The Epidemiology, Management and Therapeutic Outcomes of Subdural Empyema in Neonates with Acute Bacterial Meningitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patients, Study Design and Settings
2.2. Definitions and Data Collection
2.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients’ Demographics, Microbiology, and Clinical Features
3.2. Therapeutic Courses and Neurological Complications
3.3. Therapeutic Strategies and Final Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Basmaci, R.; Bonacorsi, S.; Bidet, P.; Biran, V.; Aujard, Y.; Bingen, E.; Béchet, S.; Cohen, R.; Levy, C. Escherichia coli meningitis features in 325 children from 2001 to 2013 in France. Clinical. Infect. Dis. 2016, 61, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okike, I.O.; Johnson, A.P.; Henderson, K.L.; Blackburn, R.M.; Muller-Pebody, B.; Ladhani, S.N.; Anthony, M.; Ninis, N.; Heath, P.T. Incidence, etiology, and outcome of bacterial meningitis in infants aged < 90 days in the United Kingdom and Republic of Ireland: Prospective, enhanced, national population-based surveillance. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 59, e150–e157. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Okike, I.O.; Ladhani, S.N.; Johnson, A.P.; Henderson, K.L.; Blackburn, R.M.; Muller-Pebody, B.; Cafferkey, M.; Anthony, M.; Ninis, N.; Heath, P.T. Clinical characteristics and risk factors for poor outcome in infants less than 90 days of age with bacterial meningitis in the United Kingdom and Ireland. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2018, 37, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, T.A.; Munoz, F.M.; Troisi, C.L.; Nolan, M.S.; Hasbun, R.; Brown, E.L.; Murray, K.O. The epidemiology of meningitis in infants under 90 days of age in a large pediatric hospital. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, M.; Fu, X.; Cai, J.; Chen, S.; Lin, Y.; Jiang, N.; Chen, S.; Lin, Z. Escherichia coli causing neonatal meningitis during 2001–2020: A study in Eastern China. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2021, 14, 3007–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchenir, L.; Renaud, C.; Khan, S.; Bitnun, A.; Boisvert, A.-A.; McDonald, J.; Bowes, J.; Brophy, J.; Barton, M.; Ting, J.; et al. The epidemiology, management, and outcomes of bacterial meningitis in infants. Pediatrics 2017, 140, e20170476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, T.; Pinho, L.; Bonifacio Andrade, E. Group B Streptococcal neonatal meningitis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2022, 35, e0007921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.H.; Duque, J.R.; Wong, J.S.C.; Chan, C.M.V.; Lam, C.S.I.; Fu, Y.M.; Cheong, K.N.; Chua, G.T.; Lee, P.P.; Ip, P.; et al. Epidemiology and trends of infective meningitis in neonates and infants less than 3 months old in Hong Kong. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 111, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sewell, E.; Roberts, J.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Association of infection in neonates and long-term neurodevelopmental outcome. Clin. Perinatol. 2021, 48, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, D.; Rashid, H.; El-Bashir, H.; Sweeney, F.; Shore, T.; Booy, R.; Viner, R.M. Impact of meningitis on intelligence and development: A systemic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kralik, S.F.; Kukreja, M.K.; Paldino, M.J.; Desai, N.K.; Vallejo, J.G. Comparison of CSF and MRI findings among neonates and infants with E coli or group B Streptococcal meningitis. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2019, 40, 1413–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Naggar, W.; Afifi, J.; McMillan, D.; Toye, J.; Ting, J.; Yoon, E.W.; Shah, P.S. Epidemiology of meningitis in Canadian neonatal intensive care units. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2019, 38, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, N.; Liu, W.; Prakash, A.; Zhang, C.; Kim, K.S. Targeting E coli invasion of the blood-brain barrier for investigating the pathogenesis and therapeutic development of E coli meningitis. Cell. Microbiol. 