Abstract
In order to contribute to an assessment of the role of food in the risks of transmission of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), a review was undertaken of research on this microorganism in milk and dairy products published from January 2001 to February 2024. A total of 186 publications were selected, 125 for dairy products and 61 for bulk-tank milk (BTM). MRSA was detected in 68.8% of the research into dairy products and 73.8% of investigations relating to BTM, although in most studies the prevalence was less than 5%. Of the set of S. aureus strains isolated, approximately 30% corresponded to MRSA. The foods most extensively contaminated with this microorganism were raw milk and some types of soft cheese. Determination of the mecA gene on its own is known not to suffice for the detection of all MRSA strains. The great diversity of techniques used to study MRSA in milk and dairy products made it difficult to draw comparisons between studies. It would thus be advisable to develop a standardized protocol for the study of this microorganism in foods.
1. Introduction
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) has become a major agent of severe nosocomial infections, with a high fatality rate [1]. MRSA is usually resistant to multiple drugs, and especially to most beta-lactam antibiotics, as a result of the synthesis of a modified penicillin-binding protein (PBP2a), encoded by the mecA gene included in the SCCmec or staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec [2]. The mecA gene has been detected in the majority of MRSA isolates from animals, humans, and the environment. Hence, although there are other genes (mecB, mecC, mecD) that are also responsible for methicillin resistance in strains of the Staphylococcaceae family, detection of the mecA gene by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is the technique usually employed to identify MRSA. Among the different existing phenotypic methods for detecting MRSA, latex agglutination has the highest sensitivity and specificity, followed by cephoxitin disc diffusion [3]. The use of selective media and chromogenic agar media containing cefoxitin may be useful for the identification of Staphylococcus aureus and MRSA. It has been suggested that the cefoxitin disk diffusion method has higher sensitivity and specificity for the detection of MRSA than the Chrom agar MRSA method [4].
MRSA strains are classified on the basis of their epidemiological origin as (1) hospital-associated or HA-MRSA, (2) community-associated or CA-MRSA, and (3) livestock-associated or LA-MRSA [5]. The earliest infections by MRSA were nosocomial; however, in the 1990s, MRSA infections began to be reported in people without prior exposure to hospital settings, leading to the identification of the community-associated type. MRSA has also been detected in cattle, with the first isolations made in Belgium in 1972 from bovine mastitis samples [6]. LA-MRSA has become a considerable potential menace to public health owing to its zoonotic capacities since it can be transmitted from animals to humans [2].
While the direct transmission of MRSA has been well studied, its role in food remains poorly understood. The classic food-borne staphylococcal disease is food poisoning resulting from the contamination of foodstuffs with enterotoxins [7]. Staff manipulating food who carry enterotoxin-producing S. aureus, which may be present in the nasal passages or on the skin, are seen as the main source of such contamination [8]. Staphylococcal food poisoning is mostly associated with improper handling of processed foodstuffs, followed by storage under conditions that allow the growth of S. aureus and the production of enterotoxins [9]. In contrast, food poisoning caused by strains of MRSA is very rare. The first outbreak of gastrointestinal illness caused by toxins produced by MRSA originated in the United States when an infected food handler caused the contamination of coleslaw [10]. From the studies cited above, it is clear that MRSA is present in food and can be a cause of food poisoning, and this fact poses a potential risk to human health. However, methicillin resistance is not a relevant factor for the production of enterotoxins and, since food poisoning is not a disease that is treated with antibiotics, MRSA should not pose, in this context, any greater risk than methicillin-susceptible S. aureus, that is, MSSA [11].
Another factor to be taken into account is the possibility of infection with MRSA during food processing or consumption. When food is cooked properly, the potential risk of infection is almost certainly minimal. However, the under-cooking of foodstuffs or their cross-contamination through contact with raw products or contaminated surfaces does pose a potential hazard to the consumer [9]. The risk depends largely on the hygiene measures adopted, the concentration of MRSA present, and the ability of the strain itself to colonize the host. In this respect, it should be noted that, in some studies, a low level of S. aureus was observed in the food samples analyzed [11]. Consequently, the transmission of MRSA to humans through the food chain is considered a minor route, and techniques that can detect very low levels of contamination are usually necessary to determine the microorganism [8].
Milk and dairy products are often contaminated with antibiotic-resistant bacteria, including S. aureus, which has become a critically important global public health problem [12]. In dairy animals, S. aureus is one of the most common causative agents of mastitis, and infected animals often excrete this bacterium in their milk. In recent years, interest in the consumption of minimally processed foods has increased, which is why the consumption of raw milk shows a growing trend. However, due to the possible presence of S. aureus in raw milk, this bacterium can be transmitted to humans through the dairy food chain and pose a risk to consumers [13]. The prevalence of S. aureus is higher in raw milk than in dairy products and pasteurized milk [12]. The hygiene and safety of raw milk can be assured by improving the health of dairy animals and hygienic practices during milking. Transportation and storage in accordance with regulatory requirements can reduce contamination of raw milk with S. aureus and staphylococcal enterotoxins [12]. Bulk tank milk has been identified as a source of MRSA, demonstrating the potential food safety risk of contaminated milk and dairy products entering the human food chain [14].
The objective of this work was thus to compile an overview of the literature available on the prevalence and types of MRSA in milk and dairy products, as well as to describe the methods used in each case. The intention was to elucidate what measures would allow better detection, identification and typing of strains.
2. Results
2.1. Dairy Products
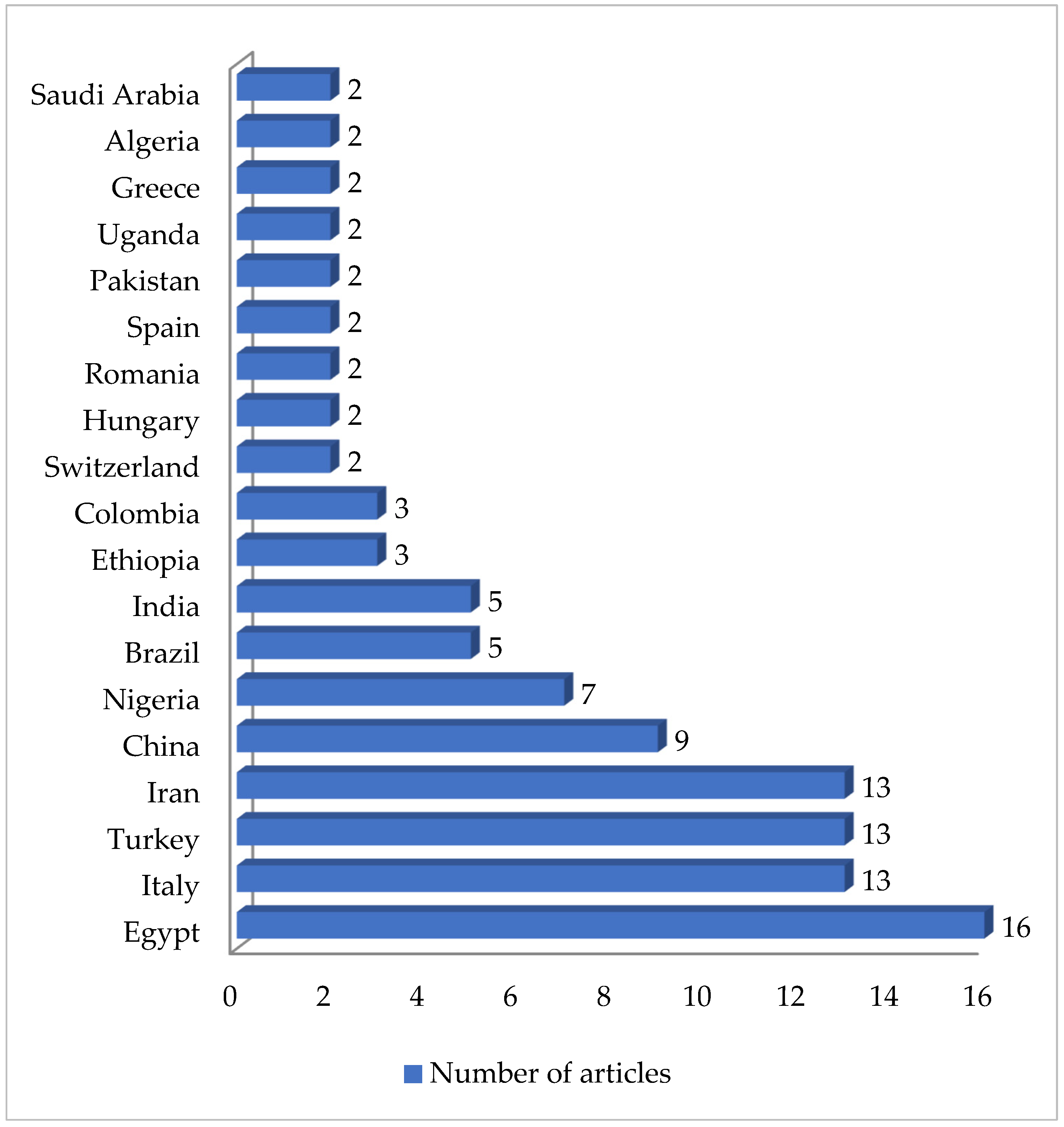
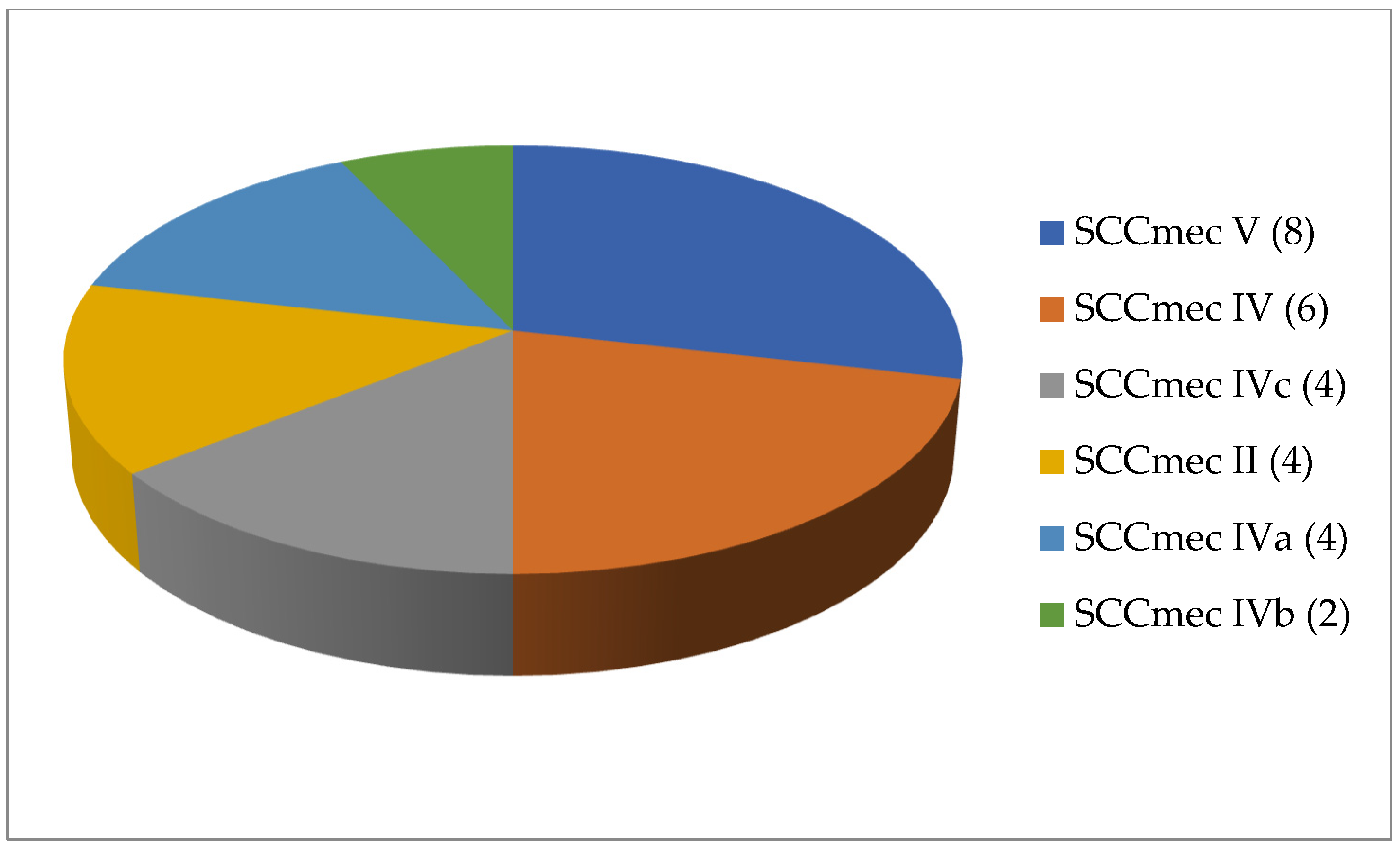
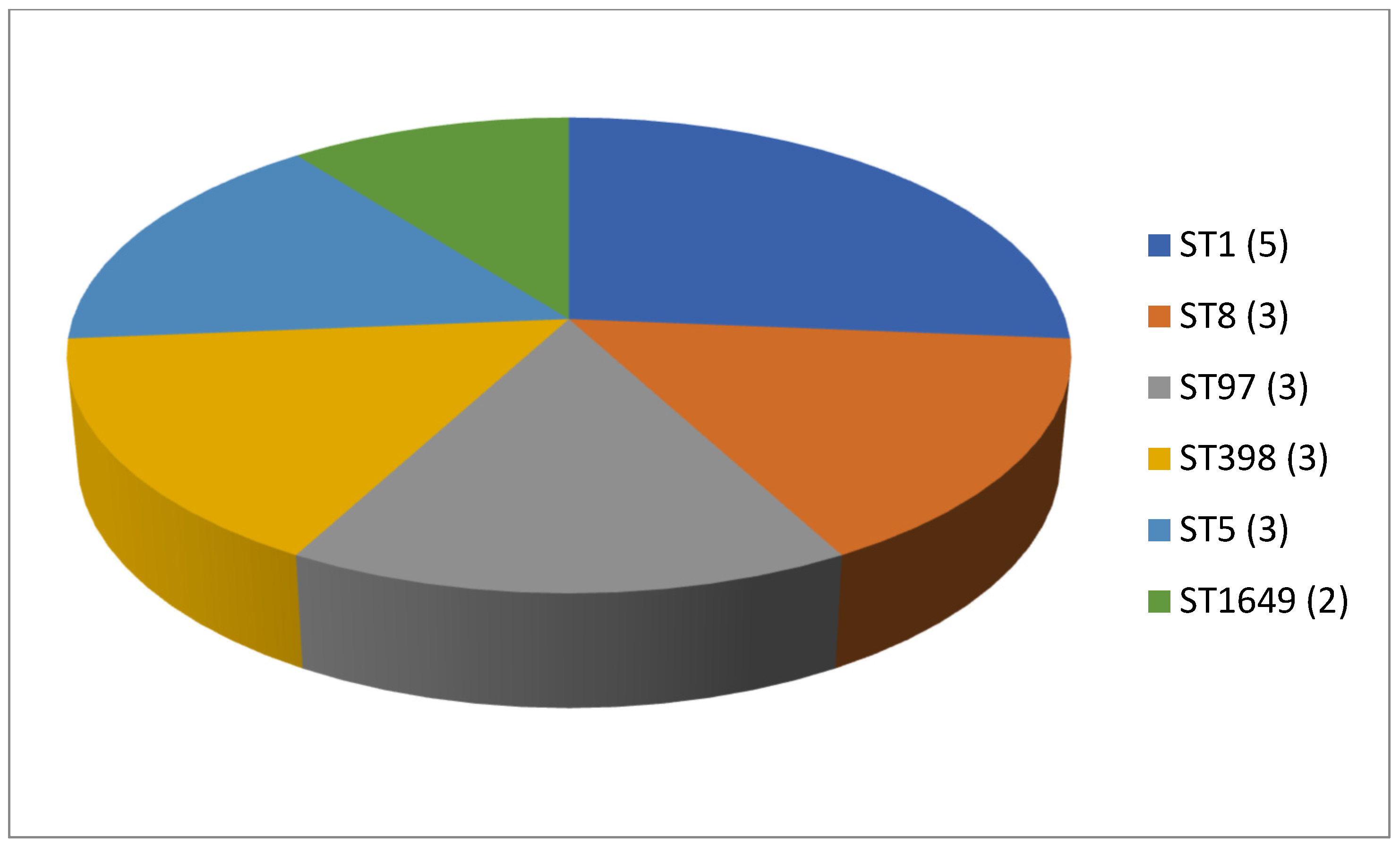
A total of 125 articles relating to dairy products were reviewed (Table 1). No prior enrichment was performed in 55.2% of this work (69 cases out of 125). Few articles (4.8%, only 6 out of 125) described the application of double enrichment to the samples, and not one had triple enrichment. In most of the pieces of work using liquid media, 14 in all, tryptone soy broth (TSB) was used as a culture medium, and in 3 of these, the broth was supplemented with 7.5% salt (NaCl). In second place came Mueller Hinton broth (MHB) supplemented with 6.5% NaCl, which was used in 5 instances. With regard to solid media, only a few articles (4.8%; 6 out of 125) mentioned the use of a chromogenic medium selective for MRSA, and only 5 articles spoke of the employment of oxacillin resistance screening agar base (ORSAB) supplemented with oxacillin at 2 milligrams per liter (2 mg/L). Regarding the method for confirming MRSA, four main techniques were used. In a clear majority of the articles (67.2%, 84 out of 125), amplification of the mecA gene was achieved by using PCR. A total of 22 articles recorded amplification of the mecA and mecC genes by PCR, whilst in 10 articles disc diffusion tests for susceptibility to cephoxitin (30 μg) and oxacillin (1 μg) were utilized. Finally, in eight pieces of work MRSA latex agglutination testing, checking for penicillin-binding protein 2a, was employed. MRSA was found in 68.8% (86 out of 125) of the investigations, although in most of the work consulted the microorganism was detected in less than 5% of the samples. The percentage with multiple resistance was around 30% of the total S. aureus strains isolated. The most frequently contaminated foods were raw milk and some types of soft cheese. Regarding the location of the research works (Figure 1), the 4 most frequent countries were Egypt (16 articles), Italy, Turkey, and Iran (13 articles each). The most detected SCCmec and ST types in the different pieces of research were SCCmec V (8 articles) and IV (6); and ST1 (5) (Figure 2 and Figure 3).
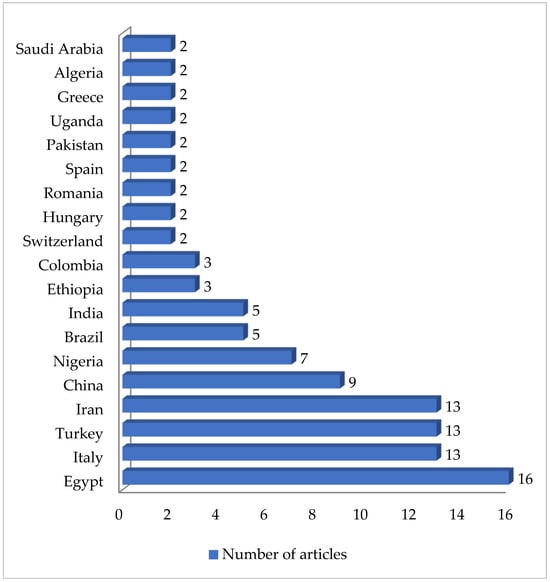
Figure 1.
Research on MRSA in dairy products grouped by location.
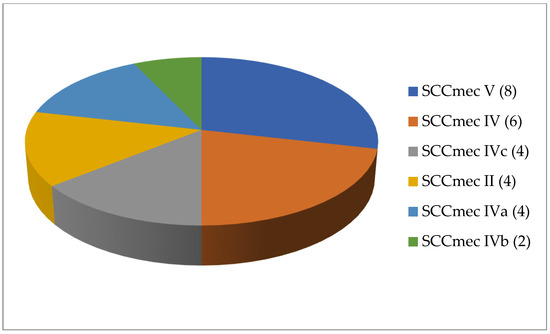
Figure 2.
