Abstract
Cellulosimicrobium species (formerly known as Oerskovia) are Gram-positive filamentous bacteria in the family Promicromonosporaceae and are more commonly found in sewage and soil. The present study aimed to identify all the published cases of Cellulosimicrobium species infections in the literature, describe the epidemiological, clinical, and microbiological characteristics, and provide data regarding its antimicrobial resistance, treatment, and outcomes. A narrative review was performed based on a PubMed and Scopus database search. In total, 38 studies provided data on 40 patients with infections by these species. The median age of patients was 52.5 years, and 55% were male. The most common infection types were bacteremia, infective endocarditis (IE), osteoarticular infections, peritoneal dialysis-associated peritonitis, and endophthalmitis. Antimicrobial resistance to vancomycin and the combination of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole was minimal, and vancomycin was the most commonly used antimicrobial for treating these infections. Overall mortality was minimal for all infections, except for bacteremia and IE, which carried high mortality rates.
1. Introduction
Novel microbiological diagnostic tools occupying modern genetic and molecular methods have recently been introduced into the practice of microbiological laboratories in large hospitals. These tools include 16s rRNA and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS). These new diagnostic modalities have led to the accurate and more frequent identification of relatively rare microorganisms [1,2]. Such microorganisms may have been very difficult identify with classical microbiological tools that assess the morphology and biochemical profile of these microorganisms [3].
Cellulosimicrobium species (formerly known as Oerskovia) are Gram-positive filamentous bacteria in the family Promicromonosporaceae and are more commonly found in sewage and soil. The genus Cellulosimicrobium was proposed in 2001 by Schumann et al. and replaced the nomenclature of Oerskovia and other relevant bacteria, such as Cellulomonas cellulans [4]. They rarely cause infections in humans, with only a few dozen cases being described in the literature until now [5]. Most studies on this pathogen are case reports with brief literature reviews. These infections often occur in patients who are immunocompromised or have other underlying conditions [5]. Due to the rarity of this microorganism, its pathogenic potential, as well as the epidemiological, clinical, and microbiological characteristics associated with these infections, have not been adequately described.
The present study aimed to identify all cases of Cellulosimicrobium species infections published in the literature and provide data about epidemiological, clinical, and microbiological characteristics, as well as data regarding antimicrobial resistance, treatment, and outcomes.
2. Materials and Methods
The methodology of the present review included screening the literature to identify studies that provided original information on human infections caused by Cellulosimicrobium species. Two investigators (A.V. and P.I.) independently searched PubMed and Scopus databases for eligible articles reporting “(Cellulosimicrobium OR Oerskovia) AND infection” until 24 February 2024. Any differences between the two investigators were solved by consensus. All data regarding infections from case reports and case series providing information at least about epidemiology, microbiology, treatment, and outcomes of Cellulosimicrobium species infections in humans were included. Reviews, either narrative or systematic, letters to the editor, and other non-original studies were excluded. Only studies in the English language were included, while those with no access to the full text, those presenting aggregated data, and those not referring to humans were also excluded. Additionally, studies without information on patients’ epidemiology and mortality were excluded. The references in the included articles were searched to identify other potentially relevant studies that may have been previously missed.
Two investigators (P.I. and A.V.) extracted all relevant information from the eligible studies. Data regarding age, epidemiology characteristics, infection site, microbiology, antimicrobial susceptibility, antimicrobial treatment, and outcomes of human Cellulosimicrobium species infections were extracted and further analyzed.
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Studies Included in the Review
The literature search yielded 133 studies. After screening all potentially eligible articles and assessing the references of the included articles, only 38 studies met the inclusion criteria and were considered for data extraction [5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42]. These 38 studies provided information on 40 patients. Among them, 19 studies were conducted in North and South America, 14 in Europe, and 5 in Asia. There were 37 case reports and 1 case series. Figure 1 shows a graphical representation of the geographical distribution of the published cases. Table 1 shows the characteristics of the included studies in the present review.
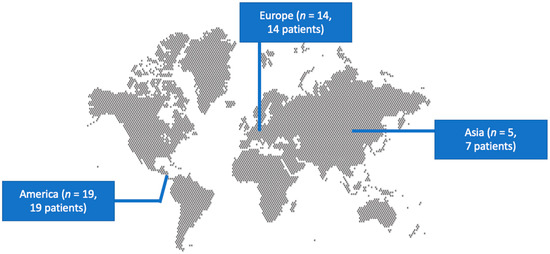
Figure 1.
Geographical distribution of Cellulosimicrobium species infections worldwide.

Table 1.
Characteristics of included studies reporting Cellulosimicrobium species infections in humans.
