An Approach to Improve Energy Efficiency during Antimicrobial Blue Light Inactivation: Application of Pulse-Width Modulation Dimming to Balance Irradiance and Irradiation Time
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
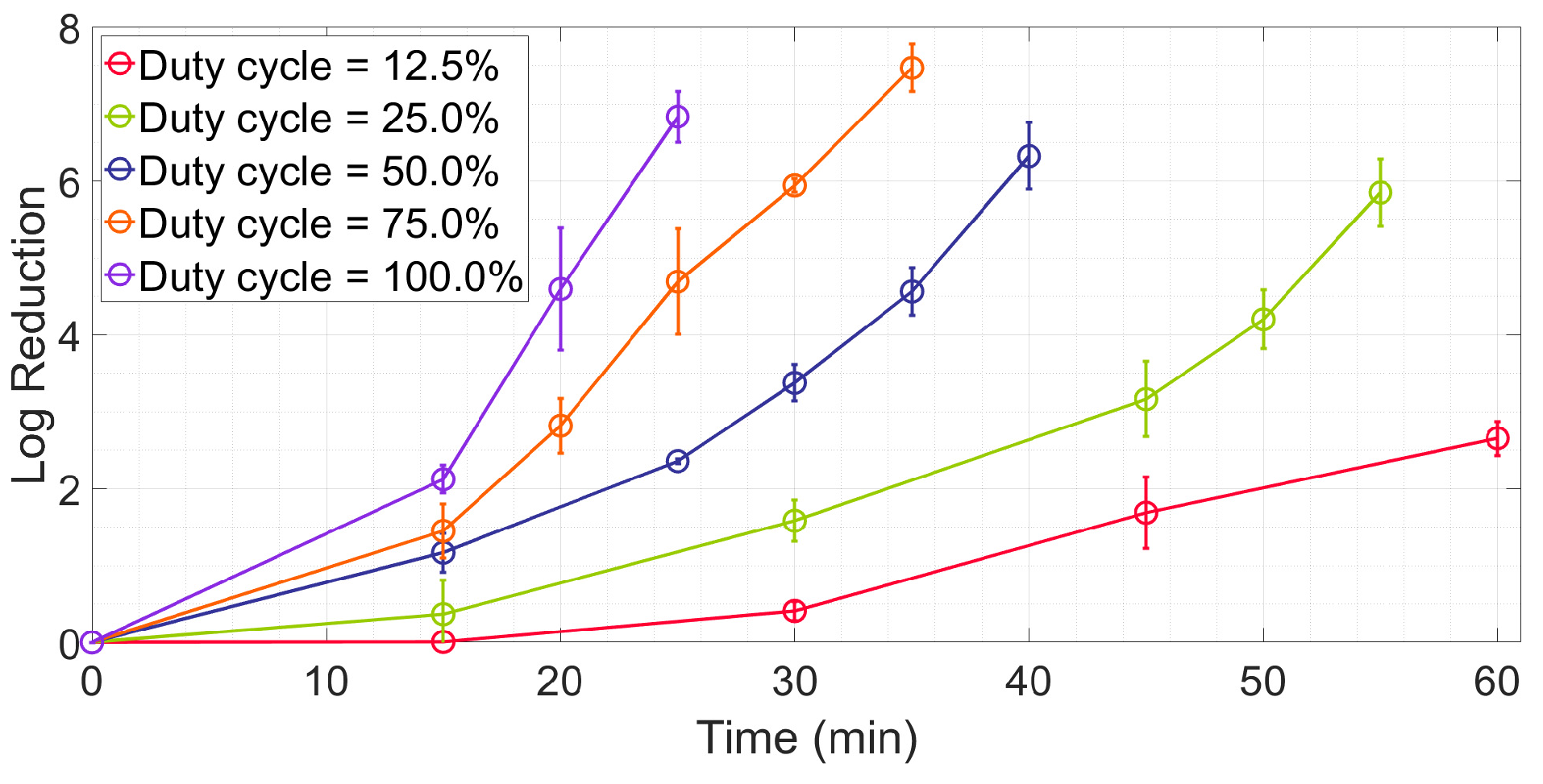
2.1. Measurement of Irradiance and Temperature at Different Duty Cycles
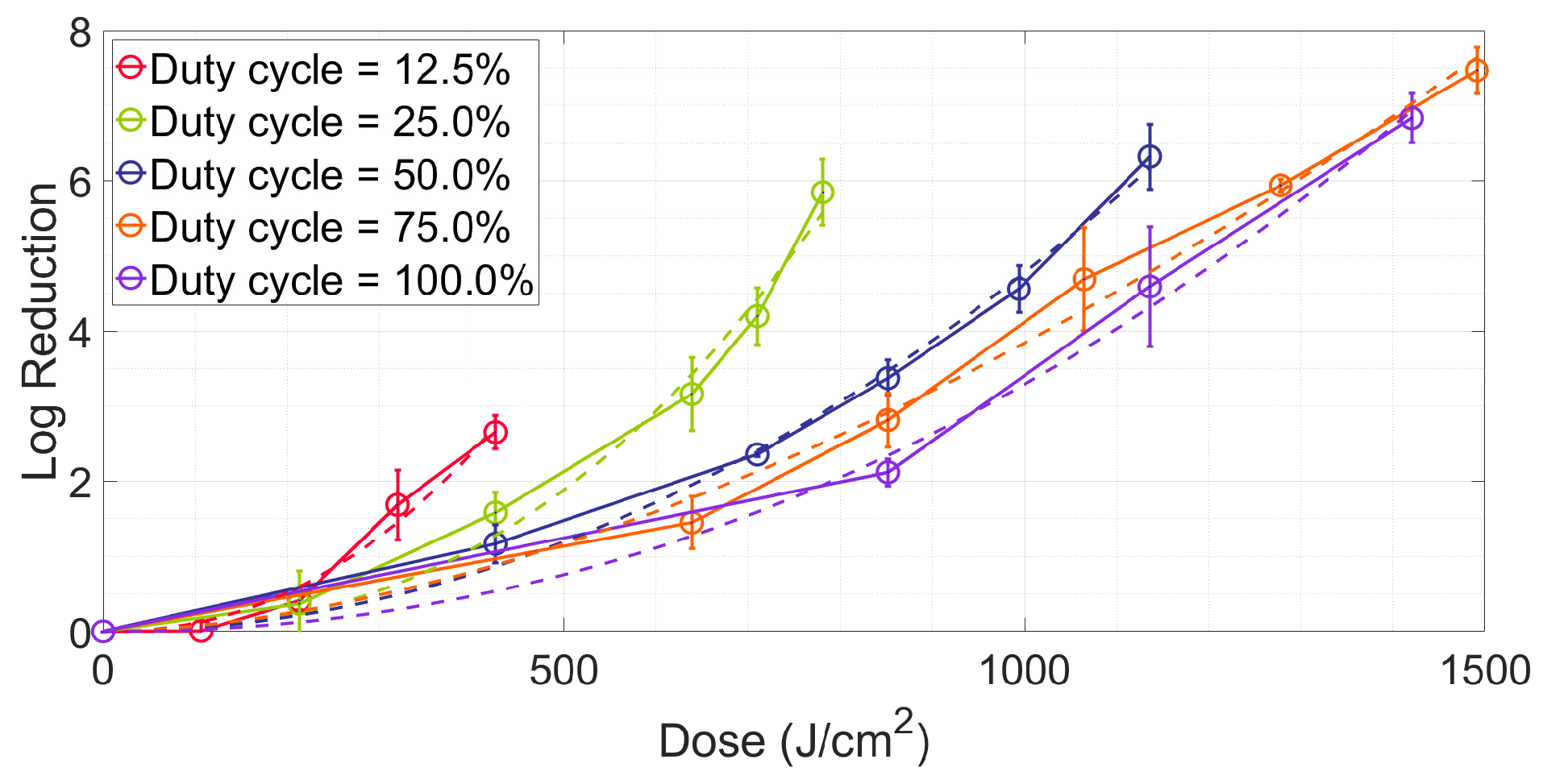
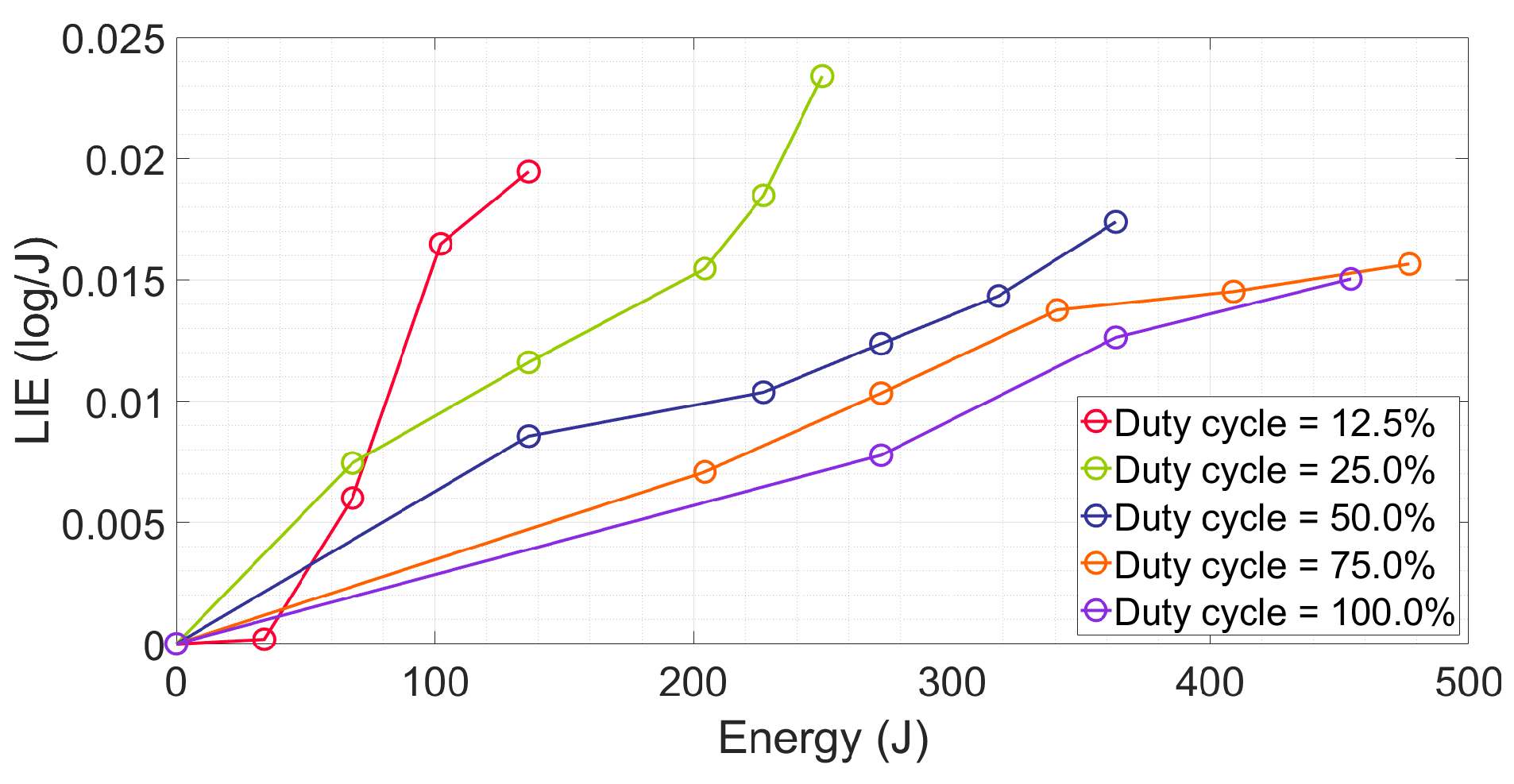
2.2. Investigating the Effects of the Duty Cycle on Energy Efficiency
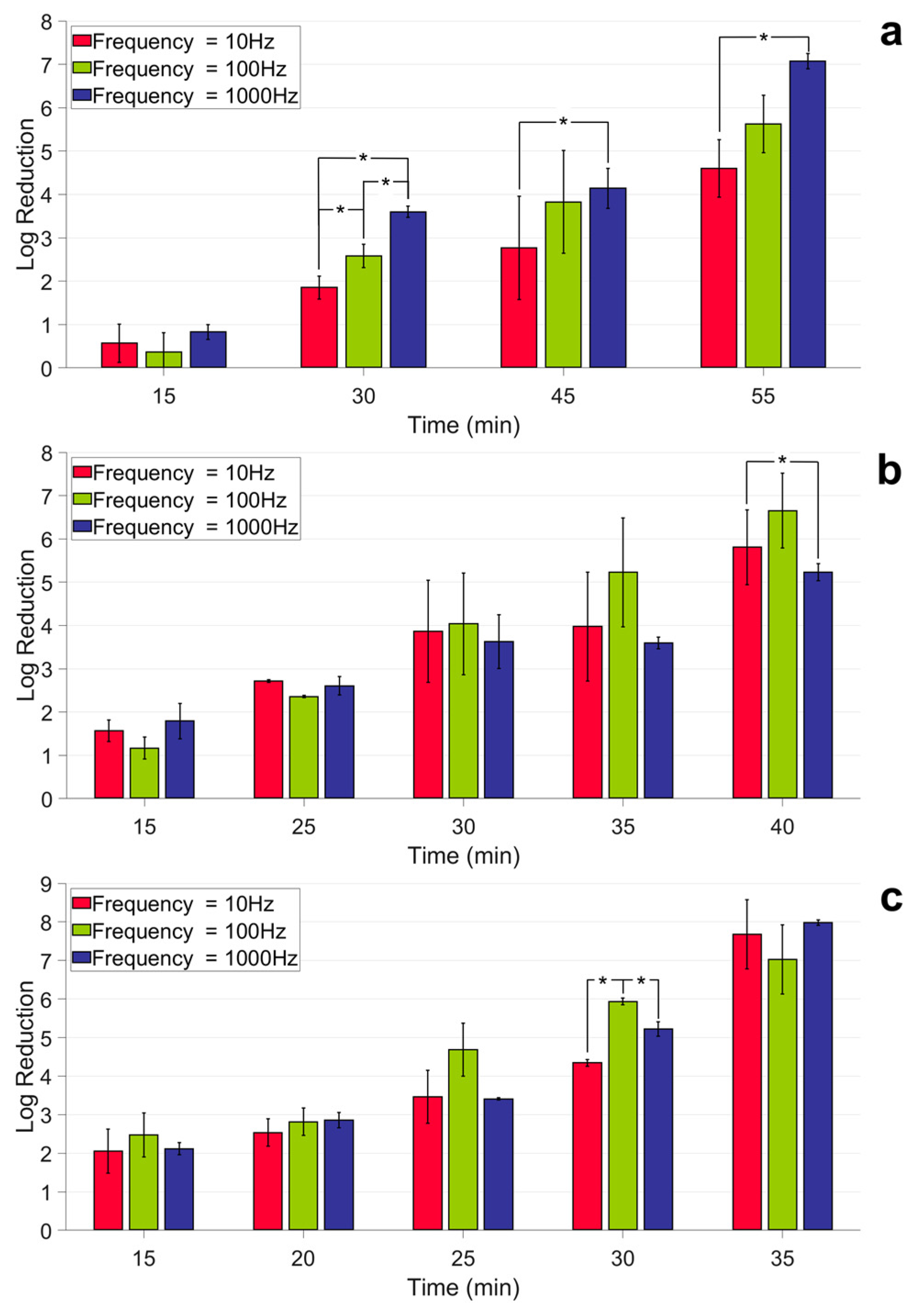
2.3. Investigating the Effects of Pulse Frequency on Inactivation
2.4. Fitting Irradiance-Time-Reduction Data Based on the 2-D Hom Model
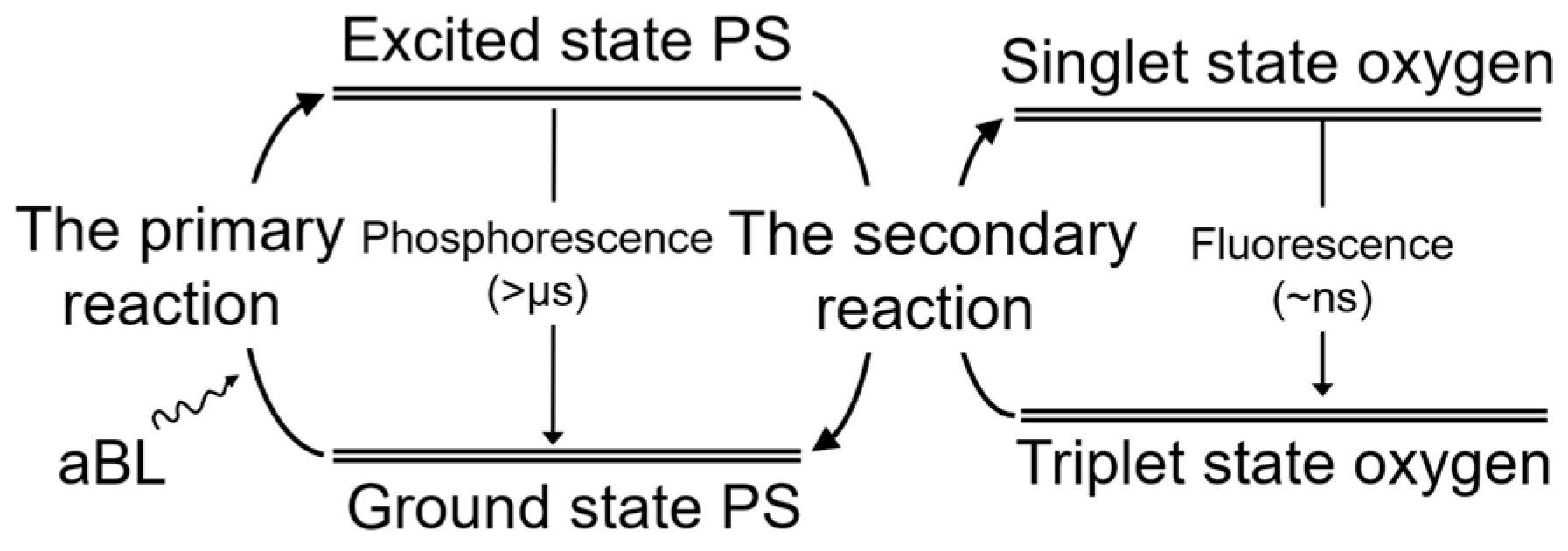
2.5. ROS Generation at the Same Energy
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains Preparation
4.2. Experimental Setup
4.2.1. LED Treatment Setup
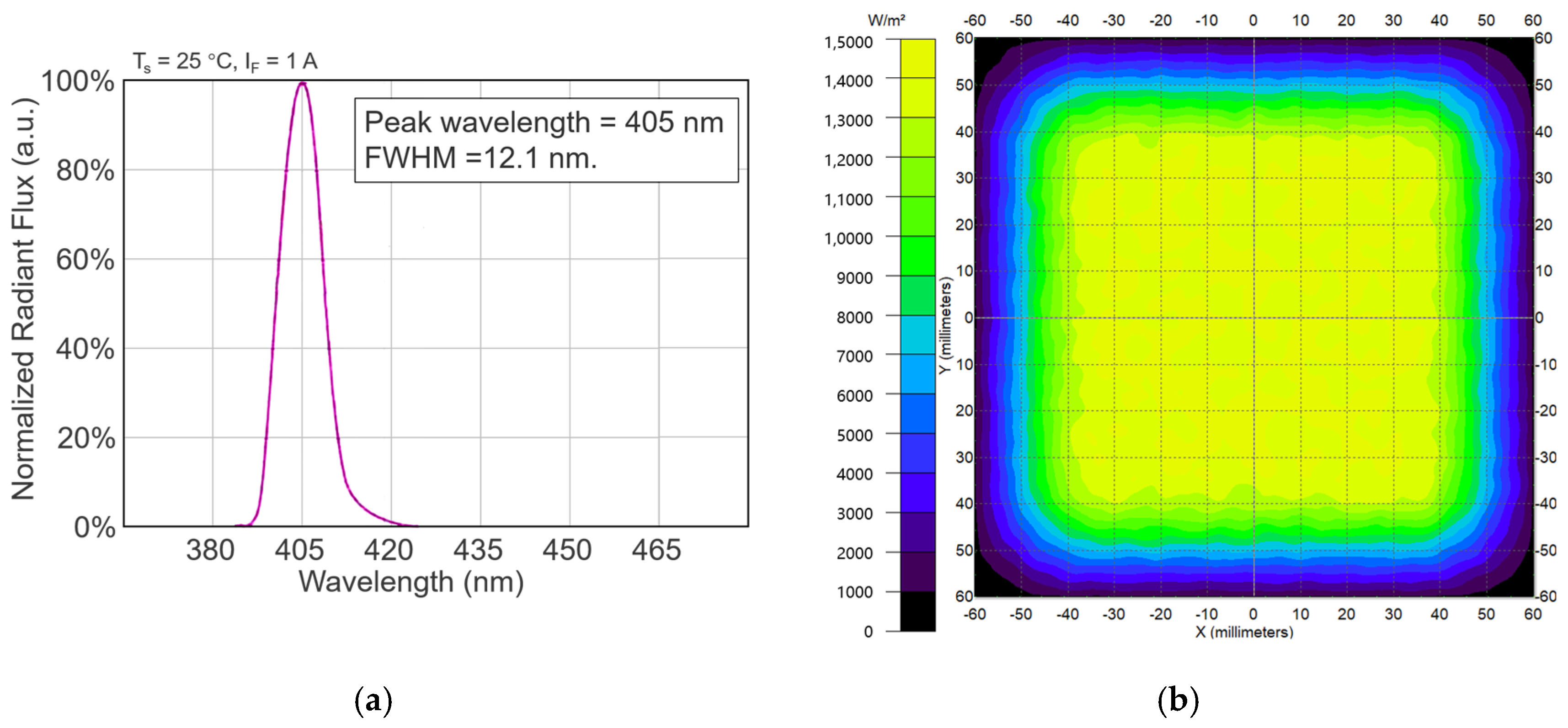
4.2.2. Optical Parameters of the Light Source
4.3. Definition of Variables
4.3.1. Inactivation Quantification
4.3.2. Duty Cycle and Pulse Frequency
4.3.3. Irradiation Dose, Irradiance, and Time
4.3.4. Energy Efficiency
4.3.5. Dose Conservation Ratio
4.3.6. Model for Bacterial Inactivation Kinetics
4.4. ROS Assay
4.5. Bacterial Enumeration
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sabino, C.P.; Ball, A.R.; Baptista, M.S.; Dai, T.; Hamblin, M.R.; Ribeiro, M.S.; Santos, A.L.; Sellera, F.P.; Tegos, G.P.; Wainwright, M. Light-Based Technologies for Management of COVID-19 Pandemic Crisis. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2020, 212, 111999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enwemeka, C.S.; Bumah, V.V.; Masson-Meyers, D.S. Light as a Potential Treatment for Pandemic Coronavirus Infections: A Perspective. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2020, 207, 111891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heßling, M.; Hönes, K.; Vatter, P.; Lingenfelder, C. Ultraviolet Irradiation Doses for Coronavirus Inactivation—Review and Analysis of Coronavirus Photoinactivation Studies. GMS Hyg. Infect. Control 2020, 15, Doc08. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maclean, M.; MacGregor, S.J.; Anderson, J.G.; Woolsey, G. Inactivation of Bacterial Pathogens Following Exposure to Light from a 405-Nanometer Light-Emitting Diode Array. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 1932–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardell, E.A.; Bucher, S.J.; Brickner, P.W.; Wang, C.; Vincent, R.L.; Becan-McBride, K.; James, M.A.; Michael, M.; Wright, J.D. Safety of Upper-Room Ultraviolet Germicidal Air Disinfection for Room Occupants: Results from the Tuberculosis Ultraviolet Shelter Study. Public Health Rep. 2008, 123, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maclean, M.; McKenzie, K.; Anderson, J.G.; Gettinby, G.; MacGregor, S.J. 405 Nm Light Technology for the Inactivation of Pathogens and Its Potential Role for Environmental Disinfection and Infection Control. J. Hosp. Infect. 2014, 88, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plavskii, V.; Mikulich, A.; Tretyakova, A.; Leusenka, I.; Plavskaya, L.; Kazyuchits, O.A.; Dobysh, I.I.; Krasnenkova, T.P. Porphyrins and Flavins as Endogenous Acceptors of Optical Radiation of Blue Spectral Region Determining Photoinactivation of Microbial Cells. J. Photochem. Photobiology. B Biol. 2018, 183, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Murray, C.; Hamblin, M.; Hooper, D.; Dai, T. Antimicrobial Blue Light Inactivation of Pathogenic Microbes: State of the Art. Drug Resist. Updat. Rev. Comment. Antimicrob. Anticancer Chemother. 2017, 33–35, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-J.; Mikš-Krajnik, M.; Kumar, A.; Ghate, V.; Yuk, H.-G. Antibacterial Effect and Mechanism of High-Intensity 405 ± 5 nm Light Emitting Diode on Bacillus Cereus, Listeria Monocytogenes, and Staphylococcus Aureus under Refrigerated Condition. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2015, 153, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leanse, L.G.; Zeng, X.; Dai, T. Potentiated Antimicrobial Blue Light Killing of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus by Pyocyanin. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2021, 215, 112109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Dong, J.; Zhang, G. Analysis and Data-Based Modeling of the Photochemical Reaction Dynamics of the Induced Singlet Oxygen in Light Therapies. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 69, 3427–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Su, P.; Ma, J.; Gong, M.; Ma, L.; Wang, J. A Singlet State Oxygen Generation Model Based on the Monte Carlo Method of Visible Antibacterial Blue Light Inactivation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2023, 239, 112628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.