Most detected staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec) types in the reviewed research on MRSA in dairy products (number of articles is indicated in parentheses).
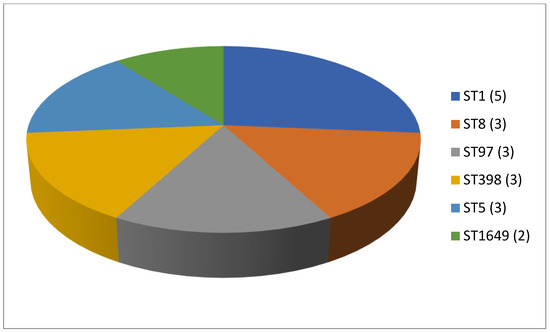
Figure 3.
Most detected sequence types (ST) in the reviewed research on MRSA in dairy products (number of articles is indicated in parentheses).
2.2. Bulk-Tank Milk
As shown in Table 2, 61 articles relating to milk in bulk tankers were reviewed. In an appreciable number of the pieces of research being reported (45.9%; 28 out of 61), no prior enrichment was performed for the isolation of MRSA. A quarter of the articles (24.6%, 15 out of 61) described double enrichment of the samples being carried out, but none mentioned triple enrichment. Regarding liquid media, MHB supplemented with 6.5% NaCl was used in 24 instances. The second commonest culture medium was TSB, mentioned in eighteen articles, with a majority of these, ten articles in total, recording supplementation with 75 mg/L of aztreonam and 3.5 mg/L of cephoxitin. With regard to solid media, some investigations (11.5%; 7 out of 61) used a selective chromogenic medium for MRSA, but only 2 referred to the use of agar-base for screening for resistance to oxacillin (ORSAB) supplemented with oxacillin (2 mg/L). As for the method of confirming MRSA, four main approaches were used. A majority of articles (59.0%, 36 out of 61) described amplification of the mecA gene by means of PCR. In 23 cases, there was amplification of the mecA and mecC genes through the use of PCR; in four, a disc diffusion test for susceptibility to cephoxitin (30 μg) and oxacillin (1 μg) was employed while in three instances the MRSA latex agglutination test, checking for penicillin-binding protein 2a, was used. MRSA strains were detected in 45 of the pieces of research, which was 73.8% of the total, although their prevalence was less than 5% in most of the reports consulted. Regarding the origin of the publications (Figure 4), it was observed that the four most frequent countries were Italy (14 articles), Germany (6 articles), and Great Britain (5 articles). The most frequently detected SCCmec and ST types are shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6. These were SCCmec V (15 articles), IVa (14), and IV (6); and ST398 (18), ST1 (8), and ST130 (5).
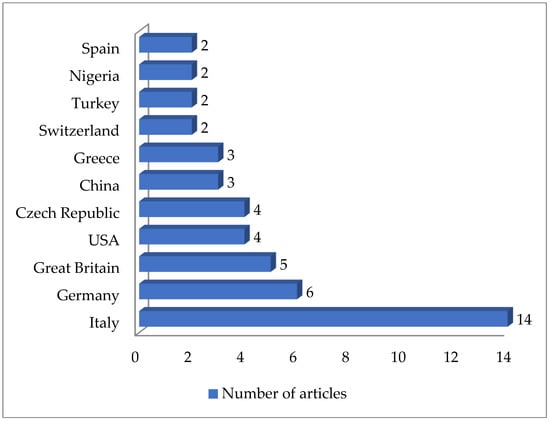
Figure 4.
Research on MRSA in milk in bulk tankers grouped by location.
Figure 4.
Research on MRSA in milk in bulk tankers grouped by location.
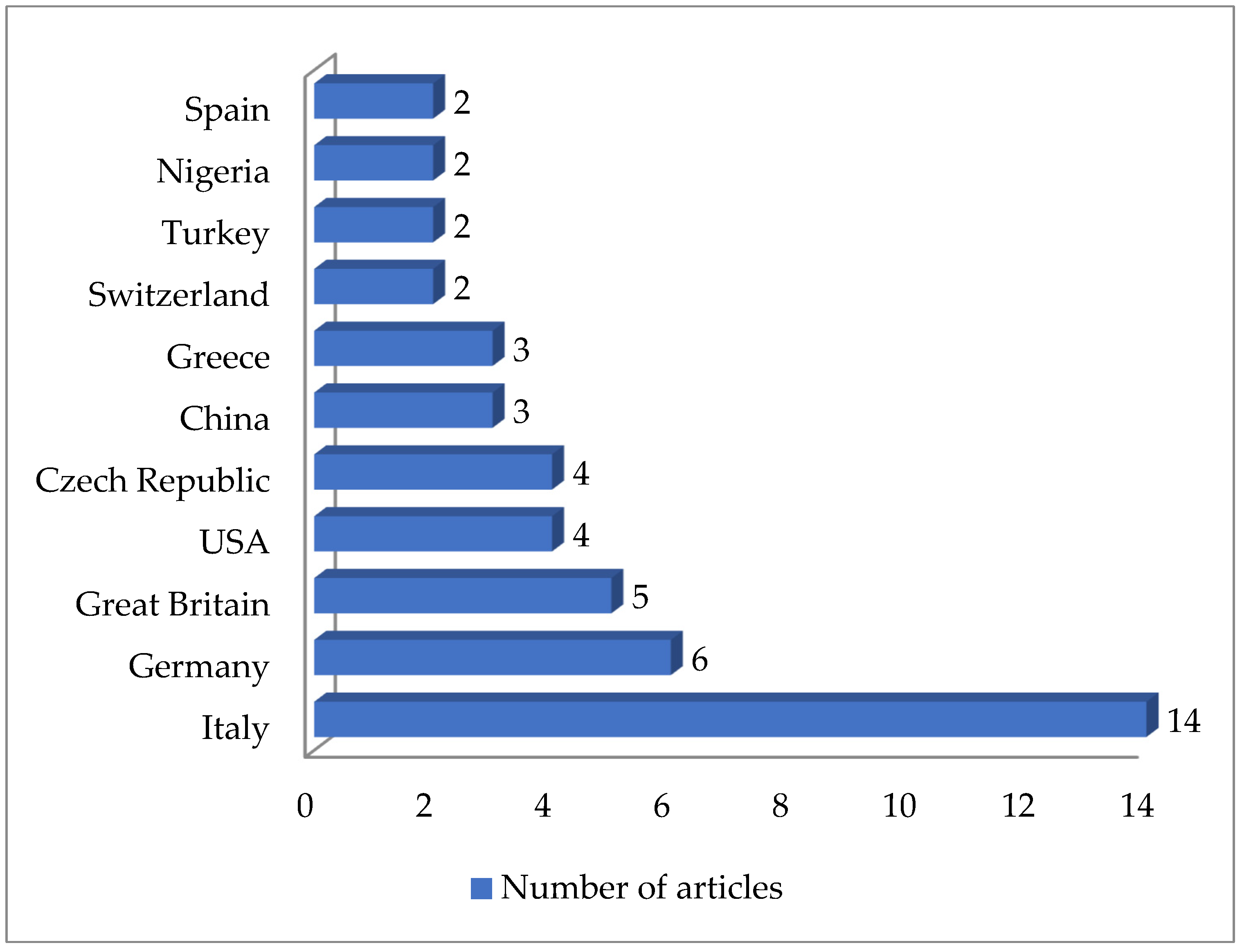
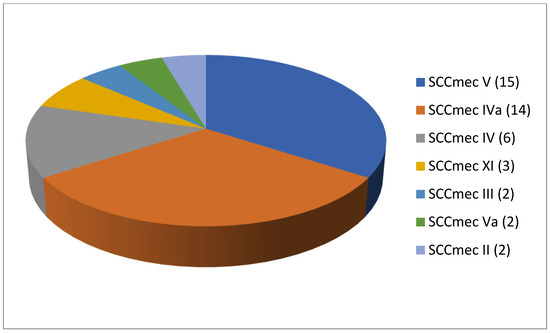
Figure 5.
Most detected staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec) types in the reviewed research on MRSA in milk in bulk tankers (number of articles is indicated in parentheses).
Figure 5.
Most detected staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec) types in the reviewed research on MRSA in milk in bulk tankers (number of articles is indicated in parentheses).
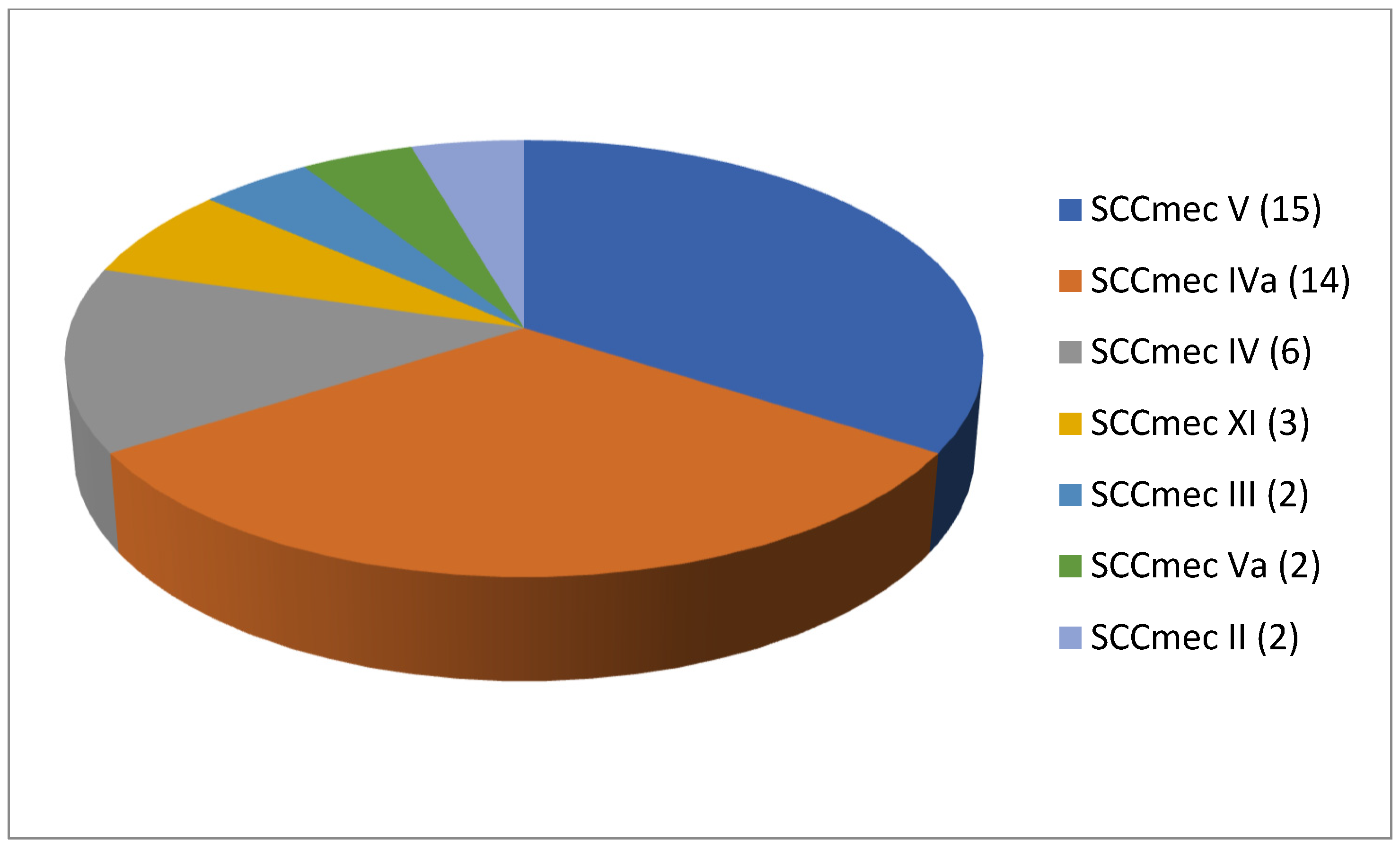
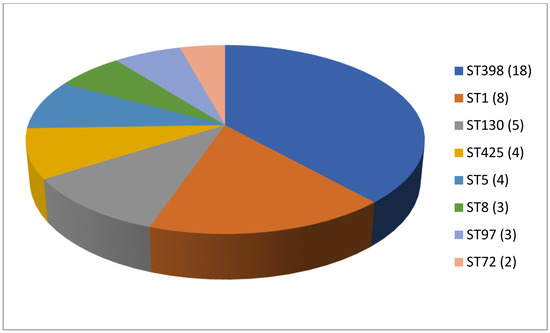
Figure 6.
Most detected sequence types (ST) in the reviewed research on MRSA in milk in bulk tankers (number of articles is indicated in parentheses).
Figure 6.
Most detected sequence types (ST) in the reviewed research on MRSA in milk in bulk tankers (number of articles is indicated in parentheses).
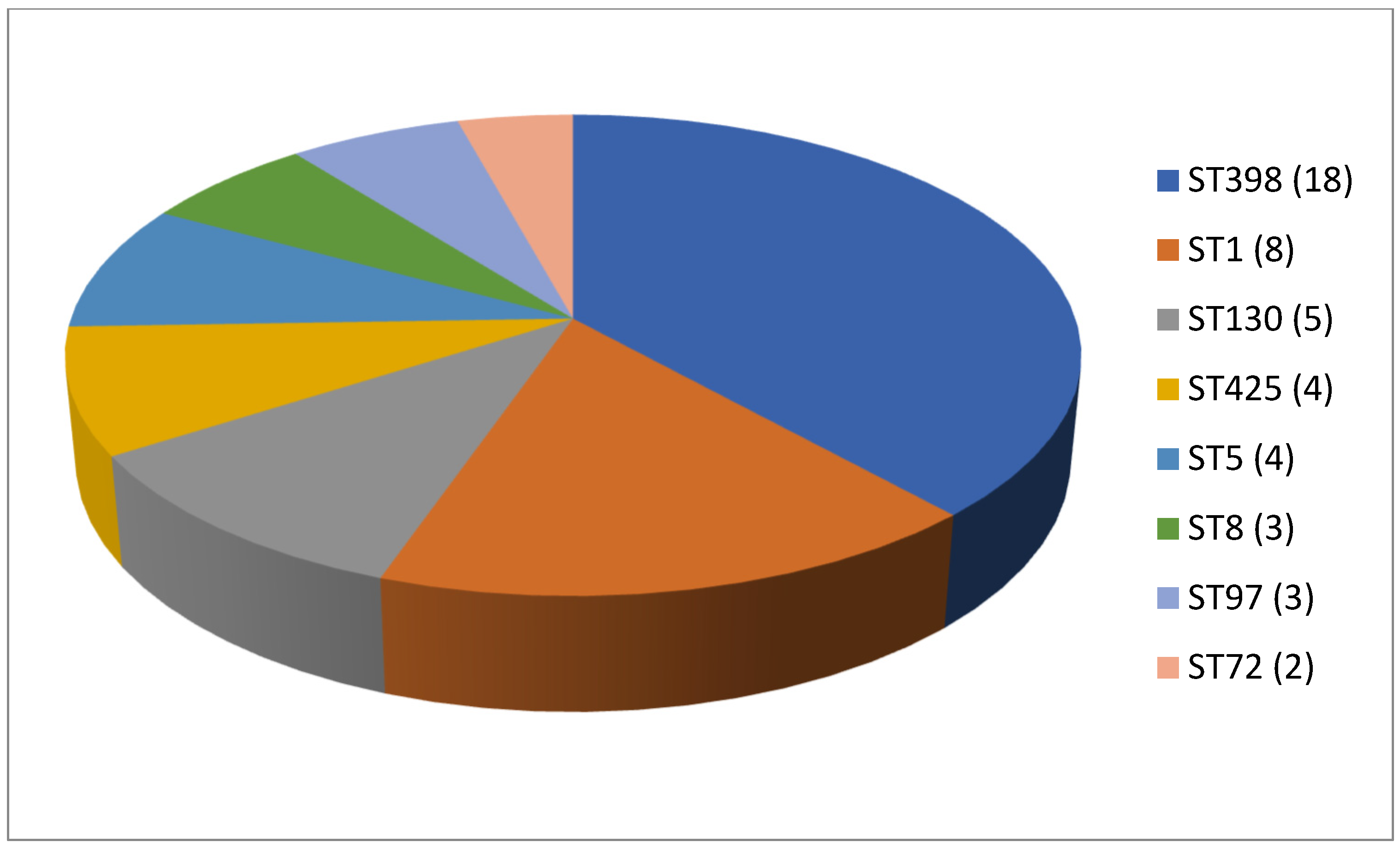

Table 1.
Prevalence of MRSA in dairy products (in the absence of clarification, the prevalence is considered based on the detection of mecA gene).
Table 1.
Prevalence of MRSA in dairy products (in the absence of clarification, the prevalence is considered based on the detection of mecA gene).
