Post-Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic Antimicrobial Resistance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Antimicrobial Resistance and Germs during the Pandemic
2.1.1. The Concept of Antimicrobial Resistance
2.1.2. Antibiotics Resistance and Germs: Gram-Negative Bacteria
2.1.3. Gram-Positive Bacteria
2.1.4. Fungi
| Type and Number of Patients | Germs’ Resistance | Main Antibiotic Resistance | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 340 outpatients/inpatients | E. coli, Klebsiella, S. aureus (MSSA), S. aureus (MRSA), P. aeruginosa., and Enterobacter species | Cotrimoxazole, piperacillin, ceftazidime, and cefepime | [38] |
| 102 ICU patients | A. baumannii, K. pneumoniae, and S. maltophilia | Carbapenem and methicillin | [39] |
| 190 ICU patients | K. pneumoniae, A. baumannii, S. maltophilia, C. albicans, and Pseudomonas spp. | Carbapenem | [40] |
| 750 ICU patients | A. baumannii, and K. pneumonia | MDR, carbapenem | [41] |
| 611 ICU patients | Acinetobacter spp. | Imipenem, meropenem, and ciprofloxacin | [42] |
| 197 ICU patients | K. pneumoniae and A. baumannii | (PDR)K. pneumoniae and (MDR) A. baumannii | [43] |
| 856 ICU patients | E. coli and K. pneumonia | Ciprofloxacin and ampicillin (E. coli); ampicillin and amoxycillin (K. pneumoniae) | [44] |
| 255 outpatients/inpatients | S. aureus and P. aeruginosa | Oxacillin, vancomycin, carbapenems, colistin, third- and fourth-generation cephalosporins | [45] |
| 7309 ICU patients | A. baumannii and E. coli | MDR | [46] |
| 3532 outpatients/inpatients | E. coli, K. pneumoniae, and P. aeruginosa | ESBL producing Enterobacterales MDR | [47] |
| 553 ICU patients | K. pneumonia and A. baumannii | Carbapenem resistant | [48] |
2.1.5. Virus and Protozoa
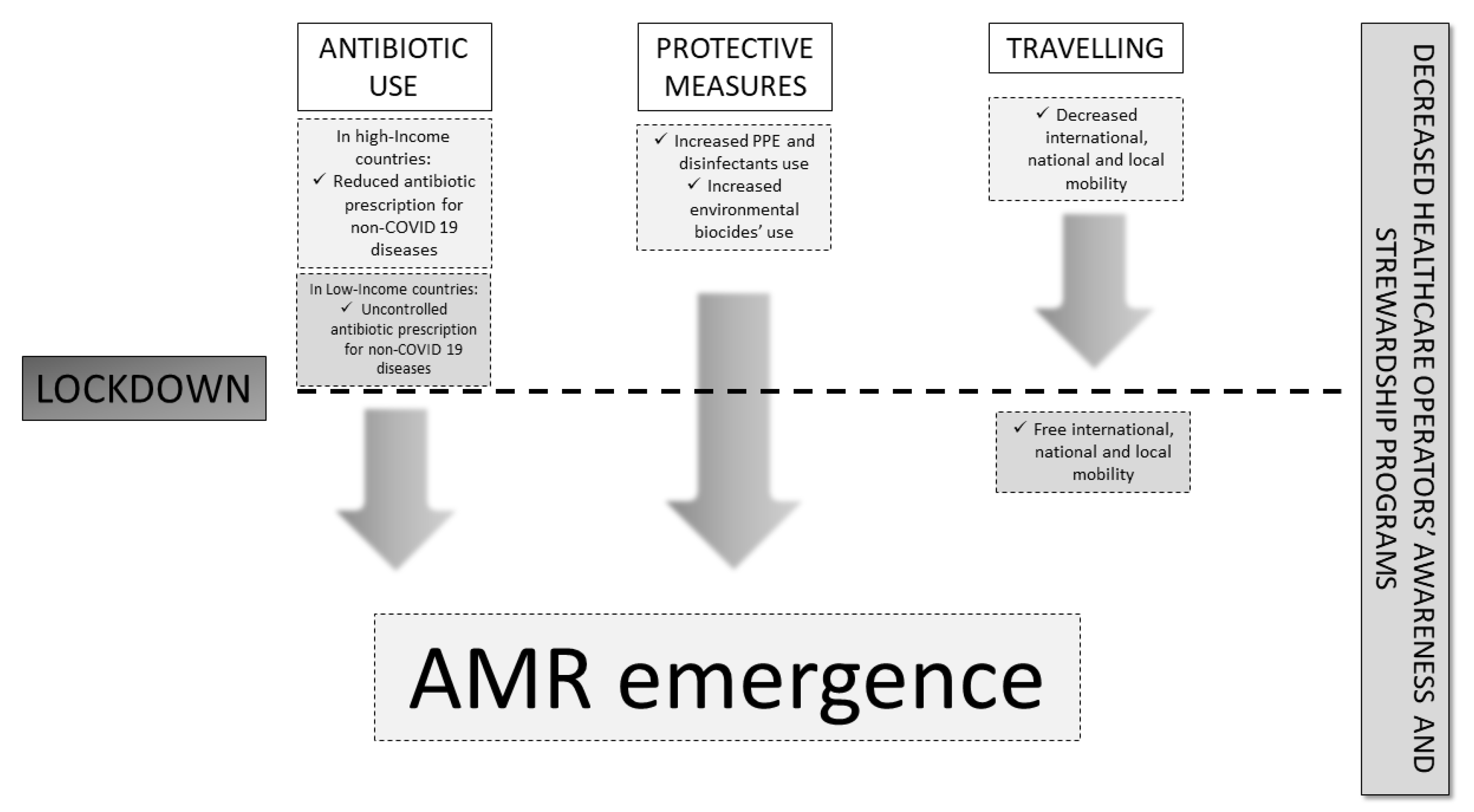
2.2. Factors Involved in AMR Development during COVID-19
2.2.1. Hospital Use of Antibiotics during the Pandemic
2.2.2. Preventive Measures: PPE and Disinfectants
2.2.3. Travel Restrictions and Re-Opening
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spotlight on Antimicrobial Resistance: The Slow Pandemic. Royal Society of Medicine Website. Available online: https://www.rsm.ac.uk/events/rsm-studios/2021-22/ceq03/ (accessed on 3 February 2022).
- O’Neil, J. Antimicrobial Resistance: Tackling a Crisis for the Health and Wealth of Nations—The Review on Antimicrobial Resistance Chaired by Wellcome Website. Available online: https://wellcomecollection.org/works/rdpck35v (accessed on 3 February 2022).
- Available online: https://www.epicentro.iss.it/antibiotico-resistenza/impatto-europa-mondo (accessed on 11 November 2023).
- COVID Live Update: 252,253,520 Cases and 5,091,111 Deaths from the Coronavirus. Worldometer Website. Available online: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/ (accessed on 3 February 2021).
- While, A. Antimicrobial resistance post-COVID-19 pandemic. Br. J. Community Nurs. 2023, 28, 422–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondilis, E.; Tarantilis, F.; Benos, A. Essential public healthcare services utilization and excess non–COVID-19 mortality in Greece. Public Health 2021, 198, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, C.M.; Bollman, E.B.; Carson, L.M.; Northrop, A.J.; Jackson, E.F.; Moresky, R.T. Assessing the indirect effects of COVID-19 on healthcare delivery, utilization and health outcomes: A scoping review. Eur. J. Public Health 2021, 31, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomczyk, S.; Taylor, A.; Brown, A.; de Kraker, M.E.A.; El-Saed, A.; Alshamrani, M.; Hendriksen, R.S.; Jacob, M.; Löfmark, S.; Perovic, O.; et al. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the surveillance, prevention and control of antimicrobial resistance: A global survey. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, 3045–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowbuth, A.A.; Asombang, A.W.; Alaboud, K.; Souque, C.; Dahu, B.M.; Pather, K.; Mwanza, M.M.; Lotfi, S.; Parmar, V.S. Gamification as an educational tool to address antimicrobial resistance: A systematic review. JAC Antimicrob. Resist. 2023, 5, dlad130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, J.M.A.; Webber, M.A.; Baylay, A.J.; Ogbolu, D.O.; Piddock, L.J.V. Molecular mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loh, B.; Chen, J.; Manohar, P.; Yu, Y.; Hua, X.; Leptihn, S. A biological inventory of prophages in A. baumannii genomes reveal distinct distributions in classes, length, and genomic positions. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 579802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, J.M.A.; Richmond, G.E.; Piddock, L.J.V. Multidrug efflux pumps in Gram-negative bacteria and their role in antibiotic resistance. Future Microbiol. 2014, 9, 1165–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chancey, S.T.; Zähner, D.; Stephens, D.S. Acquired inducible antimicrobial resistance in Gram-positive bacteria. Future Microbiol. 2012, 7, 959–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abushaheen, M.A.; Muzaheed; Fatani, A.J.; Alosaimi, M.; Mansy, W.; George, M.; Acharya, S.; Rathod, S.; Divakar, D.D.; Jhugroo, C.; et al. Antimicrobial resistance, mechanisms and its clinical significance. Dis. Mon. 2020, 66, 100971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Mallett, S.; Takwoingi, Y.; Davenport, C.F.; Hyde, C.J.; Whiting, P.F.; Deeks, J.J.; Leeflang, M.M.G.; QUADAS-C Group; Bossuyt, P.M.M.; et al. QUADAS-C: A Tool for Assessing Risk of Bias in Comparative Diagnostic Accuracy Studies. Ann. Intern. Med. 2021, 174, 1592–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Cai, P.; Cao, J.; Cai, X.; Zhang, Y. Etiology and antimicrobial resistance of secondary bacterial infections in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective analysis. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2020, 9, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.epicentro.iss.it/antibiotico-resistenza/ar-iss/RIS-1_2021.pdf (accessed on 3 February 2023).
- Perez, S. Increase in hospital-acquired carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii infection and colonization in an acute care hospital during a surge in COVID-19 admissions—New Jersey, February–July 2020. Morb. Mortal. Wkly Rep. 2020, 69, 1827–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19: U.S. Impact on Antimicrobial Resistance, Special Report 2022 [Internet]. National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases. 2022. Available online: https://stacks.cdc.gov/view/cdc/117915 (accessed on 9 August 2022).
- Langford, B.J.; Soucy, J.R.; Leung, V.; So, M.; Kwan, A.T.H.; Portnoff, J.S.; Bertagnolio, S.; Raybardhan, S.; MacFadden, D.R.; Daneman, N. Antibiotic resistance associated with the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2023, 29, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamieh, A.; Zgheib, R.; El-Sawalhi, S.; Yammine, L.; El-Hajj, G.; Zmerli, O.; Afif, C.; Rolain, J.M.; Azar, E. Trends of Multidrug-Resistant Pathogens, Difficult to Treat Bloodstream Infections, and Antimicrobial Consumption at a Tertiary Care Center in Lebanon from 2015-2020: COVID-19 Aftermath. Antibiotic 2021, 10, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemenand, O.; Coeffic, T.; Thibaut, S.; Colomb Cotinat, M.; Caillon, J.; Birgand, G. Decreasing proportion of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase among, E. coli infections during the COVID-19 pandemic in France. J. Infect. 2021, 83, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardoyo, E.H.; Suardana, I.W.; Yasa, I.W.P.S.; Sukrama, I.D.M. Antibiotics susceptibility of Escherichia coli isolates from clinical specimens before and during COVID-19 pandemic. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2021, 13, 156. [Google Scholar]
