First Insights on Resistance and Virulence Potential of Escherichia coli from Captive Birds of Prey in Portugal
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
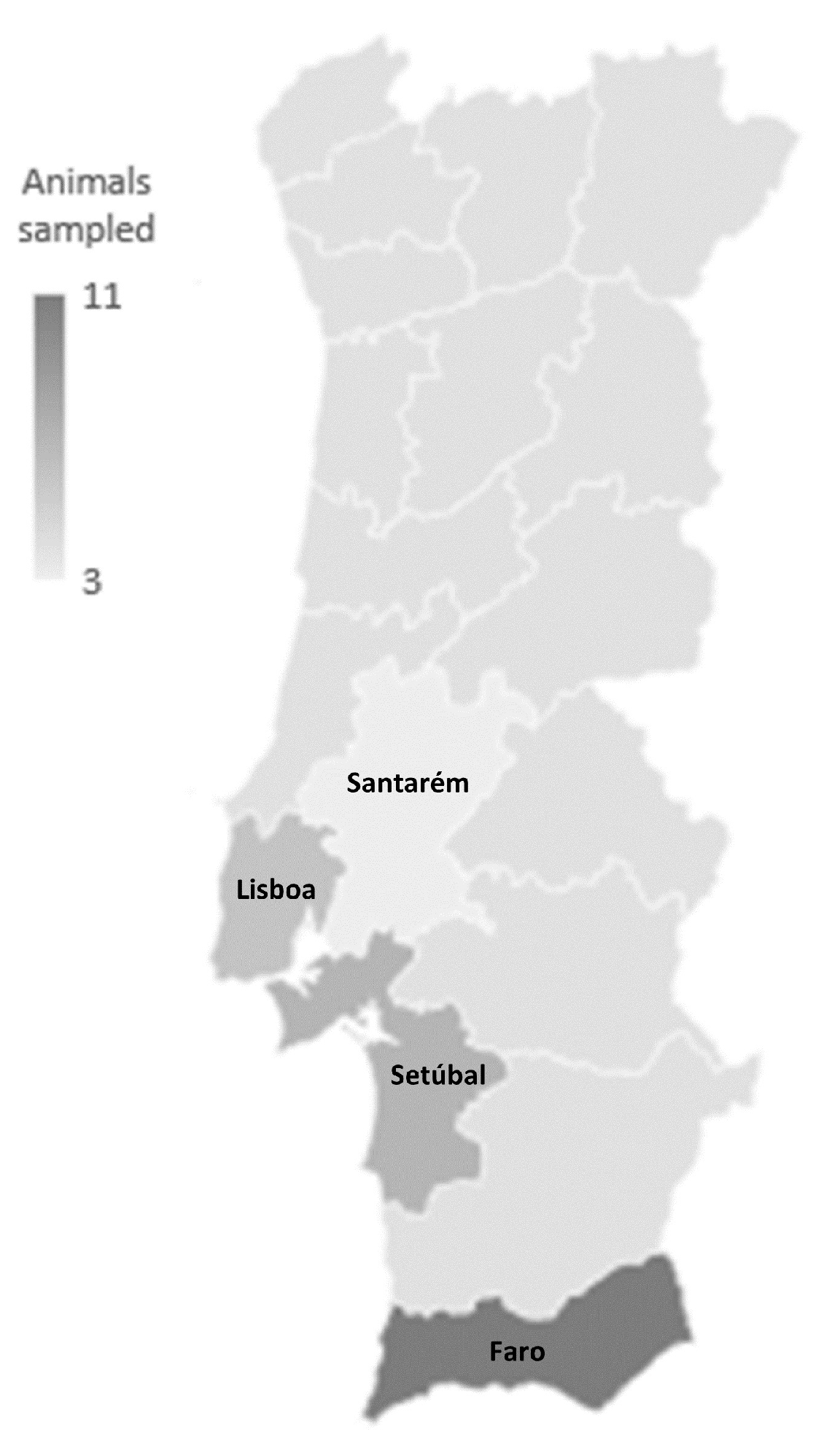
2.1. Sampled Animals and Isolate Identification
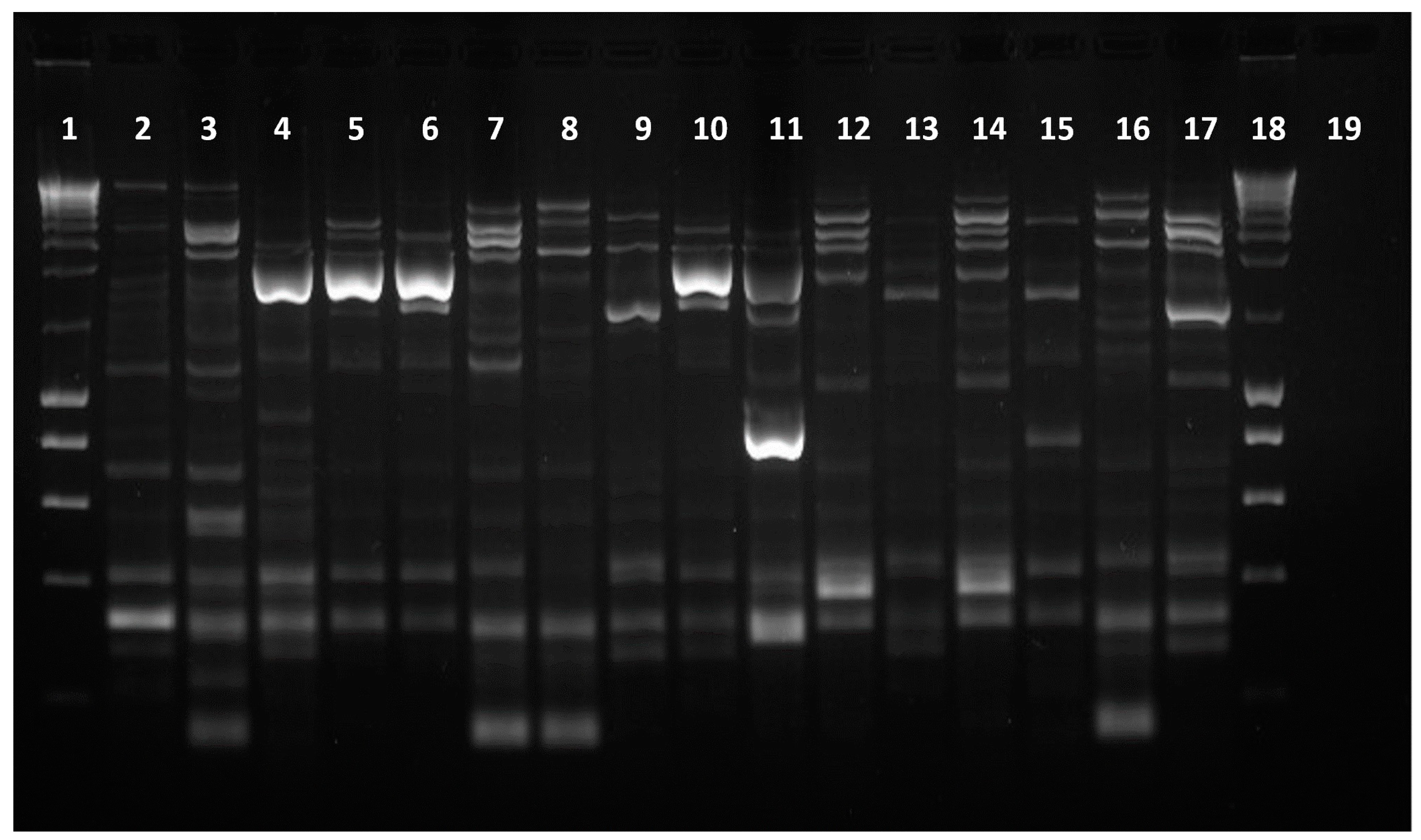
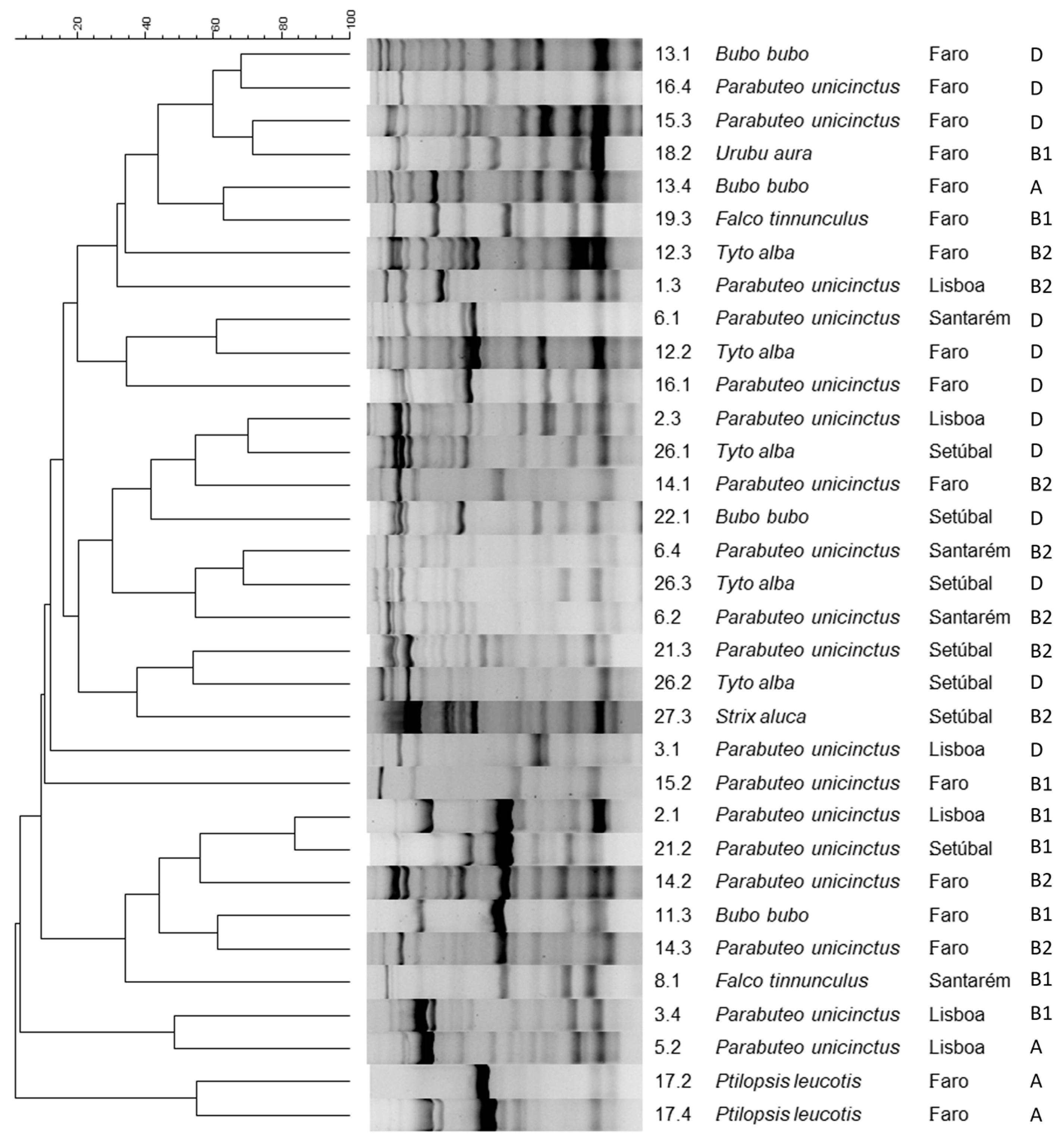
2.2. Characterization of Isolates’ DNA Fingerprint
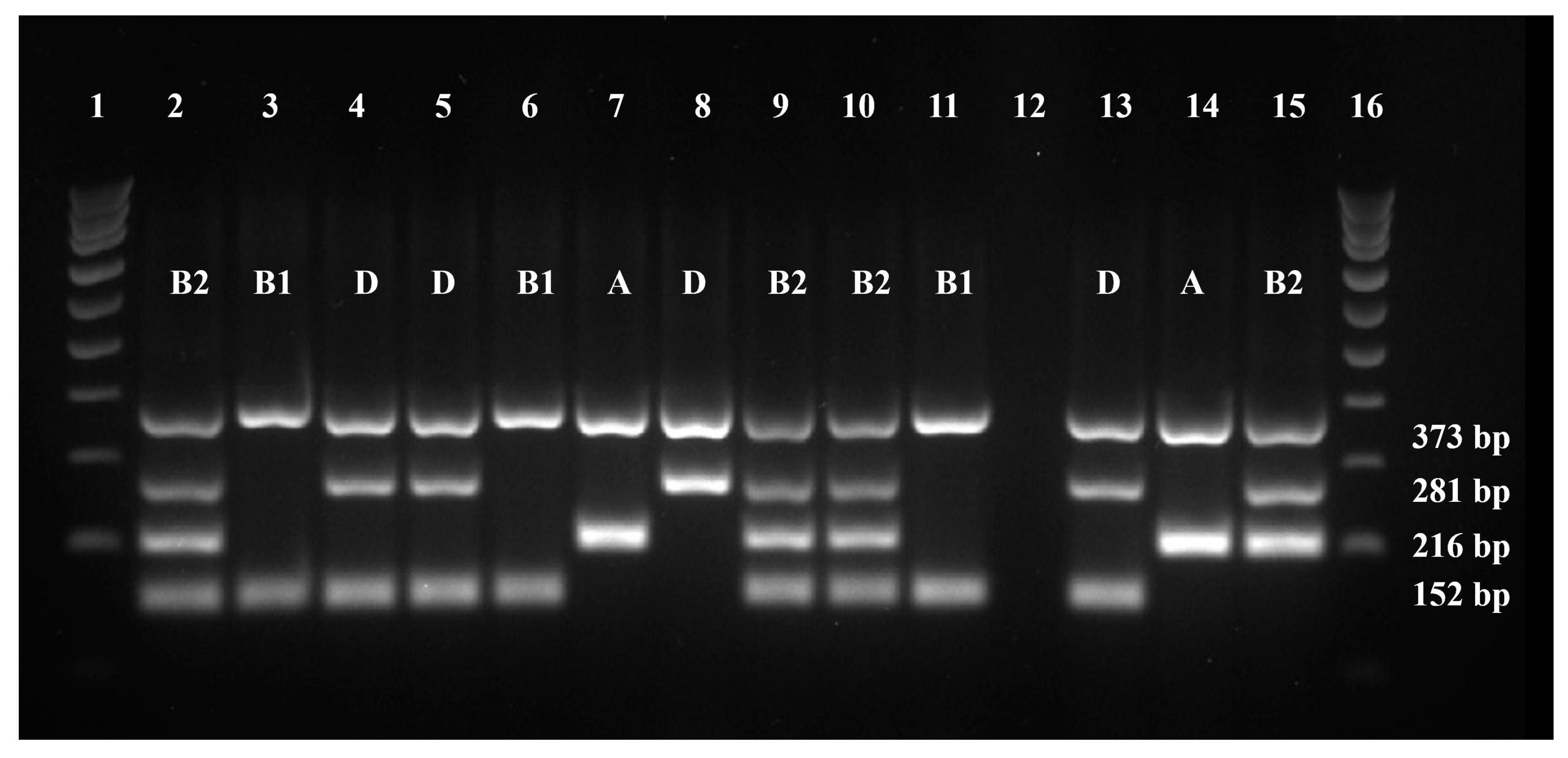
2.3. Phylogenetic Grouping
2.4. Characterization of the Isolates’ Virulence Profiles
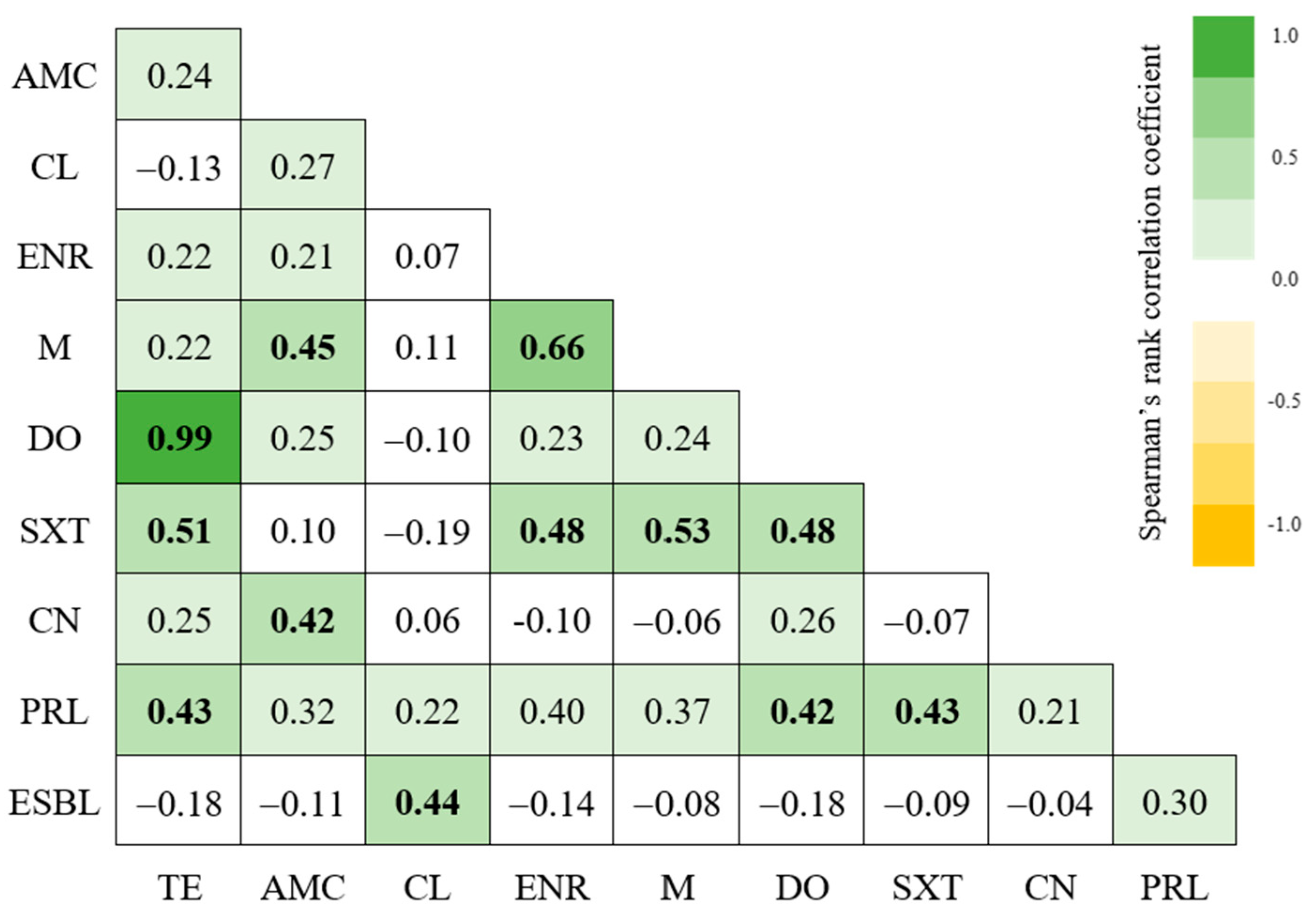
2.5. Characterization of Isolates’ Resistance Profiles
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Collection
4.2. Bacterial Isolation and Identification
4.3. Bacterial DNA Extraction
4.4. DNA Fingerprinting
4.5. Phylogenetic Grouping
4.6. Isolates’ Virulence Profiles
4.7. Isolates’ Antibiotic Resistance Profiles
4.8. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amuasi, J.H.; Lucas, T.; Horton, R.; Winkler, A.S. Reconnecting for Our Future: The Lancet One Health Commission. Lancet 2020, 395, 1469–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, N.; Joji, R.M.; Shahid, M. Evolution and Implementation of One Health to Control the Dissemination of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria and Resistance Genes: A Review. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1065796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serna, C.; Gonzalez-Zorn, B. Antimicrobial Resistance and One Health. Rev. Esp. Quimioter. 2022, 35 (Suppl. S3), 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teffo, T.R.; Fuszonecker, G.; Katona, K. Testing Pigeon Control Efficiency by Different Methods in Urban Industrial Areas, Hungary. Biol. Futur. 2022, 73, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeballos-Gross, D.; Rojas-Sereno, Z.; Salgado-Caxito, M.; Poeta, P.; Torres, C.; Benavides, J.A. The Role of Gulls as Reservoirs of Antibiotic Resistance in Aquatic Environments: A Scoping Review. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 703886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, E.; Fontana, H.; Esposito, F.; Cardoso, B.; Fuga, B.; Costa, G.C.V.; Bosqueiro, T.C.M.; Sinhorini, J.A.; Orico, L.D.; de Masi, E.; et al. Genomic Analysis of Fluoroquinolone-Resistant Leclercia Adecarboxylata Carrying the ISKpn19-Orf-qnrS1-ΔIS3-blaLAP-2 Module in a Synanthropic Pigeon, Brazil. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2023, 33, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahlstrom, C.A.; van Toor, M.L.; Woksepp, H.; Chandler, J.C.; Reed, J.A.; Reeves, A.B.; Waldenström, J.; Franklin, A.B.; Douglas, D.C.; Bonnedahl, J.; et al. Evidence for Continental-Scale Dispersal of Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria by Landfill-Foraging Gulls. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 764, 144551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semedo-Lemsaddek, T.; Pedroso, N.M.; Freire, D.; Nunes, T.; Tavares, L.; Verdade, L.M.; Oliveira, M. Otter Fecal Enterococci as General Indicators of Antimicrobial Resistance Dissemination in Aquatic Environments. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 85, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.; Freire, D.; Pedroso, N.M. Escherichia coli Is Not a Suitable Fecal Indicator to Assess Water Fecal Contamination by Otters. Braz. J. Biol. 2017, 78, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paitan, Y. Current Trends in Antimicrobial Resistance of Escherichia coli. In Escherichia coli, a Versatile Pathogen; Frankel, G., Ron, E.Z., Eds.; Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 416, pp. 181–211. ISBN 978-3-319-99663-9. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, H.A.; Elsohaby, I.; Elamin, A.M.; El-Ghafar, A.E.A.; Elsaid, G.A.; Elbarbary, M.; Mohsen, R.A.; El Feky, T.M.; El Bayomi, R.M. Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing E. coli from Retail Meat and Workers: Genetic Diversity, Virulotyping, Pathotyping and the Antimicrobial Effect of Silver Nanoparticles. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okumu, N.O.; Ngeranwa, J.J.N.; Muloi, D.M.; Ochien’g, L.; Moodley, A.; Mutisya, C.; Kiarie, A.; Wasonga, J.O.; Watson, J.; Amon-Tanoh, M.A.; et al. Risk Factors for Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli Infection in Children Aged 6–24 Months in Peri-Urban Community, Nairobi, Kenya. PLoS Glob. Public Health 2023, 3, e0002594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybak, B.; Krawczyk, B.; Furmanek-Blaszk, B.; Wysocka, M.; Fordon, M.; Ziolkowski, P.; Meissner, W.; Stepniewska, K.; Sikorska, K. Antibiotic Resistance, Virulence, and Phylogenetic Analysis of Escherichia coli Strains Isolated from Free-Living Birds in Human Habitats. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0262236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacristán, C.; Esperón, F.; Herrera-León, S.; Iglesias, I.; Neves, E.; Nogal, V.; Muñoz, M.J.; de la Torre, A. Virulence Genes, Antibiotic Resistance and Integrons in Escherichia coli Strains Isolated from Synanthropic Birds from Spain. Avian Pathol. 