| Samples | Period | Place | Detection Method | Prevalence | Identification | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 350 staphylococcal isolates from food | 2001 | Hungary | -1.1. -2.12.1. -3.4.-3.7.-3.11.-3.2. | 1% resistant to oxacillin from milk industry (mecA gene negative) | N/R | [15] |
| 915 staphylococcal strains were isolated from foods examined at the National Food Investigation Institute | 2001–2002 | Hungary | -1.1. -2.12.1. -3.4.-3.7.-3.11.-3.2. | 2 resistant to oxacillin: sausage and fresh milk (mecA gene negative) | N/R | [16] |
| 216 isolates of S. aureus from raw milk samples | July 2001–February 2002 | Rift Valley (Kenya) | -1.1. -3.4. | 17/216 (7.8%) resistance to methicillin | N/R | [17] |
| 641 milk and dairy products from retail outlets | January 2003–December 2005 | Italy | -Homogenized: 1.2. -1.1. -2.1.2. -3.2.-3.4. | 6/641 (0.9%): 4 from bovine milk and 2 from cheese (pecorino and mozzarella) | -3 strains belonged to the non-host-specific biovar -3 strains belonged to the ovine biovar | [18] |
| 24 raw milk samples and 24 Minas Frescal cheese samples from a dairy processing plant | February 2004–March 2005 | Goiás State (Brazil) | -1.1. -2.1. -3.4. | 1 isolate resistant to oxacillin from Minas Frescal cheese | N/R | [19] |
| 122 S. aureus strains came from different raw milk products (milk, curd, cheeses, butter, and whey): 81 isolates originated from cow, 22 from goat, 17 from sheep, and 2 from buffalo | N/R | Italy | -1.1. -3.1. | None | N/R | [20] |
| 148 presumptive S. aureus isolates from: 9 cheeses, 18 bovine mastitis (from raw milk samples) and 20 raw cow’s milk | 2006–2008 | Portugal | -1.1. -2.1.2. -3.2.-3.4. | -38% of the isolates were resistant to oxacillin -1/148 (0.7%) showed the presence of mecA gene (from bovine mastitis in raw milk samples) | N/R | [21] |
| 200 samples of raw milk cheese | March–September 2009 | Switzerland | -First: 1.4.3. -Second: 1.11.1. -2.14. -3.2.-3.4. | None | N/R | [22] |
| 36 S. aureus strains isolated from raw sheep’s milk cheese from dairies | N/R | Sardinia (Italy) | -1.1. -3.2.-3.4. | None | N/R | [23] |
| 127 white-brined Urfa cheese samples from supermarkets and retail outlets | January–March 2008 | Sanliurfa (Turkey) | -1.1. -2.1.1. -3.2.-3.4. | 3/40 (7.5%) of S. aureus isolates | N/R | [24] |
| 200 samples of raw milk, pasteurized milk, ice cream, traditional white pickled cheese from different supermarkets and retailer shops | March 2010–September 2011 | Sarab (Iran) | -1.9. -2.1.3. -3.2. | 4/200 (2%): 2 pasteurized milk and 2 traditional cheese | N/R | [25] |
| 200 unpackaged cheese samples: 100 white cheese and 100 Tulum cheese from retail markets | April 2008–January 2009 | Ankara (Turkey) | -1.1. -2.1.1. -3.2.-3.4. | 2/200 (1%): Tulum cheese samples | N/R | [26] |
| 300 samples from sellers: 100 raw milk, 100 pasteurized milk and 100 ice cream | During the summer in 2010 | Tabriz (Iran) | -1.9. -2.1.3. -3.2. | -20/300 (6.7%): 14 raw milk and 6 ice cream samples -20/69 (29%) of S. aureus isolates | N/R | [27] |
| 149 strains isolated from samples of food such as milk and milk derivatives | 2004–2010 | Colombia | -1.1. -2.1. -3.4.-3.2. | 5/149 (3.4%): 1 milk cream | N/R | [28] |
| 72 cheese samples (36 samples from dairy counters or refrigerated displays in grocery stores or farmer’s markets, and 36 samples from manufacturers via internet): 8 cream cheeses, 5 soft cheeses, 8 semi-hard cheeses, 1 hard and 1 processed cheese, produced from pasteurized milk, and 9 soft cheeses, 28 semi-hard- and 12 hard cheeses, made from raw milk | N/R | Hanover (Germany) | -1.4.1. -2.14. -3.2. | None | N/R | [29] |
| 404 samples of Burrata Cheese from 12 different dairies | April–July 2009 and February–June 2010 | Puglia (Italy) | -3.2.-3.4. | None | N/R | [30] |
| 100 (56 fruity, 32 vanilla, and 12 chocolate) ice cream samples | June–September 2010 | Samsun (Turkey) | -1.1. -2.1.1. -3.2. | -1/100 (1%): fruity ice cream -1/35 (2.8%) of S. aureus isolates | N/R | [31] |
| 205 samples: 40 raw milk, 40 dairy products, and 20 ice cream from markets, grand large hotel and farms | April–November 2011 | Anhui (China) | -1.1. -3.4. | None | N/R | [32] |
| 35 raw milk, 30 Kariesh cheese, and 30 ice cream from local markets and villages | December 2011–February 2012 | Dakahlia (Egypt) | -1.1. -3.4.-3.2. | 5/95 (5.3%): 3 raw milk (8.6%), 1 Kariesh cheese (3.3%) and 1 ice cream (3.3%) | N/R | [33] |
| 30 samples of cow raw milk and white raw soft cheese from markets | December 2012–February 2013 | Baghdad | -Two methods: ·1.1. ·1.3.11. -2.1.4. -3.4.-3.9. | 10/30 (33.3%): 4 raw milk (13.4%) and 6 white raw soft cheese with its whey (20%) | N/R | [34] |
| 100 samples of Erzincan tulum cheese from markets | N/R | Erzincan (Turkey) | -Homogenized: 1.7. -1.1. -2.1. -3.2.-3.4. | 10/61 (16.39%) of S. aureus isolates | N/R | [35] |
| 347 samples of traditional and commercial dairy products from retail stores: 90 cheese, 85 ice-cream, 57 butter, 36 cream, 30 yoghurt, 24 kashk and 25 Iranian dough | September 2010–July 2011 | Isfahan, Chaharmahal va Bakhtyari and Khuzestan (Iran) | -Homogenized: 1.10. -1.1. -2.1. -3.4. | Of 20 S. aureus isolates: 5 (25.0%) resistant to oxacillin and 0 to methicillin | N/R | [36] |
| 160 milk and milk product samples (30 pedha and 30 curd) from milk collection center of Co-operative milk dairies, cattle farms, individual household, milk vendors, and sweet shops | February–October 2011 | Anand, Gujarat (India) | -1.7. -2.1. -3.4. | None | N/R | [37] |
| 372 milk samples: 300 raw milk, 17 each of pasteurized milk and yogurt, and 20 ‘kindirmo’ (locally fermented milk) | N/R | Kaduna and Zaria (Nigeria) | -1.1. -2.1. -3.4.-3.2. | -18/47 of coagulase positive S. aureus were resistant to methicillin (4.8%): 14 in raw milk and 1 each in pasteurized milk and ‘kindirmo’ -4/18 of the MRSA isolates (mecA gene positive): 3 raw milk and 1 ‘kindirmo’ | N/R | [38] |
| 340 raw milk samples from dairy farms and shops: 120 cow, 140 buffalo, 40 sheep and 40 goat | N/R | Sohag Governorate (Egypt) | -1.1. -2.4.-2.1. -3.4. | Resistance to Oxacillin (MRSA): 43.1% for cow, 40% buffalo, 8.7% sheep and 6.7% goat milk | N/R | [39] |
| 100 Iranian white and feta cheese samples collected from different suppliers | N/R | Mashhad (Iran) | -1.1. -2.1.1. -3.4.-3.2. | 8/23 (34.8%) of S. aureus isolates: 2 Iranian Feta cheese and 6 Traditional white cheese | N/R | [40] |
| 623 isolates of CPS were isolated from 78 bovine raw milk cheeses by different food control Laboratories originated from: 48 cheese curd and 30 finished cheese | N/R | Switzerland | -1.1. -2.1.2.-2.3. -3.2. | 1/623 (0.2%) | spa type t127 (human origin) | [41] |
| 100 traditional cheeses samples | January–December 2012 | Azerbaijan (Iran) | -1.1. -3.2. | 23/110 (21%) of S. aureus isolates | N/R | [42] |
| 94 S. aureus isolates: 87 cow’s milk with mastitis, 6 raw cheese, and 1 milking machine swab from 12 dairy farms | N/R | Pernambuco (Brazil) | -1.5. -2.4. -3.4. | None | N/R | [43] |
| 150 S. aureus strains were collected from curd cheese manufactured at artisan level from raw sheep milk | N/R | N/R | -1.1. -2.1.2. -3.3.-3.4. | None | N/R | [44] |
| 295 raw milk samples from supermarkets and farmers markets | July 2008–December 2012 | Shaanxi (China) | -1.3.9. -2.1.1. -3.4.-3.2. | 4/295 (1.4%) | - ST9/SCCmec IVb/t899 (4) - ST9/SCCmec II/t899 (1) | [45] |
| 565 milk and dairy products samples were collected from bovine, ovine, caprine and bubaline farms: 428 raw milk, 9 thermised milk, 8 curd, 7 “Ricotta” cheese, 8 yoghurt and 105 cheese | 2011–2013 | Central Italy | -1.1. -3.2.-3.4. | 2/227 (0.9%) of S. aureus isolates: 2 different “pasta filata” cheese samples | ST1 (CC1, human CA-MRSA)/spa type t127/SCCmec IVa | [46] |
| 120 samples from retail markets, street vendors and free range (reared) sheep and goat flocks: 15 raw buffalos’ milk, 15 sheep milk, 15 goat milk, 15 yogurt, 30 Kareish cheese and 30 ice cream | N/R | Ismailia (Egypt) | -1.3. -2.2. -3.2.-3.4. | 30/120 (25%): 5 goat milk (5/15, 33.3%), 3 sheep milk (3/15, 20%), 2 buffalo milk (2/15, 13.3%), 6 yoghurt (6/15, 40%), 4 ice cream (4/30, 13.3%) and 10 Kareish cheese (10/30, 33.3%) | N/R | [47] |
| 68 CPS isolates obtained from 100 samples of artisan double cream cheese | N/R | Pamplona (Colombia) | -1.1. -2.1. -3.2. | -9/100 (9%) -12/66 (18.2%) of S. aureus isolates | N/R | [48] |
| 2650 samples: 1035 raw cow milk, 895 raw sheep milk, 450 traditional cheese and 270 kashk (prepared by prolonged boiling yogurt) from retail stores | January 2006–December 2013 | Mazandaran (Iran) | -Homogenized: 1.7. -1.1. -2.1.1. -3.4.-3.2. | 53/2650 (2%): 21 cow milk, 11 sheep milk, 15 traditional cheese and 6 kashk | N/R | [49] |
| 1069 bovine raw milk samples, 910 goat milk powder processing samples and 245 powdered infant formula | July 2008–March 2014 | China | -First: 1.2. -Second: 1.3.4. -2.1.1. -3.4.-3.2. | None | N/R | [50] |
| 1050 food samples: 671 dairy products (66 cream, 45 traditional yoghurt, 271 raw milk, 47 traditional cream, 170 cheese, and 72 butter) | September 2013–June 2014 | Hamadan (Iran) | -1.12.1. -2.1.1. -3.4.-3.5.-3.2. | 5/98 (5.1%) of S. aureus isolates: 3 raw milk and 2 cheese | N/R | [51] |
| 200 food samples sold in a black market at an EU border: milk and dairy products (36%) | July 2012–February 2013 | Galati (Romania) | -1.1. -3.4.-3.3. | None | N/R | [52] |
| 383 raw milk samples from 101 vending machines | April–October 2012 | Milan and Monza-Brianza (Italy) | -1.1. -2.1.2. -3.4. | 7/383 (1.8%): 1.9% (2/101) from vending machines | - SCCmec IV (2 vending machines) | [53] |
| 75 dairy products confiscated from passengers on flights from non-EU countries: 74 cheeses and 1 butter | April 2012–June 2013 | International Bilbao Airport (Spain) | -1.1. -3.4.-3.3. | 1/75 (1.3%): 1 cheese sample | SCCmec IVc/ST1649 (CC6) (CA-MRSA) | [54] |
| 121 samples from different food markets: dairy products (1 pasteurized milk and 5 dry cakes) | August–October 2010 | Wuhou District of Chengdu city, Sichuan Province (China) | -1.5. -2.1.1. -3.2.-3.4. | None | N/R | [55] |
| 476 cow’s cheese and 453 raw cow’s milk for vending machine collected during official monitoring activities | 2008 | Italy | -1.1. -3.5.-3.4. | None | N/R | [56] |
| 200 samples of raw milk and dairy products (Damietta cheese, Kareish cheese, ice cream, and yogurt) from retail outlets, different shops and supermarkets | June–November 2012 | Mansoura (Egypt) | -1.1. -2.1.1. -3.2.-3.4. | 106/200 (53%): raw milk (30/40, 75%), Damietta cheese (26/40, 65%), Kareish cheese (16/40, 40%), ice cream (20/40, 50%), and yogurt samples (14/40, 35%) | N/R | [57] |
| 173 milk samples from apparently healthy and mastitic cows | December 2012– December 2013 | Sharkia (Egypt) | -1.1. -3.4.-3.2. | 30/173 (17.3%) | N/R | [58] |
| 51 raw milk and 5 local cheese from retail markets | July 2012–March 2013 | Kırşehir (Turkey) | -First: 1.2. -Second: 1.12. -2.1.1. -3.2. | None | N/R | [59] |
| 90 samples of typical sheep and goat cheeses (soft and semi-hard canestrato, ricotta, and cacioricotta) from dairies | October 2013–April 2014 | Southern Italy | -1.1. -2.1.2.-2.2. -3.2. | 1/37 (2.7%) of S. aureus isolates: ricotta cheese (ovicaprine) | N/R | [60] |
| 200 samples of raw and RTE Food illegally sold from a market at the Eastern EU Border: 73 dairy products (raw milk; cheeses made of cow, sheep, or goat raw or pasteurized milk, cream, and butter), from the Republic of Moldova, Ukraine, and Bulgaria | July 2012– February 2013 | Galati (Romania) | -1.1. -2.1.2. -3.10. | 0.03% Ewe cheese and Goat cheese | spa type t524 | [61] |
| 8 MRSA isolates, obtained from samples of fresh cheese (Doble Crema) elaborated from raw cow milk in small dairies collected at the retail level | April 2012–April 2013 | Colombia | -1.1. -2.1.1. -3.3.-3.4. | Isolates from 8 cheese samples carried the mecA gene | ST8/SCCmec IV/t024 (related to the USA300, CA-MRSA) | [62] |
| 56 CPS isolates recovered from samples of raw milk | N/R | Turkey | -Homogenized: 1.7. -1.1. -2.1. -3.5.-3.2. | 2/56 (3.6%) | N/R | [63] |
| 280 samples from markets: 140 yoghurt and 140 Nono | December–April | Kaduna (Nigeria) | -1.3.12. -2.1.1. -3.4.-3.9.-3.2. | -9/280 (3.2%) were identified using the Kirby-Baeur disk diffusion: 8 in nono (5.7%) and 1 yoghurt (0.7%) -6 (66.7%) were positive for the penicillin—binding protein and 7 (76.5%) were positive for betalactamase production - None of the 9 S. aureus was found to be positive for mecA | N/R | [64] |
| 280 samples of yoghurt and nono (traditionally fermented milk) from major markets | December–April | Zaria (Nigeria) | -1.3.12. -2.1.1. -3.4.-3.9.-3.2. | -8/280 (2.9%) were identified using the Kirby–Baeur disk diffusion: 4 nono and 4 yoghurt -5/8 (62.5%) out of the 8 MRSA were positive for the penicillin—binding protein and 6 (75%) were positive for betalactamase production -None of the 8 MRSA harbored the mecA gene | N/R | [65] |
| 910 samples: 62 raw goat milk samples from a milking station and 848 samples from seven different sampling sites in four goat milk powder processing plants (including tank milk, pre-spray drying areas, spray drying areas, powder-packaging room, ground and wall, workers, and final products) | September 2012–March 2013 | Shaanxi (China) | -First: 1.2. -Second: 1.3.4. -2.1.1. -3.2.-3.4. | 1/95 (1.1%) of S. aureus isolates: from the spray drying area (fluidized bed) | N/R | [66] |
| 900 bovine milk samples from private and public farms: 450 cattle and 450 buffalo) | N/R | Faisalabad (Pakistan) | -1.1. -2.3. -3.7.-3.2.-3.4. | 306/900 (34%): 135/450 (30%) cattle and 171/450 (38%) buffalo | N/R | [67] |
| 148 milk samples, 117 ghee samples (butter from milk) and 91 sour milk samples (fermented milk) from 196 homesteads | July–August 2013 | Sanga and Kanyaryeru (Uganda) | -Transportation: 1.5. -1.1. -2.4.-2.3. -3.3.-3.4.-3.11. | 23/41 (56.1%) of the S. aureus isolates: milk (15/30, 50%) and sour milk (8/11, 72.7%) (none carried the mecC) | -SCCmec V (21/23, 91.3%): t2112 (3), t127 (2, ST1), t14299 (1), t645 (1, ST121), t1398 (2), t3992 (1, ST97), t3772 (1) and unknown (10) -SCCmec IV: unknown (1) -SCCmec IVc: t7753 (1) | [68] |
| 3760 samples of milk and dairy products from several dairies | 2008–2014 | Apulia (Italy) | -1.1. -2.2. -3.2. | 40/484 (8.3%) of S. aureus isolates: 2 mozzarella cheese, 1 stracciatella cheese, 20 cheese, 1 scamorza cheese and 16 milk | - ST152/t355/SCCmec V (27/40, 67.5%) (CA-MRSA) (stracciatella cheese, cheese and milk) -ST398/t899/SCCmec V (7/40, 20%) (LA-MRSA) (cheese) -ST398/t899/SCCmec NT (1/40, 2.5%) (LA-MRSA) (milk) - ST398/t108/SCCmec V (2/40, 5%) (LA-MRSA) (mozzarella cheese) -ST1/t127/SCCmec IVa (2/40, 5%) (human origin) (milk) -ST5/t688/SCCmec V (1/40, 2.5%) (HA- and CA-MRSA) (scamorza cheese) | [69] |
| 71 traditional raw milk cheeses from local markets | N/R | Belgrade (Serbia) | -1.1. -2.1. -3.4.-3.3. | None | N/R | [70] |
| 50 traditional cheeses (25 Carra and 25 Surk) | August 2014–May 2015 | Hatay (Turkey) | -Homogenized: 1.7. -1.1. -2.1.1. -3.4.-3.2. | None | N/R | [71] |
| 64 yoghurt samples from local bazaars and markets: 55 were unpackaged and 9 were packaged | March 2016 | Şanlıurfa-Urfa (Turkey) | -1.1. -2.1.1. -3.2. | 2/64 (3.1%): unpackaged samples | N/R | [72] |
| 421 samples at different stages of processing from five dairies: 46 raw material, 161 food-contact surfaces, 96 non-food-contact surfaces, and 118 products | December 2013–July 2014 | São Paulo, Minas Gerais and Goiás (Brazil) | -1.1. -2.1.1. -3.4. | None | N/R | [73] |
| 175 samples: 125 dairy products samples (15 yoghurt, 40 white cheese, 10 kashar cheese, 15 tulum cheese, 12 mihalic cheese, 13 curd cheese, 10 sepet cheese, and 10 butter) from farms and retail markets | N/R | Balikesir (Turkey) | -1.4.3. -2.2. -3.9.-3.2.-3.4. | - 3/175 (1.7%) by Slidex MRSA latex agglutination test: 1 sample from tulum cheese -The mecA gene was detected in only one out of 17 S. aureus isolates (5.88%) | N/R | [74] |
| 200 samples of dairy products from supermarkets: “requeijão”, “requeijão light”, “especialidade láctea type requeijão” and “especialidade láctea type requeijão light” (50 of each) | 2015 | Jaboticabal, São Paulo (Brazil) | -1.1. -2.1. -3.2.-3.4. | None | N/R | [75] |
| 71 samples of raw milk, 212 samples of sour cream, 65 samples of home-made cottage cheese, and 57 washouts from the hands of the sellers of these products from food markets | N/R | Ukraine | -1.1. -2.1.-2.11. -3.2. | 39/247 (15.8%) of S. aureus isolates | N/R | [76] |
| 72 milk samples from mothers who had delivered in the hospital. | 16 February 2014–24 April 2016 | France | -1.1. -2.12.1. -3.2.-3.4. | Among the 62 S. aureus strains ten (16.2%) were phenotypically methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) | N/R | [77] |
| 51 S. aureus strains were collected from 51 samples of 6 dairy sheep farms, including two farms with artisan dairy facilities, with a history of MRSA in BTM: 2 raw cheese samples | 2013–2015 | Latium (Italy) | -1.1. -2.1.2. -3.3. | 27/51 (52.9%): 2 raw cheese | t127 (2) | [78] |
| 69 bovine milk, whey and cheese samples from farm dairies | During a five-month winter period | Mid-Norway | -Homogenized: 1.7. -1.1. -2.1.1. -3.2.-3.4. | None | N/R | [79] |
| 868 food samples of animal origin: 447 milk and dairy products confiscated from passengers on flights from 45 non-European Union (EU) countries by the Border Authorities, as well as 10 food products illegally introduced and sold in an open market closed to an EU border (the southeast part of Romania, on the border with Republic of Moldavia) | August 2012–July 2015 | Bilbao International Airport (Spain) and Vienna International Airport (Austria) | -1.1. -2.1. -3.4.-3.3. | 26/868 (3%): 21 milk and dairy products (cow, sheep or goat milk and cheese, either fresh, brined or with spices) (none harbored the mecC gene) | -The predominant sequence type was ST5 (30.8%) (HA and CA-MRSA), followed by ST8 (15.4%), ST1649 (15.4%) (both CA-MRSA), ST1, ST7, ST22, ST72, ST97, and ST398 (LA-MRSA) - More than 75% of the isolates were SCCmec type IV: 48.9% were IVc and IVe, 22.4% IVa, and 4.1% IVh, and 24.5% were SCCmec type V - Two isolates were not typeable by SmaI-PFGE suggesting they may be ST398 (livestock clone) | [80] |
| 360 traditional cheese samples | N/R | Mazandaran (Iran) | -3.2.-3.4. | 199/224 (88.8%) of S. aureus isolates | N/R | [81] |
| 360 samples of pastry cream products sold in the local markets | June 2016– May 2017 | Amol (Iran) | -1.1. -2.1. -3.2.-3.4. | -11/360 (3.1%) -No MRSA isolate was identified amongst winter samples | N/R | [82] |
| 495 food samples from foodstuffs: 141 raw milk, 60 pasteurized milk and 80 pastry from farms and supermarkets | November 2014–November 2015 | Algeria | -1.1. -2.1.1. -3.3.-3.4. | 26/153 (17%): 11 raw milk, 2 pasteurized milk, and 1 pastry | SCCmec IV (9 raw milk, 2 pasteurized milk and 1 pastry), V (1 raw milk), and II (1 raw milk) | [83] |
| 120 samples of cheeses belonging to “traditional agri-food products”: 12 hard cheese, 20 semihard cheese and 88 fresh cheese | October 2014–May 2016 | Apulia (Italy) | -1.1. -2.1.2. -3.2. | None | N/R | [84] |
| 81 raw milk dairy products handcrafted from a total of 40 small-scale dairies: 23 raw milk, 7 curd, 39 goat or bovine cheese, 11 butter, and 1 cream | 2016 | Lombardy Region (Italy) | -1.1. -2.1.2. -3.3. | 3/163 of S. aureus isolates (1.7%) (none mecC positive) | N/R | [85] |
| 276 samples from different stages along cheese production process: 36 raw milk, 36 whey, 36 curd, 36 brine, 36 drying worktops, and 96 cheeses | 2010–2012 | Italy | -1.1. -3.3. | None | N/R | [86] |
| 115 Staphylococcus spp. isolates from and milk from healthy cows on 30 farms | November 2013–March 2014 | Tunisia | -1.4.4. -2.4. -3.3.-3.4. | 1/24 (4.2%) of S. aureus isolates (mecA positive) | ST97/t267/agr I/SCCmec V | [87] |
