Occurrence of Trace-Level Antibiotics in the Msunduzi River: An Investigation into South African Environmental Pollution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sample Collection
3.2. Chemicals and Reagents
3.3. Stock Solutions
3.4. Sample Extraction
3.5. Method Validation
3.6. Antibiotic Separation and Quantification
3.7. Environmental Risk Assessment
4. Results and Discussion
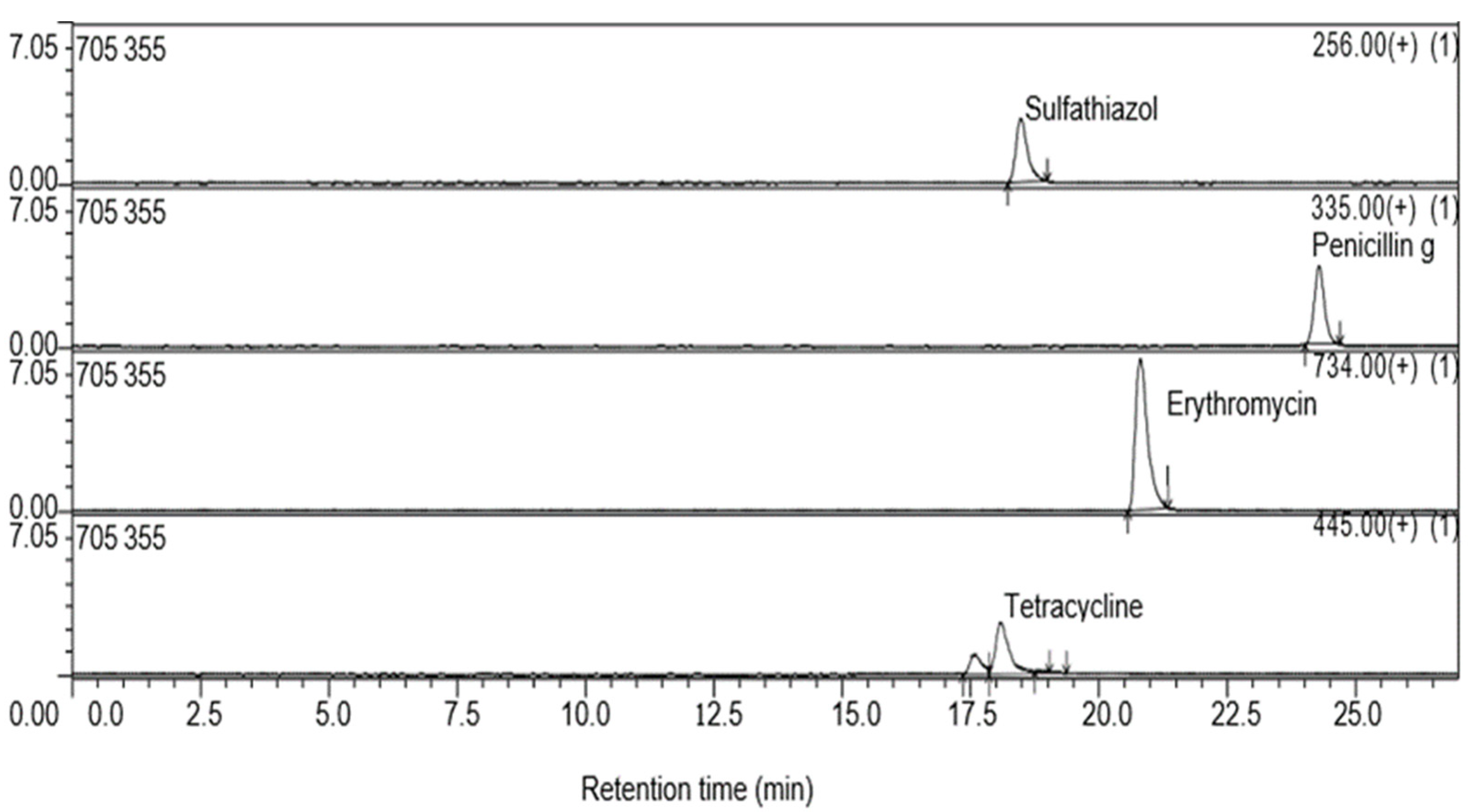
4.1. LCMS Detection of Analyzed Antibiotics
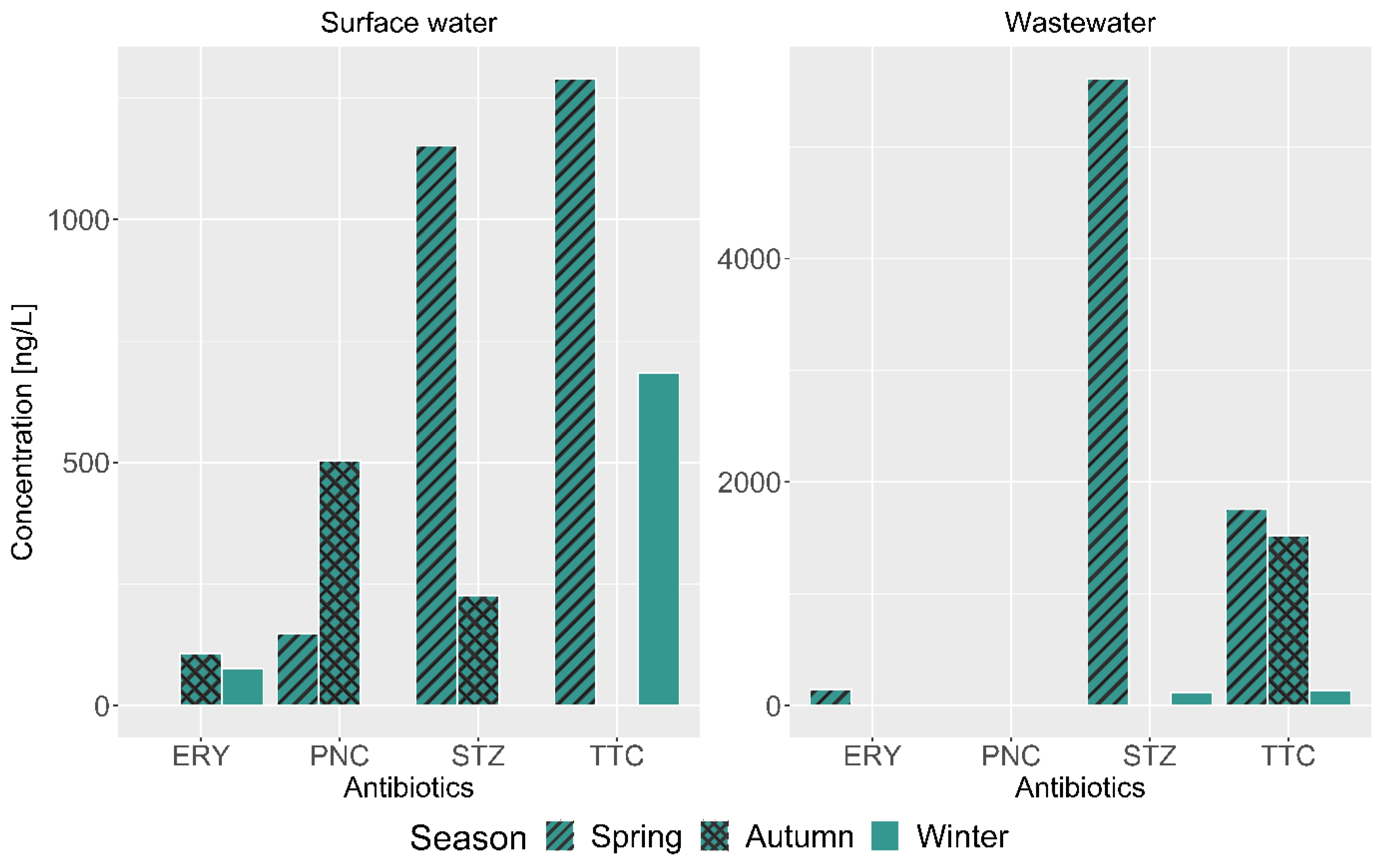
4.2. Occurrence and Concentration of Detected Antibiotics
4.3. Comparison of the Result with Previous Studies
4.4. Spatial Distribution and Seasonal Variation of Detected Antibiotics
4.5. Risk Assessment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ventola, C. The antibiotic resistance crisis: Causes and threats., P & T: A peerreviewed. J. Formul. Manag. 2015, 40, 277–278. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Cuasquer, G.J.P.; Li, Z.; Mang, H.P.; Lv, Y. Occurrence of typical antibiotics, representative antibiotic-resistant bacteria, and genes in fresh and stored source-separated human urine. Environ. Int. 2020, 146, 106280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addis, T.Z.; Adu, J.T.; Kumarasamy, M.; Demlie, M. Assessment of Existing Fate and Transport Models for Predicting Antibiotic Degradation and Transport in the Aquatic Environment: A Review. Water 2023, 15, 1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Gao, Y.; Ke, J.; Show, P.L.; Ge, Y.; Liu, Y.; Guo, R.; Chen, J. Antibiotics: An overview on the environmental occurrence, toxicity, degradation, and removal methods. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 7376–7416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Lin, C.; Lian, M.; Wang, A.; He, M.; Liu, X.; Ouyang, W. Riverine antibiotic occurrence and potential ecological risks in a low-urbanized and rural basin of the middle Yangtze River: Socioeconomic, land use, and seasonal effects. Environ. Res. 2023, 228, 115827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gothwal, R.; Shashidhar, S. Occurrence of High Levels of Fluoroquinolones in Aquatic Environment due to Effluent Discharges from Bulk Drug Manufacturers. J. Hazard. Toxic. Radioact. Waste 2017, 21, 05016003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magna, E.K.; Tornyie, F.; Ofosu-Koranteng, F.; Mensah, E.T.D.; Larbi, L.; Mbage, B. Occurrence and Environmental Risk Assessment of Antibiotics in Water and Sediment from Fish Farms in the Lower Volta Lake of Ghana. Chem. Afr. 2023, 7, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polianciuc, S.I.; Gurzău, A.E.; Kiss, B.; Ştefan, M.G.; Loghin, F. Antibiotics in the environment: Causes and consequences. Med. Pharm. Rep. 2020, 93, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonich, S.M.; Sun, P.; Casteel, K.; Dyer, S.; Wernery, D.; Garber, K.; Carr, G.; Federle, T. Probabilistic analysis of risks to US drinking water intakes from 1,4-dioxane in domestic wastewater treatment plant effluents. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2013, 9, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Ji, M.; Zhai, H.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y. Occurrence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in WWTP effluent-receiving water bodies and reclaimed wastewater treatment plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 796, 148919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faleye, A.C.; Adegoke, A.A.; Ramluckan, K.; Fick, J.; Bux, F.; Stenström, T.A. Concentration and reduction of antibiotic residues in selected wastewater treatment plants and receiving waterbodies in Durban, South Africa. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 678, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agunbiade, F.O.; Moodley, B. Occurrence and distribution pattern of acidic pharmaceuticals in surface water, wastewater, and sediment of the Msunduzi River, Kwazulu-Natal, South Africa. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanama, K.M.; Daso, A.P.; Mpenyana-Monyatsi, L.; Coetzee, M.A.A. Assessment of pharmaceuticals, personal care products, and hormones in wastewater treatment plants receiving inflows from health facilities in North West Province, South Africa. J. Toxicol. 2018, 2018, 3751930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linghu, K.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, J.; Gao, S. Occurrence, distribution and ecological risk assessment of antibiotics in Nanming river: Contribution from wastewater treatment plant and implications of urban river syndrome. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 169, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madikizela, L.M.; Chimuka, L. Occurrence of naproxen, ibuprofen, and diclofenac residues in wastewater and river water of KwaZulu-Natal Province in South Africa. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manickum, T.; John, W. Occurrence, fate and environmental risk assessment of endocrine disrupting compounds at the wastewater treatment works in Pietermaritzburg (South Africa). Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468–469, 584–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeman, C.; Dlamini, M.; Okonkwo, O.J. The impact of a Wastewater Treatment Works in Southern Gauteng, South Africa on efavirenz and nevirapine discharges into the aquatic environment. Emerg. Contam. 2017, 3, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto-Juárez, J.I.; Torres-Palma, R.A.; Botero-Coy, A.M.; Hernández, F. Pharmaceuticals and environmental risk assessment in municipal wastewater treatment plants and rivers from Peru. Environ. Int. 2021, 155, 106674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiyegoro, O.A.; Moyane, J.N.; Adegoke, A.A.; Jideani, A.I.O.; Reddy, P.; Okoh, A.I. Virulence Signatures, Integrons, and Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Bacterial Strains Recovered from Selected Commercial Dairy Products and Fresh Raw Meat. Curr. Microbiol. 2023, 80, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Xu, B.; Chen, H.; Zhao, X.; Li, G.; Zheng, Y.; Qiu, W.; Zheng, C.; Duan, L.; Wang, W. Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in groundwater, surface water, and sediment in Xiong’an New Area, China, and their relationship with antibiotic resistance genes. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 151011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igbinosa, E.O.; Obi, L.C.; Tom, M.; Okoh, A.I. Detection of potential risk of wastewater effluents for transmission of antibiotic resistance from Vibrio species as a reservoir in a peri-urban community in South Africa. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2011, 21, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, J.; Santos, R.; Monteiro, S. Antibiotic resistance genes in bacteriophages from wastewater treatment plant and hospital wastewaters. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 892, 164708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichert, G.; Hilgert, S.; Alexander, J.; de Azevedo, J.C.R.; Morck, T.; Fuchs, S.; Schwartz, T. Determination of antibiotic resistance genes in a WWTP-impacted river in surface water, sediment, and biofilm: Influence of seasonality and water quality. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 144526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.Y.; He, L.Y.; Gao, F.Z.; Zhang, M.; Chen, S.; Wu, D.L.; Liu, Y.S.; He, L.X.; Bai, H.; Ying, G.G. Antibiotic resistance genes in surface water and groundwater from mining affected environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 145516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahamanyi, N.; Mboera, L.E.G.; Matee, M.I.; Mutangana, D.; Komba, E.V.G. Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles of Thermophilic Campylobacter Species in Humans and Animals in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Microbiol. 2020, 2020, 2092478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Ogo, M.; Koike, T.; Takada, H.; Newman, B. Sulfonamide and tetracycline resistance genes in total- and culturable-bacterial assemblages in south african aquatic environments. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibanda, T.; Selvarajan, R.; Tekere, M. Urban effluent discharges as causes of public and environmental health concerns in South Africa’s aquatic milieu. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 18301–18317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molale, L.G.; Bezuidenhout, C.C. Antibiotic resistance, efflux pump genes and virulence determinants in Enterococcus spp. from surface water systems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 21501–21510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abia, A.L.K.; Baloyi, T.; Traore, A.N.; Potgieter, N. The African Wastewater Resistome: Identifying Knowledge Gaps to Inform Future Research Directions. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mbanga, J.; Amoako, D.G.; Abia, A.L.K.; Fatoba, D.; Essack, S. Genomic analysis of antibiotic-resistant Enterobacter spp. from wastewater sources in South Africa: The first report of the mobilizable colistin resistance mcr-10 gene in Africa. Ecol. Genet. Genom. 