Salmonella Prophages, Their Propagation, Host Specificity and Antimicrobial Resistance Gene Transduction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Isolates
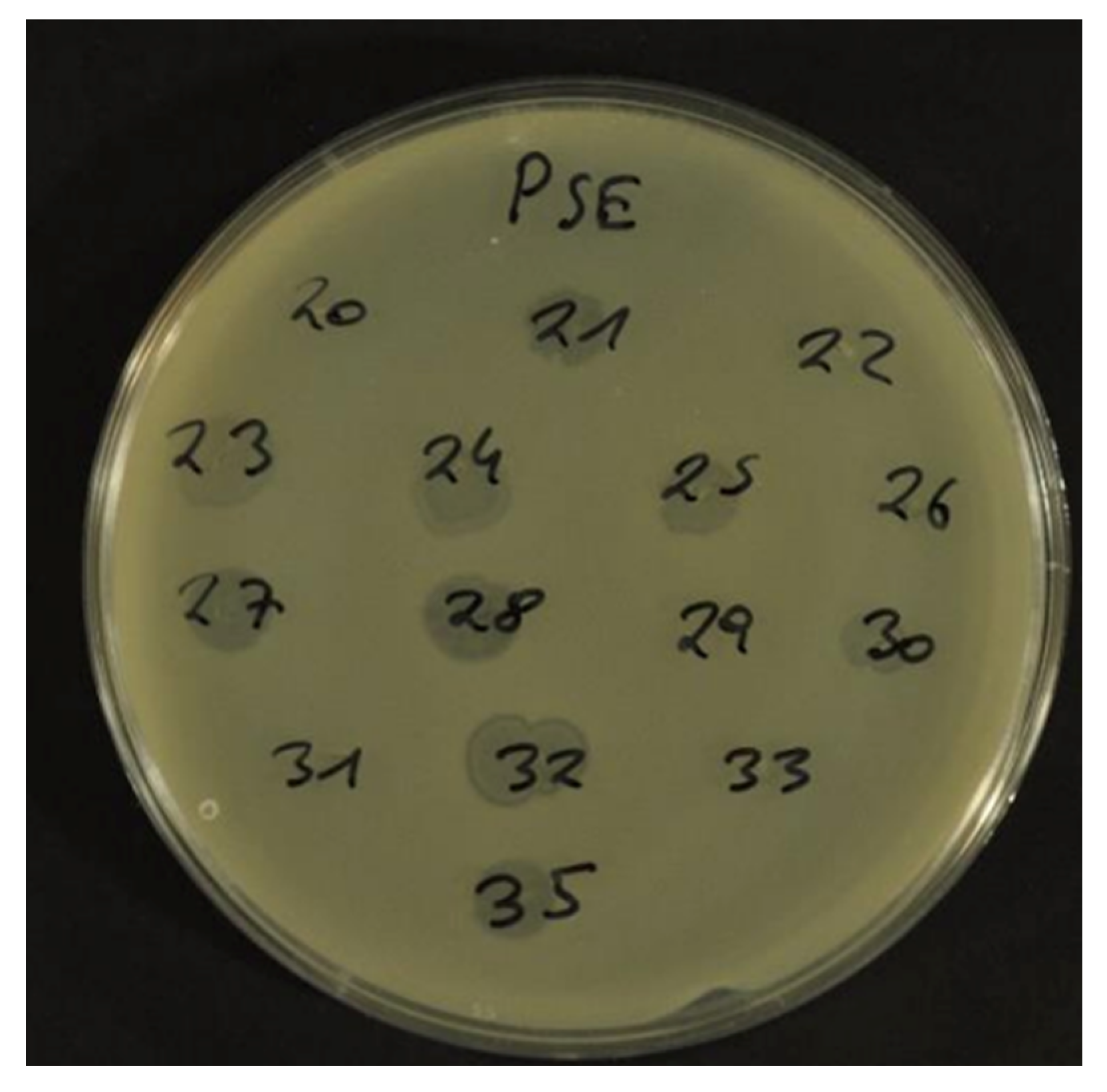
4.2. Prophage Induction
4.3. Phage Infection
4.4. Analyzing Phage DNA for Antibiotic Resistance Genes
4.5. Transduction of Antibiotic Resistance
4.6. Defining Host Range of Induced Prophage Lysates
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- EFSA and ECDC (European Food Safety Authority and European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control). The European Union One Health 2021 Zoonoses Report. EFSA J. 2022, 20, 7666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.-H.; Su, L.-H.; Chu, C.-H.; Wang, M.-H.; Yeh, C.-M.; Weill, F.-X.; Chu, C. Detection of Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Phage Types DT102, DT104, and U302 by Multiplex PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 2354–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sharkawy, H.; Tahoun, A.; El-Gohary, A.E.-G.A.; El-Abasy, M.; El-Khayat, F.; Gillespie, T.; Kitade, Y.; Hafez, H.M.; Neubauer, H.; El-Adawy, H. Epidemiological, molecular characterization and antibiotic resistance of Salmonella enterica serovars isolated from chicken farms in Egypt. Gut Pathog. 2017, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebreyes, W.A.; Altier, C. Molecular Characterization of Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica Serovar Typhimurium Isolates from Swine. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 2813–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghoddusi, A.; Nayeri Fasaei, B.; Zahraei Salehi, T.; Akbarein, H. Prevalence and characterization of multidrug resistance and variant Salmonella genomic island 1 in Salmonella isolates from cattle, poultry and humans in Iran. Zoonoses Public Health 2019, 66, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacci, C.; Boni, E.; Alpigiani, I.; Lanzoni, E.; Bonardi, S.; Brindani, F. Phenotypic and genotypic features of antibiotic resistance in Salmonella enterica isolated from chicken meat and chicken and quail carcasses. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 160, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulou, C.; Davies, R.H.; Carrique-Mas, J.J.; Evans, S.J. Salmonella serovars and their antimicrobial resistance in British turkey flocks in 1995 to 2006. Avian Pathol. 2009, 38, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Threlfall, E.J.; Ward, L.R.; Skinner, J.A.; Graham, A. Antimicrobial drug resistance in non-typhoidal salmonellas from humans in England and Wales in 1999: Decrease in multiple resistance in Salmonella enterica serotypes Typhimurium, Virchow, and Hadar. Microb. Drug Resist. 2000, 6, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) and ECDC (European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control). The European Union Summary Report on Antimicrobial Resistance in zoonotic and indicator bacteria from humans, animals and food in 2019–2020. EFSA J. 2022, 20, 7209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaRock, D.; Chaudhary, A.; Miller, S. Salmonellae interactions with host process. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliaga, L.; Mediavilla, J.D.; López de la Osa, A.; López-Gómez, M.; de Cueto, M.; Miranda, C. Nontyphoidal salmonella intracranial infections in HIV-infected patients. Clin. Infect Dis. 1997, 25, 1118–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.S.; Puthucheary, S.D.; Parasakthi, N. Extra-intestinal non-typhoidal Salmonella infections in children. Ann. Trop. Paediatr. 2000, 20, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, J.A.; Kelleher, A.; Rowe, B. Increasing ciprofloxacin resistance in salmonellas in England and Wales 1991–1994. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1996, 37, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mon, K.K.Z.; Si, Z.; Chan-Park, M.B.; Kenney, L.J. Polyimidazolium Protects against an Invasive Clinical Isolate of Salmonella Typhimurium. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2022, 66, e0059722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Ma, R.; Li, Z.; Mao, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, L.; Han, K.; Li, L.; Ma, D.; et al. Broad-Spectrum Salmonella Phages PSE-D1 and PST-H1 Controls Salmonella in Foods. Viruses 2022, 14, 2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavilla, M.; Domingo-Calap, P.; Sevilla-Navarro, S.; Lasagabaster, A. Natural Killers: Opportunities and Challenges for the Use of Bacteriophages in Microbial Food Safety from the One Health Perspective. Foods 2023, 12, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo-Rebenaque, L.; Malik, D.J.; Catalá-Gregori, P.; Marin, C.; Sevilla-Navarro, S. Gastrointestinal Dynamics of Non-Encapsulated and Microencapsulated Salmonella Bacteriophages in Broiler Production. Animals 2022, 12, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutateladze, M.; Adamia, R. Phage therapy experience at the Eliava Institute. Med. Mal. Infect. 2008, 38, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, S.; Fillol-Salom, A.; Quiles-Puchalt, N.; Ibarra-Chávez, R.; Haag, A.F.; Chen, J.; Penadés, J.R. Bacterial chromosomal mobility via lateral transduction exceeds that of classical mobile genetic elements. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, Y.F.; Taylor, V.L.; Kala, S.; Bondy-Denomy, J.; Khan, A.N.; Bona, D.; Cattoir, V.; Lory, S.; Davidson, A.R.; Maxwell, K.L. Phage Morons Play an Important Role in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Phenotypes. J. Bacteriol. 2018, 200, e00189-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groisman, E.A. In vivo Genetic Engineering with Bacteriophage Mu. Methods Enzymol. 1991, 204, 180–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Zhang, X.; Xie, X.; Tu, Z.; Gu, J.; Zhang, A. Characterization and whole-genome sequencing of broad-host-range Salmonella-specific bacteriophages for bio-control. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 143, 104119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco-Picazo, P.; Morales-Cortes, S.; Ramos-Barbero, M.D.; García-Aljaro, C.; Rodríguez-Rubio, L.; Muniesa, M. Dominance of phage particles carrying antibiotic resistance genes in the viromes of retail food sources. ISME J. 2023, 17, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, M.; Viazis, S.; Diez-Gonzalez, F. Isolation, identification and characterization of lytic, wide host range bacteriophages from waste effluents against Salmonella enterica serovars. Food Control 2014, 38, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelyuntha, W.; Sanguankiat, A.; Kovitvadhi, A.; Vongkamjan, K. Broad lytic spectrum of novel Salmonella phages on ciprofloxacin-resistant Salmonella contaminated in the broiler production chain. Vet. World 2022, 15, 2039–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanki, A.M.; Clavijo, V.; Healy, K.; Wilkinson, R.C.; Sicheritz-Pontén, T.; Millard, A.D.; Clokie, M.R.J. Development of a Phage Cocktail to Target Salmonella Strains Associated with Swine. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azari, R.; Yousefi, M.H.; Taghipour, Z.; Wagemans, J.; Lavigne, R.; Hosseinzadeh, S.; Mazloomi, S.M.; Vallino, M.; Khalatbari-Limaki, S.; Berizi, E. Application of the lytic bacteriophage Rostam to control Salmonella enteritidis in eggs. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023, 389, 110097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fillol-Salom, A.; Bacigalupe, R.; Humphrey, S.; Chiang, Y.N.; Chen, J.; Penadés, J.R. Lateral transduction is inherent to the life cycle of the archetypical Salmonella phage P22. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, G.; Bergamaschi, M.; Barbieri, G.; Franceschini, M. Kinetics of nitrite evaluated in a meat product. Meat Sci. 2013, 93, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipiak, M.; Łoś, J.M.; Łoś, M. Efficiency of induction of Shiga-toxin lambdoid prophages in Escherichia coli due to oxidative and antibiotic stress depends on the combination of prophage and the bacterial strain. J. Appl. Genet. 