Immunomodulatory Effects and Protection in Sepsis by the Antibiotic Moxifloxacin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
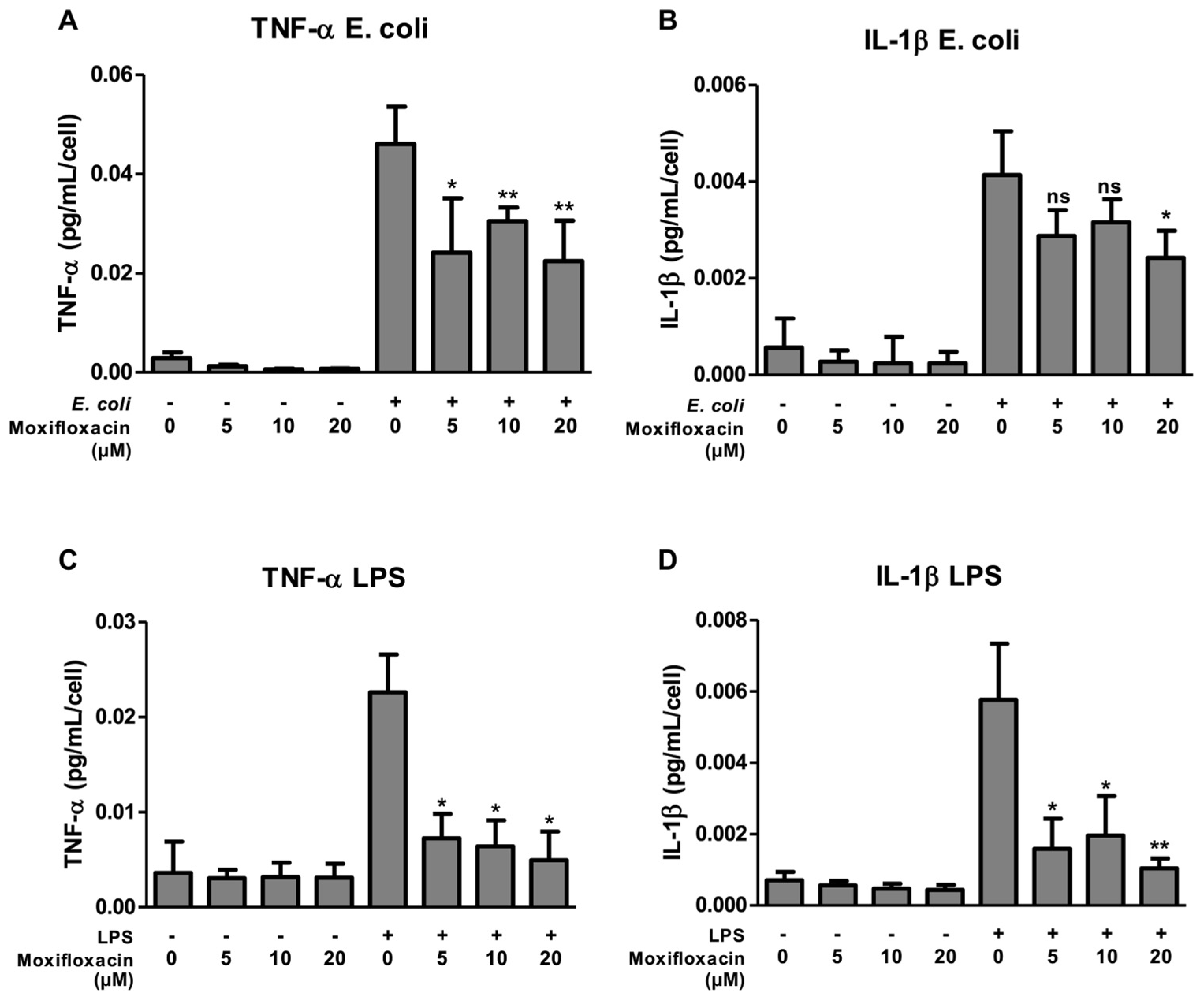
2.1. Moxifloxacin Inhibits the Secretion of IL-1β and TNF-α
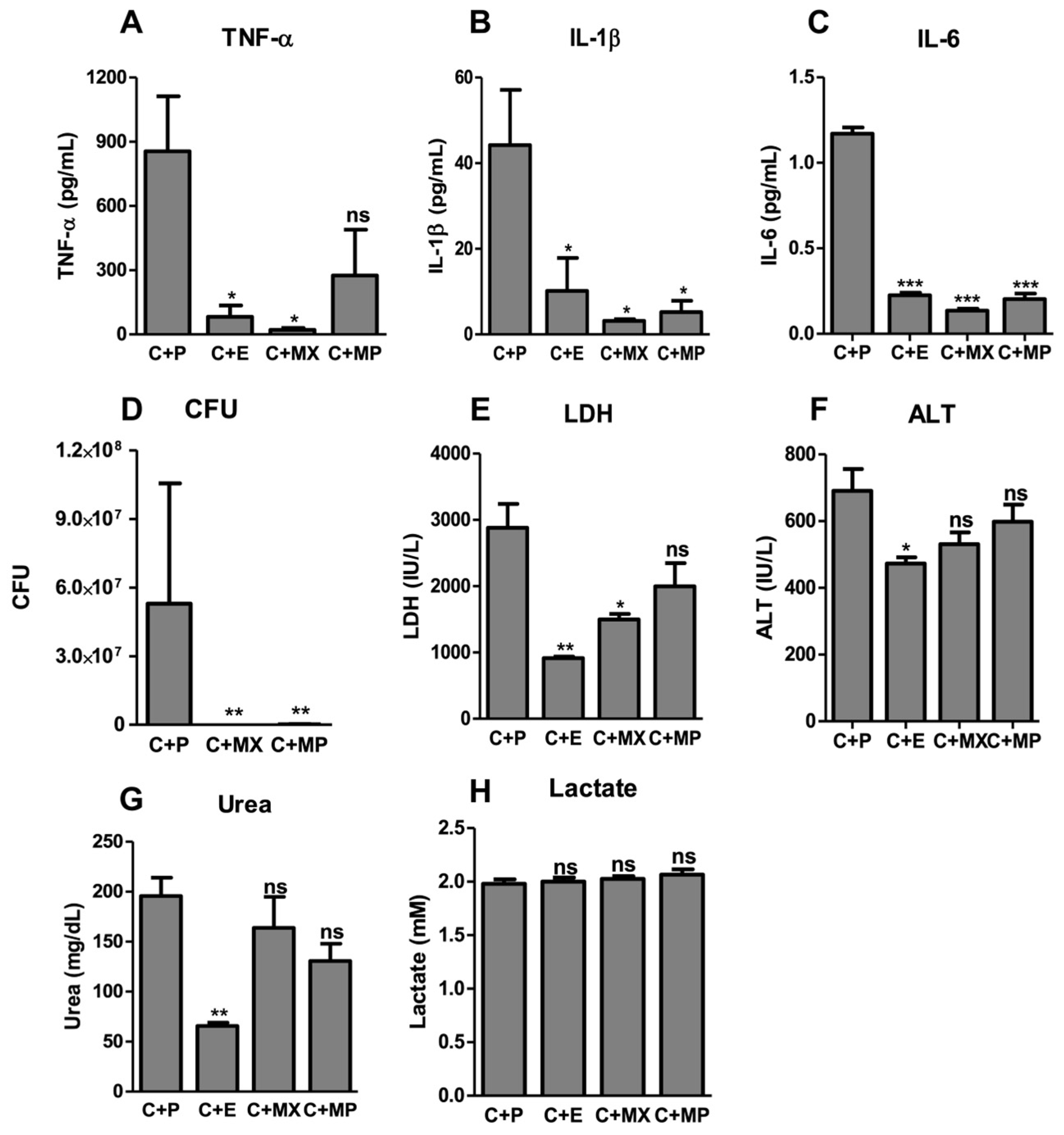
2.2. Moxifloxacin Protects against Severe Sepsis
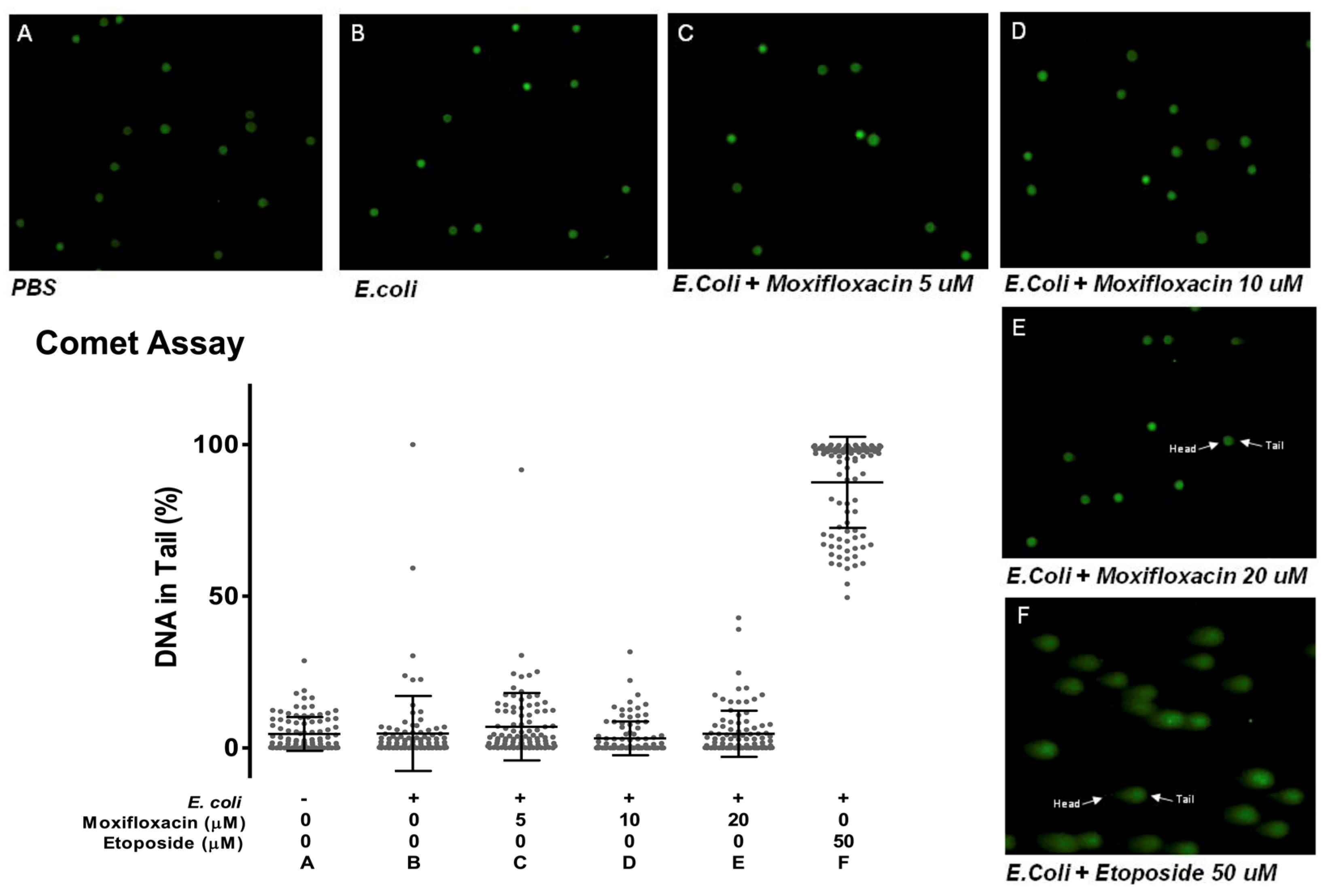
2.3. Moxifloxacin Action Is Not Due to DNA Damage
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Compounds
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. IL-1β and TNF-α Secretion
4.4. Comet Assay (Single-Cell Gel Electrophoresis)
4.5. Animal Experimental Design
4.6. Colony-Forming Units Assay
4.7. Serology and Cytokine Measurement
4.8. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Velho, T.; Santos, I.; Póvoa, P.; Ferreira, M. Sepsis: The need for tolerance not complacency. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2016, 146, w14276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, L.; Rhodes, A.; Alhazzani, W.; Antonelli, M.; Coopersmith, C.M.; French, C.; Machado, F.R.; Mcintyre, L.; Ostermann, M.; Prescott, H.C.; et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International Guidelines for Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock 2021. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 49, e1063–e1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.-D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischmann-Struzek, C.; Mellhammar, L.; Rose, N.; Cassini, A.; Rudd, K.E.; Schlattmann, P.; Allegranzi, B.; Reinhart, K. Incidence and mortality of hospital- and ICU-treated sepsis: Results from an updated and expanded systematic review and meta-analysis. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 1552–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudd, K.E.; Johnson, S.C.; Agesa, K.M.; Shackelford, K.A.; Tsoi, D.; Kievlan, D.R.; Colombara, D.V.; Ikuta, K.S.; Kissoon, N.; Finfer, S.; et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990–2017: Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Berg, M.; Van Beuningen, F.E.; Maaten, J.C.T.; Bouma, H.R. Hospital-related costs of sepsis around the world: A systematic review exploring the economic burden of sepsis. J. Crit. Care 2022, 71, 154096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timsit, J.-F.; Ruppé, E.; Barbier, F.; Tabah, A.; Bassetti, M. Bloodstream infections in critically ill patients: An expert statement. