon 1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1984, 29, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Liu, M.; Xu, S.; Ou, D.; Yu, J.; Cheng, S.; Lin, X.; Yang, Y. The effects of semi-lunar spring and neap tidal change on nitrification, denitrification, and N2O vertical distribution in the intertidal sediments of the Yangtze estuary, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 73, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreca, S.; Forni, C.; Colzani, L.; Clerici, L.; Daverio, D.; Dellavedova, P. Study on the stability of antibiotics, pesticides and drugs in water by using a straightforward procedure applying HPLC-mass spectrometric determination for analytical purposes. Separations 2021, 8, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabregat-Safont, D.; Gracia-Marín, E.; Ibáñez, M.; Pitarch, E.; Hernández, F. Analytical key issues and challenges in the LC-MS/MS determination of antibiotics in wastewater. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1239, 340739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, H.; Tao, S.; Hu, H.; Lu, X. Estimation of sorption coefficients of organic compounds with KOW. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 4, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Jing, L.; Teng, Y.; Wang, J. Characterization of antibiotics in a large-scale river system of China: Occurrence pattern, spatiotemporal distribution and environmental risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 618, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.; Xiang, Q.; Li, S.; Sun, L.; Yu, X.; Fang, L. Soil contamination with antibiotics in a typical peri-urban area in eastern China: Seasonal variation, risk assessment, and microbial responses. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 79, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Tao, H.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Zhou, Z.Y. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of tetracycline antibiotics in farmland soil in Yinchuan. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 4933–4941. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Mozaz, S.; Vaz-Moreira, I.; Della Giustina, S.V.; Llorca, M.; Barceló, D.; Schubert, S.; Berendonk, T.U.; Michael-Kordatou, I.; Fatta-Kassinos, D.; Martinez, J.L.; et al. Antibiotic residues in final effluents of European wastewater treatment plants and their impact on the aquatic environment. Environ. Int. 2020, 140, 105733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, S.; Shen, S.; Zhou, J.; Ding, G.; Zhang, K. Systematic analysis of occurrence, density and ecological risks of 45 veterinary antibiotics: Focused on family livestock farms in Erhai Lake basin, Yunnan, China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leps, J.; Smilauer, P. Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data Using CANOCO; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H.; Wan, Y.; Hu, J. Determination and source apportionment of five classes of steroid hormones in urban rivers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 7691–7698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- April, A.R.; Jason, B.B.; Michael, J.L. Toxicity of fluoroquinolone antibiotics to aquatic organisms. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2005, 24, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, T.; Nagase, H.; Eguchi, K.; Hirooka, T.; Nakamura, T.; Miyamoto, K.; Hirata, K. A novel method using cyanobacteria for ecotoxicity test of veterinary antimicrobial agents. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2007, 26, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brain, R.A.; Johnson, D.J.; Richards, S.M.; Sanderson, H.; Sibley, P.K.; Solomon, K.R. Effects of 25 pharmaceutical compounds to Lemna gibba using a seven-day static-renewal test. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2004, 23, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Białk-Bielińska, A.; Stolte, S.; Arning, J.; Uebers, U.; Böschen, A.; Stepnowski, P.; Matzke, M. Ecotoxicity evaluation of selected sulfonamides. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 928–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- di Delupis, G.D.; Macrí, A.; Civitareale, C.; Migliore, L. Antibiotics of zootechnical use: Effects of acute high and low dose contamination on Daphnia magna Straus. Aquat. Toxicol. 1992, 22, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Liguoro, M.; Fioretto, B.; Poltronieri, C.; Gallina, G. The toxicity of sulfamethazine to Daphnia magna and its additivity to other veterinary sulfonamides and trimethoprim. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 1519–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Liguoro, M.; Di Leva, V.; Dalla Bona, M.; Merlanti, R.; Caporale, G.; Radaelli, G. Sublethal effects of trimethoprim on four freshwater organisms. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 82, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eguchi, K.; Nagase, H.; Ozawa, M.; Endoh, Y.S.; Goto, K.; Hirata, K.; Miyamoto, K.; Yoshimura, H. Evaluation of antimicrobial agents for veterinary use in the ecotoxicity test using microalgae. Chemosphere 2004, 57, 1733–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halling-Sørensen, B. Algal toxicity of antibacterial agents used in intensive farming. Chemosphere 2000, 40, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, A.; Komori, K.; Nakada, N.; Kitamura, K.; Suzuki, Y. Biological effects of PPCPs on aquatic lives. and evaluation of river waters affected by different wastewater treatment levels. Water. Sci. Technol. 2008, 58, 1541–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Hou, J.; Kuo, T.; Lai, H. Toxicity of the veterinary sulfonamide antibiotic sulfamonomethoxine to five aquatic organisms. Environ. Toxicol. Phar. 2014, 38, 874–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isidori, M.; Lavorgna, M.; Nardelli, A.; Pascarella, L.; Parrella, A. Toxic and genotoxic evaluation of six antibiotics on non-target organisms. Sci. Total. Environ. 2005, 346, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Choi, K.; Jung, J.Y.; Park, S.; Kim, P.G.; Park, J. Aquatic toxicity of acetaminophen, carbamazepine, cimetidine, diltiazem and six major sulfonamides, and their potential ecological risks in Korea. Environ. Int. 2007, 33, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Park, J.; Kim, P.G.; Lee, C.; Choi, K.; Choi, K. Implication of global environmental changes on chemical toxicity-effect of water temperature, pH, and ultraviolet B irradiation on acute toxicity of several pharmaceuticals in Daphnia magna. Ecotoxicology 2010, 19, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laville, N.; Aıt-Aıssa, S.; Gomez, E.; Casellas, C.; Porcher, J.M. Effects of human pharmaceuticals on cytotoxicity, EROD activity and ROS production in fish hepatocytes. Toxicology 2004, 196, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, G.; Li, Z.; Liu, J. Effects of selected pharmaceuticals on growth, reproduction and feeding of Daphnia Magna. Fresen. Environ. Bull. 2013, 22, 2588–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, Y.; Yang, L.; Duan, S.; Zhou, F.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, B. Effects of azithromycin on feeding behavior and nutrition accumulation of Daphnia magna under the different exposure pathways. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2020, 197, 110573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, H.G. Sensitivity of Daphnia magna Straus against eight chemotherapeutic agents and two dyes. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1982, 28, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.; McDonough, S.; Ladewig, J.C.; Soares, A.M.; Nogueira, A.J.; Domingues, I. Effects of oxytetracycline and amoxicillin on development and biomarkers activities of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2013, 36, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Choi, K. Hazard assessment of commonly used agricultural antibiotics on aquatic ecosystems. Ecotoxicology 2008, 17, 526–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.H.; Zeon, S.R.; Lee, J.G.; Choi, S.H.; Shin, Y.K.; Park, K.I. In vitro and in vivo efficacy of drugs against the protozoan parasite Azumiobodo hoyamushi that causes soft tunic syndrome in the edible ascidian Halocynthia roretzi (Drasche). J. Fish. Dis. 2014, 37, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, J.C.; Lavorante, B.R.; Maria da Conceição, B.S.M.; Guilhermino, L. Influence of microplastics on the toxicity of the pharmaceuticals procainamide and doxycycline on the marine microalgae Tetraselmis chuii. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 197, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Morales, D.; Fajardo-Romero, D.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, C.E.; Cedergreen, N. Single and mixture toxicity of selected pharmaceuticals to the aquatic macrophyte Lemna minor. Ecotoxicology 2022, 31, 714–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcárcel, Y.; González Alonso, S.; Rodríguez-Gil, J.L.; Gil, A.; Catalá, M. Detection of pharmaceutically active compounds in the rivers and tap water of the Madrid Region (Spain) and potential ecotoxicological risk. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 1336–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.R.; Bell, T.A.; Lightner, D.V. Shrimp antimicrobial testing. II. Toxicity testing and safety determination for twelve antimicrobials with penaeid shrimp larvae. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 1992, 4, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollenberger, L.; Halling-Sorensen, B.; Kusk, K.O. Acute and Chronic Toxicity of Veterinary Antibiotics to Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 2000, 40, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Demeestere, K.; De Schamphelaere, K.A. The influence of pH and dissolved organic carbon on the ecotoxicity of ampicillin and clarithromycin. Sci. Tot. Environ. 2023, 904, 166781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).