- Porto, A.P.M.; Borges, I.C.; Buss, L.; Machado, A.; Bassetti, B.R.; Cocentino, B.; Bicalho, C.S.; Carrilho, C.M.D.M.; Rodrigues, C.; Neto, E.A.S.; et al. Healthcare-associated infections on the intensive care unit in 21 Brazilian hospitals during the early months of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic: An ecological study. Infect. Control. Hosp. Epidemiol. 2023, 44, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.E.; Simbartl, L.A.; Kralovic, S.M.; Clifton, M.; DeRoos, K.; McCauley, B.P.; Gauldin, N.; Flarida, L.K.; Gamage, S.D.; Jones, M.M.; et al. Healthcare-associated infections in Veterans Affairs acute-care and long-term healthcare facilities during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. Infect. Control. Hosp. Epidemiol. 2023, 44, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentivegna, E.; Luciani, M.; Arcari, L.; Santino, I.; Simmaco, M.; Martelletti, P. Reduction of multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacterial infections during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A retrospective study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeil, J.C.; Flores, A.R.; Kaplan, S.L.; Hulten, K.G. The indirect impact of the SARSCoV-2 pandemic on invasive group a Streptococcus, Streptococcus Pneumoniae and Staphylococcus Aureus infections in Houston area children. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2021, 40, e313e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langford, B.J.; So, M.; Simeonova, M.; Leung, V.; Lo, J.; Kan, T.; Raybardhan, S.; Sapin, M.E.; Mponponsuo, K.; Farrell, A.; et al. Antimicrobial resistance in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Microbe 2023, 4, e179–e191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gisselø, K.L.; Rubin, I.M.C.; Knudsen, M.S.; From-Hansen, M.; Stangerup, M.; Kavalaris, C.P.; Pinholt, M.; Mollerup, S.; Westh, H.; Bartels, M.D.; et al. Substantial Decrease in Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus faecium Outbreak Duration and Number of Patients During the Danish COVID-19 Lockdown: A Prospective Observational Study. Microb. Drug Resist. 2022, 28, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, G.; Liang, G.; Liu, W. Fungal co-infections associated with global COVID-19 pandemic: A clinical and diagnostic perspective from China. Mycopathologia 2020, 185, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinh, D.C. The molecular immunology of human susceptibility to fungal diseases: Lessons from single gene defects of immunity. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 15, 461–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posteraro, B.; Torelli, R.; Vella, A.; Leone, P.M.; De Angelis, G.; De Carolis, E.; Ventura, G.; Sanguinetti, M.; Fantoni, M. Pan-Echinocandin-Resistant Candida glabrataBloodstream Infection Complicating COVID-19: A Fatal Case Report. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, V.K.; Suneetha, K.J.; Kaur, R. A systematic analysis reveals an essential role for high-affinity iron uptake system, haemolysin and CFEM domain-containing protein in iron homoeostasis and virulence in Candida glabrata. Biochem. J. 2014, 463, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhary, A.; Tarai, B.; Singh, A.; Sharma, A. Multidrug-resistant candida auris infections in critically Ill Coronavirus disease patients, India, April–July 2020. Emerg. Infect Dis. 2020, 26, 2694–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.; Hassan, T.; Trzos-Grzybowska, M.; Thomas, J.; Quinn, A.; O’Sullivan, M.; Griffin, A.; Rogers, T.R.; Talento, A.F. Multi-triazole-resistant Aspergillus fumigatus and SARS-CoV 2 co-infection: A lethal combination. Med. Mycol. Case Rep. 2021, 31, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Hu, B.; Hu, C.; Zhu, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Xiang, H.; Cheng, Z.; Xiong, Y.