-K.; Kang, D.-H. Efficacy of Light-Emitting Diodes Emitting 395, 405, 415, and 425 Nm Blue Light for Bacterial Inactivation and the Microbicidal Mechanism. Food Res. Int. 2021, 141, 110105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoenes, K.; Bauer, R.; Meurle, T.; Spellerberg, B.; Hessling, M. Inactivation Effect of Violet and Blue Light on ESKAPE Pathogens and Closely Related Non-Pathogenic Bacterial Species—A Promising Tool Against Antibiotic-Sensitive and Antibiotic-Resistant Microorganisms. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 612367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollmerhausen, T.L.; Conneely, A.; Bennett, C.; Wagner, V.E.; Victor, J.C.; O’Byrne, C.P. Visible and UVA Light as a Potential Means of Preventing Escherichia Coli Biofilm Formation in Urine and on Materials Used in Urethral Catheters. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2017, 170, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marugán, J.; van Grieken, R.; Sordo, C.; Cruz, C. Kinetics of the Photocatalytic Disinfection of Escherichia Coli Suspensions. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2008, 82, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabino, C.P.; Wainwright, M.; dos Anjos, C.; Sellera, F.P.; Baptista, M.S.; Lincopan, N.; Ribeiro, M.S. Inactivation Kinetics and Lethal Dose Analysis of Antimicrobial Blue Light and Photodynamic Therapy. Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 2019, 28, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bache, S.E.; Maclean, M.; MacGregor, S.J.; Anderson, J.G.; Gettinby, G.; Coia, J.E.; Taggart, I. Clinical Studies of the High-Intensity Narrow-Spectrum Light Environmental Decontamination System (HINS-Light EDS), for Continuous Disinfection in the Burn Unit Inpatient and Outpatient Settings. Burns 2012, 38, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bache, S.E.; Maclean, M.; Gettinby, G.; Anderson, J.G.; MacGregor, S.J.; Taggart, I. Universal Decontamination of Hospital Surfaces in an Occupied Inpatient Room with a Continuous 405 Nm Light Source. J. Hosp. Infect. 