Streptococcus pneumoniae Infection in Patients with Asplenia: A Spanish Perspective over a 25-Year Period
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Methods
3.1. Study Design
3.2. Data Source and Study Population
3.3. Demographic and Hospitalization Data
3.4. Statistical Analysis
3.5. Ethical Statement
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Demographic and Hospitalization Data
References
- Szenborn, L.; Osipova, I.V.; Czajka, H.; Kharit, S.M.; Jackowska, T.; François, N.; Habib, M.A.; Borys, D. Immunogenicity, safety and reactogenicity of the pneumococcal non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae protein D conjugate vaccine (PHiD-CV) in 2–17-year-old children with asplenia or splenic dysfunction: A phase 3 study. Vaccine 2017, 35, 5331–5338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaswalla, P.K.; Bengtson, L.G.S.; Marshall, G.S.; Buikema, A.R.; Bancroft, T.; Schladweiler, K.M.; Koep, E.; Novy, P.; Hogea, C.S. Meningococcal vaccination in patients with newly diagnosed asplenia in the United States. Vaccine 2021, 39, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Styrt, B. Infection associated with asplenia: Risks, mechanisms, and prevention. Am. J. Med. 1990, 88, 33N–42N. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sempere, J.; Llamosí, M.; López Ruiz, B.; Del Río, I.; Pérez-García, C.; Lago, D.; Gimeno, M.; Coronel, P.; González-Camacho, F.; Domenech, M.; et al. Effect of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines and SARS-CoV-2 on antimicrobial resistance and the emergence of Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes with reduced susceptibility in Spain, 2004–2020: A national surveillance study. Lancet Microbe 2022, 3, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, J.; Hiramatsu, K.; Kenzaka, T.; Kato, T. Pneumococcal infection transmission between family members with congenital asplenia: A case report. World J. Clin. Cases 2019, 7, 4277–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Both, I.; Pollanen, M.S. Fatal pneumococcal septicemia in a girl with visceral heterotaxy and polysplenia: A case report. Forensic Sci. Med. Pathol. 2020, 16, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gea-Izquierdo, E.; Gil-Prieto, R.; Hernández-Barrera, V.; Gil-de-Miguel, Á. Respiratory syncytial virus-associated hospitalization in children aged <2 years in Spain from 2018 to 2021. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2023, 19, 2231818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Reyes, D.; Gea-Izquierdo, E.; Gil-Prieto, R.; Gil-de-Miguel, Á. Carga de hospitalización y comorbilidades relacionadas con la enfermedad neumocócica en España (2019–2021). Rev. Esp. Med. Prev. Salud Pub. 2023, 28, 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Gobierno de España. Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación. Instituto de Salud Carlos III. Protocolo de la Red Nacional de Vigilancia Epidemiológica (RENAVE). Procedimiento para la Notificación de Casos y la Vigilancia Epidemiológica de la Enfermedad Neumocócica Invasora. 2023. Available online: https://www.isciii.es/QueHacemos/Servicios/VigilanciaSaludPublicaRENAVE/EnfermedadesTransmisibles/Paginas/NeumococicaInvasora.aspx (accessed on 11 December 2023).