2014, 43, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiériot, E.; Patenaude-Monette, M.; Molina, P.; Giroux, J.-F. The Efficiency of an Integrated Program Using Falconry to Deter Gulls from Landfills. Animals 2015, 5, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, R.L.; Eberstein, K.; Scott, D.M. Birds in the Playground: Evaluating the Effectiveness of an Urban Environmental Education Project in Enhancing School Children’s Awareness, Knowledge and Attitudes towards Local Wildlife. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magiorakos, A.-P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-Resistant, Extensively Drug-Resistant and Pandrug-Resistant Bacteria: An International Expert Proposal for Interim Standard Definitions for Acquired Resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montes-Robledo, A.; Buelvas-Montes, Y.; Baldiris-Avila, R. Description of Extraintestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli Based on Phylogenetic Grouping, Virulence Factors, and Antimicrobial Susceptibility. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2023, 15, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obeng, A.S.; Rickard, H.; Ndi, O.; Sexton, M.; Barton, M. Antibiotic Resistance, Phylogenetic Grouping and Virulence Potential of Escherichia coli Isolated from the Faeces of Intensively Farmed and Free Range Poultry. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 154, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kart, D.; Kuştimur, A.S. Investigation of Gelatinase Gene Expression and Growth of Enterococcus faecalis Clinical Isolates in Biofilm Models. Turk. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 16, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Z.; Goraya, M.U.; Ali, L.; Chen, X.; Yu, D. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Eutrophication Enhance Biofilm-Related Drug Resistance in Enterococcus faecalis Isolated from Water Sources. Microb. Pathog. 2024, 186, 106501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freire, S.; Grilo, T.; Poirel, L.; Aires-de-Sousa, M. Urban Pigeons (Columba Livia) as a Source of Broad-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli in Lisbon, Portugal. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Critically Important Antimicrobials for Human Medicine, 6th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; 45p, Available online: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/312266 (accessed on 9 March 2024).