2018, 98, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Chen, J.; Amin, R.; Lu, M.; Bhayana, B.; Zhao, J.; Murray, C.; Hamblin, M.; Hooper, D.; et al. Antimicrobial Blue Light Inactivation of Gram-Negative Pathogens in Biofilms: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 213, 1380–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Gupta, A.; Huang, Y.; Murray, C.K.; Vrahas, M.S.; Sherwood, M.E.; Baer, D.G.; Hamblin, M.R.; Dai, T. Antimicrobial Blue Light Therapy for Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter Baumannii Infection in a Mouse Burn Model: Implications for Prophylaxis and Treatment of Combat-Related Wound Infections. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 209, 1963–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ferrer-Espada, R.; Baglo, Y.; Gu, Y.; Dai, T. Antimicrobial Blue Light Inactivation of Neisseria Gonorrhoeae: Roles of Wavelength, Endogenous Photosensitizer, Oxygen, and Reactive Oxygen Species. Lasers Surg. Med. 2019, 51, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, C.F.; Tomb, R.M.; Ralston, H.J.; Armstrong, J.; Anderson, J.G.; MacGregor, S.J.; Atreya, C.D.; Maclean, M. Violet-blue 405-nm Light-based Photoinactivation for Pathogen Reduction of Human Plasma Provides Broad Antibacterial Efficacy without Visible Degradation of Plasma Proteins. Photochem. Photobiol. 2022, 98, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Anjos, C.; Sellera, F.P.; de Freitas, L.M.; Gargano, R.G.; Telles, E.O.; Freitas, R.O.; Baptista, M.S.; Ribeiro, M.S.; Lincopan, N.; Pogliani, F.C.; et al. Inactivation of Milk-Borne Pathogens by Blue Light Exposure. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Kim, M.-J.; Yuk, H.-G. Influence of 405 Nm Light-Emitting Diode Illumination on the Inactivation of Listeria Monocytogenes and Salmonella Spp. on Ready-to-Eat Fresh Salmon Surface at Chilling Storage for 8 h and Their Susceptibility to Simulated Gastric Fluid. Food Control 2018, 88, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghate, V.; Kumar, A.; Kim, M.-J.; Bang, W.-S.; Zhou, W.; Yuk, H.-G. Effect of 460 Nm Light Emitting Diode Illumination on Survival of Salmonella Spp. on Fresh-Cut Pineapples at Different Irradiances and Temperatures. J. Food Eng. 2017, 196, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-J.; Tang, C.H.; Bang, W.S.; Yuk, H.-G. Antibacterial Effect of 405 ± 5 Nm Light Emitting Diode Illumination against Escherichia Coli O157:H7, Listeria Monocytogenes, and Salmonella on the Surface of Fresh-Cut Mango and Its Influence on Fruit Quality. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 244, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-J.; Bang, W.S.; Yuk, H.