- Marrie, T.J.; Tyrrell, G.J.; Majumdar, S.R.; Eurich, D.T. Asplenic patients and invasive pneumococcal disease-how bad is it these days? Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 51, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Angelski, C.L.; McKay, E.; Blackie, B. A case of functional asplenia and pneumococcal sepsis. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2011, 27, 639–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashorobi, D.; Fernandez, R. Asplenia. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ram, S.; Lewis, L.A.; Rice, P.A. Infections of people with complement deficiencies and patients who have undergone splenectomy. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 740–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squire, J.D.; Sher, M. Asplenia and Hyposplenism: An Underrecognized Immune Deficiency. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2020, 40, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagnola, E.; Fioredda, F. Prevention of life-threatening infections due to encapsulated bacteria in children with hyposplenia or asplenia: A brief review of current recommendations for practical purposes. Eur. J. Haematol. 2003, 71, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Prieto, R.; Pascual-Garcia, R.; Walter, S.; Álvaro-Meca, A.; Gil-De-Miguel, Á. Risk of hospitalization due to pneumococcal disease in adults in Spain. The CORIENNE study. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2016, 12, 1900–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvat, M.; Robnik, B.; Bizjak, K.; Vuzem, S.; Miksić, N.G. Audit of Post-Splenectomy Prophylaxis in a Single Tertiary Center in Slovenia: Where Are We and What Should Be Done? Surg. Infect. 2021, 22, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.M. Preventing infections in children and adults with asplenia. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program. 