3.2. Epidemiology of Cellulosimicrobium Species Infections
The age of patients ranged from a few days to 82 years; the median was 52.5 years. Out of 40 patients, 22 (55%) were male. Regarding their history, 15% (6 patients) had surgery during the three months before the infection’s diagnosis. Among all patients with available data, 33.3% (13 out of 39) had recently received antimicrobial therapy, 27.5% (11 out of 40) had a central venous catheter (CVC), 15% (6) had a history of end-stage renal disease (ESRD), 12.5% (5) were on peritoneal dialysis (PD), 2.5% (1) were on hemodialysis, and 15% (6) had an active malignancy, with 7.5% (3) having a hematological malignancy. Most patients with malignancies (5 out of 6) were on chemotherapy. Additionally, 10% (4) had a prosthetic cardiac valve, and 2.5% (1) had a history of previous infective endocarditis (IE).
3.3. Microbiology and Antimicrobial Resistance of Cellulosimicrobium Species Infections
Cellulosimicrobium species were isolated from the blood in 55% (22 patients), peritoneal fluid in 12.5% (5), ocular fluid in 12.5% (5), synovial fluid or tissue in 5% (2), tissue biopsy in 5% (2), cerebrospinal fluid in 2.5% (1), deep wound samples in 2.5% (1), pus culture in 2.5% (1), valve culture in 2.5% (1, who also had positive blood cultures) and bile culture in 2.5% (1). Infection was polymicrobial in 12.5% (5 patients), with the other identified species being methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, coagulase-negative Staphylococcus, and Escherichia coli in one patient, Comamonas acidovorans in another one, Myroides species in a third, Bacillus species in a fourth, and Enterobacter cloacae in the last one. Identification was based on 16s rRNA sequencing in 40% (16 patients) and MALDI-TOF MS in 15% (6). The identification method was not reported in 57.5% (23 patients).
The identified species were Cellulosimicrobium cellulans or Oerskovia xanthineolytica (the older name of the same pathogen) in 67.5% (27 patients), Oerskovia turbata in 15% (6), and Cellulosimicrobium funkei in 5% (2), while the species were not reported in 12.5% (5).
The most commonly used method for susceptibility testing was dilution in 38.1% (8 out of 21 patients with available data), disk diffusion in 28.6% (6), disk diffusion and dilution in 14.3% (3), E-test in 14.3% (3), and paper diffusion in 4.8% (1). Resistance to clindamycin was 70% (7 out of 10 patients with available data), to penicillin was 60% (12 out of 20), to aminopenicillins was 53.3% (8 out of 15), to cephalosporins was 42.9% (9 out of 21 patients with available data), to aminoglycosides was 33.3% (6 out of 18), to tetracyclines was 29.4% (5 out of 17), to carbapenems was 16.7% (2 out of 12), to the combination of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole was 8.7% (2 out of 23), and to vancomycin was 0% (0 out of 29).
3.4. Clinical Presentation of Cellulosimicrobium Species Infections
The most common Cellulosimicrobium species infections were those of the bloodstream in 55% (22 out of 40 patients), IE in 20% (8), osteoarticular infections in 15% (6), peritonitis in 12.5% (5), endophthalmitis in 12.5% (5), central nervous system infections in 5% (2), lower respiratory tract infections in 5% (2), urinary tract infections (UTIs) in 2.5% (1), and skin and soft tissue infection (SSTI) in 2.5% (1). The most common clinical symptoms were fever in 52.8% (19 out of 36 patients) and sepsis in 28.9% (11 out of 38).
3.5. Treatment and Outcomes of Cellulosimicrobium Species Infections
The antimicrobial agents more commonly used were vancomycin in 68.4% (26 out of 38 patients), cephalosporins in 28.9% (11), aminoglycosides in 26.3% (10), the combination of trimethoprim with sulfamethoxazole in 21.1% (8), rifampicin in 15.8% (6), carbapenems in 13.2% (5), penicillin in 10.5% (4), aminopenicillins in 10.5% (4), linezolid in 10.5% (4), clindamycin in 7.9% (3), macrolides in 7.9% (3), and quinolones in 7.9% (3). The median treatment duration among survivors was 21.5 days, ranging from 7 to 264 days, with an interquartile range of 14 to 57.8 days. Overall mortality was 20% (8 out of 40 patients) and was attributed directly to the infection in 17.5% (7 patients). Table 2 shows the characteristics of patients with Cellulosimicrobium species infections in total and in regards to the type of infection.

Table 2.
Characteristics of the different types of infections by Cellulosimicrobium species.