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 266–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cecconi, M.; Evans, L.; Levy, M.; Rhodes, A. Sepsis and septic shock. Lancet 2018, 392, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Zhu, L.; Jia, B.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, F.; Li, J.; Ding, N.; Zhang, C.; Hao, Y.; et al. Sepsis induces non-classic innate immune memory in granulocytes. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 113044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedeva, C. Inflammation and Cell Death of the Innate and Adaptive Immune System during Sepsis. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pons, S.; Arnaud, M.; Loiselle, M.; Arrii, E.; Azoulay, E.; Zafrani, L. Immune Consequences of Endothelial Cells’ Activation and Dysfunction During Sepsis. Crit. Care Clin. 2020, 36, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, C.W.; Gesten, F.; Prescott, H.C.; Friedrich, M.E.; Iwashyna, T.J.; Phillips, G.S.; Lemeshow, S.; Osborn, T.; Terry, K.M.; Levy, M.M. Time to Treatment and Mortality during Mandated Emergency Care for Sepsis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 2235–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, N.; Chora, A.; Raquel, H.; Pejanovic, N.; Pereira, P.; Hartleben, B.; Neves-Costa, A.; Moita, C.; Pedroso, D.; Pinto, A.; et al. Anthracyclines induce DNA damage response-mediated protection against severe sepsis. Immunity 2013, 39, 874–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjaastad, F.V.; Jensen, I.J.; Berton, R.R.; Badovinac, V.P.; Griffith, T.S. Inducing Experimental Polymicrobial Sepsis by Cecal Ligation and Puncture. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2020, 131, e110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, S.K.; Kim, C.Y.; Heidarian, M.; Berton, R.R.; Jensen, I.J.; Griffith, T.S.; Badovinac, V.P. Mouse Models of Sepsis. Curr. Protoc. 2024, 4, e997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.-L.; Li, G.; Jing, X.-Z.; Li, Y.-F.; Ye, Q.-Y.; Jia, H.-H.; Liu, S.-H.; Li, X.