2021, 21, 100104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, G.; Fang, X.; Cai, Y.; Ge, L.; Zong, H.; Yuan, X.; Yao, Z.; Zhang, Z. Occurrence, distribution, and bioaccumulation of antibiotics in coastal environment of Dalian, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 69, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Kumar, R.; Kishor, K.; Mlsna, T.; Pittman, C.U.; Mohan, D. Pharmaceuticals of emerging concern in aquatic systems: Chemistry, occurrence, effects, and removal methods. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 3510–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Hua, P.; Gui, D.; Zhang, J.; Ying, G.; Krebs, P. Occurrences, Transport Drivers, and Risk Assessments of Antibiotics in Typical Oasis Surface and Groundwater. Water Res. 2022, 225, 119138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, J.S.; Aga, D.S. Enhancing Extraction and Detection of Veterinary Antibiotics in Solid and Liquid Fractions of Manure. J. Environ. Qual. 2016, 45, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wang, C.; Xu, Z.; Chakraborty, A. A coupled method of on-line solid phase extraction with the UHPLC—MS/MS for detection of sulfonamides antibiotics residues in aquaculture. Chemosphere 2020, 254, 126765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, K.G.; Meyer, M.T. Occurrence of antibiotics in wastewater treatment facilities in Wisconsin, USA. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 361, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minh, T.B.; Leung, H.W.; Loi, I.H.; Chan, W.H.; So, M.K.; Mao, J.; Choi, D.; Lam, J.C.; Zheng, G.; Martin, M.; et al. Antibiotics in the Hong Kong metropolitan area: Ubiquitous distribution and fate in Victoria Harbour. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 1052–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vane, C.H.; Kim, A.W.; Lopes dos Santos, R.A.; Gill, J.C.; Moss-Hayes, V.; Mulu, J.K.; Mackie, J.R.; Ferreira, A.M.; Chenery, S.R.; Olaka, L.A. Impact of organic pollutants from urban slum informal settlements on sustainable development goals and river sediment quality, Nairobi, Kenya, Africa. Appl. Geochem. 2022, 146, 105468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkinson, A.J.; Murby, E.J.; Kolpin, D.W.; Costanzo, S.D. The occurrence of antibiotics in an urban watershed: From wastewater to drinking water. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 2711–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Liu, G.; Arif, M.; Shi, X.; Wang, S. Occurrence and risk assessment of antibiotics in the surface water of Chaohu Lake and its tributaries in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 151040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madikizela, L.M.; Nuapia, Y.B.; Chimuka, L.; Ncube, S.; Etale, A. Target and Suspect Screening of Pharmaceuticals and their Transformation Products in the Klip River, South Africa, using Ultra-High–Performance Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2022, 41, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milić, N.; Milanović, M.; Letić, N.G.; Sekulić, M.T.; Radonić, J.; Mihajlović, I.; Miloradov, M.V. Occurrence of antibiotics as emerging contaminant substances in aquatic environment. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2013, 23, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kairigo, P.; Ngumba, E.; Sundberg, L.R.; Gachanja, A.; Tuhkanen, T. Contamination of surface water and river sediments by antibiotic and anti-retroviral drug cocktails in low and middle-income countries: Occurrence, risk and mitigation strategies. Water 2020, 12, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madikizela, L.M.; Ncube, S.; Chimuka, L. Analysis, occurrence and removal of pharmaceuticals in African water resources: A current status. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 253, 109741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhuka, V.; Dube, S.; Nindi, M.M. Occurrence of pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs) in wastewater and receiving waters in South Africa using LC-OrbitrapTM MS. Emerg. Contam. 2020, 6, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waleng, N.J.; Nomngongo, P.N. Occurrence of pharmaceuticals in the environmental waters: African and Asian perspectives. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2022, 4, 50–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, T.P.; Duvenage, C.S.J.; Rohwer, E. The occurrence of anti-retroviral compounds used for HIV treatment in South African surface water. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 199, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, T.P.; Du Preez, C.; Steenkamp, A.; Duvenage, C.; Rohwer, E.R. Database-driven screening of South African surface water and the targeted detection of pharmaceuticals using liquid chromatography—High resolution mass spectrometry. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matongo, S.; Birungi, G.; Moodley, B.; Ndungu, P. Occurrence of selected pharmaceuticals in water and sediment of Umgeni River, KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 10298–10308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumbi, B.P.; Moodley, B.; Birungi, G.; Ndungu, P.G. Detection and quantification of acidic drug residues in South African surface water using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 1042–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oharisi Ooke, L.; Ncube, S.; Nyoni, H.; Madikizela, M.L.; Olowoyo, O.J.; Maseko, B.R. Occurrence and prevalence of antibiotics in wastewater treatment plants and effluent receiving rivers in South Africa using UHPLC-MS determination. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumbi, B.P.; Moodley, B.; Birungi, G.; Ndungu, P.G. Assessment of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs by ultrasonic-assisted extraction and GC-MS in Mgeni and Msunduzi river sediments, KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 20015–20028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motsoane, N.; Maputsoe, X.; Richards, H.; Tutu, H.; Kotze, I.; Cukrowska, E.; Chimuka, L. Development and Application of Passive Samplers for Determining the Fate of Toxic Metals in Wetlands Polluted by Mining Activities Report to the Water Research Commission; 2551/1/21; Water Resources Commission: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2021; Available online: www.wrc.org.za (accessed on 12 October 2023).
- Babić, S.; Ašperger, D.; Mutavdžić, D.; Horvat, A.J.M.; Kaštelan-Macan, M. Solid phase extraction and HPLC determination of veterinary pharmaceuticals in wastewater. Talanta 2006, 70, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. European Commission Technical Guidance Document in Support of Commission Directive 93//67/EEC on Risk As-Sessment for New Notified Substances and Commission Regulation (EC) No. 1488/94 on Risk Assessment for Existing Sub-stance, Part II. 2003. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/286208518 (accessed on 23 November 2022).
- Straub, J.O.; Oldenkamp, R.; Pfister, T.; Häner, A. Environmental Risk Assessment for the Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient Mycophenolic Acid in European Surface Waters. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2019, 38, 2259–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Yan, X.; Shen, Y.; Di, M.; Wang, J. Antibiotics in surface water and sediments from Hanjiang River, Central China: Occurrence, behavior and risk assessment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 157, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mheidli, N.; Malli, A.; Mansour, F.; Al-Hindi, M. Occurrence and risk assessment of pharmaceuticals in surface waters of the Middle East and North Africa: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Lv, K.; Deng, C.; Yu, Z.; Shi, J.; Johnson, A.C. Persistence and migration of tetracycline, sulfonamide, fluoroquinolone, and macrolide antibiotics in streams using a simulated hydrodynamic system. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 1532–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamtam, F.; Mercier, F.; Le Bot, B.; Eurin, J.; Dinh, Q.T.; Clément, M.; Chevreuil, M. Occurrence and fate of antibiotics in the Seine River in various hydrological conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 393, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Yang, M.; Hu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, H.; Jin, F. Determination of penicillin G and its degradation products in a penicillin production wastewater treatment plant and the receiving river. Water Res. 2008, 42, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirt, S.J. Penicillin Hydrolysis Rate: Its Effect on the Kinetics of Penicillin Fermentation. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 1990, 69, 259–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Calviño, D.; Bermúdez-Couso, A.; Arias-Estévez, M.; Nóvoa-Muñoz, J.C.; Fernández-Sanjurjo, M.J.; Álvarez-Rodríguez, E.; Núñez-Delgado, A. Kinetics of tetracycline, oxytetracycline, and chlortetracycline adsorption and desorption on two acid soils. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 22, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Liu, X.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J.; Qian, X.; Cui, B.; Bai, J. Photochemical transformations of tetracycline antibiotics influenced by natural colloidal particles: Kinetics, factor effects and mechanisms. Chemosphere 2019, 235, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.-J.; Li, X.-Y.; Xie, Y.-F.; Wang, X.-M. Direct photo transformation of tetracycline and sulfanomide group antibiotics in surface water: Kinetics, toxicity and site modeling. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Hu, C.; Deng, D.; Li, Y.; Luo, L. Factors affecting sorption behaviors of tetracycline to soils: Importance of soil organic carbon, pH and Cd contamination. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 197, 110572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Calviño, D.; Bermúdez-Couso, A.; Arias-Estévez, M.; Nóvoa-Muñoz, J.C.; Fernández-Sanjurjo, M.J.; Álvarez-Rodríguez, E.; Núñez-Delgado, A. Competitive adsorption/desorption of tetracycline, oxytetracycline and chlortetracycline on two acid soils: Stirred flow chamber experiments. Chemosphere 2015, 134, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, W.; Liu, K.; Guo, Y.; Ding, C.; Han, J.; Li, P. Global review of macrolide antibiotics in the aquatic environment: Sources, occurrence, fate, ecotoxicity, and risk assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 439, 129628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kümmerer, K. Antibiotics in the aquatic environment—A review—Part I. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 417–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pala-Ozkok, I.; Ubay-Cokgor, E.; Jonas, D.; Orhon, D. Kinetic and microbial response of activated sludge community to acute and chronic exposure to tetracycline. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 367, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikulik, K.; Jirbiiovb, A.; Janda, I.; Weiser, J. Susceptibility of Ribosomes of the Tetracycline-Producing Strain of Streptomyces aureofaciens to Tetracyclines. FEBS Lett. 1983, 152, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.H.; Sivachidambaram, V.; Yi, X.; Li, X.; Zhou, Z. Quantification of polyketide synthase genes in tropical urban soils using real-time PCR. J. Microbiol. Methods 2014, 106, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Che, X.; Li, C.; Cui, Z.; Su, R.; Qu, K. Indirect photodegradation of sulfadiazine in the presence of DOM: Effects of DOM components and main seawater constituents. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Cui, Z.; Bai, Y.; Su, R. Indirect photodegradation of sulfathiazole and sulfamerazine: Influence of the CDOM components and seawater factors (salinity, pH, nitrate and bicarbonate). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 750, 141762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafiriou, O.C.; True, M.B. Nitrate photolysis in seawater by sunlight. Mar. Chem. 1979, 8, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedict, K.B.; McFall, A.S.; Anastasio, C. Quantum Yield of Nitrite from the Photolysis of Aqueous Nitrate above 300 nm. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 4387–4395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.G.; Hu, Y.; Gao, M.; Guo, L.; Ji, J. Insight in degradation of tetracycline in mariculture wastewater by ultraviolet/persulfate advanced oxidation process. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agunbiade, F.O.; Moodley, B. Pharmaceuticals as emerging organic contaminants in Umgeni River water system, KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 7273–7291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatoki, O.S.; Opeolu, B.O.; Genthe, B.; Olatunji, O.S. Multi-residue method for the determination of selected veterinary pharmaceutical residues in surface water around Livestock Agricultural farms. Heliyon 2018, 4, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matongo, S.; Birungi, G.; Moodley, B.; Ndungu, P. Pharmaceutical residues in water and sediment of Msunduzi River, KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Chemosphere 2015, 134, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vumazonke, S.; Khamanga, S.M.; Ngqwala, N.P. Detection of pharmaceutical residues in surface waters of the Eastern Cape Province. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Elwafa Abdallah, M.; Nguyen, K.H.; Ebele, A.J.; Atia, N.N.; Ali, H.R.H.; Harrad, S. A single run, rapid polarity switching method for determination of 30 pharmaceuticals and personal care products in waste water using Q-Exactive Orbitrap high resolution accurate mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1588, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moslah, B.; Hapeshi, E.; Jrad, A.; Fatta-Kassinos, D.; Hedhili, A. Pharmaceuticals and illicit drugs in wastewater samples in north-eastern Tunisia. Environ. Sustain. Pollut. Prev. 2018, 25, 18226–18241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, N.; Hoang, L.; Duc, L.; Nguyen, N.M.H.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Trinh, Q.T.; Mai, N.H.; Chen, H.; Nguyen, D.D.; et al. Science of the Total Environment Occurrence and risk assessment of multiple classes of antibiotics in urban canals and lakes in Hanoi, Vietnam. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 692, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, W.J.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, E.S.; Shin, S.K.; Hwang, S.R.; Oh, J.E. Occurrence and distribution of pharmaceuticals in wastewater from households, livestock farms, hospitals and pharmaceutical manufactures. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, P.; Kim, M.; Shah, A.; Alaee, M.; Smyth, S.A. Occurrence and fate of antibiotic, analgesic/anti-inflammatory, and antifungal compounds in five wastewater treatment processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473–474, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, O.; Porcher, J.M.; Sanchez, W. Factory-discharged pharmaceuticals could be a relevant source of aquatic environment contamination: Review of evidence and need for knowledge. Chemosphere 2014, 115, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oluwatosin, O.; Adekunle, B.; Obih, U.; Arne, H. Quantification of pharmaceutical residues in wastewater impacted surface waters and sewage sludge from Lagos, Nigeria. J. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2016, 8, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, G.A.; Berglund, B.; Khan, K.M.; Lindgren, P.E.; Fick, J. Occurrence and Abundance of Antibiotics and Resistance Genes in Rivers, Canal and near Drug Formulation Facilities—A Study in Pakistan. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, H.; Liu, L.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, L.; Gin, K.Y.-H.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, J. A comprehensive study of the source, occurrence, and spatio-seasonal dynamics of 12 target antibiotics and their potential risks in a cold semi-arid catchment. Water Res. 2023, 229, 119433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, K.; Kho, Y.; Park, C.; Paek, D.; Ryu, P.; Paek, D.; Kim, M.; Kim, P.; Choi, K. Influence of water and food consumption on inadvertent antibiotics intake among general population. Environ. Res. 2010, 110, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, Y.M.; Kim, S.C.; Abd El-Azeem, S.A.M.; Kim, K.-H.; Kim, K.-R.; Kim, K.; Jeon, C.; Lee, S.S.; Ok, Y.S. Veterinary antibiotics contamination in water, sediment, and soil near a swine manure composting facility. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 1433–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Jing, L.; Teng, Y.; Wang, J. Characterization of antibiotics in a large-scale river system of China: Occurrence pattern, spatiotemporal distribution and environmental risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Gin, K.Y.H.; He, Y. Occurrence, distribution, and risk assessment of antibiotics in a subtropical river-reservoir system. Water 2018, 10, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
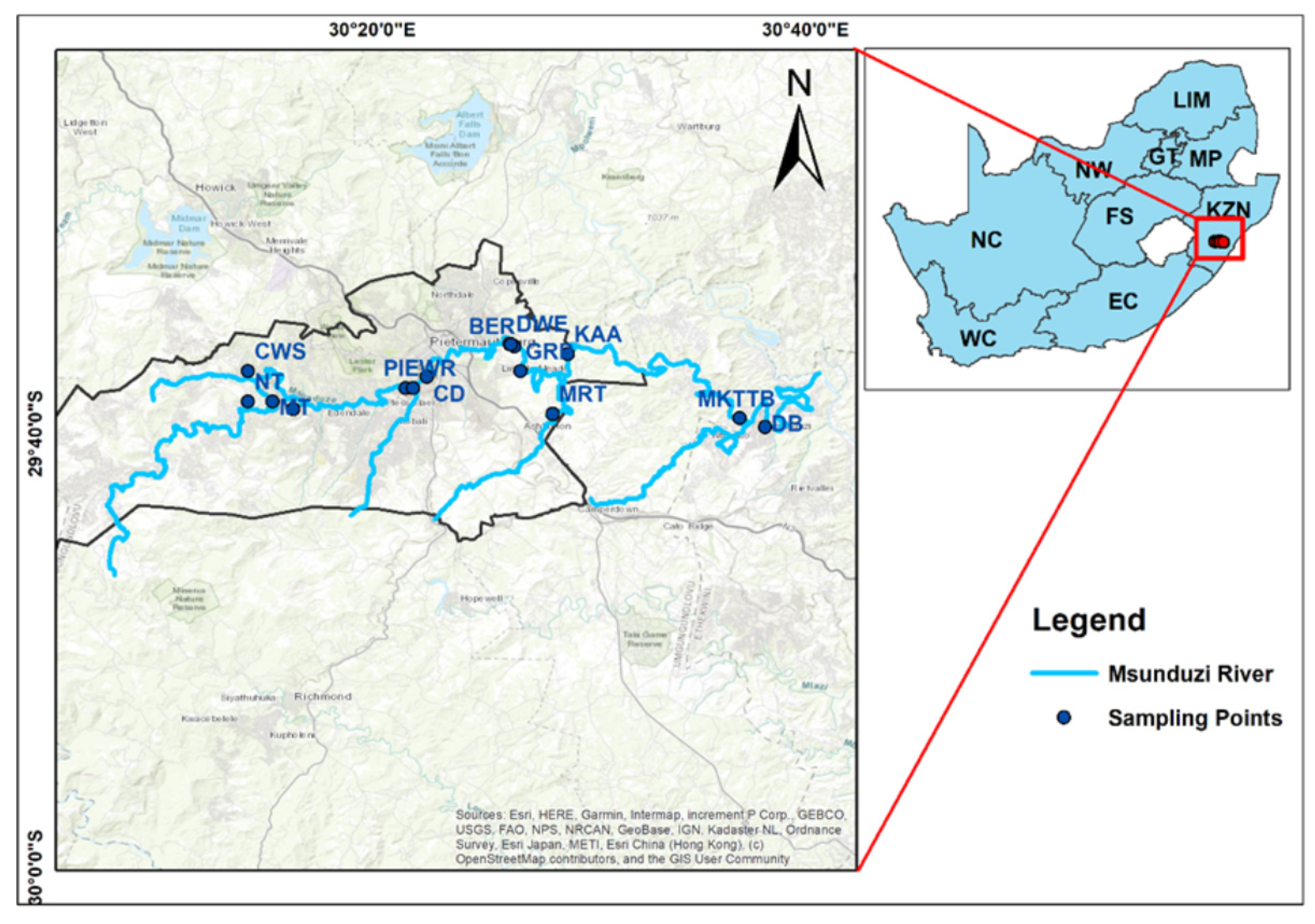

| S/No | South | East | Location | Abbreviation | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 29.64169 | 30.25631 | Msunduzi Town | MT | |
| 2 | 29.64169 | 30.23749 | Nqabeni tributary | NT | |
| 3 | 29.61837 | 30.23751 | Car wash stream | CWS | |
| 4 | 29.64755 | 30.27233 | Below Mabane tributary | BMT | |
| 5 | 29.63135 | 30.35887 | PMB Industrial effluent | PIE | Kwapata and Mvubukazi streams |
| 6 | 29.6226 | 30.375 | Camps Drift | CD | |
| 7 | 29.63136 | 30.36443 | Wilgerfontein River | WR | |
| 8 | 29.59909 | 30.44254 | River water before effluent release | BER | |
| 9 | 29.59725 | 30.43886 | Darville WWT effluent | DWWE | |
| 10 | 29.3549 | 30.2625 | River water after effluent release | DER | 1 km downstream of the effluent discharge |
| 11 | 29.61822 | 30.44724 | Gripthorpe | GRP | Bayne’s Spruit tributary |
| 12 | 29.60502 | 30.48338 | Kayeni Agricultural area | KAA | Ashburton Commercial Farm |
| 13 | 29.65112 | 30.47177 | Mpushini River tributary | MRT | |