2020, 1, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankine-Mullings, A.E.; Owusu-Ofori, S. Prophylactic antibiotics for preventing pneumococcal infection in children with sickle cell disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 10, CD003427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshita, K.; Takeuchi, N.; Takahashi, Y.; Fukasawa, C.; Hishiki, H.; Hoshino, T.; Ishiwada, N.; Shimojo, N. Pneumococcal serotype-specific IgG and opsonophagocytic activity in young Japanese patients with asplenia. Hum. Vaccins Immunother. 2021, 17, 3687–3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naciones Unidas. Informe de los Objetivos de Desarrollo Sostenible; Naciones Unidas: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Use of 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine and 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine for adults with immunocompromising conditions: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2012, 61, 816–819. [Google Scholar]
- Adamkiewicz, T.V.; Sarnaik, S.; Buchanan, G.R.; Iyer, R.V.; Miller, S.T.; Pegelow, C.H.; Rogers, Z.R.; Vichinsky, E.; Elliott, J.; Facklam, R.R.; et al. Invasive pneumococcal infections in children with sickle cell disease in the era of penicillin prophylaxis, antibiotic resistance, and 23- valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccination. J. Pediatr. 2003, 143, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnave, C.; Mertens, D.; Peetermans, W.; Cobbaert, K.; Ghesquiere, B.; Deschodt, M.; Flamaing, J. Adult vaccination for pneumococcal disease: A comparison of the national guidelines in Europe. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 38, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkineska, L.; Perifanis, V.; Vasiliadis, T. Functional hyposplenism. Hippokratia 2014, 18, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
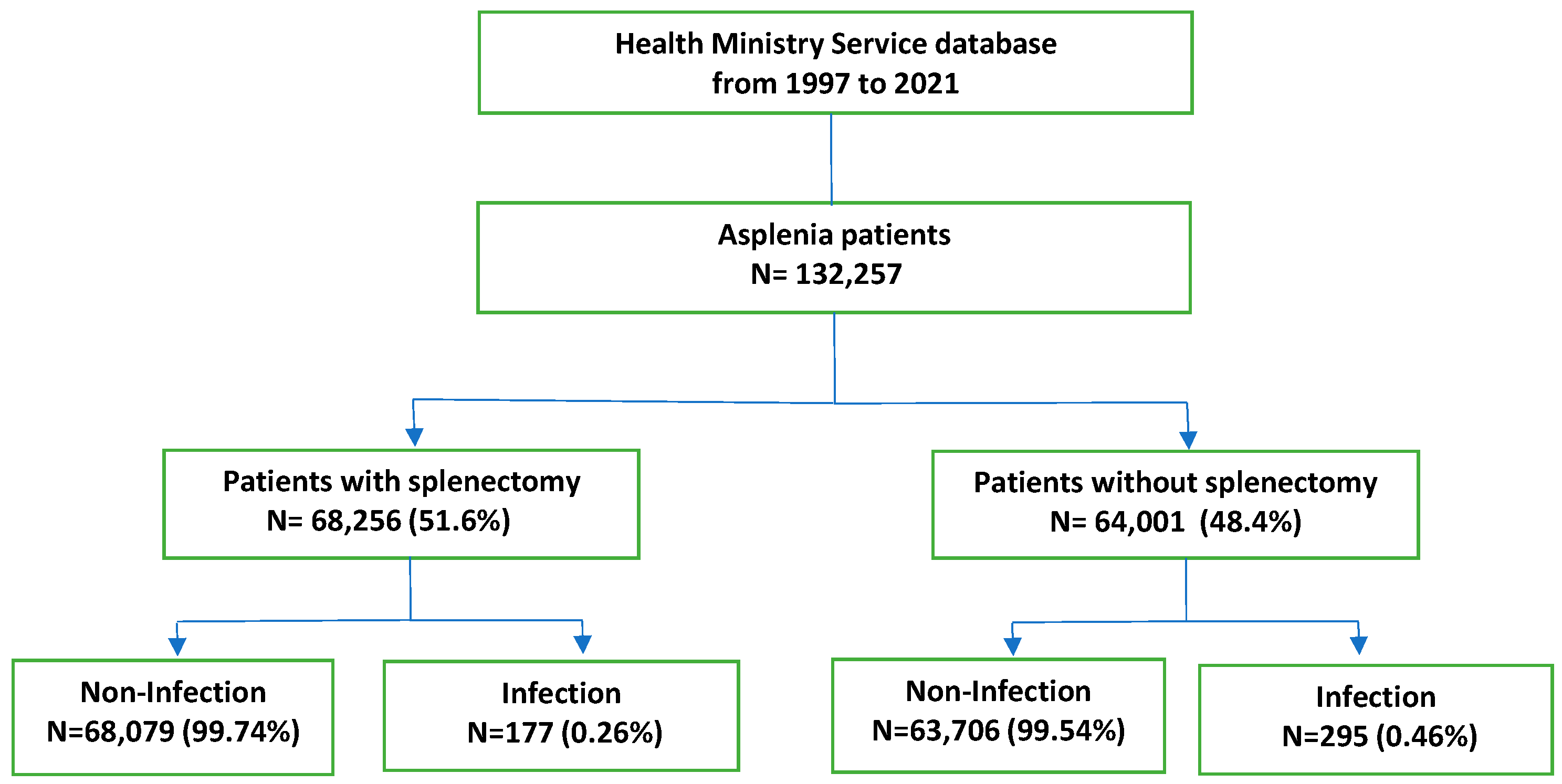
| Total | Total N = 132,257 | Non-Infection N = 131,785 | Infection N = 472 | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean, SD | 53.81 ± 21.99 | 53.79 ± 21.99 | 58.3 ± 20.03 | 0.000 | ||||
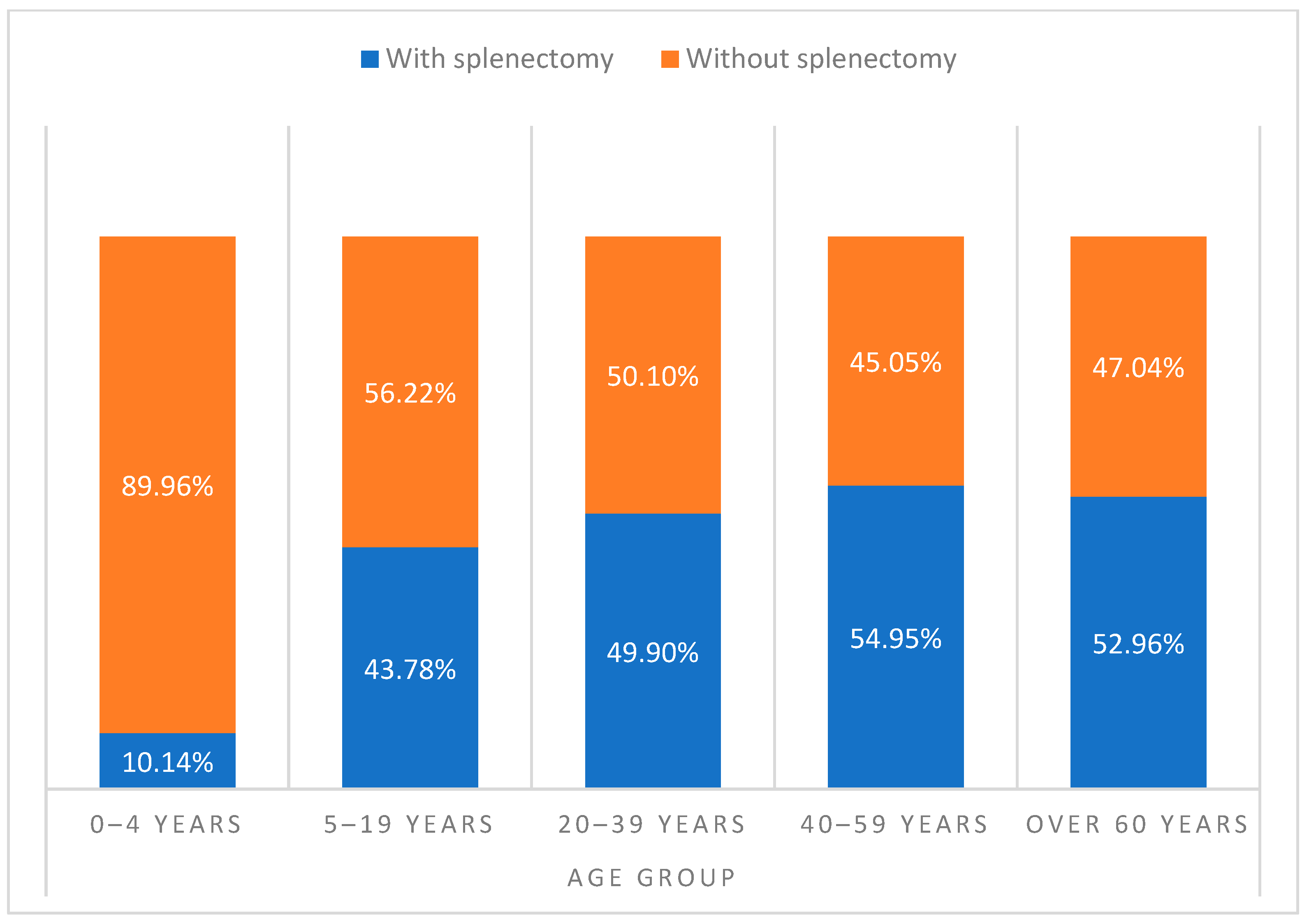
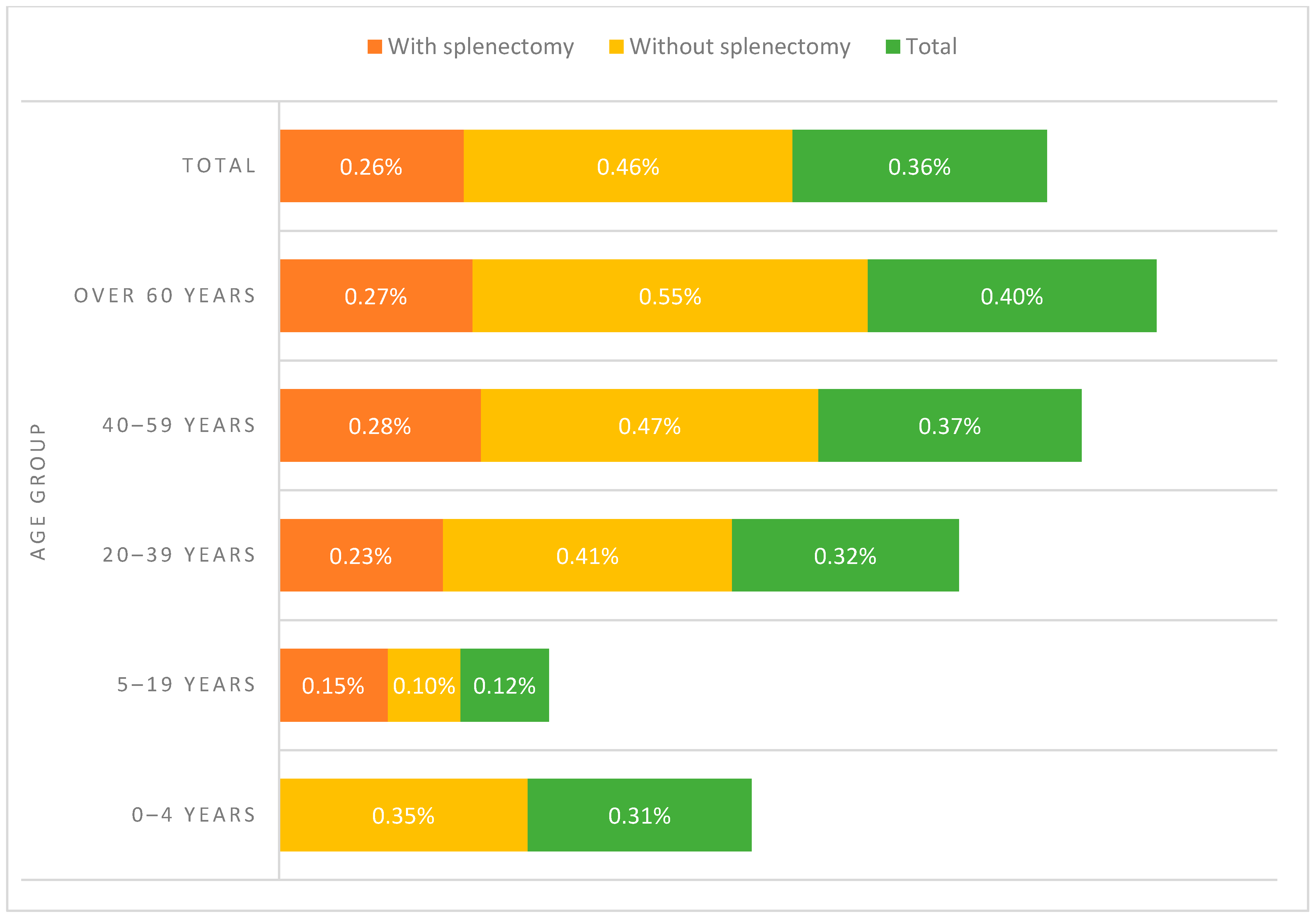