3.6. Bacteremia Due to Cellulosimicrobium Species
Twenty-two patients had bacteremia caused by Cellulosimicrobium species. The median age of bacteremic patients was 52.5 years, ranging from a few days to 82 years, and had an interquartile range of 37.5 to 70.5 years; 50% (11 out of 22 patients) were male. Among all, 27.3% (6 patients) had an active malignancy (hematological in half of them), with 23.8% (5) being on chemotherapy and 19% (4) having neutropenia. Moreover, 50% (11 patients) had a CVC, 42.9% (9) had received antimicrobial therapy during the past three months, 18.2% (4) had a prosthetic cardiac valve, and 4.5% (1) had recent cardiac surgery. Among patients with bacteremia, 36.4% (8 patients) had IE, 9.1% (2) had osteoarticular infections, 4.6% (1) had a central nervous system infection, and 4.6% (1) had an SSTI. The infection was polymicrobial in 9.1% (2 patients), and the most common clinical characteristics were fever in 84.2% (16 out of 19 patients with available data), sepsis in 52.4% (11 out of 21), and shock in 19% (4). The median duration of treatment was 21 days. Mortality was 36.4% (8 out of 22 patients) and was directly attributed to the infection in 31.8% (7).
A comparison among patients with bacteremia who survived and those who died showed that patients who died were older, were more commonly female, and were more likely to have sepsis and a diagnosis of IE. However, the small number of patients in this analysis precluded the conduct of statistical analysis. Notably, no significant differences were noted among patients with immunosuppression among these two subgroups. Table 3 shows the characteristics of patients with bacteremia in regards to patients’ outcomes.

Table 3.
Characteristics of patients with bacteremia by Cellulosimicrobium species in regards to the outcome.
3.7. Infective Endocarditis Due to Cellulosimicrobium Species
Eight patients had IE caused by Cellulosimicrobium species. The median age of patients was 67 years, ranging from 30 to 82 years, with an interquartile range of 52.3 to 80.3; 37.5% (3 out of 8 patients) were male. Among all patients, 50% (4) had a prosthetic cardiac valve, 12.5% (1) had a CVC, 12.5% (1) had hematological malignancy on chemotherapy, 12.5% (1) had a history of IE, and 12.5% (1) had a history of recent cardiac surgery. Bacteremia was present in all patients with IE, while a concurrent osteoarticular infection was present in 12.5% (1 patient). In 62.5% (5 patients), the infected valve was the aortic, in 25% (2) the mitral, and in 12.5% (1) the tricuspid. The diagnosis was facilitated by transesophageal echocardiography in 62.5% (5 patients), transthoracic echocardiography in 12.5% (1), and autopsy, in 25% (2). Fever was present in 87.5% (7 patients), sepsis in 50% (4), and shock in 12.5% (1). Heart failure was diagnosed in 25% (2 patients), embolic phenomena occurred in 37.5% (3), paravalvular abscess in 25% (2), and immunological phenomena in 12.5% (1). The median duration of treatment was 63 days. Mortality was 62.5% and was directly attributed to the infection in all patients.
3.8. Osteoarticular Cellulosimicrobium Species Infections
Six patients had osteoarticular infections caused by Cellulosimicrobium species. Their median age was 61 years (ranging from 5 to 81), while the interquartile range was 14–78.8; 83.3% (5 out of 6 patients) were male. No patient had a predisposing factor, but 50% (3) had received antimicrobial therapy during the previous three months. Among these patients, 33.3% (2 patients) had bacteremia, 16.7% (1) had IE, and 16.7% (1) had an SSTI. Infection was polymicrobial in 16.7% (1). Among patients with available data, none had fever, but 16.7% (1 patient) had sepsis. The median duration of treatment was 45.5 days. No patient died.
3.9. Cellulosimicrobium Species Peritonitis
This review identified five patients with peritonitis due to Cellulosimicrobium species. Their median age was 59 years (ranging from 13 to 70); 40% (2 patients) were male. All patients had ESRD and were on PD. The diagnosis was based on the characteristics and culture of the peritoneal fluid. The infection was polymicrobial in 20% (1 patient). Fever was present in 50% (2 out of 4 patients with available data), but no patient had sepsis or shock. The main presenting clinical symptom was abdominal pain. The median duration of treatment was 20 days. No patient died, but 40% (2) had to be transitioned to hemodialysis after the episode of PD-associated peritonitis.
3.10. Cellulosimicrobium Species Endophthalmitis
The review revealed five patients with Cellulosimicrobium species endophthalmitis; their median age was 72 years (ranging from 28 to 78), and 60% (3 of them) were male. Among these five patients, 60% (3) had surgery during the previous three months, and 40% (2) had recent ocular trauma. The diagnosis was established by the culture of intraocular fluid. The infection was exogenous in all patients. Symptoms were only local. Despite antimicrobial treatment, vitrectomy was required in all cases, and the outcome was optimal in all of them, with only a relative reduction of visual acuity.
4. Discussion
The present review summarizes the characteristics of patients with Cellulosimicrobium species infections based on previously published data and provides information regarding epidemiology, microbiology, clinical characteristics, treatment, and outcome. The most common infection types were those of the bloodstream: IE, osteoarticular infections, PD-associated peritonitis, and endophthalmitis. The most commonly used antimicrobial therapies for treating these infections were vancomycin, cephalosporins, and the combination of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole. Mortality was notable, mainly associated with bacteremia and IE.
