Bibliometric Analysis of Global Research Output on Antimicrobial Resistance among Pneumonia Pathogens (2013–2023)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
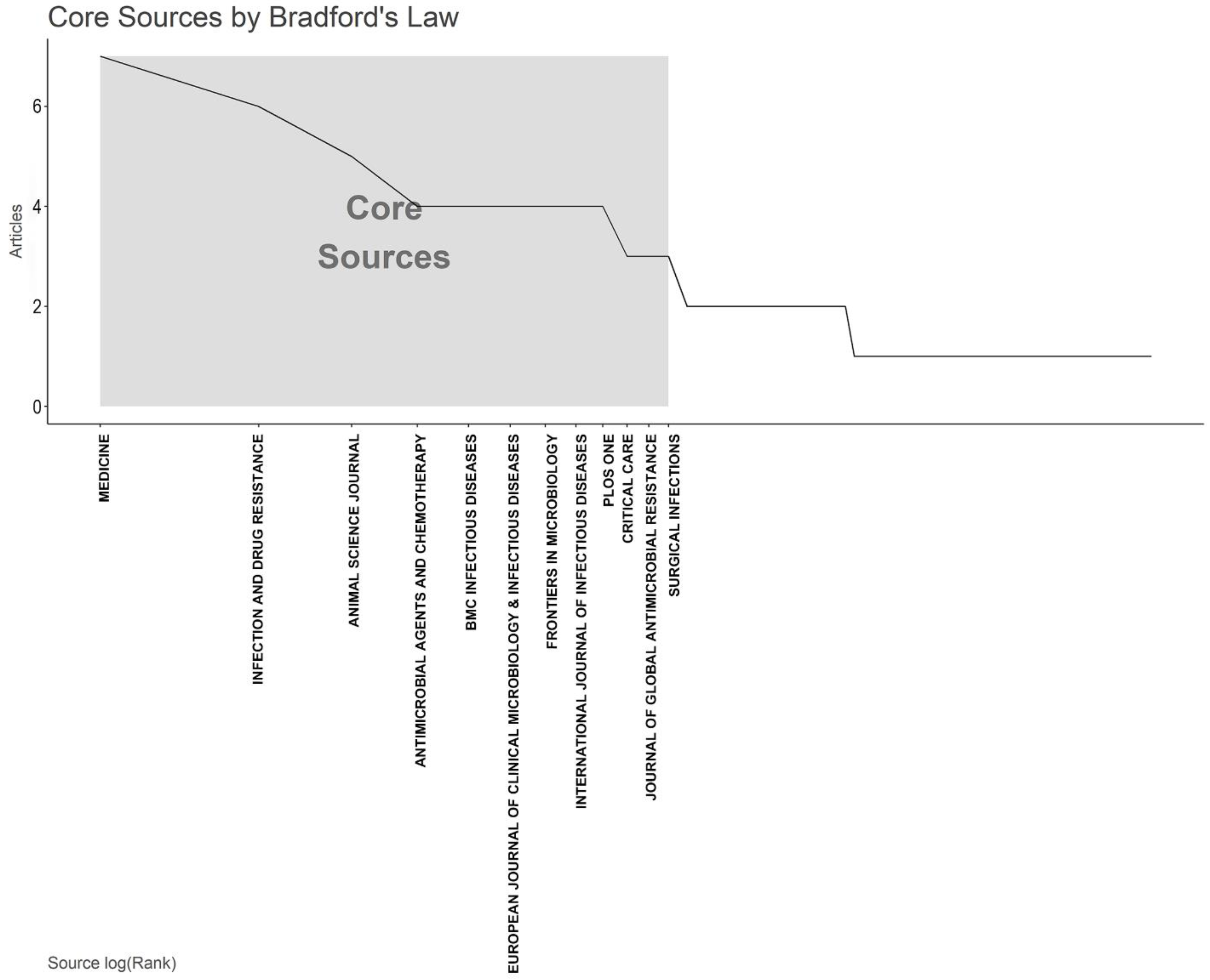
2.1. Summary of the Papers
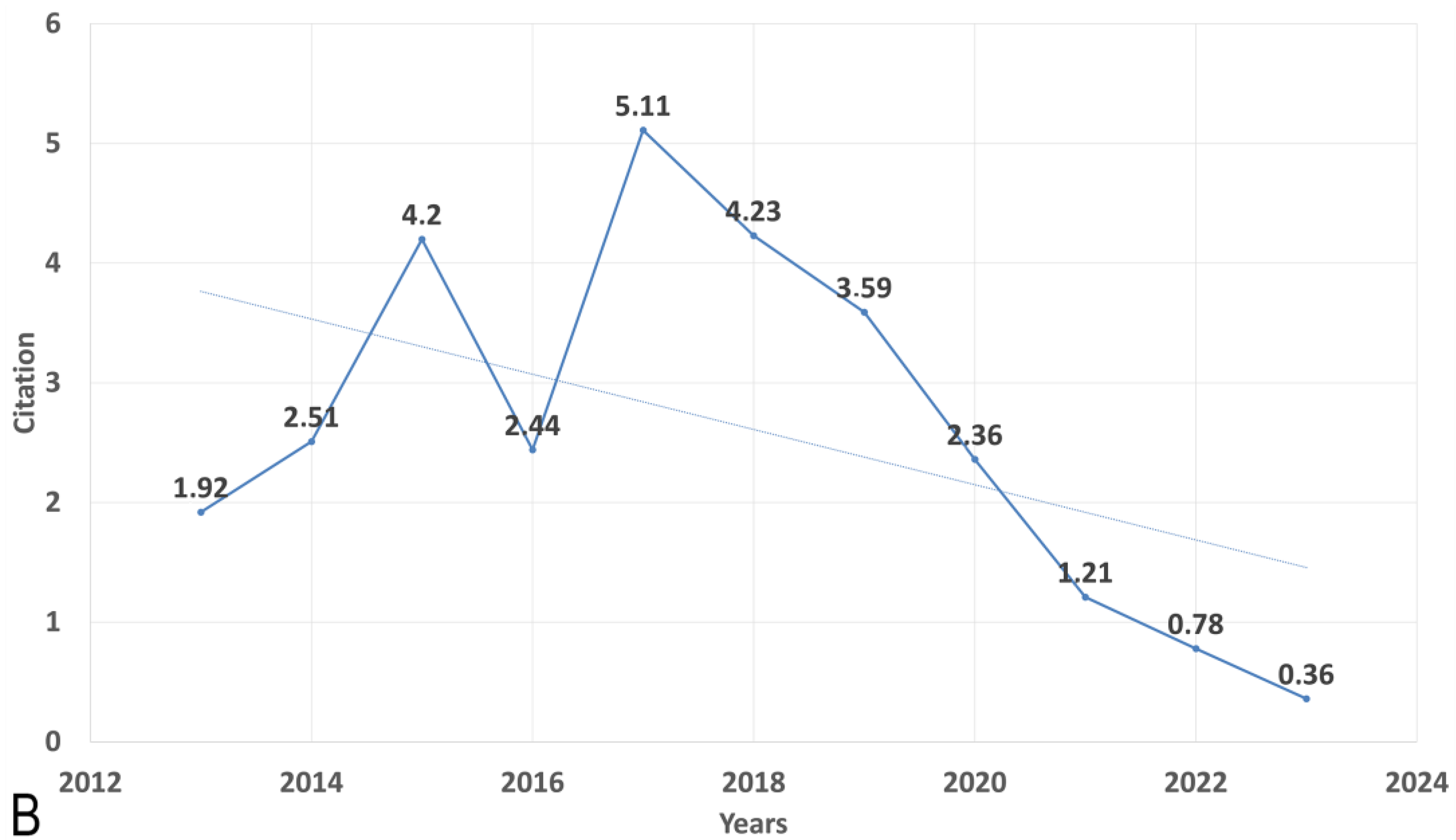
2.2. Trend of Publication and Citation
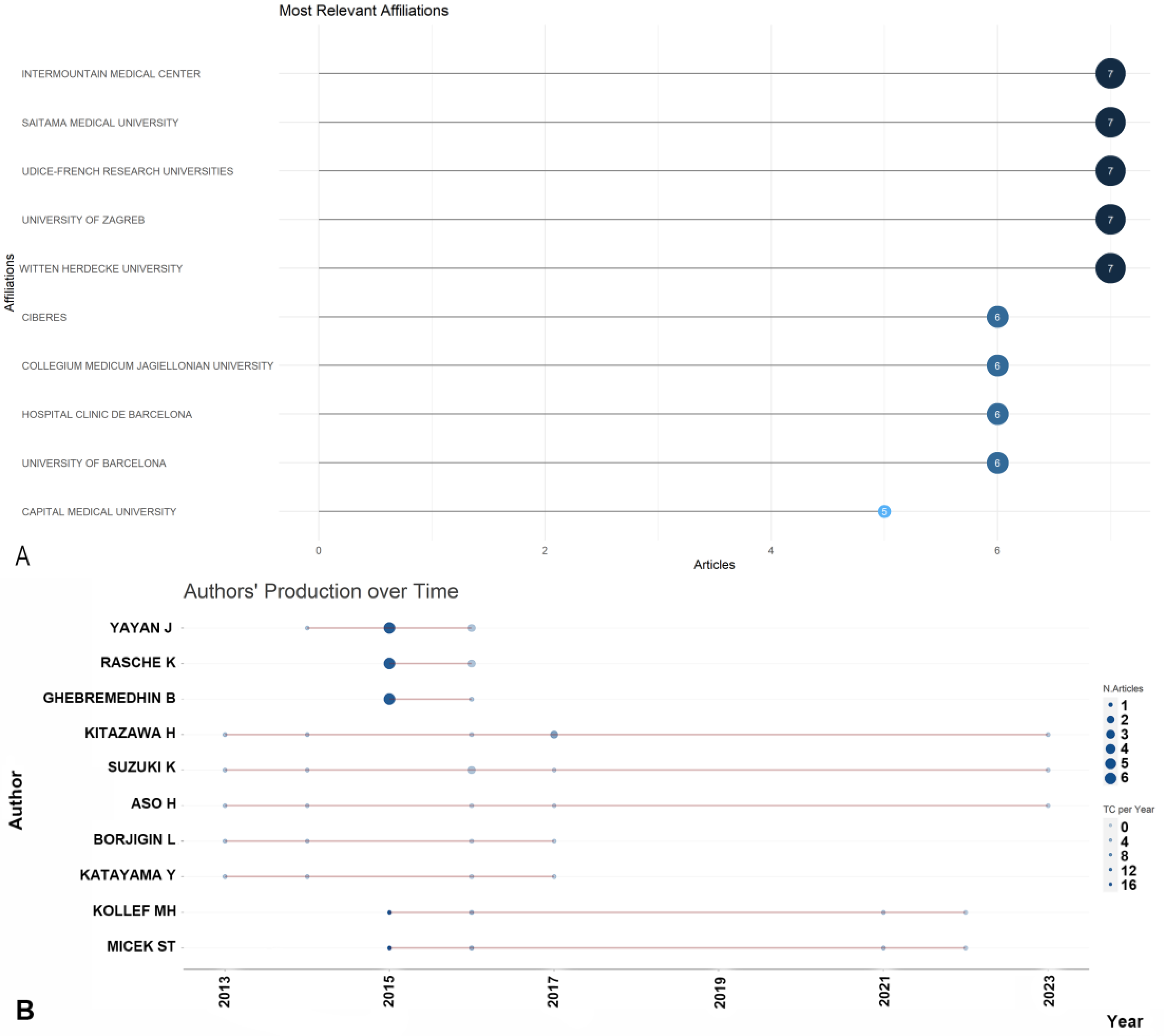
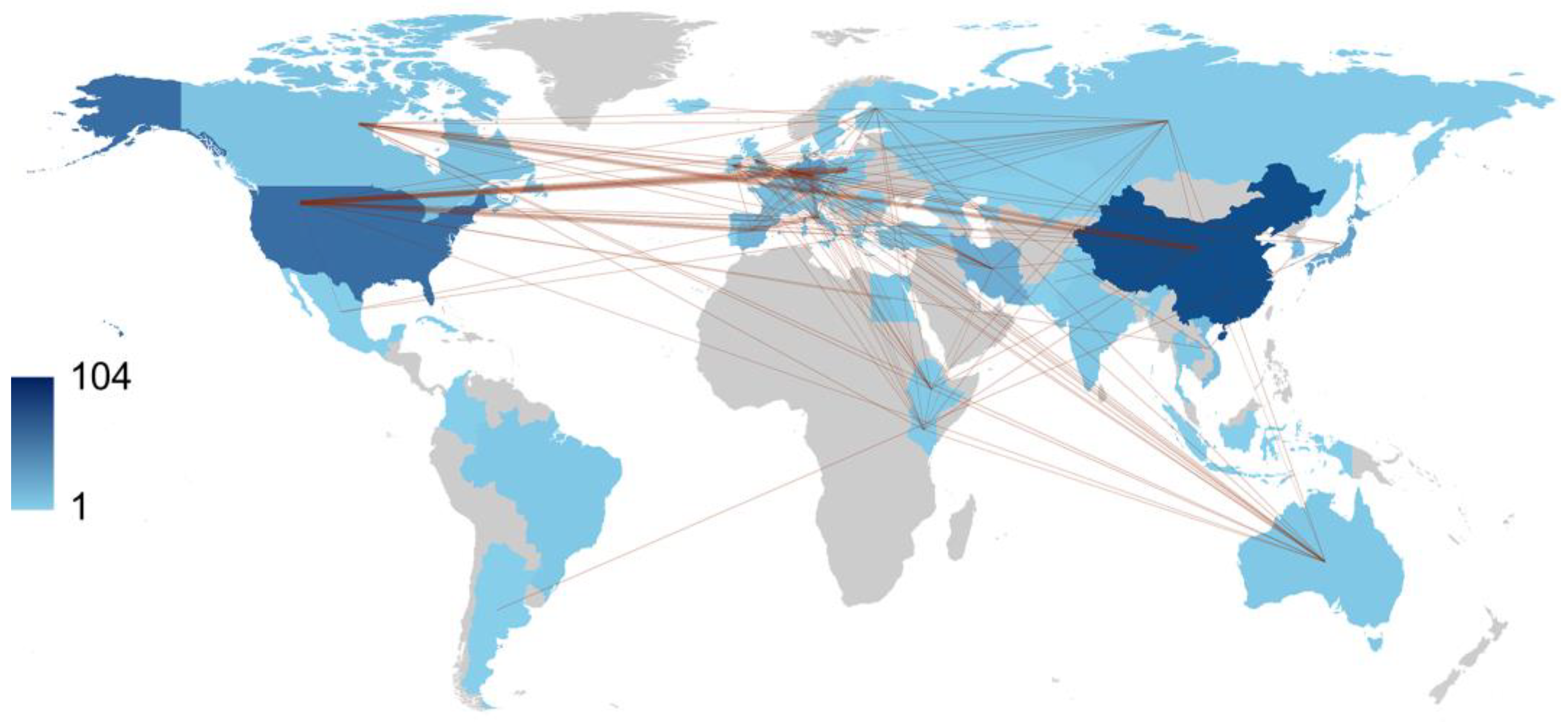
2.3. Most Productive Authors, Institutions, Countries and Their Collaboration Network
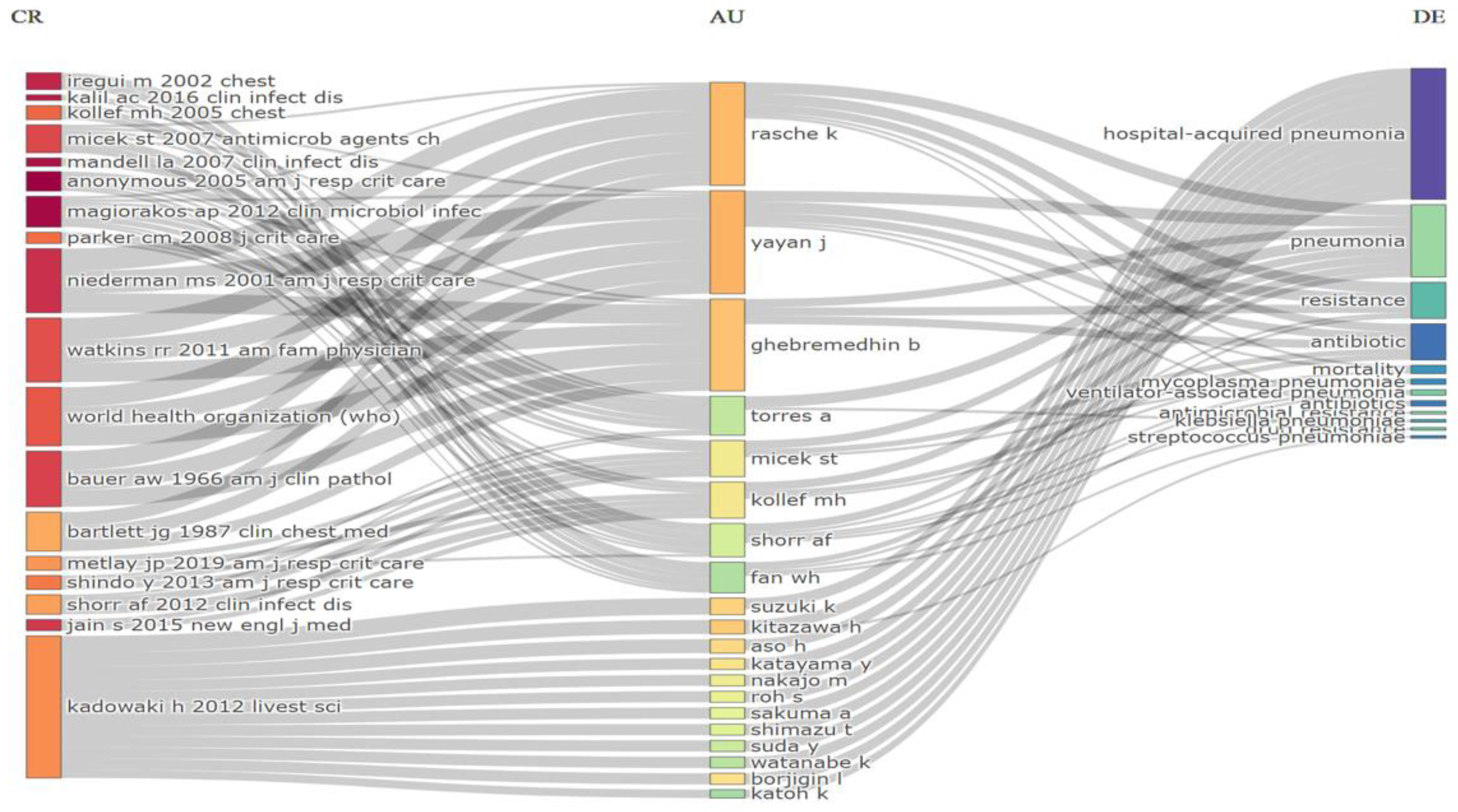
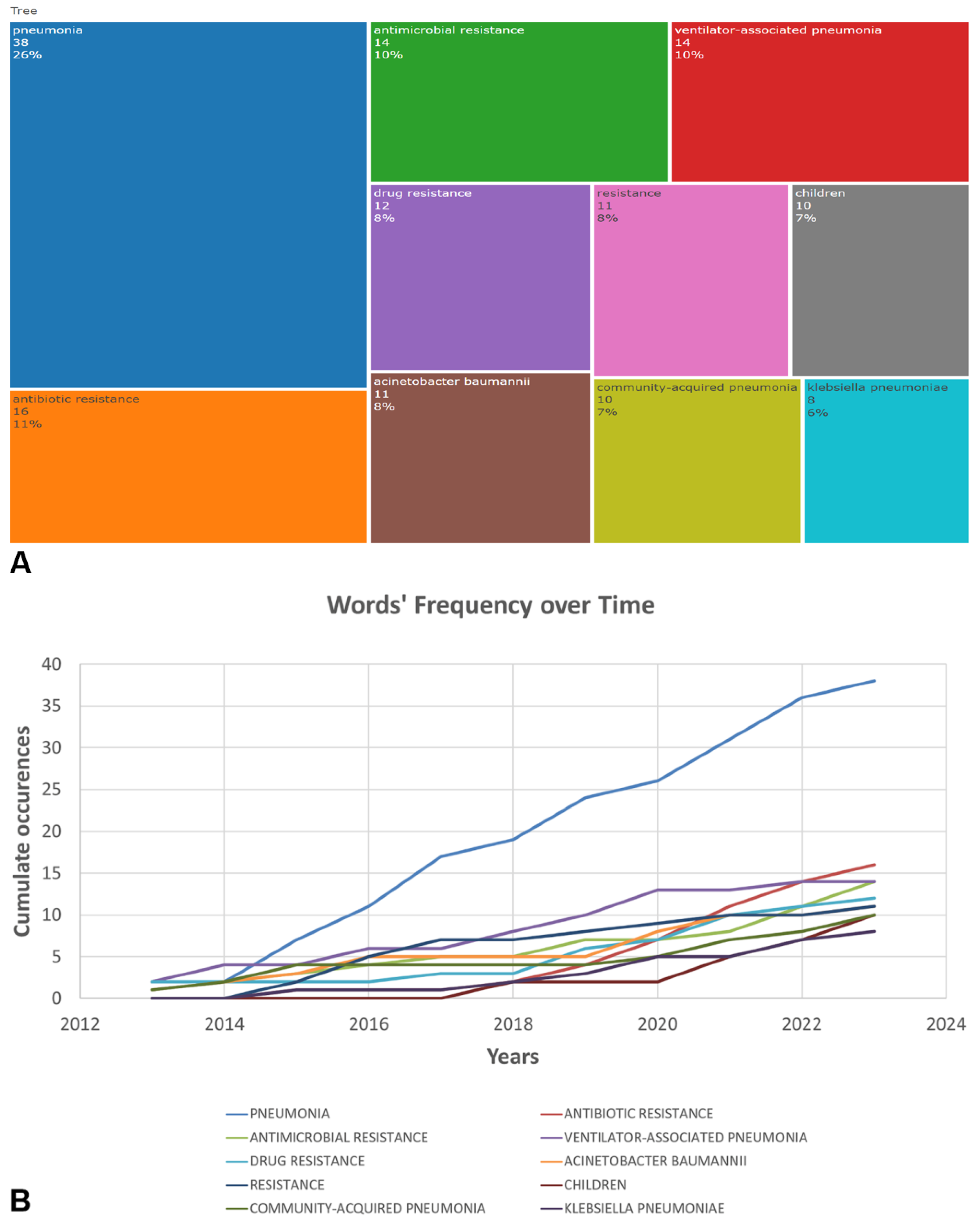
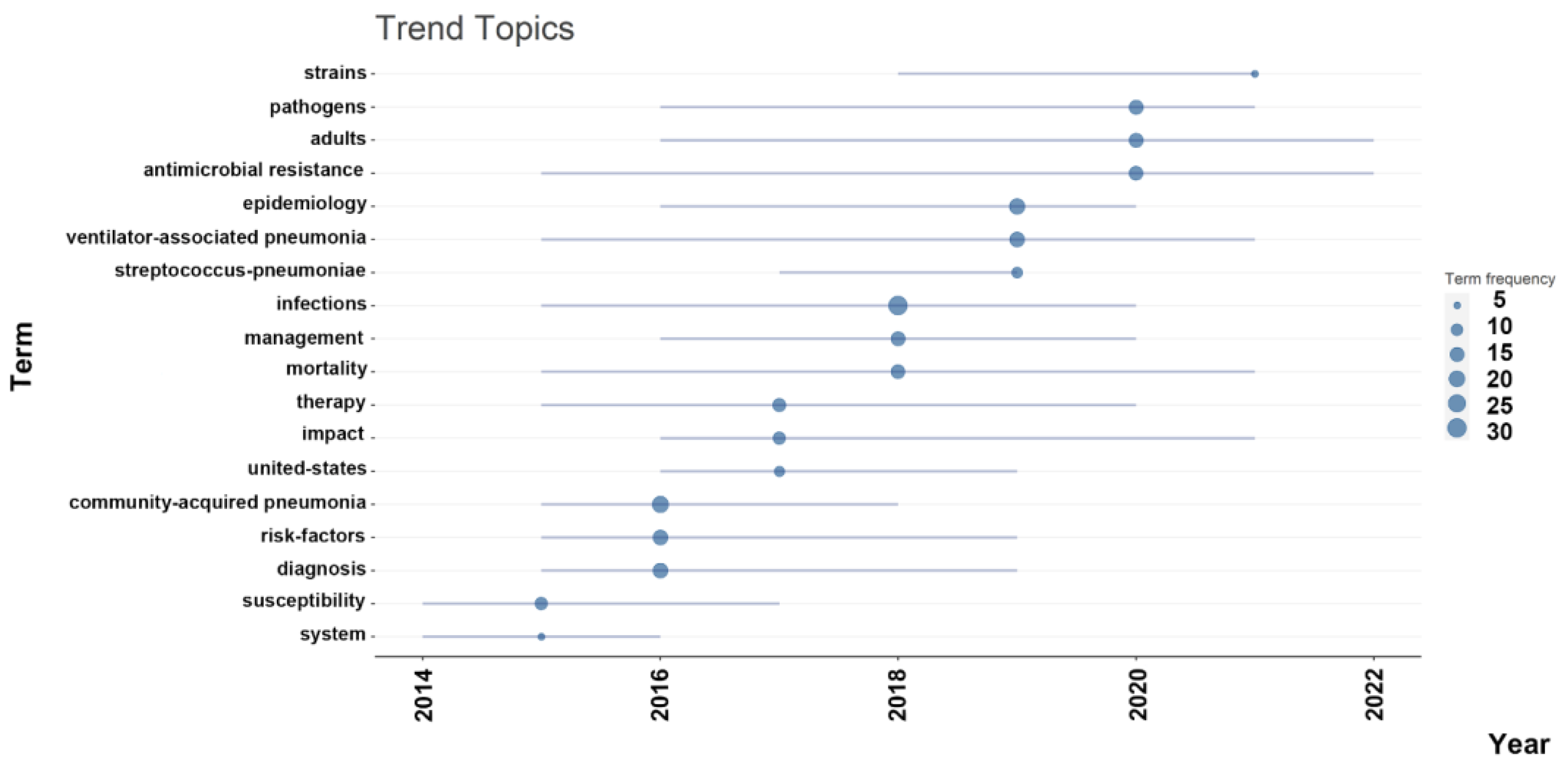
2.4. Co-Occurrence, Hotspots and Emerging Keywords
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
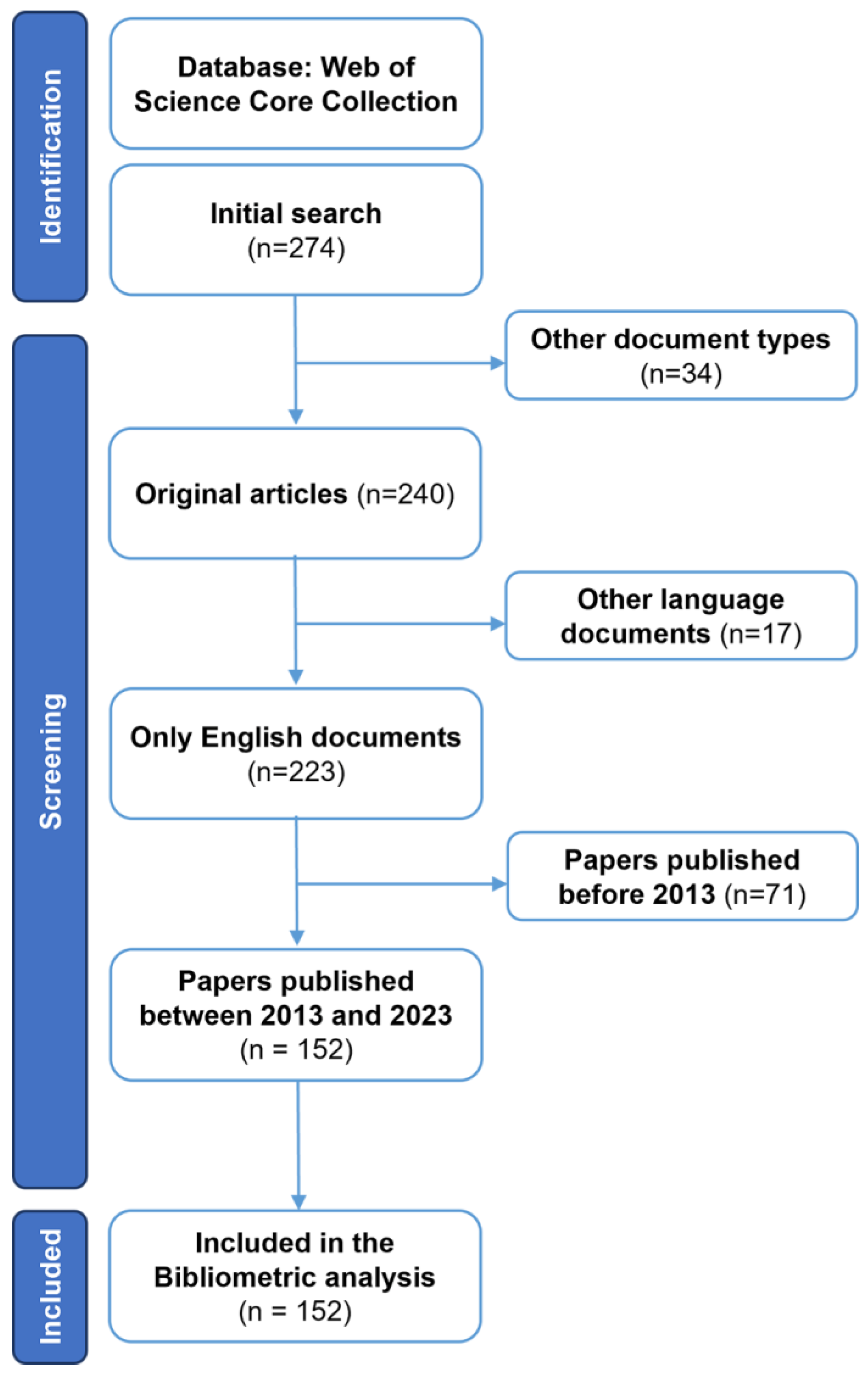
4.1. Search Results
4.2. Performance Analysis
4.3. Identification of Leading Institutions, Sources, Authors, and Collaborating Countries
4.4. Keywords Frequencies Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chokshi, A.; Sifri, Z.; Cennimo, D.; Horng, H. Global Contributors to Antibiotic Resistance. J. Glob. Infect. Dis. 2019, 11, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulingam, T.; Parumasivam, T.; Gazzali, A.M.; Sulaiman, A.M.; Chee, J.Y.; Lakshmanan, M.; Chin, C.F.; Sudesh, K. Antimicrobial resistance: Prevalence, economic burden, mechanisms of resistance and strategies to overcome. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 170, 106103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, M.A.A.; Rahman, S.; Cohall, D.; Bharatha, A.; Singh, K.; Haque, M.; Gittens-St Hilaire, M. Antimicrobial stewardship: Fighting antimicrobial resistance and protecting global public health. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 4713–4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjalkar, J.; Chandy, S.J. India’s National Action Plan for antimicrobial resistance—An overview of the context, status, and way ahead. J. Family Med. Prim. Care 2019, 8, 1828–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren-Zhang, L.; Chee-Lan, L.; Hui-Yin, Y. The awareness and perception on antimicrobial stewardship among healthcare professionals in a tertiary teaching hospital Malaysia. Arch. Pharm. Pract. 2020, 11, 50–59. [Google Scholar]
- Iskandar, K.; Molinier, L.; Hallit, S.; Sartelli, M.; Hardcastle, T.C.; Haque, M.; Lugova, H.; Dhingra, S.; Sharma, P.; Islam, S.; et al. Surveillance of antimicrobial resistance in low- and middle-income countries: A scattered picture. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2021, 10, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartelli, M.; Hardcastle, T.C.; Catena, F.; Chichom-Mefire, A.; Coccolini, F.; Dhingra, S.; Haque, M.; Hodonou, A.; Iskandar, K.; Labricciosa, F.M.; et al. Antibiotic use in low and middle-income countries and the challenges of antimicrobial resistance in surgery. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Disease, G.B.D.; Injury, I.; Prevalence, C. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1789–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaborators, G.L. Estimates of the global, regional, and national morbidity, mortality, and aetiologies of lower respiratory tract infections in 195 countries: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 1133–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koulenti, D.; Tsigou, E.; Rello, J. Nosocomial pneumonia in 27 ICUs in Europe: Perspectives from the EU-VAP/CAP study. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 36, 1999–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divino, V.; Schranz, J.; Early, M.; Shah, H.; Jiang, M.; DeKoven, M. The annual economic burden among patients hospitalized for community-acquired pneumonia (CAP): A retrospective US cohort study. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2020, 36, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cillóniz, C.; Dominedò, C.; Ielpo, A.; Ferrer, M.; Gabarrús, A.; Battaglini, D.; Bermejo-Martin, J.; Meli, A.; García-Vidal, C.; Liapikou, A.; et al. Risk and Prognostic Factors in Very Old Patients with Sepsis Secondary to Community-Acquired Pneumonia. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eshwara, V.K.; Mukhopadhyay, C.; Rello, J. Community-acquired bacterial pneumonia in adults: An update. Indian J. Med. Res. 2020, 151, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAllister, D.A.; Liu, L.; Shi, T.; Chu, Y.; Reed, C.; Burrows, J.; Adeloye, D.; Rudan, I.; Black, R.E.; Campbell, H.; et al. Global, regional, and national estimates of pneumonia morbidity and mortality in children younger than 5 years between 2000 and 2015: A systematic analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2019, 7, E47–E57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.M.S.; Abidin, A.Z.; Liew, S.M.; Roberts, J.A.; Sime, F.B. The global prevalence of multidrug-resistance among Acinetobacter baumannii causing hospital-acquired and ventilator-associated pneumonia and its associated mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Infect. 2019, 79, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilloniz, C.; Dominedo, C.; Torres, A. Multidrug resistant gram-negative bacteria in community-acquired pneumonia. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Wu, S.; Hao, M.; Zhu, J.; Ding, B.; Yang, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, M.; Yang, F.; Hu, F. The colonization of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: Epidemiology, resistance mechanisms, and risk factors in patients admitted to intensive care units in China. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 221, S206–S214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langford, B.J.; So, M.; Raybardhan, S.; Leung, V.; Westwood, D.; MacFadden, D.R.; Soucy, J.R.; Daneman, N. Bacterial co-infection and secondary infection in patients with COVID-19: A living rapid review and meta-analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 1622–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedli, O.; Gasser, M.; Cusini, A.; Fulchini, R.; Vuichard-Gysin, D.; Halder Tobler, R.; Wassilew, N.; Plüss-Suard, C.; Kronenberg, A. Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Inpatient Antibiotic Consumption in Switzerland. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, C.; Xue, G.; Zhao, H.; Feng, Y.; Li, S.; Cui, J.; Ni, S.; Sun, H. Molecular and clinical characteristics of severe Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2019, 54, 1012–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyrani, P.; Mandell, L.; Torres, A.; Tillotson, G.S. The burden of community-acquired bacterial pneumonia in the era of antibiotic resistance. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2019, 13, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.; Ip, M. Antibiotic-resistant community-acquired bacterial pneumonia. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 33, 1087–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Antimicrobial Resistance: Global Report on Surveillance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; p. 232. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, C.-C.; Chen, S.-Y.; Ko, W.-C.; Hsueh, P.-R. Increased antimicrobial resistance during the COVID-19 pandemic. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2021, 57, 106324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Liu, X.; Hu, F.; Dong, B. Pharmacotherapy of lower respiratory tract infections in elderly-focused on antibiotics. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welp, A.L.; Bomberger, J.M. Bacterial community interactions during chronic respiratory disease. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocsis, B.; Szabo, D. New treatment options for lower respiratory tract infections. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2017, 18, 1345–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzler, E.; Fraidenburg, D.R.; Scardina, T.; Danziger, L.H. Inhaled antibiotics for gram-negative respiratory infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2016, 29, 581–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, X.; Yu, W.; Wan, Y. Dyslexia: A bibliometric and visualization analysis. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 915053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Jin, Q.X.; Fang, H.; Lei, H.; Hu, J.R.; Wu, Y.Q.; Chen, J.; Wang, C.; Wan, Y.H. Analytic network process: Academic insights and perspectives analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 235, 1276–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, R.K.; Nguyen, M.H.; Chen, L.; Press, E.G.; Kreiswirth, B.N.; Clancy, C.J. Pneumonia and renal replacement therapy are risk factors for ceftazidime-avibactam treatment failures and resistance among patients with carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae infections. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e02497-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micek, S.T.; Wunderink, R.G.; Kollef, M.H.; Chen, C.; Rello, J.; Chastre, J.; Antonelli, M.; Welte, T.; Clair, B.; Ostermann, H.; et al. An international multicenter retrospective study of Pseudomonas aeruginosa nosocomial pneumonia: Impact of multidrug resistance. Crit. Care 2015, 19, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zilberberg, M.D.; Nathanson, B.H.; Sulham, K.; Fan, W.; Shorr, A.F. Carbapenem resistance, inappropriate empiric treatment and outcomes among patients hospitalized with Enterobacteriaceae urinary tract infection, pneumonia and sepsis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauguet, S.; D’Ortona, S.; Ahnger-Pier, K.; Duan, B.; Surana, N.K.; Lu, R.; Cywes-Bentley, C.; Gadjeva, M.; Shan, Q.; Priebe, G.P.; et al. Intestinal microbiota of mice influences resistance to Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 4003–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yayan, J.; Ghebremedhin, B.; Rasche, K. Antibiotic resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in pneumonia at a single university hospital center in Germany over a 10-year period. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Loeches, I.; Torres, A.; Rinaudo, M.; Terraneo, S.; de Rosa, F.; Ramirez, P.; Diaz, E.; Fernandez-Barat, L.; Li Bassi, G.L.; Ferrer, M. Resistance patterns and outcomes in intensive care unit (ICU)-acquired pneumonia. Validation of European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) classification of multidrug resistant organisms. J. Infect. 2015, 70, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Ruan, S.Y.; Pan, S.C.; Lee, T.F.; Chien, J.Y.; Hsueh, P.R. Performance of a multiplex PCR pneumonia panel for the identification of respiratory pathogens and the main determinants of resistance from the lower respiratory tract specimens of adult patients in intensive care units. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2019, 52, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilberberg, M.D.; Nathanson, B.H.; Sulham, K.; Fan, W.; Shorr, A.F. Multidrug resistance, inappropriate empiric therapy, and hospital mortality in Acinetobacter baumannii pneumonia and sepsis. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Barat, L.; Ferrer, M.; De Rosa, F.; Gabarrus, A.; Esperatti, M.; Terraneo, S.; Rinaudo, M.; Li Bassi, G.; Torres, A. Intensive care unit-acquired pneumonia due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa with and without multidrug resistance. J. Infect. 2017, 74, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, W.; Al Roomi, E.; AbdulAziz, L.R.; Rotimi, V.O. Evaluation of Curetis Unyvero, a multiplex PCR-based testing system, for rapid detection of bacteria and antibiotic resistance and impact of the assay on management of severe nosocomial pneumonia. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 2487–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donthu, N.; Kumar, S.; Mukherjee, D.; Pandey, N.; Lim, W.M. How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 133, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellegaard, O.; Wallin, J.A. The bibliometric analysis of scholarly production: How great is the impact? Scientometrics 2015, 105, 1809–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilloniz, C.; Dominedo, C.; Torres, A. An overview of guidelines for the management of hospital-acquired and ventilator-associated pneumonia caused by multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 32, 656–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, A.; Bassetti, M.; Bellelli, V.; Bianchi, L.; Marincola Cattaneo, F.; Mazzocchetti, S.; Paciacconi, E.; Cottini, F.; Schiattarella, A.; Tufaro, G. Efficacy of a fosfomycin-containing regimen for treatment of severe pneumonia caused by multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: A prospective, observational study. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2021, 10, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarda, C.; Fazal, F.; Rello, J. Management of ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) caused by resistant gram-negative bacteria: Which is the best strategy to treat? Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2019, 13, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Wu, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhong, Y. Risk factors of ventilator-associated pneumonia in critically III patients. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.Y.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Zhou, M.; Zou, X.L.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhang, T.T. Risk factors for mortality due to ventilator-associated pneumonia in a Chinese hospital: A retrospective study. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 7660–7665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippolito, M.; Misseri, G.; Catalisano, G.; Marino, C.; Ingoglia, G.; Alessi, M.; Consiglio, E.; Gregoretti, C.; Giarratano, A.; Cortegiani, A. Ventilator-associated pneumonia in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacobbe, D.R.; Battaglini, D.; Enrile, E.M.; Dentone, C.; Vena, A.; Robba, C.; Ball, L.; Bartoletti, M.; Coloretti, I.; Di Bella, S.; et al. Incidence and Prognosis of Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19: A Multicenter Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Gutierrez, E.; Mayer, M.J.; Cotter, P.D.; Narbad, A. Gut microbiota as a source of novel antimicrobials. Gut Microbes 2019, 10, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosca, A.E.; Iesanu, M.I.; Zahiu, C.D.M.; Voiculescu, S.E.; Paslaru, A.C.; Zagrean, A.M. Capsaicin and gut microbiota in health and disease. Molecules 2020, 25, 