2020, 22, e13231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzumdar, D.; Biyani, N.; Deopujari, C. Subdural empyema in children. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2018, 34, 1881–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.; Riordan, A.; Tawil, M.; Mallucci, C.; Jauhari, P.; Solomon, T.; Kneen, R. Subdural empyema caused by Neisseria meningitides: A case report and review of the literature. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2016, 35, 1156–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcinkaya, R.; Tanir, G.; Kaman, A.; Oz, F.N.; Aydin Teke, T.; Yasar Durmus, S.; Ekşioğlu, A.S.; Aycan, A.E.; Ceyhan, M. Pediatric subdural empyema as a complication of meningitis: Could CSF protein/CSF glucose ratio be used to screen for subdural empyema? Eur. J. Pediatr. 2021, 180, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xu, H.; Liu, G.; Liu, J.; Yu, H.; Chen, B.; Zheng, G.; Shu, M.; Du, L.; Xu, Z.; et al. A Multicenter Epidemiological and Pathogenic Characteristics Study of Community-Acquired Bacterial Meningitis Children in China: Results from the Chinese Pediatric Bacterial Meningitis Surveillance (CPBMS) 2019–2020. Infect. Drug Resist. 2023, 16, 6587–6601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keus, A.M.J.; Peeters, D.D.; Bekker, V.V.; Veldkamp, K.E.K.; Lambregts, M.M.; Bolt-Wieringa, J.J.; Steggerda, S.S. Neonatal Meningitis and Subdural Empyema Caused by an Unusual Pathogen. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2019, 38, e329–e331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, V.; Lakshmikantha, K.M.; Nallasamy, K.; Sudeep, K.C.; Baranwal, A.K.; Jayashree, M. Subdural empyema due to Salmonella paratyphi B in an infant: A case report and review of literature. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2018, 34, 2317–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundy, P.; Kaufman, C.; Garcia, D.; Partington, M.D.; Grabb, P.A. Intracranial subdural empyemas and epidural abscesses in children. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2019, 24, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, M.H.; Hsu, J.F.; Kuo, H.C.; Lai, M.Y.; Chiang, M.C.; Lin, Y.J.; Huang, H.-R.; Chu, S.-M.; Tsai, M.-H. Neurological Complications in Young Infants with Acute Bacterial Meningitis. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Beek, D.; Cabellos, C.; Dzupova, O.; Esposito, S.; Klein, M.; Kloek, A.T.; Leib, S.; Mourvillier, B.; Ostergaard, C.; Pagliano, P.; et al. ESCMID guideline: Diagnosis and treatment of acute bacterial meningitis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22 (Suppl. S3), S37–S62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, X.W.; Zhang, J.T.; Ma, Y.B.; He, M.W.; Yao, G.E.; Wang, W.; Qi, X.-K.; Chen, X.-Y.; Wu, L.; Wang, X.-L.; et al. Metagenomic next-generation sequencing for diagnosis of infectious encephalitis and meningitis: A large, prospective case series of 213 patients. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Chu, S.M.; Wang, H.C.; Yang, P.H.; Huang, H.R.; Chiang, M.C.; Fu, R.H.; Tsai, M.H.; Hsu, J.F. Complicated Streptococcus agalactiae sepsis with/without meningitis in young infants and newborns: The clinical and molecular characteristics and outcomes. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beers, S.R.; Wisniewski, S.R.; Garcia-Filion, P.; Tian, Y.; Hahner, T.; Berger, R.P.; Bell, M.J.; Adelson, P.D. Validity of a pediatric version of the Glasgow Outcomes Scale-Extended. J. Neurotrauma 2012, 29, 1126–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matuschek, E.; Ahman, J.; Webster, C.; Kahlmeter, G. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of colistin-evolution of seven commercial MIC products against standard broth microdilution for Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumonia, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Acinetobacter spp. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 865–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- M100-S24; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, Twenty-Fourth Informational Supplement. SLCI: Wayne, MI, USA, 2014.