| Age group | 0–4 years | 1913 | 1.45% | 1907 | 1.45% | 6 | 1.27% | 0.000 |
| 5–19 years | 10,476 | 7.92% | 10,463 | 7.94% | 13 | 2.75% | ||
| 20–39 years | 22,646 | 17.12% | 22,574 | 17.13% | 72 | 15.25% | ||
| 40–59 years | 34,696 | 26.23% | 34,568 | 26.23% | 128 | 27.12% | ||
| Over 60 years | 62,526 | 47.28% | 62,273 | 47.25% | 253 | 53.60% | ||
| Sex | Male | 81,191 | 61.39% | 80,876 | 61.37% | 315 | 66.74% | 0.017 |
| Female | 51,066 | 38.61% | 50,909 | 38.63% | 157 | 33.26% | ||
| Splenectomy | Yes | 68,256 | 51.61% | 68,079 | 51.66% | 177 | 37.50% | 0.000 |
| No | 64,001 | 48.39% | 63,706 | 48.34% | 295 | 62.50% | ||
| LOHS (Length of Hospital Stay), median, IQR | 11 ± 16 | 11 ± 16 | 18 ± 22 | 0.000 | ||||
| AMI (Acute Myocardial Infarction) | 2632 | 1.99% | 2619 | 1.99% | 13 | 2.75% | 0.234 | |
| CHF (Congestive Heart Failure) | 5909 | 4.47% | 5875 | 4.46% | 34 | 7.20% | 0.004 | |
| PVD (Peripheral Vascular Disease) | 5925 | 4.48% | 5904 | 4.48% | 21 | 4.45% | 0.974 | |
| CeVD (Cerebrovascular Disease) | 4066 | 3.07% | 4042 | 3.07% | 24 | 5.08% | 0.011 | |
| Dementia | 838 | 0.63% | 832 | 0.63% | 6 | 1.27% | 0.080 | |
| COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) | 11,938 | 9.03% | 11,858 | 9.00% | 80 | 16.95% | 0.000 | |
| Rheumatoid Disease | 1687 | 1.28% | 1671 | 1.27% | 16 | 3.39% | 0.000 | |
| PUD (Peptic Ulcer Disease) | 2465 | 1.86% | 2454 | 1.86% | 11 | 2.33% | 0.453 | |
| Diabetes | 14,730 | 11.14% | 14,680 | 11.14% | 50 | 10.59% | 0.707 | |
| Diabetes and Complications | 1298 | 0.98% | 1293 | 0.98% | 5 | 1.06% | 0.863 | |
| HP/PAPL (Hemiplegia or Paraplegia) | 1018 | 0.77% | 1015 | 0.77% | 3 | 0.64% | 0.738 | |
| RD (Renal Disease) | 5721 | 4.33% | 5691 | 4.32% | 30 | 6.36% | 0.030 | |
| Cancer | 25,214 | 19.06% | 25,127 | 19.07% | 87 | 18.43% | 0.726 | |
| AIDS | 1232 | 0.93% | 1206 | 0.92% | 26 | 5.51% | 0.000 | |
| Pulmonary Circulation Disorders | 3327 | 2.52% | 3309 | 2.51% | 18 | 3.81% | 0.071 | |
| Hypertension, Complicated | 5322 | 4.02% | 5299 | 4.02% | 23 | 4.87% | 0.347 | |