5681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, G.R.; Swetschinski, L.R.; Weaver, N.D.; Ikuta, K.S.; Mestrovic, T.; Gray, A.P.; Chung, E.; Wool, E.E.; Han, C.; Hayoon, A.G. The burden of antimicrobial resistance in the Americas in 2019: A cross-country systematic analysis. Lancet Reg. Health Am. 2023, 7, e897–e913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasz, A. Antibiotic resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1997, 24 (Suppl. S1), S85–S88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzales, B.E.; Mercado, E.H.; Pinedo-Bardales, M.; Hinostroza, N.; Campos, F.; Chaparro, E.; Del Aguila, O.; Castillo, M.E.; Saenz, A.; Reyes, I.; et al. Increase of macrolide-resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae strains after the introduction of the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in Lima, Peru. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 866186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zango, U.U.; Ibrahim, M.; Shawai, S.A.A.; Shamsuddin, I.M. A review on β-lactam antibiotic drug resistance. MOJ Drug Des. Develop. Ther. 2019, 3, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinert, R.R. The antimicrobial resistance profile of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2009, 15, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulani, M.S.; Kamble, E.E.; Kumkar, S.N.; Tawre, M.S.; Pardesi, K.R. Emerging strategies to combat ESKAPE pathogens in the era of antimicrobial resistance: A review. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ablakimova, N.; Mussina, A.Z.; Smagulova, G.A.; Rachina, S.; Kurmangazin, M.S.; Balapasheva, A.; Karimoldayeva, D.; Zare, A.; Mahdipour, M.; Rahmanifar, F. Microbial Landscape and Antibiotic-Susceptibility Profiles of Microorganisms in Patients with Bacterial Pneumonia: A Comparative Cross-Sectional Study of COVID-19 and Non-COVID-19 Cases in Aktobe, Kazakhstan. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozgur, E.S.; Horasan, E.S.; Karaca, K.; Ersoz, G.; Atis, S.N.; Kaya, A. Ventilator-associated pneumonia due to extensive drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: Risk factors, clinical features, and outcomes. Am. J. Infect. Control 2014, 42, 206–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.j.; Pan, C.Z.; Fang, C.Q.; Zhao, Z.X.; Chen, H.L.; Guo, P.H.; Zhao, Z.W. Pneumonia caused by extensive drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii among hospitalized patients: Genetic relationships, risk factors and mortality. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inchai, J.; Liwsrisakun, C.; Theerakittikul, T.; Chaiwarith, R.; Khositsakulchai, W.; Pothirat, C. Risk factors of multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii ventilator-associated pneumonia in a Medical Intensive Care Unit of University Hospital in Thailand. J. Infect. Chemother. 