| 1102 breast milk samples from pediatric patients’ mothers in a university hospital | January 2015–December 2016 | Shanghai (China) | -1.1. -2.3. -3.4.-3.2. | 15/71 (21.1%) of S. aureus isolates | -ST398 (CC398)/SCCmec V: t034 (2) and t6606 (1) (LA-MRSA) -ST398 (CC398)/t571: SCCmec IV (1) and SCCmec V (1) (LA-MRSA) -ST59 (CC59)/SCCmec IV: t172 (3), t437 (1) and t3736 (1) (CA-MRSA) -ST1 (CC1)/t127/SCCmec IV (1) -ST188 (CC1)/t189/SCCmec IV (1) -ST615 (CC72)/t324/SCCmec IV (1) -ST88 (CC78)/NT/SCCmec IV (1) -ST88 (CC78)/t15319/SCCmec V (1) | [88] |
| 117 raw milk samples from local shops | January–June 2015 | Morogoro (Tanzania) | -1.1. -2.1. -3.2.-3.4. | 2/46 (4.4%) of S. aureus isolates -CN-MRSA was 4.2% | -Only one of the coagulase-negative variants of MRSA was typeable: t2603 -The other 2 mecA positive isolates were untypable | [89] |
| 200 samples: 100 fresh milk and 100 locally produced soft cheese (wara) | N/R | Abeokuta (Nigeria) | -1.1. -2.4. -3.4.-3.9. | 50/200 (25%): 15 wara and 35 raw milk | N/R | [90] |
| 19 samples of dairy products: pre-packaged soft and hard cheese, yogurt, and butter | January–May 2016 | Epirus (Greece) | -2 methods: ·1.1. ·1.3.10. -2.1.1. -3.3.-3.4. | None | N/R | [91] |
| 400 milk samples of bovines from dairy farms and outlets | N/R | Jabalpur (India) | -First: 1.4.3. -Second: 1.3.6. -2.5. -3.2.-3.4. | The prevalence of PVL-positive S. aureus was 10.5% and all were MRSA | t657, t1839, t2526, t7286, t7684 | [92] |
| 26 samples from 21 milk collection centers from various retailers | N/R | Kampala (Uganda) | -1.3.2. -2.3.2.-2.14. -3.4.-3.3. | 1/26 (3.8%) (negative for mecA and mecC) | N/R | [93] |
| 360 samples from dairy shops, grocery stores, street vendors at different markets: 100 raw milk (caw and buffalo), 120 cheese (40 of each Kariesh cheese, white cheese, and Ras cheese), 70 yoghurt, and 70 cream | January 2016–March 2017 | Alexandria, (Egypt) | -1.1. -2.1.1. -3.4.-3.2. | -31/360 (8.6%): 11 raw milk, 1 Kariesh cheese, 9 white cheese, 3 ras cheese, 2 yoghurt, and 5 cream - 34/81 (42%) of S. aureus isolates were resistant to cefoxitin: 12 raw milk, 1 Kariesh cheese, 9 white cheese, 3 ras cheese, 2 yoghurt, and 7 cream | N/R | [94] |
| 350 samples of milk and dairy products from retail outlets: market milk, Domiati cheese, Kareish cheese, Ras cheese, cooking butter, yoghurt, and small-scale ice cream (50 of each) | April 2017–June 2018 | Assuit province (Egypt) | -1.6. -2.1.-2.4.-2.6. | 54/350 (15.4%): 9 market milk, 2 Kareish cheese, 19 Ras cheese (38%), 7 cooking butter, and 17 small-scale ice cream (34%) | N/R | [95] |
| 150 raw milk samples from retails: 80 samples from street peddlers and 70 sample from farmers | N/R | Kafr Elsheikh governorate (Egypt) | -1.7. -2.1. -3.4.-3.2. | 2/5 (40%) of S. aureus isolates | N/R | [96] |
| 650 milk and dairy products from several markets, delicatessens, and open bazaars: 190 raw milk samples (154 cow milk and 36 sheep milk), 180 cheeses, 125 yoghurts, 60 butters, 40 butter cream (raw), and 55 ice creams | May 2016–August 2017 | Bursa (Turkey) | -1.4.3. -2.2. -3.11.-3.4.-3.2. | -12/650 (1.9%): 1 butter, 8 cheese, 1 ice cream, and 2 milk samples -148/650 (22.8%) produced typical MRSA colonies on CHROMagar MRSA II: 77 cheeses, 25 butter, 23 butter cream, 15 milk, 7 ice cream, and 1 yogurt -According to oxacillin MICs, 95 isolates (64.2%) were confirmed as phenotype-positive MRSA -53 isolates (35.8%) were regarded as oxacillin (methicillin)-susceptible S. aureus -Presence of the mecA gene in 12 MRSA strains: 3 susceptibile to oxacillin (phenotype negative but mecA positive MRSA and 9 oxacillin resistant (phenotype/mecA positive) | N/R | [97] |
| 10 raw and pasteurized milk from retail vendors | N/R | Dhaka (Bangladesh) | -1.1. -2.1. -3.4.-3.2. | None | N/R | [98] |
| 305 samples were collected from four dairy plants: 74 samples of dairy products (pre-packaged soft and hard cheese, yogurt, and butter) | December 2016–May 2017 | Thrace and Macedonia (Greece) | -1.1. -2.1.1. -3.4.-3.3. | None | N/R | [99] |
| 109 samples from dairy workers and dairy products (butter) | N/R | Balaju, Kathmandu (Nepal) | -1.1. -2.4. -3.5. | 4/11 (36.4%) of S. aureus isolates in butter | N/R | [100] |
| 49 raw milk and 47 paneer cheese from street food vendors | September 2015–May 2016 | Delhi and Bareilly (India) | -2.5. -3.2.-3.1. | -7/49 (14.3%) in raw milk -None in paneer cheese | N/R | [101] |
| 190 raw cow milk samples and 80 traditional dairy products (24 butter, 3 cheese, 24 rayeb, and 29 l’ben) from 25 dairy farms, 25 milk tanks, 5 dairy units, and 4 local markets | April–September 2014 and 2015 | Tizi Ouzou (Algeria) | -1.12.1. -2.4. -3.3.-3.4. | 11/270 (4.1%): 9 raw milk and 2 acidified milk (l’ben) | ST8/t024 (all isolates) | [102] |
| 35 S. aureus strains: 3 cow milk, 2 goat milk, 7 sheep milk, and 8 cheese | December 2017– February 2019 | N/R | -3.4.-3.5.-3.2. | None | N/R | [103] |
| 13 S. aureus isolates of pasteurized milk from 258 samples | July 2011–June 2016 | China | -3.5.-3.3.-3.4. | None | N/R | [104] |
| 180 samples of milk and milk products: 34 fresh cow milk, 14 bulk milk, 66 locally fermented milk (nono), and 66 locally pasteurized milk (kindirmo) | N/R | Nasarawa (Nigeria) | -1.2. -2.1.1. -3.2.-3.4. | 9/180 (5%): bulk milk (1/14, 7.1%), nono (4/66, 6.1%), kindirmo (3/66, 4.6%), and fresh milk (1/34, 2.9%) | N/R | [105] |
| 220 dairy cows from dairy farms mastitic cows’ milk | November 2014–May 2015 | Shire, Tigray (Ethiopia) | -1.1. -2.3.1.-2.4. -3.4.-3.2. | -64/220 (29.1%) were positive for bovine mastitis -21/64 (32.8%) were found CoPS -7/21 (33.3%) of the CoPS were resistant to oxacillin (phenotypically MRSA positive). -5/7 (71.4%) of them were found to carry mecA genes | N/R | [106] |
| 139 foodstuff samples including dairy products (cheese, cottage, and yogurt) and meat products (sausages and hamburgers) belonging to 18 different brands from 29 stores | September 2015–October 2016 | Isfahan (Iran) | -1.12. -2.1.1. -3.4.-3.2. | 9.5% of S. aureus isolates | N/R | [107] |
| 200 raw milks (145 from goat and 55 from sheep) | June to September | Abeokuta (Nigeria) | -1.3.10. -2.4. -3.12.-3.4.-3.9. | 37/200 (18.5%): 14 (25.5%) sheep and 23 (15.9%) goat | N/R | [108] |
| 959 samples representing eight types of animal-based foods (pork, chicken, beef, duck, lamb, aquatic products, egg, and milk) from local markets (including 21 supermarkets and 18 wet markets) | July 2018–August 2019 | Shanghai (China) | -1.6. -2.1.1. -3.4.-3.2. | None | N/R | [109] |
| 90 raw cow milk samples from unorganized farms, milk vendors and shops | July 2018–June 2019 | Aizawl, Mizoram (India) | -1.7. -2.1.-2.4. -3.2.-3.4. | 2/39 (5.1%) of S. aureus isolates | N/R | [110] |
| 590 raw milk samples from shopping centers: 130 bovine, 120 ovine, 120 caprine, 110 camel, and 110 buffalo | 2016–2017 | Iran | -1.3.1. -2.1.1. -3.1.-3.2. | 28/39 (71.8%) of S. aureus isolates: 8 bovine, 7 ovine, 4 caprine, 1 camel, and 8 buffalo | -SCCmec IVa (8/28, 29.6%, CA-MRSA): 3 bovine, 1 ovine, 1 caprine, and 3 buffalo -V (7/28, 25%, CA-MRSA): 1 bovine, 2 ovine, 1 caprine, and 3 buffalo -III (4/28, 14.8%, HA-MRSA): 2 bovine, 1 ovine, and 1 buffalo -IVb (3/28, 11.1%, CA-MRSA): 1 bovine, 1 ovine, and 1 caprine -IVc (2/28, 7.4%, CA-MRSA): 1 ovine and 1 caprine -I (2/28, 7.4%, HA-MRSA): 1 bovine and 1 buffalo -IVd (1/28, 3.7%, CA-MRSA): 1 ovine -II (1/28, 3.7%, HA-MRSA): 1 camel | [111] |
| 200 samples from local markets, dairy shops and supermarkets: 100 raw milk, 50 Talaga cheese (made from pasteurized milk) and 50 Kareish cheese (made from raw milk) samples | N/R | Beni-Suef Governorate (Egypt) | -2.1. -3.2.-3.4. | 4/6 (66.7%) cefoxitin resistant MDR S. aureus isolates | N/R | [112] |
| 54 raw milk and 43 dairy products (23 butter, 6 rayeb, 12 l’ben, and 2 yogurt samples) from cafeteria and creameries | 2017–2018 | Tizi Ouzou (Algeria) | -2.1.1. -3.3.-3.4. | 5/59 (8.5%) of S. aureus isolates (harbored the mecA gene): 4 rayeb and 1 raw milk | ST5: t450 (1 raw milk) and t688 (4 rayeb) | [113] |
| 100 samples of pasteurized camel milk from different retail markets | March–May 2017 | Al-Riyadh (Saudi Arabia) | -1.1. -2.1.1. -3.2.-3.5.-3.4. | 10/100 (10%) | N/R | [114] |
| 50 fresh milk and 50 fermented milk from retailing outlets | Sokoto (Nigeria) | -1.1. -2.4.-2.6. -3.2. | 6/50 (12%) fresh milk and 11/50 (22%) fermented milk | N/R | [115] | |
| 210 skimmed dairy products samples from local markets: street vendor Kareish cheese, supermarket Kareish cheese, light Feta cheese, light processed cheese, light plain yoghurt, packed and unpacked skimmed milk powder (30 of each) | May 2018–August 2019 | Alexandria City (Egypt) | -1.1. -2.1.1. -3.2.-3.4. | 7/210 (3.3%): street vendor Kareish cheese (2/30, 6.7%), supermarket Kareish cheese (2/30, 6.7%), light Feta cheese (1/30, 3.3%), light plain yoghurt (1/30, 3.3%), and packed skimmed milk powder (1/30, 3.3%) | N/R | [116] |
| 50 karish cheese samples | December 2018–December 2019 | Al-Qalyubia governorate (Egypt) | -1.8. -2.1.-2.3.1. -3.4.-3.2. | 2/19 (10.5%) of S. aureus isolates | N/R | [117] |
| 100 dairy products from different farms and local grocery shops: 50 raw milk (unpasteurized) samples (origins were from 11 horses, 20 goats, 15 camels, and 4 cows) and 50 unpacked cheese samples | August 2019–March 2020 | Riyadh (Saudi Arabia) | -1.5. -2.4.-2.2.-2.4.2. -3.4.-3.13. | -51/70 (72.9%) of S. aureus isolates: 34 from raw milk (7 horses (70%), 12 goats (75%), 11 camels (91.7%), and 4 cows (100%)) and 17 from unpacked cheese -5/51 (9.8%) of MRSA isolates were positive for mecA gene (neither mecC nor mecB genes were positive): 4 raw milk (2 horses and 2 camels) and 1 unpacked cheese | Among 5 mecA-positive isolates: -4/5 SCCmec type II (80%) -the type of one isolate from cheese samples could not be detected -three isolates had two types, II + V, II + IVa, and II + IVd -one isolate had three types II + III + V | [118] |
| 140 dairy product samples (soft cheese made from raw cows’ milk) from six dairy industry sites | N/R | Jalisco (Mexico) | -2.1.1. -3.4.-3.2. | 9/63 (14%) of the S. aureus isolates | N/R | [119] |
| 255 dairy product samples from farms and retail markets: 175 raw milk and 80 traditionally processed dairy products (40 yogurt and 40 cottage cheese) | December 2019–May 2020 | Addis Ababa (Ethiopia) | -1.3.13. -2.4. -3.4.-3.3. | 20/52 (38.5%) of S. aureus isolates resistant to cefoxitin (only one of these isolates (5%) was positive for mecA gene, and none of them were positive for the mecC gene) | N/R | [120] |
| 285 samples of raw milk and unpackaged artisanal dairy products from local bazaars, retail outlets, and raw milk collection areas: 50 raw milk, 50 traditional cheeses consisting of white-pickled cheese, 50 Tulum cheese, 25 yogurt, 25 butter, 20 traditional clotted cream, 50 pastry cream, and 15 traditional Maras ice cream | January 2020–April 2021 | Central Anatolia and Mediterranean Regions (Turkey) | -1.1. -2.1.1. -3.3. | 5/285 (1.7%): -mecA gene (2): raw milk and a white pickled cheese -mecC gene (2): two different pastry creams -both mecA and mecC genes (1): pastry cream -None of the strains from Tulum cheeses were positive with either mec genes | N/R | [121] |
| 175 samples of fermented dairy products from different shops and supermarkets: 50 plain yoghurt, 50 fruit yoghurt, 50 laban rayeb, and 25 mish cheese | N/R | Dakahlia Governorate (Egypt) | -3.2. | 2/10 (20%) of selected S. aureus isolates | N/R | [122] |
| 30 Karish cheese (made from raw buffalo milk) from 10 markets | N/R | Mansoura district, Dakahlia Governorate (Egypt) | -1.3. -2.1.1. -3.2.-3.4. | 3/5 (60%) of S. aureus isolates | N/R | [123] |
| 112 samples of ‘coalho’ cheese (artisanal rennet cheese produced with raw milk) from 56 dairy producing farms | March–December 2018 | State of Ceará (Brazil) | -2.1. -3.7.-3.2. | -7/69 (10.1%) of S. aureus isolates -5/69 (7.3%) resistance to oxacillin | N/R | [124] |
| 380 raw milk samples from sales centers: 120 cow, 130 sheep, and 130 goat | The spring and summer of 2021 | Alborz (Iran) | -1.3.13. -2.1.1. -3.1.-3.2.-3.4. | 27/42 (64.3%) of S. aureus isolates: 10 cow, 9 sheep, and 8 goat | N/R | [125] |
| 109 samples of dairy cow’s milk from dairy farms | July–September 2021 | Probolinggo, East Java (Indonesia) | -1.14. -2.4. -3.1.-2.6.-3.2. | -5/54 (9.3%) of S. aureus isolates resistant to cefoxitin and oxacillin. All in ORSAB Test -2/5 (40%) were positive for the mecA gene | N/R | [126] |
| 80 milk and dairy product samples from on twelve sheep and goat farms: 18 milk samples, 28 fresh cheeses, 20 ripened cheeses, and 14 yoghurts | July–November 2021 | Czech Republic | -3.2. | 11/27 (40.7%) positive detected SA DNA samples by PCR: 6 fresh goat cheeses, 3 ripened sheep cheeses, and 2 ripened goat cheeses | N/R | [127] |
| 40 food products from retail establishments and supermarkets (20 of each): raw milk and Damietta cheese | November 2021–September 2022 | Alexandria (Egypt) | -First: 1.4.3. -Second: 1.11.3. -2.6. -3.2.-3.4. | 3/40 (7.5%): 2 raw milk and 1 Damietta cheese | N/R | [128] |
| 700 unpasteurized raw cow’s milk samples from 20 retail outlets | February 2019–March 2020 | Mansoura, Dakahliya governorate (Egypt) | -2.4. -3.4.-3.2. | 37/113 (32.7%) of PVL-positive S. aureus | N/R | [129] |
| 62 samples milk and fresh soft cheese from farms | N/R | Wielkopolskie and Zachodniopomorskie Provinces (Poland) | -1.1. -2.1. -3.4.-3.2. | 2/39 (5.1%) of S. aureus isolates | N/R | [130] |
| 69 different raw milk samples from handmade dairy products retail stores | August 2020–May 2021 | Hefei, Anhui (China) | -1.3.4. -2.7. -3.2.-3.4. | 6/50 (12%) of S. aureus isolates | -spa t030 (3) -t4431 (3) | [131] |
| 110 homemade clotted cream samples from the public bazaars: 85 cow milk, 14 water buffalo milk, and 11 cow and water buffalo milk | November 2019–December 2020 | Afyonkarahisar (Turkey) | -1.5. -2.1.1. -3.2. | None | N/R | [132] |
| 328 milk samples were collected: raw milk samples were collected from dairy farmers (n = 169) and dairy vendors (n = 139) in both the states while pasteurized milk samples were only collected from milk retail outlets/grocery shops (n = 20) in Haryana | December 2016–November 2017 | Haryana and Assam (India) | -1.14. -2.17. -3.1.-3.3. | -3 MRSA isolates from raw milk from vendors in Haryana -2 MRSA isolates from pasteurized milk | SCCmec type V | [133] |
| 354 samples of milk and milk products from the households and local markets: 123 cow milk, 148 cheese, and 83 yoghurts | May 2020–March 2021 | West Showa Zone (Ethiopia) | -1.5. -2.4. -3.4.-3.2. | None | N/R | [134] |
| 55 dairy products from various outlets: 25 raw yogurt and 30 ice cream | November 2021–January 2022 | Baghdad (Iraq) | -3.9.-3.4. | 12/28 (42.9%) of S. aureus isolates: 8 (47.1%) raw yogurt and 4 (36.4%) were ice cream | N/R | [135] |
| 30 raw milk and 60 cheese samples from different foodstuffs | August–November 2021 | Kafr El-Sheikh governorate (Egypt) | -2.6. -3.3. | -4/30 (13.3%) raw milk -3/60 (5%) cheese (none were positive for mecC) | N/R | [136] |
| 40 raw milk samples from milk stores | N/R | Faisalabad (Pakistan) | -3.4.-3.5.-3.2. | 2/73 (2.7%) of S. aureus isolates | N/R | [137] |
| 100 raw milk samples from the sales points | N/R | Van (Turkey) | -2.1. -3.4.-3.2. | 2/48 (4.2%) of S. aureus isolates | N/R | [138] |
| 380 raw milk and traditionally produced dairy samples including cow milk (50), sheep milk (40), goat milk (50), cheese (40), cream (40), butter (40), yogurt (40), doogh (40), and kashk (40) were collected from different shopping centers | September 2021–March 2022 | Urmia (Iran) | -1.3.1. -2.1.1. -3.1.-3.2.-3.4. | 38/60 (63.3%) of S. aureus isolates: 5 cow milk, 3 sheep milk, 2 goat milk, 9 cheese, 6 cream, 6 butter, 2 yogurt, 3 doogh, and 2 kashk | N/R | [139] |
N/R, Not Reported. Meaning of the numbers used in the detection method column. 1. Pre-enrichment: 1.1. without pre-enrichment; 1.2. pre-enrichment in buffered peptone water, BPW; 1.3. pre-enrichment in tryptone soy broth, TSB (1.3.1. TSB containing 10% NaCl and 1% sodium pyruvate; 1.3.2. TSB containing 4% NaCl, 1% mannitol, 4 mg/L cefoxitin, and 75 mg/L aztreonam; 1.3.3. TSB supplemented with 75 mg/L aztreonam and 3.5 mg/L cefataxime; 1.3.4. TSB containing 7.5% NaCl; 1.3.5. TSB supplemented with 5 mg/L oxacillin; 1.3.6. TSB supplemented with 75 mg/L aztreonam and 4 mg/L cefoxitin; TSB 1.3.7. supplemented with 75 mg/L aztreonam and 3.5 mg/L cefoxitin; 1.3.8. TSB supplemented with 50 mg/L aztreonam and 3.5 mg/L cefoxitin; 1.3.9. TSB at 2× containing 15% NaCl; 1.3.10. TSB containing 6.5% NaCl; 1.3.11. TSB-YE (yeast extract) at 2×; 1.3.12. TSB supplemented with 70 mg/mL NaCl; 1.3.13. TSB containing 10% NaCl); 1.4. Mueller–Hinton Broth, MHB (1.4.1. MHB containing 6% NaCl; 1.4.2. MHB containing 7.5% NaCl; 1.4.3. MHB containing 6.5% NaCl; 1.4.4. MHB containing 10% NaCl); 1.5. Brain Heart Infusion broth, BHI (1.5.1. BHI containing 2% NaCl); 1.6. sodium chloride broth (10%); 1.7. peptone water, PW; 1.8. nutrient broth, NB (1.8.1. NB containing 7.5% NaCl and oxacillin (6 μg/mL)); 1.9. cooked meat broth; 1.10. phosphate-buffered saline; 1.11. phenol red mannitol broth, PHMB (1.11.1. PHMB containing cefoxitin (5 mg/L) and aztreonam (75 mg/L); 1.11.2. PHMB containing oxacillin (4 mg/L); 1.11.3. PHMB containing ceftizoxime (5 μg/mL) and aztreonam (75 μg/mL)); 1.12. Giolitti–Cantoni broth, GCB (1.12.1. CGB supplemented with 3.5% potassium tellurite solution); 1.13. sodium chloride broth (7.5%); 1.14. mannitol salt broth (MSB); 1.15. sodium chloride broth (6.0%). 2. Solid media: 2.1. Baird–Parker agar, BP (2.1.1. BP supplemented with egg yolk tellurite emulsion; 2.1.2. BP supplemented with rabbit plasma fibrinogen (BP-RPF); 2.1.3. BP supplemented with egg yolk and potassium tellurite; 2.1.4. selective media); 2.2. selective MRSA agar (BBL CHROM agar MRSA; BD) MRSA chromogenic agar; 2.3. blood agar, BA (2.3.1. BA supplemented with sheep blood; 2.3.2. 5% bovine BA); 2.4. mannitol salt agar, MSA (2.4.1. MSA supplemented with 75 mg/L aztreonam and 6 mg/L oxacillin; 2.4.2. MSA supplemented with oxacillin (4.0 mg) (MSAO)); 2.5. HiChrome MeReSa agar plates with cefoxitin and methicillin supplement (HiMedia); 2.6. oxacillin-resistance-screening-agar-base (ORSAB) supplemented with oxacillin (2 mg/L); 2.7. tryptone soy agar, TSA (2.7.1. TSA with 5% sheep blood and 0.1% esculin); 2.8. chromogenic media (MRSA-Ident-Agar); 2.9. CNA plates (Columbia colistin and nalidixic acid); 2.10. Oxacillin Salt Screen Agar® (MHA with 4% NaCl and 6 µg/mL oxacillin)/oxacillin agar screen sensitivity disk agar-N supplemented; 2.11. Chrom-ID MRSA agar; 2.12. Columbia agar (CA) (2.12.1. CA supplemented with 5% sheep blood); 2.13. MRSA select medium; 2.14. Brilliance MRSA Agar (chromogenic selective agar for MRSA); 2.15. MRSAselect® (BioRad, Hercules, CA, USA) agar (selective chromogenic MRSA agar); 2.16. CHROMagar S. aureus; 2.17. Staphylococcus Agar (Hi-media). 3. Identification of MRSA: 3.1. Cefoxitin (30 μg) and oxacillin (1 μg) disk diffusion susceptibility tests; 3.2. PCR-based amplification of mecA gene; 3.3. PCR-based amplification of mecA and mecC genes; 3.4. antimicrobial susceptibility testing; 3.5. cefoxitin disk diffusion method; 3.6. StaphType DNA microarray assay; 3.7. oxacillin disk diffusion method; 3.8. MICs of oxacillin by broth microdilution method; 3.9. MRSA latex agglutination test (penicillin-binding protein 2a latex agglutination test); 3.10. S. aureus spa typing; 3.11. oxacillin E-test strips; 3.12. Mueller–Hinton agar containing cefoxitin and oxacillin; 3.13. PCR-based amplification of mecA, mecB and mecC genes. Baird–Parker: BP; brain heart infusion: BHI; buffered peptone water: BPW; coagulase-positive Staphylococcus: CPS; Giollotti-Cantoni Broth: GCB; Mannitol Salt Agar: MSA; Mannitol Salt Broth: MSB; Mueller–Hinton agar: MHA; Mueller–Hinton broth: MHB; Not typable: NT; peptone water: PW; phenol red mannitol broth: PHMB; ready-to-eat: RTE; Tryptone Soya Agar: TSA; Tryptone Soya Broth: TSB.

Table 2.