- Office International des Épizooties [OIE]. OIE List of Antimicrobial Agents of Veterinary Importance. 2021. Available online: https://www.woah.org/app/uploads/2021/06/a-oie-list-antimicrobials-june2021.pdf (accessed on 9 March 2024).
- Radhouani, H.; Poeta, P.; Gonçalves, A.; Pacheco, R.; Sargo, R.; Igrejas, G. Wild Birds as Biological Indicators of Environmental Pollution: Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns of Escherichia coli and Enterococci Isolated from Common Buzzards (Buteo Buteo). J. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 61, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diren Sigirci, B.; Celik, B.; Halac, B.; Adiguzel, M.C.; Kekec, I.; Metiner, K.; Ikiz, S.; Bagcigil, A.F.; Ozgur, N.Y.; Ak, S.; et al. Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles of Escherichia coli Isolated from Companion Birds. J. King Saud. Univ. Sci. 2020, 32, 1069–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, A.; Simões, R.; Oliveira, M.; Vaz-Pires, P.; Brandão, R.; da Costa, P.M. Multidrug Resistance in Wild Bird Populations: Importance of the Food Chain. J. Zoo. Wildl. Med. 2015, 46, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghnieh, W.; Fadlallah, M.; Saleh, F.; El-Hariri, S.; Sokhn, E.S. Extended Spectrum Beta-Lactamase Carriage among Elderly Residents of a Long-Term Care Facility in Beirut. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2023, 52, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.K.; Ekka, R.; Mishra, M.; Mohapatra, H. Association Study of Multiple Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence: A Strategy to Assess the Extent of Risk Posed by Bacterial Population in Aquatic Environment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos, A.; Cunha, E.; Baptista, L.; Tavares, L.; Oliveira, M. ESBL-Positive Enterobacteriaceae from Dogs of Santiago and Boa Vista Islands, Cape Verde: A Public Health Concern. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, M.; Nóbrega Carneiro, C.; Villada Rosales, A.M.; Grilo, M.; Ramiro, Y.; Cunha, E.; Nunes, T.; Tavares, L.; Sandi, J.; Oliveira, M. Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Profiles of Enterobacterales Isolated from Two-Finger and Three-Finger Sloths (Choloepus Hoffmanni and Bradypus Variegatus) of Costa Rica. PeerJ 2022, 10, e12911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Procop, G.W.; Church, D.L.; Hall, G.S.; Janda, W.M.; Koneman, E.W.; Schreckenberger, P.C.; Woods, G.L. Koneman’s Color Atlas and Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology, 7th ed.; Jones & Bartlett Learning: Massachusetts, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-1-4511-1659-5. [Google Scholar]
- Dashti, A.; Jadaon, M.; Abdulsamad, A.; Dashti, H. Heat Treatment of Bacteria: A Simple Method of DNA Extraction for Molecular Techniques. Kuwait Med. J. 2009, 41, 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, E.; Leitão, S.; Tenreiro, T.; Pomba, C.; Nunes, T.; Lopes Da Costa, L.; Mateus, L. Genomic and Phenotypic Characterization of Escherichia coli Isolates Recovered from the Uterus of Puerperal Dairy Cows. J. Dairy. Sci. 2009, 92, 6000–6010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doumith, M.; Day, M.J.; Hope, R.; Wain, J.; Woodford, N. Improved Multiplex PCR Strategy for Rapid Assignment of the Four Major Escherichia coli Phylogenetic Groups. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 3108–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clermont, O.; Christenson, J.K.; Denamur, E.; Gordon, D.M. The Clermont Escherichia coli Phylo-typing Method Revisited: Improvement of Specificity and Detection of New Phylo-groups. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2013, 5, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria Isolated from Animals, 4th ed.; Lubbers, B.V., Ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Westlakes, PA, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-1-68440-010-2, VET08. [Google Scholar]
- Comité de L’antibiogramme de la Société Française de Microbiologie—Recommandations Vétérinaires; Société Française de, M., Ed.; SFM: Paris, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 33rd ed.; Lubbers, B.V., Ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Berwyn, PA, USA, 2020; ISBN 978-1-68440-221-2, M100. [Google Scholar]