| 14 | 29.6613 | 30.63542 | Duzi Bridge | DB | Farm and Informal settlement |
| 15 | 29.3932 | 30.3709 | Mshwati River tributary | MKT | Informal settlement |
| 16 | 29.3932 | 30.3657 | Table mountain | TB | Near the joining of Umgeni River |
| Parameter | MT | NT | CWS | BMT | PIE | CD | WR | BER | DWWE | DER | GRP | KAA | MRT | DB | MKT | TB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | ||||||||||||||||
| pH | 7.0 | 7.7 | 5.8 | 6.1 | 7.7 | 8.1 | 7.7 | 7.7 | 6.7 | 7.5 | 7.6 | 7.8 | 7.6 | 7.9 | 7.2 | 7.7 |
| T (°C) | 20.4 | 24.1 | 18.8 | 14.3 | 16.4 | 17.9 | 15.4 | 15.9 | 22.4 | 23.3 | 22.0 | 22.7 | 24.5 | 20.0 | 28.9 | 22.4 |
| EC (µs/cm) | 8464.0 | 2.0 | 14.0 | 77.0 | 88.0 | 90.0 | 93.0 | 151.0 | 232.0 | 415.0 | 236.0 | 426.0 | 415.0 | 243.0 | 265.0 | 586.0 |
| TURB (FNB) | 4232.0 | 1.0 | 7.0 | 38.0 | 44.0 | 45.0 | 47.0 | 75.0 | 116.0 | 207.0 | 118.0 | 213.0 | 207.0 | 121.0 | 133.0 | 293.0 |
| ORP (mv) | 168.6 | 293.5 | 264.6 | 233.5 | 195.9 | 191.9 | 205.4 | 32.5 | 120.2 | 142.6 | 109.1 | 139.3 | 142.6 | 147.8 | 132.2 | 137.5 |
| F (ppm) | 0.1 | 0.1 | 1.1 | |||||||||||||
| Cl− (ppm) | 11.3 | 44.5 | 10.7 | 60.7 | 23.4 | 25.6 | 35.5 | 42.6 | 88.0 | 29.4 | 41.3 | 8.7 | 195.5 | 10.7 | 419.1 | 41.7 |
| NO3− (ppm) | 2.0 | 5.4 | 3.6 | 7.5 | 1.0 | 1.4 | 3.3 | 3.4 | 3.1 | 1.9 | 1.6 | 1.8 | 17.2 | 7.8 | ||
| SO42− (ppm) | 3.1 | 21.1 | 5.5 | 19.9 | 20.7 | 17.0 | 19.4 | 24.1 | 41.2 | 15.6 | 21.8 | 2.7 | 28.7 | 3.0 | 111.0 | 17.9 |
| PO43− (ppm) | 0.1 | |||||||||||||||
| Autumn | ||||||||||||||||
| pH | 7.4 | 8.3 | 8.1 | 8.2 | 7.6 | 7.5 | 7.6 | 7.6 | 7.6 | 8.0 | 7.8 | 7.6 | 7.7 | 7.6 | 7.7 | 7.9 |
| T (°C) | 18.1 | 19.6 | 23.1 | 22.7 | 22.9 | 24.3 | 24.7 | 25.9 | 27.7 | 25.1 | 23.2 | 23.4 | 23.8 | 23.5 | 23.5 | 23.8 |
| EC (µs/cm) | 70 | 90.0 | 96.0 | 89 | 96 | 105 | 413.0 | 247.0 | 547.0 | 413 | 253.0 | 252.0 | 669.0 | 253 | 871.0 | 230.0 |
| TURB (FNB) | 3.1 | 4.5 | 5.8 | 28.6 | 49.3 | 52.5 | 109.7 | 323.4 | 34.1 | 0.0 | 77.2 | 71.0 | 161.9 | 94.8 | 134.2 | 11.5 |
| ORP (mv) | 309.0 | 201.6 | 222.7 | 223.1 | 252.2 | 268.4 | 66.7 | 185.4 | 196.5 | 171.1 | 180.3 | 202.2 | 187.8 | 178.8 | 188.1 | 195.6 |
| F (ppm) | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||
| Cl− (ppm) | 5.4 | 8.6 | 9.8 | 10.1 | 19.7 | 21.4 | 36.0 | 21.0 | 63.8 | 25.1 | 23.6 | 24.6 | 100.5 | 29.4 | 329.5 | 21.9 |
| NO3− (ppm) | 3.0 | 5.5 | 5.7 | 6.2 | 8.6 | 6.8 | 6.5 | 6.8 | 4.7 | 6.5 | 6.4 | 7.8 | 0.3 | 9.6 | 3.8 | 2.1 |
| SO42− (ppm) | 2.3 | 2.5 | 2.0 | 3.5 | 2.5 | 6.8 | 3.0 | 2.7 | 2.7 | 3.7 | 3.1 | 30.7 | 3.1 | |||
| PO43− (ppm) | ||||||||||||||||
| Winter | ||||||||||||||||
| pH | 6.0 | 7.2 | 7.0 | 7.2 | 6.9 | 7.0 | 6.9 | 7.2 | 7.6 | 7.4 | 6.4 | 7.0 | 6.7 | 6.6 | 6.9 | 7.1 |
| T (°C) | 12.2 | 16.1 | 15.5 | 14.3 | 14.5 | 16.1 | 15.5 | 15.5 | 16.7 | 19.6 | 23.3 | 18.0 | 28.9 | 26.5 | 28.0 | 15.9 |
| EC (µs/cm) | 119 | 110 | 111 | 88 | 90 | 98 | 39 | 229 | 240 | 388 | 234 | 245.8 | 295 | 273 | 274 | 125 |
| TURB (FNB) | 46.2 | 63.5 | 29.3 | 210.8 | 6.0 | 133.5 | 82.0 | 30.4 | 12.0 | 17.0 | 11.6 | 204.4 | 60.5 | 15.4 | 9.4 | 0.0 |
| ORP (mv) | 301.0 | 344.7 | 327.9 | 293.7 | 346.6 | 324.0 | 305.5 | 280.4 | 246.6 | 262.7 | 226.3 | 2.2 | 241.3 | 273.2 | 254.9 | 244.2 |
| F (ppm) | 0.1 | 1.2 | ||||||||||||||
| Cl− (ppm) | 12.4 | 11.1 | 13.0 | 14.5 | 35.1 | 31.3 | 48.5 | 30.7 | 88.1 | 41.0 | 38.0 | 40.3 | 176.9 | 69.3 | 493.5 | 45.8 |
| NO3− (ppm) | 7.3 | 6.0 | 7.3 | 6.9 | 7.9 | 10.9 | 16.4 | 12.8 | 16.2 | 15.3 | 12.1 | 11.9 | 2.7 | 13.5 | 22.7 | 12.3 |
| SO42− (ppm) | 2.3 | 2.4 | 6.0 | 3.3 | 15.4 | 11.9 | 24.1 | 12.5 | 40.9 | 17.5 | 18.0 | 17.1 | 31.4 | 25.2 | 37.4 | 20.4 |
| PO43− (ppm) | 3.1 | |||||||||||||||
| Antibiotics | Log Kow (pKa) | Solubility (mg/L) | Chemical Formula | Molar Mass (g/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERY | 3.06 (8.89) | 4.2 | C37H67NO13 | 734 |
| PNC | 1.83 (2.74) | 210 | C16H18N2O4S | 334 |
| STZ | 0.05 (7.2) | 2370 | C9H9N3O2S2 | 255 |
| TTC | −1.37 (3.30) | 231 | C22H24N2O8 | 444 |
| Chromatograph | SHIMADZU LCMS-2020 | ||
| Column | Shim-Pack GIST-HP 3 µm C18 | ||
| Injection Volume (µL) | 20 | ||
| Temperature (°C) | 35 | ||
| Flow rate (mL/min) | 0.25 | ||
| Gradient Composition | Time (min) | %A | %B |
| 0 | 95 | 5 | |
| 25 | 10 | 90 | |
| 27 | 10 | 90 | |
| 32 | 95 | 5 | |
| 37 | 95 | 5 | |
| Compound | Linear Range (ng/L) | Recovery ± SD (%) | RT (min) | Precursor Ion (m/z) | LOD (ng/L) | LOQ (ng/L) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TTC | 100–10,000 | 93.2 ± 4.4 | 18 | 445 [M + H]+ | 40.22 | 137.07 | 0.996 |
| PNC | 10–10,000 | 81.3 ± 1.7 | 24 | 335 [M + H]+ | 43.19 | 143.98 | 0.892 |
| ERY | 1–100,000 | 90 ± 2.1 | 21 | 735 [M + H]+ | 15.64 | 52.14 | 0.997 |