2015, 21, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priyanka, A.; Akshatha, K.; Deekshit, V.K.; Prarthana, J.; Akhila, D.S. Klebsiella Pneumoniae Infections and Antimicrobial Drug Resistance; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 195–225. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W. Virulence evolution, molecular mechanisms of resistance and prevalence of ST11 carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in China: A review over the last 10 years. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 23, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aires-de-Sousa, M.; Ortiz de la Rosa, J.M.; Goncalves, M.L.; Pereira, A.L.; Nordmann, P.; Poirel, L. Epidemiology of carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in a hospital, Portugal. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 1632–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aria, M.; Cuccurullo, C. Bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J. Informetr. 2017, 11, 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabi, G. Bradford’s law and its application. Int. Libr. Rev. 2014, 11, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Rank | Study ID [References] | Title of the Document | Journal Name | Total Citations | DOI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Shields RK, 2018 [31] | Pneumonia and renal replacement therapy are risk factors for ceftazidime-avibactam treatment failures and resistance among patients with carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae infections | Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy | 174 | 10.1128/AAC.02497-17 |
| 2 | Micek ST, 2015 [32] | An international multicenter retrospective study of Pseudomonas aeruginosa nosocomial pneumonia: impact of multidrug resistance | Critical Care | 154 | 10.1186/s13054-015-0926-5 |
| 3 | Zilberberg MD, 2017 [33] | Carbapenem resistance, inappropriate empiric treatment and outcomes among patients hospitalized with Enterobacteriaceae urinary tract infection, pneumonia and sepsis | BMC Infectious Diseases | 131 | 10.1186/s12879-017-2383-z |
| 4 | Gauguet S, 2015 [34] | Intestinal Microbiota of Mice Influences Resistance to Staphylococcus aureus Pneumonia | Infection and Immunity | 127 | 10.1128/IAI.00037-15 |
| 5 | Yayan J, 2015 [35] | Antibiotic resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in pneumonia at a single university hospital center in Germany over a 10-year period | PLoS ONE | 105 | 10.1371/journal.pone.0139836 |
| 6 | Martin-Loeches I, 2015 [36] | Resistance patterns and outcomes in intensive care unit (ICU)-acquired pneumonia. Validation of European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) classification of multidrug resistant organisms | Journal of Infection | 105 | 10.1016/j.jinf.2014.10.004 |
| 7 | Lee SH, 2019 [37] | Performance of a multiplex PCR pneumonia panel for the identification of respiratory pathogens and the main determinants of resistance from the lower respiratory tract specimens of adult patients in intensive care units | Journal of Microbiology, Immunology and Infection | 87 | 10.1016/j.jmii.2019.10.009 |