| Paralysis | 1018 | 0.77% | 1015 | 0.77% | 3 | 0.64% | 0.738 | |
| Other Neurological Disorders | 3333 | 2.52% | 3309 | 2.51% | 24 | 5.08% | 0.000 | |
| Liver Disease | 16,525 | 12.49% | 16,461 | 12.49% | 64 | 13.56% | 0.483 | |
| Metastatic Cancer | 17,308 | 13.09% | 17,275 | 13.11% | 33 | 6.99% | 0.000 | |
| Obesity | 4987 | 3.77% | 4970 | 3.77% | 17 | 3.60% | 0.847 | |
| Alcohol Abuse | 8876 | 6.71% | 8828 | 6.70% | 48 | 10.17% | 0.003 | |
| Drug Abuse | 2537 | 1.92% | 2511 | 1.91% | 26 | 5.51% | 0.000 | |
| Any Disease | 82,018 | 62.01% | 81,677 | 61.98% | 341 | 72.25% | 0.000 | |
| Splenectomy | Total N = 68,256 | Non-Infection N = 68,079 | Infection N = 177 | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean, SD | 54.78 ± 20.09 | 54.77 ± 20.1 | 57.23 ± 19.01 | 0.104 | ||||
| Age group | 0–4 years | 194 | 0.28% | 194 | 0.28% | 0 | 0.00% | 0.475 |
| 5–19 years | 4586 | 6.72% | 4579 | 6.73% | 7 | 3.95% | ||
| 20–39 years | 11,300 | 16.56% | 11,274 | 16.56% | 26 | 14.69% | ||
| 40–59 years | 19,065 | 27.93% | 19,011 | 27.92% | 54 | 30.51% | ||
| Over 60 years | 33,111 | 48.51% | 33,021 | 48.50% | 90 | 50.85% | ||
| Sex | Male | 40,520 | 59.36% | 40,396 | 59.34% | 124 | 70.06% | 0.004 |
| Female | 27,736 | 40.64% | 27,683 | 40.66% | 53 | 29.94% | ||
| LOHS (Length of Hospital Stay), median, IQR | 13 ± 18 | 13 ± 18 | 27 ± 27 | 0.000 | ||||
| AMI (Acute Myocardial Infarction) | 985 | 1.44% | 980 | 1.44% | 5 | 2.82% | 0.123 | |
| CHF (Congestive Heart Failure) | 1645 | 2.41% | 1633 | 2.40% | 12 | 6.78% | 0.000 | |
| PVD (Peripheral Vascular Disease) | 1691 | 2.48% | 1688 | 2.48% | 3 | 1.69% | 0.502 | |
| CeVD (Cerebrovascular Disease) | 921 | 1.35% | 915 | 1.34% | 6 | 3.39% | 0.018 | |
| Dementia | 159 | 0.23% | 159 | 0.23% | 0 | 0.00% | 0.520 | |
| COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) | 4751 | 6.96% | 4734 | 6.95% | 17 | 9.60% | 0.166 | |
| Rheumatoid Disease | 645 | 0.94% | 642 | 0.94% | 3 | 1.69% | 0.302 | |
| PUD (Peptic Ulcer Disease) | 1456 | 2.13% | 1450 | 2.13% | 6 | 3.39% | 0.247 | |