- Tibussek, D.; Sinclair, A.; Yau, I.; Teatero, S.; Fittipaldi, N.; Richardson, S.E.; Mayatepek, E.; Jahn, P.; Askalan, R. Late-onset group B streptococcal meningitis has cerebrovascular complications. J. Pediatr. 2015, 166, 1187–1192.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.H.; Chen, N.Y.; Tu, P.H.; Lee, S.T.; Wu, C.T. The treatment and outcome of postmeningitic subdural empyema in infants. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2010, 6, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanu, O.O.; Esezobor, C.I.; Ojo, O.A.; Asoegwu, C.N.; Nnoli, C.; Dawang, Y.; Temiye, E. Infantile supratentorial subdural empyema managed by percutaneous aspiration: An outcome study in a Nigerian city. Sudan. J. Paediatr. 2019, 19, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou-Yang, M.C.; Tsai, M.H.; Chu, S.M.; Chen, C.C.; Yang, P.H.; Huang, H.R.; Chang, C.-M.; Fu, R.-H.; Hsu, J.-F. The Clinical Characteristics, Microbiology and Risk Factors for Adverse Outcomes in Neonates with Gram-Negative Bacillary Meningitis. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashau, R.C.; Meiring, S.T.; Dramowski, A.; Magobo, R.E.; Quan, V.C.; Perovic, O.; von Gottberg, A.; Cohen, C.; Velaphi, S.; van Schalkwyk, E.; et al. Culture-confirmed neonatal bloodstream infections and meningitis in South Africa, 2014–2019: A cross-sectional study. Lancet Glob. Health 2022, 10, e1170–e1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.M.; Huang, W.Y.; Lee, M.L.; Yang, A.D.; Chaou, K.P.; Hsieh, L.-Y. Clinical features, acute complications, and outcome of Salmonella meningitis in children under one year of age in Taiwan. BMC Infect. Dis. 2011, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, J.F.; Lu, J.J.; Chu, S.M.; Lee, W.J.; Huang, H.R.; Chiang, M.C.; Yang, P.-H.; Tsai, M.-H. The Clinical and Genetic Characteristics of Streptococcus agalactiae Meningitis in Neonates. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.J.; Chiu, N.C.; Huang, F.Y. Subdural empyema in children-20-year experience in a medical center. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2008, 41, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jim, K.K.; Brouwer, M.C.; van der Ende, A.; van de Beek, D. Subdural empyema in bacterial meningitis. Neurology 2012, 79, 2133–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahan, B.; Choi, E.Y.; Nieves, G. Cerebrospinal fluid analysis. Am. Fam. Physician 2021, 103, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jolayemi, E.O.; Bankole, O.B.; Ojo, O.A.; Bamigboye, B.; Adebayo, B.O.; Arekhandia, B.J.; Asoegwu, C.N.; Alabi, O.I.; Ifezue, U.C.; Nwawolo, C.C.; et al. Contemporary management of intracranial subdural empyema: An institutional experience. J. West Afr. Coll. Surg. 2022, 12, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kanu, O.O.; Ojo, O.; Esezobor, C.; Bankole, O.; Olatosi, J.; Ogunleye, E.; Asoegwu, C.; Eghosa, M.; Adebayo, B.; Oladele, R.; et al. Pediatric brain abscess—Etiology, management challenges and outcome in Lagos Nigeria. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2021, 12, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfield, C.M.; Sharma, J.; Dobson, S. Pediatric intracranial abscesses. J. Infect. 2015, 71 (Suppl. S1), S42–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
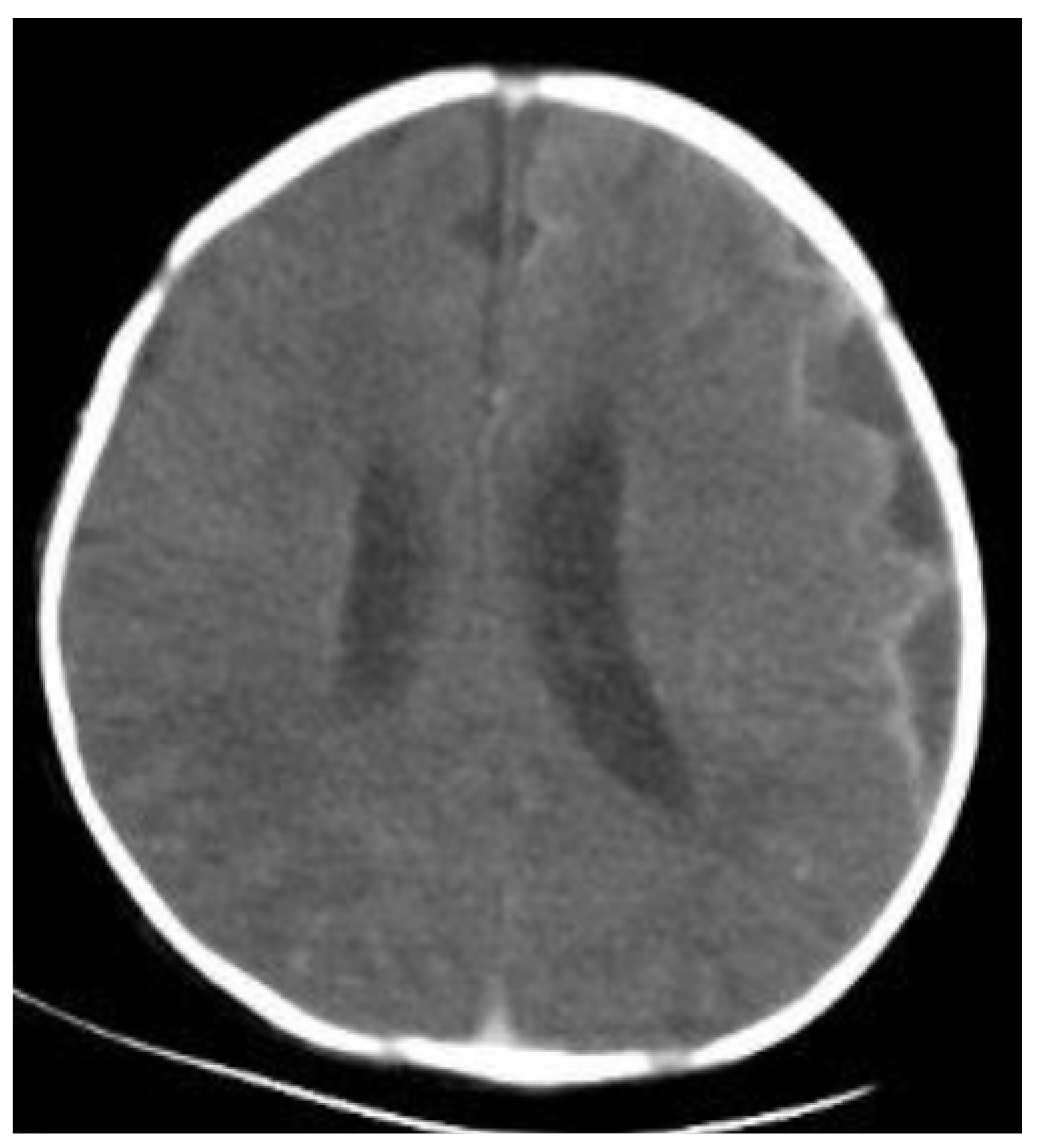
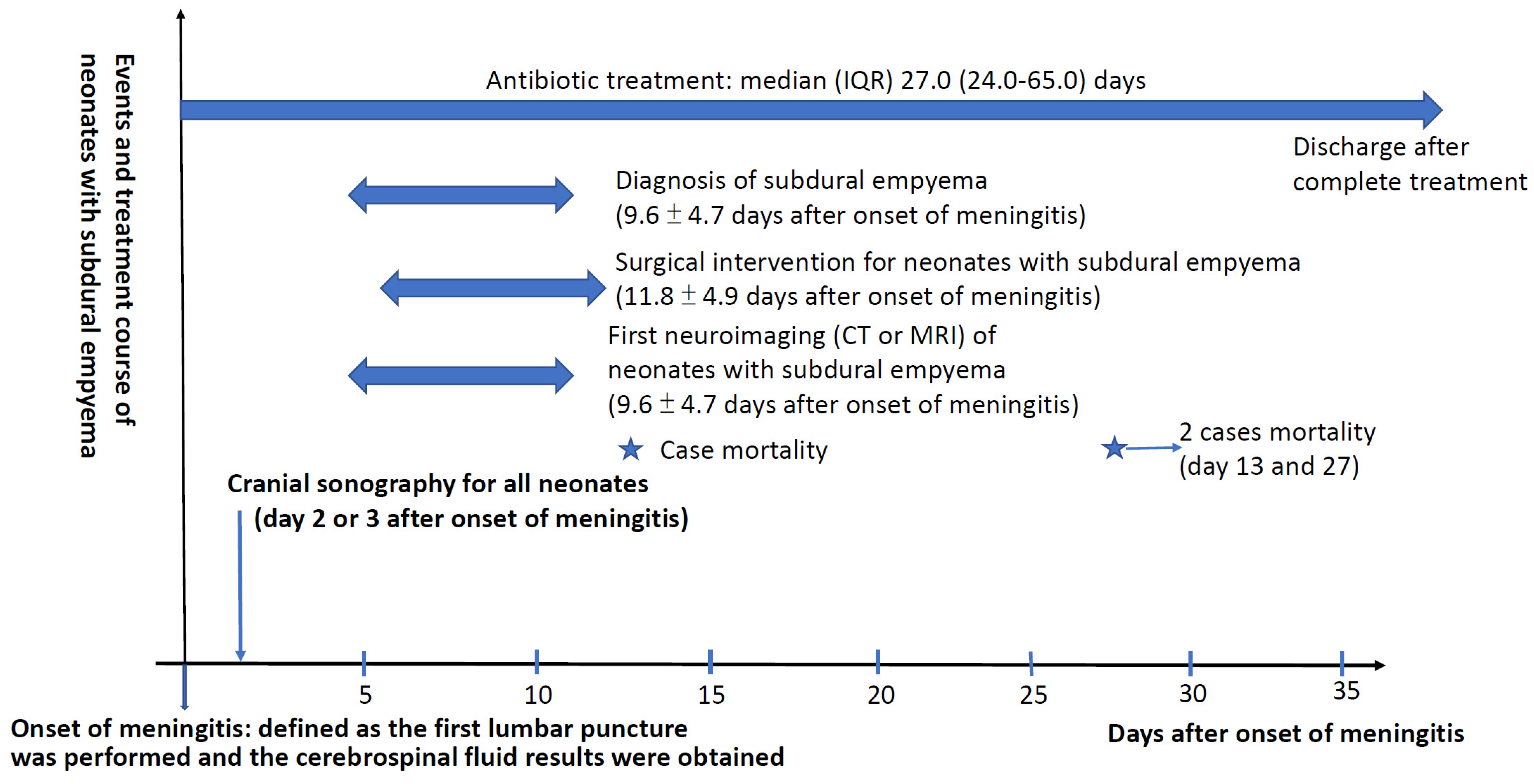

| All Cases (Total n = 153) | Cases with Subdural Empyema after Meningitis (Total n = 27) | Neonates with Bacterial Meningitis (Total n = 126) | p Values | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gestational age, (week) | 38.0 (36.0–39.0) | 37.0 (36.0–38.0) | 38.0 (36.8–40.0) | 0.314 |
| Birth body weight, (g) | 2890.0 (2490–3227.5) | 2870.0 (2500–3050) | 2890.0 (2464.0–3240.0) | 0.698 |
| Gender, (male/female, n/%) | 82 (53.6)/71 (46.4) | 15 (55.6)/12 (44.4) | 67 (53.2)/59 (46.8) | 0.836 |
| Birth by NSD/Cesarean section, n (%) | 104 (68.0)/49 (32.0) | 18 (66.7)/9 (33.3) | 86 (68.2)/40 (31.7) | 0.514 |
| 5 min Apgar score < 7, n (%) | 15 (9.8) | 3 (11.1) | 12 (9.5) | 0.628 |
| Premature rupture of membrane, n (%) | 27 (17.6) | 5 (18.5) | 22 (17.5) | 0.697 |