Prevalence of MRSA in bulk-tank milk (BTM) (in the absence of clarification, the prevalence is considered based on the detection of mecA gene).
Table 2.
Prevalence of MRSA in bulk-tank milk (BTM) (in the absence of clarification, the prevalence is considered based on the detection of mecA gene).
| Samples | Period | Place | Detection Method | Prevalence | Identification | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 farms of cows: one sample of each | June 2005–August 2006 | Hungary | -1.1. -2.1.1. -3.4. | None | N/R | [140] |
| 279 S. aureus isolates from bulk bovine milk from 279 dairy farms | July 2001 | Hokkaido (Japan) | -1.1. -2.10. -3.4.-3.2. | None | N/R | [141] |
| 70 unpasteurized milk samples from bulk milk tanks on different dairy farms | N/R | N/R | -1.8. -3.2.-3.4. | None | N/R | [142] |
| 1061 samples from 95 farms (89 cow farms, 2 goat farms, and 4 sheep farms): 478 BTM samples | 2006–2009 | Czech Republic | -First: 1.4.3. -Second: 1.3.7. -2.1.-2.15. -3.2.-3.4. | 22/299 (7.4%) of S. aureus isolates: 18 cows and 4 goats | -SCCmec IV: 13 cows, 4 goats (CA-MRSA) -SCCmec V: 5 cows (CA-MRSA) | [143] |
| 34 BTM samples from a veterinary university goat breeding farm | June 2006–March 2008 | Brno (Czech Republic) | -First: 1.4.3. -Second: 1.3.7. -2.1.-2.6. -3.2.-3.4.-3.7. | -4/34 (11.8%) | SCCmec IV/t064 | [144] |
| A single BTM sample was collected from each of 542 participating operations from dairy cows, which were collected as part of the National Animal Health Monitoring System | 2007 | California, Idaho, New Mexico, Texas, Washington, Indiana, Iowa, Kentucky, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Vermont, Virginia, and Wisconsin (USA) | -1.1. -2.2. -3.2. | None | N/R | [145] |
| 28 samples of fresh milk were collected from 7 milking containers per 4 dairy cattle farms from commercial farms | N/R | Rooigrond, Molelwane, Lokaleng and Mogosane (South Africa) | -1.1. -2.4. -3.4. | Resistant to methicillin: -Lokaleng 93.2% and Mogosane 81.2% (both communal farms) -Rooigrond: 7% -Molelwane: 5.7% | N/R | [146] |
| 100 BTM samples | March–September 2009 | Switzerland | -First: 1.4.3. -Second: 1.11.1. -2.14. -3.2.-3.4. | None | N/R | [22] |
| 193 Milk filters and 184 BTM samples were collected from 78 dairy production holdings supplying the farmhouse cheese sector | April–August 2005; September 2005–February 2006; March–August 2006 | Ireland | -1.1. -2.1. -3.4.-3.2. | None | N/R | [147] |
| 180 BTM samples of 180 dairy cow farms | 2009 | Northern Württemberg (Germany) | -First: 1.4. -Second: 1.3.7. -2.8. -3.2. | 4/180 (2.2%) | N/R | [148] |
| S. aureus LGA251 and S. aureus LGA254 were isolated from a BTM bovine sample from a farm | May 2007 | Somerset (England) | -1.1. -3.9.-3.2.-3.4. | 2/2 (100%) | ST425 (CC425): t6300 (LGA251) and t6292 (LGA254) | [149] |
| BTM samples from dairy cows of 60 dairy herds | February–September 2010 | Brandenburg, Lower Saxony and Saxony Anhalt (Germany) | -First: 1.4.3. -Second: 1.3.7. -2.14. -3.2.-3.4. | -4/60 dairy farms (6.7%) -36 MRSA isolates from bovine milk: ·5 isolates were obtained from the MRSA-positive strains of the 60 dairy farms in this study ·31 isolates originated from the Bundesinstitut für Risikobewertung (Federal Institute for Risk Assessment): 13 isolates from a national monitoring project on BTM (ZoMo 2009), and 18 other BTM isolates submitted to the National Reference Laboratory in 2009 and 2010 | -CC398: t011 (22 isolates, 61%) and t034 (14 isolates, 39%) -SCCmec V (33 isolates, 92%), III (2), and IVa (1) | [150] |
| BTM samples were collected once from all three dairy cattle herds | 2008 | Stuttgart (Southwest Germany) | -First: 1.4.3. -Second: 1.3.7. -2.8. -3.2.-3.4. | 3/3 (100%): all 3 herds | t011/SCCmec V (LA-MRSA) | [151] |
| BTM samples from 139 farms: 703 herds of cows, 1 goat herds, and 8 sheep herds | N/R | Czech and Slovak Republic | -First: 1.4.3. -Second: 1.3.7. -2.1.-2.15.-2.6. -3.2.-3.4. | -20/326 (6.1%) of S. aureus isolates: in cows | -SCCmec IV (13) -SCCmec V (7) | [152] |
| 160 milk samples (32 per HACCP level) | August 2011–January 2012 | Hawassa (South Ethiopia) | -1.1. -2.4. -3.4. | Resistant to oxacillin: -Bucket at farm level: 15% -From storage containers at milk collection center: 66.7% -From transportation container: 100% -After cooling at the pasteurization plant: 83.3% | N/R | [153] |
| 150 pooled BTM samples from 50 farms | April, May, July, August, October, and November 2009 | Minnesota | -First: 1.4.3. -Second: 1.11.2. -2.13.-2.9. -3.4.-3.3. | 2/150 (1.3%): the herd prevalence is 4% (2/50) | -ST5/unknown spa type/PFGE type close to USA100/SCCmec II (HA- MRSA) -ST8/spa type t121/PFGE type USA300/SCCmec IVa (CA-MRSA) | [154] |
| 635 samples from dairy cow herds were collected in the framework of the national monitoring | January 2009– August 2010 | Germany | -First: 1.4.3. -Second: 1.3.7. -2.14. -3.2.-3.4. | 28/635 (4.4%): 36 isolates | -CC398: t011 (22 isolates, 61%) and t034 (14 isolates, 39%) -SCCmec V (33 isolates, 92%), III (2) and IVa (1) | [155] |
| 384 samples were collected from refrigerated tanks of ewe milk | April 2009–March 2010 | Spain | -1.1. -2.1.2.-2.12.1. -3.2. | None | N/R | [156] |
| 1500 BTM samples were supplied by National Milk Laboratories Ltd., in dairy cattle | January–July 2012 | United Kingdom | -1.4.3. -2.14. -3.3. | Approximately 300 potential MRSA colonies were identified and subjected to PCR testing, yielding a total of 7 mecA MRSA isolates from 5 farms | CC398 (ST398): -t011 (6/7): 3 SCCmec IVa and 3 SCCmec V(5C2&5)c (SCCmec V harbouring the czrC gene in the J1 region) -t2546/IVa (1/7) | [157] |
| 48 samples were taken one on each of the 45 dairy farms among those having experienced MRSA isolation from BTM in the previous 3 years | October–December 2010 | Ragusa (South-Eastern Sicily) | -1.5.1. -2.4.1. -3.5.-3.2. | 21/48 (44%) | N/R | [158] |
| Bulk-tank goat’s milk of 26 farms | Monthly for 3 consecutive months | Sardinia (Italy) | -1.1. -3.2.-3.8. | None | N/R | [159] |
| 372 milk samples: 18 bulk milk | Kaduna and Zaria (Nigeria) | -1.1. -2.1. -3.4.-3.2. | 18/47 (4.8%) of coagulase-positive S. aureus were resistant to methicillin: 2 in bulk milk | N/R | [38] | |
| 601 S. aureus isolates obtained from BTM samples collected from 229 dairy sheep farms | August 2008–July 2009 | Ávila, Burgos, Cáceres, León, Madrid, Palencia, Salamanca, Segovia, Valladolid and Zamora (Spain) | -1.1. -2.1. -3.3.-3.4. | -1/229 farms (0.4%) (1/601 S. aureus isolates) contained mecC -3/229 farms (1.3%) (9/601 S. aureus isolates) tested positive for mecA | -ST130/SCCmec XI (1 mecC) -ST398 (3 mecA): SCCmec V (2) and SCCmec IVa (1) | [160] |
| BTM samples from 288 dairy farms (192 organic and 100 conventional farms) | March 2009–May 2011 | New York, Wisconsin, and Oregon (USA) | -Two methods: ·1.1.-2.7.1.-3.2. ·Two-step: 1.4.3. and 1.11.1.-2.15. -3.3. | 1/288 (0.3%) from an organic farm in New York | ST239 | [161] |
| Bovine BTM of 465 dairy farms in England (375) and Wales (90) and 625 dairy farms in Scotland, by National Milk Laboratories Ltd. | November 2011–October 2012 | Great Britain | -1.4.3. -2.14. -3.3.-3.4.-3.9. | -10/465 dairy farms were positive for mecC (2.2%): none in Wales and 2.7% in England -None in Scotland for mecC -mecA was detected on one farm in England (0.3%) | -ST425 (7/10 mecC): t6292, t742 and t6300 -CC130/t843 (3/10 mecC): ST130 (2) and ST2573 (a novel yqiL single locus variant of ST130) (1) -ST398 (mecA) | [162] |
| BTM samples were collected from dairy cattle farms (1 sample per farm per year): conventional and certified (these farms are allowed to sell raw milk to consumers) | 2009–2012 | Germany | -First: 1.4.3. -Second: 1.3.7. -Slightly modified January 2011: ·First: 1.4.1. ·Second: 1.3.8. -2.2. -3.2.-3.4. | -Conventional farms: 14/338 (4.1%, 2009) and 14/297 (4.7%, 2010) -Certified farms: 3/30 (10%, 2010) | -CC398 (29): t011 (65.5%), t034 (31%) and t1457 (3.4%) -SCCmec V (75.3% of the 632 isolates), IVa (18.5%), V* (3%) and not typeable (3%) | [163] |
| 54 BTM samples from 10 farms: 23 of ovine and 31 of goat | 2013–2014 | Czech Republic | -1.2. -2.1.1. -3.2. | None | N/R | [164] |
| 428 raw milk samples from bovine, ovine, caprine and bubaline farms | 2011–2013 | Central Italy | -1.1. -3.2.-3.4. | 1/428 (0.2%): from an ovine BTM sample | ST1 (CC1, human CA- MRSA)/spa type t127/SCCmec type IVa | [46] |
| 197 samples from 197 dairy goat farms | July–October 2012; and summer 2013 | Lombardy Region (Northern Italy) | -Two methods: ·1.1.-2.3.1.-2.1.2.-3.7.-3.3. ·Two-step: 1.4.2. and 1.3.5.-2.14.-3.3. | -4/197 (2%): 3 detected by direct plating, and 1 detected following enrichment -Persistence of MRSA on the 4 MRSA-positive farms was investigated 1 year after the first examination: 3 BTM samples retested positive for S. aureus, but only 1 was still contaminated by MRSA | -ST398/SCCmec V/t899 (3) (LA-MRSA) -ST1 (CC1)/SCCmec IVa/t127 (1) (LA-MRSA) | [165] |
| 282 raw milk samples collected from BTM | April–October 2012 | Milan and Monza-Brianza (Italy) | -1.1. -2.1.2. -3.4. | 5/282 (1.7%) | - SCCmec IV (1) and V (2) (CA-MRSA) -SCCmec I and II (2) (HA-MRSA) | [53] |
| 223 raw BTM samples from 39 goat farms | October 2011–September 2013 | Poland | -1.1. -2.1.2. -3.4.-3.2. | None | N/R | [166] |
| 248 raw milk samples from bulk tanks at 12 dairy farms | July 2010–October 2012 | Shanghai (China) | -1.1. -3.2. | 7/58 (12.1%) of S. aureus isolates | -ST965 (CC5)/t062/agr II (3) (HA-MRSA) -ST9 (CC9)/t899/agr II (2) (LA-MRSA) -ST59 (CC59)/agr I (2) (CA-MRSA) | [167] |
| 261 BTM samples collected during official monitoring activities | 2008 | Italy | -1.1. -3.5.-3.4. | 2/261 (0.8%) | ST398/spa-type t899: SCCmec type IV and V | [56] |
| A BTM sample at the end of the milking procedures from dairy sheep farm previously identified as MRSA positive by testing BTM | May 2014 | Rome (Italy) | -Two methods: ·1.1.-2.1.2.-2.2. ·1.4.3.-2.2. -3.3.-3.4. | 1/1 (100%): tested positive, after both enrichment and by direct plating | ST1 (CC1, human CA- MRSA)/spa type t127/SCCmec type IVa | [168] |
| 162 BTM samples from sheep and/or goat farms: 96 sheep milk, 49 goat milk, and 17 mixed sheep and goat milk | January–July 2014 | Apulia and Basilicata (Southern Italy) | -1.4.3. -2.15.-2.10. -3.1.-3.11.-3.2.-3.4. | 2/162 (1.2%): 1 from a sheep farm of Apulia and 1 from a goat farm of Basilicata | - ST1/t127/SCCmec IVa (sheep) - ST398/t1255/SCCmec V (LA-MRSA) (goat) | [169] |
| 844 BTM samples from dairy cattle herds | July 2012– October 2013 | Lombardy Region (Northern Italy) | -Two methods: ·1.1.-2.1.2.-3.5.-3.3. ·Two-step: 1.4.2. and 1.3.5.-2.14.-3.3. | -32/844 (3.8%) -15 strains were isolated by direct plating, 11 were detected following enrichment and 6 by both methods | -ST398 (CC398) (14) (LA-MRSA)/SCCmec V: t899 (7), t034 (2), t011 (2) and t108 (1); and SCCmec IVb/t899 (2) -ST97 (CC97) (7)/SCCmec V: t1730 (3), t4795 (2), t2421 (1) and t9295 (1) -ST1(CC1)/IVa/t127 (7) (LA-MRSA) -ST5 (CC5)/V: t535 (1) and t548 (1) -ST461 (CC5)/V/t688 (1) -ST3211 (CC22)/IV/t309 (1) | [170] |
| BTM samples from 224 dairy cows farms (that resulted positive for S. aureus at the previous annual screening) | February–March 2011 | Brescia, Bergamo, and Mantova (Northern Italy) | -First: 1.4.3. -Second: 1.3.7. -2.2. -3.3.-3.4. | 9/224 (4%) | -ST398: t899 (3), t001 (1), and t108 (1) -ST97 (CC97): t4795 (3) and t9305 (1) | [171] |
| 486 BTM samples of cow’s milk | September 2012–April 2013 | Apulia and Basilicata (southern Italy) | -1.4.3. -2.15. -3.2.-3.1.-2.10.-3.11.-3.4. | 12/486 (2.5%) | -ST1/SCCmec IVa (3 isolates; 25%): t127 (2) (CA-MRSA) and t174 (1) -ST8/unknown spa types: SCCmec IVa and V (2, 16.6%) -ST398/IVa/t899 (1) - ST398/V/t011 (1) -ST5/V/t688 (1) -ST45/IVa/t015 (1) -ST71/V/t524 (1) -ST88/IVa/t786 (1) -ST2781/V/t1730 (1) | [172] |
| 140 ovine and 35 caprine BTM samples from farms | February–May 2014 | Thessaly (Greece) | -1.1. -2.1.1. -3.4.-3.2. | 1 isolate in an ovine milk sample | t4038 | [173] |
| 165 samples: 32 samples of raw milk, 38 swabs of udder skin, 38 samples of milk from cows with subclinical mastitis, and 57 environmental samples (10 swabs of milking machines, 13 swabs of milk tanks, 10 samples of animal feed, 24 swabs from floors of farm buildings) were collected from 5 dairy farms | 2014–2016 | Sumy (Ukraine) | -1.1. -2.1.1. -3.4.-3.2. | 10/62 of S. aureus isolates (16.1%) | N/R | [174] |
| 50 raw milk samples: 20 cows’, 15 goats’, and 15 ewes’ bulk milk | August 2014–May 2015 | Hatay (Turkey) | -Homogenized: 1.7. -1.1. -2.1.1. -3.4.-3.2. | None | N/R | [71] |
| 50 cow BTM samples | N/R | Balikesir (Turkey) | -1.4.3. -2.2. -3.9.-3.2.-3.4. | 2/50 (4%) by Slidex MRSA latex agglutination test | N/R | [74] |
| 286 BTM samples from 286 dairy sheep farms | January–May 2012 | Lazio (Italy) | -1.1. -2.1.2. -3.5.-3.3.-3.4. | 2/286 (0.7%): in 2 samples from 2 different farms (1 mecA and 1 mecC) | -ST1 (CC1)/SCCmec IVa/ t127 (mecA positive) -ST130 (CC130)/SCCmec XI/t843 (mecC positive) | [175] |
| 51 S. aureus strains were collected from 51 samples of six dairy sheep farms, including two farms with artisan dairy facilities, with a history of MRSA in BTM: 11 BTM samples | 2013–2015 | Latium (Italy) | -1.1. -2.1.2. -3.3. | 27/51 (52.9%): 10 BTM | t127 (7), t1166 (1), t1773 (1) and t044 (1) | [78] |
| 57 bovine BTM samples from 12 bovine dairy farms | September–October 2017 | Jenin district (West Bank-Palestine) | -1.3. -2.4. -3.4.-3.2. | -24/39 (61.5%) of S. aureus isolates -7/12 (58.3%) of farms had MRSA contaminated BTM samples -66.7% of S. aureus isolates were identified as MRSA by the cefoxitin disk diffusion method -45.6% of bovine BTM samples were contaminated with MRSA | N/R | [176] |
| 208 BTM samples from 117 dairy farms: 44 cattle, 47 sheep, and 26 goat | December 2015–March 2016 | Jordan | -1.4.3. -2.14. -3.3.-3.4. | -54/208 (26%): 31.8% of cattle, 29.8% of sheep, and 11.5% of goat dairy farms (86 isolates) (none positive for mecC) -Prevalence bunk tank level: cattle 20% (80), sheep 38.4% (87), and goats 11.9% (42). Total 26% (209). -Prevalence farm-level: cattle 31.8% (44), sheep 29.8% (47), and goats 11.5% (26). Total 26.5% (117). | N/R | [177] |
| 165 fresh bulk milk samples from local bovine herds | N/R | Ibarapa, Oyo and Oke-Ogun (Nigeria) | N/R | 7.9% isolates identified as MSRA | N/R | [178] |
| 36 BTM samples: 10 bovine, 19 ovine, 5 caprine, and 2 mixed ovine and caprine | January–May 2016 | Epirus (Greece) | -Two methods: ·1.1. ·1.3.10. -2.1.1. -3.3.-3.4. | 1/10 (10%) bovine BTM samples | spa type t127 | [91] |
| Samples were collected from 675 dairy herds (372 conventional and 303 organic) | 2014 | Germany | ·First: 1.4.1. ·Second: 1.3.8. -2.2. -3.3.-3.4. | -36/372 (9.7%) conventional -5/303 (1.7%) organic | -Most isolates (38/41) CC398 (LA-MRSA) -Conventional (36): ·CC398: t011 (19), t034 (10), t108 (1), t2346 (1), t2576 (1), t4677 (1) and NT (1) ·CC1/t127 (1) ·CC9/t1430 (1) -Organic (5): ·CC398: t011 (2) and t034 (2) ·CC22/t790 (1) | [179] |
| 286 BTM samples from 286 dairy farms | 2014–2015 | Denmark | -1.4.3. -2.14. -3.8.-3.3. | 8/286 (2.8%) | -CC398/SCCmec Vc/t034/mecA positive (LA-MRSA, 7/8) -CC130/t843/mecC (LA-MRSA, 1/8) | [180] |
| 18 raw BTM samples from four dairy plants: 9 bovine, 7 ovine, and 2 caprine | December 2016–May 2017 | Thrace and Macedonia (Greece) | -1.1. -2.1.1. -3.4.-3.3. | 2/18 (11.1%): 1 ovine raw milk (1/7, 14.3%) and 1 bovine raw milk (1/9, 11.1%) | -t044 (ovine raw milk) -t337 (bovine raw milk) | [99] |
| 150 BTM samples from healthy cows from 63 different dairy farms | N/R | Shanghai (China) | -1.13. -2.16.-2.1. -3.2.-3.4. | 2/79 (2.5%) of S. aureus isolates | LA-MRSA ST398/SCCmec type V/spa type t034 (2) | [181] |
| 363 bovine BTM samples from 363 dairy farms | September 2015–February 2016 | England and Wales | -1.4.3. -2.14. -3.5.-3.3. | 3/363 (0.8%) | -SCCmec IVa(2B) (1 mecA): ST398 - SCCmec XI(8E) (2 mecC): ST130 and ST425 | [182] |
| 123 raw milk samples (99 from goats and 24 from ewes) collected on farm level from tank milk or from milk churn | February–May 2019 | Switzerland | -First: 1.4.3. -Second: 1.3.3. -2.14. -3.6.-3.2. | 4 goats’ milk samples (4%), but from none of the ewes’ milk samples | - CC398 (3, mecA) - CC8 (1, mecA) | [183] |
| 75 buffalo BTM samples from 75 farms | April 2017–May 2018 | Italy | -1.4.3. -2.15. -3.2.-3.1.-2.10.-3.11.-3.4. | 3/75 (4%) | -ST1/t127/Va (2) -ST72/t3092/V (1) (CA-MRSA) | [184] |
| 50 bovine BTM samples from dairy farms | 2017–2018 | Fayoum city (Egypt) | -1.7. -2.1. -3.4.-3.7.-3.2. | -4/50 (8%) -9/50 (18%) resistant to oxacillin | N/R | [185] |
| 697 BTM samples from dairy farms | January 2017–April 2018 | England and Wales (Great Britain) | -1.15. -2.14. -3.3.-3.4. | 6/697 (0.9%): 4 mecC and 2 mecA | 4 mecC: -ST425 (3): t6292 (2) and t10855 (1) - ST4652/t843 (1) 2 mecA: - ST398/t034 - ST5/t002 | [186] |
| 365 pooled BTM samples (189 winter and 176 summer samples) from 189 herds | January 2016–January 2017 | Wisconsin, Minnesota, California, Ohio, Indiana, New York, South Dakota, Iowa, Michigan, Idaho, Maine, Montana, Texas, Georgia, Vermont, Florida and Washington (United States) | -1.1. -2.3. -3.2. | 1/124 (0.8%) of S. aureus isolates (0.5%; 1 of 189 herds) | ST72-CC8, spa type t126 | [187] |
| 418 pooled BTM samples from 418 different dairy farms | September 2015–July 2017 | Shandong (China) | -1.6. -2.1.3.-2.3.1. -3.4.-3.3. | 3/418 (0.7%) cefoxitin-resistant isolates (only one isolate carried mecA, and none of the isolates carried mecC) | -ST97, ST2779, and ST3191 -t002, t267, and t437 | [13] |
| 290 samples of raw cow’s milk from milk storage tanks in cattle farms and milk supply places | May–December 2016 | Urmia city (Iran) | -3.7.-3.2. | -7/44 (16%) of S. aureus isolates were resistant to oxacillin: 1 from the tanks and 6 from the raw milk supply centers -5 isolates had mecA gene: 4 milk supply centers and 1 milk tanks | N/R | [188] |
| 97 bulk tank sheep’s milk samples from a different farm | January–February 2020 | Tuscany and Lazio (Italy) | -1.4.3. -2.4.2. -3.4.-3.3. | -1/97 (1%) -None of the isolates were positive for mecC gene | spa-type t127 | [189] |
For interpretation, see Table 1.
3. Discussion
The prevalence of MRSA in milk and dairy products varies greatly between studies, which could reflect the heterogeneity of both the methods used and the type of samples analyzed (geographic origin, size, manufacturing technology, use of raw or pasteurized milk, sample storage, and handling) [12].
The source of S. aureus contamination of raw milk on dairy farms could be from the animals themselves or from the product processing environment, such as animal housing or water. Greater contamination is expected the lower the personal hygiene and that of utensils [190].
S. aureus is one of the main causative agents of subclinical mastitis worldwide and is also frequently isolated from animals with clinical mastitis [191]. Most MRSA infections on dairy farms are related to the continued use of antibiotics on animals and physical contact between dairy cows and milkers. Therefore, it is possible that this infection is transmitted through farmers’ hands during milking [192].
Bulk tank milk (BTM) analysis is a simple, rapid, and economical alternative or complement to determine the microbiological quality of milk quarter samples. Quantitative BTM testing is useful for pathogens whose increased presence in bulk milk can lead to a higher risk of the bacteria spreading and a higher risk of new infections on the farm. BTM tests can mainly be used for the early detection of infection risks from microorganisms that are transmitted during milking and which, due to their high rate of spread, represent a massive threat to udder health on dairy farms. In the case of S. aureus, the risk of infected cows increases with increasing herd size and the associated increase in milkings per group. Thus, a limit higher than 10 cfu of S. aureus/mL of bulk milk is considered to considerably increase the risk of infection [193]. In most of the articles reviewed, MRSA is confirmed by identification of the mecA gene by PCR, and in some articles the mecC gene is included, allowing greater recovery of positive samples. The PCR method cannot be performed in all laboratories due to cost and resource limitations. To find MRSA, the limitations of PCR can be circumvented by using the disk diffusion method with cefoxitin and oxacillin, followed by investigation using ORSAB [192].