| Diabetes | 6611 | 9.69% | 6601 | 9.70% | 10 | 5.65% | 0.069 | |
| Diabetes and Complications | 336 | 0.49% | 335 | 0.49% | 1 | 0.56% | 0.890 | |
| HP/PAPL (Hemiplegia or Paraplegia) | 228 | 0.33% | 227 | 0.33% | 1 | 0.56% | 0.594 | |
| RD (Renal Disease) | 1858 | 2.72% | 1855 | 2.72% | 3 | 1.69% | 0.400 | |
| Cancer | 18,305 | 26.82% | 18,252 | 26.81% | 53 | 29.94% | 0.347 | |
| AIDS | 424 | 0.62% | 416 | .61% | 8 | 4.52% | 0.000 | |
| Pulmonary Circulation Disorders | 674 | 0.99% | 672 | 0.99% | 2 | 1.13% | 0.848 | |
| Hypertension, Complicated | 1471 | 2.16% | 1467 | 2.15% | 4 | 2.26% | 0.923 | |
| Paralysis | 228 | 0.33% | 227 | 0.33% | 1 | 0.56% | 0.594 | |
| Other Neurological Disorders | 1123 | 1.65% | 1118 | 1.64% | 5 | 2.82% | 0.217 | |
| Liver Disease | 4713 | 6.90% | 4705 | 6.91% | 8 | 4.52% | 0.210 | |
| Metastatic Cancer | 12,211 | 17.89% | 12,188 | 17.90% | 23 | 12.99% | 0.089 | |
| Obesity | 2225 | 3.26% | 2218 | 3.26% | 7 | 3.95% | 0.602 | |
| Alcohol Abuse | 3188 | 4.67% | 3174 | 4.66% | 14 | 7.91% | 0.041 | |
| Drug Abuse | 1029 | 1.51% | 1025 | 1.51% | 4 | 2.26% | 0.411 | |
| Any Disease | 43,105 | 63.15% | 42,985 | 63.14% | 120 | 67.80% | 0.200 | |
| No Splenectomy | Total N = 64,001 | Non-Infection N = 63,706 | Infection N = 295 | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean, SD | 52.77 ± 23.8 | 52.74 ± 23.81 | 58.94 ± 20.63 | 0.000 | ||||
| Age group | 0–4 years | 1719 | 2.69% | 1713 | 2.69% | 6 | 2.03% | 0.000 |
| 5–19 years | 5890 | 9.20% | 5884 | 9.24% | 6 | 2.03% | ||
| 20–39 years | 11,346 | 17.73% | 11,300 | 17.74% | 46 | 15.59% | ||
| 40–59 years | 15,631 | 24.42% | 15,557 | 24.42% | 74 | 25.08% | ||
| Over 60 years | 29,415 | 45.96% | 29,252 | 45.92% | 163 | 55.25% | ||
| Sex | Male | 40,671 | 63.55% | 40,480 | 63.54% | 191 | 64.75% | 0.668 |
| Female | 23,330 | 36.45% | 23,226 | 36.46% | 104 | 35.25% | ||
| LOHS (Length of Hospital Stay), median, IQR | 10 ± 12 | 10 ± 12 | 13 ± 14 | 0.000 | ||||
| AMI (Acute Myocardial Infarction) | 1647 | 2.57% | 1639 | 2.57% | 8 | 2.71% | 0.880 | |