| Onset of bacterial meningitis (day), median (IQR) | 30.0 (13.0–69.5) | 30.0 (21.0–47.0) | 36.0 (11.0–82.0) | 0.476 |
| Early-onset sepsis (≤7 days), n (%) | 27 (17.6) | 3 (11.1) | 24 (19.0) | |
| Late-onset sepsis (8–90 days), n (%) | 126 (82.4) | 24 (88.9) | 102 (81.0) | |
| Clinical features *, n (%) | ||||
| Fever (≥38.3 °C) | 110 (71.9) | 23 (85.2) | 87 (69.0) | 0.025 |
| Seizure (within 3 days after onset of meningitis) | 62 (40.5) | 22 (81.5) | 40 (31.7) | <0.001 |
| Apnea, bradycardia and/or cyanosis | 91 (59.5) | 17 (63.0) | 74 (58.7) | 0.245 |
| Ventilator requirement | 0.131 | |||
| Room air | 62 (40.5) | 10 (37.0) | 52 (41.3) | |
| Nasal canula | 9 (5.9) | 3 (11.1) | 6 (4.8) | |
| Non-invasive ventilator (N-CPAP and N-IMV) | 16 (10.4) | 4 (14.8) | 12 (9.5) | |
| Intubation | 56 (36.6) | 7 (25.9) | 49 (38.9) | |
| High-frequency oscillatory ventilator | 10 (6.5) | 3 (11.1) | 7 (5.5) | 0.053 |
| Abdominal distension and/or vomiting | 92 (60.1) | 18 (66.7) | 74 (58.7) | 0.520 |
| Hypoglycemia | 26 (17.0) | 5 (18.5) | 21 (16.6) | 0.782 |
| Hypotension | 54 (35.1) | 12 (44.4) | 42 (33.3) | 0.277 |
| Severe sepsis | 73 (47.7) | 16 (59.3) | 57 (45.2) | 0.133 |
| Disseminated intravascular coagulopathy | 31 (20.3) | 7 (25.9) | 24 (19.0) | 0.286 |
| Requirement of blood transfusion ** | 89 (58.2) | 19 (70.4) | 70 (55.6) | 0.114 |
| Laboratory data at onset of GBS bacteremia, n (%) | ||||
| Leukocytosis (WBC > 20,000/L) | 79 (51.6) | 18 (66.7) | 61 (48.4) | 0.065 |
| Leukopenia (WBC < 4000/L) | 52 (34.0) | 9 (33.3) | 43 (34.1) | 1.000 |
| Shift to left in WBC (immature > 20%) | 35 (22.9) | 8 (29.6) | 27 (21.4) | 0.247 |
| Anemia (hemoglobin level < 11.5 g/dL) | 80 (52.3) | 16 (59.3) | 64 (50.8) | 0.279 |
| Thrombocytopenia (platelet < 150,000/uL) | 42 (27.5) | 8 (29.6) | 34 (27.0) | 0.474 |
| Metabolic acidosis | 54 (35.3) | 11 (40.7) | 43 (34.1) | 0.329 |
| Coagulopathy | 52 (34.0) | 11 (40.7) | 41 (32.5) | 0.274 |
| C-reactive protein (mg/dL), median (IQR) | 121.0 (50.6–187.4) | 116.5 (70.0–155.5) | 108.0 (52.5–179.8) | 0.616 |
