Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Antimicrobials in Critically Ill Obese Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
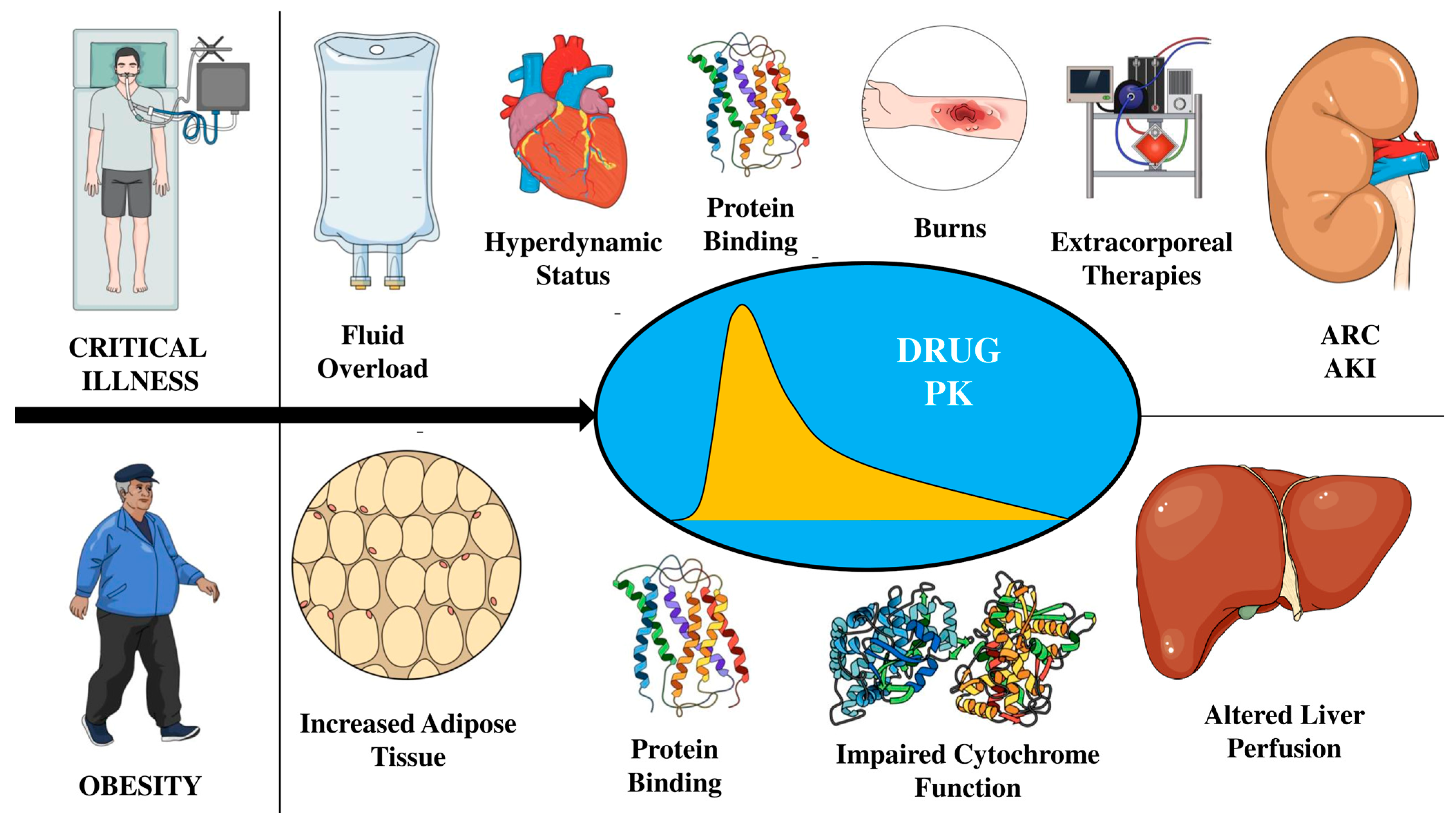
3. The Concept of PK/PD Changes in Critically Ill Patients
4. PK/PD Changes in Obese Patients
5. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring
6. TDM in Obese Critically Ill Patients
6.1. Antifungal Agents
6.1.1. Echinocandins
6.1.2. Azoles
6.2. Antiviral Agents
6.3. Antibacterial Drugs
6.3.1. β-Lactams
6.3.2. Glycopeptides
6.3.3. Quinolones
6.3.4. Aminoglycosides
7. Recommendations
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hanley, M.J.; Abernethy, D.R.; Greenblatt, D.J. Effect of Obesity on the Pharmacokinetics of Drugs in Humans. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2010, 49, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pai, M.P.; Bearden, D.T. Antimicrobial Dosing Considerations in Obese Adult Patients: Insights from the Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists. Pharmacotherapy 2007, 27, 1081–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keating, C.; Backholer, K.; Gearon, E.; Stevenson, C.; Swinburn, B.; Moodie, M.; Carter, R.; Peeters, A. Prevalence of class-I, class-II and class-III obesity in Australian adults between 1995 and 2011–12. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2015, 9, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, T.; Yang, W.; Chen, C.-S.; Reynolds, K.; He, J. Global burden of obesity in 2005 and projections to 2030. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 1431–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Solh, A.; Sikka, P.; Bozkanat, E.; Jaafar, W.; Davies, J. Morbid Obesity in the Medical ICU. Chest 2001, 120, 1989–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fgren, M.L.; Poromaa, I.S.M.; Stjerndahl, J.H. Postoperative infections and antibiotic prophylaxis for hysterectomy in Sweden: A study by the Swedish National Register for Gynecologic Surgery. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2004, 83, 1202–1207. [Google Scholar]
- Baik, I.; Curhan, G.C.; Rimm, E.B.; Bendich, A.; Willett, W.C.; Fawzi, W.W. A Prospective Study of Age and Lifestyle Factors in Relation to Community-Acquired Pneumonia in US Men and Women. Arch. Intern. Med. 2000, 160, 3082–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttunen, R.; Syrjänen, J. Obesity and the risk and outcome of infection. Int. J. Obes. 2012, 37, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.A.; Lipman, J. Pharmacokinetic issues for antibiotics in the critically ill patient. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 37, 840–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Póvoa, P.; Moniz, P.; Pereira, J.G.; Coelho, L. Optimizing Antimicrobial Drug Dosing in Critically Ill Patients. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.A.; Roberts, M.S.; Semark, A.; Udy, A.A.; Kirkpatrick, C.M.; Paterson, D.L.; Roberts, M.J.; Kruger, P.; Lipman, J. Antibiotic dosing in the ‘at risk’ critically ill patient: Linking pathophysiology with pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics in sepsis and trauma patients. BMC Anesthesiol. 2011, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conil, J.M.; Georges, B.; Lavit, M.; Laguerre, J.; Samii, K.; Houin, G.; Saivin, S. A population pharmacokinetic approach to ceftazidime use in burn patients: Influence of glomerular filtration, gender and mechanical ventilation. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2007, 64, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buijk, S.L.C.E.; Gyssens, I.C.; Mouton, J.W.; Van Vliet, A.; Verbrugh, H.A.; Bruining, H.A. Pharmacokinetics of ceftazidime in serum and peritoneal exudate during continuous versus intermittent administration to patients with severe intra-abdominal infections. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2002, 49, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoff, B.M.; Maker, J.H.; Dager, W.E.; Heintz, B.H. Antibiotic Dosing for Critically Ill Adult Patients Receiving Intermittent Hemodialysis, Prolonged Intermittent Renal Replacement Therapy, and Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy: An Update. Ann. Pharmacother. 2020, 54, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, M.A.; Sieg, A.C. Evaluation of Altered Drug Pharmacokinetics in Critically Ill Adults Receiving Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2017, 37, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Derendorf, H. Antimicrobial tissue concentrations. Infect. Dis. Clin. North Am. 2003, 17, 599–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulldemolins, M.; Roberts, J.A.; Rello, J.; Paterson, D.L.; Lipman, J. The Effects of Hypoalbuminaemia on Optimizing Antibacterial Dosing in Critically Ill Patients. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2011, 50, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sime, F.B.; Roberts, M.S.; Peake, S.L.; Lipman, J.; Roberts, J.A. Does Beta-lactam Pharmacokinetic Variability in Critically Ill Patients Justify Therapeutic Drug Monitoring? A Systematic Review. Ann. Intensiv. Care 2012, 2, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumi, C.D.; Heffernan, A.J.; Lipman, J.; Roberts, J.A.; Sime, F.B. What Antibiotic Exposures Are Required to Suppress the Emergence of Resistance for Gram-Negative Bacteria? A Systematic Review. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2019, 58, 1407–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, L.A.; Edwards, W.A.D.; Dellinger, E.P.; Simonowitz, D.A. Influence of weight on aminoglycoside pharmacokinetics in normal weight and morbidly obese patients. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1983, 24, 643–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brill, M.J.E.; Diepstraten, J.; van Rongen, A.; van Kralingen, S.; van den Anker, J.N.; Knibbe, C.A.J. Impact of Obesity on Drug Metabolism and Elimination in Adults and Children. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2012, 51, 277–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Mui, E.; Holubar, M.K.; Deresinski, S.C. Comprehensive Guidance for Antibiotic Dosing in Obese Adults. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2017, 37, 1415–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abernethy, D.R.; Greenblatt, D.J.; Divoll, M.; Smith, R.B.; Shader, R.I. The Influence of Obesity on the Pharmacokinetics of Oral Alprazolam and Triazolam. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1984, 9, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedek’, I.H.; Iii’, W.D.F.; Griffen, W.O.; Bell, R.M.; Blouin, R.A.; Mcnamara’, P.J. Serum al-acid glycoprotein and the binding of drugs in obesity. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1983, 16, 751–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, B.; Craig, W.A.; England, A.C.; Elliott, R.L. Effect of Free Fatty Acids on Protein Binding of Antimicrobial Agents. J. Infect. Dis. 1981, 143, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hites, M.; Taccone, F.S.; Wolff, F.; Cotton, F.; Beumier, M.; De Backer, D.; Roisin, S.; Lorent, S.; Surin, R.; Seyler, L.; et al. Case-Control Study of Drug Monitoring of β-Lactams in Obese Critically Ill Patients. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alobaid, A.S.; Wallis, S.C.; Jarrett, P.; Starr, T.; Stuart, J.; Lassig-Smith, M.; Mejia, J.L.O.; Roberts, M.S.; Lipman, J.; Roberts, J.A. Effect of Obesity on the Population Pharmacokinetics of Meropenem in Critically Ill Patients. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 4577–4584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Infection Section of European Society of Intensive Care Medicine (ESICM); Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic and Critically Ill Patient Study Groups of European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID); Infectious Diseases Group of International Association of Therapeutic Drug Monitoring and Clinical Toxicology (IATDMCT); Infections in the ICU and Sepsis Working Group of International Society of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (ISAC); Abdul-Aziz, M.H.; Alffenaar, J.W.C.; Bassetti, M.; Bracht, H.; Dimopoulos, G.; Marriott, D.; et al. Antimicrobial therapeutic drug monitoring in critically ill adult patients: A Position Paper#. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 1127–1153. [Google Scholar]
- Lodise, T.P.; Lomaestro, B.; Graves, J.; Drusano, G.L. Larger Vancomycin Doses (at Least Four Grams per Day) Are Associated with an Increased Incidence of Nephrotoxicity. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 1330–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, R.G.; A Hazlewood, K.; Brouse, S.D.; Giuliano, C.A.; Haase, K.K.; Frei, C.R.; Forcade, N.A.; Bell, T.; Bedimo, R.J.; A Alvarez, C. Empiric guideline-recommended weight-based vancomycin dosing and nephrotoxicity rates in patients with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: A retrospective cohort study. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013, 14, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, G.; Brinkman, A.; Benefield, R.J.; Carlier, M.; De Waele, J.J.; El Helali, N.; Frey, O.; Harbarth, S.; Huttner, A.; McWhinney, B.; et al. An international, multicentre survey of -lactam antibiotic therapeutic drug monitoring practice in intensive care units. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 1416–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebchen, U.; Paal, M.; Scharf, C.; Schroeder, I.; Grabein, B.; Zander, J.; Siebers, C.; Zoller, M. The ONTAI study–a survey on antimicrobial dosing and the practice of therapeutic drug monitoring in German intensive care units. J. Crit. Care 2020, 60, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandaradura, I.; Alffenaar, J.; Cotta, M.O.; Daveson, K.; Day, R.O.; Van Hal, S.; Imani, S. Emerging therapeutic drug monitoring of anti-infective agents in Australian hospitals: Availability, performance and barriers to implementation. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 88, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cusumano, J.A.; Klinker, K.P.; Huttner, A.; Luther, M.K.; Roberts, J.A.; LaPlante, K.L. Towards precision medicine: Therapeutic drug monitoring–guided dosing of vancomycin and β-lactam antibiotics to maximize effectiveness and minimize toxicity. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2020, 77, 1104–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilworth, T.J.; Schulz, L.T.; Micek, S.T.; Kollef, M.H.; Rose, W.E. β-Lactam Therapeutic Drug Monitoring in Critically Ill Patients: Weighing the Challenges and Opportunities to Assess Clinical Value. Crit. Care Explor. 2022, 4, e0726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.K.; Chen, Y.L.; Chen, K.; Zhang, X.L.; Du, G.H.; He, B.; Li, D.-K.; Liu, Y.-N.; Yang, K.-H.