In a large number of articles, the typification of MRSA strains is not performed, especially in the case of milk in bulk tanker samples. CA-MRSA strains carry SCCmec types IV and V but HA-MRSA strains carry SCCmec types I, II, and III, and SCCmec V and SCCmec IV are the most common types between them. LA-MRSA clones are various between countries, e.g., the CC9 clone was uncovered in Asia but the CC398 clone was uncovered in Europe and the USA [118]. The mecC gene located in the new SCCmec type XI has been observed. LA-MRSA strains evolved independently from common HA-MRSA or CA-MRSA usually found in humans and mainly belong to ST398, as the predominant MRSA type in dairy herds in Europe. MRSA isolates from intramammary infections of ruminants are also associated with ST1, ST97, ST5, and ST130 [14].
4. Materials and Methods
Various databases, including Web of Science, Scopus, Pubmed, and ScienceDirect, were consulted so as to produce an inventory of all relevant studies on the prevalence of MRSA in milk and dairy products. All work carried out between January 2001 and February 2024 was reviewed. The key words used to search for articles were “prevalence or incidence”, “MRSA”, “methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus”, followed by the terms for each of the food groups evaluated. No language, article type, or text availability conditions were applied. A total of 125 items were identified for dairy products and 61 for bulk-tank milk (BTM).
The results were ordered by year of publication and, within each year, by alphabetical order of the authors of the articles. The dates and places of the studies, the prevalence of MRSA (in the absence of any additional clarification, only determination of the mecA gene was considered in the detection of the microorganism), and the typing of the MRSA strains found in the study were analyzed. A numerical code, explained at the foot of Table 1 and Table 2, was created to pinpoint which protocol among the different techniques for identifying MRSA had been followed in each of the pieces of research described.
5. Conclusions
In the majority of investigations carried out into milk and dairy products, MRSA was detected, although with a low prevalence, generally less than 5%. In order to avoid strain identification errors, the mecB and mecC genes should be determined as well as the mecA gene. The great diversity of methods used for the determination of MRSA makes comparisons between studies difficult. This points to a need for a standardized protocol for the study of this microorganism in foods.
Funding
This research was funded by the MINISTERIO DE CIENCIA E INNOVACIÓN, grant numbers RTI2018-098267-R-C33 and PID2022-142329OB-C31, and the JUNTA DE CASTILLA Y LEÓN (CONSEJERÍA DE EDUCACIÓN), grant number LE018P20. Camino González-Machado is a recipient of a predoctoral research fellowship from the Ministerio de Universidades (Programa de Formación de Profesorado Universitario, FPU).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Horváth, A.; Dobay, O.; Sahin-Tóth, J.; Juhász, E.; Pongrácz, J.; Iván, M.; Fazakas, E.; Kristóf, K. Characterisation of antibiotic resistance, virulence, clonality and mortality in MRSA and MSSA bloodstream infections at a tertiary-level hospital in Hungary: A 6-year retrospective study. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2020, 19, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullahi, I.N.; Fernández-Fernández, R.; Juárez-Fernández, G.; Martínez-Álvarez, S.; Eguizábal, P.; Zarazaga, M.; Lozano, C.; Torres, C. Wild animals are reservoirs and sentinels of Staphylococcus aureus and MRSA clones: A problem with “One Health” concern. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, D.; Shashindran, N.; Kumar, A.; Vinodh, V.; Biswas, L.; Biswas, R. Comparison of phenotypic MRSA detection methods with PCR for mecA gene in the background of emergence of oxacillin-susceptible MRSA. Microb. Drug Resist. 2021, 27, 1190–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhoi, P.; Swain, B.; Otta, S. Detection of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus using chromogenic agar and their antimicrobial susceptibility pattern. Int. J. Cur. Res. Rev. 2021, 13, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Liu, L.; Wei, J.; Xu, B. Progress in the prevalence, classification and drug resistance mechanisms of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Infect. Drug Resist. 2023, 16, 3271–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, M.C.; Chowdhury, T.; Hossain, M.T.; Hasan, M.M.; Zahran, E.; Rahman, M.M.; Zinnah, K.M.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Hossain, F.M.A. Zoonotic linkage and environmental contamination of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in dairy farms: A one health perspective. One Health 2024, 18, 100680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, K.G.; Sinha, D.K.; Singh, D.K. Food-borne Infections and Intoxications. In Veterinary Public Health & Epidemiology: Veterinary Public Health-Epidemiology-Zoonosis-One Health; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 185–200. [Google Scholar]
- Belhout, C.; Elgroud, R.; Butaye, P. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and other methicillin-resistant staphylococci and Mammaliicoccus (MRNaS) associated with animals and food products in Arab countries: A Review. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sergelidis, D.; Angelidis, A.S. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: A controversial food-borne pathogen. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 64, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, T.F.; Kellum, M.E.; Porter, S.S.; Bell, M.; Schaffner, W. An outbreak of community-acquired foodborne illness caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 82–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluytmans, J. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in food products: Cause for concern or case for complacency? Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2010, 16, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Jin, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Shi, X.; Zhao, C. Prevalence, antibiotic resistance, and enterotoxin genes of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from milk and dairy products worldwide: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162, 111969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.N.; Yuan, X.M.; Hu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.L.; Zhang, Q.; Yuan, X.X.; Wang, W.B.; Liu, Y.Q. Prevalence and characterization of Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bulk tank milk in Shandong dairy farms. Food Control 2021, 50, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titouche, Y.; Akkou, M.; Houali, K.; Auvray, F.; Hennekinne, J.A. Role of milk and milk products in the spread of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in the dairy production chain. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 3699–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaszanyitzky, É.J.; Janosi, S.Z.; Egyed, Z.; Ágost, G.; Semjen, G. Antibiotic resistance of staphylococci from humans, food and different animal species according to data of the Hungarian resistance monitoring system in 2001. Acta Vet. Hung. 2003, 51, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaszanyitzky, É.J.; Egyed, Z.; Jánosi, S.; Keserű, J.; Gál, Z.; Szabo, I.; Veres, Z.; Somogyi, P. Staphylococci isolated from animals and food with phenotypically reduced susceptibility to β-lactamase-resistant β-lactam antibiotics. Acta Vet. Hung. 2004, 52, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shitandi, A.; Mwangi, M. Occurrence of multiple antimicrobial resistance among Staphylococcus aureus isolates from Kenyan milk. J. Food Technol. Afr. 2004, 9, 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Normanno, G.; Corrente, M.; La Salandra, G.; Dambrosio, A.; Quaglia, N.C.; Parisi, A.; Greco, G.; Bellacicco, A.L.; Virgilio, S.; Celano, G.V. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus MRSA in foods of animal origin product in Italy. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 117, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- André, M.C.D.P.B.; Campos, M.R.H.; Borges, L.J.; Kipnis, A.; Pimenta, F.C.; Serafini, Á.B. Comparison of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from food handlers, raw bovine milk and Minas Frescal cheese by antibiogram and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis following SmaI digestion. Food Control 2008, 19, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morandi, S.; Brasca, M.; Andrighetto, C.; Lombardi, A.; Lodi, R. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of Staphylococcus aureus strains from Italian dairy products. Int. J. Microbiol. 2009, 2009, 501362:1–501362:7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, V.; Lopes, C.; Castro, A.; Silva, J.; Gibbs, P.; Teixeira, P. Characterization for enterotoxin production, virulence factors, and antibiotic susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from various foods in Portugal. Food Microbiol. 2009, 26, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, H.; Koller, S.; Giezendanner, N.; Stephan, R.; Zweifel, C. Prevalence and characteristics of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in humans in contact with farm animals, in livestock, and in food of animal origin, Switzerland, 2009. Eurosurveillance 2010, 15, 19542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spanu, V.; Virdis, S.; Scarano, C.; Cossu, F.; De Santis, E.P.L.; Cosseddu, A.M. Antibiotic resistance assessment in S. aureus strains isolated from raw sheep’s milk cheese. Vet. Res. Commun. 2010, 34, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kav, K.; Col, R.; Ardic, M. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from white-brined Urfa cheese. J. Food Prot. 2011, 74, 1788–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirzaei, H.; Tofighi, A.; Sarabi, H.K.; Farajli, M. Prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in raw milk and dairy products in Sarab by culture and PCR techniques. J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2011, 10, 3107–3111. [Google Scholar]
- Can, H.Y.; Celik, T.H. Detection of enterotoxigenic and antimicrobial resistant S. aureus in Turkish cheeses. Food Cont. 2012, 24, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, H.; Farhoudi, H.; Tavassoli, H.; Farajli, M.; Monadi, A. Presence and antimicrobial susceptibility of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus in raw and pasteurized milk and ice cream in Tabriz by culture and PCR techniques. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2012, 6, 6224–6229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanegas-López, M.C.; Moreno, E.J.; Rueda, R.V.; Chirivi, S.J.; Garzón, A.; Arévalo, A.S.; Martínez, F.M.; Gardeazábal, P.A.; Baquero, C. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolated from Colombian foods. Can. Cent. Acad. Art Sci. 2012, 2, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinke, C.; Winter, M.; Mohr, E.; Krömker, V. Occurrence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in cheese produced in German Farm-Dairies. Adva. Microbiol. 2012, 2, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dambrosio, A.; Quaglia, N.C.; Saracino, M.; Malcangi, M.; Montagna, C.; Quinto, M.; Lorusso, V.; Normanno, G. Microbiological quality of Burrata cheese produced in Puglia Region: Southern Italy. J. Food Prot. 2013, 76, 1981–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gücükoğlu, A.; Çadirci, Ö.; Terzi, G.; Kevenk, T.O.; Alişarli, M. Determination of enterotoxigenic and methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus in ice cream. J. Food Sci. 2013, 78, M738–M741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.K.; Liu, S.Y.; Hu, W.F.; Zheng, T.L.; Xu, J.G. Molecular biological characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from food. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2013, 236, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, R.M.; Bayourni, M.A.; Abd El Aal, S.F.A. MRSA detection in raw milk, some dairy products and hands of dairy workers in Egypt, a mini-survey. Food Control 2013, 33, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaan, M.H.G.; AL-Shammary, A.H.A. Detection of methicillin or multidrug resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in locally produced raw milk and soft cheese in Baghdad markets. Iraqi J. Vet. Med. 2013, 37, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özpinar, N.; Gümüşsoy, K.S. Phenotypic and genotypic determination of antibiotic resistant and biofilm forming Staphylococcus aureus isolated in Erzincan tulum cheese. Kafkas Üniversitesi Vet. Fakültesi Derg. 2013, 19, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, E. Enterotoxigenicity of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from traditional and commercial dairy products marketed in Iran. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2013, 44, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thaker, H.C.; Brahmbhatt, M.N.; Nayak, J.B. Isolation and identification of Staphylococcus aureus from milk and milk products and their drug resistance patterns in Anand, Gujarat. Vet. World 2013, 6, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umaru, G.A.; Kabir, J.; Umoh, V.J.; Bello, M.; Kwaga, J.K. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in fresh and fermented milk in Zaria and Kaduna, Nigeria. Int. J. Drug Res. Technol. 2013, 3, 67–75. [Google Scholar]
- Abo-Shama, U.H. Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from cattle, buffalo, sheep and goat’s raw milk in Sohag governorate, Egypt. Assiut. Vet. Med. J. 2014, 60, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arefi, F.; Mohsenzadeh, M.; Razmyar, J. Isolation, antimicrobial susceptibility and mecA gene analysis of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Iranian white cheeses. Iran. J. Vet. Res. 2014, 15, 127–131. [Google Scholar]
- Hummerjohann, J.; Naskova, J.; Baumgartner, A.; Graber, H.U. Enterotoxin-producing Staphylococcus aureus genotype B as a major contaminant in Swiss raw milk cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 1305–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanehbandi, D.; Baradaran, B.; Sadigh-Eteghad, S.; Zarredar, H. Occurrence of methicillin resistant and enterotoxigenic Staphylococcus aureus in traditional cheeses in the north west of Iran. Natl. Sch. Res. Not. 2014, 2014, 129580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silveira-Filho, V.M.; Luz, I.S.; Campos, A.P.F.; Silva, W.M.; Barros, M.P.S.; Medeiros, E.; Freitas, M.F.L.; Mota, R.A.; Sena, M.J.; Leal-Balbino, T.C. Antibiotic resistance and molecular analysis of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from cow’s milk and dairy products in Northeast Brazil. J. Food Prot. 2014, 77, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spanu, V.; Scarano, C.; Cossu, F.; Pala, C.; Spanu, C.; de Santis, E.P.L. Antibiotic resistance traits and molecular subtyping of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from raw sheep milk cheese. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, M2066–M2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, G.; Xia, X.; Yang, B.; Xi, M.; Meng, J. Antimicrobial susceptibility and molecular typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in retail foods in Shaanxi, China. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2014, 11, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carfora, V.; Caprioli, A.; Marri, N.; Sagrafoli, D.; Boselli, C.; Giacinti, G.; Giangolini, G.; Sorbara, L.; Dottarelli, S.; Battisti, A.; et al. Enterotoxin genes, enterotoxin production, and methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus isolated from milk and dairy products in Central Italy. Int. Dairy J. 2015, 42, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadel, H.M.; Ismail, J. Occurrence and zoonotic importance of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in raw milk and some dairy products at Ismailia city, Egypt. Zagazig Vet. J. 2015, 43, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, F.; Santos, J. Presencia de Staphylococcus aureus meticilina-resistentes en queso doble crema artesanal. Rev. UDCA Actual. Divulg. Cient. 2015, 18, 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Jamali, H.; Paydar, M.; Radmehr, B.; Ismail, S.; Dadrasnia, A. Prevalence and antibiotic resistance of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from raw milk and dairy products. Food Control 2015, 54, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wu, C.; Wang, X.; Meng, J. Prevalence and characterization of methicillin susceptible Staphylococcus aureus ST398 isolates from retail foods. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 196, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashouf, R.Y.; Hosseini, S.M.; Mousavi, S.M.; Arabestani, M.R. Prevalence of enterotoxin genes and antibacterial susceptibility pattern of Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from animal originated foods in West of Iran. Oman Med. J. 2015, 30, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oniciuc, E.A.; Ariza-Miguel, J.; Bolocan, A.S.; Diez-Valcarce, M.; Rovira, J.; Hernández, M.; Fernández-Natal, I.; Nicolau, A.I.; Rodríguez-Lázaro, D. Foods from black market at EU border as a neglected route of potential methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus transmission. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 209, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riva, A.; Borghi, E.; Cirasola, D.; Colmegna, S.; Borgo, F.; Amato, E.; Pontello, M.M.; Morace, G. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in raw milk: Prevalence, SCCmec typing, enterotoxin characterization, and antimicrobial resistance patterns. J. Food Prot. 2015, 78, 1142–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Lázaro, D.; Ariza-Miguel, J.; Diez-Valcarce, M.; Fernández-Natal, I.; Hernández, M.; Rovira, J. Foods confiscated from non-EU flights as a neglected route of potential methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus transmission. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 209, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Zhang, R.; Chen, J.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, C.; Yue, H.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Shi, H. Incidence and characterization of Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from food markets. Ann. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traversa, A.; Gariano, G.R.; Gallina, S.; Bianchi, D.M.; Orusa, R.; Domenis, L.; Cavallerio, P.; Fossati, L.; Serra, R.; Decastelli, L. Methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from food and wild animal carcasses in Italy. Food Microbiol. 2015, 52, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ashmawy, M.A.; Sallam, K.I.; Abd-Elghany, S.M.; Elhadidy, M.; Tamura, T. Prevalence, Molecular characterization, and antimicrobial susceptibility of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from milk and dairy products. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2016, 13, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, A.M.; Attia, A.M.; Abd El-Hamid, M.I.; El-Shorbagy, I.M.; Abd El-Kader, S.A. Genetic basis of resistance waves among methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates recovered from milk and meat products in Egypt. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2016, 62, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avşaroğlu, M.D. Prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from various foods of animal origin in Kırşehir, Turkey and their enterotoxigenicity. Turkish J. Agricul.—Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 4, 1179–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basanisi, M.G.; Nobili, G.; La Bella, G.; Russo, R.; Spano, G.; Normanno, G.; La Salandra, G. Molecular characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from sheep and goat cheeses in southern Italy. Small Rumin. Res. 2016, 135, 17–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciolacu, L.; Stessl, B.; Bolocan, A.S.; Oniciuc, E.A.; Wagner, M.; Rychli, K.; Nicolau, A.I. Tracking foodborne pathogenic bacteria in raw and ready-to-eat food illegally sold at the eastern EU border. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2016, 13, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, F.C.; García-López, M.L.; Santos, J.A. Short communication: Characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from raw milk fresh cheese in Colombia. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 7872–7876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siriken, B.; Yildirim, T.; Güney, A.K.; Erol, I.; Durupinar, B. Prevalence and molecular characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in foods of animal origin, Turkey. J. Food Prot. 2016, 79, 1990–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, R.Z.; Mustapha, B.M. Isolation and identification of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) from traditionally fermented milk “nono” and yoghurt in Kaduna Metropolis, Nigeria. Food Sci. Qual. Manage 2016, 55, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Usman, R.Z.; Mustapha, B.M.; Mohammed, F.I. Isolation and identification of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) from traditionally fermented milk “Nono” and yoghurt in Zaria Metropolis, Nigeria. Int. J. Compr. Leading Res. Sci. 2016, 2, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Wang, X.; Ge, W.; Wu, C. Prevalence and characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from goat milk powder processing plants. Food Control 2016, 59, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aqib, A.I.; Ijaz, M.; Anjum, A.A.; Malik, M.A.R.; Mehmood, K.; Farooqi, S.H.; Hussain, K. Antibiotic susceptibilities and prevalence of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolated from bovine milk in Pakistan. Acta Trop. 2017, 176, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiimwe, B.B.; Baldan, R.; Trovato, A.; Cirillo, D.M. Prevalence and molecular characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus, including methicillin resistant strains, isolated from bulk can milk and raw milk products in pastoral communities of South-West Uganda. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basanisi, M.G.; La Bella, G.; Nobili, G.; Franconieri, L.; La Salandra, G. Genotyping of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolated from milk and dairy products in South Italy. Food Microbiol. 2017, 62, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulajic, S.; Colovic, S.; Misic, D.; Djordjevic, J.; Savic-Radovanovic, R.; Asanin, J.; Ledina, T. Enterotoxin production and antimicrobial susceptibility in staphylococci isolated from traditional raw milk cheeses in Serbia. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B Pestic. Food Contam. Agric. Wastes 2017, 52, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Can, H.Y.; Elmalı, M.; Karagöz, A. Molecular typing and antimicrobial susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from raw milk, cheese, minced meat, and chicken meat samples. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2017, 37, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, M.; Yiğin, A.; Kiliç Altun, S.; Dinç, H.; Erol, S. Identification of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in yoghurts from Şanlıurfa by real-time PCR. J. Appl. Biol. Sci. 2017, 11, 4–6. [Google Scholar]
- Dittmann, K.K.; Chaul, L.T.; Lee, S.H.I.; Corassin, C.H.; Fernandes de Oliveira, C.A.; Pereira De Martinis, E.C.; Alves, V.F.; Gram, L.; Oxaram, V. Staphylococcus aureus in some Brazilian dairy industries: Changes of contamination and diversity. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ektik, N.; Gökmen, M.; Çibik, R. The prevalence and antibiotic resistance of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in milk and dairy products in Balikesir, Turkey. J. Hell. Vet. Med. Soc. 2017, 68, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachiya, J.D.O.; Rossi, G.A.M.; Ribeiro, L.F.; Sato, R.A.; Silva, H.O.; Vidal, A.M.C.; Amaral, L.A.D. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus spp. isolated from curd cheese “requeijão” and “especialidade láctea type requeijão” sold in Brazil. Ciência Rural 2017, 47, e20170008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kukhtyn, M.D.; Horyuk, Y.V.; Horyuk, V.V.; Yaroshenko, T.Y.; Vichko, O.I.; Pokotylo, O.S. Biotype characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from milk and dairy products of private production in the western regions of Ukraine. Regul. Mech. Biosyst. 2017, 8, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leke, A.; Goudjil, S.; Mullie, C.; Grognet, S.; Biendo, M. PCR detection of staphylococcal enterotoxin genes and exfoliative toxin genes in methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus strains from raw human breast milk. Clin. Nutr. Exp. 2017, 14, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Macori, G.; Giacinti, G.; Bellio, A.; Gallina, S.; Bianchi, D.M.; Sagrafoli, D.; Marri, N.; Giangolini, G.; Amatiste, S.; Decastelli, L. Molecular epidemiology of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus in the ovine dairy chain and in farm-related humans. Toxins 2017, 9, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehli, L.; Hoel, S.; Thomassen, G.M.B.; Jakobsen, A.N.; Karlsen, H. The prevalence, genetic diversity and antibiotic resistance of Staphylococcus aureus in milk, whey, and cheese from artisan farm dairies. Int. Dairy J. 2017, 65, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Lázaro, D.; Oniciuc, E.A.; García, P.G.; Gallego, D.; Fernández-Natal, I.; Dominguez-Gil, M.; Eiros-Bouza, J.M.; Wagner, M.; Nicolau, A.I.; Hernández, M. Detection and characterization of Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant S. aureus in foods confiscated in EU Borders. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizkhani, M.; Tooryan, F. Contamination of traditional cheese in Mazandaran Province to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Mazan. Uni. Med. Sci. 2018, 28, 47–56. [Google Scholar]
- Azizkhani, M.; Tooryan, F. Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in pastry cream products sold in Amol (Iran). Iran. J. Vet. Med. 2018, 12, 167–174. [Google Scholar]
- Chaalal, W.; Chaalal, N.; Bourafa, N.; Kihal, M.; Diene, S.M.; Rolain, J.M. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from food products in Western Algeria. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2018, 15, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dambrosio, A.; Ioanna, F.; Storelli, M.M.; Castiglia, D.; Giannico, F.; Colonna, M.A.; De Rosa, M.; Quaglia, N.C. Microbiological quality and safety of cheeses belonging to “Traditional Agri-Food Products” (T.A.P.) produced in Southern Italy. J. Food Saf. 2018, 38, 12539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipello, V.; Tilola, M.; Zani, L.; Bertasi, B.; Luini, M.V.; Finazzi, G. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from traditional dairy products of small-scale alpine farms. Ital. J. Food Sci. 2018, 31, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johler, S.; Macori, G.; Bellio, A.; Acutis, P.L.; Gallina, S.; Decastelli, L. Short communication: Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolated along the raw milk cheese production process in artisan dairies in Italy. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 2915–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khemiri, M.; Abbassi, M.S.; Couto, N.; Mansouri, R.; Hammami, S.; Pomba, C. Genetic characterisation of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from milk and nasal samples of healthy cows in Tunisia: First report of ST97-t267-agrI-SCCmecV MRSA of bovine origin in Tunisia. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2018, 14, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhan, X.; Huang, W.; Wang, X. Breast milk is a potential reservoir for livestock-associated Staphylococcus aureus and community-associated Staphylococcus aureus in Shanghai, China. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, J.; Ziwa, M.H.; Hounmanou, Y.M.G.; Kisanga, A.; Tuntufye, H.N. Molecular typing and antimicrobial susceptibility of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bovine milk in Tanzania. Int. J. Microbiol. 2018, 2018, 4287431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omoshaba, E.O.; Ojo, O.E.; Sofela, O.; Onifade, O.I. Prevalence and antibiotic resistance patterns of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in raw milk and soft cheese (wara) sold in Abeokuta, Nigeria. Sokoto J. Vet. Sci. 2018, 16, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Papadopoulos, P.; Papadopoulos, T.; Angelidis, A.S.; Boukouvala, E.; Zdragas, A.; Papa, A.; Hadjichristodoulou, C.; Sergelidis, D. Prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus and of methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) along the production chain of dairy products in north-western Greece. Food Microbiol. 2018, 69, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, N.; Sharma, V.; Shrivastav, A.; Nayak, A.; Rai, A.K. Prevalence and characterization of Panton-Valentine Leukocidin-positive Staphylococcus aureus in bovine milk in Jabalpur district of Madhya Pradesh, India. Vet. World. 2018, 11, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wachtmeister, L. Antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus pseudintermedius isolated from milk, cattle and dogs in and around Kampala, Uganda. Uppsala 2018, 63, 1–49. [Google Scholar]
- Abd El Halem, S.G.; Attia, I.A.; El-Dera, H.B.; El Seedy, A.S. Prevalence and antibiotic resistance of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from raw milk and dairy products collected from Alexandria, Egypt. Alex. J. Fd. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.A.H.; Saad Maharik, N.M.; Valero, A.; Kamal, S.M. Incidence of enterotoxigenic Staphylococcus aureus in milk and Egyptian artisanal dairy products. Food Control 2019, 104, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Rahman, R.T.A.; Talat, D.; Azer, T.M.; Ibrahim, M.S. Detection of Staphylococci in milk samples in retails in Kafr Elsheikh Governorate, Egypt. Eur. J. Pharm. Med. Res. 2019, 6, 92–97. [Google Scholar]
- Elal Mus, T.; Cetinkaya, F.; Karahan, H.; Gurbuz, I.B.; Degirmenci, G. Investigation of mecA gene, virulence traits and antibiotic resistance profiles in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from dairy products. J. Food Saf. 2019, 39, e12620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Parveen, S.; Rahman, M.; Huq, M.; Nabi, A.; Khan, Z.U.M.; Ahmed, N.; Wagenaar, J.A. Occurrence and characterization of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus in processed raw foods and ready-to-eat foods in an urban setting of a developing country. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, P.; Papadopoulos, T.; Angelidis, A.S.; Kotzamanidis, C.; Zdragas, A.; Papa, A.; Filioussis, G.; Sergelidis, D. Prevalence, antimicrobial susceptibility and characterization of Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from dairy industries in north-central and north-eastern Greece. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 291, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjana, K.C.; Timilsina, G.; Singh, A.; Sharma, S. Detection of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus in dairy products and anterior nares of dairy workers. Tribhuvan Univ. J. Microbiol. 2019, 6, 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- Sivakumar, M.; Dubal, Z.B.; Kumar, A.; Bhilegaonkar, K.; Vinodh Kumar, O.R.; Kumar, S.; Kadwalia, A.; Shagufta, B.; Grace, M.R.; Ramees, T.P.; et al. Virulent methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in street vended foods. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 1116–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titouche, Y.; Hakem, A.; Houali, K.; Meheut, T.; Vingadassalon, N.; Ruiz-Ripa, L.; Salmi, D.; Chergui, A.; Chenouf, N.; Hennekinne, J.A.; et al. Emergence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) ST8 in raw milk and traditional dairy products in the Tizi Ouzou area of Algeria. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 6876–6884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitale, M.; Galluzzo, P.; Buffa, P.G.; Carlino, E.; Spezia, O.; Alduina, R. Comparison of antibiotic resistance profile and biofilm production of Staphylococcus aureus isolates derived from human specimens and animal-derived samples. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Huang, J.; Zhang, F.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Pang, R.; Zeng, H.; Yang, X.; Chen, M.; Wang, J. Prevalence and characterization of food-related methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in China. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliyu, Y.; Abdullahi, I.O.; Whong, C.Z.; Olalekan, B.O.; Reuben, C.R. Occurrence and antibiotic susceptibility of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in fresh milk and milk products in Nasarawa State, North-Central Nigeria. J. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2020, 12, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girmay, W.; Gugsa, G.; Taddele, H.; Tsegaye, Y.; Awol, N.; Ahmed, M.; Feleke, A. Isolation and identification of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) from milk in shire dairy farms, Tigray, Ethiopia. Vet. Med. Int. 2020, 2020, 8833973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoveida, L.; Ataei, B.; Amirmozafari, N.; Noormohammadi, Z. Species variety, antibiotic susceptibility patterns and prevalence of enterotoxin genes in Staphylococci isolated from foodstuff in Central Iran. Iran. J. Public Health 2020, 49, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omoshaba, E.O.; Ojo, O.; Oyekunle, M.; Sonibare, A.; Adebayo, A. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolated from raw milk and nasal swabs of small ruminants in Abeokuta, Nigeria. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2020, 52, 2599–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, C.; Shang, D.; Yang, J.; Chen, B.; Chang, J.; Jin, F.; Shi, C. Prevalence of multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates with strong biofilm formation ability among animal-based food in Shanghai. Food Control 2020, 112, 107106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, D.; Motina, E.; Deka, D.; Dutta, T.K.; Singh, N.S.; Lalmuanpuia, J. Detection of virulence genes of Staphylococcus aureus in raw cow milk from Aizawl district of Mizoram, India. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2020, 8, 703–707. [Google Scholar]
- Rahi, A.; Kazemeini, H.; Jafariaskari, S.; Seif, A.; Hosseini, S.; Dehkordi, F.S. Genotypic and phenotypic-based assessment of antibiotic resistance and profile of staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec in the methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus recovered from raw milk. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeinhom, M.; Abed, A. Prevalence, characterization, and control of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from raw milk and Egyptian soft cheese. J. Vet. Med. Res. 2020, 27, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titouche, Y.; Houali, K.; Ruiz-Ripa, L.; Vingadassalon, N.; Nia, Y.; Fatihi, A.; Cauquil, A.; Bouchez, P.; Bouhier, L.; Torres, C.; et al. Enterotoxin genes and antimicrobial resistance in Staphylococcus aureus isolated from food products in Algeria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yehia, H.M.; Al-Masoud, A.H.; Alarjani, K.M.; Alamri, M.S. Prevalence of methicillin-resistant (mecA gene) and heat-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains in pasteurized camel milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 5947–5963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusuf, Y.; Aliyu, M.I.; Bello, S.A.; Fatima, B.; Abdullahi, A.; Aliyu, M.D. Occurrence of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in some retailed animal products in Sokoto, Nigeria. Alexandria J. Vet. Sci. 2020, 64, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed-Ahmed, Z.A.; Ahmed, A.A.; Amer, A.A.; Abdelshahid, Y.S. Foodborne methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (FB-MRSA) in skimmed dairy products in Egypt: Prevalence, molecular characterization, and antimicrobial susceptibility. Alexandria J. Vet. Sci. 2020, 64, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdeen, E.E.; Mousa, W.S.; Abdelsalam, S.Y.; Heikal, H.S.; Shawish, R.R. Prevalence, and Characterization of coagulase positive Staphylococci from food products and human specimens in Egypt. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghizzi, M.; Shami, A. The prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus in milk and dairy products in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 7098–7104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avila-Novoa, M.G.; González-Gómez, J.P.; Guerrero-Medina, P.J.; Cardona-López, M.A.; Ibarra-Velazquez, L.M.; Velazquez-Suarez, N.Y.; Morales-del Río, J.A.; Gutiérrez-Lomelí, M. Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) strains isolated from dairy products: Relationship of ica-dependent/independent and components of biofilms produced in vitro. Int. Dairy J. 2021, 119, 105066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemma, F.; Alemayehu, H.; Stringer, A.; Eguale, T. Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility profile of Staphylococcus aureus in milk and traditionally processed dairy products in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. BioMed. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 5576873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taban, B.M.; Hassankhani, A.; Aytac, S.A. Investigation of mecA-and mecC-positive Staphylococcus aureus from raw milk and traditional artisanal dairy foods. Int. J. Food Prop. 2021, 24, 954–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El latif, R.A.E.M.; Ali, M.E.S.E.S.; Abdelkhalek, A. Prevalence and characterization of some pathogenic bacteria in fermented milk products and mish cheese in Dakahalia Governorate, Egypt. J. Adv. Vet. Res. 2022, 12, 446–450. [Google Scholar]
- Badawy, B.; Elafify, M.; Farag, A.M.; Moustafa, S.M.; Sayed-Ahmed, M.Z.; Moawad, A.A.; Algammal, A.M.; Ramadan, H.; Eltholth, M. Ecological distribution of virulent multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in livestock, environment, and dairy products. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Aguiar, F.R.; Rocha, L.Q.; Barboza, M.M.; Sampaio, T.L.; Nogueira, N.A.; de Menezes, R.R. Occurrence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in ‘coalho’cheese produced in Brazil. J. Dairy Res. 2022, 89, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabiri, E.; Mashak, Z. Antimicrobial resistance properties and enterotoxigenic gene profile of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus isolates from raw milk. J. Positive School Psychol. 2022, 6, 1244–1252. [Google Scholar]