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients With 2019 Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA 2020, 323, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denning, D.W.; Park, S.; Lass-Florl, C.; Fraczek, M.G.; Kirwan, M.; Gore, R.; Smith, J.; Bueid, A.; Moore, C.B.; Bowyer, P.; et al. High-frequency triazole resistance found In nonculturable Aspergillus fumigatus from lungs of patients with chronic fungal disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoudi, H. Bacterial co-infections and antibiotic resistance in patients with COVID-19. GMS Hyg. Infect. Control. 2020, 15, Doc35. [Google Scholar]
- Obeidat, H.; El-Nasser, Z.; Amarin, Z.; Qablan, A.; Gharaibeh, F. The impact of COVID-19 pandemic on healthcare associated infections: A teaching hospital experience. Medicine 2023, 102, e33488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, L.; Xi, Y.; Lin, Z.; Pan, Y.; Song, B.; Li, C.A.; Zheng, X.; Zhong, M.; Jiang, L.; Pan, C.; et al. Secondary infection in severe and critical COVID-19 patients in China: A multicenter retrospective study. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2021, 10, 8557–8570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palanisamy, N.; Vihari, N.; Meena, D.S.; Kumar, D.; Midha, N.; Tak, V.; Sharma, A.; Bohra, G.K.; Kothari, N.; Dutt, N.; et al. Clinical profile of bloodstream infections in COVID-19 patients: A retrospective cohort study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Despotovic, A.; Milosevic, B.; Cirkovic, A.; Vujovic, A.; Cucanic, K.; Cucanic, T.; Stevanovic, G. The Impact of COVID-19 on the Profile of Hospital-Acquired Infections in Adult Intensive Care Units. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meawed, T.E.; Ahmed, S.M.; Mowafy, S.M.S.; Samir, G.M.; Anis, R.H. Bacterial and fungal ventilator associated pneumonia in critically ill COVID-19 patients during the second wave. J. Infect. Public Health 2021, 14, 1375–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeshan, B.; Karobari, M.I.; Afzal, N.; Siddiq, A.; Basha, S.; Basheer, S.N.; Peeran, S.W.; Mustafa, M.; Daud, N.H.A.; Ahmed, N.; et al. The Usage of Antibiotics by COVID-19 Patients with Comorbidities: The Risk of Increased Antimicrobial Resistance. Antibiotics 2021, 11, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, P.; Maiorino, M.I.; Macera, M.; Signoriello, G.; Castellano, L.; Scappaticcio, L.; Longo, M.; Gicchino, M.; Campitiello, F.; Bellastella, G.; et al. Antibiotic resistance in diabetic foot infection: How it changed with COVID-19 pandemic in a tertiary care center. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 175, 108797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, V.; Jain, C.; Singh, N.P.; Alsulimani, A.; Gupta, C.; Dar, S.A.; Haque, S.; Das, S. Paradigm Shift in Antimicrobial Resistance Pattern of Bacterial Isolates during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatas, M.; Yasar-Duman, M.; Tünger, A.; Çilli, F.; Aydemir, S.; Özenci, V. Secondary bacterial infections and antimicrobial resistance in COVID-19: Comparative evaluation of pre-pandemic and pandemic-era, a retrospective single center study. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2021, 20, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourajam, S.; Kalantari, E.; Talebzadeh, H.; Mellali, H.; Sami, R.; Soltaninejad, F.; Amra, B.; Sajadi, M.; Alenaseri, M.; Kalantari, F.; et al. Secondary Bacterial Infection and Clinical Characteristics in Patients With COVID-19 Admitted to Two Intensive Care Units of an Academic Hospital in Iran During the First Wave of the Pandemic. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 784130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Towns, A.M.; Mengue Eyi, S.; van Andel, T. Traditional medicine and childcare in Western Africa: Mothers’ knowledge, folk illnesses, and patterns of healthcare-seeking behavior. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataba, E.; Dorkenoo, A.M.; Nguepou, C.T.; Bakai, T.; Tchadjobo, T.; Kadzahlo, K.D.; Yakpa, K.; Atcha-Oubou, T. Potential Emergence of Plasmodium Resistance to Artemisinin Induced by the Use of Artemisia annua for Malaria and COVID-19 Prevention in Sub-African Region. Acta Parasitol. 2022, 67, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welz, A.N.; Emberger-Klein, A.; Menrad, K. Why people use herbal medicine: Insights from a focus-group study in Germany. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Septembre-Malaterre, A.; Lalarizo Rakoto, M.; Marodon, C.; Bedoui, Y.; Nakab, J.; Simon, E.; Hoarau, L.; Savriama, S.; Strasberg, D.; Guiraud, P.; et al. Artemisia annua, a traditional plant brought to light. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balikagala, B.; Fukuda, N.; Ikeda, M.; Katuro, O.T.; Tachibana, S.I.; Yamauchi, M.; Opio, W.; Emoto, S.; Anywar, D.A.; Kimura, E.; et al. Evidence of Artemisinin-Resistant Malaria in Africa. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schüz, M.L.; Dallmeyer, L.; Fragkou, P.C.; Omony, J.; Krumbein, H.; Hünerbein, B.L.; Skevaki, C. Global prevalence of respiratory virus infections in adults and adolescents during the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2023, 137, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, S.; Klein, J.; Robertson, A.J.; Peña-Hernández, M.A.; Lin, M.J.; Roychoudhury, P.; Lu, P.; Fournier, J.; Ferguson, D.; Mohamed Bakhash, S.A.K.; et al. De novo emergence of a remdesivir resistance mutation during treatment of persistent SARS-CoV-2 infection in an immunocompromised patient: A case report. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donovan-Banfield, I.; Penrice-Randal, R.; Goldswain, H.; Rzeszutek, A.M.; Pilgrim, J.; Bullock, K.; Saunders, G.; Northey, J.; Dong, X.; Ryan, Y.; et al. Characterisation of SARS-CoV-2 genomic variation in response to molnupiravir treatment in the AGILE Phase Iia clinical trial. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S. A parallel and silent emerging pandemic: Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) amid COVID-19 pandemic. J. Infect. Public Health. 2023, 16, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contou, D.; Claudinon, A.; Pajot, O.; Micaëlo, M.; Longuet Flandre, P.; Dubert, M.; Cally, R.; Logre, E.; Fraissé, M.; Mentec, H.; et al. Bacterial and viral co-infections in patients with severe SARS-CoV 2 pneumonia admitted to a French ICU. Ann. Intensive Care 2020, 10, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifipour, E.; Shams, S.; Esmkhani, M.; Khodadadi, J.; Fotouhi-Ardakani, R.; Koohpaei, A.; Doosti, Z.; Ej Golzari, S. Evaluation of bacterial co-infections of the respiratory tract in COVID-19 patients admitted to ICU. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderon, M.; Li, A.; Bazo-Alvarez, J.C.; Dennis, J.; Baker, K.F.; Schim van der Loeff, I.; Hanrath, A.T.; Capstick, R.; Payne, B.A.I.; Weiand, D.; et al. Evaluation of procalcitonin-guided antimicrobial stewardship in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 pneumonia. JAC Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 3, dlab133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottesman, T.; Fedorowsky, R.; Yerushalmi, R.; Lellouche, J.; Nutman, A. An outbreak of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in a COVID19 dedicated hospital. Infect. Prev. Pract. 2021, 3, 100113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinohara, D.R.; Dos Santos Saalfeld, S.M.; Martinez, H.V.; Altafini, D.D.; Costa, B.B.; Fedrigo, N.H.; Tognim, M.C.B. Outbreak of endemic carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in a coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)-specific intensive care unit. Infect. Control. Hosp. Epidemiol. 