-J.; Li, H.; Huang, R.; et al. Assessment of clinical sepsis-associated biomarkers in a septic mouse model. J. Int. Med. Res. 2018, 46, 2410–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.K.; Choudhury, S. Experimental Protocol for Cecal Ligation and Puncture Model of Polymicrobial Sepsis and Assessment of Vascular Functions in Mice. In Traumatic and Ischemic Injury, Methods in Molecular Biology; Tharakan, B., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 1717, pp. 161–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahrner, R.; Beyoğlu, D.; Beldi, G.; Idle, J. Metabolomic markers for intestinal ischemia in a mouse model. J. Surg. Res. 2012, 178, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humma, Z.E.; Patel, P. Moxifloxacin. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK599511/ (accessed on 26 July 2024).
- Reuveni, D.; Halperin, D.; Shalit, I.; Priel, E.; Fabian, I. Moxifloxacin enhances etoposide-induced cytotoxic, apoptotic and anti-topoisomerase II effects in a human colon carcinoma cell line. Int. J. Oncol. 2010, 37, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabian, I.; Reuveni, D.; Levitov, A.; Halperin, D.; Priel, E.; Shalit, I. Moxifloxacin enhances antiproliferative and apoptotic effects of etoposide but inhibits its proinflammatory effects in THP-1 and Jurkat cells. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 95, 1038–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korwek, Z.; Sewastianik, T.; Bielak-Zmijewska, A.; Mosieniak, G.; Alster, O.; Moreno-Villaneuva, M.; Burkle, A.; Sikora, E. Inhibition of ATM blocks the etoposide-induced DNA damage response and apoptosis of resting human T cells. DNA Repair 2012, 11, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, A.; Møller, P.; Gajski, G.; Vodenková, S.; Abdulwahed, A.; Anderson, D.; Bankoglu, E.E.; Bonassi, S.; Boutet-Robinet, E.; Brunborg, G.; et al. Measuring DNA modifications with the comet assay: A compendium of protocols. Nat. Protoc. 2023, 18, 929–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weitering, T.J.; Takada, S.; Weemaes, C.M.R.; Van Schouwenburg, P.A.; Van Der Burg, M. ATM: Translating the DNA Damage Response to Adaptive Immunity. Trends Immunol. 2021, 42, 350–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, A.; Niederman, M.S.; Chastre, J.; Ewig, S.; Fernandez-Vandellos, P.; Hanberger, H.; Kollef, M.; Bassi, G.L.; Luna, C.M.; Martin-Loeches, I.; et al. International ERS/ESICM/ESCMID/ALAT guidelines for the management of hospital-acquired pneumonia and ventilator-associated pneumonia: Guidelines for the management of hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP)/ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) of the European Respiratory Society (ERS), European Society of Intensive Care Medicine (ESICM), European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID) and Asociación Latinoamericana del Tórax (ALAT). Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1700582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquale, T.R.; Tan, J.S. Nonantimicrobial effects of antibacterial agents. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2005, 40, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araujo, F. Effect of moxifloxacin on secretion of cytokines by human monocytes stimulated with lipopolysaccharide. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 8, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Song, M.; Kim, S. Effect of moxifloxacin on production of proinflammatory cytokines from human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Antimicrob. Agents 2003, 47, 3704–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, T.; Shalit, I.; Blau, H.; Werber, S.; Halperin, D.; Levitov, A.; Fabian, I. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Moxifloxacin on Activated Human Monocytic Cells: Inhibition of NF-κB and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Activation and of Synthesis of Proinflammatory Cytokines. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 1974–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.A.; Slifer, T.R.; Araujo, F.G.; Suzuki, Y.; Remington, J.S. Protection against lipopolysaccharide-induced death by fluoroquinolones. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 3169–3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labro, M. Interference of antibacterial agents with phagocyte functions: Immunomodulation or ‘immuno-fairy tales’? Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 13, 615–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmann, K.; Moita, L.F. Physiologic disruption and metabolic reprogramming in infection and sepsis. Cell Metab. 2024, 36, 927–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colaço, H.G.; Barros, A.; Neves-Costa, A.; Seixas, E.; Pedroso, D.; Velho, T.; Willmann, K.L.; Faisca, P.; Grabmann, G.; Yi, H.-S.; et al. Tetracycline Antibiotics Induce Host-Dependent Disease Tolerance to Infection. Immunity 2021, 54, 53–67.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollock, J.; Chalmers, J.D. The immunomodulatory effects of macrolide antibiotics in respiratory disease. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 71, 102095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunkhorst, F.M.; Oppert, M.; Marx, G.; Bloos, F.; Ludewig, K.; Putensen, C.; Nierhaus, A.; Jaschinski, U.; Meier-Hellmann, A.; Weyland, A.; et al. Effect of empirical treatment with moxifloxacin and meropenem vs meropenem on sepsis-related organ dysfunction in patients with severe sepsis: A randomized trial. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2012, 307, 2390–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savion, S.T.V.; Blank, M.; Shepshelovich, J.; Fishman, P.; Shoenfeld, Y. Ciprofloxacin Affects Pregnancy Loss in CBA/JxDBA/2J Mice Possibly via Elevation of Interleukin-3 and Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor. Am. J. 2000, 44, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blank, M.; George, J.; Fishman, P.; Levy, Y.; Toder, V.; Savion, S.; Barak, V.; Koike, T.; Shoenfeld, Y. Ciprofloxacin immunomodulation of experimental antiphospholipid syndrome associated with elevation of interleukin-3 and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor expression. Arthritis Rheum. 1998, 41, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Velho, T.R.; Raquel, H.; Figueiredo, N.; Neves-Costa, A.; Pedroso, D.; Santos, I.; Willmann, K.; Moita, L.F. Immunomodulatory Effects and Protection in Sepsis by the Antibiotic Moxifloxacin. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13080742
Velho TR, Raquel H, Figueiredo N, Neves-Costa A, Pedroso D, Santos I, Willmann K, Moita LF. Immunomodulatory Effects and Protection in Sepsis by the Antibiotic Moxifloxacin. Antibiotics. 2024; 13(8):742. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13080742
Chicago/Turabian StyleVelho, Tiago R., Helena Raquel, Nuno Figueiredo, Ana Neves-Costa, Dora Pedroso, Isa Santos, Katharina Willmann, and Luís F. Moita. 2024. "Immunomodulatory Effects and Protection in Sepsis by the Antibiotic Moxifloxacin" Antibiotics 13, no. 8: 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13080742
APA StyleVelho, T. R., Raquel, H., Figueiredo, N., Neves-Costa, A., Pedroso, D., Santos, I., Willmann, K., & Moita, L. F. (2024). Immunomodulatory Effects and Protection in Sepsis by the Antibiotic Moxifloxacin. Antibiotics, 13(8), 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13080742