Few reports of Cellulosimicrobium species infections in humans exist in the literature so far. Thus, the epidemiological, microbiological, and clinical characteristics have not been adequately described. The present review has revealed 40 patients with adequate information regarding Cellulosimicrobium species infections. Most patients were male, and the median age was 52.5 years. Most studies were conducted in North America and Europe. However, this geographic distribution may be due to the presence of advanced diagnostic techniques, such as MALDI-TOF MS and 16s rRNA, used in these geographical areas for pathogens’ identification since such techniques are more commonly found in the Western world. Hence, the geographic distribution shown herein may not represent the true epidemiology of the pathogens since, in areas where such diagnostic techniques are unavailable, the pathogens may have probably been misidentified.
This review identified different predisposing factors for different types of Cellulosimicrobium species infections. Half of the patients with Cellulosimicrobium species bacteremia had a CVC at diagnosis. At the same time, antimicrobial therapy use during the previous three months was also common among these patients. Finally, about one out of four patients with bacteremia had a history of an active malignancy. These characteristics imply a mode of transmission that is mainly of healthcare-associated origin. Infections such as the respiratory tract, urinary tract, surgical sites, and bloodstream are a few common examples of healthcare-associated infections (HAIs). The most common pathogens associated with HAIs are S. aureus, Enterobacterales, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter baumannii, Enterococcus species, and Candida species [43]. HAIs constitute a significant concern in everyday practice since they are potentially preventable causes of patient harm. Hence, implementing specific measures by healthcare practitioners, such as hand hygiene and appropriate procedures for inserting and maintaining CVCs and urinary tract catheters, can significantly reduce HAIs [44,45,46,47,48]. This implies that implementing an appropriate infection control process could reduce the likelihood of bacteremia caused by Cellulosimicrobium species, among other more frequent pathogens. However, even though these infections could be healthcare-associated, community-associated acquisition may also be frequent, at least in some patients. For example, species of the genus Cellulosimicrobium have been identified as members of the salivary microbiome [49]. The fact that patients with bacteremia by these pathogens were frequently diagnosed with active malignancy and were more commonly on chemotherapy and neutropenics could imply an increased likelihood for the development of infection among patients with significant immunosuppression. Indeed, immunosuppression is associated with an increased risk of infection [50], and patients with cancer have an increased likelihood of infections by common pathogens as well as by uncommon, less frequent ones [51]. The type of immunosuppression is the main predicament for the pathogen that causes infection in immunosuppressed individuals. Hence, in cases of defects in cell-mediated immunity, infections by Nocardia, Cryptococcus, Pneumocystis jiroveci, Histoplasma, or other endemic dimorphic fungi are more frequent [51]. In patients with neutropenia, as in the case of patients with bacteremia in the present review, P. aeruginosa, Aspergillus, Mucor, and other pathogens are more frequent [51].
The present study noted classical predisposing factors associated with IE in patients infected by Cellulosimicrobium species, which included prosthetic cardiac valves, previous episodes of IE, and recent cardiac surgery. These factors have been extensively described in the literature among patients with IE [52,53,54].
PD is a classical risk factor for peritonitis. In these patients, Gram-positive pathogens are more common, including staphylococci, both coagulase-negative and S. aureus, with methicillin resistance being a significant problem from a clinical perspective [55,56]. However, other pathogens such as Gram-negative bacteria, fungi, mycobacteria, or rare Gram-positive bacilli have also been described as causes of PD-associated peritonitis [57]. This underlines the need for clinicians caring for such patients to be aware of the likelihood of the identification of rare pathogens.
Finally, in patients with endophthalmitis, trauma or recent surgery were noted in the history of all patients, thus defining these infections as exogenous. Indeed, exogenous endophthalmitis is the most common type of endophthalmitis, with Gram-positive pathogens, mainly coagulase-negative staphylococci, being among the most commonly identified pathogens [58]. This may reflect the strong association of this condition with recent ophthalmological surgical procedures.
Identifying rare bacteria, such as Cellulosimicrobium species, could be difficult from a microbiological perspective. Indeed, in the present review, advanced molecular methods such as MALDI-TOF or 16s rRNA gene sequencing were commonly used for pathogen identification. These advanced techniques may be required for accurate pathogen identification in cases of rare bacteria but may be relatively unavailable by the majority of microbiological laboratories [59].