| Cerebrospinal fluid examinations | ||||
| WBC count (/L), median (IQR) | 32.2 (11.5–480.0) | 300.0 (50.0–2593.8) | 25.9 (10.8–380.0) | 0.011 |
| Protein level (mg/dL), median (IQR) | 274.6 (111.6–417.2) | 333.0 (275.5–493.5) | 233.0 (92.7–370.0) | 0.006 |
| Glucose level (mg/dL), median (IQR) | 31.0 (7.0–52.0) | 12.0 (5.0–30.5) | 37.5 (12.8–54.3) | 0.003 |
| Pathogens | 0.189 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae (GBS) | 54 (35.3) | 12 (44.4) | 42 (33.3) | |
| E. coli | 39 (25.5) | 9 (33.3) | 30 (23.8) | |
| Other gram-negative bacilli | 28 (18.3) | 4 (14.8) | 24 (19.0) | |
| Other gram-positive cocci | 21 (13.7) | 2 (7.4) | 19 (15.1) | |
| CSF culture-negative cases | 11 (7.2) | 0 (0) | 11 (8.7) |
| Neurological Complications, Sequelae and Death | Neonates with Subdural Empyema after Meningitis (n = 27) | Neonates with Bacterial Meningitis (n = 126) | p Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Any neurological complications | 27 (100.0) | 98 (77.8) | <0.001 |
| Seizure with anti-convulsants at discharge | 23 (85.2) | 44 (34.9) | <0.001 |
| Subdural effusion | 22 (81.5) | 42 (33.3) | <0.001 |
| Increased intracranial pressure | 8 (29.6) | 32 (25.4) | 0.636 |
| Ventriculomegaly | 14 (51.9) | 48 (38.1) | 0.280 |
| Hydrocephalus | 8 (29.6) | 23 (18.3) | 0.196 |
| Encephalomalacia | 4 (14.8) | 11 (8.7) | 0.335 |
| Subependymal hemorrhage | 2 (7.4) | 21 (16.7) | 0.222 |
| Intraventricular hemorrhage | 2 (7.4) | 12 (9.5) | 0.663 |
| Ventriculitis | 3 (11.1) | 13 (10.3) | 0.903 |
| Periventricular leukomalacia | 7 (25.9) | 4 (3.2) | 0.001 |
| Infarction | 3 (11.1) | 9 (7.1) | 0.486 |
| Brain atrophy | 1 (3.7) | 2 (1.6) | 0.187 |
| Discharge with neurological sequelae | 14 (56.6) | 54 (47.8) | 0.260 |
| Final mortality * | 2 (7.4) | 13 (10.3) | 0.463 |
| Parameters | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p Value | Adjusted OR (95% CI) | p Value | |
| Preterm birth (GA < 37 weeks) | 2.28 (1.08–4.81) | 0.030 | 1.83 (0.76–4.25) | 0.194 |
| Septic shock | 2.11 (1.01–4.39) | 0.047 | 1.99 (0.58–6.84) | 0.282 |