| CHF (Congestive Heart Failure) | 4264 | 6.66% | 4242 | 6.66% | 22 | 7.46% | 0.583 | |
| PVD (Peripheral Vascular Disease) | 4234 | 6.62% | 4216 | 6.62% | 18 | 6.10% | 0.722 | |
| CeVD (Cerebrovascular Disease) | 3145 | 4.91% | 3127 | 4.91% | 18 | 6.10% | 0.344 | |
| Dementia | 679 | 1.06% | 673 | 1.06% | 6 | 2.03% | 0.102 | |
| COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) | 7187 | 11.23% | 7124 | 11.18% | 63 | 21.36% | 0.000 | |
| Rheumatoid Disease | 1042 | 1.63% | 1029 | 1.62% | 13 | 4.41% | 0.000 | |
| PUD (Peptic Ulcer Disease) | 1009 | 1.58% | 1004 | 1.58% | 5 | 1.69% | 0.870 | |
| Diabetes | 8119 | 12.69% | 8079 | 12.68% | 40 | 13.56% | 0.651 | |
| Diabetes and Complications | 962 | 1.50% | 958 | 1.50% | 4 | 1.36% | 0.835 | |
| HP/PAPL (Hemiplegia or Paraplegia) | 790 | 1.23% | 788 | 1.24% | 2 | 0.68% | 0.386 | |
| RD (Renal Disease) | 3863 | 6.04% | 3836 | 6.02% | 27 | 9.15% | 0.024 | |
| Cancer | 6909 | 10.80% | 6875 | 10.79% | 34 | 11.53% | 0.685 | |
| AIDS | 808 | 1.26% | 790 | 1.24% | 18 | 6.10% | 0.000 | |
| Pulmonary Circulation Disorders | 2653 | 4.15% | 2637 | 4.14% | 16 | 5.42% | 0.270 | |
| Hypertension, Complicated | 3851 | 6.02% | 3832 | 6.02% | 19 | 6.44% | 0.759 | |
| Paralysis | 790 | 1.23% | 788 | 1.24% | 2 | 0.68% | 0.386 | |
| Other Neurological Disorders | 2210 | 3.45% | 2191 | 3.44% | 19 | 6.44% | 0.005 | |
| Liver Disease | 11,812 | 18.46% | 11,756 | 18.45% | 56 | 18.98% | 0.815 | |
| Metastatic Cancer | 5097 | 7.96% | 5087 | 7.99% | 10 | 3.39% | 0.004 | |
| Obesity | 2762 | 4.32% | 2752 | 4.32% | 10 | 3.39% | 0.433 | |
| Alcohol Abuse | 5688 | 8.89% | 5654 | 8.88% | 34 | 11.53% | 0.110 | |
| Drug Abuse | 1508 | 2.36% | 1486 | 2.33% | 22 | 7.46% | 0.000 | |
| Any Disease | 38,913 | 60.80% | 38,692 | 60.74% | 221 | 74.92% | 0.000 | |
| Variable | Total | Splenectomy | No Splenectomy | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p-Value | OR(95% CI) | p-Value | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | ||
| Age | 5–19 years | 1(reference) | - | 1 (reference) | - | 1 (reference) | - |