- Thukral, S.; Gaind, R.; Khan, M. Evaluation of a Modified Double-Disc Synergy Test for Detection of Extended Spectrum β-Lactamases in AMPC β-Lactamase-Producing Proteus Mirabilis. Indian. J. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 26, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.M.; Singh, H.L. Comparative Evaluation of Six Phenotypic Methods for Detecting Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2014, 8, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Species | Common Name | Samples (n = 27) |
|---|---|---|
| Parabuteo unicinctus | Harris’s hawk | 11 |
| Bubo bubo | Eurasian Eagle-Owl | 4 |
| Falco tinnunculus | Common Kestrel | 4 |
| Tyto alba | Western Barn Owl | 2 |
| Bubo bengalensis | Rock Eagle-Owl | 1 |
| Bubo virginianus | Great Horned Owl | 1 |
| Falco biarmicus | Lanner Falcon | 1 |
| Ptilopsis leucotis | Northern White-faced Owl | 1 |
| Strix aluco | Tawny Owl | 1 |
| Urubu aura | Turkey vulture | 1 |
| Total | 27 |
| Antimicrobial Category | Antimicrobial Agent | Disk Content | Number of Isolates (n = 33) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Susceptible | Intermediate | Resistant | |||
| Tetracyclines | Tetracycline | 30 μg | 22 | - | 11 |
| Doxycycline | 30 μg | 22 | 1 | 10 | |
| Aminoglycosides | Gentamicin | 10 μg | 32 | - | 1 |
| Folate pathway inhibitors | Sulfamethoxazole/ Trimethoprim | 25 μg | 29 | - | 4 |
| Penicillins + β-lactamase inhibitors | Amoxycillin/ Clavulanic Acid | 30 μg | 28 | 5 | - |
| Antipseudomonal Penicillins | Piperacillin | 100 μg | 19 | - | 14 |
| First-generation Cephalosporin | Cephalexin | 30 μg | 10 | 19 | 4 |
| Fluoroquinolone | Enrofloxacin | 5 μg | 25 | 5 | 3 |
| Marbofloxacin | 5 μg | 30 | - | 3 | |
| Marker | Primer Direction | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) | Product Length (bp) | Positive Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| gadA | Forward | GATGAAATGGCGTTGGCGCAAG | 373 | E. coli J96 E. coli KS52 Isolate 16.1 |
| Reverse | GGCGGAAGTCCCAGACGATATCC | |||
| chuA | Forward | ATGATCATCGCGGCGTGCTG | 281 | E. coli J96 Isolate 16.1 |
| Reverse | AAACGCGCTCGCGCCTAAT | |||
| yjaA | Forward | TGTTCGCGATCTTGAAAGCAAACGT | 216 | E. coli J96 E. coli KS52 |
| Reverse | ACCTGTGACAAACCGCCCTCA | |||
| TSPE4.C2 | Forward | GCGGGTGAGACAGAAACGCG | 152 | Isolate 16.1 |
| Reverse | TTGTCGTGAGTTGCGAACCCG |
| Markers | Product Length (bp) | Phylogenetic Group | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B1 | B2 | D | |||||
| gadA | 373 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| chuA | 281 | + | + | + | + | |||
| yjaA | 216 | + | + | + | ||||
| TSPE4.C2 | 152 | + | + | + | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Magalhães, R.; Abreu, R.; Pereira, G.; Cunha, E.; Silva, E.; Tavares, L.; Chambel, L.; Oliveira, M. First Insights on Resistance and Virulence Potential of Escherichia coli from Captive Birds of Prey in Portugal. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 379. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13050379
Magalhães R, Abreu R, Pereira G, Cunha E, Silva E, Tavares L, Chambel L, Oliveira M. First Insights on Resistance and Virulence Potential of Escherichia coli from Captive Birds of Prey in Portugal. Antibiotics. 2024; 13(5):379. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13050379
Chicago/Turabian StyleMagalhães, Rita, Raquel Abreu, Gonçalo Pereira, Eva Cunha, Elisabete Silva, Luís Tavares, Lélia Chambel, and Manuela Oliveira. 2024. "First Insights on Resistance and Virulence Potential of Escherichia coli from Captive Birds of Prey in Portugal" Antibiotics 13, no. 5: 379. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13050379
APA StyleMagalhães, R., Abreu, R., Pereira, G., Cunha, E., Silva, E., Tavares, L., Chambel, L., & Oliveira, M. (2024). First Insights on Resistance and Virulence Potential of Escherichia coli from Captive Birds of Prey in Portugal. Antibiotics, 13(5), 379. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13050379