| Respiratory failure (requirement of intubation) | 2.53 (1.12–5.74) | 0.026 | 1.35 (0.39–4.78) | 0.712 |
| Concurrent bacteremia | 0.78 (0.41–1.50) | 0.462 | ||
| GBS versus gram-negative bacilli | 0.74 (0.38–1.67) | 0.862 | ||
| High protein level in CSF | 0.93 (0.46–1.87) | 0.835 | ||
| Early-onset sepsis | 4.26 (1.51–12.04) | 0.006 | 3.38 (1.10–8.04) | 0.027 |
| The presence of subdural empyema | 1.72 (0.83–3.55) | 0.218 | 1.42 (0.87–2.56) | 0.356 |
| Seizure at onset | 2.48 (1.28–4.81) | 0.007 | 2.45 (1.15–4.56) | 0.013 |
| Thrombocytopenia (platelet count < 150,000/μL) | 0.89 (0.41–1.91) | 0.762 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, W.-J.; Tsai, M.-H.; Hsu, J.-F.; Chu, S.-M.; Chen, C.-C.; Yang, P.-H.; Huang, H.-R.; Chi, M.-C.; Lee, C.-W.; Ou-Yang, M.-C. The Epidemiology, Management and Therapeutic Outcomes of Subdural Empyema in Neonates with Acute Bacterial Meningitis. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 377. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13040377
Lee W-J, Tsai M-H, Hsu J-F, Chu S-M, Chen C-C, Yang P-H, Huang H-R, Chi M-C, Lee C-W, Ou-Yang M-C. The Epidemiology, Management and Therapeutic Outcomes of Subdural Empyema in Neonates with Acute Bacterial Meningitis. Antibiotics. 2024; 13(4):377. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13040377
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Wei-Ju, Ming-Horng Tsai, Jen-Fu Hsu, Shih-Ming Chu, Chih-Chen Chen, Peng-Hong Yang, Hsuan-Rong Huang, Miao-Ching Chi, Chiang-Wen Lee, and Mei-Chen Ou-Yang. 2024. "The Epidemiology, Management and Therapeutic Outcomes of Subdural Empyema in Neonates with Acute Bacterial Meningitis" Antibiotics 13, no. 4: 377. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13040377
APA StyleLee, W.-J., Tsai, M.-H., Hsu, J.-F., Chu, S.-M., Chen, C.-C., Yang, P.-H., Huang, H.-R., Chi, M.-C., Lee, C.-W., & Ou-Yang, M.-C. (2024). The Epidemiology, Management and Therapeutic Outcomes of Subdural Empyema in Neonates with Acute Bacterial Meningitis. Antibiotics, 13(4), 377. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13040377