Given the rarity of Cellulosimicrobium species, there are no guidelines for treating infections caused by this microorganism. Thus, the antimicrobial resistance patterns of these species are of great interest. The majority of studies included herein provided some information about the antimicrobial susceptibility of these species. The available data showed high resistance to clindamycin, aminopenicillins, penicillin, cephalosporins, quinolones, and aminoglycosides. On the contrary, antimicrobial resistance to the combination of trimethoprim with sulfamethoxazole was minimal, and resistance to vancomycin was zero. Notably, the present review has revealed that Cellulosimicrobium species infections may frequently be healthcare-associated. This may be of clinical importance in terms of antimicrobial resistance since resistant pathogens prevail in the hospital environment, either by selection of resistant microorganisms after exposure to antimicrobials or by transfer of genes providing resistance from other microorganisms [60,61,62]. Thus, even though this microorganism’s resistance mechanisms have not been elucidated, and it is unknown whether mobile genetic elements could lead to acquired resistance from other multidrug-resistant hospital bacteria, the possibility of developing significant antimicrobial resistance may exist [63]. It is of interest that scarce literature suggests that specific isolates of unknown clinical significance may have multiple mechanisms of resistance involving multidrug efflux pumps, multidrug-resistant transporters, metallo-beta-lactamases, and even a vancomycin-resistant protein [64]. Hence, it sounds reasonable that the most frequently used antimicrobial agent in the studies included in this review was vancomycin. Based on these data, clinicians caring for patients with these infections could use vancomycin as an empirical treatment until antimicrobial susceptibility data are available to allow appropriate de-escalation.
In the present review, mortality was high in bacteremic patients, which could have been related to their active malignancy or the associated treatment [65]. Mortality was even higher in patients with IE and was higher compared to cases of IE by other microorganisms reported in the literature [52,53,54]. However, the small number of patients with IE in the present review may preclude the extraction of firm conclusions. Larger numbers of patients with IE should be studied to evaluate the outcome of IE by this pathogen more accurately.
The present review has some limitations. First, despite the thorough search methodology, some studies may have been missed due to the search strategy. Additionally, due to the rarity of these infections, only case reports and case series were included in the review. Finally, some information was missing in the original studies; thus, this review only presents and analyzes the available data from the included studies.
5. Conclusions
This study provides essential data about the epidemiology, clinical characteristics, microbiology, antimicrobial susceptibility, treatment, and outcomes of Cellulosimicrobium species infections. The most common infections were those of the bloodstream IE, osteoarticular infections, PD-associated peritonitis, and endophthalmitis. Among patients with bacteremia, active malignancy and the presence of CVC were common. Peritonitis only occurred in patients with PD, and endophthalmitis was exogenous due to recent surgery or trauma in all patients. Susceptibility to vancomycin and the combination of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole was very high, and vancomycin was the most commonly used antimicrobial for treatment. The infection’s outcome depended on its type, with mortality being high in patients with bacteremia and IEs and minimal in all other patients.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.I.; methodology, P.I. and A.V.; software, P.I. and A.V.; validation, P.I.; formal analysis, P.I. and A.V.; investigation, A.V. and P.I.; data curation, P.I.; writing—original draft preparation, P.I. and A.V.; writing—review and editing, G.S.; visualization, P.I.; supervision, P.I. and G.S.; project administration, P.I. and G.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Clarridge, J.E. Impact of 16S rRNA Gene Sequence Analysis for Identification of Bacteria on Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 17, 840–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, P.C.Y.; Lau, S.K.P.; Teng, J.L.L.; Tse, H.; Yuen, K.-Y. Then and Now: Use of 16S rDNA Gene Sequencing for Bacterial Identification and Discovery of Novel Bacteria in Clinical Microbiology Laboratories. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Off. Publ. Eur. Soc. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 908–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Li, J.; Yan, S.; Sun, H.; Tan, C.; Liu, M.; Liu, K.; Zhang, H.; Zou, M.; Xiao, X. Identification of Pathogen(s) in Infectious Diseases Using Shotgun Metagenomic Sequencing and Conventional Culture: A Comparative Study. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, P.; Weiss, N.; Stackebrandt, E. Reclassification of Cellulomonas cellulans (Stackebrandt and Keddie 1986) as Cellulosimicrobium cellulans Gen. Nov., Comb. Nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2001, 51, 1007–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; He, C.; Tian, R.; Wang, R. A Case Report of the Differential Diagnosis of Cellulosimicrobium cellulans-Infected Endocarditis Combined with Intracranial Infection by Conventional Blood Culture and Second-Generation Sequencing. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reller, L.B. Bacterial Endocarditis Caused by Oerskovia turbata. Ann. Intern. Med. 1975, 83, 664–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruikshank, J.G.; Gawler, A.H.; Shaldon, C. Oerskovia Species: Rare Opportunistic Pathogens (Plate XLI). J. Med. Microbiol. 1979, 12, 513–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kailath, E.J.; Goldstein, E.; Wagner, F.H. Meningitis Caused by Oerskovia Xanthineolytica. Am. J. Med. Sci. 1988, 295, 216–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeProwse, C.R.; McNeil, M.M.; McCarty, J.M. Catheter-Related Bacteremia Caused by Oerskovia turbata. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1989, 27, 571–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guss, W.J.; Ament, M.E. Oerskovia Infection Caused by Contaminated Home Parenteral Nutrition Solution. Arch. Intern. Med. 1989, 149, 1457–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rihs, J.D.; McNeil, M.M.; Brown, J.M.; Yu, V.L. Oerskovia Xanthineolytica Implicated in Peritonitis Associated with Peritoneal Dialysis: Case Report and Review of Oerskovia Infections in Humans. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1990, 28, 1934–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truant, A.L.; Satishchandran, V.; Eisenstaedt, R.; Richman, P.; McNeil, M.M. Oerskovia Xanthineolytica and Methicillin-resistantStaphylococcus Aureus in a Patient with Cirrhosis and Variceal Hemorrhage. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1992, 11, 950–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, C.L.; Chapin-Robertson, K.; Reeves Dill, S.; Martino, R.L. Oerskovia Xanthineolytica Bacteremia in an Immunocompromised Patient with Pneumonia. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1994, 18, 259–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lair, M.I.; Bentolila, S.; Grenet, D.; Cahen, P.; Honderlick, P. Oerskovia turbata and Comamonas acidovorans Bacteremia in a Patient with AIDS. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1996, 15, 424–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, J.D.; McCarthy, M.C.; Decker, C.F. Oerskovia Xanthineolytica Bacteremia in an Immunocompromised Host: Case Report and Review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1996, 22, 554–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Harrington, R.D.; Lewis, C.G.; Aslanzadeh, J.; Stelmach, P.; Woolfrey, A.E. Oerskovia Xanthineolytica Infection of a Prosthetic Joint: Case Report and Review. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1996, 34, 1821–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borra, S.; Kleinfeld, M. Peritonitis Caused by Oerskovia Xanthineolytica in a Patient on Chronic Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis (CAPD). Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1996, 27, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellerbroek, P.; Kuipers, S.; Rozenberg-Arska, M.; Verdonck, L.; Petersen, E. Oerskovia Xanthineolytica: A New Pathogen in Bone Marrow Transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1998, 22, 503–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lujan-Zilbermann, J.; Jones, D.; DeVincenzo, J. Oerskovia Xanthineolytica Peritonitis: Case Report and Review. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 1999, 18, 738–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbina, B.Y.; Gohh, R.; Fischer, S.A. Oerskovia Xanthineolytica Endocarditis in a Renal Transplant Patient: Case Report and Review of the Literature. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2003, 5, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heym, B.; Gehanno, P.; Friocourt, V.; Bougnoux, M.-E.; Le Moal, M.; Husson, C.; Leibowitch, J.; Nicolas-Chanoine, M.-H. Molecular Detection of Cellulosimicrobium cellulans as the Etiological Agent of a Chronic Tongue Ulcer in a Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Positive Patient. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 4269–4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Rowlinson, M.-C.; Bruckner, D.A.; Hinnebusch, C.; Nielsen, K.; Deville, J.G. Clearance of Cellulosimicrobium cellulans Bacteremia in a Child without Central Venous Catheter Removal. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 2650–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.; Padmini, S.; Govindan, V.; Appalaraju, B. Oerskovia turbata and Myroides Species: Rare Isolates from a Case of Acalculus Cholecystitis. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 25, 297–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, J.D.; Montecino, R.; Winograd, J.M.; Ferraro, M.; Michelow, I.C. Pyogenic Flexor Tenosynovitis Associated with Cellulosimicrobium cellulans. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 4106–4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, P.-C.; Chen, Y.-S.; Lee, S.S.-J. Infective Endocarditis and Osteomyelitis Caused by Cellulomonas: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2009, 65, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casanova-Román, M.; Sanchez-Porto, A.; Gomar, J.L.; Casanova-Bellido, M. Early-Onset Neonatal Sepsis Due to Cellulosimicrobium cellulans. Infection 2010, 38, 321–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akcakaya, A.A.; Sargin, F.; Erbil, H.H.; Yazici, S.; Yaylali, S.A.; Mesci, C.; Ergin, S.; Midilli, K. A Cluster of Acute-Onset Postoperative Endophthalmitis over a 1-Month Period: Investigation of an Outbreak Caused by Uncommon Species. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2011, 95, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaru-ampornpan, P.; Agarwal, A.; Midha, N.K.; Kim, S.J. Traumatic Endophthalmitis Due to Cellulosimicrobium cellulans. Case Rep. Ophthalmol. Med. 2011, 2011, 469607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkar, H.; Li, A.; Bunce, N.; Duffy, K.; Malnick, H.; Shah, J.J. Cellulosimicrobium funkei: First Report of Infection in a Nonimmunocompromised Patient and Useful Phenotypic Tests for Differentiation from Cellulosimicrobium cellulans and Cellulosimicrobium terreum. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 1175–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancourt Castellanos, L.; Ponz Clemente, E.; Fontanals Aymerich, D.; Blasco Cabañas, C.; Marquina Parra, D.; Grau Pueyo, C.; García García, M. First case of peritoneal infection due to Oerskovia turbata (Cellulosimicrobium funkei). Nefrol. Publicacion Of. Soc. Espanola Nefrol. 2011, 31, 223–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magro-Checa, C.; Chaves-Chaparro, L.; Parra-Ruiz, J.; Peña-Monje, A.; Rosales-Alexander, J.L.; Salvatierra, J.; Raya, E. Septic Arthritis Due to Cellulosimicrobium cellulans. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 4391–4393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delport, J.; Wakabayashi, A.T.; Anantha, R.V.; Lannigan, R.; John, M.; McCormick, J.K. Cellulosmicrobium cellulans Isolated from a Patient with Acute Renal Failure. JMM Case Rep. 2014, 1, e000976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sug Kim, J.; Won Lee, T.; Gyoo Ihm, C.; Jin Kim, Y.; Mi Moon, S.; Joo Lee, H.; Hwan Jeong, K. CAPD Peritonitis Caused by Co-Infection with Cellulosimicrobium cellulans (Oerskovia xanthineolytica) and Enterobacter Cloacae: A Case Report and Literature Review. Intern. Med. 2015, 54, 627–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Coletta-Griborio, E.; Rodriguez Portela, G.; Núñez García, J.M.; Bratos-Pérez, M.Á. Bacteremia Due to Cellulosimicrobium cellulans Associated with Central Catheter for Hemodialysis. Enfermedades Infecc. Microbiol. Clínica 2017, 35, 62–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponce-Alonso, M.; Del Campo, R.; Fortun, J.; Cantón, R.; Morosini, M.-I. First Description of Late Recurrence of Catheter-Associated Bacteraemia Due to Cellulosimicrobium cellulans. Enfermedades Infecc. Microbiol. Clínica 2017, 35, 131–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzales Zamora, J.A.; Camps, N. Bacteremia Caused by Cellulosimicrobium in a Bone Marrow Transplant Patient: A Case Report and Literature Review. IDCases 2018, 11, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oikonomou, K.; Mcwilliams, C.; Moussa, M. Oerskovia Species Bacteremia in a Diabetic Patient. J. Glob. Infect. Dis. 2018, 10, 113–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monticelli, J.; Gerloni, R.; Farina, C.; Knezevich, A.; Dore, F.; Luzzati, R. Cellulosimicrobium cellulans Aortic Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis. Access Microbiol. 2019, 1, e000068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivero, M.; Alonso, J.; Ramón, M.F.; Gonzales, N.; Pozo, A.; Marín, I.; Navascués, A.; Juanbeltz, R. Infections Due to Cellulosimicrobium Species: Case Report and Literature Review. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohowetz, L.J.; Patel, N.A.; Yannuzzi, N.A.; Fan, K.C.; Miller, D.; Flynn, H.W., Jr. Post-Traumatic Endophthalmitis Caused by Oerskovia turbata. Case Rep. Ophthalmol. 2019, 10, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández Martínez, P.; Santiago Setién, I.; De Malet Pintos-Fonseca, A. Infección por Oerskovia turbata. Med. Clínica 2020, 155, 135–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trindade Torres, M.; Sousa Nunes, B.; Varandas, L.; Maltez, F. Actinomycetoma by Cellulosimicrobium cellulans in a Young Man from Guinea-Bissau: Short Literature Review Regarding a Case Report. Acta Médica Port. 2023, 37, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabó, S.; Feier, B.; Capatina, D.; Tertis, M.; Cristea, C.; Popa, A. An Overview of Healthcare Associated Infections and Their Detection Methods Caused by Pathogen Bacteria in Romania and Europe. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Wu, Y.-Y.; Zou, J.-N.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, J.; Huang, H.-Y.; Xiong, L.-J. Impact of a Bundle on Prevention and Control of Healthcare Associated Infections in Intensive Care Unit. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 35, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apisarnthanarak, A.; Ratz, D.; Greene, M.T.; Khawcharoenporn, T.; Weber, D.J.; Saint, S. National Survey of Practices to Prevent Health Care-Associated Infections in Thailand: The Role of Prevention Bundles. Am. J. Infect. Control 2017, 45, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righi, E.; Aggazzotti, G.; Ferrari, E.; Giovanardi, C.; Busani, S.; Rinaldi, L.; Girardis, M. Trends in Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia: Impact of a Ventilator Care Bundle in an Italian Tertiary Care Hospital Intensive Care Unit. Am. J. Infect. Control 2014, 42, 1312–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soundaram, G.V.; Sundaramurthy, R.; Jeyashree, K.; Ganesan, V.; Arunagiri, R.; Charles, J. Impact of Care Bundle Implementation on Incidence of Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection: A Comparative Study in the Intensive Care Units of a Tertiary Care Teaching Hospital in South India. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. Peer-Rev. Off. Publ. Indian Soc. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 24, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanj, S.S.; Zahreddine, N.; Rosenthal, V.D.; Alamuddin, L.; Kanafani, Z.; Molaeb, B. Impact of a Multidimensional Infection Control Approach on Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection Rates in an Adult Intensive Care Unit in Lebanon: International Nosocomial Infection Control Consortium (INICC) Findings. Int. J. Infect. Dis. IJID Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Infect. Dis. 2013, 17, e686–e690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Lu, W.; Tu, Q.; Ge, Y.; He, J.; Zhou, Y.; Gou, Y.; Van Nostrand, J.D.; Qin, Y.; Li, J.; et al. Preliminary Analysis of Salivary Microbiome and Their Potential Roles in Oral Lichen Planus. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dropulic, L.K.; Lederman, H.M. Overview of Infections in the Immunocompromised Host. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.K.; Liu, C.; Dadwal, S.S. Infectious Disease Complications in Patients with Cancer. Crit. Care Clin. 2021, 37, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papakonstantinou, P.E.; Samonis, G.; Andrianaki, A.M.; Christofaki, M.; Dimopoulou, D.; Papadakis, J.; Gikas, A.; Kofteridis, D.P. Epidemiology, Microbiological and Clinical Features, Treatment, and Outcomes of Infective Endocarditis in Crete, Greece. Infect. Chemother. 2018, 50, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosioni, J.; Hernandez-Meneses, M.; Téllez, A.; Pericàs, J.; Falces, C.; Tolosana, J.M.; Vidal, B.; Almela, M.; Quintana, E.; Llopis, J.; et al. The Changing Epidemiology of Infective Endocarditis in the Twenty-First Century. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2017, 19, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannitsioti, E.; Pefanis, A.; Gogos, C.; Lekkou, A.; Dalekos, G.N.; Gatselis, N.; Georgiadou, S.; Nikou, P.; Vrettou, A.; Rigopoulos, A.; et al. Evolution of Epidemiological Characteristics of Infective Endocarditis in Greece. Int. J. Infect. Dis. IJID Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Infect. Dis. 2021, 106, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-H.; Huang, C.-H.; Kuo, M.-C.; Lin, S.-Y.; Hsu, C.-H.; Lee, C.-Y.; Chiu, Y.-W.; Chen, Y.-H.; Lu, P.-L. Microbiology of Peritoneal Dialysis-Related Infection and Factors of Refractory Peritoneal Dialysis Related Peritonitis: A Ten-Year Single-Center Study in Taiwan. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. Wei Mian Yu Gan Ran Za Zhi 2019, 52, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelenitsky, S.A.; Howarth, J.; Lagacé-Wiens, P.; Sathianathan, C.; Ariano, R.; Davis, C.; Verrelli, M. Microbiological Trends and Antimicrobial Resistance in Peritoneal Dialysis-Related Peritonitis, 2005 to 2014. Perit. Dial. Int. J. Int. Soc. Perit. Dial. 2017, 37, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yang, G.; Wang, P.; Wang, X.; Xiong, Z.; He, Y.; Xiong, Z. Evolution of Peritoneal Dialysis-Associated Peritonitis: Pathogen, Antibiotic Resistance, and the Impact of Lymphocyte Count on Treatment Outcomes. Infect. Drug Resist. 2024, 17, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keynan, Y.; Finkelman, Y.; Lagacé-Wiens, P. The Microbiology of Endophthalmitis: Global Trends and a Local Perspective. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Eur. Soc. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 31, 2879–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-F.; Hou, X.; Xiao, M.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, J.-W.; Zhou, M.-L.; Huang, J.-J.; Zhang, J.-J.; Xu, Y.-C.; Hsueh, P.-R. Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) Analysis for the Identification of Pathogenic Microorganisms: A Review. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzidic, S.; Bedeković, V. Horizontal Gene Transfer-Emerging Multidrug Resistance in Hospital Bacteria. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2003, 24, 519–526. [Google Scholar]
- Reygaert, W.C. An Overview of the Antimicrobial Resistance Mechanisms of Bacteria. AIMS Microbiol. 2018, 4, 482–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultan, I.; Rahman, S.; Jan, A.T.; Siddiqui, M.T.; Mondal, A.H.; Haq, Q.M.R. Antibiotics, Resistome and Resistance Mechanisms: A Bacterial Perspective. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partridge, S.R.; Kwong, S.M.; Firth, N.; Jensen, S.O. Mobile Genetic Elements Associated with Antimicrobial Resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, e00088-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenzaka, T.; Ishimoto, Y.; Tani, K. Draft Genome Sequence of Multidrug-Resistant Cellulosimicrobium Sp. Strain KWT-B, Isolated from Feces of Hirundo Rustica. Genome Announc. 2017, 5, e00641-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islas-Muñoz, B.; Volkow-Fernández, P.; Ibanes-Gutiérrez, C.; Villamar-Ramírez, A.; Vilar-Compte, D.; Cornejo-Juárez, P. Bloodstream Infections in Cancer Patients. Risk Factors Associated with Mortality. Int. J. Infect. Dis. IJID Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Infect. Dis. 2018, 71, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).