-G. 405 ± 5 Nm Light Emitting Diode Illumination Causes Photodynamic Inactivation of Salmonella spp. on Fresh-Cut Papaya without Deterioration. Food Microbiol. 2017, 62, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-J.; Adeline Ng, B.X.; Zwe, Y.H.; Yuk, H.-G. Photodynamic Inactivation of Salmonella Enterica Enteritidis by 405 ± 5-Nm Light-Emitting Diode and Its Application to Control Salmonellosis on Cooked Chicken. Food Control 2017, 82, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.; Gänzle, M.; Roopesh, M.S. Antimicrobial Activity and Drying Potential of High Intensity Blue Light Pulses (455 Nm) Emitted from LEDs. Food Res. Int. 2021, 148, 110601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, K.; Maclean, M.; Timoshkin, I.V.; MacGregor, S.J.; Anderson, J.G. Enhanced Inactivation of Escherichia coli and Listeria monocytogenes by Exposure to 405nm Light under Sub-Lethal Temperature, Salt and Acid Stress Conditions. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 170, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leanse, L.G.; Goh, X.S.; Cheng, J.-X.; Hooper, D.C.; Dai, T. Dual-Wavelength Photo-Killing of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e134343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yawale, P.R.; Wagh, V.G.; Shaligram, A.D. Impact of Current Controlled Dimming on Spectral Characteristics of High Power LEDs. Opt. Laser Technol. 2019, 115, 289–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Mohseni, M.; Taghipour, F. Application of Ultraviolet Light-Emitting Diodes (UV-LEDs) for Water Disinfection: A Review. Water Res. 2016, 94, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, K.-C.; Wang, S.-C.; Liu, Y.-H. Dimming Techniques Focusing on the Improvement in Luminous Efficiency for High-Brightness LEDs. Electronics 2021, 10, 2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, J.B.; Maclean, M.; Given, M.J.; Wilson, M.P.; Judd, M.D.; Timoshkin, I.V.; MacGregor, S.J. Efficacy of Pulsed 405-Nm Light-Emitting Diodes for Antimicrobial Photodynamic Inactivation: Effects of Intensity, Frequency, and Duty Cycle. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2017, 35, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bumah, V.V.; Masson-Meyers, D.S.; Enwemeka, C.S. Pulsed 450 Nm Blue Light Suppresses MRSA and Propionibacterium Acnes in Planktonic Cultures and Bacterial Biofilms. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2020, 202, 111702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson-Meyers, D.S.; Bumah, V.V.; Castel, C.; Castel, D.; Enwemeka, C.S. Pulsed 450 Nm Blue Light Significantly Inactivates Propionibacterium Acnes More than Continuous Wave Blue Light. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2020, 202, 111719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvedova, A.; Kocis-Koval, M.; Valik, L. Effect of Salt and Temperature on the Growth of Escherichia Coli PSII. Acta Aliment. 2021, 50, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lui, G.Y.; Roser, D.; Corkish, R.; Ashbolt, N.J.; Stuetz, R. Point-of-Use Water Disinfection Using Ultraviolet and Visible Light-Emitting Diodes. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 553, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Ghate, V.; Kim, M.-J.; Zhou, W.; Khoo, G.H.; Yuk, H.-G. Kinetics of Bacterial Inactivation by 405nm and 520nm Light Emitting Diodes and the Role of Endogenous Coproporphyrin on Bacterial Susceptibility. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2015, 149, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leanse, L.G.; Harrington, O.D.; Fang, Y.; Ahmed, I.; Goh, X.S.; Dai, T. Evaluating the Potential for Resistance Development to Antimicrobial Blue Light (at 405 Nm) in Gram-Negative Bacteria: In Vitro and in Vivo Studies. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Anjos, C.; Sabino, C.P.; Bueris, V.; Fernandes, M.R.; Pogliani, F.C.; Lincopan, N.; Sellera, F.P. Antimicrobial Blue Light Inactivation of International Clones of Multidrug-Resistant Escherichia coli ST10, ST131 and ST648. Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 2019, 27, 51–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, X.-Y.; Lin, Y.-L.; Xu, B.; Cao, T.-C.; Tang, Y.-L.; Pan, Y.; Gao, Z.-C.; Gao, N.-Y. Enhanced Inactivation of E. coli by Pulsed UV-LED Irradiation during Water Disinfection. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholtes, K.; Linden, K.G. Pulsed and Continuous Light UV LED: Microbial Inactivation, Electrical, and Time Efficiency. Water Res. 2019, 165, 114965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamblin, M.R.; Abrahamse, H. Oxygen-Independent Antimicrobial Photoinactivation: Type III Photochemical Mechanism? Antibiotics 2020, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, M.S.; Cadet, J.; Di Mascio, P.; Ghogare, A.A.; Greer, A.; Hamblin, M.R.; Lorente, C.; Nunez, S.C.; Ribeiro, M.S.; Thomas, A.H.; et al. Type I and Type II Photosensitized Oxidation Reactions: Guidelines and Mechanistic Pathways. Photochem. Photobiol. 