| 0–4 years | 2.15 (0.82–5.68) | 0.121 | - | - | 3.41 (1.1–10.61) | 0.034 | |
| 20–39 years | 2.51 (1.39–4.54) | 0.002 | 1.49 (0.64–3.44) | 0.354 | 3.65 (1.56–8.58) | 0.003 | |
| 40–59 years | 2.71 (1.51–4.87) | 0.001 | 1.83 (0.81–4.13) | 0.145 | 3.65 (1.56–8.52) | 0.003 | |
| Over 60 years | 2.83 (1.58–5.06) | 0.000 | 1.74 (0.77–3.92) | 0.182 | 4 (1.73–9.27) | 0.001 | |
| Sex | Female | 1 (reference) | - | 1 (reference) | - | 1 (reference) | - |
| Male | 1.27 (1.04–1.54) | 0.016 | 1.63 (1.18–2.25) | 0.003 | 1.09 (0.86–1.39) | 0.465 | |
| Comorbidities | No | 1 (reference) | - | 1 (reference) | - | 1 (reference) | - |
| Yes | 1.38 (1.1–1.73) | 0.005 | 1.1 (0.77–1.57) | 0.593 | 1.61 (1.2–2.16) | 0.001 | |
| Causes of asplenia | Splenectomy | 1 (reference) | - | - | |||
| No splenectomy | 1.82 (1.51–2.19) | 0.000 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gea-Izquierdo, E.; Rodríguez-Caravaca, G.; Gil-Prieto, R.; Hernández-Barrera, V.; Gil-de-Miguel, Á. Streptococcus pneumoniae Infection in Patients with Asplenia: A Spanish Perspective over a 25-Year Period. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13010104
Gea-Izquierdo E, Rodríguez-Caravaca G, Gil-Prieto R, Hernández-Barrera V, Gil-de-Miguel Á. Streptococcus pneumoniae Infection in Patients with Asplenia: A Spanish Perspective over a 25-Year Period. Antibiotics. 2024; 13(1):104. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13010104
Chicago/Turabian StyleGea-Izquierdo, Enrique, Gil Rodríguez-Caravaca, Ruth Gil-Prieto, Valentín Hernández-Barrera, and Ángel Gil-de-Miguel. 2024. "Streptococcus pneumoniae Infection in Patients with Asplenia: A Spanish Perspective over a 25-Year Period" Antibiotics 13, no. 1: 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13010104
APA StyleGea-Izquierdo, E., Rodríguez-Caravaca, G., Gil-Prieto, R., Hernández-Barrera, V., & Gil-de-Miguel, Á. (2024). Streptococcus pneumoniae Infection in Patients with Asplenia: A Spanish Perspective over a 25-Year Period. Antibiotics, 13(1), 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13010104