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; et al. Therapeutic drug monitoring of vancomycin: A guideline of the Division of Therapeutic Drug Monitoring, Chinese Pharmacological Society. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 3020–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashbee, H.R.; Barnes, R.A.; Johnson, E.M.; Richardson, M.D.; Gorton, R.; Hope, W.W. Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) of antifungal agents: Guidelines from the British Society for Medical Mycology. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 1162–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Vianen, W.; de Marie, S.; ten Kate, M.T.; Mathot, R.A.A.; Bakker-Woudenberg, I.A.J.M. Caspofungin: Antifungal activity in vitro, pharmacokinetics, and effects on fungal load and animal survival in neutropenic rats with invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2006, 57, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louie, A.; Deziel, M.; Liu, W.; Drusano, M.F.; Gumbo, T.; Drusano, G.L. Pharmacodynamics of Caspofungin in a Murine Model of Systemic Candidiasis: Importance of Persistence of Caspofungin in Tissues to Understanding Drug Activity. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 5058–5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maseda, E.; Grau, S.; Luque, S.; Castillo-Mafla, M.-P.; Suárez-De-La-Rica, A.; Montero-Feijoo, A.; Salgado, P.; Gimenez, M.-J.; García-Bernedo, C.A.; Gilsanz, F.; et al. Population pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics of micafungin against Candida species in obese, critically ill, and morbidly obese critically ill patients. Crit. Care 2018, 22, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsuk-De Moor, A.; Sysiak-Sławecka, J.; Rypulak, E.; Borys, M.; Piwowarczyk, P.; Raszewski, G.; Onichimowski, D.; Czuczwar, M.; Wiczling, P. Nonstationary Pharmacokinetics of Caspofungin in ICU Patients. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e00345-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Märtson, A.-G.; van der Elst, K.C.M.; Veringa, A.; Zijlstra, J.; Beishuizen, A.; van der Werf, T.S.; Kosterink, J.G.W.; Neely, M.; Alffenaar, J.-W. Caspofungin Weight-Based Dosing Supported by a Population Pharmacokinetic Model in Critically Ill Patients. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e00905–e00920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Hoppe-Tichy, T.; Geiss, H.K.; Rastall, A.C.; Swoboda, S.; Schmidt, J.; Weigand, M.A. Factors influencing caspofungin plasma concentrations in patients of a surgical intensive care unit. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 60, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferriols-Lisart, R.; Aguilar, G.; Pérez-Pitarch, A.; Puig, J.; Ezquer-Garín, C.; Alós, M. Plasma concentrations of caspofungin in a critically ill patient with morbid obesity. Crit. Care 2017, 21, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Ruhnke, M.; Meersseman, W.; Paiva, J.A.; Kantecki, M.; Damle, B. Pharmacokinetics of Anidulafungin in Critically Ill Patients with Candidemia/Invasive Candidiasis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 1672–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zomp, A.; Bookstaver, P.B.; Ahmed, Y.; Turner, J.E.; King, C. Micafungin therapy in a critically ill, morbidly obese patient. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 66, 2678–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasmann, R.E.; Smit, C.; Ter Heine, R.; Koele, S.E.; Van Dongen, E.P.H.; Wiezer, R.M.J.; Burger, D.M.; Knibbe, C.A.J.; Brüggemann, R.J.M. Pharmacokinetics and probability of target attainment for micafungin in normal-weight and morbidly obese adults. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasmann, R.E.; ter Heine, R.; van Dongen, E.P.; Burger, D.M.; Lempers, V.J.; Knibbe, C.A.J.; Brüggemann, R.J. Pharmacokinetics of Anidulafungin in Obese and Normal-Weight Adults. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e00063-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinnollareddy, M.G.; Roberts, J.A.; Lipman, J.; Akova, M.; Bassetti, M.; De Waele, J.J.; Kaukonen, K.M.; Koulenti, D.; Martin, C.; Montravers, P.; et al. Pharmacokinetic variability and exposures of fluconazole, anidulafungin, and caspofungin in intensive care unit patients: Data from multinational Defining Antibiotic Levels in Intensive care unit (DALI) patients Study. Crit. Care 2015, 19, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Baldelli, S.C.; Märtson, A.-G.M.; Stocker, S.; Alffenaar, J.-W.; Cattaneo, D.; Marriott, D.J.F.F. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of the Echinocandin Antifungal Agents: Is There a Role in Clinical Practice? A Position Statement of the Anti-Infective Drugs Committee of the International Association of Therapeutic Drug Monitoring and Clinical Toxicology. Ther. Drug Monit. 2022, 44, 198–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baracaldo-Santamaría, D.; Cala-Garcia, J.D.; Medina-Rincón, G.J.; Rojas-Rodriguez, L.C.; Calderon-Ospina, C.A. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Antifungal Agents in Critically Ill Patients: Is There a Need for Dose Optimisation? Antibiotics 2022, 11, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-López, A. Antifungal therapeutic drug monitoring: Focus on drugs without a clear recommendation. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 1481–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai Mangalore, R.; Ashok, A.; Lee, S.J.; Romero, L.; Peel, T.N.; Udy, A.A.; Peleg, A.Y. Beta-Lactam Antibiotic Therapeutic Drug Monitoring in Critically Ill Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 75, 1848–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, B.; Mahul, M.; Breilh, D.; Legeron, R.; Signe, J.; Jean-Pierre, H.; Uhlemann, A.C.; Molinari, N.; Jaber, S. Repeated Piperacillin-Tazobactam Plasma Concentration Measurements in Severely Obese Versus Nonobese Critically Ill Septic Patients and the Risk of Under– and Overdosing*. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 45, e470–e478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturm, A.W.; Allen, N.; Rafferty, K.D.; Fish, D.N.; Toschlog, E.; Newell, M.; Waibel, B. Pharmacokinetic Analysis of Piperacillin Administered with Tazobactam in Critically Ill, Morbidly Obese Surgical Patients. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2014, 34, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheatham, S.C.; Fleming, M.R.; Healy, D.P.; Chung, E.K.; Shea, K.M.; Humphrey, M.L.; Kays, M.B. Steady-state pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of meropenem in morbidly obese patients hospitalized in an intensive care unit: The Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2014, 54, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, J.A.; Lipman, J. Optimal Doripenem Dosing Simulations in Critically Ill Nosocomial Pneumonia Patients With Obesity, Augmented Renal Clearance, and Decreased Bacterial Susceptibility*. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 41, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taccone, F.S.; Cotton, F.; Roisin, S.; Vincent, J.-L.; Jacobs, F. Optimal Meropenem Concentrations To Treat Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Septic Shock. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 2129–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulla, A.; Dijkstra, A.; Hunfeld, N.G.M.; Endeman, H.; Bahmany, S.; Ewoldt, T.M.J.; Muller, A.E.; Van Gelder, T.; Gommers, D.; Koch, B.C.P. Failure of target attainment of beta-lactam antibiotics in critically ill patients and associated risk factors: A two-center prospective study (EXPAT). Crit. Care 2020, 24, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alobaid, A.S.; Brinkmann, A.; Frey, O.R.; Roehr, A.C.; Luque, S.; Grau, S.; Wong, G.; Abdul-Aziz, M.H.; Roberts, M.S.; Lipman, J.; et al. What is the effect of obesity on piperacillin and meropenem trough concentrations in critically ill patients? J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blouin, R.A.; Bauer, L.A.; Miller, D.D.; Record, K.E.; Griffen, W.O. Vancomycin pharmacokinetics in normal and morbidly obese subjects. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1982, 21, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, J.A.; Taccone, F.S.; Udy, A.A.; Vincent, J.-L.; Jacobs, F.; Lipman, J. Vancomycin Dosing in Critically Ill Patients: Robust Methods for Improved Continuous-Infusion Regimens. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 2704–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.-Y.; Li, D.; Hu, Z.-J.; Zhao, C.-C.; Bai, J.; Du, W.-L. Vancomycin dosing in an obese patient with acute renal failure: A case report and review of literature. World J. Clin. Cases 2022, 10, 6218–6226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, S.P.; Hanes, S.D. Unexplained increases in serum vancomycin concentration in a morbidly obese patient. Intensiv. Crit. Care Nurs. 2017, 39, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuhasna, S.; Al Jundi, A.H. Therapeutic drug monitoring of vancomycin in an obese patient with renal insufficiency. J. Anaesthesiol. Clin. Pharmacol. 2011, 27, 531–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, D.C.; Waite, L.H.; Alexander, D.P.; DeRyke, C.A. Performance of a vancomycin dosage regimen developed for obese patients. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2012, 69, 944–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosmisky, D.E.; Griffiths, C.L.; Templin, M.A.; Norton, J.; Martin, K.E. Evaluation of a New Vancomycin Dosing Protocol in Morbidly Obese Patients. Hosp. Pharm. 2015, 50, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafelski, S.; Yi, H.; Ismaeel, F.; Krannich, A.; Spies, C.; Nachtigall, I. Obesity in critically ill patients is associated with increased need of mechanical ventilation but not with mortality. J. Infect. Public Health 2016, 9, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.; Krop, L.C.; Johns, T.; Pai, M.P. Individualized Vancomycin Dosing in Obese Patients: A Two-Sample Measurement Approach Improves Target Attainment. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2015, 35, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utrup, T.R.; Mueller, E.W.; Healy, D.P.; Calicut, R.A.; Peterson, J.D.; Hurford, W.E. High-Dose Ciprofloxacin for Serious Gram-Negative Infection in an Obese, Critically III Patient Receiving Continuous Venovenous Hemodiafiltration. Ann. Pharmacother. 2010, 44, 1660–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanretty, A.M.; Moore, W.S.; Chopra, A.; Cies, J.J. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Levofloxacin in an Obese Adolescent: A Case Report. J. Pediatr. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 25, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velissaris, D.; Karamouzos, V.; Marangos, M.; Pierrakos, C.; Karanikolas, M. Pharmacokinetic Changes and Dosing Modification of Aminoglycosides in Critically Ill Obese Patients: A Literature Review. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2014, 6, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blouin, R.A.; Mann, H.J.; Griffen, W.O.; Bauer, L.A.; Record, K.E. Tobramycin pharmacokinetics in morbidly obese patients. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1979, 26, 508–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erstad, B.L. Dosing of medications in morbidly obese patients in the intensive care unit setting. Intensiv. Care Med. 2004, 30, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polso, A.K.; Lassiter, J.L.; Nagel, J.L. Impact of hospital guideline for weight-based antimicrobial dosing in morbidly obese adults and comprehensive literature review. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2014, 39, 584–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taccone, F.S.; Laterre, P.-F.; Spapen, H.; Dugernier, T.; Delattre, I.; Layeux, B.; De Backer, D.; Wittebole, X.; Wallemacq, P.; Vincent, J.-L.; et al. Revisiting the loading dose of amikacin for patients with severe sepsis and septic shock. Crit. Care 2010, 14, R53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buijk, S.; Mouton, J.; Gyssens, I.; Verbrugh, H.; Bruining, H. Experience with a once-daily dosing program of aminoglycosides in critically ill patients. Intensiv. Care Med. 2002, 28, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Antimicrobial Class | PK/PD Target | TDM Target |
|---|---|---|
| Antifungal Agents | ||
| Azoles | ||
| Voriconazole | Cmin ≥ 1–2 mg/L | Cmin: 2–6 mg/L (prophylaxis or treatment) |
| Itraconazole | Cmin ≥ 0.25–0.5 mg/L (Prophylaxis) Cmin ≥ 1 mg/L (treatment) | Cmin > 0.5–1 mg/L |
| Posaconazole | Cmin > 0.5 (prophylaxis) Cmin > 1 mg/L (treatment) | Cmin > 0.5–0.7 mg/L (prophylaxis) Cmin > 1 mg/L (treatment) |
| Fluconazole | AUC0–24/MIC ≥ 55–100 | / |
| Antiviral agents | Unclear | / |
| Antibacterial agents | ||
| β-lactams | 50–100% fT > MIC | II: 100% fT > MIC CI: Css > MIC |
| Glycopeptides | ||
| Vancomycin | AUC0–24/MIC ≥ 400 Cmin > 10–20 mg/L | II: Cmin ≥ 15–20 mg/L (for severe infections) CI: Css 20–25 mg/L |
| Teicoplanin | Cmin ≥ 10 mg/L | Cmin ≥ 15–30 mg/L |
| Linezolid | AUC0–24/MIC ≥ 80–120 ≥85% fT > MIC | Cmin: 2–7 mg/L |
| Quinolones | AUC0–24/MIC ≥ 125–250 Cmax/MIC ≥ 12 | Cmax/MIC ≥ 8–12 |
| Aminoglycosides | ||
| Amikacin | Cmax/MIC ≥ 8–10 | Cmax/MIC ≥ 8–10 Cmin < 2.5 mg/L |
| Gentamicin | AUC0–24/MIC ≥ 110 Cmax/MIC ≥ 8–10 | Cmax/MIC ≥ 8–10 Cmin < 0.5 mg/L |
| Tobramycin | AUC0–24/MIC ≥ 110 Cmax/MIC ≥ 8–10 | Cmax/MIC ≥ 8–10 Cmin < 0.5 mg/L |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gorham, J.; Taccone, F.S.; Hites, M. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Antimicrobials in Critically Ill Obese Patients. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12071099
Gorham J, Taccone FS, Hites M. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Antimicrobials in Critically Ill Obese Patients. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(7):1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12071099
Chicago/Turabian StyleGorham, Julie, Fabio S. Taccone, and Maya Hites. 2023. "Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Antimicrobials in Critically Ill Obese Patients" Antibiotics 12, no. 7: 1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12071099
APA StyleGorham, J., Taccone, F. S., & Hites, M. (2023). Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Antimicrobials in Critically Ill Obese Patients. Antibiotics, 12(7), 1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12071099