| STZ | 10–10,000 | 91.3 ± 3.6 | 18 | 256 [M + H]+ | 37.4 | 112.68 | 0.961 |
| Antibiotics | MT | NT | CWS | BMT | PIE | CD | WR | BER | DWWE | DER | GRP | KAA | MRT | DB | MKT | TB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | ||||||||||||||||
| PNC | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | <LOQ | <LOQ | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| TTC | ND | ND | ND | ND | <LOQ | 158.42 | ND | <LOQ | 1756.51 | 1290.43 | ND | ND | <LOQ | 577.63 | ND | ND |
| ERY | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | 142.63 | <LOQ | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| STZ | ND | ND | ND | ND | 164.64 | 183.47 | ND | ND | 5613.58 | 1151.25 | ND | 162.88 | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Autumn | ||||||||||||||||
| PNC | ND | ND | ND | <LOQ | ND | ND | 503.30 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| TTC | ND | ND | ND | <LOQ | ND | ND | <LOQ | ND | 1519.65 | 720 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| ERY | ND | ND | ND | <LOQ | <LOQ | ND | ND | ND | <LOQ | ND | ND | ND | 106.63 | ND | ND | ND |
| STZ | ND | ND | ND | <LOQ | ND | ND | ND | ND | <LOQ | ND | ND | ND | ND | 226.18 | ND | ND |
| Winter | ||||||||||||||||
| PNC | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | <LOQ | ND | <LOQ | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| TTC | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | <LOQ | 684.11 | ND | 138.03 | ND | ND | ND | ND | <LOQ | ND | ND |
| ERY | ND | ND | ND | 76.3 | ND | ND | ND | ND | <LOQ | ND | <LOQ | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| STZ | <LOQ | ND | <LOQ | ND | ND | ND | ND | <LOQ | 120.74 | <LOQ | ND | ND | <LOQ | ND | ND | ND |
| Concentration (ng/L) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibiotics | This Study | Other Studies | Country | Citation |
| Wastewater effluent | ||||
| TTC | 1756.51 | 853 | Vietnam | [84] |
| 1420 | Korea | [37] | ||
| ERY | 142.63 | 275 | Egypt | [82] |
| 1187 | Tunisia | [83] | ||
| 2350 | Korea | [85] | ||
| 48,520 | Vietnam | [84] | ||
| PNC | <LOQ | 11 | Canada | [86] |
| 13,500 | Korea | [85] | ||
| STZ | 5613.58 | 350 | USA | [36] |
| 16 | Canada | [86] | ||
| 5000 | Korea | [87] | ||
| 600 | Australia | [39] | ||
| Surface water | ||||
| TTC | 1290.43 | 50 | Nigeria | [88] |
| 138 | Tunisia | [83] | ||
| 120 | Pakistan | [89] | ||
| 138 | Vietnam | [84] | ||
| 430 | China | [90] | ||
| ERY | 106.63 | 1000 | Nigeria | [88] |
| 61 | Egypt | [82] | ||
| 741 | Vietnam | [84] | ||
| 17 | China | [90] | ||
| 310 | Pakistan | [89] | ||
| PNC | 503.30 | 668 | China | [40] |
| 250 | Australia | [39] | ||
| STZ | 1151.25 | 253 | Korea | [91] |
| 4610 | Korea | [92] | ||
| Antibiotics | MEC (ng/L) | Organism | MIC (ng/L) | AF | PNEC (ng/L) | RQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TTC | 686.118 | Algae | 50,000 (NOEC) a | 10 | 5000 | 0.114 |
| Fish | 500 b | 50 | 11.43 | |||
| Daphnids | 10000 b | 1000 | 0.571 | |||
| PNG | 503.3 | Algae | 6.51 × 1010 b | 1000 | 6.51 × 106 | 0.000008 |
| Fish | 2.05 × 1013 b | 2.05 × 1010 | 0 | |||
| Daphnids | 1.32 × 1011 b | 1.32 × 108 | 0.000004 | |||
| ERY | 91.465 | Algae | 2000 b,c | 50 | 40 | 2.286 |
| Fish | 108 b | 2 × 106 | 0.00004 | |||
| Daphnids | 220,000 b | 4400 | 0.02 | |||
| STZ | 377.684 | Algae | 1.31 × 107 (NOEC) a | 1000 | 13,100 | 0.02 |
| Fish | 5108 b | 500,000 | 0.0007 | |||
| Daphnids | 2.2 × 108 b | 220,000 | 0.0017 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Addis, T.Z.; Adu, J.T.; Kumarasamy, M.; Demlie, M. Occurrence of Trace-Level Antibiotics in the Msunduzi River: An Investigation into South African Environmental Pollution. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13020174
Addis TZ, Adu JT, Kumarasamy M, Demlie M. Occurrence of Trace-Level Antibiotics in the Msunduzi River: An Investigation into South African Environmental Pollution. Antibiotics. 2024; 13(2):174. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13020174
Chicago/Turabian StyleAddis, Temesgen Zelalem, Joy Tuoyo Adu, Muthukrishnavellaisamy Kumarasamy, and Molla Demlie. 2024. "Occurrence of Trace-Level Antibiotics in the Msunduzi River: An Investigation into South African Environmental Pollution" Antibiotics 13, no. 2: 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13020174
APA StyleAddis, T. Z., Adu, J. T., Kumarasamy, M., & Demlie, M. (2024). Occurrence of Trace-Level Antibiotics in the Msunduzi River: An Investigation into South African Environmental Pollution. Antibiotics, 13(2), 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13020174