- Khairullah, A.R.; Rehman, S.; Sudjarwo, S.A.; Effendi, M.H.; Ramandinianto, S.C.; Gololodo, M.A.; Widodo, A.; Riwu, K.H.P.; Kurniawati, D.A. Detection of mecA gene and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolated from milk and risk factors from farms in Probolinggo, Indonesia. F1000Research 2022, 11, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langova, D.; Slana, I.; Okunkova, J.; Moravkova, M.; Florianova, M.; Markova, J. First evidence of the presence of the causative agent of caseous lymphadenitis—Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis in dairy products produced from the milk of small ruminants. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nossair, M.A.; Elaadli, H.; Mansour, A.M.; Shaaban, S.I.; Khatab, S.A.; Severin, M. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance profile of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from food products and food handlers in Egypt. Alexandria J. Vet. Sci. 2022, 75, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadat, A.; Shata, R.R.; Farag, A.M.M.; Ramadan, H.; Alkhedaide, A.; Soliman, M.M.; Elbadawy, M.; Abugomaa, A.; Awad, A. Prevalence and characterization of PVL-Positive Staphylococcus aureus isolated from raw cow’s milk. Toxins 2022, 14, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczuka, E.; Porada, K.; Wesołowska, M.; Łęska, B. Occurrence and characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from dairy products. Molecules 2022, 27, 4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Shen, J.; Zhu, C.; Ma, K.; Fang, M.; Li, B.; Wang, W.; Xue, T. Antibiotics resistance and virulence of Staphylococcus aureus isolates isolated from raw milk from handmade dairy retail stores in Hefei City, China. Foods 2022, 11, 2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakan, A.H.; Şeker, E. Investigation of methicillin and Panton-Valentine Leukocidin genes in Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from clotted creams sold in Afyonkarahisar. Kocatepe Vet. J. 2022, 15, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, T.K.; Shome, B.R.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Goyal, N.K.; Lundkvist, Å.; Deka, R.P.; Shome, R.; Venugopal, N.; Grace, D.; Sharma, G.; et al. Molecular characterization of methicillin-resistant staphylococci from the dairy value chain in two Indian States. Pathogens 2023, 12, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feyissa, N.; Alemu, T.; Jirata Birri, D.; Dessalegn, A. Isolation, identification, and determination of antibiogram characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus in cow milk and milk products (yoghurt and cheese) in West Showa Zone, Ethiopia. Int. Dairy J. 2023, 137, 105503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaan, M.H.G.; Tarek, A.M.; Abdullah, S.S. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Staphylococcus aureus in some types of dairy products in Baghdad markets. J. Dis. Global Health 2023, 16, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeim, D.E.; Eldesoukey, I.E.; Moawad, A.A.; Ahmed, A.M. Molecular detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from different foodstuffs in Egypt. Vet. Res. Forum. 2023, 14, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qamar, M.U.; Aatika; Chughtai, M.I.; Ejaz, H.; Mazhari, B.B.Z.; Maqbool, U.; Alanazi, A.; Alruwaili, Y.; Junaid, K. Antibiotic-resistant bacteria, antimicrobial resistance genes, and antibiotic residue in food from animal sources: One Health Food Safety Concern. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncay, R.M.; Sancak, Y.C. Antimicrobial resistance properties, biofilm, and mecA gene presence in Staphylococcus aureus isolated from raw milk sold in Van, Türkiye. Turk. J Agric. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 11, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashak, Z.; Khadivi, F. Incidence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in milk and dairy and assessment genotypic and phenotypic properties of antibiotic resistance. Res. Sq. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peles, F.; Wagner, M.; Varga, L.; Hein, I.; Rieck, P.; Gutser, K.; Kereszturi, P.; Kardos, G.; Turcsanyi, I.; Beri, B.; et al. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from bovine milk in Hungary. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 118, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, E.; Katsuda, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Nishimori, K.; Uchida, I.; Higashide, M.; Ishikawa, E.; Sasaki, T.; Eguchi, M. Bacteriological characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from humans and bulk milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, A.M. Antimicrobial resistance and heat sensitivity of oxacillin-resistant, mecA-positive Staphylococcus spp. from unpasteurized milk. J. Food Prot. 2008, 71, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šťástková, Z.; Karpíšková, S.; Karpíšková, R. Findings of methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus in livestock. Czech J. Food Sci. 2009, 27, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stastkova, Z.; Karpiskova, S.; Karpiskova, R. Occurrence of methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus at a goat breeding farm. Vet. Med. 2009, 54, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virgin, J.E.; Van Slyke, T.M.; Lombard, J.E.; Zadoks, R.N. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus detection in US bulk tank milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 4988–4991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ateba, C.N.; Mbewe, M.; Moneoang, M.S.; Bezuidenhout, C.C. Antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from milk in the Mafikeng Area, North West province, South Africa. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2010, 106, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, B.; O’Mahony, E.; Buckley, J.; O’Brien, S.; Fanning, S. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from dairy animals in Ireland. Zoonoses Public Health 2010, 57, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, A.; Rau, J.; Horlacher, S.; Spohr, M. Verbreitung von Methicillin-resistenten Staphylokokken in Tankmilch und Mastitismilchproben aus Nord-Württemberg. Tierärztl Umschau 2011, 66, 195–200. [Google Scholar]
- García-Álvarez, L.; Holden, M.T.; Lindsay, H.; Webb, C.R.; Brown, D.F.; Curran, M.D.; Walpole, E.; Brooks, K.; Pickard, D.J.; Teale, C.; et al. Meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus with a novel mecA homologue in human and bovine populations in the UK and Denmark: A descriptive study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2011, 11, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreausukon, K.; Fetsch, A.; Kraushaar, B.; Alt, K.; Müller, K.; Krömker, V.; Zessin, K.H.; Tenhagen, B.A. Characterization of MRSA from bulk tank milk of dairy herds using a commercial microarray. In Udder Health and Communication; Wageningen Academic: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 233–241. [Google Scholar]
- Spohr, M.; Rau, J.; Friedrich, A.; Kitich, G.; Fetsch, A.; Guerra, B.; Hammerl, J.A.; Tenhagen, B.A. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in three dairy herds in sothwest Germany. Zoonoses Public Health 2011, 58, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyletělova, M.; Vlkova, H.; Manga, I. Occurrence and characteristics of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative staphylococci in raw milk manufacturing. Czech. J. Food Sci 2011, 29, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daka, D.; Silassie, S.; Yihdego, D. Antibiotic-resistance Staphylococcus aureus isolated from cow’s milk in the Hawassa area, South Ethiopia. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2012, 11, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haran, K.; Godden, S.; Boxrud, D.; Jawahir, S.; Bender, J.; Sreevatsan, S. Prevalence and characterization of Staphylococcus aureus, including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, isolated from bulk tank milk from Minnesota dairy farm. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreausukon, K.; Fetsch, A.; Kraushaar, B.; Alt, K.; Müller, K.; Krömker, V.; Zessin, K.H.; Käsbohrer, A.; Tenhagen, B.A. Prevalence, antimicrobial resistance, and molecular characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from bulk tank milk of dairy herds. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 4382–4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linage, B.; Rodríguez-Calleja, J.M.; Otero, A.; García-López, M.L.; Santos, J.A. Characterization of coagulase-positive staphylococci isolated from tank and silo ewe milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 1639–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, G.K.; Larsen, J.; Harrison, E.M.; Larsen, A.R.; Morgan, F.J.; Peacock, S.J.; Parkhill, J.; Zadoks, R.N.; Holmes, M.A. First detection of livestock-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus CC398 in bulk tank milk in the United Kingdom. Euro Surveill. 2012, 17, 20337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoci, E.; Pinzone, M.R.; Nunnari, G.; Stefani, S.; Cacopardo, B. Prevalence and molecular characteristics of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) among subjects working on bovine dairy farms. Le Infez. Med. 2013, 21, 125–129. [Google Scholar]
- Spanu, V.; Scarano, C.; Virdis, S.; Melito, S.; Spanu, C.; De Santis, E.P. Population structure of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bulk tank goat’s milk. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2013, 10, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariza-Miguel, J.; Hernández, M.; Fernández-Natal, I.; Rodríguez-Lázaro, D. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Harboring mecC in Livestock in Spain. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 4067–4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicconi-Hogan, K.; Belomestnykh, N.; Gamroth, M.; Ruegg, P.; Tikofsky, L.; Schukken, Y. Short communication: Prevalence of methicillin resistance in coagulase-negative staphylococci and Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bulk milk on organic and conventional dairy farms in the United States. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 2959–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, G.K.; Morgan, F.J.E.; Harrison, E.M.; Peacock, S.J.; Parkhill, J.; Zadoks, R.N.; Holmes, M.A. Prevalence and properties of mecC methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in bovine bulk tank milk in Great Britain. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenhagen, B.A.; Vossenkuhl, B.; Käsbohrer, A.; Alt, K.; Kraushaar, B.; Guerra, B.; Schroeter, A.; Fetsch, A. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in cattle food chains—Prevalence, diversity, and antimicrobial resistance in Germany. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 92, 2741–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanovičová, K.; Skočková, A.; Št’ástková, Z.; Koláčková, I.; Karpíšková, R. The bacteriological quality of goat and ovine milk. Potravinárstvo Sci. J. Food Ind. 2015, 9, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortimiglia, C.; Bianchini, V.; Franco, A.; Caprioli, A.; Battisti, A.; Colombo, L.; Stradiotto, K.; Vezzoli, F.; Luini, M. Short communication: Prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant S. aureus in bulk tank milk from dairy goat farms in Northern Italy. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 2307–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rola, J.G.; Sosnowski, M.; Ostrowska, M.; Osek, J. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of coagulase-positive staphylococci isolated from raw goat milk. Small Rumin. Res. 2015, 123, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Bai, Y.; Xu, J.; Carter, M.Q.; Shi, C.; Shi, X. Genetic diversity and virulence potential of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from raw and processed food commodities in Shanghai. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 195, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carfora, V.; Giacinti, G.; Sagrafoli, D.; Marri, N.; Giangolini, G.; Alba, P.; Feltrin, F.; Sorbara, L.; Amoruso, R.; Caprioli, A.; et al. Methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus in dairy sheep and in-contact humans: An intra-farm study. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 4251–4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruso, M.; Latorre, L.; Santagada, G.; Fraccalvieri, R.; Miccolupo, A.; Sottili, R.; Palazzo, L.; Parisi, A. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in sheep and goat bulk tank milk from Southern Italy. Small Rumin. Res. 2016, 135, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortimiglia, C.; Luini, M.; Bianchini, V.; Marzagalli, L.; Vezzoli, F.; Avisani, D.; Bertoletti, M.; Ianzano, A.; Franco, A.; Battisti, A. Prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus and of methicillin-resistant S. aureus clonal complexes in bulk tank milk from dairy cattle herds in Lombardy Region (Northern Italy). Epidemiol. Infect. 2016, 144, 3046–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locatelli, C.; Cremonesi, P.; Bertocchi, L.; Zanoni, M.G.; Barberio, A.; Drigo, I.; Varisco, G.; Castiglioni, B.; Bronzo, V.; Moroni, P. Short communication: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in bulk tank milk of dairy cows and effect of swine population density. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 2151–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, A.; Caruso, M.; Normanno, G.; Latorre, L.; Sottili, R.; Miccolupo, A.; Fraccalvieri, R.; Santagada, G. Prevalence, antimicrobial susceptibility and molecular typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in bulk tank milk from southern Italy. Food Microbiol. 2016, 58, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pexara, A.; Solomakos, N.; Sergelidis, D.; Angelidis, A.; Govaris, A. Occurrence and antibiotic resistance of enterotoxigenic Staphylococcus aureus in raw ovine and caprine milk in Greece. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2016, 96, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berhilevych, O.M.; Kasianchuk, V.; Kukhtyn, M.; Lotskin, I.; Garkavenko, T.; Shubin, P. Characteristics of antibiotic sensitivity of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from dairy farms in Ukraine. Regul. Mech. Biosyst. 2017, 8, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacinti, G.; Carfora, V.; Caprioli, A.; Sagrafoli, D.; Marri, N.; Giangolini, G.; Amoruso, R.; Iurescia, M.; Stravino, F.; Dottarelli, S.; et al. Prevalence and characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus carrying mecA or mecC and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus in dairy sheep farms in central Italy. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 7857–7863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adwan, G.; Isayed, H. Prevalence and characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bulk tank milk dairy cow farms in West Bank-Palestine. Microbiol. Res. J. Int. 2018, 23, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaidat, M.M.; Bani Salman, A.E.; Roess, A.A. High prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of mecA Staphylococcus aureus in dairy cattle, sheep, and goat bulk tank milk in Jordan. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2018, 50, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olatoye, I.O.; Uba, U.C.; Akintunde, S.O. Prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus contamination in bovine milk from local dairy herd in Oyo State, Nigeria. Trop. Vet. 2018, 36, 87–93. [Google Scholar]
- Tenhagen, B.A.; Alt, K.; Pfefferkorn, B.; Wiehle, B.; Käsbohrer, A.; Fetsch, A. Short communication: Methicilin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in conventional and organic dairy herds in Germany. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 3380–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.E.; Ronco, T.; Stegger, M.; Sieber, R.N.; Fertner, M.E.; Martin, H.L.; Farre, M.; Toft, N.; Larsen, A.R.; Pedersen, K. LA-MRSA CC398 in dairy cattle and veal calf farms indicates spillover from pig production. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Li, J.; Ali, T.; Kalim, K.; Wang, H.; Song, L.; Li, Z.; Ren, X.; Ma, F.; Zou, M.; et al. Emergence of livestock-associated MRSA ST398 from bulk tank milk, China. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 3471–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, E.A.; Paterson, G.K. Prevalence and characterisation of methicillin-resistant staphylococci from bovine bulk tank milk in England and Wales. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 22, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friker, B.; Morach, M.; Püntener, S.; Cernela, N.; Horlbog, J.; Stephan, R. Assessing the microbiological quality of raw goats’ and ewes’ tank milk samples in Switzerland. Int. Dairy J. 2020, 102, 104609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovanni, N.; Marta, C.; Elisa, S.; Rosa, F.; Loredana, C.; Alessandra, B.; Antonio, P. Occurrence and characteristics of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in buffalo bulk tank milk and the farm workers in Italy. Food Microbiol. 2020, 91, 103509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, H.; Koraney, N.; Hefny, E.; Ali, S.; Abdel Mawgoud, S.; Eltokhy, E. Phenotypic and genotypic profiling of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from human and bovine milk. Egyptian J. Agricul. Res. 2021, 99, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Ba, X.; Holmes, M.A. Prevalence and characterization of mecC MRSA in bovine bulk tank milk in Great Britain, 2017–2018. JAC Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 3, dlaa125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, K.; Godden, S.M.; Royster, E.E.; Crooker, B.A.; Johnson, T.J.; Smith, E.A.; Sreevatsan, S. Prevalence, antibiotic resistance, virulence and genetic diversity of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bulk tank milk samples of U.S. dairy herds. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modaresi, R.; Tajik, H.; Mardani, K. Prevalence of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Raw Cow’s Milk Collected from Storage Tanks and Milk Supply Centers in Urmia City, Iran, and Determination of Their Antibiotic Resistance. Stud. Med. Sci. 2022, 33, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turchi, B.; Turini, L.; Tartufoli, L.; Paolieri, G.; Mauceri, R.; Pedonese, F.; Bertelloni, F. Low prevalence of bacteria harbouring the main transferable genes coding for β-lactams resistance in ovine bulk tank milk produced in Central Italy. Small Rumin. Res. 2024, 231, 107197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibebu, L.; Belete, Y.; Tigabu, E.; Tsegaye, W. Prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and potential risk factors in selected dairy farms at the interface of animal and human in Bishoftu, Ethiopia. Vet. Med. Res. Rep. 2021, 12, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Király, J.; Hajdučková, V.; Gregová, G.; Szabóová, T.; Pilipčinec, E. Resistant S. aureus isolates capable of producing biofilm from the milk of dairy cows with subclinical mastitis in Slovakia. Agriculture 2024, 14, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairullah, A.R.; Kurniawan, S.C.; Silaen, O.S.M.; Effendi, M.H.; Sudjarwo, S.A.; Ramandinianto, S.C.; Rehman, S. Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolation and mecA gene detection from milk and farmer hand swab in Tulungagung, Indonesia. Trop. Anim. Sci. J. 2023, 46, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortstegge, J.; Krömker, V. Prevalence of contagious mastitis pathogens in bulk tank milk from dairy farms in lower Saxony, Germany. Hygiene 2024, 4, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).