2022, 43, 815–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieringer, T.D.; Furukawa, D.; Graber, C.J.; Stevens, V.W.; Jones, M.M.; Rubin, M.A.; Goetz, M.B. Inpatient antibiotic utilization in the Veterans’ Health Administration during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. Infect. Control. Hosp. Epidemiol. 2021, 42, 751–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UK Health Security Agency. English Surveillance Programme for Antimicrobial Utilisation and Resistance (ESPAUR) Report 2020 to 2021. UK Government Website. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/englishsurveillance-programme-antimicrobial-utilisation-and-resistance-espaurreport (accessed on 22 February 2023).
- Winders, H.R.; Bailey, P.; Kohn, J.; Faulkner-Fennell, C.M.; Utley, S.; Lantz, E.; Sarbacker, L.; Justo, J.A.; Bookstaver, P.B.; Weissman, S.; et al. Change in Antimicrobial Use during COVID-19 Pandemic in South Carolina Hospitals: A Multicenter Observational Cohort Study. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 2021, 58, 106453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, M.G.; Ubiergo, L.; Vicino, M.; Cuevas, G.; Argarana, F. Rising incidence of carbapenem resistant isolates: An Argentinian hospital’s experience. More trouble in the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic. IberoAmerican J. Med. 2022, 4, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.H.; Drew, D.A.; Graham, M.S.; Joshi, A.D.; Guo, C.G.; Ma, W.; Mehta, R.S.; Warner, E.T.; Sikavi, D.R.; Lo, C.H.; et al. Risk of COVID-19 among front-line health-care workers and the general community: A prospective cohort study. Lancet Public Health 2020, 5, e475–e483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, K.; Kashihara, E.; Kanai, O.; Hata, H.; Yasoda, A.; Odagaki, T.; Mio, T. Increasing Burden of Nursing Care on the Treatment of COVID-19 Patients in the Aging Society: Analyses During the First to the Third Wave of Pandemic in Kyoto City, Japan. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 767110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, S.B. Active efflux, a common mechanism for biocide and antibiotic resistance. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 92, 65S–71S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Yang, L.; Liu, Z.; Han, J.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, Y.; Sheng, Y.; Zhu, L.; Hu, B. Excessive disinfection aggravated the environmental prevalence of antimicrobial resistance during COVID-19 pandemic. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 882, 163598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Lu, H.; Zhua, L. Molecular mechanism of antibiotic resistance induced by mono- and twin-chained quaternary ammonium compounds. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 832, 155090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castanheira, M.; Griffin, M.A.; Deshpande, L.M.; Mendes, R.E.; Jones, R.N.; Flamm, R.K. Detection of mcr-1 among Escherichia coli clinical isolates collected worldwide as part of the SENTRY Antimicrobial Surveillance Program in 2014 and 2015. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 5623–5624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.; Walsh, T.R.; Yi, L.X.; Zhang, R.; Spencer, J.; Doi, Y.; Tian, G.; Dong, B.; Huang, X.; et al. Emergence of plasmid-mediated colistin resistance mechanism MCR-1 in animals and human beings in China: A microbiological and molecular biological study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, L.M.; Lovegrove, M.C.; Shehab, N.; Tsay, S.; Budnitz, D.S.; Geller, A.I.; Lind, J.N.; Roberts, R.M.; Hicks, L.A.; Kabbani, S. Trends in US Outpatient Antibiotic Prescriptions During the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e652–e660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, B.D.; Shurgold, J.; Smith, G.; MacFadden, D.R.; Schwartz, K.L.; Daneman, N.; Gravel Tropper, D.; Brooks, J. The impact of COVID-19 on community antibiotic use in Canada: An ecological study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2022, 28, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Högberg, L.D.; Vlahovi´c-Palcevski, V.; Pereira, C.; Weist, K.; Monnet, D.L.; ESAC Net study group. Decrease in community antibiotic consumption during the COVID-19 pandemic, EU/EEA, 2020. Eurosurveillance 2021, 26, 2101020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seneghini, M.; Rüfenacht, S.; Babouee-Flury, B.; Flury, D.; Schlegel, M.; Kuster, S.P.; Kohler, P.P. It is complicated: Potential short- and long-term impact of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) on antimicrobial resistance-An expert review. Antimicrob. Steward Healthc. Epidemiol. 2022, 2, e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seasonal Influenza—Annual Epidemiological Report for 2020–2021. European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control Website. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/seasonal-influenza-annualepidemiological-report-2020-2021 (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- Britton, P.N.; Hu, N.; Saravanos, G.; Shrapnel, J.; Davis, J.; Snelling, T.; Dalby-Payne, J.; Kesson, A.M.; Wood, N.; Macartney, K.; et al. COVID-19 public health measures and respiratory syncytial virus. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2020, 4, e42–e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brueggemann, A.B.; Jansen van Rensburg, M.J.; Shaw, D.; McCarthy, N.D.; Jolley, K.A.; Maiden, M.C.J.; van der Linden, M.P.G.; Amin-Chowdhury, Z.; Bennett, D.E.; Borrow, R.; et al. Changes in the incidence of invasive disease due to Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Neisseria meningitidis during the COVID-19 pandemic in 26 countries and territories in the Invasive Respiratory Infection Surveillance Initiative: A prospective analysis of surveillance data. Lancet Digit. Health 2021, 3, e360–e370. [Google Scholar]
- Belachew, S.A.; Hall, L.; Erku, D.A.; Selvey, L.A. No prescription? No problem: Drivers of nonprescribed sale of antibiotics among community drug retail outlets in low- and middle-income countries: A systematic review of qualitative studies. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boccabella, L.; Palma, E.G.; Abenavoli, L.; Scarlata, G.G.M.; Boni, M.; Ianiro, G.; Santori, P.; Tack, J.F.; Scarpellini, E. Post-Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic Antimicrobial Resistance. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13030233
Boccabella L, Palma EG, Abenavoli L, Scarlata GGM, Boni M, Ianiro G, Santori P, Tack JF, Scarpellini E. Post-Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic Antimicrobial Resistance. Antibiotics. 2024; 13(3):233. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13030233
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoccabella, Lucia, Elena Gialluca Palma, Ludovico Abenavoli, Giuseppe Guido Maria Scarlata, Mariavirginia Boni, Gianluca Ianiro, Pierangelo Santori, Jan F. Tack, and Emidio Scarpellini. 2024. "Post-Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic Antimicrobial Resistance" Antibiotics 13, no. 3: 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13030233
APA StyleBoccabella, L., Palma, E. G., Abenavoli, L., Scarlata, G. G. M., Boni, M., Ianiro, G., Santori, P., Tack, J. F., & Scarpellini, E. (2024). Post-Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic Antimicrobial Resistance. Antibiotics, 13(3), 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13030233