2017, 93, 912–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.M.; Ghogare, A.A.; Greer, A.; Zhu, T.C. On the in Vivo Photochemical Rate Parameters for PDT Reactive Oxygen Species Modeling. Phys. Med. Biol. 2017, 62, R1–R48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Farrell, T.J.; Patterson, M.S. A Dynamic Model for ALA-PDT of Skin: Simulation of Temporal and Spatial Distributions of Ground-State Oxygen, Photosensitizer and Singlet Oxygen. Phys. Med. Biol. 2010, 55, 5913–5932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Dong, J.; Yin, H.; Zhang, G. Blue Light Therapy to Treat Candida Vaginitis with Comparisons of Three Wavelengths: An in Vitro Study. Lasers Med. Sci. 2020, 35, 1329–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadenas, E. Biochemistry of oxygen toxicity. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1989, 58, 79–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, H.; Uefuji, H.; Sakihama, Y. Bleaching of the Red Anthocyanin Induced by Superoxide Radical. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1996, 332, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Lin, S.; Qin, H.; Jiang, H.; Liu, M. The Parameters Affecting Antimicrobial Efficiency of Antimicrobial Blue Light Therapy: A Review and Prospect. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsen, K.; Tsen, S.; Chang, C.; Hung, C.; Wu, T.; Kiang, J. Inactivation of Viruses by Coherent Excitations with a Low Power Visible Femtosecond Laser. Virol. J. 2007, 4, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Hirota, K.; Yumoto, H.; Matsuo, T.; Miyake, Y.; Ichikawa, T. Enhanced Germicidal Effects of Pulsed UV-LED Irradiation on Biofilms: Germicidal Effects of Pulsed UV-LED. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 109, 2183–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wengraitis, S.; McCubbin, P.; Wade, M.M.; Biggs, T.D.; Hall, S.; Williams, L.I.; Zulich, A.W. Pulsed UV-C Disinfection of Escherichia Coli With Light-Emitting Diodes, Emitted at Various Repetition Rates and Duty Cycles. Photochem. Photobiol. 2013, 89, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bialka, K.L.; Demirci, A.; Puri, V.M. Modeling the Inactivation of Escherichia Coli O157:H7 and Salmonella Enterica on Raspberries and Strawberries Resulting from Exposure to Ozone or Pulsed UV-Light. J. Food Eng. 2008, 85, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