| 8 | Zilberberg MD, 2016 [38] | Multidrug resistance, inappropriate empiric therapy, and hospital mortality in Acinetobacter baumannii pneumonia and sepsis | Critical Care | 76 | 10.1186/s13054-016-1392-4 |
| 9 | Fernandez-Barat L, 2017 [39] | Intensive care unit-acquired pneumonia due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa with and without multidrug resistance | Journal of Infection | 65 | 10.1016/j.jinf.2016.11.008 |
| 10 | Jamal W, 2014 [40] | Evaluation of Curetis Unyvero, a multiplex PCR-based testing system, for rapid detection of bacteria and antibiotic resistance and impact of the assay on management of severe nosocomial pneumonia | Journal of Clinical Microbiology | 59 | 10.1128/JCM.00325-14 |
| Sources | Articles |
|---|---|
| Clinical Infectious Diseases | 238 |
| Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy | 227 |
| Journal of Clinical Microbiology | 114 |
| American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine | 110 |
| Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy | 110 |
| Clinical Microbiology and Infection | 100 |
| PLOS ONE | 92 |
| Chest | 90 |
| Critical Care Medicine | 81 |
| Country | Number of Articles |
|---|---|
| China | 104 |
| USA | 101 |
| Japan | 50 |
| Spain | 32 |
| Vietnam | 30 |
| Iran | 27 |
| Germany | 26 |
| UK | 24 |
| South Korea | 19 |
| India | 13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ablakimova, N.; Smagulova, G.A.; Rachina, S.; Mussina, A.Z.; Zare, A.; Mussin, N.M.; Kaliyev, A.A.; Shirazi, R.; Tanideh, N.; Tamadon, A. Bibliometric Analysis of Global Research Output on Antimicrobial Resistance among Pneumonia Pathogens (2013–2023). Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12091411
Ablakimova N, Smagulova GA, Rachina S, Mussina AZ, Zare A, Mussin NM, Kaliyev AA, Shirazi R, Tanideh N, Tamadon A. Bibliometric Analysis of Global Research Output on Antimicrobial Resistance among Pneumonia Pathogens (2013–2023). Antibiotics. 2023; 12(9):1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12091411
Chicago/Turabian StyleAblakimova, Nurgul, Gaziza A. Smagulova, Svetlana Rachina, Aigul Z. Mussina, Afshin Zare, Nadiar M. Mussin, Asset A. Kaliyev, Reza Shirazi, Nader Tanideh, and Amin Tamadon. 2023. "Bibliometric Analysis of Global Research Output on Antimicrobial Resistance among Pneumonia Pathogens (2013–2023)" Antibiotics 12, no. 9: 1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12091411
APA StyleAblakimova, N., Smagulova, G. A., Rachina, S., Mussina, A. Z., Zare, A., Mussin, N. M., Kaliyev, A. A., Shirazi, R., Tanideh, N., & Tamadon, A. (2023). Bibliometric Analysis of Global Research Output on Antimicrobial Resistance among Pneumonia Pathogens (2013–2023). Antibiotics, 12(9), 1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12091411