2020, 61, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, K.; Lu, Y.T.; Brenner, T.; Falardeau, J.; Wang, S. Prophage Diversity Across Salmonella and Verotoxin-Producing Escherichia coli in Agricultural Niches of British Columbia, Canada. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 853703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiley, L.; Fang, N.X.; Micalizzi, G.R.; Bates, J. Distribution of Gifsy-3 and of variants of ST64B and Gifsy-1 prophages amongst Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium isolates: Evidence that combinations of prophages promote clonality. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayrhofer, S.; Paulsen, P.; Smulders, F.J.; Hilbert, F. Antimicrobial resistance profile of five major food-borne pathogens isolated from beef, pork and poultry. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 97, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, M.; Pajunen, M.I.; Jun, J.W.; Skurnik, M. T4-like Bacteriophages Isolated from Pig Stools Infect Yersinia pseudotuberculosis and Yersinia pestis Using LPS and OmpF as Receptors. Viruses 2021, 13, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacífico, C.; Hilbert, M.; Sofka, D.; Dinhopl, N.; Pap, I.J.; Aspöck, C.; Hilbert, F. Characterization of Bacteria and Inducible Phages in an Intensive Care Unit. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacher-Pirklbauer, A.; Klein-Jöbstl, D.; Sofka, D.; Blanc-Potard, A.B.; Hilbert, F. Phylogenetic Groups and Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in Escherichia coli from Different Meat Species. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shousha, A.; Awaiwanont, N.; Sofka, D.; Smulders, F.J.; Paulsen, P.; Szostak, M.P.; Humphrey, T.; Hilbert, F. Bacteriophages Isolated from Chicken Meat and the Horizontal Transfer of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 4600–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Lysate | blaTEM | cmlA | strA | sul1 | sul2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PS1 | + | ||||
| PS2 | + | ||||
| PS3 | + | ||||
| PS4 | + | ||||
| PS9 | + | ||||
| PS14 | + | ||||
| PS17 | + | ||||
| PS19 | + | ||||
| PS21 | + | + | + | ||
| PS25 | + | ||||
| PS26 | + | ||||
| PS27 | + | + | + | ||
| PS28 | + | + | |||
| PS33 | + | + | |||
| PS45 | + | ||||
| PS46 | + | ||||
| PS47 | + | ||||
| PSL18B | + | + | |||
| PSL36B | + | ||||
| PSLs157 | + | + |
| Serovar/Strain | Number of Lysates Serovar Typhimurium | Number of Lysates from Serovar Enteritidis |
|---|---|---|
| ATCC 14028 | 40 | 0 |
| DSM 17420 | 28 | 4 |
| Blockley | 3 | 0 |
| Heidelberg | 34 | 2 |
| Parathyphi B | 5 | 1 |
| Typhimurium | 0 | 0 |
| Virchow | 36 | 3 |
| Hadar | 2 | 0 |
| Rissen | 2 | 0 |
| Kentucky | 2 | 0 |
| B-Group | 6 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trofeit, L.; Sattler, E.; Künz, J.; Hilbert, F. Salmonella Prophages, Their Propagation, Host Specificity and Antimicrobial Resistance Gene Transduction. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030595
Trofeit L, Sattler E, Künz J, Hilbert F. Salmonella Prophages, Their Propagation, Host Specificity and Antimicrobial Resistance Gene Transduction. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(3):595. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030595
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrofeit, Lisa, Elisabeth Sattler, Johannes Künz, and Friederike Hilbert. 2023. "Salmonella Prophages, Their Propagation, Host Specificity and Antimicrobial Resistance Gene Transduction" Antibiotics 12, no. 3: 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030595
APA StyleTrofeit, L., Sattler, E., Künz, J., & Hilbert, F. (2023). Salmonella Prophages, Their Propagation, Host Specificity and Antimicrobial Resistance Gene Transduction. Antibiotics, 12(3), 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030595