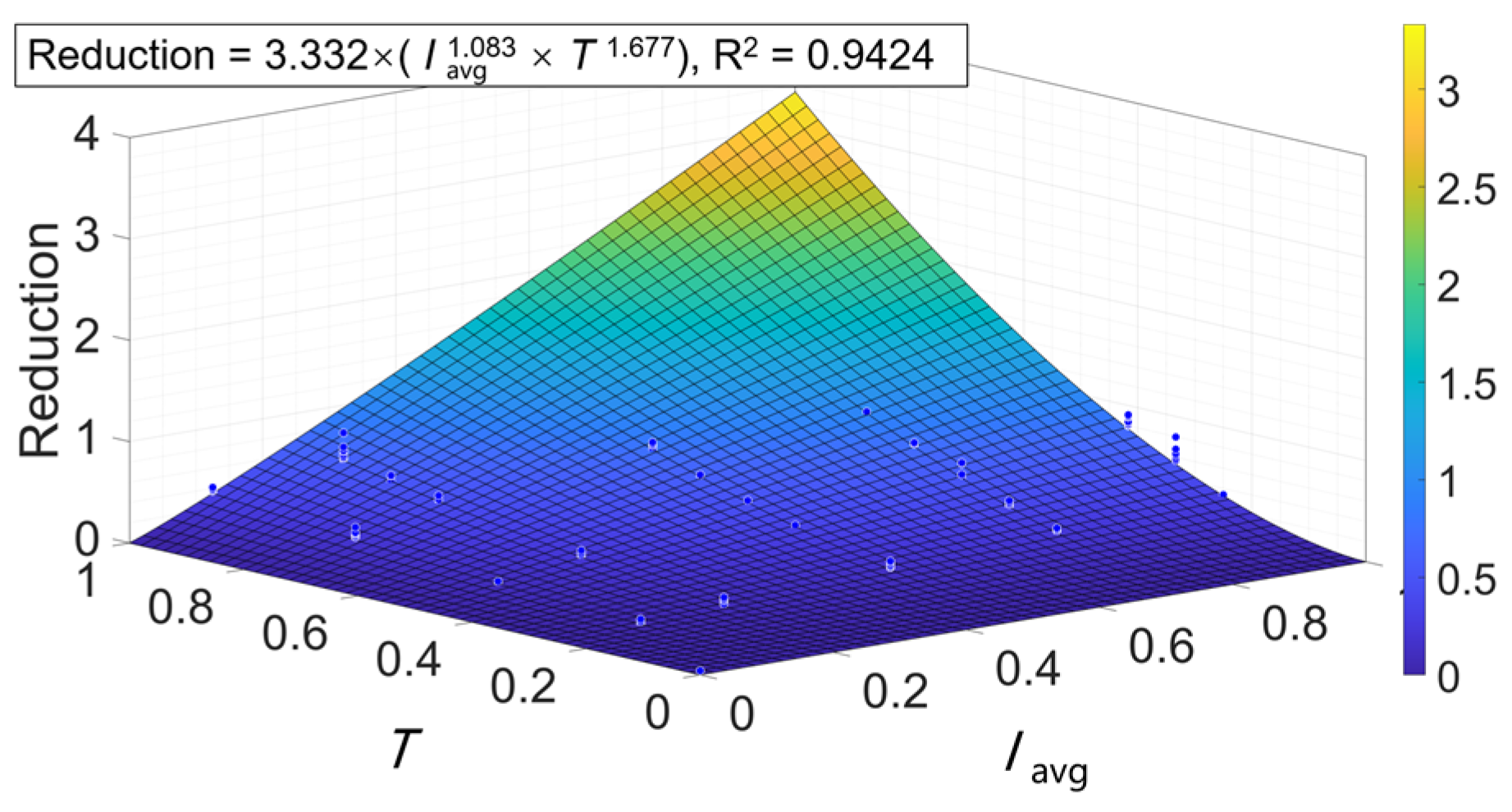



| Irradiance (mW/cm2) | R2 | RMSE | T3d (min) | T5d (min) | D3d (J/cm2) | D5d (J/cm2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12.5% | 119.88 | 4.47 × 10−6 | 2.20 | 0.9800 | 0.1920 | 61.88 | 78.05 | 445.06 | 561.38 |
| 25.0% | 239.76 | 5.09 × 10−7 | 2.43 | 0.9885 | 0.2746 | 42.05 | 51.87 | 604.88 | 746.12 |
| 50.0% | 479.51 | 4.77 × 10−6 | 2.00 | 0.9943 | 0.1946 | 27.56 | 35.58 | 792.88 | 1023.61 |
| 75.0% | 719.27 | 2.64 × 10−5 | 1.72 | 0.9920 | 0.2826 | 20.07 | 27.01 | 866.25 | 1165.60 |
| 100.0% | 959.02 | 1.40 × 10−6 | 2.12 | 0.9949 | 0.2605 | 16.65 | 21.19 | 958.33 | 1219.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Su, P.; Ma, J.; Tan, Y.; Gong, M.; Ma, L. An Approach to Improve Energy Efficiency during Antimicrobial Blue Light Inactivation: Application of Pulse-Width Modulation Dimming to Balance Irradiance and Irradiation Time. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1431. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12091431
Zhang W, Su P, Ma J, Tan Y, Gong M, Ma L. An Approach to Improve Energy Efficiency during Antimicrobial Blue Light Inactivation: Application of Pulse-Width Modulation Dimming to Balance Irradiance and Irradiation Time. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(9):1431. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12091431
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Wanqing, Ping Su, Jianshe Ma, Ying Tan, Mali Gong, and Liya Ma. 2023. "An Approach to Improve Energy Efficiency during Antimicrobial Blue Light Inactivation: Application of Pulse-Width Modulation Dimming to Balance Irradiance and Irradiation Time" Antibiotics 12, no. 9: 1431. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12091431
APA StyleZhang, W., Su, P., Ma, J., Tan, Y., Gong, M., & Ma, L. (2023). An Approach to Improve Energy Efficiency during Antimicrobial Blue Light Inactivation: Application of Pulse-Width Modulation Dimming to Balance Irradiance and Irradiation Time. Antibiotics, 12(9), 1431. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12091431







